| Revision as of 11:54, 7 August 2011 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:Wi← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 18:37, 15 December 2024 edit undoEsculenta (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users58,616 edits added a paragraph about function of calcium oxalate in lichens | ||
| (225 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Calcium salt of oxalic acid}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=April 2022}} | |||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| |Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 443494972 | |||
| |Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | Name = Calcium oxalate | |||
| |verifiedrevid = 443496090 | |||
| | ImageFile = Calcium oxalate resonance.png | |||
| |PIN = Calcium oxalate | |||
| | ImageSize = 200px | |||
| | |
|SystematicName = Calcium ethanedioate | ||
| | |
|IUPACName = | ||
| |OtherNames = Oxalate of lime | |||
| | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| |ImageFile = Calcium oxalate resonance.png | |||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| |ImageSize = 150px | |||
| | ChemSpiderID = 30549 | |||
| |ImageName = Calcium oxalate | |||
| | InChI = 1/C2H2O4.Ca/c3-1(4)2(5)6;/h(H,3,4)(H,5,6);/q;+2/p-2 | |||
| |ImageFile1 = 246802-ICSDox.png | |||
| | InChIKey = QXDMQSPYEZFLGF-NUQVWONBAM | |||
| |ImageSize1 = 150px | |||
| | ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| |ImageName1 = structure of calcium oxalate dihydrate | |||
| | ChEBI = 60579 | |||
| |ImageCaption1 = Structure of calcium oxalate dihydrate{{legend|mediumspringgreen|], Ca}}{{legend|grey|], C}}{{legend|red|], O}}{{legend|white|], H}} | |||
| | SMILES = C(=O)(C(=O)). | |||
| |Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| |ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C2H2O4.Ca/c3-1(4)2(5)6;/h(H,3,4)(H,5,6);/q;+2/p-2 | |||
| |ChemSpiderID = 30549 | |||
| | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| |InChI = 1/C2H2O4.Ca/c3-1(4)2(5)6;/h(H,3,4)(H,5,6);/q;+2/p-2 | |||
| | StdInChIKey = QXDMQSPYEZFLGF-UHFFFAOYSA-L | |||
| |InChIKey = QXDMQSPYEZFLGF-NUQVWONBAM | |||
| | CASNo = 25454-23-3 | |||
| |ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| | CASOther = (anhydrous)<br>5794-28-5 (monohydrate) | |||
| |ChEMBL = 3184709 | |||
| | PubChem = 16212978 | |||
| |ChEBI = 60579 | |||
| |EINECS = 209-260-1 | |||
| |KEGG = C17478 | |||
| |SMILES = C(=O)(C(=O)). | |||
| |StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| |StdInChI = 1S/C2H2O4.Ca/c3-1(4)2(5)6;/h(H,3,4)(H,5,6);/q;+2/p-2 | |||
| |StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| |StdInChIKey = QXDMQSPYEZFLGF-UHFFFAOYSA-L | |||
| |CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} | |||
| |CASNo = 5794-28-5 | |||
| |CASNo_Comment = (monohydrate) | |||
| |CASNo2 = 25454-23-3 | |||
| |CASNo2_Comment = (dihydrate) | |||
| |CASNo3 = 192389-49-4 | |||
| |CASNo3_Comment = (trihydrate) | |||
| |CASNo2_Ref = {{cascite|changed|??}} | |||
| |UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| |UNII = 4PP86KK527 | |||
| |UNII_Comment = (monohydrate) | |||
| |PubChem = 16212978 | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| | |
|Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| | |
|Formula = {{chem2|CaC2O4}} | ||
| |Ca=1|C=2|O=4 | |||
| | MolarMass = 128.097 g/mol, anhydrous<br />146.112 g/mol, monohydrate | |||
| | |
|Appearance = colourless or white crystals (anhydrous and hydrated forms) | ||
| | |
|Density = 2.20 g/cm<sup>3</sup>, monohydrate<ref name=Acta/> | ||
| |Solubility = 0.61 mg/(100 g) {{chem2|H2O}} (20 °C)<ref>{{cite book |editor1-last=Haynes |editor1-first=W. |title=Handbook of Chemistry and Physics |date=2015–2016 |publisher=CRC Press |page=4-55 |edition=96th}}</ref> | |||
| | Solubility = 0.00067 g/100 ml (20 °C) | |||
| |SolubilityProduct = 2.7 × 10<sup>−9</sup> for {{chem2|CaC2O4}}<ref name="Euler_Ksp">{{Cite web |title=K<sub>sp</sub> Table: Solubility product constants near 25 °C |author=Euler |work=chm.uri.edu |access-date=10 June 2021 |url= https://www.chm.uri.edu/weuler/chm112/refmater/KspTable.html |language=English}}</ref> | |||
| | MeltingPt = 200°C, decomposes (monohydrate) | |||
| |MeltingPtC = 200 | |||
| }} | |||
| |MeltingPt_notes = decomposes (monohydrate) | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section3 = {{Chembox Hazards | |||
| '''Calcium oxalate''' (in archaic terminology, '''oxalate of lime''') is a chemical compound that forms needle-shaped crystals, known in plants as ]. A major constituent of human ], the chemical is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in ]. Its chemical formula is CaC<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub> or Ca (COO)<sub>2</sub>. | |||
