| Revision as of 13:00, 9 August 2004 view sourceChameleon (talk | contribs)7,877 editsm punct.← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 11:05, 26 December 2024 view source Alexeyevitch (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers28,656 edits →Naming: c/e | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Largest living species of dolphin}} | |||
| {{Taxobox_begin | color = pink | name = '''Orca'''}}<br>{{StatusConcern}} | |||
| {{Other uses}} | |||
| {{Taxobox_section_image}} | |||
| {{Redirect|Killer Whale|''The Avengers'' episode|Killer Whale (The Avengers){{!}}Killer Whale {{(-}}''The Avengers'')|1962 tokusatsu film|Killer Whale (film){{!}}''Killer Whale'' (film)}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{pp-move-indef}} | |||
| {{Taxobox_begin_placement | color = pink}} | |||
| {{pp-semi-indef}} | |||
| {{Taxobox_regnum_entry | taxon = ]ia}} | |||
| {{Use Canadian English|date=April 2020}} | |||
| {{Taxobox_phylum_entry | taxon = ]}} | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=April 2020}} | |||
| {{Taxobox_classis_entry | taxon = ]}} | |||
| {{Speciesbox | |||
| {{Taxobox_ordo_entry | taxon = ]}} | |||
| | fossil_range = ] to recent{{fossil range|Late Miocene|Recent|<ref>{{cite web|url=https://paleobiodb.org/classic/checkTaxonInfo?taxon_no=64541|title=''Orcinus orca'' Linnaeus 1758|work=Fossilworks|access-date=17 December 2021|archive-date=December 12, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211212184046/http://www.fossilworks.org/cgi-bin/bridge.pl?a=taxonInfo&taxon_no=64541|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| {{Taxobox_familia_entry | taxon = ]}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{Taxobox_genus_entry | taxon = '''''Orcinus'''''}} | |||
| | name = Orca<br />Killer whale<ref name=MSW3>{{MSW3 Cetacea|id=14300074}}</ref> | |||
| {{Taxobox_species_entry | taxon = '''''orca'''''}} | |||
| | image = Killerwhales jumping.jpg | |||
| {{Taxobox_end_placement}} | |||
| | image_alt = Two killer whales jump above the sea surface, showing their black, white and grey colouration. The closer whale is upright and viewed from the side, while the other whale is arching backward to display its underside. | |||
| {{Taxobox_section_binomial | color = pink | binomial_name = Orcinus orca | author = ] | date = ]}} | |||
| | image_caption = {{longitem|Transient orcas near ], eastern ], ]}} | |||
| <tr><td align="center"> | |||
| | image2 = Female orca scale.png | |||
| ] | |||
| | image2_alt = Diagram showing a 5.4 meter (18 foot) female killer whale compared to a 1.8 meter (5 foot 11 inches) human scuba diver. | |||
| {{Taxobox_end}} | |||
| | image2_caption = {{longitem|5.4 meter (18 foot) female killer whale compared to 1.8 meter (5 foot 11 inches) human scuba diver}} | |||
| The '''Orca''' (''Orcinus orca'') is the largest member of the ] ]. It is the second-most widely distributed mammal on Earth after humans, and is found in all the world's oceans. It also a versatile ], eating fish, turtles, birds, seals, sharks and even other juvenile and small ]ns. This puts the Orca at the pinnacle of the marine ]. | |||
| | status = DD | |||
| | status_system = IUCN3.1 | |||
| | status_ref = <ref name="iucn status 19 November 2021">{{cite iucn |author=Reeves|first1= R. |author2=Pitman|first2= R. L.|author3=Ford|first3= J. K. B. |date=2017 |title=''Orcinus orca'' |volume=2017 |page=e.T15421A50368125 |doi=10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T15421A50368125.en |access-date=19 November 2021}}</ref> | |||
| | status2 = CITES_A2 | |||
| | status2_system = CITES | |||
| | status2_ref = <ref name = "CITES">{{Cite web|title=Appendices {{!}} CITES|url=https://cites.org/eng/app/appendices.php|access-date=2022-01-14|website=cites.org|archive-date=December 5, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171205014647/https://cites.org/eng/app/appendices.php|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | genus = Orcinus | |||
| | species = orca | |||
| | authority = (], ])<ref>{{ITIS |id=180469 |taxon=''Orcinus orca'' (Linnaeus, 1758) |access-date=March 9, 2011}}</ref> | |||
| | synonyms = *''Delphinus orca'' {{small|Linnaeus, 1758}} | |||
| *''Delphinus gladiator'' {{small|Bonnaterre, 1789}} | |||
| *''Orca gladiator'' {{small|(Bonnaterre, 1789)}} | |||
| | range_map = Orca_range.svg | |||
| | range_map_alt = A world map shows killer whales are found throughout every ocean, except parts of the Arctic. They are also absent from the Black and Baltic seas. | |||
| | range_map_caption = {{legend2|#0577AF|''Orcinus orca'' ]|outline=gray}} | |||
| }} | |||
| The '''orca''' ('''''Orcinus orca'''''), or '''killer whale''', is a ] and the largest member of the ] family. It is the only ] species in the genus '']'' and is recognizable by its black-and-white patterned body. A ], it is found in diverse marine environments, from ] to ] to tropical seas. | |||
| Orcas are ]s with a diverse diet. Individual populations often specialize in particular types of prey. This includes a variety of ], ]s, ], and ]s such as ] and other ]. They are highly ]; some populations are composed of highly stable ] family groups (pods). Their sophisticated hunting techniques and vocal behaviors, often specific to a particular group and passed along from generation to generation, are considered to be manifestations of ]. | |||
| The Orca is also commonly known as the '''Killer Whale''' and sometimes as the '''Great Killer Whale'''. This name reflects the animal's reputation as a magnificent and fearsome creature of the sea that dates back to ]. These days it is recognised that the "whale" is, from a ] perspective, a dolphin and moreover does not represent a danger to humans - no attack on a human by an Orca in wildlife has ever been recorded. | |||
| The ] assesses the orca's ] as ] because of the likelihood that two or more orca types are ]. Some local populations are considered ] or ] due to prey depletion, ], pollution (by ]), capture for ]s,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Fisheries |first=NOAA |date=2024-02-05 |title=Southern Resident Killer Whale (Orcinus orca) {{!}} NOAA Fisheries |url=https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/west-coast/endangered-species-conservation/southern-resident-killer-whale-orcinus-orca#:~:text=All%20three%20Southern%20Resident%20pods,now%20numbers%20in%20the%2070s. |access-date=2024-12-09 |website=NOAA |language=en}}</ref> and ]. In late 2005, the ]s were placed on the ]. | |||
| Orcas are not usually a threat to humans, and no fatal attack has ever been documented in their natural habitat. There have been cases of ] at marine theme parks. | |||
| ==Naming== | ==Naming== | ||
| Orcas, despite being dolphins, are commonly called 'killer whales' due to a mistranslation of the Spanish 'asesino de ballenas' (literally 'whale killer'), reflecting their historical predation on whales.<ref name="whales.org">{{cite web |title=Facts about orcas (killer whales) |url=https://us.whales.org/whales-dolphins/facts-about-orcas/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220208153903/https://us.whales.org/whales-dolphins/facts-about-orcas/ |archive-date=February 8, 2022 |access-date=8 February 2022 |website=Whales.org |publisher=Whale & Dolphin Conservation USA}}</ref> Since the 1960s, the use of "orca" instead of "killer whale" has steadily grown in common use.<ref name="price">{{cite web|first=Mary |last=Price|url=https://blog.nwf.org/2013/07/orcas-how-science-debunked-superstition/|title=Orcas: How Science Debunked Superstition|publisher=National Wildlife Federation|date=22 July 2013|access-date=30 July 2020|archive-date=January 31, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170131095114/http://blog.nwf.org/2013/07/orcas-how-science-debunked-superstition/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The genus name ''Orcinus'' means 'of the kingdom of the dead',{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|Balcomb|2000|p=69}} or 'belonging to ]'.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120815082034/http://www.seaworld.org/animal-info/info-books/killer-whale/scientific-classification.htm |date=August 15, 2012 }}, Seaworld.org, September 23, 2010, Retrieved September 9, 2010.</ref> ] originally used ''orca''<ref>{{cite dictionary |url= https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0059%3Aentry%3Dorca1 |title= orca |last1= Lewis |first1= Charlton T. |last2= Short |first2= Charles |dictionary= A Latin Dictionary |edition= |publisher= Perseus Digital Library |date= 1879 |access-date= October 7, 2022 |archive-date= October 7, 2022 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20221007112944/https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0059:entry%3Dorca1 |url-status= live }}</ref> ({{plural form}} ''orcae'') for these animals, possibly borrowing ] {{lang|grc|ὄρυξ}} (''óryx''), which referred (among other things) to a whale species, perhaps a ].<ref name="Liddel">{{cite web |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3Do)%2Fruc |title=ὄρυξ |last1=Liddell |first1=Henry George |last2=Scott |first2=Robert |work=A Greek-English Lexicon |publisher=Perseus Digital Library |date=1940 |access-date=October 9, 2023 |archive-date=May 26, 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240526021534/https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3Do)%2Fruc |url-status=live }}</ref> As part of the ] ], the species is more closely related to other oceanic dolphins than to other whales.<ref>{{cite book |last= Best |first= P. B. |year= 2007 |title= Whales and Dolphins of the Southern African Subregion|publisher= Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-521-89710-5}}</ref> | |||
| Since the 1960s ''Orca'' has steadily grown in popularity as the common name used to identify the species and is now more popular than the traditional name, ''Killer Whale'', amongst those in the field. However the latter is still widely used by the general public. | |||
| They are sometimes referred to as 'blackfish', a name also used for other whale species. 'Grampus' is a former name for the species, but is now seldom used. This meaning of 'grampus' should not be confused with the genus '']'', whose only member is ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Leatherwood |first1=Stephen |first2=Larry J. |last2=Hobbs |date=1988 |url=https://archive.org/details/whalesdolphinsp000leat/page/118 |title=Whales, dolphins, and porpoises of the eastern North Pacific and adjacent Arctic waters: a guide to their identification |page=118 |publisher=Courier Dover Publications |isbn=0-486-25651-0 |access-date= January 28, 2010}}</ref> | |||
| There are several reasons for the change. Firstly having the word "whale" in the name of a species that is really a dolphin is liable to cause needless confusion. Secondly the species is called Orca in most other European languages and, as there has been a steady increase in the amount of (cross-border) research into the species, there has been a convergence in naming. | |||
| ==Taxonomy== | |||
| However ] has also played a role in the name change. The "Killer" in Killer Whale is often wrongly assumed to imply that the creature will kill humans. This historical reputation is downplayed by "rebranding" the species with a different name. It is commonly accepted that "Killer Whale" is an eighteenth century mistranslation of the name given by Spanish sailors for the species — which would properly be translated as "whale-killer". That the original name was itself a mistranslation has also strengthened the case for "Orca". | |||
| {{multiple image |align=right |direction=vertical |width= | |||
| |image1=Orcinus citoniensis.JPG |caption1='']'' fossil, an extinct species of the same genus, Museo Capellini in ] | |||
| |image2=Naturalis Biodiversity Center - Museum - Workshop - Lecture hall, killer whale skeleton suspended from ceiling2.jpg |caption2=Modern orca skeleton, ], Leiden | |||
