| Revision as of 17:16, 9 March 2006 view sourceAivazovsky (talk | contribs)25,346 editsm →Memorial← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 03:51, 28 November 2024 view source Bitspectator (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,072 editsm →End of World War I | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|1915–1917 mass murder in the Ottoman Empire}} | |||
| {{History of Armenia}} | |||
| {{Featured article}} | |||
| The '''Armenian Genocide''' (also known as the '''Armenian ]''' or the '''Armenian Massacre''') is a term which refers to the forced mass evacuation and ] of hundreds of thousands or over a million ], during the government of the ] from ] to ] in the ]. Several facts in connection with the event are a matter of ongoing dispute between parts of the international community and ]. Although it is generally agreed that events said to comprise what is termed the Armenian Genocide did occur, the Turkish government rejects that it was ], on the alleged basis that the deaths among the Armenians, were not a result of a state-sponsored plan of mass extermination, but from the result of inter-ethnic strife, disease and famine during the turmoil of ]. | |||
| {{Pp-vandalism|small=yes}} | |||
| <!--This article has been placed on a one-revert rule. Any editor who makes more than one revert on this article (and this revert must be discussed on the talk page) in a 24-hour period will be blocked. Please edit cooperatively, and seek consensus and compromise rather than edit-war.--> | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=July 2018}} | |||
| {{Use shortened footnotes|date=June 2022}} | |||
| {{Infobox civilian attack | |||
| Despite this thesis, most Armenian, Western, and an ] believe that the massacres were a case of genocide. For example, most Western sources point to the sheer scale of the ]. The event is also said to be the second-most studied case of genocide, and often draws comparison with ]. To date 24 countries, as discussed below, have officially recognized and accepted its authenticity as Genocide. | |||
| | title = Armenian genocide | |||
| | partof = ] | |||
| | image = Column of deportees walking through Harput vilayet during the Armenian genocide.jpg | |||
| | image_size = | |||
| | alt = see caption | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| | caption = Column of Armenian deportees guarded by ]s in ] | |||
| | location = ] | |||
| | coordinates = | |||
| | date = 1915–1917{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=245, 330}}{{sfn|Bozarslan et al.|2015|p=187}} | |||
| | type = ], ], ] | |||
| |target = ] | |||
| | fatalities = ]{{sfn|Morris|Ze'evi|2019|p=1}} | |||
| | perps = ] | |||
| |}} | |||
| The '''Armenian genocide'''{{efn|Also known by ].|name=names}} was the systematic destruction of the ] in the ] during ]. Spearheaded by the ruling ] (CUP), it was implemented primarily through the mass murder of around one million Armenians during ]es to the ] and the ] of others, primarily women and children. | |||
| Before World War I, Armenians occupied a somewhat protected, but subordinate, place in Ottoman society. Large-scale massacres of Armenians had occurred ] and ]. The Ottoman Empire suffered a series of military defeats and territorial losses—especially during the 1912–1913 ]—leading to fear among CUP leaders that the Armenians would seek independence. During their invasion of ] and ] territory in 1914, ] massacred local Armenians. Ottoman leaders took isolated instances of ] as evidence of a widespread rebellion, though no such rebellion existed. Mass deportation was intended to permanently forestall the possibility of Armenian autonomy or independence. | |||
| ==The situation of the Armenians in Anatolia== | |||
| {{main|Ottoman Armenian Population}} | |||
| In ], before ], there were an estimated two million Armenians in the ], the vast majority of whom were of the ] faith, with a small number of the ] and ] faiths. While the Armenian population in Eastern ] (also called ]) was large and clustered, there were large numbers of Armenians in the western part of the Ottoman Empire. Many lived in the capital city of ]. | |||
| On 24 April 1915, the Ottoman authorities ] hundreds of Armenian intellectuals and leaders from ]. At the orders of ], an estimated 800,000 to 1.2 million Armenians were sent on death marches to the Syrian Desert in 1915 and 1916. Driven forward by paramilitary escorts, the deportees were deprived of food and water and subjected to robbery, ], and massacres. In the Syrian Desert, the survivors were dispersed into ]. In 1916, another wave of massacres was ordered, leaving about 200,000 deportees alive by the end of the year. Around 100,000 to 200,000 Armenian women and children were forcibly converted to Islam and integrated into Muslim households. Massacres and ] of Armenian survivors continued through the ] after World War I, carried out by ]. | |||
| Until the late ], the Armenians were referred to as ''millet-i sadika'' (loyal nation) by the Ottomans. This meant that they were living in harmony with other ethnic groups and without any major conflict with the central authority. However the Christian Armenians were subject to Islamic ] laws, which gave them fewer legal rights than Muslim fellow citizens. The Tanzimat gave more rights to the minorities in the middle of the 19th century. However, the long ruling ] suspended the constitution early in his reign and ruled as he saw fit. Despite pressure on the Sultan by the major European countries to treat the Christian minorities more gently, abuses only increased. | |||
| This genocide put an end to more than two thousand years of Armenian civilization in eastern ]. Together with the mass murder and expulsion of ] and ] Christians, it enabled the creation of an ] Turkish state, the ]. The Turkish government maintains that the deportation of Armenians was a legitimate action that ]. {{As of|2023|post=,}} 34 countries have ], concurring with the academic consensus. | |||
| The single event that started the chain is most likely the Russian victory over the Ottoman Empire in the ]. At the end of this war the Russians took control over a large part of Armenian territory (including the city of ]). The Russians claimed they were the supporters of Christians within the Ottoman Empire and now they were clearly militarily superior to the Ottomans. The weakening control of the Ottoman government over its empire in the following 15 years led many Armenians to believe that they could regain independence from them. | |||
| {{TOC limit|3}} | |||
| == Background == | |||
| A minor Armenian unrest in ] was suppressed with brutality in ]. Armenian communities were then attacked for the next three years with no apparent direction from the government but equally without much protection offered either. See the ] for more details. According to most estimates, 80,000 to 300,000 Armenians were killed between 1894 and 1897. | |||
| {{further|Causes of the Armenian genocide}} | |||
| == |
=== Armenians in the Ottoman Empire === | ||
| {{main|Armenians in the Ottoman Empire}} | |||
| Just five years before ], the Ottoman Empire came under the control of the ]. The old Sultan Hamid was deposed and his timid younger brother ] was installed as a figurehead ruler. At first some Armenian ] supported the Young Turks, in hopes that there would be a significant change for the better. Some Armenians were elected to the newly restored Ottoman ], and some remained in the parliament throughout the war. | |||
| ]: ], ], ], ], ] and ]. Most villages populated by Armenians were in these provinces.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=279}}]] | |||
| The presence of ] in ] has been documented since the ], about 1,500 years before ] under the ].{{sfn|Ahmed|2006|p=1576}} The ] ] as its national religion in the ], establishing the ].{{sfn|Payaslian|2007|pp=34–35}} Following the end of the ] in 1453, two Islamic empires—the ] and the Iranian ]—contested ], which was permanently separated from ] (held by the Safavids) by the 1639 ].{{sfn|Payaslian|2007|pp=105–106}} The Ottoman Empire was multiethnic and multireligious,{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=11, 15}} and its ] offered non-Muslims a subordinate but protected place in society.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=12}} ] encoded Islamic superiority but guaranteed property rights and freedom of worship to non-Muslims ('']'') in exchange for ].{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=5, 7}} | |||
| On the eve of ] in 1914, around two million Armenians lived in Ottoman territory, mostly in Anatolia, a region with a total population of 15–17.5 million.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=xviii}} According to the ]'s estimates for 1913–1914, there were 2,925 Armenian towns and villages in the Ottoman Empire, of which 2,084 were in the ] adjacent to the Russian border.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=279}} Armenians were a minority in most places where they lived, alongside Turkish and ] Muslim and ] neighbors.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=xviii}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=279}} According to the Patriarchate's figure, 215,131 Armenians lived in urban areas, especially ], ], and ].{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=279}} Although most Ottoman Armenians were peasant farmers, they were overrepresented in commerce. As ], despite the wealth of some Armenians, their overall political power was low, making them especially vulnerable.{{sfn|Bloxham|2005|pp=8–9}} | |||
| In 1914, the Ottoman government passed a new law to support the war effort that required all adult males - up to the age of forty-five - to either be recruited in the Ottoman army or to pay special fees in order to be excluded from service. As a result of this law, most able-bodied men left their homes, leaving only the women, children, and elderly in the Armenian communities. Most of the Armenian recruits were later executed or forced into hard labor work gangs. In the cities of Marash and Zeytoon, Armenian men were conscripted regardless of whether they paid the military tax or not. | |||
| === Land conflict and reforms === | |||
| ==In the context of War in Eastern Ottoman== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|Caucasus Campaign}} | |||
| Armenians in the eastern provinces lived in semi-] conditions and commonly encountered ], ], and unpunished crimes against them including robberies, murders, and sexual assaults.{{sfn|Astourian|2011|p=60}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=19}} Beginning in 1839, the Ottoman government issued ] to centralize power and equalize the status of Ottoman subjects regardless of religion. The reforms to equalize the status of non-Muslims were strongly opposed by Islamic clergy and Muslims in general, and remained mostly theoretical.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=9}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=8, 40}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=26–27}} Because of the abolition of the ] in the mid-nineteenth century, the Ottoman government began to directly tax Armenian peasants who had previously paid taxes only to Kurdish landlords. The latter continued to exact levies illegally.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=19, 53}}{{sfn|Astourian|2011|pp=60, 63}} | |||
| From the mid-nineteenth century, Armenians faced large-scale ] as a consequence of the ] and the arrival of ] and immigrants (mainly ]) following the ].{{sfn|Astourian|2011|pp=56, 60}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=19, 21}}{{sfn|Göçek|2015|p=123}} In 1876, when Sultan ] came to power, the state began to confiscate Armenian-owned land in the eastern provinces and give it to Muslim immigrants as part of a systematic policy to reduce the Armenian population of these areas. This policy lasted until World War I.{{sfn|Astourian|2011|pp=62, 65}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=55}} These conditions led to a substantial decline in the population of the Armenian highlands; 300,000 Armenians left the empire, and others moved to towns.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=271}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=54–56}} Some Armenians joined ], of which the most influential was the ] (ARF), founded in 1890. These parties primarily sought reform within the empire and found only limited support from Ottoman Armenians.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=87–88}} | |||
| While it is believed by many that the Armenian genocide was conducted following the declaration of war on late October 1914, according to some sources, on February 1914, during a Turkish-German meeting, a proposition to evacuate the Ottoman Armenians was already put on table. Other pre-war anti-Armenian measures are reported. Donald Bloxham writes for example that in the summer of 1914, Armenian settlements on the Ottoman borders were plundered by Ottoman forces, while ] in his collection of German records includes reports of excess against the Armenian population in late December 1914, soon after the war began. | |||
| Russia's decisive victory in the ] forced the Ottoman Empire to cede parts of eastern Anatolia, the ], and ].{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=94–95, 105}} ] at the 1878 ], the ] agreed to carry out reforms and guarantee the physical safety of its Armenian subjects, but there was no enforcement mechanism;{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=95–96}} conditions continued to worsen.{{sfn|Astourian|2011|p=64}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=97}} The Congress of Berlin marked the emergence of the ] in international diplomacy as Armenians were for the first time used by the ] to interfere in Ottoman politics.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=96}} Although Armenians had been called the "loyal millet" in contrast to Greeks and others who had previously challenged Ottoman rule, the authorities began to perceive Armenians as a threat after 1878.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=48–49}} In 1891, Abdul Hamid created the ] from Kurdish tribes, allowing them to act with impunity against Armenians.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|pp=75–76}}{{sfn|Astourian|2011|p=64}} From 1895 to 1896 the empire saw ]; at least 100,000 Armenians were killed{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|pp=11, 65}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=129}} primarily by Ottoman soldiers and mobs let loose by the authorities.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=129–130}} Many Armenian villages were forcibly converted to Islam.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=271}} The Ottoman state bore ultimate responsibility for the killings,{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=130}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=11}} whose purpose was violently restoring the previous social order in which Christians would unquestioningly accept Muslim supremacy,{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=131}} and forcing Armenians to emigrate, thereby decreasing their numbers.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=266}} | |||
| The Ottoman Empire entered into World War I on October 29, 1914. The Ottoman army, under their war minister ], soon attacked the Russian forces around the city of ], in what was then Russian territory. Early in 1915 the Turkish army was utterly defeated (at the ]) with massive loss of life. The Russian forces under General ] counter-attacked into Turkish territory, where the Armenian and Muslim communities were interleaved. Taking advantage of common religion and the recent discomfort of the Armenian community in the Ottoman Empire, Russia promoted Armenian nationalism (there were also many Russian-Armenians in the Russian army). At the same time, some Armenians had begun advocating an independent state. | |||
| === Young Turk Revolution === | |||
| On March 2, the Armenians of ] were evacuated by Ottoman authorities. With Russian forces approaching Lake Van, the regional administrator ordered the execution of five Armenian leaders, and a revolt resulted in ] on April 20,{{ref|Van1}} against the Ottoman government and in favor of the Russians (according to Turkish sources). On the other hand, it is said that the governor of Van, Jevdet, under the pretext of preventing an Armenian rebellion, justified the attack on the town by the Ottoman army.{{ref|Van2}} Nogales for example, reported a plan set by Jevdet to kill every Armenian male in Van. The Russians finally captured Van in late May of 1915. In August the Russian army left and the Turks re-occupied Van. Then in September the Russians forced the Ottoman army out of Van for the second time.{{ref|Van3}} By the end of the war, the town of Van was empty and in ruins. | |||
| {{Main|Young Turk Revolution}} | |||
| Abdul Hamid's despotism prompted the formation of an opposition movement, the ], which sought to overthrow him and restore the 1876 ], which he had suspended in 1877.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=92–93, 99, 139–140}} One faction of the Young Turks was the secret and revolutionary ] (CUP), based in ], from which the charismatic conspirator ] (later Talaat Pasha{{efn|name=Talaatbey|Talaat previously had the title "]," and so was known as "Talaat Bey" until he gained the title "]" in 1917.{{Sfn|Kieser|2018|p=2}}}}) emerged as a leading member.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=46–47}} Although skeptical of a growing, exclusionary ] in the Young Turk movement, the ARF decided to ally with the CUP in December 1907.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=152–153}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=50}} In 1908, the CUP came to power in the ], which began with a string of CUP assassinations of leading officials in ].{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=53–54}}{{sfn|Göçek|2015|p=192}} Abdul Hamid was forced to reinstate the 1876 constitution and restore the ], which was celebrated by Ottomans of all ethnicities and religions.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=54–55}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=154–156}} Security improved in parts of the eastern provinces after 1908 and the CUP took steps to reform the local ],{{sfn|Kaligian|2017|pp=89–91}} although tensions remained high.{{sfn|Kaligian|2017|pp=82–84}} Despite an agreement to reverse the land usurpation of the previous decades in the 1910 Salonica Accord between the ARF and the CUP, the latter made no efforts to carry this out.{{sfn|Kaligian|2017|pp=86–92}}{{sfn|Astourian|2011|p=66}} | |||
| ] after the ]|alt=Destroyed cityscape with ruined buildings and rubble in the street]] | |||
| ==Genocide== | |||
| In early 1909 ] was launched by conservatives and some liberals who opposed the CUP's increasingly repressive governance.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=165–166}} When news of the countercoup reached ], armed Muslims attacked the Armenian quarter and Armenians returned fire. Ottoman soldiers did not protect Armenians and instead armed the rioters.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=168–169}} Between 20,000 and 25,000 people, mostly Armenians, were ] and nearby towns.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=171}} Unlike the 1890s massacres, the events were not organized by the central government but instigated by local officials, intellectuals, and Islamic clerics, including CUP supporters in Adana.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=172}} Although the massacres went unpunished, the ARF continued to hope that reforms to improve security and restore lands were forthcoming, until late 1912, when they broke with the CUP and appealed to the European powers.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=152–153}}{{sfn|Astourian|2011|pp=66–67}}{{sfn|Kaligian|2017|p=92}} On 8 February 1914, the CUP reluctantly agreed to ] brokered by ] that provided for the appointment of two European inspectors for the entire Ottoman east and putting the Hamidiye regiments in reserve. CUP leaders feared that these reforms, which were never implemented, could lead to partition and cited them as a reason for the elimination of the Armenian population in 1915.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=163–164}}{{sfn|Akçam|2019|pp=461–462}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=203, 359}} | |||
| ]'s response to being decisively defeated at the Battle of Sarikamis was, in part, to blame the Armenians. He ordered that all Armenian recruits in the Ottoman forces be disarmed, demobilized and assigned to labor camps. Most of the Armenian recruits were either executed or turned into road laborers - few survived. | |||
| ===Balkan Wars=== | |||
| On ] ] (four days after the beginning of the troubles in Van), the Young Turk government arrested several hundred - or, according to Turkish records, over two thousand{{ref|intellectuals}} - Armenian intellectuals. It is believed that most of these were soon executed. This was quickly followed - ] ] - by orders from ] (Minister of the Interior) for the forced evacuation of hundreds of thousands - possibly over a million - Armenians from across all of Anatolia (except parts of the western coast) to ] and what is today ]. Many went to the Syrian town of ] and the surrounding desert. The fact that the Turkish government ordered the evacuation of ethnic Armenians at this time is not in dispute. It is claimed, based on a good deal of anecdotal evidence, that the Ottoman government did not provide any facilities to care for the Armenians during their evacuation, nor when they arrived. The Ottoman troops escorting the Armenians have been implicated in not only allowed others to rob, kill and rape the Armenians, but often participated in these activities themselves. In any event, the foreseeable consequence of the government's decision to move the Armenians led to a significant number of deaths. | |||
| {{Main|Balkan Wars}} | |||
| ] parading with loot in Phocaea (modern-day ], Turkey) on ]. In the background are Greek refugees and burning buildings.|alt=see caption]] | |||
| The 1912 ] resulted in the ]{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=184–185}} and the mass expulsion of Muslims from the Balkans.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=167}} Ottoman Muslim society was incensed by the atrocities committed against Balkan Muslims, intensifying anti-Christian sentiment and leading to a desire for revenge.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=185, 363}}{{sfn|Üngör|2012|p=50}} Blame for the loss was assigned to all Christians, including the Ottoman Armenians, many of whom had fought on the Ottoman side.{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|pp=169, 171}} The Balkan Wars put an end to the ] movement for pluralism and coexistence;{{sfn|Bloxham|Göçek|2008|p=363}} instead, the CUP turned to an increasingly radical Turkish nationalism to preserve the empire.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=156}} CUP leaders such as Talaat and ] came to blame non-Muslim population concentrations in strategic areas for many of the empire's problems, concluding by mid-1914 that they were internal tumors to be excised.{{sfn|Kaligian|2017|pp=97–98}} Of these, Ottoman Armenians were considered the most dangerous, because CUP leaders feared that their homeland in Anatolia—claimed as the last refuge of the Turkish nation—would break away from the empire as the Balkans had.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=193}}{{sfn|Göçek|2015|p=191}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=156}} | |||
| In January 1913, the CUP ], installed a ], and strictly repressed all real or perceived internal enemies.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=189–190}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=133–134, 136, 138, 172}} After the coup, the CUP shifted the demography of border areas by resettling Balkan Muslim refugees while coercing Christians to emigrate; immigrants were promised property that had belonged to Christians.{{sfn|Kaligian|2017|pp=95, 97}} When parts of Eastern Thrace were reoccupied by the Ottoman Empire during the ] in mid-1913, there was a campaign of looting and intimidation against Greeks and Armenians, forcing many to emigrate.{{sfn|Kaligian|2017|pp=96–97}} Around 150,000 Greek Orthodox from the ] were ] in May and June 1914 by ], who were secretly backed by the CUP and sometimes joined by the ].{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=193, 211–212}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=169, 176–177}}{{sfn|Kaligian|2017|p=98}} Historian ] states that the perceived success of the Greek deportations allowed CUP leaders to envision even more radical policies "as yet another extension of a policy of ] through ]".{{sfn|Bjørnlund|2008|p=51}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ==Ottoman entry into World War I== | |||