| |MainHazards = Harmful, Irritant | |||
| |GHSPictograms = {{GHS07}} | |||
| |GHSSignalWord = Warning | |||
| |HPhrases = {{H-phrases|302|312}} | |||
| |PPhrases = {{P-phrases|280}} | |||
| |NFPA-H = 2 | |||
| |NFPA-F = 1 | |||
| |NFPA-R = 1 | |||
| |ExternalSDS = | |||
| }} | |||
| |Section4 = {{Chembox Related | |||
| |OtherCations = ]<br />]<br/>]<br/>]<br/>]<br/>]<br />]<br />] | |||
| |OtherAnions = ]<br />]<br />] | |||
| |OtherCompounds = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | |||
| ] (calcium oxalate dihydrate) emerging from the amorphous central part of the stone (the horizontal length of the picture represents 0.5 mm of the figured original)]] | |||
| '''Calcium oxalate''' (in archaic terminology, '''oxalate of lime''') is a ] ] of ] with the chemical formula {{chem2|CaC2O4}} or {{chem2|Ca(COO)2}}. It forms hydrates {{chem2|CaC2O4*''n''H2O}}, where ''n'' varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate {{chem2|CaC2O4*H2O}} occurs naturally as the mineral ], forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as ]s. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate {{chem2|CaC2O4*2H2O}}, which occurs naturally as the mineral ], and trihydrate {{chem2|CaC2O4*3H2O}}, which occurs naturally as the mineral ], are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Cultural groups with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as those in ], reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them.<ref name=Arno14>{{Citation |mode=cs1 |last1=Arnold |first1=Michael A. |year=2014 |title=''Pandanus tectorius'' S. Parkinson |website=Aggie Horticulture |publisher=Texas A&M University |url=https://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/syllabi/206/Lists/Fourth%20Edition/Pandanustectorius.pdf |access-date=30 September 2020 |archive-date=31 August 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210831185729/https://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/syllabi/206/Lists/Fourth%20Edition/Pandanustectorius.pdf |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|author=WebMD Editorial|title=Foods High in Oxalates|url=https://www.webmd.com/diet/foods-high-in-oxalates|access-date=30 January 2022|website=WebMD|language=en}}</ref> They are a constituent in 76% of human ].<ref name="Singh">{{cite journal |last1=Singh |first1=Prince |last2=Enders |first2=Felicity T. |last3=Vaughan |first3=Lisa E. |last4=Bergstralh |first4=Eric J. |last5=Knoedler |first5=John J. |last6=Krambeck |first6=Amy E. |last7=Lieske |first7=John C. |last8=Rule |first8=Andrew D. |title=Stone Composition Among First-Time Symptomatic Kidney Stone Formers in the Community |journal=Mayo Clinic Proceedings |date=October 2015 |volume=90 |issue=10 |pages=1356–1365 |doi=10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.07.016|pmid=26349951 |pmc=4593754}}</ref> Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in ]. | |||
| ==Occurrence== | ==Occurrence== | ||
| Many plants accumulate calcium oxalate as it has been reported in more than 1000 different genera of plants.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Francesci|first=V.R.|author2=Nakata|title=Calcium oxalate in plants: formation and function|journal=Annu Rev Plant Biol|volume=56|year=2005|issue=56|pages=41–71|doi=10.1146/annurev.arplant.56.032604.144106|pmid=15862089}}</ref> The calcium oxalate accumulation is linked to the detoxification of calcium ({{chem2|Ca(2+)}}) in the plant.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Martin|first=G|author2=Matteo Guggiari|author3=Daniel Bravo|author4=Jakob Zopfi|author5=Guillaume Cailleau|author6=Michel Aragno|author7=Daniel Job|author8=Eric Verrecchia|author9=Pilar Junier|title=Fungi, bacteria and soil pH: the oxalate–carbonate pathway as a model for metabolic interaction|journal=Environmental Microbiology|year=2012|volume=14|issue=11|pages=2960–2970|doi=10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02862.x|pmid=22928486|url=https://zenodo.org/record/3436719}}{{Dead link|date=February 2022 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes}}</ref> Upon decomposition, the calcium oxalate is oxidised by bacteria, fungi, or wildfire to produce the soil nutrient ].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Parsons |first1=Robert F. |last2=Attiwill |first2=Peter M. |last3=Uren |first3=Nicholas C. |last4=Kopittke |first4=Peter M. |title=Calcium oxalate and calcium cycling in forest ecosystems |journal=Trees |date=1 April 2022 |volume=36 |issue=2 |pages=531–536 |doi=10.1007/s00468-021-02226-4 |s2cid=239543937}}</ref> | |||