| |image3=Orcinus orca 3d scan Natural History Museum University of Pisa C 301.stl|caption3 = 3D model of skeleton | |||
| }} | |||
| ''Orcinus orca'' is the only recognized ] species in the genus '']'', and one of many animal species originally described by ] in his landmark 1758 ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Linnaeus |first=C. |author-link=Carl Linnaeus |title=Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I |volume=v.1 |edition=] |publisher=Holmiae. (Laurentii Salvii) |year=1758 |page=824 |url=https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/10277#page/92/mode/1up |language=la |access-date=January 14, 2018 |archive-date=March 25, 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170325030419/http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/10277#page/92/mode/1up |url-status=live }}</ref> ] wrote the first scientific description of an orca in his ''Piscium & aquatilium animantium natura'' of 1558, part of the larger '']'', based on examination of a dead ] animal in the ] that had attracted a great deal of local interest.<ref name="Greifswald church"> (in German). St. Mary's Church, Greifswald. Retrieved February 16, 2010</ref> | |||
| The orca is one of 35 species in the ], which first appeared about 11 million years ago. The orca lineage probably branched off shortly thereafter.{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|p=19}} Although it has morphological similarities with the ], the ] and the ]s, a study of cytochrome b gene sequences indicates that its closest extant relatives are the snubfin dolphins of the genus '']''.<ref name=leduc> | |||
| However there are many who prefer the original name on account of the fact that it is a good description of a species that does indeed kill many animals (just not humans). These supporters of the original name point out that the naming heritage is not limited to Spanish sailors. Indeed the scientific name itself is ] for "a whale that brings death". To the Haida tribes of British Columbia the animal was called ''skana'' or "killing demon". The Aleuts of Alaska call it ''polossatik'' or "the feared one". Japanese call them ''Shachi'', believed to come from ancient words meaning "a fish that helps fishermen by herding fish, bringing good catch". | |||
| {{cite journal |doi= 10.1111/j.1748-7692.1999.tb00833.x|last1=LeDuc |first1=R. G. |last2=Perrin |first2=W. F. |last3=Dizon |first3=A. E. |year=1999 |title= Phylogenetic relationships among the delphinid cetaceans based on full cytochrome b sequences | |||
| |journal= Marine Mammal Science |volume=15 |pages=619–648 |issue=3|bibcode=1999MMamS..15..619L |issn = 0824-0469}}</ref> However, a more recent (2018) study places the orca as a ] to the Lissodelphininae, a ] that includes '']'' and '']''.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Horreo|first1= Jose L.|year=2018|title=New insights into the phylogenetic relationships among the oceanic dolphins (Cetacea: Delphinidae)|journal=Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research|volume=57|issue=2|pages=476–480|doi=10.1111/jzs.12255|s2cid=91933816|doi-access=free}}</ref> In contrast, a 2019 phylogenetic study found the orca to be the second most ] member of the Delphinidae, with only the ] (''Leucopleurus acutus'') being more basal.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=McGowen|first1=Michael R.|last2=Tsagkogeorga|first2=Georgia|last3=Álvarez-Carretero|first3=Sandra|last4=dos Reis|first4=Mario|last5=Struebig|first5=Monika|last6=Deaville|first6=Robert|last7=Jepson|first7=Paul D.|last8=Jarman|first8=Simon|last9=Polanowski|first9=Andrea|last10=Morin|first10=Phillip A.|last11=Rossiter|first11=Stephen J.|date=2019-10-21|title=Phylogenomic Resolution of the Cetacean Tree of Life Using Target Sequence Capture|url=https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syz068|journal=Systematic Biology|volume=69|issue=3|pages=479–501|doi=10.1093/sysbio/syz068|issn=1063-5157|pmc=7164366|pmid=31633766}}</ref> | |||
| ===Types=== | |||
| Finally, another name is '''''Grampus'''''. This is now seldom-used. | |||
| <!-- Please do not add any more examples to this section. This subject already has its own article --> | |||
| {{further information|Orca types and populations}} | |||
| The three to five types of orcas may be distinct enough to be considered different ],<ref name=baird>{{harv|Baird|2002}}. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111108150031/http://courses.washington.edu/mb351/readings/baird.pdf |date=November 8, 2011 }}. Contract report to the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada. Also published as {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100714010207/http://www.cascadiaresearch.org/robin/kwstatus2001.pdf |date=July 14, 2010 }} ''The Canadian Field-Naturalist'' '''115''' (4) (2001), 676–701. Retrieved January 26, 2010.</ref> ], or possibly even ]<ref name="Pitman2003">{{cite journal |last1=Pitman|first1= Robert L. |last2=Ensor|first2= Paul |year=2003 |url=http://swfsc.noaa.gov/uploadedFiles/Divisions/PRD/Programs/Ecology/PitmanandEnsor2003JCRM.pdf |title=Three forms of killer whales (''Orcinus orca'') in Antarctic waters |journal=Journal of Cetacean Research and Management |volume=5 |issue=2 |pages=131–139 |doi= 10.47536/jcrm.v5i2.813 |s2cid= 52257732 |access-date=January 9, 2010 |archive-date=April 27, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200427185038/https://swfsc.noaa.gov/uploadedFiles/Divisions/PRD/Programs/Ecology/PitmanandEnsor2003JCRM.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> (see ]). The ] reported in 2008, "The ] of this genus is clearly in need of review, and it is likely that ''O. orca'' will be split into a number of different species or at least subspecies over the next few years."<ref name="iucn status 19 November 2021" /> Although large variation in the ecological distinctiveness of different orca groups complicate simple differentiation into types,<ref name="de bruyn et al. 2013">{{Cite journal |last1=De Bruyn |first1=P. J. N. |last2=Tosh |first2=C. A. |last3=Terauds |first3=A. |doi=10.1111/j.1469-185X.2012.00239.x |title=Killer whale ecotypes: Is there a global model? |journal=] |volume=88 |issue=1 |pages=62–80 |year=2013 |pmid=22882545 |hdl=2263/21531|s2cid=6336624 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> research off the west coast of North America has identified fish-eating "residents", mammal-eating "transients" and "offshores".{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|Balcomb|2000|pp=16–21}} Other populations have not been as well studied, although specialized fish and mammal eating orcas have been distinguished elsewhere.<ref name="Jefferson et al. 1991">{{cite journal |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2907.1991.tb00291.x |last1=Jefferson |first1=T. A. |last2=Stacey |first2=P. J. |last3=Baird |first3=R. W. |year=1991 |url=http://swfsc.noaa.gov/uploadedFiles/Divisions/PRD/Publications/Jeffersonetal.1991(8).pdf |title=A review of killer whale interactions with other marine mammals: predation to co-existence |journal=] |volume=21 |pages=151–180 |issue=4 |access-date=February 23, 2010 |archive-date=July 22, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110722004728/http://swfsc.noaa.gov/uploadedFiles/Divisions/PRD/Publications/Jeffersonetal.1991(8).pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> Mammal-eating orcas in different regions were long thought likely to be closely related, but genetic testing has refuted this hypothesis.<ref name=Schrope>{{cite journal |title=Food chains: Killer in the kelp |journal=Nature |author=Schrope|first1= Mark |volume=445 |pages=703–705 |year=2007 |doi=10.1038/445703a |pmid=17301765 |issue=7129 |bibcode=2007Natur.445..703S |s2cid=4421362 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |author1=Josh D. McInnes |author2=Andrew W. Trites |author3=Chelsea R. Mathieson |author4=Marilyn E. Dahlheim |author5=Jeffrey E. Moore |author6=Paula A. Olson |author7=Kevin M. Lester |title=Evidence for an Oceanic Population of Killer Whales (Orcinus orca) in Offshore Waters of California and Oregon |url=https://www.aquaticmammalsjournal.org/article/evidence-for-an-oceanic-population-of-killer-whales-orcinus-orca-in-offshore-waters-of-california-and-oregon/ |journal=Aquatic Mammals |date=2024 |access-date=2024-03-22| volume= 50| issue= 2 }|pages= 93–106|language=en-US |doi=10.1578/am.50.2.2024.93}}</ref> | |||
| A 2024 study supported the elevation of Eastern North American resident and transient orcas as distinct species, ''O. ater'' and ''O. rectipinnus'' respectively.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Morin|first1=P. A.|last2=McCarthy|first2=M. L.|last3=Fung|first3=C. W.|last4=Durban|first4=J. W.|last5=Parsons|first5=K. M.|last6=Perrin|first6=W. F.|last7=Taylor|first7=B. L.|last8=Jefferson|first8=T. A.|last9=Archer|first9=F. I.|year=2024|title=Revised taxonomy of eastern North Pacific killer whales (Orcinus orca): Bigg's and resident ecotypes deserve species status|journal=Royal Society Open Science|volume=11|issue=3|doi=10.1098/rsos.231368|pmid=38545612 |pmc=10966402|bibcode=2024RSOS...1131368M }}</ref> The ] declined to recognize the two species, citing uncertainty as to whether the types constituted unique species or subspecies. "Pending a more complete global review and revision", the Society provisionally recognized them as subspecies ''Orcinus orca ater'' and ''O. o. rectipinnus'', with ''O. o. orca'' as the ].<ref name="SMM">{{cite web |title=List of Marine Mammal Species and Subspecies |url=https://marinemammalscience.org/science-and-publications/list-marine-mammal-species-subspecies/ |website=MarineMammalScience.org |publisher=] |date=June 2024}}</ref> | |||
| ==Taxonomy and evolution== | |||
| Four types have been documented in the ], Types A–D. Two dwarf species, named '']'' and '']'', were described during the 1980s by Soviet researchers, but most cetacean researchers are skeptical about their status.<ref name="Pitman2003"/> Complete ] indicates the two Antarctic groups (types B and C) should be recognized as distinct species, as should the North Pacific transients, leaving the others as subspecies pending additional data.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Complete mitochondrial genome phylogeographic analysis of killer whales (''Orcinus orca'') indicates multiple species |first1=Phillip A. |last1= Morin |first2=Frederick |last2= Archer |first3=Andrew D. |last3= Foote |first4=Julia |last4= Vilstrup |first5=Eric E. |last5= Allen |first6=Paul |last6= Wade |first7=John |last7= Durban |first8=Kim |last8= Parsons |first9=Robert |last9= Pitman|journal=Genome Research | doi=10.1101/gr.102954.109 |pmid=20413674 |volume=20 |pages=908–916 |year=2010 |issue=7 |pmc=2892092}}</ref> A 2019 study of Type D orcas also found them to be distinct from other populations and possibly even a unique species.<ref name="Pitman et al. 2010">{{cite journal |last1=Pitman |first1=Robert L. |last2=Durban |first2=John W. |last3=Greenfelder |first3=Michael |last4=Guinet |first4=Christophe |last5=Jorgensen |first5=Morton |last6=Olson |first6=Paula A. |last7=Plana |first7=Jordi |last8=Tixier |first8=Paul |last9=Towers |first9=Jared R. |title=Observations of a distinctive morphotype of killer whale (''Orcinus orca''), type D, from subantarctic waters |journal=Polar Biology |date=August 7, 2010 |volume=34 |issue=2 |pages=303–306 |doi=10.1007/s00300-010-0871-3 |s2cid=20734772 }}</ref> | |||
| The Orca is the sole species in the genus ''Orcinus''. It is one of thirty-five species in the dolphin family. Like the ] genus ''Physeter'', ''Orcinus'' is a genus with a single, abundant species with no immediate relatives from a cladistic point of view, thus palaeontologists believe that the Orca is a prime candidate to have an anagenetic evolutionary history - that is the evolution of ancestral to descendent species without splitting of the lineage. If true, this would make the Orca one of the oldest dolphin species, although it is unlikely to be as old the family itself - which is known to date back at least five million years. | |||
