| Revision as of 07:37, 18 February 2011 editحسن علي البط (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers19,940 edits removed Category:Aromatic amines; added Category:Anilines using HotCat← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:00, 3 July 2024 edit undo0dorkmann (talk | contribs)258 editsm img | ||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 22 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{unreferenced|date=December 2008}} | |||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = |
||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| |ImageFile=Dimethylphenylenediamine.png | |||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = 414584828 | ||
| |ImageSize=200px | |||
| | ImageFile=N,N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine.svg | |||
| |IUPACName=N,N-dimethylbenzene-1,4-diamine | |||
| | PIN=''N''<sup>1</sup>,''N''<sup>1</sup>-Dimethylbenzene-1,4-diamine | |||
| |OtherNames= |
| OtherNames= ''p''-Aminodimethylaniline; ''N'',''N''-Dimethyl-''p''-phenylenediamine; 4-(Dimethylamino)aniline; ''p''-Amino-''N'',''N''-dimethylaniline; ''p''-(Dimethylamino)aniline; DMPPDA; Dimethyl-''p''-phenylenediamine; 4-Amino-''N'',''N''-dimethylaniline; ''p''-Dimethylaminophenylamine; DMPD | ||
| |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | |
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | ||
| | ChemSpiderID = |
| ChemSpiderID = 13884246 | ||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite}} | | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | ||
| | CASNo=99-98-9 |
| CASNo=99-98-9 | ||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|changed|FDA}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | UNII = 7GZH2FMK7X | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | PubChem=7472 | ||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | | SMILES=CN(C)C1=CC=C(C=C1)N | ||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| |Section2={{Chembox Properties | |Section2={{Chembox Properties | ||
| | C=8 | H=12 | N=2 | |||
| | Formula=C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>12</sub>N<sub>2</sub> | |||
| | Appearance=Reddish-violet crystals<ref name=Merck>'']'', 11th Edition, '''3242'''</ref> | |||
| | MolarMass=136.19428 | |||
| | MeltingPtC = 53 | |||
| | Appearance= | |||
| | MeltingPt_ref = <ref name=Merck/> | |||
| | Density= | |||
| | BoilingPtC= 262 | |||
| | MeltingPt= | |||
| | BoilingPt_ref = <ref name=Merck/> | |||
| | BoilingPt= | |||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| | Solubility= | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| |Section3={{Chembox Hazards | |||
| | MainHazards= | |||
| | FlashPt= | |||
| | Autoignition= | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine''' is an ]. It has been used as an accelerator for the vulcanization of rubber.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Geer |first1=W. C. |last2=Bedford |first2=C. W. |date= January 24, 1925 |title= The History of Organic Accelerators in the Rubber Industry|journal= Industrial and Engineering Chemistry|volume= 17|issue= 4|pages= 393–396 |doi=10.1021/ie50184a021 |author1-link=William C. Geer }}</ref> It can be used in ]s. | |||
| '''Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine''' is a molecule used in the ]. | |||
| ==Synthesis== | |||
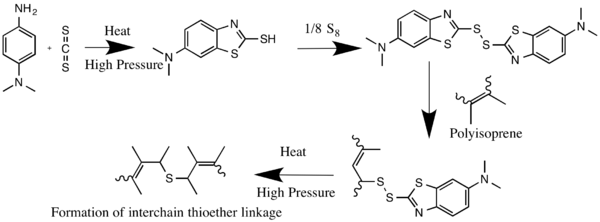
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine is made by the ] of ] followed by reduction. | |||
| ==Applications== | |||
| Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine can be converted to ] by reaction with ] and ] in several steps:<ref>{{cite encyclopedia|author=Horst Berneth|title=Azine Dyes|encyclopedia=Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry|year=2012|publisher=Wiley-VCH|place=Weinheim|doi=10.1002/14356007.a03_213.pub3|isbn=9783527303854 }}</ref> | |||
| :] | |||
| {{organic-compound-stub}} | |||
| It is used as accelerator for the vulcanization of rubber, being first converted to the corresponding ]. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| :] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:00, 3 July 2024

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name N,N-Dimethylbenzene-1,4-diamine | |
| Other names p-Aminodimethylaniline; N,N-Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine; 4-(Dimethylamino)aniline; p-Amino-N,N-dimethylaniline; p-(Dimethylamino)aniline; DMPPDA; Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine; 4-Amino-N,N-dimethylaniline; p-Dimethylaminophenylamine; DMPD | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.552 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H12N2 |
| Molar mass | 136.198 g·mol |
| Appearance | Reddish-violet crystals |
| Melting point | 53 °C (127 °F; 326 K) |
| Boiling point | 262 °C (504 °F; 535 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine is an amine. It has been used as an accelerator for the vulcanization of rubber. It can be used in oxidase tests.
Synthesis
Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine is made by the nitrosylation of dimethylaniline followed by reduction.
Applications
Dimethyl-4-phenylenediamine can be converted to methylene blue by reaction with dimethylaniline and sodium thiosulfate in several steps:
It is used as accelerator for the vulcanization of rubber, being first converted to the corresponding mercaptobenzothiazole.
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 3242
- Geer, W. C.; Bedford, C. W. (January 24, 1925). "The History of Organic Accelerators in the Rubber Industry". Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 17 (4): 393–396. doi:10.1021/ie50184a021.
- Horst Berneth (2012). "Azine Dyes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_213.pub3. ISBN 9783527303854.