| Revision as of 23:39, 6 November 2011 editCodename:Iceman (talk | contribs)26 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 02:06, 25 December 2023 edit undo1234qwer1234qwer4 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers197,944 edits →Applications: links | ||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 16 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{no footnotes|date=November 2011}} | |||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| | verifiedrevid = 459434931 | |||
| | ImageFile = Julolidine.png | | ImageFile = Julolidine.png | ||
| | |
| ImageFile_Ref = {{Chemboximage|correct|??}} | ||
| | |
| ImageName = Diagram showing structure of julolidine | ||
| | PIN = 2,3,6,7-Tetrahydro-1''H'',5''H''-pyridoquinoline | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | OtherNames = | |||
| | IUPACName = Julolidine | |||
| ⚫ | |Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | OtherNames = 2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H,5H-benzoquinolizine | |||
| | CASNo = 479-59-4 | | CASNo = 479-59-4 | ||
| | |
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | ||
| ⚫ | | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | UNII = 8ERL3KJ6GQ | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | PubChem = 68069 | ||
| | SMILES = C1CC2=C3C(=CC=C2)CCCN3C1 | |||
| | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | ChemSpiderID = 61383 | |||
| | SMILES = c13c2c(ccc1)CCCN2CCC3 | |||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C12H15N/c1-4-10-6-2-8-13-9-3-7-11(5-1)12(10)13/h1,4-5H,2-3,6-9H2 | |||
| | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | |||
| | StdInChIKey = DZFWNZJKBJOGFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| ⚫ | |Section2={{Chembox Properties | ||
| | C=12 | H=15 | N=1 | |||
| ⚫ | | Appearance = | ||
| ⚫ | | Density = 1.003 g/mL | ||
| | MeltingPtC = 35 | |||
| ⚫ | | BoilingPt = | ||
| | RefractIndex = 1.568 | |||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| |Section7={{Chembox Hazards | |||
| | FlashPtC = 110 | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | Formula = C<sub>12</sub>H<sub>15</sub>N | |||
| | MolarMass = 173.26 g/mol | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | MeltingPt = 35 °C | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | Refractive index = 1.568 | |||
| | Flash point = 110 °C | |||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| '''Julolidine''' is a ] ] ]. It has the formula C<sub>12</sub>H<sub>15</sub>N. | '''Julolidine''' is a ] ] ]. It has the formula C<sub>12</sub>H<sub>15</sub>N. | ||
| == Synthesis == | == Synthesis == | ||
| ⚫ | The first synthesis of julolidine was first reported by G. Pinkus in 1892.<ref>Pinkus, G. Ueber die Einwirkung von Trimethylenchlorbromid auf einige aromatische Amine und Amide. ] 1892, 25 (2), 2798–2806</ref> | ||
| Synthesized of Julolidine was first reported by | |||
| G. Pinkus in 1892. | |||
| ==Applications== | ==Applications== | ||
| This compound and its derivatives have found recent | This compound and its derivatives have found recent interest as ] materials, ] | ||
| ⚫ | substances, ] substrates in analytical ], dye intermediates, potential antidepressants | ||
| interest as photoconductive materials, chemiluminescence | |||
| and tranquilizers, ] materials, high sensitivity ] materials, and for improving color stability in photography. | |||
| substances, chromogenic substrates in analytical | |||
| ⚫ | redox reactions, dye intermediates, potential antidepressants | ||
| and tranquilizers, nonlinear optical materials, | |||
| high sensitivity photopolymerizable materials, | |||
| and for improving color stability in photography. | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| ==External links== | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| * |
* {{cite journal | doi = 10.1021/jo9519118| pmid = 11667174| title = Convenient Synthesis of Julolidines Using Benzotriazole Methodology| journal = The Journal of Organic Chemistry| volume = 61| issue = 9| pages = 3117| year = 1996| last1 = Katritzky| first1 = Alan R.| last2 = Rachwal| first2 = Bogumila| last3 = Rachwal| first3 = Stanislaw| last4 = Abboud| first4 = Khalil A.}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{uncategorized|date=November 2011}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 02:06, 25 December 2023
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2,3,6,7-Tetrahydro-1H,5H-pyridoquinoline | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.851 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C12H15N |
| Molar mass | 173.259 g·mol |
| Density | 1.003 g/mL |
| Melting point | 35 °C (95 °F; 308 K) |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.568 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
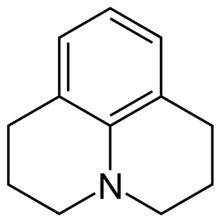
Julolidine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. It has the formula C12H15N.
Synthesis
The first synthesis of julolidine was first reported by G. Pinkus in 1892.
Applications
This compound and its derivatives have found recent interest as photoconductive materials, chemiluminescence substances, chromogenic substrates in analytical redox reactions, dye intermediates, potential antidepressants and tranquilizers, nonlinear optical materials, high sensitivity photopolymerizable materials, and for improving color stability in photography.
References
- Pinkus, G. Ueber die Einwirkung von Trimethylenchlorbromid auf einige aromatische Amine und Amide. Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft 1892, 25 (2), 2798–2806
External links
- Katritzky, Alan R.; Rachwal, Bogumila; Rachwal, Stanislaw; Abboud, Khalil A. (1996). "Convenient Synthesis of Julolidines Using Benzotriazole Methodology". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 61 (9): 3117. doi:10.1021/jo9519118. PMID 11667174.