| Quantities of calcium oxalate are found in many tropical house plants. Calcium oxalate is a poisonous substance that can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and could even be fatal. | |||
| The ]ous plant dumb cane ('']'') contains the substance and on ingestion can prevent speech and be suffocating. It is also found in ] (in large quantities in the leaves) and in species of '']'', '']'', ], ], ] leaves, ]s, and '']'' and in ] in varying amounts. Insoluble calcium oxalate crystals are found in plant stems, roots, and leaves and produced in ]. Kidney stone sufferers should not eat plants high in oxalates. | |||
| ] | |||
| The ]ous plant dumb cane ('']'') contains the substance and on ingestion can prevent speech and be suffocating. It is also found in ], ] (in large quantities in the leaves), ], ] and in species of '']'', ], '']'', ], ], tea leaves, ]s, Virginia creeper ('']''), and '']'' and in ] in varying amounts. Plants of the genus '']'' contain enough calcium oxalate that consumption of parts of the plant can result in uncomfortable symptoms. Insoluble calcium oxalate crystals are found in plant stems, roots, and leaves and produced in ]s. ] plants exude calcium oxalates upon harvest of the orchid seed pods and may cause ]. | |||
| Calcium oxalate, as 'beerstone', is a brownish precipitate that tends to accumulate within vats, barrels and other containers used in the ] of ]. If not completely removed in a cleaning process, beerstone will leave an unsanitary surface that can harbour microorganisms.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.birkocorp.com/Brewing/beerstone.html|title=Removing Beerstone|accessdate=2007-08-06|last=Johnson|first=Dana|date=23 March 1998|work=Modern Brewery Age|publisher=Birko Corporation R&D}}</ref> Beerstone is composed of calcium and magnesium salts and various organic compounds left over from the brewing process; it promotes the growth of unwanted microorganisms that can adversely affect or even ruin the flavor of a batch of beer. | |||
| Calcium oxalate crystals are commonly found in ]s, where they occur in two mineral forms: weddellite (CaC<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>·(2+x)H<sub>2</sub>O) and whewellite (CaC<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>·H<sub>2</sub>O). These crystals can form both on the surface of the lichen as a powdery coating called {{lichengloss|pruina}} and within the internal structures of the lichen ]. The type and distribution of these crystals often correlates with environmental conditions: weddellite typically forms in dry environments and can serve as a water source for the lichen, while whewellite is more common in moist habitats. In addition to water regulation, calcium oxalate crystals in lichens serve several protective functions, including shielding against excessive sunlight and potentially helping to neutralize pollutants such as ]. The formation of these crystals is linked to the lichen's ability to dissolve calcium from rocky ] through the production of oxalic acid, with the amount of calcium oxalate often correlating with the calcium content of the substrate on which the lichen grows.<ref name="Wilk & Osyczka 2024">{{cite journal |last1=Wilk |first1=Karina |last2=Osyczka |first2=Piotr |title=Crystalline deposit in lichens: Determination of crystals with regard to practical application in standard taxonomic studies |journal=Acta Mycologica |volume=59 |date=2024-11-14 |doi=10.5586/am/193965 |doi-access=free |pages=1–11}}</ref> | |||
| Calcium oxalate, as '''‘beerstone’''', is a brownish precipitate that tends to accumulate within vats, barrels, and other containers used in the brewing of beer. If not removed in a cleaning process, beerstone will leave an unsanitary surface that can harbour microorganisms.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.howtohomebrewbeers.com/2018/05/beerstone-removal.html|title=What is beerstone (and how to remove it)|access-date=28 May 2018|last=Ryan|first=James|date=27 May 2018}}</ref> Beerstone is composed of calcium and magnesium salts and various organic compounds left over from the brewing process; it promotes the growth of unwanted microorganisms that can adversely affect or even ruin the flavour of a batch of beer. | |||
| Calcium oxalate crystals in the urine are the most common constituent of human ], and calcium oxalate crystal formation is also one of the toxic effects of ]. | Calcium oxalate crystals in the urine are the most common constituent of human ], and calcium oxalate crystal formation is also one of the toxic effects of ]. | ||