| ==Characteristics== | |||
| ==Physical characteristics== | |||
| ] | |||
| Orcas are the largest extant members of the dolphin family. Males typically range from {{cvt|6|to|8|m}} long and weigh in excess of {{cvt|6|t}}. Females are smaller, generally ranging from {{cvt|5|to|7|m}} and weighing about {{cvt|3|to|4|t}}.{{sfn|Baird|2002|p=129}} Orcas may attain larger sizes as males have been recorded at {{cvt|9.8|m}} and females at {{cvt|8.5|m}}.<ref name="Heyning1988"/> Large males can reach a weight of over {{cvt|10|t}}.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Webber |first1=Marc A. |last2=Jefferson |first2=Thomas Allen |last3=Pitman |first3=Robert L. |title=Marine Mammals of the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Identification |date=28 July 2015 |publisher=Academic Press |isbn=978-0-12-409592-2 |page=189 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=sc-cBAAAQBAJ |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Anderson |first1=Robert |last2=Waayers |first2=Robyn |last3=Knight |first3=Andrew |title=Orca Behavior and Subsequent Aggression Associated with Oceanarium Confinement |journal=Animals |date=August 2016 |volume=6 |issue=8 |pages=49 |doi=10.3390/ani6080049 |doi-access=free |pmid=27548232 |pmc=4997274 |language=en |issn=2076-2615}}</ref> Calves at birth weigh about {{cvt|180|kg}} and are about {{cvt|2.4|m}} long.<ref>{{cite magazine|last=Olsen|first=Ken|date=2006|magazine=National Wildlife|volume=44|issue=6|pages= 22–30|title=Orcas on the edge|issn=0028-0402}}</ref><ref>{{cite magazine|last=Stewart|first=Doug|date=2001|magazine=National Wildlife|volume=39 |issue=1|pages=54–59|title=Tales of two orcas|issn=0028-0402}}</ref> The skeleton of the orca is typical for an oceanic dolphin, but more robust.<ref name="Heyning1988">{{cite journal | last1 = Heyning | first1 = J. E. | last2 = Dahlheim | first2 = M. E. | year = 1988 | title = ''Orcinus orca'' | url = http://www.science.smith.edu/msi/pdf/i0076-3519-304-01-0001.pdf | journal = Mammalian Species | issue = 304 | pages = 1–9 | doi = 10.2307/3504225 | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120118134712/http://www.science.smith.edu/msi/pdf/i0076-3519-304-01-0001.pdf | archive-date = January 18, 2012 | df = mdy-all | jstor = 3504225 | s2cid = 253914153 }}</ref> | |||
| With their distinctive pigmentation,<ref name="Heyning1988"/> adult orcas are seldom confused with any other species.{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|p=20}} When seen from a distance, juveniles can be confused with ]s or ]s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://wildwhales.org/other-species/ |title=Wild Whales|publisher=Vancouver Aquarium |access-date=March 23, 2012|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120405040406/http://wildwhales.org/other-species/|archive-date=April 5, 2012}}</ref> The orca is mostly black but with sharply bordered white areas. The entire lower jaw is white and from here, the colouration stretches across the underside to the genital area; narrowing and expanding some, and extending into lateral flank patches close to the end. The tail fluke (fin) is also white on the underside, while the eyes have white oval-shaped patches behind and above them, and a grey or white "saddle patch" exists behind the dorsal fin and across the back.<ref name="Heyning1988"/><ref name=Perrin2/> Males and females also have different patterns of black and white skin in their genital areas.{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|Balcomb|2000|p=45}} In newborns, the white areas are yellow or orange coloured.<ref name="Heyning1988"/><ref name=Perrin2>{{cite book|editor-first1=William F.|editor-last1=Perrin|editor-first2=Bernd |editor-last2= Wursig|editor-first3=J. G. M. 'Hans' |editor-last3=Thewissen|title=Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals|year=2009|publisher=Academic Press|isbn=978-0-08-091993-5|last=Ford|first=John K. B. |contribution=Killer Whale|pages=550–556}}</ref> Antarctic orcas may have pale grey to nearly white backs.{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|p=20}} Some Antarctic orcas are brown and yellow due to ] in the water.<ref name="Pitman2003"/> Both ] and ] orcas have been documented.<ref name="Heyning1988"/> | |||
| The animals are distinctively marked, with a black back, white chest and sides and a white patch above and behind the eye. They have a heavy and stocky body and a large ]. Males can be up to 9.5 metres long (a little over 31 feet) and weigh in excess of 6 tons; females are smaller, reaching 8.5 metres (about 28 feet) at most and a weight of about 5 tons. Calves at birth weight about 180 kg and are about 2.4 metres long (about 8 feet). At about 1.8m (about 6 feet), the dorsal fin of the male is taller than the female's, and more upright. | |||
| ] | |||
| Large male Orca are very distinctive and are unlikely to be confused with any other sea creature. In temperate waters females and juveniles could be confused with various other species, such as the ] or ], when seen from a distance. | |||
| Orca ]s are large and rounded, resembling paddles, with those of males significantly larger than those of females. ]s also exhibit ], with those of males about {{cvt|1.8|m}} high, more than twice the size of the female's, with the male's fin more like an elongated ], whereas the female's is more curved.<ref>. American Cetacean Society. Retrieved January 2, 2009</ref> In the skull, adult males have longer lower jaws than females, as well as larger ]s.{{sfn|Heptner|Nasimovich|Bannikov|Hoffmann|1996|p=681}} The snout is blunt and lacks the beak of other species.<ref name="Heyning1988"/> The orca's teeth are very strong, and its jaws exert a powerful grip; the upper teeth fall into the gaps between the lower teeth when the mouth is closed. The firm middle and back teeth hold prey in place, while the front teeth are inclined slightly forward and outward to protect them from powerful jerking movements.{{sfn|Heptner|Nasimovich|Bannikov|Hoffmann|1996|p=683}} | |||
| Orcas have good eyesight above and below the water, excellent hearing, and a good sense of touch. They have exceptionally sophisticated ] abilities, detecting the location and characteristics of prey and other objects in the water by emitting clicks and listening for echoes,{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|pp=30–32}} as do other members of the dolphin family. The mean body temperature of the orca is {{cvt|36|to|38|C}}.<ref name="seaworld1">{{cite web|url=http://www.seaworld.org/animal-info/info-books/killer-whale/adaptations.htm |title=Killer Whales — Adaptations for an Aquatic Environment |publisher=Seaworld.org |access-date=September 14, 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130904021401/http://www.seaworld.org/animal-info/info-books/killer-whale/adaptations.htm |archive-date=September 4, 2013 }}</ref><ref>N. W. Kasting, S. A. L. Adderly, T. Safford, K. G. Hewlett (1989). "Thermoregulation in Beluga (''Delphinapterus luecas'') and Killer (''Orcinus orca'') Whales"</ref> Like most marine mammals, orcas have a layer of insulating ] ranging from {{cvt|7.6|to|10|cm}} thick beneath the skin.<ref name="seaworld1"/> The pulse is about 60 heartbeats per minute when the orca is at the surface, dropping to 30 beats/min when submerged.<ref name="Spencer, Gornall & Poulter (1967)">{{cite journal |last1=Spencer |first1=M. P. |last2=((Gornall 3rd)) |first2=T. A. |last3=Poulter |first3=T. C. |date=1967 |title=Respiratory and cardiac activity of killer whales |journal=Journal of Applied Physiology |volume=22 |issue=5 |pages=974–981 |doi=10.1152/jappl.1967.22.5.974|pmid=6025756 }}</ref> | |||
| Most life history data about Orca has been obtained from long-term surveys of the population off the coast off ] and ] and by monitoring captive whales. The completeness of the study and highly structured nature of the pods in this population mean that the information is detailed and accurate, however, transient groups and groups in other oceans may have slightly different characteristics. Females become mature at around 15 years of age. From then they periods of ] cycling with non-cycling periods of between three and sixteen months. The gestation period varies from fifteen to eighteen months. Mothers calve about once every five years. In analysed resident pods, birth occurs at any time of year, with the most popular months being those in winter. New-born mortality is very high - one survey suggested that nearly half of all calves fail to reach the age of six months. Calves nurse for up to two years, but will start to take solid food at about twelve months. Mothers breed until the age of 40, meaning that on average they raise five children. Typically females live to the age of fifty, but may survive well into their eighties or nineties in exceptional cases. Males become sexually active at the age of 15, and live to about 30 on average, and to 50 in exceptional cases. | |||
| An individual orca can often be identified from its dorsal fin and saddle patch. Variations such as nicks, scratches, and tears on the dorsal fin and the pattern of white or grey in the saddle patch are unique. Published directories contain identifying photographs and names for hundreds of North Pacific animals. Photographic identification has enabled the local population of orcas to be counted each year rather than estimated, and has enabled great insight into life cycles and social structures.{{sfn|Obee|Ellis|1992|pp=1–27}} | |||
| ==Range and distribution== | |||
| ==Range and habitat== | |||
| The Orca is the second-most widely distributed mammal in the world, after the human. They are found in all oceans and most seas including, unusually for cetaceans, the ] and ]s. However cooler temperate and ] are preferred. Although sometimes spotted in deep water, coastal areas are generally preferred to pelagic environments. | |||
| <!-- Please do not add any more examples to this section. This subject already has its own article --> | |||
| {{further information|Orca types and populations}} | |||
| ]|alt=A killer whale bursts forward out of the water. Its head is just starting to point downward, and is about a body width above the surface.]] | |||
| Orcas are found in all oceans and most seas. Due to their ], numbers, and density, relative distribution is difficult to estimate,<ref name=Forney2007>{{Cite book |last1=Forney |first1=K. A. |last2=Wade |first2=P. |year=2007 |chapter=Worldwide distribution and abundance of killer whales |chapter-url=http://swfsc.noaa.gov/publications/FED/00851.pdf |title=Whales, whaling and ocean ecosystems |editor1-last=Estes |editor1-first=James A. |editor2-last=DeMaster |editor2-first=Douglas P. |editor3-last=Doak |editor3-first=Daniel F. |editor4-last=Williams |editor4-first=Terrie M. |editor-last5=Brownell |editor5-first=Robert L. Jr. |publisher=University of California Press |place=Berkeley |pages=145–162 |isbn=978-0-520-24884-7 |access-date=February 25, 2014 |archive-date=August 7, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200807161432/https://swfsc.noaa.gov/publications/FED/00851.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> but they clearly prefer higher latitudes and coastal areas over ] environments.{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|p=21}} Areas which serve as major study sites for the species include the coasts of ], Norway, the ] of Argentina, the ], New Zealand and parts of the west coast of North America, from ] to ].{{sfn|Baird|2002|p=128}} Systematic surveys indicate the highest densities of orcas (>0.40 individuals per 100 km<sup>2</sup>) in the northeast Atlantic around the ] coast, in the north Pacific along the ], the ] and in the ] off much of the coast of ]. They are considered "common" (0.20–0.40 individuals per 100 km<sup>2</sup>) in the eastern Pacific along the coasts of ], ] and ], in the North Atlantic Ocean around ] and the ].<ref name=Forney2007/> | |||
| ] | |||