| The Ottoman government ordered the evacuation or deportation of many Armenians living in Anatolia, Syria, and Mesopotamia. In the city of Edessa (modern ]) the local Armenian population, worried about their fate, revolted (early ]) against the Ottoman government and took control of the old city. Ottoman forces attacked the city and bombarded it with artillery but the Armenians resisted. The German General in command of the closest Ottoman army to the city, ], arrived and negotiated a deal with the Armenians. In exchange for an Armenian surrender and disarmament, the Ottoman government agreed not to deport them. However, the Ottoman government broke the terms of the agreement and did deport the Armenians. | |||
| ] | |||
| A few days after the outbreak of World War I, the CUP concluded ] on 2 August 1914.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=214–215}} The same month, CUP representatives went to ] demanding that, in the event of war with ], the ARF incite ] to intervene on the Ottoman side. Instead, the delegates resolved that Armenians should fight for the countries of their citizenships.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=223–224}} During its war preparations, the Ottoman government recruited thousands of prisoners to join the paramilitary ],{{sfn|Üngör|2016|pp=16–17}} which initially focused on stirring up revolts among Muslims behind Russian lines beginning before the empire officially entered the war.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=233–234}} On 29 October 1914, the empire ] on the side of the ] by launching a ] on Russian ports in the ].{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=218}} Many Russian Armenians were enthusiastic about the war, but Ottoman Armenians were more ambivalent, afraid that supporting Russia would bring retaliation. Organization of ] by Russian Armenians, later joined by some Ottoman Armenian deserters, further increased Ottoman suspicions against their Armenian population.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=221–222}} | |||
| Wartime requisitions were often corrupt and arbitrary, and disproportionately targeted Greeks and Armenians.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=225}} Armenian leaders urged young men to accept ], but many soldiers of all ethnicities and religions deserted due to difficult conditions and concern for their families.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=226–227}} At least 10 percent of Ottoman Armenians were mobilized, leaving their communities bereft of fighting-age men and therefore largely unable to organize armed resistance to deportation in 1915.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=242}}{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=179}} During the Ottoman ] and ], the Special Organization massacred local Armenians and ].{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=243–244}}{{sfn|Üngör|2016|p=18}} Beginning in November 1914, provincial governors of Van, Bitlis, and Erzerum sent many telegrams to the central government pressing for more severe measures against the Armenians, both regionally and throughout the empire.{{sfn|Akçam|2019|p=475}} These requests were endorsed by the central government already before 1915.{{sfn|Akçam|2019|pp=478–479}} Armenian civil servants were dismissed from their posts in late 1914 and early 1915.{{sfn|Üngör|2016|p=19}} In February 1915, the CUP leaders decided to disarm Armenians serving in the army and transfer them to ]s.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=244}} The Armenian soldiers in labor battalions were systematically executed, although many skilled workers were spared until 1916.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=248–249}} | |||
| It is believed that over a million were deported. The word "deportation" could be considered as misleading (and some would prefer the word "relocation", as the former means banishment outside a country's borders; it is said that ]s, for example, were not "deported" during ]). Many historians believe that the evacuations were, in practice, a method of mass execution which led to the deaths of many of the Armenian population by forcing them to march endlessly through desert, without food or water or enough protection from local Kurdish or Turkish bandits, and that the members of the special organization were charged to escort the convoys (which meant their destruction). | |||
| == Onset of genocide == | |||
| ==The Camps== | |||
| {{further|Causes of the Armenian genocide#Wartime radicalization}} | |||
| <!-- Image with unknown copyright status removed: ] --> | |||
| ] | |||
| It is believed that twenty-five major ] (Dayr az-Zawr, Ra's Al Gul, Bonzanti, Mamoura, Intili, Islahiye, Radjo, Katma, Karlik, Azaz, Akhterim, Mounboudji, Bab, Tefridje, Lale, Meskene, Sebil, Dipsi, Abouharar, Hamam, Sebka, Marat, Souvar, Hama, Homs and Kahdem) existed,{{ref|camps1}} under the command of ], one of the right hands of ]. The majority of the camps were situated near the Iraqi and Syrian frontiers, and some were only temporary transit camps.{{ref|camps2}} Others are said to have been used only as temporary mass burial zones—such as Radjo, Katma, and Azaz—that were closed in Fall 1915.{{ref|camps3}} Some authors also maintain that the camps Lale, Tefridje, Dipsi, Del-El, and Ra's al-'Ain were built specifically for those who had a life expectancy of a few days.{{ref|camps4}} Like in the cases of the Jewish KAPOs in the concentration camps, the majority of the guards inside the camps were Armenians.{{ref|camps5}} | |||
| ], 1915|alt=Two armed men standing by a ruined wall, surrounded by skulls and other human remains<!-- alt=Photograph of two Russian soldiers in a ruined village looking at skeletal remains -->]] | |||
| Minister of War Enver Pasha took over command of the Ottoman armies for the invasion of Russian territory, and tried to encircle the ] at the ], fought from December 1914 to January 1915. Unprepared for the harsh winter conditions,{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=241–242}} his forces were routed, losing more than 60,000 men.{{sfn|Akçam|2012|p=157}} The retreating Ottoman army destroyed dozens of Ottoman Armenian villages in Bitlis vilayet, massacring their inhabitants.{{sfn|Üngör|2016|p=19}} Enver publicly blamed his defeat on Armenians who he claimed had actively sided with the Russians, a theory that became a consensus among CUP leaders.{{sfn|Üngör|2016|pp=18–19}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=243}} Reports of local incidents such as weapons caches, severed telegraph lines, and occasional killings confirmed preexisting beliefs about Armenian treachery and fueled paranoia among CUP leaders that a coordinated Armenian conspiracy was plotting against the empire.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=248}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=235–238}} Discounting contrary reports that most Armenians were loyal, the CUP leaders decided that the Armenians had to be eliminated to save the empire.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=248}} | |||
| Massacres of Armenian men were occurring in the vicinity of ] in Van vilayet from December 1914.{{sfn|Akçam|2019|p=472}} ARF leaders attempted to keep the situation calm, warning that even justifiable self-defense could lead to escalation of killing.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=255}} The governor, ], ordered the Armenians of ] to hand over their arms on 18 April 1915, creating a dilemma: If they obeyed, the Armenians expected to be killed, but if they refused, it would provide a pretext for massacres. Armenians fortified themselves in Van and repelled ] that began on 20 April.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=257}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=319}} During the siege, Armenians in surrounding villages were massacred at Djevdet's orders. Russian forces captured Van on 18 May, finding 55,000 corpses in the province—about half its prewar Armenian population.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=259–260}} Djevdet's forces proceeded to Bitlis and attacked Armenian and Assyrian/Syriac villages; the men were killed immediately, many women and children were kidnapped by local Kurds, and others marched away to be killed later. By the end of June, there were only a dozen Armenians in the vilayet.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=287, 289}} | |||
| Even though nearly all the camps, including all the major ones, were open air, the rest of the mass killings in other minor camps, was not limited to direct killings; but also to mass burning,{{ref|burning}} poisoning{{ref|poisoning}} and drowning.{{ref|drowning}} | |||
| The first deportations of Armenians were proposed by ], the commander of the ], in February 1915 and targeted Armenians in ] (specifically ], ], Adana, ], ], and ]) who were relocated to the area around ] in central Anatolia.{{sfn|Dündar|2011|p=281}} In late March or early April, the ] decided on the large-scale removal of Armenians from areas near the front lines.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=247–248}} During the night of 23–24 April 1915 hundreds of Armenian political activists, intellectuals, and community leaders were ]. This order from Talaat, intended to eliminate the Armenian leadership and anyone capable of organizing resistance, eventually resulted in the murder of most of those arrested.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=10}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|pp=251–252}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=271–272}} The same day, Talaat banned all Armenian political organizations{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=273}} and ordered that the Armenians who had previously been removed from Cilicia be deported again, from central Anatolia—where they would likely have survived—to the ].{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=274–275}}{{sfn|Akçam|2012|p=188}} | |||
| ==The Special Organization (Teşkilat-ı Mahsusa)== | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ] | |||
| == Systematic deportations == | |||
| While there was an official 'special organization' founded in ] ] by the Ottoman government, a second organization that participated in what led to the destruction of the Ottoman Armenian community was founded by the ]. This organization technically appeared in ] ] and was supposed to differ from the one already existing in one important point; mostly according to the military court, it was meant to be a "government in a government" (needing no orders to act). | |||
| {{See also|Population transfer in the Ottoman Empire}} | |||
| ===Aims=== | |||
| Later in 1914, the Ottoman government decided to influence the direction the special organization was to take by releasing criminals from central prisons to be the central elements of this newly formed special organization. According to the Mazhar commissions attached to the tribunal as soon as November 1914, 124 criminals were released from Pimian prison. Many other releases followed; in Ankara a few months later, 49 criminals were released from its central prison. Little by little from the end of 1914 to the beginning of 1915, hundreds, then thousands of prisoners were freed to form the members of this organization. Later, they were charged to escort the convoys of Armenian deportees. Vehib, commander of the Ottoman third army, called those members of the special organization, the “butchers of the human species.” | |||
| {{Quotebox|width=28em | |||
| | quote = We have been blamed for not making a distinction between guilty and innocent Armenians. was impossible. Because of the nature of things, one who was still innocent today could be guilty tomorrow. The concern for the safety of Turkey simply had to silence all other concerns. | source = —]{{efn|name=Talaatbey}}<!--Note that he is called "Talaat Bei" - "Talaat Bey' in German - in the article, because he did not get the title "Pasha" until 1917 --> in '']'', <!--Urls of : Full issue: https://content.staatsbibliothek-berlin.de/zefys/SNP27646518-19160504-1-0-0-0.pdf , pages: https://content.staatsbibliothek-berlin.de:443/zefys/SNP27646518-19160504-1-4-0-0/full/full/0/default.jpg and https://content.staatsbibliothek-berlin.de/zefys/SNP27646518-19160504-1-4-0-0.pdf -->{{sfn|Ihrig|2016|pp=162–163}}{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=168}}}} | |||
| During World War I, the CUP—whose central goal was to preserve the Ottoman Empire—came to identify Armenian civilians as an existential threat.{{sfn|Akçam|2012|p=337}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=245}} CUP leaders held Armenians—including women and children—collectively guilty for betraying the empire, a belief that was crucial to deciding on genocide in early 1915.{{sfn|Akçam|2019|p=457}}{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|pp=166–167}} At the same time, the war provided an opportunity to enact what Talaat called the "definitive solution to the Armenian Question".{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=245}}{{sfn|Dündar|2011|p=284}} The CUP wrongly believed that the Russian Empire sought to annex eastern Anatolia, and ordered the genocide in large part to prevent this eventuality.{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|p=202}} The genocide was intended to permanently eliminate any possibility that Armenians could achieve autonomy or independence in the empire's eastern provinces.{{sfn|Watenpaugh|2013|p=284}} Ottoman records show the government aimed to reduce Armenians to no more than five percent of the local population in the sources of deportation and ten percent in the destination areas. This goal could not be accomplished without mass murder.{{sfn|Akçam|2012|pp=242, 247–248}}{{sfn|Dündar|2011|p=282}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=261}} | |||
| The deportation of Armenians and resettlement of Muslims in their lands was part of a broader project intended to permanently restructure the demographics of Anatolia.{{sfn|Kaiser|2019|loc=6}}{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=102}}{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|p=254}} Armenian homes, businesses, and land were preferentially allocated to Muslims from outside the empire, nomads, and the estimated 800,000 (largely Kurdish) Ottoman subjects displaced because of the war with Russia. Resettled Muslims were spread out (typically limited to 10 percent in any area) among larger Turkish populations so that they would lose their distinctive characteristics, such as non-Turkish languages or nomadism.{{sfn|Gingeras|2016|pp=176–177}} These migrants were exposed to harsh conditions and, in some cases, violence or restriction from leaving their new villages.{{sfn|Gingeras|2016|p=178}} The ethnic cleansing of Anatolia—the Armenian genocide, ], and ] after World War I—paved the way for the formation of an ethno-national Turkish state.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=349, 364}}{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=311}} In September 1918, Talaat emphasized that regardless of losing the war, he had succeeded at "transforming Turkey to a nation-state in Anatolia".{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=376}}{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|p=227}} | |||
| The organization was led by the Central Committee Members ], ], ], and former Director of Public Security ]. The headquarters of Behaeddin Sakir were in ], from where he directed the forces of the Eastern vilayets. Aziz, Atif and Nazim Beys operated in Istanbul, and their decisions were approved and implemented by ], the Military Governor of Istanbul. | |||
| Deportation amounted to a death sentence; the authorities planned for and intended the death of the deportees.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=384}}{{sfn|Dündar|2011|pp=276–277}}{{sfn|Üngör|2012|p=54}} Deportation was only carried out behind the front lines, where no active rebellion existed, and was only possible in the absence of widespread resistance. Armenians who lived in the war zone were instead killed in massacres.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|pp=366, 383}} Although ostensibly undertaken for security reasons,{{sfn|Mouradian|2018|p=148}} the deportation and murder of Armenians did not grant the empire any military advantage and actually undermined the Ottoman war effort.{{sfn|Rogan|2015|p=184}} The empire faced a dilemma between its goal of eliminating Armenians and its practical need for their labor; those Armenians retained for their skills, in particular for manufacturing in war industries, were indispensable to the logistics of the Ottoman Army.{{sfn|Cora|2020|pp=50–51}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=317}} By late 1915, the CUP had extinguished Armenian existence from eastern Anatolia.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=240}} | |||
| According to the same commissions and other records, the criminals were chosen by a process of selection. They had to be ruthless butchers to be selected as a member of the special organization. The Mazhar commission, during the military court, has provided some lists of those criminals. In one instance, of 65 criminals released, 50 were in prison for murder. Such a disproportionate ratio between those condemned for murder; and others imprisoned for minor crimes is reported to have been generalized. This selection process of criminals was, according to some researchers in the field of comparative genocide studies, who specialize in the Armenian cases, clearly indicative of the government's intention to commit mass murder of its Armenian population. | |||
| {{Wide image|Armenian Genocide Map-en.svg|1000px|alt=Map showing locations where Armenians were killed, deportation routes, and transit centers, as well as locations of Armenian resistance|Map of the Armenian genocide in 1915}} | |||
| ==Military Trials, Istanbul, 1919== | |||
| Many of those responsible for the genocide were sentenced to death in absentia, after having escaped trial in ]. It is believed that the accused succeeded in destroying the majority of the documents that could be used as evidence against them before they escaped. ], the ], described the destruction of documents: “Just before the Armistice, officials had been going to the archives department at night and making clean sweep of most of the documents.” Aydemir, S.S., on the other hand, writes in his "Makedonyadan Ortaasyaya Enver Pasa.": | |||
| ===Administrative organization=== | |||
| :“Before the flight of the top Ittihadist leaders, Talat Pasa stopped by at the waterfront residence of one of his friends on the shore of Arnavudköy, depositing there suitcase of documents. It is said that the documents were burned in the basement's furnace. Indeed ... the documents and other papers of Ittihad's Central Committee are nowhere to be found.” | |||
| ] | |||
| On 23 May 1915, Talaat ordered the deportation of all Armenians in Van, Bitlis, and Erzerum.{{sfn|Kaiser|2019|loc=10}}{{sfn|Üngör|2012|p=53}} To grant a cover of legality to the deportation, already well underway in the eastern provinces and Cilicia, the ] approved the ], which allowed authorities to deport anyone deemed suspect.{{sfn|Üngör|2012|p=53}}{{sfn|Dündar|2011|p=283}}{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=96}} On 21 June, Talaat ordered the deportation of all Armenians throughout the empire, even ], {{convert|2,000|km|sp=us}} from the Russian front.{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=97}} Following the elimination of the Armenian population in eastern Anatolia, in August 1915, the Armenians of western Anatolia and ] were targeted for deportation. Some areas with a very low Armenian population and some cities, including Constantinople, were partially spared.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=378}}{{sfn|Akçam|2012|pp=399–400}} | |||
| Overall, national, regional, and local levels of governance cooperated with the CUP in the perpetration of genocide.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=247}} The Directorate for the Settlement of Tribes and Immigrants (IAMM) coordinated the deportation and the resettlement of Muslim immigrants in the vacant houses and lands. The IAMM, under the control of Talaat's ], and the Special Organization, which took orders directly from the CUP Central Committee, all closely coordinated their activities.{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|pp=89–90}} A dual-track system was used to communicate orders; those for the deportation of Armenians were communicated to the provincial governors through official channels, but orders of a criminal character, such as those calling for annihilation, were sent through party channels and destroyed upon receipt.{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|pp=92–93}}{{sfn|Akçam|2012|pp=194–195}} Deportation convoys were mostly escorted by gendarmes or local militia. The killings near the front lines were carried out by the Special Organization, and those farther away also involved local militias, bandits, gendarmes, or Kurdish tribes depending on the area.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=376}} Within the area controlled by the ], which held eastern Anatolia, the army was only involved in genocidal atrocities in the vilayets of Van, Erzerum, and Bitlis.{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=94}} | |||
| The martial court established the will of the Ittheadists to eliminate the Armenians physically, via its special organization. The Court Martial, Istanbul, 1919: | |||
| Many perpetrators came from the Caucasus (] and Circassians), who identified the Armenians with their Russian oppressors. Nomadic Kurds committed many atrocities during the genocide, but settled Kurds only rarely did so.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=810}} Perpetrators had several motives, including ideology, revenge, desire for Armenian property, and ].{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=352}} To motivate perpetrators, state-appointed ]s encouraged the killing of Armenians{{sfn|Üngör|2012|p=58}} and killers were entitled to a third of Armenian ] (another third went to local authorities and the last to the CUP). Embezzling beyond that was punished.{{sfn|Kaiser|2019|loc=35, 37}}{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|pp=98–99}} Ottoman politicians and officials who opposed the genocide were dismissed or assassinated.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=247}}{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=94}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|pp=246–247}} The government decreed that any Muslim who harbored an Armenian against the will of the authorities would be executed.{{sfn|Üngör|2012|p=61}}{{sfn|Akçam|2012|pp=327–328}} | |||
| :"The Court Martial taking into consideration the above-named crimes declares, unanimously, the culpability as principle factors of these crimes the fugitives Talat Pasha, former Grand Vizir, Enver Efendi, former War Minister, struck off the register of the Imperial Army, Cemal Efendi, former Navy Minister, struck off too from the Imperial Army, and Dr. Nazim Efendi, former Minister of Education, members of the General Council of the Union & Progress, representing the moral person of that party;... the Court Martial pronounces, in accordance with said stipulations of the Law the death penalty against Talat, Enver, Cemal, and Dr. Nazim." | |||
| ===Death marches=== | |||
| ==The Position of Turkish authorities== | |||
| ] visited ] and found nearby gorges choked with corpses and hundreds of bodies floating in the lake.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=91}}|alt=Color photograph of a lake with gorges leading into it]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Although the majority of able-bodied Armenian men had been conscripted into the army, others deserted, paid the exemption tax, or fell outside the age range of conscription. Unlike the earlier massacres of Ottoman Armenians, in 1915 Armenians were not usually killed in their villages, to avoid destruction of property or unauthorized looting. Instead, the men were usually separated from the rest of the deportees during the first few days and executed. Few resisted, believing it would put their families in greater danger.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=376}} Boys above the age of twelve (sometimes fifteen) were treated as adult men.{{sfn|Maksudyan|2020|pp=121–122}} Execution sites were chosen for proximity to major roads and for rugged terrain, lakes, wells, or cisterns to facilitate the concealment or disposal of corpses.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=91}}{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=377}}{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=93}} The convoys would stop at a nearby transit camp, where the escorts would demand a ransom from the Armenians. Those unable to pay were murdered.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=376}} Units of the Special Organization, often wearing gendarme uniforms, were stationed at the killing sites; escorting gendarmes often did not participate in killing.{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=93}} | |||