| == Chemical properties == | |||
| Hydrated forms of the compound occur naturally as three mineral species: ] (monohydrate, known from some coal beds), ] (dihydrate) and a very rare trihydrate called caoxite. | |||
| Calcium oxalate is a combination of calcium ions and the conjugate base of ], the oxalate anion. Its aqueous solutions are slightly basic because of the basicity of the oxalate ion. The basicity of calcium oxalate is weaker than that of ], due to its lower solubility in water. Solid calcium oxalate hydrate has been characterized by ]. It is a ] featuring planar oxalate anions linked to calcium, which also has water ]s.<ref name=Acta>{{cite journal|journal=Acta Crystallogr. B|year=1981|volume=37|issue=4|pages=826–829|title=The Structure of Whewellite, CaC<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub><sup>.</sup>H<sub>2</sub>O, at 328 K|author=S. Deganello|doi=10.1107/S056774088100441X|doi-access=}}</ref> | |||
| == |
==Medical significance== | ||
| Calcium oxalate can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. | |||
| Even a small dose of calcium oxalate is enough to cause intense sensations of burning in the mouth and throat, swelling, and choking that could last for up to two weeks.<ref>. Informa Healthcare.</ref> In greater doses it can cause severe digestive upset, breathing difficulties, coma or even death. Recovery from severe oxalate poisoning is possible, but permanent liver and kidney damage may have occurred. | |||
| ===Morphology and diagnosis=== | |||
| The stalks of plants in the '']'' genus produce the most severe oxalate reactions. The needle-like oxalate crystals produce pain and swelling when they contact lips, tongue, oral mucosa, conjunctiva, or skin. ] primarily is due to direct trauma from the needle-like crystals and, to a lesser extent, by other plant toxins (e.g., ]s, enzymes). | |||
| The monohydrate and dihydrate can be distinguished by the shape of the respective crystals. | |||
| * Calcium oxalate ''dihydrate'' crystals are ]. A large portion of the crystals in a urine sediment will have this type of morphology, as they can grow at any pH and naturally occur in normal urine. | |||
| * Calcium oxalate ''monohydrate'' crystals vary in shape, and can be shaped like dumbbells, spindles, ovals, or picket fences, the last of which is most commonly seen due to ].<ref>{{cite web|title=Urine Crystals|url=https://ahdc.vet.cornell.edu/clinpath/modules/UA-ROUT/crystsed.htm|website=ahdc.vet.cornell.edu/|publisher=Cornell University|access-date=12 July 2014}}</ref> | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| File:Calcium oxalate crystals in urine.jpg|Urine microscopy showing calcium oxalate crystals in the urine. The ] crystal morphology is clearly visible. | |||
| File:Calcium oxalate crystals (urine) - kalsiyum oksalat kristalleri (idrar) - 01.png|Urine microscopy showing a ''calcium oxalate monohydrate'' crystal (dumbbell shaped) and a ''calcium oxalate dihydrate'' crystal (envelope shaped) along with several erythrocytes. | |||
| File:Calcium oxalate crystals (urine) - kalsiyum oksalat kristalleri (idrar) - 02.png|Urine microscopy showing several ''calcium oxalate monohydrate'' crystals (dumbbell shaped, some of them clumped) and a ''calcium oxalate dihydrate'' crystal (envelope shaped) along with several erythrocytes. | |||
| File:Calcium Oxalate Detail.png|Urinary sediment showing several calcium oxalate crystals. 40X | |||
| File:Urine crystals comparison.png|Comparison of different types of urinary stones. | |||
| File:Histopathology of a breast cyst with calcium oxalate crystals, annotated.jpg|Histopathology of calcium oxalate crystals in a benign breast cyst, H&E stain. In the breast, they can be seen on ] and are usually benign, but can be associated with ].<ref>Image by Mikael Häggström, MD.<br>- Reference for benign/LCIS association: {{cite web|url=https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastcalcification.html|title=Microcalcifications|author=Hind Warzecha, M.D.|website=Pathology Outlines}} Last author update: 1 June 2010</ref> | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Kidney stones=== | |||
| Depending on the plant ingested, mild (Elephant Ear '']'') to more severe (], '']'') can cause compromised airways. One bite on the ''Arisaema'' seed pod will result in immediate swelling and burning. It will take over 12 hours for the swelling to subside.{{Citation needed|date=September 2010}} | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| | direction = horizontal | |||