| In the Antarctic, orcas range up to the edge of the ] and are believed to venture into the denser pack ice, finding open ] much like ] whales in the Arctic. However, orcas are merely seasonal visitors to Arctic waters, and do not approach the pack ice in the summer. With the rapid ] decline in the ], their range now extends deep into the northwest Atlantic.<ref>{{cite news|last=Kwan|first= Jennifer|url=http://uk.reuters.com/article/dcbrights-killerwhales-dc-idUKN1922990620070119|title= Canada Finds Killer Whales Drawn to Warmer Arctic|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170817162253/http://uk.reuters.com/article/dcbrights-killerwhales-dc-idUKN1922990620070119 |archive-date=August 17, 2017 |publisher= Reuters|date= January 22, 2007}}</ref> Occasionally, orcas swim into freshwater rivers. They have been documented {{convert|100|mi|km|abbr=on}} up the ] in the United States.{{sfn|Baird|2002|p=10}}<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nwfsc.noaa.gov/research/divisions/cb/ecosystem/marinemammal/kwnewsletter/documents/email10.28.03ltrkillerwhalesnewsletter1.pdf |title=Southern Resident Killer Whale Research |orig-date=October 2003 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140306171050/http://www.nwfsc.noaa.gov/research/divisions/cb/ecosystem/marinemammal/kwnewsletter/documents/email10.28.03ltrkillerwhalesnewsletter1.pdf |archive-date=March 6, 2014 |publisher=Northwest Fisheries Science Center |date=February 14, 2007 |access-date=January 26, 2010}}</ref> They have also been found in the ] in Canada and the ] in Japan.{{sfn|Baird|2002|p=10}} | |||
| Migration patterns are poorly understood. Each summer, the same individuals appear off the coasts of British Columbia and Washington. Despite decades of research, where these animals go for the rest of the year remains unknown. Transient pods have been sighted from southern Alaska to central California.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|pp=24–29}} | |||
| The Orca is particularly highly concentrated in the North-east Pacific basin where ] curves into ], off the coast of ] and off the coast of northern ]. They are regularly sighted in Antarctic waters right up to the ice-pack, and indeed are believed to venture under the pack and survive breathing in air pockets like the ]. In the Arctic however the species is rarely seen in winter as it does not approach the ice pack. It does visit these waters during summer. | |||
| ===Population=== | |||
| Information for off-shore regions and tropical waters is more scarce but widespread, if not frequent, sightings indicate that the Orca can survive in most water temperatures. No estimate for the total worldwide population exists. Local estimates include 70–80,000 in the Antarctic, 8,000 in the tropical Pacific (although tropical waters are not the Orca's preferred environment, the sheer size of this area — 19 million square kilometres — means there are thousands of whales), up to 2,000 off Japan, 1,500 off the cooler north-east Pacific and 500 off Norway. Adding very rough estimates for unsurveyed areas the total population could be around 100,000. | |||
| Worldwide population estimates are uncertain, but recent consensus suggests a minimum of 50,000 (2006).{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|2006}}<ref name="iucn status 19 November 2021" /><ref name=noaa>{{cite web |title=Killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') |website=NOAA Fisheries |publisher=Office of Protected Resources, ] |url=http://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/pr/species/mammals/whales/killer-whale.html |access-date=August 15, 2017 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170709160557/http://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/pr/species/mammals/whales/killer-whale.html |archive-date=July 9, 2017 }}</ref> Local estimates include roughly 25,000 in the Antarctic, 8,500 in the tropical Pacific, 2,250–2,700 off the cooler northeast Pacific and 500–1,500 off Norway.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=46}} Japan's Fisheries Agency estimated in the 2000s that 2,321 orcas were in the seas around Japan.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090822013642/http://sha-chi.jp/en/contents/japanorca_01e.htm |date=August 22, 2009 }}, sha-chi.jp. Retrieved February 17, 2010</ref><ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140301122413/http://ika-net.jp/en/our-actions/coastal-small-cetacean-conservation/215-ten-years-after-taiji-orca-capture |date=March 1, 2014 }}, January 28, 2007. Iruka (dolphin) and Kujira (whale) Action Network (IKAN): Iruma, Saitama Prefecture, Japan. Retrieved February 17, 2010</ref> | |||
| ==Feeding== | |||
| ==Social behaviour== | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | direction = vertical | |||
| | width = | |||
| | image1 = Orcinus orca (Vestfjord).jpg | |||
| | caption1 = Tail-slapping in ], Norway | |||
| | image2 = Killer Whale chasing Chinook.jpg | |||
| | caption2 = Resident orca pursuing a chinook salmon | |||
| }} | |||
| Orcas are ]s, meaning that they themselves have no natural predators. They are sometimes called "wolves of the sea", because they hunt in groups like wolf packs.<ref name=marinebio>{{cite web|url=http://marinebio.org/species.asp?id=84|title=''Orcinus orca'' – Orca (Killer Whale)|access-date=June 26, 2007|publisher=Marinebio.org|archive-date=July 13, 2012|archive-url=https://archive.today/20120713081944/http://marinebio.org/species.asp?id=84|url-status=deviated}}</ref> Orcas hunt varied prey including fish, ]s, mammals, ]s, and ].{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=17}} Different populations or ecotypes may specialize, and some can have a dramatic impact on prey species.<ref>{{cite journal|author= Morell|first1= Virginia |title= Killer Whales Earn Their Name |journal=Science|pages= 274–276 |volume= 331 |year= 2011|doi= 10.1126/science.331.6015.274|pmid= 21252323|issue= 6015|bibcode= 2011Sci...331..274M }}</ref> However, whales in tropical areas appear to have more generalized diets due to lower food productivity.<ref name="Baird2006">{{cite journal|author=Baird|first1= R. W.|display-authors=etal|year=2006|title=Killer whales in Hawaiian waters: information on population identity and feeding habits|journal=Pacific Science|volume=60|issue=4|pages=523–530|doi=10.1353/psc.2006.0024|url=http://www.cascadiaresearch.org/files/Projects/Hawaii/Baird%20et%20al%20Hawaii%20killer%20whales.pdf|hdl=10125/22585|s2cid=16788148|access-date=October 23, 2017|archive-date=October 23, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171023063253/http://www.cascadiaresearch.org/files/Projects/Hawaii/Baird%20et%20al%20Hawaii%20killer%20whales.pdf|url-status=live|hdl-access=free}}</ref><ref name="Wier">{{cite journal|author=Weir|first1= C. R.|last2=Collins|first2= T.|last3=Carvalho|first3= I.|last4=Rosenbaum|first4= H. C.|year=2010|title=Killer whales (''Orcinus orca'') in Angolan and Gulf of Guinea waters, tropical West Africa|journal=Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom|volume=90|issue=8|pages=1601–1611|doi=10.1017/S002531541000072X|bibcode= 2010JMBUK..90.1601W|s2cid=84721171|url=http://www.escolademar.pt/wp-content/uploads/pdf_docs/artigos/Weir_et_al_2010_final.pdf|archive-url=http://arquivo.pt/wayback/20140930081828/http://www.escolademar.pt/wp%2Dcontent/uploads/pdf_docs/artigos/Weir_et_al_2010_final.pdf|url-status=dead|archive-date=September 30, 2014}}</ref> Orcas spend most of their time at shallow depths,<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Miller |first1=Patrick James O'Malley |last2=Shapiro |first2=Ari Daniel |last3=Deecke |first3=Volker Bernt |title=The diving behaviour of mammal-eating killer whales : variations with ecological not physiological factors |journal=Canadian Journal of Zoology |date=November 2010 |volume=88 |issue=11 |pages=1103–1112 |doi=10.1139/Z10-080 |url=http://insight.cumbria.ac.uk/id/eprint/1976/1/Deecke_TheDivingBehaviour.pdf |quote=Overall, the whales spent 50% of their time 8 m or shallower and 90% of their time 40 m or shallower |access-date=August 23, 2020 |archive-date=July 20, 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180720202137/http://insight.cumbria.ac.uk/id/eprint/1976/1/Deecke_TheDivingBehaviour.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> but occasionally dive several hundred metres depending on their prey.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Reisinger |first1=Ryan R. |last2=Keith |first2=Mark |last3=Andrews |first3=Russel D. |last4=de Bruyn |first4=P. J. N. |title=Movement and diving of killer whales (''Orcinus orca'') at a Southern Ocean archipelago |journal=Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology |date=December 2015 |volume=473 |pages=90–102 |doi=10.1016/j.jembe.2015.08.008 |bibcode=2015JEMBE.473...90R |quote=maximum dive depths were 767.5 and 499.5 m |hdl=2263/49986 |url=https://figshare.com/articles/poster/Movement_and_diving_of_killer_whales_Orcinus_orca_at_a_Southern_Ocean_archipelago/3426920 |hdl-access=free |access-date=December 6, 2021 |archive-date=June 30, 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220630074802/https://figshare.com/articles/poster/Movement_and_diving_of_killer_whales_Orcinus_orca_at_a_Southern_Ocean_archipelago/3426920 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Towers |first1=Jared R |last2=Tixier |first2=Paul |last3=Ross |first3=Katherine A |last4=Bennett |first4=John |last5=Arnould |first5=John P Y |last6=Pitman |first6=Robert L |last7=Durban |first7=John W |last8=Northridge |first8=Simon |title=Movements and dive behaviour of a toothfish-depredating killer and sperm whale |journal=ICES Journal of Marine Science |date=January 2019 |volume=76 |issue=1 |pages=298–311 |doi=10.1093/icesjms/fsy118 |s2cid=91256980 |quote=The killer whale dove >750 m on five occasions while depredating (maximum: 1087 m), but these deep dives were always followed by long periods (3.9–4.6 h) of shallow (<100 m) diving.|doi-access=free |hdl=10536/DRO/DU:30120094 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Fish=== | |||
| Orca have a complex system of social grouping. The most basic unit is the matriline. A matriline consists of a single female Orca (the matriarch) and her descendants. The sons and daughters of the matriarch form part of the line as do the sons and daughters of those daughters (the sons and daughters of the sons join the matriline of their mates) and so on down the family tree. Because females can live for up to ninety years, it is not uncommon for four or even five generations of whale living in the same line. These matrilineal groups are highly stable over many years. Individuals will only split off from their matrilineal group for a few hours at a time at most in order to mate or forage. No permanent "casting out" of an individual from a matriline has ever been recorded. The average matriline size as recorded in north-east Pacific waters is nine animals. | |||
| Fish-eating orcas prey on around 30 species of fish. Some populations in the ] and ] sea specialize in ] and follow that fish's autumnal migration to the Norwegian coast. ] account for 96% of northeast Pacific residents' diet, including 65% of large, fatty ].{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=18}} ] are also eaten, but smaller ] and ] are not a significant food item. Depletion of specific prey species in an area is, therefore, cause for concern for local populations, despite the high diversity of prey.{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|2006}} On average, an orca eats {{convert|227|kg|lb}} each day.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/facts/orca |title=National Geographic creature feature|last1=Hughes |first1=Catherine D.|date=March 2014 |access-date=July 25, 2007<!--valid url/arch confirm :11 23 June 2023 Dave-->|archive-date=June 2, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230602193556/https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/facts/orca |url-status=live }}</ref> While salmon are usually hunted by an individual whale or a small group, herring are often caught using ]: the orcas force the herring into a tight ball by releasing bursts of bubbles or flashing their white undersides. They then slap the ball with their tail flukes, stunning or killing up to 15 fish at a time, then eating them one by one. Carousel feeding has been documented only in the Norwegian orca population, as well as some oceanic dolphin species.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Similä|first1= T. |last2=Ugarte|first2= F. |year=1993 |title=Surface and underwater observations of cooperatively feeding killer whales in Northern Norway |journal=Canadian Journal of Zoology |volume=71 |pages=1494–1499 |doi=10.1139/z93-210 |issue=8|bibcode= 1993CaJZ...71.1494S }}</ref> | |||