| At least 150,000 Armenians passed through ] from June 1915, where a series of transit camps were set up to control the flow of victims to the killing site at the nearby ] gorge.{{sfn|Kaiser|2019|loc=3, 22}} Thousands of Armenians were killed near ], pushed by paramilitaries off the cliffs.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=91}} More than 500,000 Armenians passed through the Firincilar plain south of ], one of the deadliest areas during the genocide. Arriving convoys, having passed through the plain to approach the ] highlands, would have found gorges already filled with corpses from previous convoys.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=377}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=93}} Many others were held in tributary valleys of the ], ], or ] and systematically executed by the Special Organization.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=90}} Armenian men were often drowned by being tied together back-to-back before being thrown in the water, a method that was not used on women.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=92}} | |||
| :''Further information: ] | |||
| ] | |||
| Turkey does not accept that the deaths of 1915 were the result of a state intention to eliminate the Armenian people. Turkey holds the position that the deaths were the result of the turmoils of World War I and that the Ottoman Empire fought against Russian backed Armenian militia. There is also disagreement over the number of casualties, Turkey states that according to demographic studies there were fewer than 1.5 million Armenians living in the Ottoman Empire, suggesting figures of over a million Armenian deaths to be over inflated. Turkey believes the number of deaths to be ranging from 200,000 to 600,000 which it considers to be lower than the number of Muslims who perished between 1912-22. | |||
| Authorities viewed disposal of bodies through rivers as a cheap and efficient method, but it caused widespread pollution downstream. So many bodies floated down the Tigris and Euphrates that they sometimes blocked the rivers and needed to be cleared with explosives. Other rotting corpses became stuck to the riverbanks, and still others traveled as far as the ]. The rivers remained polluted long after the massacres, causing epidemics downstream.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=95}} Tens of thousands of Armenians died along the roads and their bodies were buried hastily or, more often, simply left beside the roads. The Ottoman government ordered the corpses to be cleared as soon as possible to prevent both photographic documentation and disease epidemics, but these orders were not uniformly followed.{{sfn|Akçam|2018|p=158}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=94}} | |||
| Women and children, who made up the great majority of deportees, were usually not executed immediately, but subjected to hard marches through mountainous terrain without food and water. Those who could not keep up were left to die or shot.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|pp=92–93}} During 1915, some were forced to walk as far as {{convert|1,000|km|sp=us}} in the summer heat.{{sfn|Üngör|2012|p=54}} Some deportees from western Anatolia were allowed to travel ].{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=378}} There was a distinction between the convoys from eastern Anatolia, which were eliminated almost in their entirety, and those from farther west, which made up most of those surviving to reach Syria.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=808}} For example, around 99 percent of Armenians deported from Erzerum did not reach their destination.{{sfn|Üngör|2012|p=53}} | |||
| More recently, lower figures of Armenian casualties were presented by Yusuf Halacoglu, the director of the Turkish history foundation. In his said calculations, he estimates that a total of 56,000 Armenians perished during the period due to war conditions, and less than 10 thousand were actually killed. In his other research, he maintains that over 500,000 Turks were killed by Armenians. While the Turkish government now publicizes those figures of Turks allegedly being killed by Armenians, the other research of Halacoglu, which claims that fewer than 10 thousand Armenians were killed, is still absent from the Turkish foreign affairs publications. | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| ===Islamization=== | |||
| ]" after the war|alt=Several women dressed in Arab clothing and posed in front of a wall]] | |||
| The Islamization of Armenians, carried out as a systematic state policy involving the bureaucracy, police, judiciary, and clergy, was a major structural component of the genocide.{{sfn|Akçam|2012|pp=314, 316}}{{sfn|Kurt|2016|loc=2, 21}} An estimated 100,000 to 200,000 Armenians were Islamized,{{sfn|Akçam|2012|p=331}} and it is estimated that as many as two million Turkish citizens in the early 21st century ].{{sfn|Watenpaugh|2013|p=291}} Some Armenians were allowed to convert to Islam and evade deportation, but the regime insisted on their destruction wherever their numbers exceeded the five to ten percent threshold, or there was a risk of them being able to preserve their nationality and culture.{{sfn|Akçam|2012|pp=290–291}} Talaat Pasha personally authorized conversion of Armenians and carefully tracked the loyalty of converted Armenians until the end of the war.{{sfn|Kurt|2016|loc=5, 13–14}} Although the first and most important step was conversion to Islam, the process also required the eradication of ]s, ], and ], and for women, ] to a Muslim.{{sfn|Kurt|2016|loc=15}} Although Islamization was the most feasible opportunity for survival, it also transgressed Armenian moral and social norms.{{sfn|Kurt|2016|loc=5}} | |||
| The CUP allowed Armenian women to marry into Muslim households, as these women would lose their Armenian identity.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=377}} Young women and girls were often appropriated as house servants or ]. Some boys were abducted to work as forced laborers for Muslim individuals.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=377}}{{sfn|Watenpaugh|2013|pp=291–292}} Some children were forcibly seized, while others were sold or given up by their parents to save their lives.{{sfn|Akçam|2012|p=314}}{{sfn|Watenpaugh|2013|pp=284–285}} Special state-run orphanages were also set up with strict procedures intending to deprive their charges of an Armenian identity.{{sfn|Kurt|2016|loc=17}} Most Armenian children who survived the genocide endured exploitation, hard labor without pay, forced conversion to Islam, and ].{{sfn|Watenpaugh|2013|pp=291–292}} Armenian women captured during the journey ended up in Turkish or Kurdish households; those who were Islamized during the second phase of the genocide found themselves in an ] or ] environment.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|pp=757–758}} | |||
| Turkey also criticizes similarities with the Holocaust, stating that unlike the Armenians, the Jewish population of Germany and Europe did not agitate for separation. Genocide scholars answer to those claims, that Holocaust revisionists also claim that the Jews agitated to destroy Germany by allying with the Soviet Union to bring Bolshevism into Germany, which according to them would mean the annihilation of the German people. | |||
| The ], sexual abuse, and prostitution of Armenian women were all very common.{{sfn|Akçam|2012|p=312}} Although Armenian women tried to avoid sexual violence, suicide was often the only alternative.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|pp=377–378}} Deportees were displayed naked in ] and sold as sex slaves in some areas, constituting an important source of income for accompanying gendarmes.{{sfn|Akçam|2012|pp=312–315}} Some were sold in Arabian slave markets to Muslim ] pilgrims and ended up as far away ] ].{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=758}} | |||
| Those who support the genocide theses state that Turkey is denying its past and accuse it of suppressing international attempts to recognize a genocide. To support their positions, they point to the fact that mention of an Armenian genocide almost anywhere in the world was met with rebukes from Turkish Ambassadors, while mention of it in Turkey itself led to the possibility of prosecution. | |||
| ===Confiscation of property=== | |||
| In ], ],Turkish Prime Minister ] invited Turkish, Armenian and international ]s to form a Commission to establish the events of 1915. The offer was accepted by Armenia but with a condition of having first good relations with the Turkish state. | |||
| {{main|Confiscation of Armenian properties in Turkey|National economy (Turkey)}} | |||
| ], the official residence of the ], was confiscated from Ohannes Kasabian, an Armenian businessman, in 1915.{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|pp=245–246}}|alt=Black and white photograph of a manor house]] | |||
| A secondary motivation for genocide was the destruction of the Armenian bourgeoisie to make room for a Turkish and Muslim middle class{{sfn|Watenpaugh|2013|p=284}} and build a statist ] controlled by Muslim Turks.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=810}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=273}} The campaign to Turkify the economy began in June 1914 with a law that obliged many non-Muslim merchants to hire Muslims. Following the deportations, the businesses of the victims were taken over by Muslims who were often incompetent, leading to economic difficulties.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=202}} The genocide had catastrophic effects on the Ottoman economy; Muslims were disadvantaged by the deportation of skilled professionals and entire districts fell into famine following their farmers' deportation.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=316–317}} The Ottoman and Turkish governments passed a series of ] to manage and redistribute property confiscated from Armenians.{{sfn|Akçam|Kurt|2015|p=2}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|pp=203–204}} Although the laws maintained that the state was simply administering the properties on behalf of the absent Armenians, there was no provision to return them to the owners—it was presumed that they had ceased to exist.{{sfn|Akçam|Kurt|2015|pp=11–12}} | |||
| Historians ] and ] argue that "The Republic of Turkey and its legal system were built, in a sense, on the seizure of Armenian cultural, social, and economic wealth, and on the removal of the Armenian presence."{{sfn|Akçam|Kurt|2015|p=2}} The proceeds from the sale of confiscated property was often used to fund the deportation of Armenians and resettlement of Muslims, as well as for army, militia, and other government spending.{{sfn|Akçam|2012|pp=256–257}} Ultimately this formed much of the basis of the industry and economy of the post-1923 republic, endowing it with ].{{sfn|Üngör|Polatel|2011|p=80}}{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=189}} The dispossession and exile of Armenian competitors enabled many lower-class Turks (i.e. peasantry, soldiers, and laborers) to rise to the middle class.{{sfn|Üngör|Polatel|2011|p=80}} Confiscation of Armenian assets continued into the second half of the twentieth century,{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=268}} and in 2006 the ] ruled that property records from 1915 must be kept closed to protect national security.{{sfn|Akçam|Kurt|2015|p=3}} Outside Istanbul, the traces of Armenian existence in Turkey, including churches and monasteries, libraries, '']s'', and ] and ], have been systematically erased, beginning during the war and continuing for decades afterward.{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|pp=64–65}}{{sfn|Göçek|2015|p=411}}{{sfn|Suciyan|2015|p=59}} | |||
| Relations between Turkey and Armenia remain frozen. Turkey has closed its land borders with Armenia, citing Armenian military control of ] and occupation of surrounding Azerbaijani territories. Armenia has repeatedly declared that it is ready for relations and an open border without preconditions, however Turkey claims that opening its borders would show support for the occupation of Nagorno-Karabagh. | |||
| == Destination == | |||
| == Stance taken by Turkish intellectuals == | |||
| {{further|Deir ez-Zor camps|Ras al-Ayn camps}} | |||
| ===Opposition to the genocide thesis=== | |||
| ] | |||
| ''Further information: ''] | |||
| ] near ]|alt=Thin stream of water surrounded by greenery and banks, above which is desert]] | |||
| The first arrivals in mid-1915 were accommodated in ]. From mid-November, the convoys were denied access to the city and redirected along the Baghdad Railway or the Euphrates towards ]. The first transit camp was established at Sibil, east of Aleppo; one convoy would arrive each day while another would depart for ] or ].{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=97}} Dozens of concentration camps were set up in Syria and ].{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=625}} By October 1915, some 870,000 deportees had reached Syria and Upper Mesopotamia. Most were repeatedly transferred between camps, being held in each camp for a few weeks, until there were very few survivors.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=98}} This strategy physically weakened the Armenians and spread disease, so much that some camps were shut down in late 1915 due to the threat of disease spreading to the Ottoman military.{{sfn|Shirinian|2017|p=21}}{{sfn| Kévorkian|2011|pp=633–635}} In late 1915, the camps around Aleppo were liquidated and the survivors were forced to march to ]; the camps around Ras al-Ayn were closed in early 1916 and the survivors sent to Deir ez-Zor.{{sfn|Mouradian|2018|p=155}} | |||
| Almost all Turkish intellectuals, scientists and historians accept that many Armenians died during the conflict, but they do not necessarily classify these events as genocide. Some academics point to the disputed number of mostly ]ish casualties killed by Armenians during the period, and argue that Armenians were ordered to relocate to save the victimized Kurds and Turks. | |||
| In general, Armenians were denied food and water during and after their forced march to the Syrian desert;{{sfn|Shirinian|2017|p=21}}{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=380}} many died of starvation, exhaustion, or disease, especially ], ], and ].{{sfn|Shirinian|2017|p=21}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=96}} Some local officials gave Armenians food; others took bribes to provide food and water.{{sfn|Shirinian|2017|p=21}} Aid organizations were officially barred from providing food to the deportees, although some circumvented these prohibitions.{{sfn|Shirinian|2017|p=23}} Survivors testified that some Armenians refused aid as they believed it would only prolong their suffering.{{sfn|Shirinian|2017|pp=20–21}} The guards raped female prisoners and also allowed Bedouins to raid the camps at night for looting and rape; some women were forced into marriage.{{sfn|Mouradian|2018|p=152}}{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=380}} Thousands of Armenian children were sold to childless Turks, Arabs, and Jews, who would come to the camps to buy them from their parents.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=98}} In the western ], governed by the ] under Djemal Pasha, there were no concentration camps or large-scale massacres, rather Armenians were resettled and recruited to work for the war effort. They had to convert to Islam or face deportation to another area.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|pp=673–674}} | |||
| ===Support for the genocide thesis=== | |||
| Some Turkish intellectuals support the genocide thesis despite opposition from Turkish nationalists; these include ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| The ability of the Armenians to adapt and survive was greater than the perpetrators expected.{{sfn|Kaiser|2010|p=384}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=693}} A loosely organized, Armenian-led resistance network based in Aleppo succeeded in helping many deportees, saving Armenian lives.{{sfn|Mouradian|2018|p=154}} At the beginning of 1916 some 500,000 deportees were alive in Syria and Mesopotamia.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=808}} Afraid that surviving Armenians might return home after the war, Talaat Pasha ordered a second wave of massacres in February 1916.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=259, 265}} Another wave of deportations targeted Armenians remaining in Anatolia.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|pp=695, 808}} More than 200,000 Armenians were killed between March and October 1916, often in remote areas near Deir ez-Zor and on parts of the ] valley, where their bodies would not create a public health hazard.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=262}}{{sfn|Kévorkian|2014|p=107}} The massacres killed most of the Armenians who had survived the camp system.{{sfn|Mouradian|2018|p=155}} | |||
| The reasons why some Turkish intellectuals accept theses of genocide are threefold. | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| == International reaction == | |||
| ]|alt=Modestly dressed woman carrying a child and surrounded by foodstuffs provided by relief efforts. The caption says "Lest they perish".]] | |||
| The Ottoman Empire tried to prevent journalists and photographers from documenting the atrocities, threatening them with arrest.{{sfn|Leonard|2004|p=297}}{{sfn|Akçam|2018|p=157}} Nevertheless, substantiated reports of mass killings were ].{{sfn|Leonard|2004|p=300}}{{sfn|de Waal|2015|p=2}} On 24 May 1915, the ] (Russia, Britain, and France) ] the Ottoman Empire for "] and civilization", and threatened to hold the perpetrators accountable.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=308}} Witness testimony was published in books such as '']'' (1916) and '']'' (1918), raising public awareness of the genocide.{{sfn|Tusan|2014|pp=57–58}} | |||
| The ] was a military ally of the Ottoman Empire during World War I.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=298}} German diplomats approved limited removals of Armenians in early 1915, and ] against the genocide,{{sfn|Kieser|Bloxham|2014|pp=600, 606–607}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=20–21}} which has been a source of controversy.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=298}}{{sfn|Ihrig|2016|p=134}} | |||
| First, they cite the fact that the organization members were criminals, and that those criminals were specifically sent to escort the Armenians. This is regarded as sufficient evidence of the government's criminal intent. Second, the fact that Armenians living outside the war zone were also removed, contradicts the thesis of military necessity put forward by the Ottoman government. Thirdly, it is argued that the thesis of simple relocation is flawed, due to the government's lack of dispositions which a “resettlement” would require. This lack of dispositions has been emphasized as evidence of the government's intent to eliminate the displaced Armenians. Dr. ], a Turkish specialist, writes on this point: | |||
| :“The fact that neither at the start of the deportations, nor ''en route'', and nor at the locations, which were declared to be their initial halting places, were there any single arrangement required for the organization of a people's migration, is sufficient proof of the existence of this plan of annihilation.” | |||
| Relief efforts were organized in dozens of countries to raise money for Armenian survivors. By 1925, people in 49 countries were organizing "Golden Rule Sundays" during which they consumed the diet of Armenian refugees, to raise money for humanitarian efforts.{{sfn|Anderson|2011|p=200}} Between 1915 and 1930, ] raised $110 million (${{Inflation|US|.11|1930|fmt=c|r=1}} billion adjusted for inflation) for refugees from the Ottoman Empire.<ref>{{cite web |title=History |url=https://www.neareast.org/who-we-are/ |website=] |access-date=10 March 2021 |archive-date=3 June 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150603200305/https://www.neareast.org/who-we-are/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| These Turkish intellectuals believe that 800,000 or more Armenians lost their lives during the events (Orhan Pamuk counting a million Armenians and 30 000 Kurds). Others put the number between 300,000 and 600,000. | |||
| == |
==Aftermath== | ||
| ===End of World War I=== | |||
| During a February 2005 interview with '']'', ], a famous Turkish ], made statements implicating Turkey in massacres against Armenians and persecution of the Kurds, declaring: "Thirty thousand Kurds and a million Armenians were killed in these lands and nobody but me dares to talk about it". Subjected to a ], he left Turkey, before returning in ] in order to defend his right to ]: "What happened to the Ottoman Armenians in 1915 was a major thing that was hidden from the Turkish nation; it was a taboo. But we have to be able to talk about the past" . The Turkish government then brought criminal charges against him. On January 23, 2006, however, the charges of "insulting Turkishness" were dropped, a move welcomed by the EU - that they had been brought at all was still a matter of contention for European politicians. | |||
| ] | |||
| Intentional, state-sponsored killing of Armenians mostly ceased by the end of January 1917, although sporadic massacres and starvation continued.{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=330}} Both contemporaries{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=721}}{{sfn|de Waal|2015|p=20}} and later historians have estimated that around 1 million Armenians ],{{sfn|Morris|Ze'evi|2019|p=1}}{{sfn|de Waal|2015|p=35}} with figures ranging from 600,000 to 1.5 million deaths.{{sfn|Morris|Ze'evi|2019|p=486}} Between 800,000 and 1.2 million Armenians were deported,{{sfn|Morris|Ze'evi|2019|p=486}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=354–355}} and contemporaries estimated that by late 1916 only 200,000 were still alive.{{sfn|Morris|Ze'evi|2019|p=486}} As the ] advanced in 1917 and 1918 ], they liberated around 100,000 to 150,000 Armenians working for the Ottoman military under abysmal conditions, not including those held by Arab tribes.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2020|pp=151–152}} | |||
| As a result of the ] and the subsequent ], the Russian army withdrew and Ottoman forces advanced into eastern Anatolia.{{sfn|Payaslian|2007|pp=148–149}} The ] was proclaimed in May 1918, at which time 50 percent of its population were refugees and 60 percent of its territory was under Ottoman occupation.{{sfn|Payaslian|2007|pp=150–151}} Ottoman troops withdrew from parts of Armenia following the October 1918 ].{{sfn|Payaslian|2007|pp=152–153}} From 1918 to 1920, Armenian militants committed revenge killings of thousands of Muslims, which have been cited as a retroactive excuse for genocide.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=367}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=342}} In 1918, at least 200,000 people in Armenia, mostly refugees, died from starvation or disease, in part due to a Turkish blockade of food supplies{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=706}} and the deliberate destruction of crops in eastern Armenia by Turkish troops, both before and after the armistice.{{sfn|Shirinian|2017|p=24}} | |||
| == International stances == | |||
| {{see also|Post Armenian Genocide timeline}} | |||
| Armenians organized a coordinated effort known as '']'' ({{lit|the gathering of orphans}}) that reclaimed thousands of kidnapped and Islamized Armenian women and children.{{sfn|Ekmekçioğlu|2013|pp=534–535}} Armenian leaders abandoned traditional ] to classify children born to Armenian women and their Muslim captors as Armenian.{{sfn|Ekmekçioğlu|2013|pp=530, 545}} An orphanage in ] held 25,000 orphans, the largest number in the world.{{sfn|de Waal|2015|p=76}} In 1920, the Armenian Patriarchate of Constantinople reported it was caring for 100,000 orphans, estimating that another 100,000 remained captive.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=759}} | |||
| There is a general agreement among Western historians that the Armenian Genocide did happen. The ] (the major body of scholars who study genocide in North America and Europe), for instance, formally recognize the event and consider it to be undeniable. Some consider denial to be a form of ] or/and ]. | |||
| === Trials === | |||
| ] | |||
| {{main|Prosecution of Ottoman war criminals after World War I|Turkish courts-martial of 1919–1920|l2=Ottoman Special Military Tribunal}} | |||
| However, this academic recognition has not always been followed by governments and media. Many governments, including the ], the ] and ], do not officially use the word genocide to describe these events, due in part to their strong ] and commercial ties with Turkey (such as the ]), although some individual government officials have used the term. Many newspapers for a long time would not use the word ''genocide'' without disclaimers such as "alleged" and many continue to do so. A number of those policies have now been reversed so that even casting doubt on the term is against editorial policy, as is the case with the '']''. | |||