| | total_width = 250 | |||
| | footer = Calcium oxalate monohydrate stones can be spiculated, resembling the head of a ]. | |||
| | image1 = Spiculated kidney stone.jpg | |||
| | image2 = Head of a morning star.jpg | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Main|Kidney stone disease#Diagnosis}} | |||
| About 76% of kidney stones are partially or entirely of the calcium oxalate type.<ref name="Singh"/> They form when urine is persistently saturated with calcium and oxalate. Between 1% and 15% of people globally are affected by kidney stones at some point.<ref name=BMJ2016>{{cite journal|last1=Morgan|first1=Monica S C|last2=Pearle|first2=Margaret S|title=Medical management of renal stones|journal=BMJ|year=2016|volume=352|pages=i52|issn=1756-1833|doi=10.1136/bmj.i52|pmid=26977089|s2cid=28313474}}</ref><ref name=":3">{{Cite journal|date=6 September 2020|title=Prevalence and Trends in Kidney Stone Among Adults in the USA: Analyses of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2018 Data|url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2405456920302248|journal=European Urology Focus|language=en|doi=10.1016/j.euf.2020.08.011|issn=2405-4569|last1=Abufaraj|first1=Mohammad|last2=Xu|first2=Tianlin|last3=Cao|first3=Chao|last4=Waldhoer|first4=Thomas|last5=Seitz|first5=Christian|last6=d'Andrea|first6=David|last7=Siyam|first7=Abdelmuez|last8=Tarawneh|first8=Rand|last9=Fajkovic|first9=Harun|last10=Schernhammer|first10=Eva|last11=Yang|first11=Lin|last12=Shariat|first12=Shahrokh F.|volume=7 |issue=6 |pages=1468–1475 |pmid=32900675|s2cid=221572651|doi-access=free}}</ref> In 2015, they caused about 16,000 deaths worldwide.<ref name=GBD2015De>{{cite journal | vauthors = Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, etal | collaboration = GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators | title = Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 | journal = Lancet | volume = 388 | issue = 10053 | pages = 1459–1544 | date = October 2016 | pmid = 27733281 | pmc = 5388903 | doi = 10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1}}</ref> | |||
| Some of the oxalate in urine is produced by the body. Calcium and oxalate in the diet play a part but are not the only factors that affect the formation of calcium oxalate stones. Dietary oxalate is an organic ion found in many vegetables, fruits, and nuts. Calcium from bone may also play a role in kidney stone formation. | |||
| ===Treatment=== | |||
| In one study of modulators of calcium oxalate crystallization in urine, magnesium-] was shown to inhibit CaO{{sub|{{mvar|x}}}} (calcium oxalate) crystallization, “probably via actions of the citrate, but not the Mg.” This was in comparison to magnesium, citrate, and magnesium citrate. Currently the preparation of magnesium-potassium citrate that was used in one positive study is not available in the United States. <ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Schwille |first1=P. O. |last2=Schmiedl |first2=A. |last3=Herrmann |first3=U. |last4=Fan |first4=J. |last5=Gottlieb |first5=D. |last6=Manoharan |first6=M. |last7=Wipplinger |first7=J. |date=1999-05-01 |title=Magnesium, citrate, magnesium citrate and magnesium-alkali citrate as modulators of calcium oxalate crystallization in urine: observations in patients with recurrent idiopathic calcium urolithiasis. |url=https://doi.org/10.1007/s002400050097 |journal=Urological Research |language=en |volume=27 |issue=2 |pages=117–126 |doi=10.1007/s002400050097 |pmid=10424393 |s2cid=1506052 |issn=1434-0879}}</ref> | |||
| Medication administered at the ER may include ], ], or ], all intravenously. Although this most likely will be a localized reaction, it will be treated by the ER as an ] reaction.{{Citation needed|date=September 2010}} | |||
| ==Industrial applications== | |||
| ==References== | |||
| Calcium oxalate is used in the manufacture of ].<ref name="HummelCrotonDataSheet">{{cite web |url=http://www.hummelcroton.com/datasheet/caox.html |title=Calcium Oxalate Data Sheet|publisher=Hummel Croton Inc. |access-date=23 April 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <references /> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| {{Calcium compounds}} | {{Calcium compounds}} | ||
| {{Oxalates}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=September 2010}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Calcium Oxalate}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:37, 15 December 2024
Calcium salt of oxalic acid

| |