| In New Zealand, ]s and ] appear to be important prey, including ]s, ] and ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ], and ]s.<ref name=orcashark>{{cite journal|author=Visser|first1= Ingrid N.|year=2005|title=First Observations of Feeding on Thresher (''Alopias vulpinus'') and Hammerhead (''Sphyrna zygaena'') Sharks by Killer Whales (''Orcinus orca'') Specialising on Elasmobranch Prey|journal=Aquatic Mammals|volume=31|issue=1|pages=83–88|doi=10.1578/AM.31.1.2005.83}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Visser|first1= Ingrid N. |first2=Jo|last2= Berghan |last3= van Meurs|first3= Rinie|first4=Dagmar |last4=Fertl |year=2000 |title=Killer Whale (''Orcinus orca'') Predation on a Shortfin Mako Shark (''Isurus oxyrinchus'') in New Zealand Waters |journal=Aquatic Mammals |volume=26 |issue=3 |pages=229–231 |url=http://aquaticmammalsjournal.org/share/AquaticMammalsIssueArchives/2000/AquaticMammals_26-03/26-03_Berghan.pdf |access-date=May 3, 2014 |archive-date=January 26, 2012 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20120126035026/http://aquaticmammalsjournal.org/share/AquaticMammalsIssueArchives/2000/AquaticMammals_26-03/26-03_Berghan.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> With sharks, orcas may herd them to the surface and strike them with their tail flukes,<ref name=orcashark/> while bottom-dwelling rays are cornered, pinned to the ground and taken to the surface.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Visser|first1= Ingrid N.|year=1999|title=Benthic foraging on stingrays by killer whales (''Orcinus orca'') in New Zealand waters|journal=Marine Mammal Science|volume=15|issue=1|pages=220–227 |doi=10.1111/j.1748-7692.1999.tb00793.x|bibcode= 1999MMamS..15..220V}}</ref> In other parts of the world, orcas have preyed on ]s,<ref name=Engelbrecht/> ]s,<ref>{{cite web |last1=O'Sullivan |first1=J. B. |title=A fatal attack on a whale shark ''Rhincodon typus'', by killer whales ''Orcinus orca'' off Bahia de Los Angeles, Baja California |year=2000 |url=http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fish/meetings/abst2000c.htm |work=American Elasmobranch Society 16th Annual Meeting, June 14–20, 2000 |location=La Paz, B.C.S., México |access-date=February 18, 2010 |archive-date=February 28, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100228204745/http://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/fish/meetings/abst2000c.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Pancaldi |first1=Francesca |last2=Ayres |first2=Kathryn A. |last3=Gallagher |first3=Austin J. |last4=Moskito |first4=James |last5=Williamson |first5=Kelsey C. |last6=Higuera Rivas |first6=Jesús Erick |date=2024-11-29 |title=Killer whales (Orcinus orca) hunt, kill and consume the largest fish on Earth, the whale shark (Rhincodon typus) |journal=Frontiers in Marine Science |language=English |volume=11 |doi=10.3389/fmars.2024.1448254 |doi-access=free |issn=2296-7745}}</ref> and even ]s.<ref name=Engelbrecht>{{cite journal|last1=Engelbrecht|first1=T. M.|last2=Kock|first2= A. A.|last3=O'Riain|first3= M. J.|year=2019|title=Running scared: when predators become prey|journal=Ecosphere |volume=10|issue=1|page=e02531 |doi=10.1002/ecs2.2531|doi-access=free|bibcode=2019Ecosp..10E2531E }}</ref><ref name=Pyle>{{cite journal |last1=Pyle |first1=Peter |last2=Schramm|first2= Mary Jane |last3=Keiper|first3= Carol |last4=Anderson|first4= Scot D. |title=Predation on a white shark (''Carcharodon carcharias'') by a killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') and a possible case of competitive displacement |journal=] |year=1999 |url=http://www.prbo.org/cms/docs/marine/MMS.pdf |volume=15 |issue=2 |pages=563–568 |doi=10.1111/j.1748-7692.1999.tb00822.x |bibcode=1999MMamS..15..563P |access-date=April 28, 2014 |archive-date=March 22, 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120322070431/http://www.prbo.org/cms/docs/marine/MMS.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> Competition between orcas and white sharks is probable in regions where their diets overlap.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Heithaus |first=Michael |title=Predator–prey and competitive interactions between sharks (order Selachii) and dolphins (suborder Odontoceti): a review |journal=Journal of Zoology |volume=253 |issue=1 |pages=53–68 |year=2001 |url=http://www.science.fau.edu/sharklab/courses/elasmobiology/readings/heithaus.pdf |doi=10.1017/S0952836901000061 |citeseerx=10.1.1.404.130 |access-date=January 18, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160115113304/http://www.science.fau.edu/sharklab/courses/elasmobiology/readings/heithaus.pdf |archive-date=January 15, 2016 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The arrival of orcas in an area can cause white sharks to flee and forage elsewhere.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Jorgensen|first1= S. J.|display-authors=etal|year=2019 |title=Killer whales redistribute white shark foraging pressure on seals|journal=Scientific Reports|volume=9|issue=1|page=6153 |doi=10.1038/s41598-019-39356-2 |pmid=30992478|pmc=6467992|bibcode=2019NatSR...9.6153J}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Towner |first1=AV |last2=Watson |first2=RGA |last3=Kock |first3=AA |last4=Papastamatiou |first4=Y |last5=Sturup |first5=M |last6=Gennari |first6=E |last7=Baker |first7=K |last8=Booth |first8=T |last9=Dicken |first9=M |last10=Chivell |first10=W |last11=Elwen |first11=S |date=2022-04-03 |title=Fear at the top: killer whale predation drives white shark absence at South Africa's largest aggregation site |url=https://doi.org/10.2989/1814232X.2022.2066723 |journal=African Journal of Marine Science |volume=44 |issue=2 |pages=139–152 |doi=10.2989/1814232X.2022.2066723 |bibcode=2022AfJMS..44..139T |s2cid=250118179 |issn=1814-232X}}</ref> Orcas appear to target the liver of sharks.<ref name=Engelbrecht/><ref name=Pyle/> In one case a single orca was observed killing and eating a great white shark on its own.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Towner |first1=A |last2=Micarelli |first2=P |last3=Hurwitz |first3=D |last4=Smale |first4=Mj |last5=Booth |first5=Aj |last6=Stopforth |first6=C |last7=Jacobs |first7=E |last8=Reinero |first8=Fr |last9=Ricci |first9=V |last10=Di Bari |first10=A |last11=Gavazzi |first11=S |last12=Carugno |first12=G |last13=Mahrer |first13=M |last14=Gennari |first14=E |date=2024 |title=Further insights into killer whales Orcinus orca preying on white sharks Carcharodon carcharias in South Africa |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.2989/1814232X.2024.2311272 |journal=African Journal of Marine Science |volume=46 |issue=1 |language=en |pages=1–5 |doi=10.2989/1814232X.2024.2311272 |bibcode=2024AfJMS..46....1T |issn=1814-232X}}</ref> | |||
| Matrilines tend to congregate with a small number of other matrilines to form a ''pod'', consisting on average of about 18 animals. Members of a pod all have the same dialect (see the song section below) and consist of closely related matriline fragments. Unlikely matrilines, pods will split apart for days or weeks at a time in order to carry out foraging before joining back together. The average pod size is 18 animals. The largest recorded pod is 49 animals. | |||
| ===Mammals and birds=== | |||
| The next level of grouping is the ''clan''. A clan consists of those pods which have a similar dialect. Again the relationship between pods appears to be genealogical, consisting of fragments of families with a common heritage on the maternal side. Different clans can occupy the same geographical area and so pods from different clans are often recorded travelling together. When resident pods come together to travel as a clan they greet each other by forming two parallel lines akin to a "face off" before mingling with each other. | |||
| Orcas are sophisticated and effective predators of ]s. They are recorded to prey on other cetacean species, usually smaller dolphins and ]s such as ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s and ]s.<ref name=Perrin/><ref name=Perrin2/> While hunting these species, orcas usually have to chase them to exhaustion. For highly social species, orca pods try to separate an individual from its group. Larger groups have a better chance of preventing their prey from escaping, which is killed by being thrown around, rammed and jumped on. Arctic orcas may attack ]s and ]s stuck in pools enclosed by sea ice, the former are also driven into shallower water where juveniles are grabbed.<ref name=Perrin/> By contrast, orcas appear to be wary of ]s, which have been recorded to ] and chase them.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Selbmann, A.|display-authors=etal|year=2022|title=Occurrence of long-finned pilot whales (''Globicephala melas'') and killer whales (''Orcinus orca'') in Icelandic coastal waters and their interspecific interactions|journal=Acta Ethol|volume=25 |issue=3 |pages=141–154 |doi=10.1007/s10211-022-00394-1|pmid=35694552 |pmc=9170559 |s2cid=249487897 }}</ref> Nevertheless, possible predation on ] has been recorded in ], and one study suggests ] are among Caribbean Orcas' prey.<ref>{{cite journal |first= Filipa |last= Samarra |title= Prey of killer whales (Orcinus orca) in Iceland |journal= PLOS ONE |year= 2018 |volume= 13 |issue= 12 |page= 6|doi= 10.1371/journal.pone.0207287|doi-access= free |pmid= 30540762 |pmc= 6291266 |bibcode= 2018PLoSO..1307287S |hdl= 20.500.11815/1095 |hdl-access= free }} </ref><ref>{{cite journal |first= Jeremy |last= Kiszka |title= Feeding Ecology of Elusive Caribbean Killer Whales Inferred From Bayesian Stable Isotope Mixing Models and Whalers' Ecological Knowledge |journal= Frontiers in Marine Science |year= 2021 |volume= 8 |doi= 10.3389/fmars.2021.648421|doi-access= free }}</ref> Killer whales have been recorded attacking short-finned pilot whales in ] as well.<ref>{{cite journal |last= Gonzalez-Pestana |first= Adriana |title= Killer whale (Orcinus Orca) occurrence and interactions with marine mammals off Peru |journal= Pacific Science |year= 2019 |volume=73 |issue= 2 |page= 262-273 |doi= 10.2984/73.2.7}}</ref> | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The final layer of association, perhaps more arbitrary and imposed by humans than the other very natural divisions, is called the ''community'' and is loosely defined as the set of clans that are regularly seen mixing with each other. Communities do not follow a discernible familial or vocal patterns. | |||