| Following the armistice, Allied governments championed the prosecution of Armenian genocide perpetrators.{{sfn|Dadrian|Akçam|2011|pp=23–24}} Grand Vizier ] publicly recognized that 800,000 Ottoman citizens of Armenian origin had died as a result of state policy{{sfn|Dadrian|Akçam|2011|p=47}} and stated that "humanity, civilizations are shuddering, and forever will shudder, in face of this tragedy".{{sfn|Dadrian|Akçam|2011|p=49}} The postwar Ottoman government held the ], by which it sought to pin the Armenian genocide onto the CUP leadership while exonerating the Ottoman Empire as a whole, therefore avoiding ].{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|p=207}} The court ruled that "the crime of mass murder" of Armenians was "organized and carried out by the top leaders of CUP".{{sfn|Dadrian|Akçam|2011|p=120}} Eighteen perpetrators (including Talaat, Enver, and Djemal) were sentenced to death, of whom only three were ultimately executed as the remainder had fled and were tried '']''.{{sfn|Üngör|2012|p=62}}{{sfn|Dadrian|Akçam|2011|pp=24, 195}} The 1920 ], which awarded Armenia ], eliminated the Ottoman government's purpose for holding the trials.{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|p=217}} Prosecution was hampered by a widespread belief among Turkish Muslims that the actions against the Armenians were not punishable crimes.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2011|p=810}} Increasingly, the genocide was considered necessary and justified to establish a Turkish nation-state.{{sfn|Göçek|2011|pp=45–46}} | |||
| On 15 March 1921, ] in Berlin as part of ] to kill the perpetrators of the Armenian genocide.{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|pp=126–127}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=403–404, 409}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|p=346}} The trial of his admitted killer, ], focused on Talaat's responsibility for genocide. Tehlirian was acquitted by a German jury.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=344–346}}{{sfn|Ihrig|2016|pp=226–227, 235, 262, 293, "Trial in Berlin" ''passim''}} | |||
| In recent years, parliaments of a number of countries with citizens of Armenian descent, have officially recognized the event as genocide. Two recent examples are ] and ]. In Switzerland, Turkish historian ] has faced charges of violation of Swiss laws against ] as a result of a speech he made in ] in ]. Turkish entry talks with the ] were met with a number of calls to consider the event as ], though it was eventually not a specific stipulation. | |||
| ===Turkish War of Independence=== | |||
| Countries officially recognizing the Armenian genocide include ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| {{Further|Turkish war crimes}}] by ] in 1922 or 1923|alt=Caravan of people traveling in a line]] | |||
| ], early 1920s|alt=Crowded tent camp stretching out a long distance]] | |||
| The CUP regrouped as the ] to fight the ],{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=338–339}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=319}}{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|p=242}} relying on the support of perpetrators of the genocide and those who had profited from it.{{sfn|Zürcher|2011|p=316}}{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|p=155}} This movement saw the return of Armenian survivors as a mortal threat to its nationalist ambitions and the interests of its supporters. The return of survivors was therefore impossible in most of Anatolia{{sfn|Bozarslan ''et al.''|2015|p=311}}{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|p=242}} and thousands of Armenians who tried were murdered.{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|pp=229–230}} Historian ] states that the war of independence was "intended to complete the genocide by finally eradicating Armenian, Greek, and Syriac survivors".{{sfn|Kévorkian|2020|p=165}} In 1920 ], a Turkish general, ] with orders "to eliminate Armenia physically and politically".{{sfn|Kévorkian|2020|pp=164–165}}{{sfn|Nichanian|2015| p=238}} Nearly 100,000 Armenians were massacred in ] by the Turkish army and another 100,000 fled from ] during the ].{{sfn|Nichanian|2015| p=238}} According to Kévorkian, only the ] prevented another genocide.{{sfn|Kévorkian|2020|pp=164–165}} | |||
| The victorious nationalists subsequently declared the ] in 1923.{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|p=244}} CUP war criminals were granted immunity{{sfn|Dadrian|Akçam|2011|p=104}} and later that year, the ] established Turkey's current borders and provided for the ]. Its protection provisions for non-Muslim minorities had no enforcement mechanism and were disregarded in practice.{{sfn|Kieser|2018|p=28}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=367–368}} | |||
| International bodies that recognize the Armenian genocide include the ], the ], the ], and the ], the ], based on a report prepared for ], the ], the ], the ], the ], the ] , the ] (an unofficial organisation with no parliamentary powers), and the ]. | |||
| Armenian survivors were left mainly in three locations. About 295,000 Armenians had fled to Russian-controlled territory during the genocide and ended up mostly in ]. An estimated 200,000 Armenian refugees settled in the Middle East, forming a new wave of the ].{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|pp=103–104}} In the Republic of Turkey, about ] and another 200,000 lived in the provinces, largely women and children who had been forcibly converted.{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|p=104}} Though Armenians in Constantinople faced discrimination, they were allowed to maintain their cultural identity, unlike those elsewhere in Turkey{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|p=104}}{{sfn|Suciyan|2015|p=27}} who continued to face forced Islamization and kidnapping of girls after 1923.{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|p=203}}{{sfn|Suciyan|2015|p=65}} Between 1922 and 1929, the Turkish authorities eliminated surviving Armenians from southern Turkey, expelling thousands to ].{{sfn|Kévorkian|2020|p=161}} | |||
| Although there is no federal recognition of the Armenian Genocide, 39 of the 50 U.S. states including ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ] recognize the Armenian Genocide. | |||
| == Legacy == | |||
| The ] voted to officially recognize the Armenian Genocide. The federal government, in opposing the motion, did not express a position on whether the genocide took place. | |||
| According to historian ], the Armenian genocide reached an "iconic status" as "the apex of horrors conceivable" before ].{{sfn|Anderson|2011|p=199}} It was described by contemporaries as "the murder of a nation", "race extermination",{{sfn|Ihrig|2016|pages=9, 55}} "the greatest crime of the ages", and "the blackest page in modern history".{{sfn|de Waal|2015|p=21}}{{sfn|Kieser|2018|pp=289–290}} According to historian ], in Germany, the ] viewed post-1923 Turkey as a post-genocidal paradise and, "], its 'lessons', tactics, and 'benefits', into their own worldview".{{sfn|Ihrig|2016|pp=349, 354}} | |||
| === Turkey === | |||
| == Casualties, 1914 to 1923 == | |||
| {{See also|Armenian genocide denial}} | |||
| ] | |||
| In the 1920s, ] and ] replaced Armenians as the perceived ] of the Turkish state. ], weak ], lack of ], and especially the ]—thus justifying ]—are among the main legacies of the genocide in Turkey.{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|pp=263–264}} In postwar Turkey, the perpetrators of the genocide were hailed as martyrs of the national cause.{{sfn|Nichanian|2015|p=242}} Turkey's official denial of the Armenian genocide continues to rely on the CUP's ] of its actions. The Turkish government maintains that the mass deportation of Armenians was a legitimate action to combat an existential threat to the empire, but that there was no intention to exterminate the Armenian people.{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=xii, 361}}{{sfn|Akçam|2012|pp=xi, 451}} The government's position is supported by the majority of Turkish citizens.{{sfn|Göçek|2015|p=1}} Many Kurds, who themselves have suffered political repression in Turkey, ].{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|pp=273–275}}{{sfn|Galip|2020|pp=162–163}} | |||
| {{main|Ottoman Armenian casualties}} | |||
| While there is no clear consensus as to how many Armenians lost their lives during what is called the Armenian genocide and what followed, there seems to be a consensus among Western scholars, with the exception of few dissident and Turkish national historians, as to the period between 1914 to 1923, over a million Armenians might have perished. The recent tendency seems to be, either presenting 1.2 million as a figure or even 1.5 million, while more moderately, "over a million" is presented, as the Turkish historian Fikret Adanir estimates, but this estimate excludes what followed 1917 - 1918. | |||
| The Turkish state perceives open discussion of the genocide as a threat to national security because of its connection with the foundation of the republic, and for decades strictly ] it.{{sfn|Akçam|Kurt|2015|pp=3–4}}{{sfn|Galip|2020|p=3}} In 2002, the ] came to power and relaxed censorship to a certain extent, and the profile of the issue was raised by the 2007 ] of ], a Turkish-Armenian journalist known for his advocacy of reconciliation.{{sfn|Galip|2020|pp=3–4}} Although the AK Party softened the state denial rhetoric, describing Armenians as part of the Ottoman Empire's war losses,{{sfn|Ben Aharon|2019|p=339}} during the 2010s political repression and censorship increased again.{{sfn|Galip|2020|pp=83–85}} Turkey's century-long effort to prevent any recognition or mention of the genocide in foreign countries has included millions of dollars in lobbying,{{sfn|Göçek|2015|p=2}} as well as intimidation and threats.{{sfn|Chorbajian|2016|p=178}} | |||
| == Memorial == | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The idea for the memorial came in ], at the commemoration of the 50th anniversary of the genocide. Two years later the memorial (by ]s Kalashian and Mkrtchyan) was completed at the Tsitsernakaberd hill above the ] ] in ]. The 44 metre ] symbolizes the national rebirth of ]. 12 slabs are positioned in a circle, representing 12 lost provinces in present day ]. In the centre of the circle, in depth of 1.5 metres, there is an eternal flame. Along the park at the memorial there is a 100 metre wall with names of towns and villages where massacres are known to have taken place. In ] a small underground circular ] was opened at the other end of the park where one can learn basic information about the events in ]. Some photos taken by ] ]s (Turkish allies during ]) including photos taken by ] and some publications about the genocide are also displayed. Near the museum is a spot where foreign statesmen plant trees in memory of the genocide. | |||
| Each April 24th (Armenian Genocide Commemoration Holiday) hundreds of thousands of people walk to the genocide monument and lay flowers (usually red carnations or tulips) around the eternal flame. Armenians around the world mark the genocide in different ways, and many memorials have been built in Armenian Diaspora communities. | |||
| === Armenia and Azerbaijan === | |||
| ==The Armenian Genocide In Popular Culture== | |||
| ] on a hill above ]|alt=Spiky monument perched on a hill above a large city]] | |||
| The well-known ] band ], four musicians all of Armenian descent but living in California, wrote the song "] (Politically Lying, Unholy, Cowardly Killers.)" about this genocide in their ]. The booklet reads: ''"System Of A Down would like to dedicate this song to the memory of the 1.5 million victims of the Armenian Genocide, perpetrated by the Turkish Government in 1915."'' Other songs, including ] from their new album, ], are also sometimes believed to be about the Armenian genocide. | |||
| ] is commemorated on 24 April each year in Armenia and abroad, the anniversary of the ].{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|p=110}}{{sfn|Ben Aharon|2019|p=347}} On 24 April 1965, 100,000 Armenians ], and diaspora Armenians demonstrated across the world in favor of recognition of the genocide and annexing land from Turkey.{{sfn|de Waal|2015|pp=140, 142}}{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|p=110}} A memorial was completed two years later, at ] above Yerevan.{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|p=110}}{{sfn|de Waal|2015|pp=146–147}} | |||
| ], Armenians and Turkic ] have been involved in a ] over ], an Armenian enclave internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan. Initially involving peaceful demonstrations by Armenians, the conflict turned violent and has featured massacres by both sides, resulting in the displacement of more than half a million people.{{sfn|Bloxham|2005|pp=232–233}}{{sfn|Cheterian|2015|pp=279–282}}{{sfn|de Waal|2015|pp=196–197}} During the conflict, the Azerbaijani and Armenian governments have regularly accused each other of plotting genocide.{{sfn|Bloxham|2005|pp=232–233}} Azerbaijan has also joined the Turkish effort to deny the Armenian genocide.{{sfn|Koinova|2017|p=122}} | |||
| The Armenian Genocide is also a popular theme in Armenian works of literature, and is a major theme of ]'s film '']'' (2002). | |||
| ===International recognition=== | |||
| == See also == | |||
| {{ |
{{Main|Armenian genocide recognition}} | ||
| [[File:States recognising the Armenian Genocide recoloured.svg|thumb|upright=1.4|{{legend|#009e73|National legislatures that have passed resolutions recognizing the Armenian genocide}} | |||
| {{Wikiquote}} | |||
| {{legend|#d55e00|States that explicitly deny the Armenian genocide}}|alt=see Commons description for full list of countries depicted]] | |||
| {{Wikisourcecat|Armenian Genocide}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * '']'', a ] by ] | |||
| * '']'', a ] by ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], United States High Commissioner in Turkey (1919-27). | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| In response to continuing denial by the Turkish state, many Armenian diaspora activists have lobbied for international formal recognition of the Armenian genocide, an effort that has become a central concern of the Armenian diaspora.{{sfn|Koinova|2017|pp=112, 221–222}}{{sfn|de Waal|2015|p=3}} From the 1970s onward, many countries avoided recognition to preserve good relations with Turkey.{{sfn|Ben Aharon|2019|pp=340–341}} {{As of|2023}}, 31 ] have formally recognized the genocide, along with ] and the ].{{sfn|Koinova|2017|p=117}}<ref>{{cite web |title=Countries that Recognize the Armenian Genocide |url=https://www.armenian-genocide.org/recognition_countries.html |website=] |access-date=2023-12-14 |archive-date=14 September 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190914185246/https://www.armenian-genocide.org/recognition_countries.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Azerbaijan, Pakistan, and Turkey explicitly deny the genocide. | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| # {{note|intellectuals}} More exactly, 2345, See: Uras E., Tarihte Ermenliler ve Ermeni Meselesi, 2nd ed., (Istanbul, 1976), p.612 | |||
| # {{note|Van1}} See, for example, Huseyin Chelik, ''The 1915 Armenian Revolt in Van: Eyewitness Testimony'', in ''The Armenians in the Late Ottoman Period'', The Turkish Historical Society For The Council Of Culture, Arts And Publications Of The Grand National Assembly Of Turkey, Ankara, 2001, pp. 87-108 | |||
| # {{note|Van2}} Ussher, Clarence D. and Grace Knapp, A''n American Physician in Turkey; A Narrative of Adventures in Peace and in War''. Boston and New York City: Houghton Mifflin Co., 1917. More particularly the chapters, XVII, XVIII and XIX (which is titled FUN FOR JEVDET BEY.) | |||
| # {{note|Van3}} Rafael de Nogales, ''Four Years Beneath the Crescent'' Published in London, 1926, end of chapter V and VI. | |||
| # {{note|camps1}} See, for example, ''Le Siècle des camps'' by Joël Kotek and Pierre Rigoulot, JC Lattes, 2000. Also, ''Ahmed Djémal pacha et le sort des déportés arméniens de Syrie-Palestine'' by Raymond H. Kévorkian, in ''Der Völkermord an den Armeniern und die Shoah'', Zürich: Chronos, 2002. by Hans-Lukas KIESER et Dominik J. SCHALLER (dir.), and from the same author: ''L’extermination des déportés arméniens ottomans dans les camps de concentration de Syrie-Mésopotamie (1915-1916), la deuxième phase du génocide'', in ''Revue d’Histoire arménienne contemporaine'' II (1998). Concentration camps map, in, J.M. Winter, professor at Yale, ''America and the Armenian Genocide of 1915'', Cambridge University Press (January, 2004). | |||
| # {{note|camps2}} Ibid. | |||
| # {{note|camps3}} Ibid. | |||
| # {{note|camps4}} Ibid. | |||
| # {{note|camps5}} Ibid. | |||
| # {{note|burning}} Eitan Belkind was a ] member, who infiltrated the Ottoman army as an official. He was assigned to the headquarters of Camal Pasha. He claims to have witnessed the burning of 5000 Armenians, quoted in Yair Auron, ''The Banality of Indifference: Zionism and the Armenian Genocide''. New Brunswick, N.J., 2000, pp. 181, 183. Lt. Hasan Maruf, of the Ottoman army, describes how a population of a village were taken all together, and then burned. See, British Foreign Office 371/2781/264888, Appendices B., p. 6). Also, the Commander of the Third Army, Vehib's 12 pages affidavit, which was dated December 5, 1918, presented in the Trabzon trial series (March 29, 1919) included in the Key Indictment(published in ''Takvimi Vekayi'', No. 3540, May 5, 1919), report such a mass burning of the population of an entire village near Mus. S. S. McClure write in his work, ''Obstacles to Peace,'' Houghton Mifflin Company, 1917. pp. 400-401, that in Bitlis, Mus and Sassoun, ''The shortest method for disposing of the women and children concentrated in tile various camps was to burn them.'' And also that, ''Turkish prisoners who had apparently witnessed some of these scenes were horrified and maddened at the remembering the sight. They told the Russians that the stench of the burning human flesh permeated the air for many days after.'' The Germans, Ottoman allies, also witnessed the way Armenians were burned according to the Israeli historian, Bat Ye’or, who writes: ''The Germans, allies of the Turks in the First World War, … saw how civil populations were shut up in churches and burned, or gathered en masse in camps, tortured to death, and reduced to ashes,…'' (See: B. Ye'or, ''The Dhimmi. The Jews and Christians under Islam,'' Trans. from the French by D. Maisel P. Fenton and D. Liftman, Cranbury, N.J.: Frairleigh Dickinson University, 1985. p. 95) | |||
| # {{note| poisoning}} During the Trabzon trial series, of the Martial court (from the sittings between March 26 and Mat 17, 1919), the Trabzons Health Services Inspector Dr. Ziya Fuad wrote in a report that Dr. Saib, caused the death of children with the injection of morphine, the information was allegedly provided by two physicians (Drs. Ragib and Vehib), both Dr. Saib colleagues at Trabzons Red Crescent hospital, where those atrocities were said to have been committed. (See: Vahakn N. Dadrian, ''The Turkish Military Tribunal’s Prosecution of the Authors of the Armenian Genocide: Four Major Court-Martial Series,'' Genocide Study Project, H. F. Guggenheim Foundation, published in ''The Holocaust and Genocide Studies,'' Volume 11, Number 1, Spring 1997). Dr. Ziya Fuad, and Dr. Adnan, public health services director of Trabzon, submitted affidavits, reporting a cases, in which, two school buildings were used to organize children and then sent them on the mezzanine, to kill them with a toxic gas equipment. This case was presented during the Session 3, p.m., 1 April 1919, also published in the Constantinople newspaper Renaissance, 27 April 1919 (for more information, see: Vahakn N. Dadrian, ''The Role of Turkish Physicians in the World War I Genocide of Ottoman Armenians,'' in ''The Holocaust and Genocide Studies'' 1, no. 2 (1986): 169-192). The Turkish surgeon, Dr. Haydar Cemal wrote in ''Türkce Istanbul,'' No. 45, 23 December 1918, also published in ''Renaissance,'' 26 December 1918, that ''on the order of the Chief Sanitation Office of the IIIrd Army in January 1916, when the spread of typhus was an acute problem, innocent Armenians slated for deportation at Erzican were inoculated with the blood of typhoid fever patients without rendering that blood ‘inactive’.'' Jeremy Hugh Baron writes : ''Individual doctors were directly involved in the massacres, having poisoned infants, killed children and issued false certificates of death from natural causes. Nazim's brother-in-law Dr. Tevfik Rushdu, Inspector-General of Health Services, organized the disposal of Armenian corpses with thousands of kilos of lime over six months; he became foreign secretary from 1925 to 1938.'' (See: Jeremy Hugh Baron, ''Genocidal Doctors,'' publish in ''Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine,'' November, 1999, 92, pp.590-593). The psychiatrist, Robert Jay Lifton, writes in a parenthesis when introducing the crimes of NAZI doctors in his book ''Nazi Doctors: Medical Killing and the Psychology of Genocide,'' Basic Books, (1986) p. xii: ''(Perhaps Turkish doctors, in their participation in the genocide against the Armenians, come closest, as I shall later suggest).'' | |||
| # {{note| drowning}} Oscar S. Heizer, the American consul at Trabzon, reports: ''This plan did not suit Nail Bey .... Many of the children were loaded into boats and taken out to sea and thrown overboard.'' (See: U.S. National Archives. R.G. 59. 867. 4016/411. April 11, 1919 report.) The Italian consul of Trabzon in 1915, Giacomo Gorrini, writes: ''I saw thousands of innocent women and children placed on boats which were capsized in the Black Sea.'' (See: ''Toronto Globe'', August 26, 1915) Hoffman Philip, the American Charge at Constantinople chargé d'affairs, writes: ''Boat loads sent from Zor down the river arrived at Ana, one thirty miles away, with three fifths of passengers missing.'' (Cipher telegram, July 12, 1916. U.S. National Archives, R.G. 59.867.48/356.) The Trabzon trials reported Armenians having been drown in the Black Sea. (''Takvimi Vekdyi'', No. 3616, August 6, 1919, p. 2.) | |||
| ===Cultural depictions=== | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{main|Armenian genocide in culture}} | |||
| * Akcam, Taner, From Empire to Republic: Turkish Nationalism and the Armenian Genocide, Zed Books, 2004 | |||
| After meeting Armenian survivors in the Middle East, Austrian–Jewish writer ] wrote '']'', a fictionalized retelling of the successful Armenian uprising in ], as a warning of the dangers of ].{{sfn|Ihrig|2016|pp=1–2}} According to Ihrig, the book, released in 1933, is among the most important works of twentieth-century literature to address genocide and "is still considered essential reading for Armenians worldwide".{{sfn|Ihrig|2016|p=364}} The genocide became a central theme in English-language ].{{sfn|Der Mugrdechian|2016|p=273}} The first film about the Armenian genocide, ''],'' was released in 1919 as a fundraiser for Near East Relief, based on ] of ], who played herself.{{sfn|Marsoobian|2016|pp=73–74}}{{sfn|Tusan|2014|pp=69–70}}{{sfn|de Waal|2015|pp=77–78}} Since then more films about the genocide have been made, although it took several decades for any of them to reach a mass-market audience.{{sfn|Marsoobian|2016|p=73}} The ] paintings of ] were influenced by his experience of the genocide.{{sfn|Miller|2010|p=393}} More than ] have been erected in 32 countries to commemorate the event.<ref>{{cite web |title=Memorials to the Armenian Genocide |url=https://www.armenian-genocide.org/memorials.html |website=] |access-date=25 February 2021 |archive-date=9 August 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170809033251/http://www.armenian-genocide.org/memorials.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| * Akcam, Taner, A Shameful Act: The Armenian Genocide and the Question of Turkish Responsibility, Metropolitan Books, 2006 | |||
| * {{cite book | author=Balakian, Peter | title=The Burning Tigris: The Armenian Genocide and America's Response | publisher=HarperCollins | year=2003 | id=ISBN 0060198400}} | |||
| === Archives and historiography === | |||
| * Bartov, Omer, Mirrors of Destruction: War, Genocide and Modern Identity, Oxford Univ. Press, 2000 | |||
| {{see also|Kemalist historiography}} | |||
| * Dadrian, Vahakn, N., The History of the Armenian Genocide: Ethnic Conflict from the Balkans to Anatolia to the Caucasus, Berghahn Books, 1995 | |||
| The genocide is extensively documented in the archives of Germany, Austria, the United States, Russia, France, and the United Kingdom,{{sfn|Dadrian|Akçam|2011|p=4}} as well as the ], despite ].{{sfn|Akçam|2012|pp=xxii–xxiii, 25–26}} There are also thousands of ] from Western missionaries and Armenian survivors.{{sfn|Bloxham|Göçek|2008|p=345}}{{sfn|Chorbajian|2016|p=168}}{{sfn|Akçam|2018|p=11}} Polish-Jewish lawyer ], who coined the term '']'' in 1944, became interested in war crimes after reading about the 1921 trial of Soghomon Tehlirian for the assassination of Talaat Pasha. Lemkin recognized the fate of the Armenians as one of the most significant genocides in the twentieth century.{{sfn|de Waal|2015|pp=132–133}}{{sfn|Ihrig|2016|pp=9, 370–371}} Almost all historians and scholars outside Turkey, and an increasing number of Turkish scholars, recognize the destruction of Armenians in the Ottoman Empire as genocide.{{sfn|Göçek|2015|p=1}}{{sfn|Suny|2015|pp=374–375}} | |||