 Structure of calcium oxalate dihydrate Calcium, Ca Carbon, C Oxygen, O Hydrogen, H | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Calcium oxalate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name Calcium ethanedioate | |
| Other names Oxalate of lime | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.419 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | CaC2O4 |
| Molar mass | 128.096 g·mol |
| Appearance | colourless or white crystals (anhydrous and hydrated forms) |
| Density | 2.20 g/cm, monohydrate |
| Melting point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) decomposes (monohydrate) |
| Solubility in water | 0.61 mg/(100 g) H2O (20 °C) |
| Solubility product (Ksp) | 2.7 × 10 for CaC2O4 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
| Main hazards | Harmful, Irritant |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms | 
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302, H312 |
| Precautionary statements | P280 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |
 |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External SDS |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Calcium carbonate Calcium acetate Calcium formate |
| Other cations | Sodium oxalate Beryllium oxalate Magnesium oxalate Strontium oxalate Barium oxalate Radium oxalate Iron(II) oxalate Iron(III) oxalate |
| Related compounds | Oxalic acid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |

Calcium oxalate (in archaic terminology, oxalate of lime) is a calcium salt of oxalic acid with the chemical formula CaC2O4 or Ca(COO)2. It forms hydrates CaC2O4·nH2O, where n varies from 1 to 3. Anhydrous and all hydrated forms are colorless or white. The monohydrate CaC2O4·H2O occurs naturally as the mineral whewellite, forming envelope-shaped crystals, known in plants as raphides. The two rarer hydrates are dihydrate CaC2O4·2H2O, which occurs naturally as the mineral weddellite, and trihydrate CaC2O4·3H2O, which occurs naturally as the mineral caoxite, are also recognized. Some foods have high quantities of calcium oxalates and can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal. Cultural groups with diets that depend highly on fruits and vegetables high in calcium oxalate, such as those in Micronesia, reduce the level of it by boiling and cooking them. They are a constituent in 76% of human kidney stones. Calcium oxalate is also found in beerstone, a scale that forms on containers used in breweries.
Occurrence
Many plants accumulate calcium oxalate as it has been reported in more than 1000 different genera of plants. The calcium oxalate accumulation is linked to the detoxification of calcium (Ca) in the plant. Upon decomposition, the calcium oxalate is oxidised by bacteria, fungi, or wildfire to produce the soil nutrient calcium carbonate.
The poisonous plant dumb cane (Dieffenbachia) contains the substance and on ingestion can prevent speech and be suffocating. It is also found in sorrel, rhubarb (in large quantities in the leaves), cinnamon, turmeric and in species of Oxalis, Araceae, Arum italicum, taro, kiwifruit, tea leaves, agaves, Virginia creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia), and Alocasia and in spinach in varying amounts. Plants of the genus Philodendron contain enough calcium oxalate that consumption of parts of the plant can result in uncomfortable symptoms. Insoluble calcium oxalate crystals are found in plant stems, roots, and leaves and produced in idioblasts. Vanilla plants exude calcium oxalates upon harvest of the orchid seed pods and may cause contact dermatitis.
Calcium oxalate crystals are commonly found in lichens, where they occur in two mineral forms: weddellite (CaC2O4·(2+x)H2O) and whewellite (CaC2O4·H2O). These crystals can form both on the surface of the lichen as a powdery coating called pruina and within the internal structures of the lichen thallus. The type and distribution of these crystals often correlates with environmental conditions: weddellite typically forms in dry environments and can serve as a water source for the lichen, while whewellite is more common in moist habitats. In addition to water regulation, calcium oxalate crystals in lichens serve several protective functions, including shielding against excessive sunlight and potentially helping to neutralize pollutants such as sulfur dioxide. The formation of these crystals is linked to the lichen's ability to dissolve calcium from rocky substrates through the production of oxalic acid, with the amount of calcium oxalate often correlating with the calcium content of the substrate on which the lichen grows.