| Orcas also prey on larger species such as ]s, ]s, ]s and ].<ref name=Perrin/><ref name=Perrin2/> On three separate occasions in 2019 orcas were recorded to have killed ]s off the south coast of Western Australia, including an estimated {{convert|18|–|22|m|sp=us|adj=on}} individual.<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Totterdell, J. A.|author2=Wellard, R.|author3=Reeves, I. M.|author4=Elsdon, B.|author5=Markovic, P.|author6=Yoshida, M.|author7=Fairchild, A.|author8=Sharp, G.|author9=Pitman, R.|year=2022|title=The first three records of killer whales (''Orcinus orca'') killing and eating blue whales (''Balaenoptera musculus'')|journal=Marine Mammal Science|volume=38 |issue=3 |pages=1286–1301 |doi=10.1111/mms.12906|bibcode=2022MMamS..38.1286T | s2cid=246167673 }}</ref> Large whales require much effort and coordination to kill and orcas often target calves. A hunt begins with a chase followed by a violent attack on the exhausted prey. Large whales often show signs of orca attack via tooth rake marks.<ref name=Perrin/> Pods of female sperm whales sometimes protect themselves by forming a protective circle around their calves with their flukes facing outwards, using them to repel the attackers.<ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.1111/j.1748-7692.2001.tb01000.x|author=Pitman|first1= Robert L.|url=http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/usdeptcommercepub/507/|title=Killer Whale Predation on Sperm Whales: Observations and Implications|journal=Marine Mammal Science|volume=17|issue=3|pages=494–507|year=2001|bibcode=2001MMamS..17..494P |display-authors=etal|access-date=February 25, 2014|archive-date=December 11, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151211133004/http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/usdeptcommercepub/507/|url-status=live}}</ref> There is also evidence that humpback whales will defend against or mob orcas who are attacking either humpback calves or juveniles as well as members of other species.<ref name=mobbing>{{cite journal|title=Humpback whales interfering when mammal-eating killer whales attack other species: Mobbing behavior and interspecific altruism?|journal=Marine Mammal Science | doi=10.1111/mms.12343|volume=33|pages=7–58|year=2016 | last1 = Pitman | first1 = Robert L.|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| ], great whales may have been the major food source for orcas. The introduction of modern whaling techniques may have aided orcas by the sound of ] indicating the availability of prey to scavenge, and compressed air inflation of whale carcasses causing them to float, thus exposing them to scavenging. However, the devastation of great whale populations by unfettered whaling has possibly reduced their availability for orcas, and caused them to expand their consumption of smaller marine mammals, thus contributing to the decline of these as well.<ref name="EMM2009">{{cite book|last=Estes|first=James|editor=Perrin, William F.|others=Wursig, Bernd & Thewissen, J. G. M.|title=Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2rkHQpToi9sC&pg=PA360|date=February 26, 2009|publisher=Academic Press|isbn=978-0-08-091993-5|pages=357–361|chapter=Ecological effects of marine mammals|access-date=December 30, 2015|archive-date=May 9, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160509133131/https://books.google.com/books?id=2rkHQpToi9sC&pg=PA360|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In the northeast Pacific there have been three communities identified: | |||
| :The southern community (1 clan, 3 pods, 83 orca as of 2000) | |||
| :The northern community (3 clans, 16 pods, 214 orca as of 2000) | |||
| :The south Alaskan community (2 clans, 11 pods, 211 orca as of 2000) | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| It should be emphasised that these hierarchies are valid for resident groups only. Transient, mammal-eating groups are generally smaller because, although they too are based on matrilines, males are much more likely to split off to live a solitary life. Transient groups however still have a looser connection defined by their dialect. | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | direction = vertical | |||
| | image1=Orcas in Punta Norte Valdes Peninsula - panoramio.jpg| | |||
| | caption1= Orca beaching to capture sea lion along ] | |||
| | image2=Killer Whales Hunting a Crabeater Seal.jpg | |||
| | caption2=Orcas swimming in close synchronization to create a wave to wash the ] off the floe | |||
| }} | |||
| Other marine mammal prey includes ] species such as ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s, ]s and ]es.<ref name=Perrin>{{cite book|editor-first1=William F.|editor-last1=Perrin|editor-first2=Bernd |editor-last2= Wursig|editor-first3=J. G. M. 'Hans' |editor-last3=Thewissen|title=Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals|year=2009|publisher=Academic Press|isbn=978-0-08-091993-5|last=Weller|first=D. W. |contribution=Predation on marine mammals|pages=927–930}}</ref><ref name=Perrin2/> Often, to avoid injury, orcas disable their prey before killing and eating it. This may involve throwing it in the air, slapping it with their tails, ramming it, or breaching and landing on it.{{sfn|Heimlich|Boran|2001|p=45}} In steeply banked beaches off ], Argentina, and the ], orcas feed on South American sea lions and ]s in shallow water, even ] temporarily to grab prey before wriggling back to the sea. Beaching, usually fatal to cetaceans, is not an instinctive behaviour, and can require years of practice for the young.{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|p=29}} Orcas can then release the animal near juvenile whales, allowing the younger whales to practice the difficult capture technique on the now-weakened prey.{{sfn|Heimlich|Boran|2001|p=45}}{{sfn|Baird|2002|pp=61–62}} In the Antarctic, type B orcas hunt ]s and other prey by "wave-hunting". They ] to locate them on resting on ice floes, and then swim in groups to create waves that wash over the floe. This washes the prey into the water, where other orcas lie in wait.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Pitman|first1=R. L.|last2=Durban|first2=J. W.|year=2011|title=Cooperative hunting behavior, prey selectivity and prey handling by pack ice killer whales (''Orcinus orca''), type B, in Antarctic Peninsula waters|journal=Marine Mammal Science|volume=28|issue=1|pages=16–36|doi=10.1111/j.1748-7692.2010.00453.x|url=http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1305&context=usdeptcommercepub|access-date=July 27, 2023|archive-date=August 2, 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230802073930/https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1305&context=usdeptcommercepub|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Visser |first1=Ingrid N. |last2=Smith |first2=Thomas G. |last3=Bullock |first3=Ian D. |last4=Green |first4=Geoffrey D. |last5=Carlsson |first5=Olle G. L. |last6=Imberti |first6=Santiago |doi=10.1111/j.1748-7692.2007.00163.x |title=Antarctic peninsula killer whales (''Orcinus orca'') hunt seals and a penguin on floating ice |year=2008 |pages=225–234 |volume=24 |journal=Marine Mammal Science |url=http://www.grupofalco.com.ar/pedefes/Visser%20et%20al%202008.%20Antarctic%20killer%20whales%20on%20ice%20-%20Marine%20Mammals%20Science.pdf |issue=1 |bibcode=2008MMamS..24..225V |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110531161550/http://www.grupofalco.com.ar/pedefes/Visser%20et%20al%202008.%20Antarctic%20killer%20whales%20on%20ice%20-%20Marine%20Mammals%20Science.pdf |archive-date=May 31, 2011 }}</ref> | |||
| In the ], a decline in ] populations in the 1990s was controversially attributed by some scientists to orca predation, although with no direct evidence.<ref>Pinell, Nadine, et al. " {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170630063238/http://wildwhales.org/?p=132 |date=June 30, 2017 }}" B.C. Cetacean Sightings Network, June 1, 2004. Retrieved March 13, 2010</ref> The decline of sea otters followed a decline in seal populations,{{efn|According to Baird,{{sfn|Baird|2002|p=23}} killer whales prefer harbour seals to sea lions and porpoises in some areas.}}<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151107004222/http://www2.gi.alaska.edu/ScienceForum/ASF14/1418.html |date=November 7, 2015 }} Ned Rozell, Article #1418, Alaska Science Forum, December 10, 1998. Retrieved February 26, 2010</ref> which in turn may be substitutes for their original prey, now decimated by industrial whaling.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Springer|first1=A. M.|title=Sequential megafaunal collapse in the North Pacific Ocean: An ongoing legacy of industrial whaling?|journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences|volume=100|pages=12223–12228|year=2003|doi=10.1073/pnas.1635156100|issue=21|bibcode=2003PNAS..10012223S|pmid=14526101|pmc=218740|doi-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Demaster|first1=D.|last2=Trites|first2=A.|last3=Clapham|first3=P.|last4=Mizroch|first4=S.|last5=Wade|first5=P. |last6=Small|first6=R.|last7=Hoef|first7=J.|title=The sequential megafaunal collapse hypothesis: Testing with existing data |journal=Progress in Oceanography|year=2006|doi=10.1016/j.pocean.2006.02.007|volume=68|issue=2–4|pages=329–342 |bibcode=2006PrOce..68..329D}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Estes|first1=J. A.|last2=Doak|first2=D. F.|last3=Springer|first3=A. M.|last4=Williams|first4=T. M.|title=Causes and consequences of marine mammal population declines in southwest Alaska: a food-web perspective|journal=Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences|volume=364|pages=1647–1658|year=2009|doi=10.1098/rstb.2008.0231|issue=1524|pmid=19451116|pmc=2685424}}</ref> Orcas have been observed preying on ], such as ] swimming between islands off the northwest coast of North America.{{sfn|Baird|2002|p=23}}<ref name="BairdBaird2006">{{cite book|first1=Robert W.|last1=Baird|first2=Robin W.|last2=Baird|title=Killer Whales of the World: Natural History and Conservation|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Rjksm-5-ap4C&pg=PA23|access-date=February 2, 2011|date=August 31, 2006|publisher=Voyageur Press|isbn=978-0-7603-2654-1|pages=23–|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110721191653/http://books.google.com/books?id=Rjksm-5-ap4C&pg=PA23|archive-date=July 21, 2011|url-status=live}}</ref> Orca ] has also been reported based on analysis of stomach contents, but this is likely to be the result of scavenging remains dumped by whalers.{{sfn|Baird|2002|p=124}} One orca was also attacked by its companions after being shot.<ref name="Jefferson et al. 1991"/> Although resident orcas have never been observed to eat other marine mammals, they occasionally harass and kill porpoises and seals for no apparent reason.{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|Balcomb|2000|p=19}} Some dolphins recognize resident orcas as harmless and remain in the same area.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Chung |first1=Emily |title=Killer whales eat dolphins. So why are these dolphins tempting fate? |url=https://www.cbc.ca/news/science/pacific-white-sided-dolphins-southern-resident-killer-whales-1.5021585 |publisher=] |date=2019-02-18 |access-date=August 7, 2023 |archive-date=August 7, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230807195251/https://www.cbc.ca/news/science/pacific-white-sided-dolphins-southern-resident-killer-whales-1.5021585 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The day-to-day behaviour of Orca is generally divided into four activities - foraging, travelling, resting and socializing. Orca are generally enthusiastic in their socializing, exhibiting a wide range of ], ], tail-slapping and head-stands. All-male groups often interact with erect penises. Whether this is interaction is part of play or a display of dominance is not known. | |||
| Orcas do consume ]s but are more likely to kill and leave them uneaten. ] species recorded as prey in Antarctic and sub-Antarctic waters include ]s, ]s, ]s and ]s.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Pitman|first1=R. L.|last2=Durban|first2=J. W.|year=2010|title=Killer whale predation on penguins in Antarctica|journal=Polar Biology|volume=33|issue=11|pages=1589–1594|doi=10.1007/s00300-010-0853-5|bibcode=2010PoBio..33.1589P |s2cid=44055219 }}</ref> Orcas in many areas may prey on ]s and ]s.{{sfn|Baird|2002|p=14}} A captive orca at ] discovered it could regurgitate fish onto the surface, attracting sea gulls, and then eat the birds. Four others then learned to copy the behaviour.<ref>{{Cite news |agency=Associated Press |url=http://news.mongabay.com/2005/0907-ap.html |title=Whale uses fish as bait to catch seagulls then shares strategy with fellow orcas |date=September 7, 2005 |access-date=February 18, 2010 |archive-date=March 22, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100322204614/http://news.mongabay.com/2005/0907-ap.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| == Diet == | |||