| * Dündar, Fuat, Ittihat ve Terakki'nin Müslümanlari Iskan Politikasi (1913-18), Iletisim, 2001 | |||
| * ], The First Holocaust. In ''The Great War for Civilisation - The Conquest of the Middle East''; (October 2005) London. Fourth Estate, pp.388-436. ISBN 184115007X | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| * Gust, Wolfgang, Der Völkermord an den Armeniern, Zu Klampen, 2005 | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| * Lepsius, Johannes, Deutschland und Armenien 1914-1918, Sammlung diplomatischer Aktenstücke, Donat & Temmen Verlag, 1986 | |||
| * Lewy, Guenter, The Armenian Massacres in Ottoman Turkey: A Disputed Genocide, University of Utah Press, Salt Lake City, 2005 (NEW PUBLICATION) | |||
| * {{cite book | author=McCarthy, Justin | title=Death and Exile: The Ethnic Cleansing of Ottoman Muslims, 1821-1922 | publisher=Darwin Press, Incorporated | year=1996 | id=ISBN 0878500944}} | |||
| * Melson, Robert, Revolution and Genocide. On the Origins of the Armenian Genocide and the Holocaust, The University of Chicago Press, 1996 | |||
| * Power, Samantha, "A Problem from Hell": America and the Age of Genocide, Harper 2003 | |||
| * Wallimann, Isidor (ed.): Genocide and the Modern Age: Etiology and Case Studies of Mass Death, Syracuse Univ. Press, 2000 | |||
| * {{Web reference | title=The Armenian Genocide: A Bibliography | work=University of Michigan, Dearborn: Armenian Research Center | URL=http://www.umd.umich.edu/dept/armenian/facts/gen_bib1.html | date=March 18 | year=2005}} | |||
| * {{Web reference | title=The Armenian Genocide: A Supplemental Bibliography, 1993-1996 | work=University of Michigan, Dearborn: Armenian Research Center | URL=http://www.umd.umich.edu/dept/armenian/facts/gen_bib2.html | date=March 18 | year=2005}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| ===Websites supporting the genocide theses=== | |||
| {{Reflist|19em}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| === |
===Sources=== | ||
| {{Main|Bibliography of the Armenian genocide}} | |||
| * ''Rockland Journal-News'' | |||
| ====Books==== | |||
| * | |||
| {{refbegin|indent=yes|35em}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book| last=Akçam| first=Taner| author-link=Taner Akçam|title=The Young Turks' Crime against Humanity: The Armenian Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing in the Ottoman Empire| date=2012| publisher=]|isbn=978-0-691-15333-9|title-link=The Young Turks' Crime against Humanity: The Armenian Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing in the Ottoman Empire}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Akçam |first1=Taner|title-link=Killing Orders|title=Killing Orders: Talat Pasha's Telegrams and the Armenian Genocide |date=2018 |publisher=] |isbn=978-3-319-69787-1 |language=en}} | |||
| * . 22:15 minute Real Audio. Guests: Peter Balakian, Zanku Armenian. Interviewer: Amy Goodman. ]. Friday, ] ]. Retrieved ] ]. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Akçam |first1=Taner |last2=Kurt |first2=Ümit |author2-link=Ümit Kurt (historian) |title=The Spirit of the Laws: The Plunder of Wealth in the Armenian Genocide |date=2015 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-78238-624-7}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bloxham |first1=Donald|author-link=Donald Bloxham |title=The Great Game of Genocide: Imperialism, Nationalism, and the Destruction of the Ottoman Armenians|title-link=The Great Game of Genocide |date=2005 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-19-927356-0 |language=en}} | |||
| * , Roger W. Smith, Eric Markusen and Robert Jay Lifton. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bozarslan |first1=Hamit |last2=Duclert |first2=Vincent |last3=Kévorkian |first3=Raymond H. |author1-link=:fr:Hamit Bozarslan |author2-link=:fr:Vincent Duclert |title=Comprendre le génocide des arméniens{{snd}}1915 à nos jours |date=2015 |publisher={{ill|Tallandier|fr|Éditions Tallandier}} |isbn=979-10-210-0681-2 |language=fr |trans-title=Understanding the Armenian genocide: 1915 to the present day|ref={{sfnref|Bozarslan et al.|2015}}}} | |||
| * Obelus.org | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Cheterian |first1=Vicken|author-link=Vicken Cheterian |title=Open Wounds: Armenians, Turks and a Century of Genocide |date=2015 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-84904-458-5 |language=en}} | |||
| * Guenter Lewy published an article in the ''Middle East Quarterly'' (Fall 2005) denying the Armenian Genocide. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Dadrian |first1=Vahakn N. |last2=Akçam |first2=Taner |author1-link=Vahakn Dadrian |title=Judgment at Istanbul: The Armenian Genocide Trials |date=2011 |publisher=Berghahn Books |isbn=978-0-85745-286-3}} | |||
| * ''Time Europe Magazine'', Vol. 166, No. 16, October 17, 2005, Letters. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=de Waal |first1=Thomas |author1-link=Thomas de Waal |title=Great Catastrophe: Armenians and Turks in the Shadow of Genocide |date=2015 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-935069-8}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Galip |first1=Özlem Belçim |title=New Social Movements and the Armenian Question in Turkey: Civil Society vs. the State |date=2020 |publisher=Springer International Publishing |isbn=978-3-030-59400-8}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Gingeras |first1=Ryan |author1-link=Ryan Gingeras |title=Fall of the Sultanate: The Great War and the End of the Ottoman Empire 1908–1922 |date=2016 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-967607-1 |language=en}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Göçek |first1=Fatma Müge |author1-link=Fatma Müge Göçek |title=Denial of Violence: Ottoman Past, Turkish Present and Collective Violence Against the Armenians, 1789–2009 |date=2015 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-933420-9 |title-link=Denial of Violence}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Ihrig|first=Stefan|author-link=Stefan Ihrig|date=2016|title=Justifying Genocide: Germany and the Armenians from Bismarck to Hitler|title-link=Justifying Genocide|publisher=]|isbn=978-0-674-50479-0}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Kévorkian |first1=Raymond |author1-link=Raymond Kévorkian |title=The Armenian Genocide: A Complete History|title-link=The Armenian Genocide: A Complete History |date=2011 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-85771-930-0 |language=en}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Kieser |first1=Hans-Lukas |author1-link=Hans-Lukas Kieser |title=] |date=2018 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-1-4008-8963-1 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Morris |first1=Benny|author-link=Benny Morris |last2=Ze'evi |first2=Dror|author2-link=Dror Ze'evi |title=The Thirty-Year Genocide: Turkey's Destruction of Its Christian Minorities, 1894–1924|title-link=The Thirty-Year Genocide |date=2019 |publisher=Harvard University Press |isbn=978-0-674-91645-6}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Nichanian |first1=Mikaël |author1-link=:fr:Mikaël Nichanian |title=Détruire les Arméniens. Histoire d'un génocide |date=2015 |publisher=] |isbn=978-2-13-062617-6 |language=fr|trans-title=Destroying the Armenians: History of a Genocide}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Payaslian |first1=Simon|author-link=Simon Payaslian |title=The History of Armenia: From the Origins to the Present |date=2007 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |isbn=978-1-4039-7467-9 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Rogan |first1=Eugene |author1-link=Eugene Rogan |title=The Fall of the Ottomans: The Great War in the Middle East |date=2015 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-465-05669-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Suciyan |first1=Talin |title=The Armenians in Modern Turkey: Post-Genocide Society, Politics and History |date=2015 |publisher=I.B. Tauris |isbn=978-0-85772-773-2 }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Suny |first1=Ronald Grigor|author-link=Ronald Grigor Suny |title="They Can Live in the Desert but Nowhere Else": A History of the Armenian Genocide|title-link=They Can Live in the Desert but Nowhere Else |date=2015 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-1-4008-6558-1}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last1=Üngör|first1=Uğur Ümit|last2=Polatel|first2=Mehmet|author-link1=Uğur Ümit Üngör|author-link2=|title=Confiscation and Destruction: The Young Turk Seizure of Armenian Property|year=2011|publisher=]|isbn=978-1-4411-3578-0}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ====Chapters==== | |||
| ===Websites opposing the genocide theses=== | |||
| {{refbegin|indent=yes|35em}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Ahmed |first1=Ali |title=Encyclopedia of the Developing World |date=2006 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-57958-388-0 |pages=1575–1578 |language=en |chapter=Turkey}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Anderson |first1=Margaret Lavinia|author-link=Margaret L. Anderson |title=A Question of Genocide: Armenians and Turks at the End of the Ottoman Empire |title-link=A Question of Genocide|date=2011 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-539374-3 |language=en |chapter=Who Still Talked about the Extermination of the Armenians?|pages=199–217}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Astourian |first1=Stephan|chapter=The Silence of the Land: Agrarian Relations, Ethnicity, and Power|pages=55–81 |title=A Question of Genocide: Armenians and Turks at the End of the Ottoman Empire|date=2011 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-539374-3}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bloxham |first1=Donald |last2=Göçek |first2=Fatma Müge |title=The Historiography of Genocide |date=2008 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan UK |isbn=978-0-230-29778-4 |pages=344–372 |language=en |chapter=The Armenian Genocide}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Chorbajian |first1=Levon |author-link1=Levon Chorbajian |title=The Armenian Genocide Legacy |date=2016 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan UK |isbn=978-1-137-56163-3 |pages=167–182 |language=en |chapter='They Brought It on Themselves and It Never Happened': Denial to 1939}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Cora |first1=Yaşar Tolga |title=Not All Quiet on the Ottoman Fronts: Neglected Perspectives on a Global War, 1914–1918 |date=2020 |publisher=Ergon-Verlag |isbn=978-3-95650-777-9 |pages=49–72 |chapter=Towards a Social History of the Ottoman War Economy: Manufacturing and Armenian Forced Skilled-Laborers}} | |||
| * — in French (with a little English), covering history and allegations | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Der Mugrdechian |first1=Barlow|author-link=Barlow Der Mugrdechian |title=The Armenian Genocide Legacy |date=2016 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan UK |isbn=978-1-137-56163-3 |pages=273–286 |language=en |chapter=The Theme of Genocide in Armenian Literature}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Dündar |first1=Fuat|author-link=Fuat Dündar |title=A Question of Genocide: Armenians and Turks at the End of the Ottoman Empire|date=2011 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-539374-3 |language=en |chapter=Pouring a People into the Desert: The "Definitive Solution" of the Unionists to the Armenian Question|pages=276–286}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Göçek |first1=Fatma Müge|chapter=Reading Genocide: Turkish Historiography on 1915|pages=42–52 |title=A Question of Genocide: Armenians and Turks at the End of the Ottoman Empire |date=2011 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-539374-3}} | |||
| * , Official view of Republic of Turkey | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Kaiser |first1=Hilmar |authorlink=Hilmar Kaiser |title=The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies |publisher= Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-923211-6 |language=en |chapter=Genocide at the Twilight of the Ottoman Empire|date= 2010|pages=365–385}} | |||
| * - A site documenting the massacre of Turks and Azeris by Armenians | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Kaligian |first1=Dikran |title=Genocide in the Ottoman Empire: Armenians, Assyrians, and Greeks, 1913–1923 |date=2017 |publisher=Berghahn Books |isbn=978-1-78533-433-7 |language=en |chapter=Convulsions at the End of Empire: Thrace, Asia Minor, and the Aegean|pages=82–104}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Kévorkian |first1=Raymond |title=Destruction and Human Remains: Disposal and Concealment in Genocide and Mass Violence |date=2014 |publisher=Manchester University Press |isbn=978-1-84779-906-7 |pages=89–116 |chapter-url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctt1wn0s3n.9 |language=en |chapter=Earth, Fire, Water: or How to Make the Armenian Corpses Disappear |jstor=j.ctt1wn0s3n.9 |access-date=<!-- none --> |archive-date=16 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210416013901/https://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctt1wn0s3n.9 |url-status=dead }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Kévorkian |first1=Raymond |title=Collective and State Violence in Turkey: The Construction of a National Identity from Empire to Nation-State |date=2020 |publisher=Berghahn Books |isbn=978-1-78920-451-3 |pages=147–173 |language=en |chapter=The Final Phase: The Cleansing of Armenian and Greek Survivors, 1919–1922}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Kieser |first1=Hans-Lukas |last2=Bloxham |first2=Donald |title=]: Volume 1: Global War |date=2014 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-511-67566-9 |pages=585–614 |chapter=Genocide}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Koinova |first1=Maria |title=Diaspora as Cultures of Cooperation: Global and Local Perspectives |date=2017 |publisher=Springer International Publishing |isbn=978-3-319-32892-8 |pages=111–129 |language=en |chapter=Conflict and Cooperation in Armenian Diaspora Mobilisation for Genocide Recognition}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Leonard |first1=Thomas C. |title=America and the Armenian Genocide of 1915 |date=2004 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-521-82958-8 |pages=294–308 |chapter=When news is not enough: American media and Armenian deaths}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Maksudyan |first1=Nazan |author1-link=Nazan Maksudyan |title=Gendering Global Humanitarianism in the Twentieth Century: Practice, Politics and the Power of Representation |date=2020 |publisher=Springer International Publishing |isbn=978-3-030-44630-7 |pages=117–142 |language=en |chapter=The Orphan Nation: Gendered Humanitarianism for Armenian Survivor Children in Istanbul, 1919–1922}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Marsoobian |first1=Armen|authorlink=Armen T. Marsoobian |title=The History of Genocide in Cinema: Atrocities on Screen |date=2016 |publisher=Bloomsbury Publishing |isbn=978-1-78673-047-3 |pages=73–86 |language=en |chapter=The Armenian Genocide in Film: Overcoming Denial and Loss}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Mouradian |first1=Khatchig|author-link=Khatchig Mouradian |title=Internment during the First World War: A Mass Global Phenomenon |date=2018 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-315-22591-3 |pages=145–161 |language=en |chapter=Internment and destruction: Concentration camps during the Armenian genocide, 1915–16}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Üngör |first=Uğur Ümit |title=Holocaust and Other Genocides |date=2012 |publisher=] / Amsterdam University Press |isbn=978-90-4851-528-8 |pages=45–72 |url=https://www.niod.nl/sites/niod.nl/files/Holocaust%20and%20other%20genocides.pdf |language=en |chapter=The Armenian Genocide, 1915 |chapter-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210508050001/https://www.niod.nl/sites/niod.nl/files/Armenian%20genocide.pdf |access-date=3 July 2021 |archive-date=25 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210425062732/https://www.niod.nl/sites/niod.nl/files/Holocaust%20and%20other%20genocides.pdf |url-status=dead }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Üngör |first1=Uğur Ümit |title=The Armenian Genocide Legacy |date=2016 |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan UK |isbn=978-1-137-56163-3 |pages=11–25 |language=en |chapter=The Armenian Genocide in the Context of 20th-Century Paramilitarism}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Zürcher|first=Erik Jan|author-link=Erik Jan Zürcher|chapter=Renewal and Silence: Postwar Unionist and Kemalist Rhetoric on the Armenian Genocide|pages=306–316 |title=A Question of Genocide: Armenians and Turks at the End of the Ottoman Empire |date=2011 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-539374-3}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==== |
====Journal articles==== | ||
| {{refbegin|indent=yes|35em}} | |||
| * O. Faruk Logoglu is the ambassador of Turkey to the United States. | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Akçam |first1=Taner |title=When Was the Decision to Annihilate the Armenians Taken? |journal=] |date=2019 |volume=21 |issue=4 |pages=457–480 |doi=10.1080/14623528.2019.1630893 |s2cid=<!-- --> | issn = 1462-3528}} | |||
| * Dr. Sedat Laciner is a member of Turkish Armenian Relations National Committee and International Strategic Research Organization. | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Ben Aharon |first1=Eldad |title=Recognition of the Armenian Genocide after its Centenary: A Comparative Analysis of Changing Parliamentary Positions |journal=] |date=2019 |volume=13 |issue=3 |pages=339–352 |doi=10.1080/23739770.2019.1737911 |doi-access=free |hdl=1887/92270 |hdl-access=free }} | |||
| * Bruce Fein is an attorney and a frequent The Washington Times contributor | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Bjørnlund |first1=Matthias|authorlink=Matthias Bjørnlund|title=The 1914 cleansing of Aegean Greeks as a case of violent Turkification |journal=Journal of Genocide Research |date=2008 |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=41–58 |doi=10.1080/14623520701850286 |s2cid=<!-- --> }} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1= Ekmekçioğlu |first1=Lerna|author-link= Lerna Ekmekçioğlu |title=A Climate for Abduction, a Climate for Redemption: The Politics of Inclusion during and after the Armenian Genocide |journal=] |date=2013 |volume=55 |issue=3 |pages=522–553 |doi=10.1017/S0010417513000236 |jstor=23526015 |hdl=1721.1/88911 |s2cid=<!-- --> |hdl-access=free }} | |||
| * on ] ] to the Members of US House of Representatives (*.pdf file) | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Kaiser |first1=Hilmar |title=Financing the Ruling Party and Its Militants in Wartime:The Armenian Genocide and the Kemah Massacres of 1915 |journal=] |date=2019 |issue=12 |pages=7–31 |doi=10.4000/eac.1942 |doi-access=free }} | |||
| * published in International Herald Tribune on ] ] | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Kurt |first1=Ümit |title=Cultural Erasure: The Absorption and Forced Conversion of Armenian Women and Children, 1915–1916 |journal=Études arméniennes contemporaines |date=2016 |issue=7 |doi=10.4000/eac.997 |doi-access=free }} | |||
| * Guenter Lewy is professor emeritus of political science, University of Massachusetts, and the author of The Armenian Massacres in Ottoman Turkey: A Disputed Genocide (University of Utah Press, 2005). | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Miller |first1=Angela |title=Achilles the Bitter: Gorky and the Genocide |journal=Oxford Art Journal |date=2010 |volume=33 |issue=3 |pages=392–396 |doi=10.1093/oxartj/kcq025 }} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Shirinian |first1=George N. |title=Starvation and Its Political Use in the Armenian Genocide |journal=Genocide Studies International |date=2017 |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=8–37 |id={{Project MUSE|680838}} |doi=10.3138/gsi.11.1.01 |s2cid=<!-- --> }} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Tusan |first1=Michelle |title='Crimes against Humanity': Human Rights, the British Empire, and the Origins of the Response to the Armenian Genocide |journal=] |date=2014 |volume=119 |issue=1 |pages=47–77 |doi=10.1093/ahr/119.1.47 |doi-access=free }} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Watenpaugh |first1=Keith David |authorlink=Keith David Watenpaugh |title='Are There Any Children for Sale?': Genocide and the Transfer of Armenian Children (1915–1922) |journal=] |date=2013 |volume=12 |issue=3 |pages=283–295 |doi=10.1080/14754835.2013.812410 |s2cid=<!-- --> }} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| ===Independent Studies=== | |||
| {{Sister project links|Armenian Genocide|s=Portal:Armenian Genocide|d=Q80034|collapsible=collapsed}} | |||
| * by Center for Global Studies, American University | |||
| * | |||
| :: (*.doc file) "The Turkish Economic and Social Studies Foundation (TESEV) and the Armenian Sociological Association (HASA) have organized a Mutual Perceptions Research Project. Each group is carrying out sociological research to identify key issues of cultural understanding between the neighboring countries, including the perception of Turks by Armenians and of Armenians by Turks. The study focuses on the perceptions of the majority populations in each country. The combined results will constitute study findings. Representatives from each team met in Yerevan and fieldwork was undertaken in both countries. The results of the research were presented at an international seminar jointly organized by TESEV and HASA in Tbilisi, Georgia." | |||
| * | |||
| * Turkish Armenian Reconciliation Commission (TARC) | |||
| * by ] | |||
| :: (*.pdf file) Armenian and Turkish versions of the report are also available on the above mentioned website. | |||
| {{Armenian Genocide}} | |||
| * , professor Alfred De Zayas report. Professor De Zaya is an ex-secretary of the United Nations Human Rights Committee. | |||
| {{bots|deny=Citation bot}} | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| |title=Related articles | |||
| |list1= | |||
| {{Armenia topics}} | |||
| {{World War I}} | |||
| {{Turkish nationalism}} | |||
| {{Genocide topics}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Portal bar|Turkey|Genocide|Asia<!--For Armenia-->|Europe<!--For Armenia-->}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 03:51, 28 November 2024
1915–1917 mass murder in the Ottoman Empire
| Armenian genocide | |
|---|---|
| Part of World War I | |
 Column of Armenian deportees guarded by gendarmes in Harput vilayet Column of Armenian deportees guarded by gendarmes in Harput vilayet | |
| Location | Ottoman Empire |
| Date | 1915–1917 |
| Target | Ottoman Armenians |
| Attack type | Genocide, death march, Islamization |
| Deaths | 600,000–1.5 million |
| Perpetrators | Committee of Union and Progress |
The Armenian genocide was the systematic destruction of the Armenian people and identity in the Ottoman Empire during World War I. Spearheaded by the ruling Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), it was implemented primarily through the mass murder of around one million Armenians during death marches to the Syrian Desert and the forced Islamization of others, primarily women and children.
Before World War I, Armenians occupied a somewhat protected, but subordinate, place in Ottoman society. Large-scale massacres of Armenians had occurred in the 1890s and 1909. The Ottoman Empire suffered a series of military defeats and territorial losses—especially during the 1912–1913 Balkan Wars—leading to fear among CUP leaders that the Armenians would seek independence. During their invasion of Russian and Persian territory in 1914, Ottoman paramilitaries massacred local Armenians. Ottoman leaders took isolated instances of Armenian resistance as evidence of a widespread rebellion, though no such rebellion existed. Mass deportation was intended to permanently forestall the possibility of Armenian autonomy or independence.
On 24 April 1915, the Ottoman authorities arrested and deported hundreds of Armenian intellectuals and leaders from Constantinople. At the orders of Talaat Pasha, an estimated 800,000 to 1.2 million Armenians were sent on death marches to the Syrian Desert in 1915 and 1916. Driven forward by paramilitary escorts, the deportees were deprived of food and water and subjected to robbery, rape, and massacres. In the Syrian Desert, the survivors were dispersed into concentration camps. In 1916, another wave of massacres was ordered, leaving about 200,000 deportees alive by the end of the year. Around 100,000 to 200,000 Armenian women and children were forcibly converted to Islam and integrated into Muslim households. Massacres and ethnic cleansing of Armenian survivors continued through the Turkish War of Independence after World War I, carried out by Turkish nationalists.