Calcium oxalate, as ‘beerstone’, is a brownish precipitate that tends to accumulate within vats, barrels, and other containers used in the brewing of beer. If not removed in a cleaning process, beerstone will leave an unsanitary surface that can harbour microorganisms. Beerstone is composed of calcium and magnesium salts and various organic compounds left over from the brewing process; it promotes the growth of unwanted microorganisms that can adversely affect or even ruin the flavour of a batch of beer.
Calcium oxalate crystals in the urine are the most common constituent of human kidney stones, and calcium oxalate crystal formation is also one of the toxic effects of ethylene glycol poisoning.
Chemical properties
Calcium oxalate is a combination of calcium ions and the conjugate base of oxalic acid, the oxalate anion. Its aqueous solutions are slightly basic because of the basicity of the oxalate ion. The basicity of calcium oxalate is weaker than that of sodium oxalate, due to its lower solubility in water. Solid calcium oxalate hydrate has been characterized by X-ray crystallography. It is a coordination polymer featuring planar oxalate anions linked to calcium, which also has water ligands.
Medical significance
Calcium oxalate can produce sores and numbing on ingestion and may even be fatal.
Morphology and diagnosis
The monohydrate and dihydrate can be distinguished by the shape of the respective crystals.
- Calcium oxalate dihydrate crystals are octahedral. A large portion of the crystals in a urine sediment will have this type of morphology, as they can grow at any pH and naturally occur in normal urine.
- Calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals vary in shape, and can be shaped like dumbbells, spindles, ovals, or picket fences, the last of which is most commonly seen due to ethylene glycol poisoning.
-
 Urine microscopy showing calcium oxalate crystals in the urine. The octahedral crystal morphology is clearly visible.
Urine microscopy showing calcium oxalate crystals in the urine. The octahedral crystal morphology is clearly visible.
-
 Urine microscopy showing a calcium oxalate monohydrate crystal (dumbbell shaped) and a calcium oxalate dihydrate crystal (envelope shaped) along with several erythrocytes.
Urine microscopy showing a calcium oxalate monohydrate crystal (dumbbell shaped) and a calcium oxalate dihydrate crystal (envelope shaped) along with several erythrocytes.
-
 Urine microscopy showing several calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals (dumbbell shaped, some of them clumped) and a calcium oxalate dihydrate crystal (envelope shaped) along with several erythrocytes.
Urine microscopy showing several calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals (dumbbell shaped, some of them clumped) and a calcium oxalate dihydrate crystal (envelope shaped) along with several erythrocytes.
-
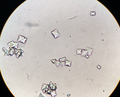 Urinary sediment showing several calcium oxalate crystals. 40X
Urinary sediment showing several calcium oxalate crystals. 40X
-
 Comparison of different types of urinary stones.
Comparison of different types of urinary stones.
-
 Histopathology of calcium oxalate crystals in a benign breast cyst, H&E stain. In the breast, they can be seen on mammography and are usually benign, but can be associated with lobular carcinoma in situ.
Histopathology of calcium oxalate crystals in a benign breast cyst, H&E stain. In the breast, they can be seen on mammography and are usually benign, but can be associated with lobular carcinoma in situ.
Kidney stones

 Calcium oxalate monohydrate stones can be spiculated, resembling the head of a morning star.
Main article: Kidney stone disease § Diagnosis
Calcium oxalate monohydrate stones can be spiculated, resembling the head of a morning star.
Main article: Kidney stone disease § Diagnosis
About 76% of kidney stones are partially or entirely of the calcium oxalate type. They form when urine is persistently saturated with calcium and oxalate. Between 1% and 15% of people globally are affected by kidney stones at some point. In 2015, they caused about 16,000 deaths worldwide.
Some of the oxalate in urine is produced by the body. Calcium and oxalate in the diet play a part but are not the only factors that affect the formation of calcium oxalate stones. Dietary oxalate is an organic ion found in many vegetables, fruits, and nuts. Calcium from bone may also play a role in kidney stone formation.
In one study of modulators of calcium oxalate crystallization in urine, magnesium-alkali citrate was shown to inhibit CaOx (calcium oxalate) crystallization, “probably via actions of the citrate, but not the Mg.” This was in comparison to magnesium, citrate, and magnesium citrate. Currently the preparation of magnesium-potassium citrate that was used in one positive study is not available in the United States.
Industrial applications
Calcium oxalate is used in the manufacture of ceramic glazes.