| ==Behaviour== | |||
| ] | |||
| ], often lifting their entire bodies out of the water.|alt=A killer whale leaping out of the water is about to land on its back.]] | |||
| Day-to-day orca behaviour generally consists of ], travelling, resting and socializing. Orcas frequently engage in ] such as breaching (jumping completely out of the water) and tail-slapping. These activities may have a variety of purposes, such as courtship, communication, dislodging ]s, or ]. ] is a behaviour in which a whale holds its head above water to view its surroundings.{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|p=64}} Resident orcas swim alongside ]s and other ]s.<ref name="OCR 11-2019">{{cite news |last=Connelly |first=Laylan |title=Videos show killer whales frantically hunting for dolphins off San Clemente |publisher=] |url=https://www.ocregister.com/2019/07/30/videos-show-killer-whales-in-a-frantic-hunt-for-dolphins-off-san-clemente/ |date=July 30, 2019 |access-date=November 24, 2019 |archive-date=December 10, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191210204422/https://www.ocregister.com/2019/07/30/videos-show-killer-whales-in-a-frantic-hunt-for-dolphins-off-san-clemente/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Orcas will engage in ], that is, killing that is not designed to be for food. As an example, a BBC film crew witnessed orca in ] playing with a male ] to exhaustion, but not eating it.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3f-FsAUcqMs|title=Orcas Kill, But Not Just for Food (2:06)|website=YouTube|date=April 19, 2022|language=en|access-date=2 June 2023|archive-date=June 2, 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230602121314/https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3f-FsAUcqMs|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The array of species on which Orca prey is extremely diverse. Specific populations tend to specialise on particular prey species even at the expense of ignoring other potential prey. For example some populations in the Norwegian and Greenland sea specialise on ] and follow that fish's migratory path to the Norwegian coast each Autumn. Other populations in the area prey on seals. This diversification of feeding amongst overlapping species is unique to Orca amongst ]s. | |||
| Some orcas have been observed swimming with dead ], resembling hats.<ref>{{cite web | title=Why orcas wear dead salmon as 'hats' remains a mystery, scientists say | website=CBC | date=November 30, 2024 | url=https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/orca-dead-salmon-hat-1.7397920 | access-date=December 1, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| The Orca is the only cetacean species to regularly prey on other cetaceans, and this is the reason for its other common name Killer Whales. Twenty-two species have been recorded as preyed on, either through an examination of stomach contents, examining scarring on the other cetacean's body or by simply observing the feeding taking place. Pods of Orca will even take larger whales such as ]s, ]s, ]s, or even young ]s. A group of Orca take a young Blue Whale by chasing it and its mother through the sea, wearing them out. Eventually the Orca manage to separate the pair and then surround the younger whale, thereby preventing it from returning to the sea's surface in order to breathe. Once the whale has drowned, the Orca are free to feed on it. | |||
| ===Social structure=== | |||
| There has also been one recorded case of probable Orca ]. A survey carried out by V. I. Shevenko in the temperate areas of the South Pacific in 1975 recorded two male Orca whose stomach contained the remains of other Orca. Of the 30 Orca captured and examined in this survey, 11 had empty stomachs — an unusually high percentage that indicates the Orca were forced to cannibalism through a lack of food. | |||
| Orcas are notable for their complex societies. Only ]s and ]s live in comparably complex ]s.{{sfn|Heimlich|Boran|2001|p=35}} Due to orcas' complex social bonds, many marine experts have concerns about how humane it is to keep ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.keepwhaleswild.org/ |title=Keep Whales Wild |publisher=Keep Whales Wild |date=January 14, 2011 |access-date=February 16, 2011 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101216065407/http://www.keepwhaleswild.org/ |archive-date=December 16, 2010 }}</ref> | |||
| Resident orcas in the eastern North Pacific live in particularly complex and stable social groups. Unlike any other known mammal social structure, resident whales live with their mothers for their entire lives. These family groups are based on ]s consisting of the eldest female (matriarch) and her sons and daughters, and the descendants of her daughters, etc. The average size of a matriline is 5.5 animals. Because females can reach age 90, as many as four generations travel together. These matrilineal groups are highly stable. Individuals separate for only a few hours at a time, to mate or forage. With one exception, an orca named ], no permanent separation of an individual from a resident matriline has been recorded.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=12}} | |||
| More commonly Orca prey on thirty species of ], particularly ], ], ], ] and ]. ]s, ]s and very occasionally even ]s are taken for their nutrient-rich livers. There is also believed to be an element of competition elimination in taking these sharks. Other marine mammals, including most species of ] and ], are also taken by polar populations. ] and ]s are taken less frequently. Seven species of bird are also taken, including all ] species as well as sea birds such as ]s. ]s, such as ]es and a wide range of ], are also targets. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Orca are very inventive and playful in their killing. They sometimes will throw seals to one another through the air in order to stun and kill the animal. Whilst salmon are usually hunted by a single or small group of individuals, herring are often caught using ]. That is, the Orca force the herring into a tight ball by releasing walls of bubbles or flashing their white underside. The Orca then lunge up through the ball, eating several fish in one swoop. Sealions are killed by ] or by being slapped and stunned by a tail fluke. | |||
| Closely related matrilines form loose aggregations called pods, usually consisting of one to four matrilines. Unlike matrilines, pods may separate for weeks or months at a time.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=12}} ] testing indicates resident males nearly always mate with females from other pods.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=39}} Clans, the next level of resident social structure, are composed of pods with similar dialects, and common but older maternal heritage. Clan ranges overlap, mingling pods from different clans.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=12}} The highest association layer is the community, which consists of pods that regularly associate with each other but share no maternal relations or dialects.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Ford|first1= J. K. B.|last2=Ellis|first2= G. M.|last3=Balcomb|first3= K. C.|year=1999|title=Killer Whales: The Natural History and Genealogy of ''Orcinus orca'' in British Columbia and Washington State|publisher=University of British Columbia Press|page=25|isbn=978-0774804691}}</ref> | |||
| Transient pods are smaller than resident pods, typically consisting of an adult female and one or two of her offspring. Males typically maintain stronger relationships with their mothers than other females. These bonds can extend well into adulthood. Unlike residents, extended or permanent separation of transient offspring from natal matrilines is common, with juveniles and adults of both sexes participating. Some males become "rovers" and do not form long-term associations, occasionally joining groups that contain reproductive females.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=13}} As in resident clans, transient community members share an acoustic repertoire, although regional differences in vocalizations have been noted.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=14}} | |||
| More specialized feeding techniques are used by various populations around the world. In Patagonia, Orca feed on ] and ] pups by forcing them on to beaches, even to the extent of stranding themselves, albeit temporarily. Orca will ] to locate seals resting on ice floes, and then create a wave to wash over the floe, causing the seal to be thrown into the water where a second Orca waits to kill it. | |||
| As with residents and transients, the lifestyle of these whales appears to reflect their diet; fish-eating orcas off Norway have resident-like social structures, while mammal-eating orcas in Argentina and the ] behave more like transients.{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|Balcomb|2000|p=27}} | |||
| On average the Orca eats 60kg of food a day. With this huge variety of prey, and no predators other than man, the Orca is very much at the top of the ]. | |||
| Orcas of the same sex and age group may engage in physical contact and synchronous surfacing. These behaviours do not occur randomly among individuals in a pod, providing evidence of "friendships".<ref>{{cite journal|author=Weiss|first1= M. N.|display-authors=etal|year=2021|title=Age and sex influence social interactions, but not associations, within a killer whale pod|journal=Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences|volume=288|issue=1953|doi=10.1098/rspb.2021.0617|pmid=34130498|pmc=8206696|hdl=10871/125706|hdl-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|author=Lesté-Lasserre|first1=Christa|date=June 17, 2021|title=Killer whales form killer friendships, new drone footage suggests|journal=Science|url=https://www.science.org/content/article/killer-whales-form-killer-friendships-new-drone-footage-suggests|access-date=June 18, 2021|archive-date=December 5, 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221205121706/https://www.science.org/content/article/killer-whales-form-killer-friendships-new-drone-footage-suggests|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==Song== | |||
| ===Vocalizations=== | |||
| ] | |||
| <div class="no-print"> | |||
| {| class="toccolours" style="float:right; clear:right; margin-left: 1em;" | |||
| |- style="text-align: center;" | |||
| |'''Multimedia relating to the orca''' | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{listen | |||
| |filename = Killer whale.ogg | |||
| |title = Orca calls | |||
| |description = | |||
| |format = ] | |||
| |filename2 = Killer whale simple.ogg | |||
| |title2 = Orca calls at a distance | |||
| |description2 = | |||
| |format2 = ] | |||
| |filename3 = Killer whale residents broadband.ogg | |||
| |title3 = Vocalizations of an orca | |||
| |description3 = | |||
| |format3 = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| |} | |||
| </div> | |||
| {{See also|Whale vocalization{{!}}Whale sound}} | |||
| Like all ], orcas depend heavily on underwater sound for orientation, feeding, and communication. They produce three categories of sounds: clicks, whistles, and pulsed calls. Clicks are believed to be used primarily for navigation and discriminating prey and other objects in the surrounding environment, but are also commonly heard during social interactions.<ref name=noaa/> | |||