This genocide put an end to more than two thousand years of Armenian civilization in eastern Anatolia. Together with the mass murder and expulsion of Assyrian/Syriac and Greek Orthodox Christians, it enabled the creation of an ethnonationalist Turkish state, the Republic of Turkey. The Turkish government maintains that the deportation of Armenians was a legitimate action that cannot be described as genocide. As of 2023, 34 countries have recognized the events as genocide, concurring with the academic consensus.
Background
Further information: Causes of the Armenian genocideArmenians in the Ottoman Empire
Main article: Armenians in the Ottoman Empire
The presence of Armenians in Anatolia has been documented since the sixth century BCE, about 1,500 years before the arrival of Turkmens under the Seljuk dynasty. The Kingdom of Armenia adopted Christianity as its national religion in the fourth century CE, establishing the Armenian Apostolic Church. Following the end of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, two Islamic empires—the Ottoman Empire and the Iranian Safavid Empire—contested Western Armenia, which was permanently separated from Eastern Armenia (held by the Safavids) by the 1639 Treaty of Zuhab. The Ottoman Empire was multiethnic and multireligious, and its millet system offered non-Muslims a subordinate but protected place in society. Sharia law encoded Islamic superiority but guaranteed property rights and freedom of worship to non-Muslims (dhimmis) in exchange for a special tax.
On the eve of World War I in 1914, around two million Armenians lived in Ottoman territory, mostly in Anatolia, a region with a total population of 15–17.5 million. According to the Armenian Patriarchate's estimates for 1913–1914, there were 2,925 Armenian towns and villages in the Ottoman Empire, of which 2,084 were in the Armenian highlands adjacent to the Russian border. Armenians were a minority in most places where they lived, alongside Turkish and Kurdish Muslim and Greek Orthodox Christian neighbors. According to the Patriarchate's figure, 215,131 Armenians lived in urban areas, especially Constantinople, Smyrna, and Eastern Thrace. Although most Ottoman Armenians were peasant farmers, they were overrepresented in commerce. As middleman minorities, despite the wealth of some Armenians, their overall political power was low, making them especially vulnerable.
Land conflict and reforms

Armenians in the eastern provinces lived in semi-feudal conditions and commonly encountered forced labor, illegal taxation, and unpunished crimes against them including robberies, murders, and sexual assaults. Beginning in 1839, the Ottoman government issued a series of reforms to centralize power and equalize the status of Ottoman subjects regardless of religion. The reforms to equalize the status of non-Muslims were strongly opposed by Islamic clergy and Muslims in general, and remained mostly theoretical. Because of the abolition of the Kurdish emirates in the mid-nineteenth century, the Ottoman government began to directly tax Armenian peasants who had previously paid taxes only to Kurdish landlords. The latter continued to exact levies illegally.
From the mid-nineteenth century, Armenians faced large-scale land usurpation as a consequence of the sedentarization of Kurdish tribes and the arrival of Muslim refugees and immigrants (mainly Circassians) following the Russo-Circassian War. In 1876, when Sultan Abdul Hamid II came to power, the state began to confiscate Armenian-owned land in the eastern provinces and give it to Muslim immigrants as part of a systematic policy to reduce the Armenian population of these areas. This policy lasted until World War I. These conditions led to a substantial decline in the population of the Armenian highlands; 300,000 Armenians left the empire, and others moved to towns. Some Armenians joined revolutionary political parties, of which the most influential was the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (ARF), founded in 1890. These parties primarily sought reform within the empire and found only limited support from Ottoman Armenians.
Russia's decisive victory in the 1877–1878 war forced the Ottoman Empire to cede parts of eastern Anatolia, the Balkans, and Cyprus. Under international pressure at the 1878 Congress of Berlin, the Ottoman government agreed to carry out reforms and guarantee the physical safety of its Armenian subjects, but there was no enforcement mechanism; conditions continued to worsen. The Congress of Berlin marked the emergence of the Armenian question in international diplomacy as Armenians were for the first time used by the Great Powers to interfere in Ottoman politics. Although Armenians had been called the "loyal millet" in contrast to Greeks and others who had previously challenged Ottoman rule, the authorities began to perceive Armenians as a threat after 1878. In 1891, Abdul Hamid created the Hamidiye regiments from Kurdish tribes, allowing them to act with impunity against Armenians. From 1895 to 1896 the empire saw widespread massacres; at least 100,000 Armenians were killed primarily by Ottoman soldiers and mobs let loose by the authorities. Many Armenian villages were forcibly converted to Islam. The Ottoman state bore ultimate responsibility for the killings, whose purpose was violently restoring the previous social order in which Christians would unquestioningly accept Muslim supremacy, and forcing Armenians to emigrate, thereby decreasing their numbers.
Young Turk Revolution
Main article: Young Turk RevolutionAbdul Hamid's despotism prompted the formation of an opposition movement, the Young Turks, which sought to overthrow him and restore the 1876 Constitution of the Ottoman Empire, which he had suspended in 1877. One faction of the Young Turks was the secret and revolutionary Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), based in Salonica, from which the charismatic conspirator Mehmed Talaat (later Talaat Pasha) emerged as a leading member. Although skeptical of a growing, exclusionary Turkish nationalism in the Young Turk movement, the ARF decided to ally with the CUP in December 1907. In 1908, the CUP came to power in the Young Turk Revolution, which began with a string of CUP assassinations of leading officials in Macedonia. Abdul Hamid was forced to reinstate the 1876 constitution and restore the Ottoman parliament, which was celebrated by Ottomans of all ethnicities and religions. Security improved in parts of the eastern provinces after 1908 and the CUP took steps to reform the local gendarmerie, although tensions remained high. Despite an agreement to reverse the land usurpation of the previous decades in the 1910 Salonica Accord between the ARF and the CUP, the latter made no efforts to carry this out.

In early 1909 an unsuccessful countercoup was launched by conservatives and some liberals who opposed the CUP's increasingly repressive governance. When news of the countercoup reached Adana, armed Muslims attacked the Armenian quarter and Armenians returned fire. Ottoman soldiers did not protect Armenians and instead armed the rioters. Between 20,000 and 25,000 people, mostly Armenians, were killed in Adana and nearby towns. Unlike the 1890s massacres, the events were not organized by the central government but instigated by local officials, intellectuals, and Islamic clerics, including CUP supporters in Adana. Although the massacres went unpunished, the ARF continued to hope that reforms to improve security and restore lands were forthcoming, until late 1912, when they broke with the CUP and appealed to the European powers. On 8 February 1914, the CUP reluctantly agreed to reforms brokered by Germany that provided for the appointment of two European inspectors for the entire Ottoman east and putting the Hamidiye regiments in reserve. CUP leaders feared that these reforms, which were never implemented, could lead to partition and cited them as a reason for the elimination of the Armenian population in 1915.
Balkan Wars
Main article: Balkan Wars
The 1912 First Balkan War resulted in the loss of almost all of the empire's European territory and the mass expulsion of Muslims from the Balkans. Ottoman Muslim society was incensed by the atrocities committed against Balkan Muslims, intensifying anti-Christian sentiment and leading to a desire for revenge. Blame for the loss was assigned to all Christians, including the Ottoman Armenians, many of whom had fought on the Ottoman side. The Balkan Wars put an end to the Ottomanist movement for pluralism and coexistence; instead, the CUP turned to an increasingly radical Turkish nationalism to preserve the empire. CUP leaders such as Talaat and Enver Pasha came to blame non-Muslim population concentrations in strategic areas for many of the empire's problems, concluding by mid-1914 that they were internal tumors to be excised. Of these, Ottoman Armenians were considered the most dangerous, because CUP leaders feared that their homeland in Anatolia—claimed as the last refuge of the Turkish nation—would break away from the empire as the Balkans had.
In January 1913, the CUP launched another coup, installed a one-party state, and strictly repressed all real or perceived internal enemies. After the coup, the CUP shifted the demography of border areas by resettling Balkan Muslim refugees while coercing Christians to emigrate; immigrants were promised property that had belonged to Christians. When parts of Eastern Thrace were reoccupied by the Ottoman Empire during the Second Balkan War in mid-1913, there was a campaign of looting and intimidation against Greeks and Armenians, forcing many to emigrate. Around 150,000 Greek Orthodox from the Aegean coast were forcibly deported in May and June 1914 by Muslim bandits, who were secretly backed by the CUP and sometimes joined by the regular army. Historian Matthias Bjørnlund states that the perceived success of the Greek deportations allowed CUP leaders to envision even more radical policies "as yet another extension of a policy of social engineering through Turkification".
Ottoman entry into World War I
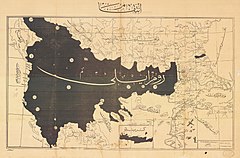
A few days after the outbreak of World War I, the CUP concluded an alliance with Germany on 2 August 1914. The same month, CUP representatives went to an ARF conference demanding that, in the event of war with Russia, the ARF incite Russian Armenians to intervene on the Ottoman side. Instead, the delegates resolved that Armenians should fight for the countries of their citizenships. During its war preparations, the Ottoman government recruited thousands of prisoners to join the paramilitary Special Organization, which initially focused on stirring up revolts among Muslims behind Russian lines beginning before the empire officially entered the war. On 29 October 1914, the empire entered World War I on the side of the Central Powers by launching a surprise attack on Russian ports in the Black Sea. Many Russian Armenians were enthusiastic about the war, but Ottoman Armenians were more ambivalent, afraid that supporting Russia would bring retaliation. Organization of Armenian volunteer units by Russian Armenians, later joined by some Ottoman Armenian deserters, further increased Ottoman suspicions against their Armenian population.
Wartime requisitions were often corrupt and arbitrary, and disproportionately targeted Greeks and Armenians. Armenian leaders urged young men to accept conscription into the army, but many soldiers of all ethnicities and religions deserted due to difficult conditions and concern for their families. At least 10 percent of Ottoman Armenians were mobilized, leaving their communities bereft of fighting-age men and therefore largely unable to organize armed resistance to deportation in 1915. During the Ottoman invasion of Russian and Persian territory, the Special Organization massacred local Armenians and Assyrian/Syriac Christians. Beginning in November 1914, provincial governors of Van, Bitlis, and Erzerum sent many telegrams to the central government pressing for more severe measures against the Armenians, both regionally and throughout the empire. These requests were endorsed by the central government already before 1915. Armenian civil servants were dismissed from their posts in late 1914 and early 1915. In February 1915, the CUP leaders decided to disarm Armenians serving in the army and transfer them to labor battalions. The Armenian soldiers in labor battalions were systematically executed, although many skilled workers were spared until 1916.
Onset of genocide
Further information: Causes of the Armenian genocide § Wartime radicalization

Minister of War Enver Pasha took over command of the Ottoman armies for the invasion of Russian territory, and tried to encircle the Russian Caucasus Army at the Battle of Sarikamish, fought from December 1914 to January 1915. Unprepared for the harsh winter conditions, his forces were routed, losing more than 60,000 men. The retreating Ottoman army destroyed dozens of Ottoman Armenian villages in Bitlis vilayet, massacring their inhabitants. Enver publicly blamed his defeat on Armenians who he claimed had actively sided with the Russians, a theory that became a consensus among CUP leaders. Reports of local incidents such as weapons caches, severed telegraph lines, and occasional killings confirmed preexisting beliefs about Armenian treachery and fueled paranoia among CUP leaders that a coordinated Armenian conspiracy was plotting against the empire. Discounting contrary reports that most Armenians were loyal, the CUP leaders decided that the Armenians had to be eliminated to save the empire.
Massacres of Armenian men were occurring in the vicinity of Bashkale in Van vilayet from December 1914. ARF leaders attempted to keep the situation calm, warning that even justifiable self-defense could lead to escalation of killing. The governor, Djevdet Bey, ordered the Armenians of Van to hand over their arms on 18 April 1915, creating a dilemma: If they obeyed, the Armenians expected to be killed, but if they refused, it would provide a pretext for massacres. Armenians fortified themselves in Van and repelled the Ottoman attack that began on 20 April. During the siege, Armenians in surrounding villages were massacred at Djevdet's orders. Russian forces captured Van on 18 May, finding 55,000 corpses in the province—about half its prewar Armenian population. Djevdet's forces proceeded to Bitlis and attacked Armenian and Assyrian/Syriac villages; the men were killed immediately, many women and children were kidnapped by local Kurds, and others marched away to be killed later. By the end of June, there were only a dozen Armenians in the vilayet.
The first deportations of Armenians were proposed by Djemal Pasha, the commander of the Fourth Army, in February 1915 and targeted Armenians in Cilicia (specifically Alexandretta, Dörtyol, Adana, Hadjin, Zeytun, and Sis) who were relocated to the area around Konya in central Anatolia. In late March or early April, the CUP Central Committee decided on the large-scale removal of Armenians from areas near the front lines. During the night of 23–24 April 1915 hundreds of Armenian political activists, intellectuals, and community leaders were rounded up in Constantinople and across the empire. This order from Talaat, intended to eliminate the Armenian leadership and anyone capable of organizing resistance, eventually resulted in the murder of most of those arrested. The same day, Talaat banned all Armenian political organizations and ordered that the Armenians who had previously been removed from Cilicia be deported again, from central Anatolia—where they would likely have survived—to the Syrian Desert.
Systematic deportations
See also: Population transfer in the Ottoman EmpireAims
—Talaat Pasha in Berliner Tageblatt, 4 May 1916We have been blamed for not making a distinction between guilty and innocent Armenians. was impossible. Because of the nature of things, one who was still innocent today could be guilty tomorrow. The concern for the safety of Turkey simply had to silence all other concerns.
During World War I, the CUP—whose central goal was to preserve the Ottoman Empire—came to identify Armenian civilians as an existential threat. CUP leaders held Armenians—including women and children—collectively guilty for betraying the empire, a belief that was crucial to deciding on genocide in early 1915. At the same time, the war provided an opportunity to enact what Talaat called the "definitive solution to the Armenian Question". The CUP wrongly believed that the Russian Empire sought to annex eastern Anatolia, and ordered the genocide in large part to prevent this eventuality. The genocide was intended to permanently eliminate any possibility that Armenians could achieve autonomy or independence in the empire's eastern provinces. Ottoman records show the government aimed to reduce Armenians to no more than five percent of the local population in the sources of deportation and ten percent in the destination areas. This goal could not be accomplished without mass murder.
The deportation of Armenians and resettlement of Muslims in their lands was part of a broader project intended to permanently restructure the demographics of Anatolia. Armenian homes, businesses, and land were preferentially allocated to Muslims from outside the empire, nomads, and the estimated 800,000 (largely Kurdish) Ottoman subjects displaced because of the war with Russia. Resettled Muslims were spread out (typically limited to 10 percent in any area) among larger Turkish populations so that they would lose their distinctive characteristics, such as non-Turkish languages or nomadism. These migrants were exposed to harsh conditions and, in some cases, violence or restriction from leaving their new villages. The ethnic cleansing of Anatolia—the Armenian genocide, Assyrian genocide, and expulsion of Greeks after World War I—paved the way for the formation of an ethno-national Turkish state. In September 1918, Talaat emphasized that regardless of losing the war, he had succeeded at "transforming Turkey to a nation-state in Anatolia".
Deportation amounted to a death sentence; the authorities planned for and intended the death of the deportees. Deportation was only carried out behind the front lines, where no active rebellion existed, and was only possible in the absence of widespread resistance. Armenians who lived in the war zone were instead killed in massacres. Although ostensibly undertaken for security reasons, the deportation and murder of Armenians did not grant the empire any military advantage and actually undermined the Ottoman war effort. The empire faced a dilemma between its goal of eliminating Armenians and its practical need for their labor; those Armenians retained for their skills, in particular for manufacturing in war industries, were indispensable to the logistics of the Ottoman Army. By late 1915, the CUP had extinguished Armenian existence from eastern Anatolia.
 Map of the Armenian genocide in 1915
Map of the Armenian genocide in 1915
Administrative organization

On 23 May 1915, Talaat ordered the deportation of all Armenians in Van, Bitlis, and Erzerum. To grant a cover of legality to the deportation, already well underway in the eastern provinces and Cilicia, the Council of Ministers approved the Temporary Law of Deportation, which allowed authorities to deport anyone deemed suspect. On 21 June, Talaat ordered the deportation of all Armenians throughout the empire, even Adrianople, 2,000 kilometers (1,200 mi) from the Russian front. Following the elimination of the Armenian population in eastern Anatolia, in August 1915, the Armenians of western Anatolia and European Turkey were targeted for deportation. Some areas with a very low Armenian population and some cities, including Constantinople, were partially spared.
Overall, national, regional, and local levels of governance cooperated with the CUP in the perpetration of genocide. The Directorate for the Settlement of Tribes and Immigrants (IAMM) coordinated the deportation and the resettlement of Muslim immigrants in the vacant houses and lands. The IAMM, under the control of Talaat's Ministry of the Interior, and the Special Organization, which took orders directly from the CUP Central Committee, all closely coordinated their activities. A dual-track system was used to communicate orders; those for the deportation of Armenians were communicated to the provincial governors through official channels, but orders of a criminal character, such as those calling for annihilation, were sent through party channels and destroyed upon receipt. Deportation convoys were mostly escorted by gendarmes or local militia. The killings near the front lines were carried out by the Special Organization, and those farther away also involved local militias, bandits, gendarmes, or Kurdish tribes depending on the area. Within the area controlled by the Third Army, which held eastern Anatolia, the army was only involved in genocidal atrocities in the vilayets of Van, Erzerum, and Bitlis.
Many perpetrators came from the Caucasus (Chechens and Circassians), who identified the Armenians with their Russian oppressors. Nomadic Kurds committed many atrocities during the genocide, but settled Kurds only rarely did so. Perpetrators had several motives, including ideology, revenge, desire for Armenian property, and careerism. To motivate perpetrators, state-appointed imams encouraged the killing of Armenians and killers were entitled to a third of Armenian movable property (another third went to local authorities and the last to the CUP). Embezzling beyond that was punished. Ottoman politicians and officials who opposed the genocide were dismissed or assassinated. The government decreed that any Muslim who harbored an Armenian against the will of the authorities would be executed.
Death marches

Although the majority of able-bodied Armenian men had been conscripted into the army, others deserted, paid the exemption tax, or fell outside the age range of conscription. Unlike the earlier massacres of Ottoman Armenians, in 1915 Armenians were not usually killed in their villages, to avoid destruction of property or unauthorized looting. Instead, the men were usually separated from the rest of the deportees during the first few days and executed. Few resisted, believing it would put their families in greater danger. Boys above the age of twelve (sometimes fifteen) were treated as adult men. Execution sites were chosen for proximity to major roads and for rugged terrain, lakes, wells, or cisterns to facilitate the concealment or disposal of corpses. The convoys would stop at a nearby transit camp, where the escorts would demand a ransom from the Armenians. Those unable to pay were murdered. Units of the Special Organization, often wearing gendarme uniforms, were stationed at the killing sites; escorting gendarmes often did not participate in killing.
At least 150,000 Armenians passed through Erzindjan from June 1915, where a series of transit camps were set up to control the flow of victims to the killing site at the nearby Kemah gorge. Thousands of Armenians were killed near Lake Hazar, pushed by paramilitaries off the cliffs. More than 500,000 Armenians passed through the Firincilar plain south of Malatya, one of the deadliest areas during the genocide. Arriving convoys, having passed through the plain to approach the Kahta highlands, would have found gorges already filled with corpses from previous convoys. Many others were held in tributary valleys of the Tigris, Euphrates, or Murat and systematically executed by the Special Organization. Armenian men were often drowned by being tied together back-to-back before being thrown in the water, a method that was not used on women.

Authorities viewed disposal of bodies through rivers as a cheap and efficient method, but it caused widespread pollution downstream. So many bodies floated down the Tigris and Euphrates that they sometimes blocked the rivers and needed to be cleared with explosives. Other rotting corpses became stuck to the riverbanks, and still others traveled as far as the Persian Gulf. The rivers remained polluted long after the massacres, causing epidemics downstream. Tens of thousands of Armenians died along the roads and their bodies were buried hastily or, more often, simply left beside the roads. The Ottoman government ordered the corpses to be cleared as soon as possible to prevent both photographic documentation and disease epidemics, but these orders were not uniformly followed.
Women and children, who made up the great majority of deportees, were usually not executed immediately, but subjected to hard marches through mountainous terrain without food and water. Those who could not keep up were left to die or shot. During 1915, some were forced to walk as far as 1,000 kilometers (620 mi) in the summer heat. Some deportees from western Anatolia were allowed to travel by rail. There was a distinction between the convoys from eastern Anatolia, which were eliminated almost in their entirety, and those from farther west, which made up most of those surviving to reach Syria. For example, around 99 percent of Armenians deported from Erzerum did not reach their destination.
Islamization

The Islamization of Armenians, carried out as a systematic state policy involving the bureaucracy, police, judiciary, and clergy, was a major structural component of the genocide. An estimated 100,000 to 200,000 Armenians were Islamized, and it is estimated that as many as two million Turkish citizens in the early 21st century may have at least one Armenian grandparent. Some Armenians were allowed to convert to Islam and evade deportation, but the regime insisted on their destruction wherever their numbers exceeded the five to ten percent threshold, or there was a risk of them being able to preserve their nationality and culture. Talaat Pasha personally authorized conversion of Armenians and carefully tracked the loyalty of converted Armenians until the end of the war. Although the first and most important step was conversion to Islam, the process also required the eradication of Armenian names, language, and culture, and for women, immediate marriage to a Muslim. Although Islamization was the most feasible opportunity for survival, it also transgressed Armenian moral and social norms.