See also
References
- ^ S. Deganello (1981). "The Structure of Whewellite, CaC2O4H2O, at 328 K". Acta Crystallogr. B. 37 (4): 826–829. doi:10.1107/S056774088100441X.
- Haynes, W., ed. (2015–2016). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (96th ed.). CRC Press. p. 4-55.
- Euler. "Ksp Table: Solubility product constants near 25 °C". chm.uri.edu. Retrieved 10 June 2021.
- Arnold, Michael A. (2014). "Pandanus tectorius S. Parkinson" (PDF). Aggie Horticulture. Texas A&M University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 August 2021. Retrieved 30 September 2020.
- WebMD Editorial. "Foods High in Oxalates". WebMD. Retrieved 30 January 2022.
- ^ Singh, Prince; Enders, Felicity T.; Vaughan, Lisa E.; Bergstralh, Eric J.; Knoedler, John J.; Krambeck, Amy E.; Lieske, John C.; Rule, Andrew D. (October 2015). "Stone Composition Among First-Time Symptomatic Kidney Stone Formers in the Community". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 90 (10): 1356–1365. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.07.016. PMC 4593754. PMID 26349951.
- Francesci, V.R.; Nakata (2005). "Calcium oxalate in plants: formation and function". Annu Rev Plant Biol. 56 (56): 41–71. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.56.032604.144106. PMID 15862089.
- Martin, G; Matteo Guggiari; Daniel Bravo; Jakob Zopfi; Guillaume Cailleau; Michel Aragno; Daniel Job; Eric Verrecchia; Pilar Junier (2012). "Fungi, bacteria and soil pH: the oxalate–carbonate pathway as a model for metabolic interaction". Environmental Microbiology. 14 (11): 2960–2970. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02862.x. PMID 22928486.
- Parsons, Robert F.; Attiwill, Peter M.; Uren, Nicholas C.; Kopittke, Peter M. (1 April 2022). "Calcium oxalate and calcium cycling in forest ecosystems". Trees. 36 (2): 531–536. doi:10.1007/s00468-021-02226-4. S2CID 239543937.
- Wilk, Karina; Osyczka, Piotr (14 November 2024). "Crystalline deposit in lichens: Determination of crystals with regard to practical application in standard taxonomic studies". Acta Mycologica. 59: 1–11. doi:10.5586/am/193965.
- Ryan, James (27 May 2018). "What is beerstone (and how to remove it)". Retrieved 28 May 2018.
- "Urine Crystals". ahdc.vet.cornell.edu/. Cornell University. Retrieved 12 July 2014.
- Image by Mikael Häggström, MD.
- Reference for benign/LCIS association: Hind Warzecha, M.D. "Microcalcifications". Pathology Outlines. Last author update: 1 June 2010 - Morgan, Monica S C; Pearle, Margaret S (2016). "Medical management of renal stones". BMJ. 352: i52. doi:10.1136/bmj.i52. ISSN 1756-1833. PMID 26977089. S2CID 28313474.
- Abufaraj, Mohammad; Xu, Tianlin; Cao, Chao; Waldhoer, Thomas; Seitz, Christian; d'Andrea, David; Siyam, Abdelmuez; Tarawneh, Rand; Fajkovic, Harun; Schernhammer, Eva; Yang, Lin; Shariat, Shahrokh F. (6 September 2020). "Prevalence and Trends in Kidney Stone Among Adults in the USA: Analyses of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2018 Data". European Urology Focus. 7 (6): 1468–1475. doi:10.1016/j.euf.2020.08.011. ISSN 2405-4569. PMID 32900675. S2CID 221572651.
- Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, et al. (GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators) (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
- Schwille, P. O.; Schmiedl, A.; Herrmann, U.; Fan, J.; Gottlieb, D.; Manoharan, M.; Wipplinger, J. (1 May 1999). "Magnesium, citrate, magnesium citrate and magnesium-alkali citrate as modulators of calcium oxalate crystallization in urine: observations in patients with recurrent idiopathic calcium urolithiasis". Urological Research. 27 (2): 117–126. doi:10.1007/s002400050097. ISSN 1434-0879. PMID 10424393. S2CID 1506052.
- "Calcium Oxalate Data Sheet". Hummel Croton Inc. Retrieved 23 April 2017.
| Calcium compounds | |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen & halogens | |
| Chalcogens | |
| Pnictogens | |
| Group 13 & 14 | |
| Trans metals | |
| Organics | |
| Compounds of the oxalate ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||