The CUP allowed Armenian women to marry into Muslim households, as these women would lose their Armenian identity. Young women and girls were often appropriated as house servants or sex slaves. Some boys were abducted to work as forced laborers for Muslim individuals. Some children were forcibly seized, while others were sold or given up by their parents to save their lives. Special state-run orphanages were also set up with strict procedures intending to deprive their charges of an Armenian identity. Most Armenian children who survived the genocide endured exploitation, hard labor without pay, forced conversion to Islam, and physical and sexual abuse. Armenian women captured during the journey ended up in Turkish or Kurdish households; those who were Islamized during the second phase of the genocide found themselves in an Arab or Bedouin environment.
The rape, sexual abuse, and prostitution of Armenian women were all very common. Although Armenian women tried to avoid sexual violence, suicide was often the only alternative. Deportees were displayed naked in Damascus and sold as sex slaves in some areas, constituting an important source of income for accompanying gendarmes. Some were sold in Arabian slave markets to Muslim Hajj pilgrims and ended up as far away as Tunisia or Algeria.
Confiscation of property
Main articles: Confiscation of Armenian properties in Turkey and National economy (Turkey)
A secondary motivation for genocide was the destruction of the Armenian bourgeoisie to make room for a Turkish and Muslim middle class and build a statist national economy controlled by Muslim Turks. The campaign to Turkify the economy began in June 1914 with a law that obliged many non-Muslim merchants to hire Muslims. Following the deportations, the businesses of the victims were taken over by Muslims who were often incompetent, leading to economic difficulties. The genocide had catastrophic effects on the Ottoman economy; Muslims were disadvantaged by the deportation of skilled professionals and entire districts fell into famine following their farmers' deportation. The Ottoman and Turkish governments passed a series of Abandoned Properties Laws to manage and redistribute property confiscated from Armenians. Although the laws maintained that the state was simply administering the properties on behalf of the absent Armenians, there was no provision to return them to the owners—it was presumed that they had ceased to exist.
Historians Taner Akçam and Ümit Kurt argue that "The Republic of Turkey and its legal system were built, in a sense, on the seizure of Armenian cultural, social, and economic wealth, and on the removal of the Armenian presence." The proceeds from the sale of confiscated property was often used to fund the deportation of Armenians and resettlement of Muslims, as well as for army, militia, and other government spending. Ultimately this formed much of the basis of the industry and economy of the post-1923 republic, endowing it with capital. The dispossession and exile of Armenian competitors enabled many lower-class Turks (i.e. peasantry, soldiers, and laborers) to rise to the middle class. Confiscation of Armenian assets continued into the second half of the twentieth century, and in 2006 the National Security Council ruled that property records from 1915 must be kept closed to protect national security. Outside Istanbul, the traces of Armenian existence in Turkey, including churches and monasteries, libraries, khachkars, and animal and place names, have been systematically erased, beginning during the war and continuing for decades afterward.
Destination
Further information: Deir ez-Zor camps and Ras al-Ayn camps

The first arrivals in mid-1915 were accommodated in Aleppo. From mid-November, the convoys were denied access to the city and redirected along the Baghdad Railway or the Euphrates towards Mosul. The first transit camp was established at Sibil, east of Aleppo; one convoy would arrive each day while another would depart for Meskene or Deir ez-Zor. Dozens of concentration camps were set up in Syria and Upper Mesopotamia. By October 1915, some 870,000 deportees had reached Syria and Upper Mesopotamia. Most were repeatedly transferred between camps, being held in each camp for a few weeks, until there were very few survivors. This strategy physically weakened the Armenians and spread disease, so much that some camps were shut down in late 1915 due to the threat of disease spreading to the Ottoman military. In late 1915, the camps around Aleppo were liquidated and the survivors were forced to march to Ras al-Ayn; the camps around Ras al-Ayn were closed in early 1916 and the survivors sent to Deir ez-Zor.
In general, Armenians were denied food and water during and after their forced march to the Syrian desert; many died of starvation, exhaustion, or disease, especially dysentery, typhus, and pneumonia. Some local officials gave Armenians food; others took bribes to provide food and water. Aid organizations were officially barred from providing food to the deportees, although some circumvented these prohibitions. Survivors testified that some Armenians refused aid as they believed it would only prolong their suffering. The guards raped female prisoners and also allowed Bedouins to raid the camps at night for looting and rape; some women were forced into marriage. Thousands of Armenian children were sold to childless Turks, Arabs, and Jews, who would come to the camps to buy them from their parents. In the western Levant, governed by the Ottoman Fourth Army under Djemal Pasha, there were no concentration camps or large-scale massacres, rather Armenians were resettled and recruited to work for the war effort. They had to convert to Islam or face deportation to another area.
The ability of the Armenians to adapt and survive was greater than the perpetrators expected. A loosely organized, Armenian-led resistance network based in Aleppo succeeded in helping many deportees, saving Armenian lives. At the beginning of 1916 some 500,000 deportees were alive in Syria and Mesopotamia. Afraid that surviving Armenians might return home after the war, Talaat Pasha ordered a second wave of massacres in February 1916. Another wave of deportations targeted Armenians remaining in Anatolia. More than 200,000 Armenians were killed between March and October 1916, often in remote areas near Deir ez-Zor and on parts of the Khabur valley, where their bodies would not create a public health hazard. The massacres killed most of the Armenians who had survived the camp system.
International reaction

The Ottoman Empire tried to prevent journalists and photographers from documenting the atrocities, threatening them with arrest. Nevertheless, substantiated reports of mass killings were widely covered in Western newspapers. On 24 May 1915, the Triple Entente (Russia, Britain, and France) formally condemned the Ottoman Empire for "crimes against humanity and civilization", and threatened to hold the perpetrators accountable. Witness testimony was published in books such as The Treatment of Armenians in the Ottoman Empire (1916) and Ambassador Morgenthau's Story (1918), raising public awareness of the genocide.
The German Empire was a military ally of the Ottoman Empire during World War I. German diplomats approved limited removals of Armenians in early 1915, and took no action against the genocide, which has been a source of controversy.
Relief efforts were organized in dozens of countries to raise money for Armenian survivors. By 1925, people in 49 countries were organizing "Golden Rule Sundays" during which they consumed the diet of Armenian refugees, to raise money for humanitarian efforts. Between 1915 and 1930, Near East Relief raised $110 million ($2 billion adjusted for inflation) for refugees from the Ottoman Empire.
Aftermath
End of World War I
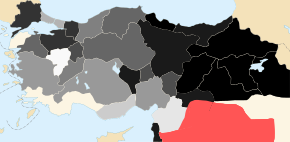
Intentional, state-sponsored killing of Armenians mostly ceased by the end of January 1917, although sporadic massacres and starvation continued. Both contemporaries and later historians have estimated that around 1 million Armenians died during the genocide, with figures ranging from 600,000 to 1.5 million deaths. Between 800,000 and 1.2 million Armenians were deported, and contemporaries estimated that by late 1916 only 200,000 were still alive. As the British Army advanced in 1917 and 1918 northwards through the Levant, they liberated around 100,000 to 150,000 Armenians working for the Ottoman military under abysmal conditions, not including those held by Arab tribes.
As a result of the Bolshevik Revolution and the subsequent separate peace with the Central Powers, the Russian army withdrew and Ottoman forces advanced into eastern Anatolia. The First Republic of Armenia was proclaimed in May 1918, at which time 50 percent of its population were refugees and 60 percent of its territory was under Ottoman occupation. Ottoman troops withdrew from parts of Armenia following the October 1918 Armistice of Mudros. From 1918 to 1920, Armenian militants committed revenge killings of thousands of Muslims, which have been cited as a retroactive excuse for genocide. In 1918, at least 200,000 people in Armenia, mostly refugees, died from starvation or disease, in part due to a Turkish blockade of food supplies and the deliberate destruction of crops in eastern Armenia by Turkish troops, both before and after the armistice.
Armenians organized a coordinated effort known as vorpahavak (lit. 'the gathering of orphans') that reclaimed thousands of kidnapped and Islamized Armenian women and children. Armenian leaders abandoned traditional patrilineality to classify children born to Armenian women and their Muslim captors as Armenian. An orphanage in Alexandropol held 25,000 orphans, the largest number in the world. In 1920, the Armenian Patriarchate of Constantinople reported it was caring for 100,000 orphans, estimating that another 100,000 remained captive.
Trials
Main articles: Prosecution of Ottoman war criminals after World War I and Ottoman Special Military TribunalFollowing the armistice, Allied governments championed the prosecution of Armenian genocide perpetrators. Grand Vizier Damat Ferid Pasha publicly recognized that 800,000 Ottoman citizens of Armenian origin had died as a result of state policy and stated that "humanity, civilizations are shuddering, and forever will shudder, in face of this tragedy". The postwar Ottoman government held the Ottoman Special Military Tribunal, by which it sought to pin the Armenian genocide onto the CUP leadership while exonerating the Ottoman Empire as a whole, therefore avoiding partition by the Allies. The court ruled that "the crime of mass murder" of Armenians was "organized and carried out by the top leaders of CUP". Eighteen perpetrators (including Talaat, Enver, and Djemal) were sentenced to death, of whom only three were ultimately executed as the remainder had fled and were tried in absentia. The 1920 Treaty of Sèvres, which awarded Armenia a large area in eastern Anatolia, eliminated the Ottoman government's purpose for holding the trials. Prosecution was hampered by a widespread belief among Turkish Muslims that the actions against the Armenians were not punishable crimes. Increasingly, the genocide was considered necessary and justified to establish a Turkish nation-state.
On 15 March 1921, Talaat was assassinated in Berlin as part of a covert operation of the ARF to kill the perpetrators of the Armenian genocide. The trial of his admitted killer, Soghomon Tehlirian, focused on Talaat's responsibility for genocide. Tehlirian was acquitted by a German jury.
Turkish War of Independence
Further information: Turkish war crimes

The CUP regrouped as the Turkish nationalist movement to fight the Turkish War of Independence, relying on the support of perpetrators of the genocide and those who had profited from it. This movement saw the return of Armenian survivors as a mortal threat to its nationalist ambitions and the interests of its supporters. The return of survivors was therefore impossible in most of Anatolia and thousands of Armenians who tried were murdered. Historian Raymond Kévorkian states that the war of independence was "intended to complete the genocide by finally eradicating Armenian, Greek, and Syriac survivors". In 1920 Kâzım Karabekir, a Turkish general, invaded Armenia with orders "to eliminate Armenia physically and politically". Nearly 100,000 Armenians were massacred in Transcaucasia by the Turkish army and another 100,000 fled from Cilicia during the French withdrawal. According to Kévorkian, only the Soviet occupation of Armenia prevented another genocide.
The victorious nationalists subsequently declared the Republic of Turkey in 1923. CUP war criminals were granted immunity and later that year, the Treaty of Lausanne established Turkey's current borders and provided for the Greek population's expulsion. Its protection provisions for non-Muslim minorities had no enforcement mechanism and were disregarded in practice.
Armenian survivors were left mainly in three locations. About 295,000 Armenians had fled to Russian-controlled territory during the genocide and ended up mostly in Soviet Armenia. An estimated 200,000 Armenian refugees settled in the Middle East, forming a new wave of the Armenian diaspora. In the Republic of Turkey, about 100,000 Armenians lived in Constantinople and another 200,000 lived in the provinces, largely women and children who had been forcibly converted. Though Armenians in Constantinople faced discrimination, they were allowed to maintain their cultural identity, unlike those elsewhere in Turkey who continued to face forced Islamization and kidnapping of girls after 1923. Between 1922 and 1929, the Turkish authorities eliminated surviving Armenians from southern Turkey, expelling thousands to French-mandate Syria.
Legacy
According to historian Margaret Lavinia Anderson, the Armenian genocide reached an "iconic status" as "the apex of horrors conceivable" before World War II. It was described by contemporaries as "the murder of a nation", "race extermination", "the greatest crime of the ages", and "the blackest page in modern history". According to historian Stefan Ihrig, in Germany, the Nazis viewed post-1923 Turkey as a post-genocidal paradise and, "incorporated the Armenian genocide, its 'lessons', tactics, and 'benefits', into their own worldview".
Turkey
See also: Armenian genocide denialIn the 1920s, Kurds and Alevis replaced Armenians as the perceived internal enemy of the Turkish state. Militarism, weak rule of law, lack of minority rights, and especially the belief that Turkey is constantly under threat—thus justifying state violence—are among the main legacies of the genocide in Turkey. In postwar Turkey, the perpetrators of the genocide were hailed as martyrs of the national cause. Turkey's official denial of the Armenian genocide continues to rely on the CUP's justification of its actions. The Turkish government maintains that the mass deportation of Armenians was a legitimate action to combat an existential threat to the empire, but that there was no intention to exterminate the Armenian people. The government's position is supported by the majority of Turkish citizens. Many Kurds, who themselves have suffered political repression in Turkey, have recognized and condemned the genocide.
The Turkish state perceives open discussion of the genocide as a threat to national security because of its connection with the foundation of the republic, and for decades strictly censored it. In 2002, the AK Party came to power and relaxed censorship to a certain extent, and the profile of the issue was raised by the 2007 assassination of Hrant Dink, a Turkish-Armenian journalist known for his advocacy of reconciliation. Although the AK Party softened the state denial rhetoric, describing Armenians as part of the Ottoman Empire's war losses, during the 2010s political repression and censorship increased again. Turkey's century-long effort to prevent any recognition or mention of the genocide in foreign countries has included millions of dollars in lobbying, as well as intimidation and threats.
Armenia and Azerbaijan

Armenian Genocide Remembrance Day is commemorated on 24 April each year in Armenia and abroad, the anniversary of the deportation of Armenian intellectuals. On 24 April 1965, 100,000 Armenians protested in Yerevan, and diaspora Armenians demonstrated across the world in favor of recognition of the genocide and annexing land from Turkey. A memorial was completed two years later, at Tsitsernakaberd above Yerevan.
Since 1988, Armenians and Turkic Azeris have been involved in a conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh, an Armenian enclave internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan. Initially involving peaceful demonstrations by Armenians, the conflict turned violent and has featured massacres by both sides, resulting in the displacement of more than half a million people. During the conflict, the Azerbaijani and Armenian governments have regularly accused each other of plotting genocide. Azerbaijan has also joined the Turkish effort to deny the Armenian genocide.
International recognition
Main article: Armenian genocide recognition
In response to continuing denial by the Turkish state, many Armenian diaspora activists have lobbied for international formal recognition of the Armenian genocide, an effort that has become a central concern of the Armenian diaspora. From the 1970s onward, many countries avoided recognition to preserve good relations with Turkey. As of 2023, 31 UN member states have formally recognized the genocide, along with Pope Francis and the European Parliament. Azerbaijan, Pakistan, and Turkey explicitly deny the genocide.
Cultural depictions
Main article: Armenian genocide in cultureAfter meeting Armenian survivors in the Middle East, Austrian–Jewish writer Franz Werfel wrote The Forty Days of Musa Dagh, a fictionalized retelling of the successful Armenian uprising in Musa Dagh, as a warning of the dangers of Nazism. According to Ihrig, the book, released in 1933, is among the most important works of twentieth-century literature to address genocide and "is still considered essential reading for Armenians worldwide". The genocide became a central theme in English-language Armenian-American literature. The first film about the Armenian genocide, Ravished Armenia, was released in 1919 as a fundraiser for Near East Relief, based on the survival story of Aurora Mardiganian, who played herself. Since then more films about the genocide have been made, although it took several decades for any of them to reach a mass-market audience. The abstract expressionist paintings of Arshile Gorky were influenced by his experience of the genocide. More than 200 memorials have been erected in 32 countries to commemorate the event.
Archives and historiography
See also: Kemalist historiographyThe genocide is extensively documented in the archives of Germany, Austria, the United States, Russia, France, and the United Kingdom, as well as the Ottoman archives, despite systematic purges of incriminating documents by Turkey. There are also thousands of eyewitness accounts from Western missionaries and Armenian survivors. Polish-Jewish lawyer Raphael Lemkin, who coined the term genocide in 1944, became interested in war crimes after reading about the 1921 trial of Soghomon Tehlirian for the assassination of Talaat Pasha. Lemkin recognized the fate of the Armenians as one of the most significant genocides in the twentieth century. Almost all historians and scholars outside Turkey, and an increasing number of Turkish scholars, recognize the destruction of Armenians in the Ottoman Empire as genocide.
Notes
- Also known by other names.
- ^ Talaat previously had the title "Bey," and so was known as "Talaat Bey" until he gained the title "Pasha" in 1917.
References
- Suny 2015, pp. 245, 330.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, p. 187.
- ^ Morris & Ze'evi 2019, p. 1.
- ^ Kévorkian 2011, p. 279.
- Ahmed 2006, p. 1576.
- Payaslian 2007, pp. 34–35.
- Payaslian 2007, pp. 105–106.
- Suny 2015, pp. 11, 15.
- Suny 2015, p. 12.
- Suny 2015, pp. 5, 7.
- ^ Suny 2015, p. xviii.
- Bloxham 2005, pp. 8–9.
- Astourian 2011, p. 60.
- Suny 2015, p. 19.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 9.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 8, 40.
- Suny 2015, pp. 26–27.
- Suny 2015, pp. 19, 53.
- Astourian 2011, pp. 60, 63.
- Astourian 2011, pp. 56, 60.
- Suny 2015, pp. 19, 21.
- Göçek 2015, p. 123.
- Astourian 2011, pp. 62, 65.
- Suny 2015, p. 55.
- ^ Kévorkian 2011, p. 271.
- Suny 2015, pp. 54–56.
- Suny 2015, pp. 87–88.
- Suny 2015, pp. 94–95, 105.
- Suny 2015, pp. 95–96.
- ^ Astourian 2011, p. 64.
- Suny 2015, p. 97.
- Suny 2015, p. 96.
- Suny 2015, pp. 48–49.
- Kévorkian 2011, pp. 75–76.
- Kévorkian 2011, pp. 11, 65.
- Suny 2015, p. 129.
- Suny 2015, pp. 129–130.
- Suny 2015, p. 130.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 11.
- Suny 2015, p. 131.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 266.
- Suny 2015, pp. 92–93, 99, 139–140.
- Kieser 2018, p. 2.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 46–47.
- Suny 2015, pp. 152–153.
- Kieser 2018, p. 50.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 53–54.
- Göçek 2015, p. 192.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 54–55.
- Suny 2015, pp. 154–156.
- Kaligian 2017, pp. 89–91.
- Kaligian 2017, pp. 82–84.
- Kaligian 2017, pp. 86–92.
- Astourian 2011, p. 66.
- Suny 2015, pp. 165–166.
- Suny 2015, pp. 168–169.
- Suny 2015, p. 171.
- Suny 2015, p. 172.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 152–153.
- Astourian 2011, pp. 66–67.
- Kaligian 2017, p. 92.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 163–164.
- Akçam 2019, pp. 461–462.
- Suny 2015, pp. 203, 359.
- Suny 2015, pp. 184–185.
- Kieser 2018, p. 167.
- Suny 2015, pp. 185, 363.
- Üngör 2012, p. 50.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, pp. 169, 171.
- Bloxham & Göçek 2008, p. 363.
- ^ Kieser 2018, p. 156.
- Kaligian 2017, pp. 97–98.
- Suny 2015, p. 193.
- Göçek 2015, p. 191.
- Suny 2015, pp. 189–190.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 133–134, 136, 138, 172.
- Kaligian 2017, pp. 95, 97.
- Kaligian 2017, pp. 96–97.
- Suny 2015, pp. 193, 211–212.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 169, 176–177.
- Kaligian 2017, p. 98.
- Bjørnlund 2008, p. 51.
- Suny 2015, pp. 214–215.
- Suny 2015, pp. 223–224.
- Üngör 2016, pp. 16–17.
- Suny 2015, pp. 233–234.
- Suny 2015, p. 218.
- Suny 2015, pp. 221–222.
- Suny 2015, p. 225.
- Suny 2015, pp. 226–227.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 242.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, p. 179.
- Suny 2015, pp. 243–244.
- Üngör 2016, p. 18.
- Akçam 2019, p. 475.
- Akçam 2019, pp. 478–479.
- ^ Üngör 2016, p. 19.
- Suny 2015, p. 244.
- Suny 2015, pp. 248–249.
- Suny 2015, pp. 241–242.
- Akçam 2012, p. 157.
- Üngör 2016, pp. 18–19.
- Suny 2015, p. 243.
- ^ Suny 2015, p. 248.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 235–238.
- Akçam 2019, p. 472.
- Suny 2015, p. 255.
- Suny 2015, p. 257.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 319.
- Suny 2015, pp. 259–260.
- Suny 2015, pp. 287, 289.
- Dündar 2011, p. 281.
- Suny 2015, pp. 247–248.
- Kieser 2018, p. 10.
- Kévorkian 2011, pp. 251–252.
- Suny 2015, pp. 271–272.
- Suny 2015, p. 273.
- Suny 2015, pp. 274–275.
- Akçam 2012, p. 188.
- Ihrig 2016, pp. 162–163.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, p. 168.
- Akçam 2012, p. 337.
- ^ Suny 2015, p. 245.
- Akçam 2019, p. 457.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, pp. 166–167.
- Dündar 2011, p. 284.
- Nichanian 2015, p. 202.
- ^ Watenpaugh 2013, p. 284.
- Akçam 2012, pp. 242, 247–248.
- Dündar 2011, p. 282.
- Kieser 2018, p. 261.
- Kaiser 2019, 6.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, p. 102.
- Nichanian 2015, p. 254.
- Gingeras 2016, pp. 176–177.
- Gingeras 2016, p. 178.
- Suny 2015, pp. 349, 364.
- ^ Bozarslan et al. 2015, p. 311.
- Kieser 2018, p. 376.
- Nichanian 2015, p. 227.
- ^ Kaiser 2010, p. 384.
- Dündar 2011, pp. 276–277.
- ^ Üngör 2012, p. 54.
- Kaiser 2010, pp. 366, 383.
- Mouradian 2018, p. 148.
- Rogan 2015, p. 184.
- Cora 2020, pp. 50–51.
- Suny 2015, p. 317.
- Kieser 2018, p. 240.
- Kaiser 2019, 10.
- ^ Üngör 2012, p. 53.
- Dündar 2011, p. 283.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, p. 96.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, p. 97.
- ^ Kaiser 2010, p. 378.
- Akçam 2012, pp. 399–400.
- ^ Kieser 2018, p. 247.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, pp. 89–90.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, pp. 92–93.
- Akçam 2012, pp. 194–195.
- ^ Kaiser 2010, p. 376.
- ^ Bozarslan et al. 2015, p. 94.
- ^ Kévorkian 2011, p. 810.
- Suny 2015, p. 352.
- Üngör 2012, p. 58.
- Kaiser 2019, 35, 37.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, pp. 98–99.
- Kévorkian 2011, pp. 246–247.
- Üngör 2012, p. 61.
- Akçam 2012, pp. 327–328.
- ^ Kévorkian 2014, p. 91.
- Maksudyan 2020, pp. 121–122.
- ^ Kaiser 2010, p. 377.
- ^ Bozarslan et al. 2015, p. 93.
- Kaiser 2019, 3, 22.
- Kévorkian 2014, p. 93.
- Kévorkian 2014, p. 90.
- Kévorkian 2014, p. 92.
- Kévorkian 2014, p. 95.
- Akçam 2018, p. 158.
- Kévorkian 2014, p. 94.
- Kévorkian 2014, pp. 92–93.
- ^ Kévorkian 2011, p. 808.
- Akçam 2012, pp. 314, 316.
- Kurt 2016, 2, 21.
- Akçam 2012, p. 331.
- Watenpaugh 2013, p. 291.
- Akçam 2012, pp. 290–291.
- Kurt 2016, 5, 13–14.
- Kurt 2016, 15.
- Kurt 2016, 5.
- ^ Watenpaugh 2013, pp. 291–292.
- Akçam 2012, p. 314.
- Watenpaugh 2013, pp. 284–285.
- Kurt 2016, 17.
- Kévorkian 2011, pp. 757–758.
- Akçam 2012, p. 312.
- Kaiser 2010, pp. 377–378.
- Akçam 2012, pp. 312–315.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 758.
- Cheterian 2015, pp. 245–246.
- Kieser 2018, p. 273.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 202.
- Suny 2015, pp. 316–317.
- ^ Akçam & Kurt 2015, p. 2.
- Kévorkian 2011, pp. 203–204.
- Akçam & Kurt 2015, pp. 11–12.
- Akçam 2012, pp. 256–257.
- ^ Üngör & Polatel 2011, p. 80.
- Bozarslan et al. 2015, p. 189.
- Kieser 2018, p. 268.
- Akçam & Kurt 2015, p. 3.
- Cheterian 2015, pp. 64–65.
- Göçek 2015, p. 411.
- Suciyan 2015, p. 59.
- Kévorkian 2014, p. 97.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 625.
- ^ Kévorkian 2014, p. 98.
- ^ Shirinian 2017, p. 21.
- Kévorkian 2011, pp. 633–635.
- ^ Mouradian 2018, p. 155.
- ^ Kaiser 2010, p. 380.
- Kévorkian 2014, p. 96.
- Shirinian 2017, p. 23.
- Shirinian 2017, pp. 20–21.
- Mouradian 2018, p. 152.
- Kévorkian 2011, pp. 673–674.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 693.
- Mouradian 2018, p. 154.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 259, 265.
- Kévorkian 2011, pp. 695, 808.
- Kieser 2018, p. 262.
- Kévorkian 2014, p. 107.
- Leonard 2004, p. 297.
- Akçam 2018, p. 157.
- Leonard 2004, p. 300.
- de Waal 2015, p. 2.
- Suny 2015, p. 308.
- Tusan 2014, pp. 57–58.
- ^ Suny 2015, p. 298.
- Kieser & Bloxham 2014, pp. 600, 606–607.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 20–21.
- Ihrig 2016, p. 134.
- Anderson 2011, p. 200.
- "History". Near East Foundation. Archived from the original on 3 June 2015. Retrieved 10 March 2021.
- Suny 2015, p. 330.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 721.
- de Waal 2015, p. 20.
- de Waal 2015, p. 35.
- ^ Morris & Ze'evi 2019, p. 486.
- Suny 2015, pp. 354–355.
- Kévorkian 2020, pp. 151–152.
- Payaslian 2007, pp. 148–149.
- Payaslian 2007, pp. 150–151.
- Payaslian 2007, pp. 152–153.
- Kieser 2018, p. 367.
- Suny 2015, p. 342.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 706.
- Shirinian 2017, p. 24.
- Ekmekçioğlu 2013, pp. 534–535.
- Ekmekçioğlu 2013, pp. 530, 545.
- de Waal 2015, p. 76.
- Kévorkian 2011, p. 759.
- Dadrian & Akçam 2011, pp. 23–24.
- Dadrian & Akçam 2011, p. 47.
- Dadrian & Akçam 2011, p. 49.
- Nichanian 2015, p. 207.
- Dadrian & Akçam 2011, p. 120.
- Üngör 2012, p. 62.
- Dadrian & Akçam 2011, pp. 24, 195.
- Nichanian 2015, p. 217.
- Göçek 2011, pp. 45–46.
- Cheterian 2015, pp. 126–127.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 403–404, 409.
- Suny 2015, p. 346.
- Suny 2015, pp. 344–346.
- Ihrig 2016, pp. 226–227, 235, 262, 293, "Trial in Berlin" passim.
- Suny 2015, pp. 338–339.
- Kieser 2018, p. 319.
- ^ Nichanian 2015, p. 242.
- Zürcher 2011, p. 316.
- Cheterian 2015, p. 155.
- Nichanian 2015, pp. 229–230.
- Kévorkian 2020, p. 165.
- ^ Kévorkian 2020, pp. 164–165.
- ^ Nichanian 2015, p. 238.
- Nichanian 2015, p. 244.
- Dadrian & Akçam 2011, p. 104.
- Kieser 2018, p. 28.
- Suny 2015, pp. 367–368.
- Cheterian 2015, pp. 103–104.
- ^ Cheterian 2015, p. 104.
- Suciyan 2015, p. 27.
- Cheterian 2015, p. 203.
- Suciyan 2015, p. 65.
- Kévorkian 2020, p. 161.
- Anderson 2011, p. 199.
- Ihrig 2016, pp. 9, 55.
- de Waal 2015, p. 21.
- Kieser 2018, pp. 289–290.
- Ihrig 2016, pp. 349, 354.
- Nichanian 2015, pp. 263–264.
- Suny 2015, pp. xii, 361.
- Akçam 2012, pp. xi, 451.
- ^ Göçek 2015, p. 1.
- Cheterian 2015, pp. 273–275.
- Galip 2020, pp. 162–163.
- Akçam & Kurt 2015, pp. 3–4.
- Galip 2020, p. 3.
- Galip 2020, pp. 3–4.
- Ben Aharon 2019, p. 339.
- Galip 2020, pp. 83–85.
- Göçek 2015, p. 2.
- Chorbajian 2016, p. 178.
- ^ Cheterian 2015, p. 110.
- Ben Aharon 2019, p. 347.
- de Waal 2015, pp. 140, 142.
- de Waal 2015, pp. 146–147.
- ^ Bloxham 2005, pp. 232–233.
- Cheterian 2015, pp. 279–282.
- de Waal 2015, pp. 196–197.
- Koinova 2017, p. 122.
- Koinova 2017, pp. 112, 221–222.
- de Waal 2015, p. 3.
- Ben Aharon 2019, pp. 340–341.
- Koinova 2017, p. 117.
- "Countries that Recognize the Armenian Genocide". Armenian National Institute. Archived from the original on 14 September 2019. Retrieved 14 December 2023.
- Ihrig 2016, pp. 1–2.
- Ihrig 2016, p. 364.
- Der Mugrdechian 2016, p. 273.
- Marsoobian 2016, pp. 73–74.
- Tusan 2014, pp. 69–70.
- de Waal 2015, pp. 77–78.
- Marsoobian 2016, p. 73.
- Miller 2010, p. 393.
- "Memorials to the Armenian Genocide". Armenian National Institute. Archived from the original on 9 August 2017. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- Dadrian & Akçam 2011, p. 4.
- Akçam 2012, pp. xxii–xxiii, 25–26.
- Bloxham & Göçek 2008, p. 345.
- Chorbajian 2016, p. 168.
- Akçam 2018, p. 11.
- de Waal 2015, pp. 132–133.
- Ihrig 2016, pp. 9, 370–371.
- Suny 2015, pp. 374–375.
Sources
Main article: Bibliography of the Armenian genocideBooks
- Akçam, Taner (2012). The Young Turks' Crime against Humanity: The Armenian Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing in the Ottoman Empire. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-15333-9.
- Akçam, Taner (2018). Killing Orders: Talat Pasha's Telegrams and the Armenian Genocide. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-3-319-69787-1.
- Akçam, Taner; Kurt, Ümit (2015). The Spirit of the Laws: The Plunder of Wealth in the Armenian Genocide. Berghahn Books. ISBN 978-1-78238-624-7.
- Bloxham, Donald (2005). The Great Game of Genocide: Imperialism, Nationalism, and the Destruction of the Ottoman Armenians. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-927356-0.
- Bozarslan, Hamit ; Duclert, Vincent ; Kévorkian, Raymond H. (2015). Comprendre le génocide des arméniens – 1915 à nos jours [Understanding the Armenian genocide: 1915 to the present day] (in French). Tallandier [fr]. ISBN 979-10-210-0681-2.
- Cheterian, Vicken (2015). Open Wounds: Armenians, Turks and a Century of Genocide. Hurst. ISBN 978-1-84904-458-5.
- Dadrian, Vahakn N.; Akçam, Taner (2011). Judgment at Istanbul: The Armenian Genocide Trials. Berghahn Books. ISBN 978-0-85745-286-3.
- de Waal, Thomas (2015). Great Catastrophe: Armenians and Turks in the Shadow of Genocide. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-935069-8.
- Galip, Özlem Belçim (2020). New Social Movements and the Armenian Question in Turkey: Civil Society vs. the State. Springer International Publishing. ISBN 978-3-030-59400-8.
- Gingeras, Ryan (2016). Fall of the Sultanate: The Great War and the End of the Ottoman Empire 1908–1922. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-967607-1.
- Göçek, Fatma Müge (2015). Denial of Violence: Ottoman Past, Turkish Present and Collective Violence Against the Armenians, 1789–2009. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-933420-9.
- Ihrig, Stefan (2016). Justifying Genocide: Germany and the Armenians from Bismarck to Hitler. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-50479-0.
- Kévorkian, Raymond (2011). The Armenian Genocide: A Complete History. I.B. Tauris. ISBN 978-0-85771-930-0.
- Kieser, Hans-Lukas (2018). Talaat Pasha: Father of Modern Turkey, Architect of Genocide. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-8963-1.
- Morris, Benny; Ze'evi, Dror (2019). The Thirty-Year Genocide: Turkey's Destruction of Its Christian Minorities, 1894–1924. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-91645-6.
- Nichanian, Mikaël (2015). Détruire les Arméniens. Histoire d'un génocide [Destroying the Armenians: History of a Genocide] (in French). Presses Universitaires de France. ISBN 978-2-13-062617-6.
- Payaslian, Simon (2007). The History of Armenia: From the Origins to the Present. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4039-7467-9.
- Rogan, Eugene (2015). The Fall of the Ottomans: The Great War in the Middle East. Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-05669-9.
- Suciyan, Talin (2015). The Armenians in Modern Turkey: Post-Genocide Society, Politics and History. I.B. Tauris. ISBN 978-0-85772-773-2.
- Suny, Ronald Grigor (2015). "They Can Live in the Desert but Nowhere Else": A History of the Armenian Genocide. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-6558-1.
- Üngör, Uğur Ümit; Polatel, Mehmet (2011). Confiscation and Destruction: The Young Turk Seizure of Armenian Property. Continuum. ISBN 978-1-4411-3578-0.
Chapters
- Ahmed, Ali (2006). "Turkey". Encyclopedia of the Developing World. Routledge. pp. 1575–1578. ISBN 978-1-57958-388-0.
- Anderson, Margaret Lavinia (2011). "Who Still Talked about the Extermination of the Armenians?". A Question of Genocide: Armenians and Turks at the End of the Ottoman Empire. Oxford University Press. pp. 199–217. ISBN 978-0-19-539374-3.
- Astourian, Stephan (2011). "The Silence of the Land: Agrarian Relations, Ethnicity, and Power". A Question of Genocide: Armenians and Turks at the End of the Ottoman Empire. Oxford University Press. pp. 55–81. ISBN 978-0-19-539374-3.
- Bloxham, Donald; Göçek, Fatma Müge (2008). "The Armenian Genocide". The Historiography of Genocide. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 344–372. ISBN 978-0-230-29778-4.
- Chorbajian, Levon (2016). "'They Brought It on Themselves and It Never Happened': Denial to 1939". The Armenian Genocide Legacy. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 167–182. ISBN 978-1-137-56163-3.
- Cora, Yaşar Tolga (2020). "Towards a Social History of the Ottoman War Economy: Manufacturing and Armenian Forced Skilled-Laborers". Not All Quiet on the Ottoman Fronts: Neglected Perspectives on a Global War, 1914–1918. Ergon-Verlag. pp. 49–72. ISBN 978-3-95650-777-9.
- Der Mugrdechian, Barlow (2016). "The Theme of Genocide in Armenian Literature". The Armenian Genocide Legacy. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 273–286. ISBN 978-1-137-56163-3.
- Dündar, Fuat (2011). "Pouring a People into the Desert: The "Definitive Solution" of the Unionists to the Armenian Question". A Question of Genocide: Armenians and Turks at the End of the Ottoman Empire. Oxford University Press. pp. 276–286. ISBN 978-0-19-539374-3.
- Göçek, Fatma Müge (2011). "Reading Genocide: Turkish Historiography on 1915". A Question of Genocide: Armenians and Turks at the End of the Ottoman Empire. Oxford University Press. pp. 42–52. ISBN 978-0-19-539374-3.
- Kaiser, Hilmar (2010). "Genocide at the Twilight of the Ottoman Empire". The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies. Oxford University Press. pp. 365–385. ISBN 978-0-19-923211-6.
- Kaligian, Dikran (2017). "Convulsions at the End of Empire: Thrace, Asia Minor, and the Aegean". Genocide in the Ottoman Empire: Armenians, Assyrians, and Greeks, 1913–1923. Berghahn Books. pp. 82–104. ISBN 978-1-78533-433-7.
- Kévorkian, Raymond (2014). "Earth, Fire, Water: or How to Make the Armenian Corpses Disappear". Destruction and Human Remains: Disposal and Concealment in Genocide and Mass Violence. Manchester University Press. pp. 89–116. ISBN 978-1-84779-906-7. JSTOR j.ctt1wn0s3n.9. Archived from the original on 16 April 2021.
- Kévorkian, Raymond (2020). "The Final Phase: The Cleansing of Armenian and Greek Survivors, 1919–1922". Collective and State Violence in Turkey: The Construction of a National Identity from Empire to Nation-State. Berghahn Books. pp. 147–173. ISBN 978-1-78920-451-3.
- Kieser, Hans-Lukas; Bloxham, Donald (2014). "Genocide". The Cambridge History of the First World War: Volume 1: Global War. Cambridge University Press. pp. 585–614. ISBN 978-0-511-67566-9.
- Koinova, Maria (2017). "Conflict and Cooperation in Armenian Diaspora Mobilisation for Genocide Recognition". Diaspora as Cultures of Cooperation: Global and Local Perspectives. Springer International Publishing. pp. 111–129. ISBN 978-3-319-32892-8.
- Leonard, Thomas C. (2004). "When news is not enough: American media and Armenian deaths". America and the Armenian Genocide of 1915. Cambridge University Press. pp. 294–308. ISBN 978-0-521-82958-8.
- Maksudyan, Nazan (2020). "The Orphan Nation: Gendered Humanitarianism for Armenian Survivor Children in Istanbul, 1919–1922". Gendering Global Humanitarianism in the Twentieth Century: Practice, Politics and the Power of Representation. Springer International Publishing. pp. 117–142. ISBN 978-3-030-44630-7.
- Marsoobian, Armen (2016). "The Armenian Genocide in Film: Overcoming Denial and Loss". The History of Genocide in Cinema: Atrocities on Screen. Bloomsbury Publishing. pp. 73–86. ISBN 978-1-78673-047-3.
- Mouradian, Khatchig (2018). "Internment and destruction: Concentration camps during the Armenian genocide, 1915–16". Internment during the First World War: A Mass Global Phenomenon. Routledge. pp. 145–161. ISBN 978-1-315-22591-3.
- Üngör, Uğur Ümit (2012). "The Armenian Genocide, 1915" (PDF). Holocaust and Other Genocides (PDF). NIOD Institute for War, Holocaust and Genocide Studies / Amsterdam University Press. pp. 45–72. ISBN 978-90-4851-528-8. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 April 2021. Retrieved 3 July 2021.
- Üngör, Uğur Ümit (2016). "The Armenian Genocide in the Context of 20th-Century Paramilitarism". The Armenian Genocide Legacy. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 11–25. ISBN 978-1-137-56163-3.
- Zürcher, Erik Jan (2011). "Renewal and Silence: Postwar Unionist and Kemalist Rhetoric on the Armenian Genocide". A Question of Genocide: Armenians and Turks at the End of the Ottoman Empire. Oxford University Press. pp. 306–316. ISBN 978-0-19-539374-3.
Journal articles
- Akçam, Taner (2019). "When Was the Decision to Annihilate the Armenians Taken?". Journal of Genocide Research. 21 (4): 457–480. doi:10.1080/14623528.2019.1630893. ISSN 1462-3528.
- Ben Aharon, Eldad (2019). "Recognition of the Armenian Genocide after its Centenary: A Comparative Analysis of Changing Parliamentary Positions". Israel Journal of Foreign Affairs. 13 (3): 339–352. doi:10.1080/23739770.2019.1737911. hdl:1887/92270.
- Bjørnlund, Matthias (2008). "The 1914 cleansing of Aegean Greeks as a case of violent Turkification". Journal of Genocide Research. 10 (1): 41–58. doi:10.1080/14623520701850286.
- Ekmekçioğlu, Lerna (2013). "A Climate for Abduction, a Climate for Redemption: The Politics of Inclusion during and after the Armenian Genocide". Comparative Studies in Society and History. 55 (3): 522–553. doi:10.1017/S0010417513000236. hdl:1721.1/88911. JSTOR 23526015.
- Kaiser, Hilmar (2019). "Financing the Ruling Party and Its Militants in Wartime:The Armenian Genocide and the Kemah Massacres of 1915". Études arméniennes contemporaines (12): 7–31. doi:10.4000/eac.1942.
- Kurt, Ümit (2016). "Cultural Erasure: The Absorption and Forced Conversion of Armenian Women and Children, 1915–1916". Études arméniennes contemporaines (7). doi:10.4000/eac.997.
- Miller, Angela (2010). "Achilles the Bitter: Gorky and the Genocide". Oxford Art Journal. 33 (3): 392–396. doi:10.1093/oxartj/kcq025.
- Shirinian, George N. (2017). "Starvation and Its Political Use in the Armenian Genocide". Genocide Studies International. 11 (1): 8–37. doi:10.3138/gsi.11.1.01. Project MUSE 680838.
- Tusan, Michelle (2014). "'Crimes against Humanity': Human Rights, the British Empire, and the Origins of the Response to the Armenian Genocide". The American Historical Review. 119 (1): 47–77. doi:10.1093/ahr/119.1.47.
- Watenpaugh, Keith David (2013). "'Are There Any Children for Sale?': Genocide and the Transfer of Armenian Children (1915–1922)". Journal of Human Rights. 12 (3): 283–295. doi:10.1080/14754835.2013.812410.
External links
- Armenian Genocide – Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Armenia
- The Armenian Genocide Institute-Museum
- Timeline of the genocide by Raymond Kévorkian
| Armenian genocide | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Background | |||
| Genocide |
| ||
| Demography | |||
| Resistance | |||
| Perpetrators | |||
| International response | |||
| Prosecution | |||
| Cultural depictions |
| ||
| Aftermath | |||
| Related | |||
- Armenian genocide
- Genocide of indigenous peoples in Europe
- Genocide of indigenous peoples in Asia
- Massacres of Armenians
- Massacres in the Ottoman Empire
- Armenia–Turkey relations
- 1915 in Armenia
- 1915 in the Ottoman Empire
- Committee of Union and Progress
- Persecution of Christians in the Ottoman Empire
- Ethnic cleansing in Europe
- Ethnic cleansing in Asia
- Death marches
- History of West Azerbaijan province
- 20th-century massacres
- Events that led to courts-martial
- World War I crimes by the Ottoman Empire