| Northeast Pacific resident groups tend to be much more vocal than transient groups in the same waters.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=20}} Residents feed primarily on ] and ] salmon, which are insensitive to orca calls (inferred from the audiogram of Atlantic salmon). In contrast, the ] prey of transients hear whale calls well and thus transients are typically silent.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=20}} Vocal behaviour in these whales is mainly limited to surfacing activities and milling (slow swimming with no apparent direction) after a kill.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Deeck|first1= V. B.|last2=Ford|first2= J. K. B.|last3=Slater|first3= P. J. B.|year=2005|title=The vocal behaviour of mammal-eating killer whales: communicating with costly calls|journal=Animal Behaviour|volume=69|issue=2|pages=395–405|doi=10.1016/j.anbehav.2004.04.014|s2cid=16899659}}</ref> | |||
| As with other dolphins, Orca are very vocal animals. They produce a variety of clicks and whistles that are used for communication and ]. The type of noises made vary with activity. Whilst resting, perhaps unsurprisingly, they are much quieter, just emitting an occasional call that is distinct from those heard when engaging in more active behaviour. | |||
| All members of a resident pod use similar calls, known collectively as a ]. Dialects are composed of specific numbers and types of discrete, repetitive calls. They are complex and stable over time.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Foote|first1= A. D.|last2=Osborne|first2= R. W.|last3=Hoelzel|first3= A.|year=2008|title=Temporal and contextual patterns of killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') call type production|journal=Ethology|volume=114|issue=6|pages=599–606|doi=10.1111/j.1439-0310.2008.01496.x|bibcode= 2008Ethol.114..599F}}</ref> Call patterns and structure are distinctive within matrilines.<ref name=vocal/> Newborns produce calls similar to their mothers, but have a more limited repertoire.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=14}} Individuals likely learn their dialect through contact with pod members.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Filatova|first1= Olga A.|last2=Fedutin|first2= Ivan D.|last3=Burdin|first3= Alexandr M.|last4=Hoyt|first4= Erich|year=2007|url=http://russianorca.com/Doc/Science/structure_repert.pdf|title=The structure of the discrete call repertoire of killer whales ''Orcinus orca'' from Southeast Kamchatka|journal=Bioacoustics|volume=16|pages=261–280|doi=10.1080/09524622.2007.9753581|issue=3|bibcode= 2007Bioac..16..261F|s2cid=56304541|access-date=February 23, 2010|archive-date=July 15, 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110715214729/http://russianorca.com/Doc/Science/structure_repert.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> Family-specific calls have been observed more frequently in the days following a calf's birth, which may help the calf learn them.<ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.coloradocollege.edu/dept/ev/Research/Faculty/OVALItems/pdf_Papers/SpongCalvesPaper.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110527060306/http://www.coloradocollege.edu/dept/ev/Research/Faculty/OVALItems/pdf_Papers/SpongCalvesPaper.pdf |archive-date=May 27, 2011 |last1=Weiß |first1=Brigitte M. |journal=The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America |volume=119 |last2=Ladich |issue=1 |first2=Friedrich |last3=Spong |first3=Paul |last4=Symonds |first4=Helena |year=2006 |pmid=16454316 |title=Vocal behaviour of resident killer whale matrilines with newborn calves: The role of family signatures |doi=10.1121/1.2130934 |pages=627–635 |bibcode=2006ASAJ..119..627W |url-status=dead }}</ref> Dialects are probably an important means of maintaining group identity and cohesiveness. Similarity in dialects likely reflects the degree of relatedness between pods, with variation growing over time.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|pp=15–16}} When pods meet, dominant call types decrease and subset call types increase. The use of both call types is called biphonation. The increased subset call types may be the distinguishing factor between pods and inter-pod relations.<ref name=vocal>{{cite journal|author=Kremers|first1= D.|last2=Lemasson|first2= A.|last3=Almunia|first3= J.|last4=Wanker|first4= R.|year=2012|title=Vocal sharing and individual acoustic distinctiveness within a group of captive orcas (''Orcinus orca'')|journal=Journal of Comparative Psychology|volume=126|issue=4|pages=433–445|doi=10.1037/a0028858|pmid=22866769}}</ref> | |||
| Resident pods of Orca tend to be much more vocal than transient groups. Scientists surmise that there are two main reasons for this. Firstly resident Orca stay within the same social groups for much longer, thus developing more complicated social relationships resulting in greater vocalizations. Transient groups tend to stay together for much more fleeting amounts of time (usually just a period of hours or days) and thus communicate less. | |||
| Dialects also distinguish types. Resident dialects contain seven to 17 (mean = 11) distinctive call types. All members of the North American west coast transient community express the same basic dialect, although minor regional variation in call types is evident. Preliminary research indicates offshore orcas have group-specific dialects unlike those of residents and transients.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|pp=15–16}} | |||
| Secondly transient Orca are much more likely to feed on marine mammals than fish-loving resident pods. Orca hunting for mammals to eat naturally must be quieter to avoid the possibility of detection. For this reason hunting Orca tend to use just a single click (called a "cryptic click") for echolocation rather than the long train of clicks observed in other species. | |||
| Norwegian and Icelandic ]-eating orcas appear to have different vocalizations for activities like hunting.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Simon|first1= M.|last2=McGregor|first2= P. K.|last3=Ugarte|first3= F.|year=2007|title=The relationship between the acoustic behaviour and surface activity of killer whales (''Orcinus orca'') that feed on herring (''Clupea harengus'')|journal=Acta Ethologica|volume=10|issue=2|pages=47–53|doi=10.1007/s10211-007-0029-7|s2cid=29828311}}</ref> A population that live in ], ] have 28 complex burst-pulse and whistle calls.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://newatlas.com/science/smallest-killer-whale-large-musical-repertoire/|title=The smallest killer whale has a large musical repertoire|last=Szondy|first=David|date=February 26, 2020|website=New Atlas|language=en-US|url-status=live|access-date=February 27, 2020|archive-date=February 27, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200227234559/https://newatlas.com/science/smallest-killer-whale-large-musical-repertoire/}}</ref> | |||
| An interesting feature of resident pods is the existence of regional dialects. Each pod has its own "songs" or sets of particular whistles and clicks, that it will repeat over and over. Every member of the pod seems to know all the songs of the pod. Thus it is not possible to identify a single animal using voice alone; only a dialectal group. A particular song might be known by only one group, or shared amongst several. The degree to which to two groups have their songs in common appears to be a function of their genealogical closeness rather than their geographical closeness. Thus two groups that share a common set of ancestors but have not grown apart in distance are likely to have a similar set of songs. This suggests that songs are passed from mother to child during the nursing period. | |||
| ===Intelligence=== | |||
| ''See also: ]'' | |||
| {{Main|Cetacean intelligence}} | |||
| Orcas have the second-heaviest brains among marine mammals<ref name=spear>{{cite news|last=Spear|first= Kevin|url=https://www.orlandosentinel.com/2010/03/06/killer-whales-how-smart-are-they/ |title=Killer whales: How smart are they?|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150908001401/http://articles.orlandosentinel.com/2010-03-06/news/os-seaworld-killer-whale-brains-20100302_1_killer-whales-orcas-dolphin-or-porpoise |archive-date=September 8, 2015 |work=Orlando Sentinel|date= March 7, 2010|url-status=live|access-date= March 7, 2010}}</ref> (after ]s, which have the largest brain of any animal).<ref>{{Cite news|last=Dunham|first=Will|date=2017-10-16|title=Big and brilliant: complex whale behavior tied to brain size|language=en|work=Reuters|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-science-whales-idUSKBN1CL30I|access-date=2020-12-23|archive-date=July 19, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210719045118/https://www.reuters.com/article/us-science-whales-idUSKBN1CL30I|url-status=live}}</ref> Orcas have more ] and more cortical neurons than any mammal, including humans.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Ridgway |first1=Sam H. |last2=Brownson |first2=Robert H. |last3=Van Alstyne |first3=Kaitlin R. |last4=Hauser |first4=Robert A. |date=2019-12-16 |editor-last=Li |editor-first=Songhai |title=Higher neuron densities in the cerebral cortex and larger cerebellums may limit dive times of delphinids compared to deep-diving toothed whales |journal=PLOS ONE |language=en |volume=14 |issue=12 |pages=e0226206 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0226206 |issn=1932-6203 |pmc=6914331 |pmid=31841529 |bibcode=2019PLoSO..1426206R |doi-access=free }}</ref> They can be ] in captivity and are often described as intelligent,<ref name=cbs2010/>{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|p=67}} although defining and measuring "intelligence" is difficult in a species whose environment and behavioural strategies are very different from those of humans.{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|p=67}} Orcas imitate others, and seem to deliberately teach skills to their kin. Off the ], mothers push their calves onto the beach, waiting to pull the youngster back if needed.{{sfn|Heimlich|Boran|2001|p=45}}{{sfn|Baird|2002|pp=61–62}} In March 2023, a female orca was spotted with a newborn ] in ].<ref>{{cite news | url=https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2023/mar/10/killer-whale-orca-adopts-abducts-pilot-whale-calf-aoe | title='Extraordinary' sighting of orca with baby pilot whale astounds scientists | newspaper=The Guardian | date=March 10, 2023 | last1=Weston | first1=Phoebe }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| == Orca in history == | |||
| People who have interacted closely with orcas offer numerous ] demonstrating the whales' curiosity, playfulness, and ability to solve problems. Alaskan orcas have not only learned how to steal fish from ], but have also overcome a variety of techniques designed to stop them, such as the use of unbaited lines as decoys.{{sfn|Obee|Ellis|1992|p=42}} Once, fishermen placed their boats several miles apart, taking turns retrieving small amounts of their catch, in the hope that the whales would not have enough time to move between boats to steal the catch as it was being retrieved. The tactic worked initially, but the orcas figured it out quickly and split into groups.{{sfn|Obee|Ellis|1992|p=42}} | |||
| In other anecdotes, researchers describe incidents in which wild orcas playfully tease humans by repeatedly moving objects the humans are trying to reach,<ref name=BF>{{Cite journal |year=2005 |title=Killer whale games |journal=Blackfish Sounder |volume=13 |page=5 |url=http://www.killerwhale.org/BFS/BFS_13.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071011062137/http://www.killerwhale.org/BFS/BFS_13.pdf |archive-date=October 11, 2007 |url-status=dead}}</ref> or suddenly start to toss around a chunk of ice after a human throws a snowball.<ref>Pitman, Robert L. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200915041640/https://www.livescience.com/3284-scientist-snowball-fight-killer-whale.html |date=September 15, 2020 }}. ''Live Science'', February 6, 2009. Retrieved March 7, 2010</ref> | |||
| Although only scientifically identified as species in 1758, the Orca has been known to man since time immemorial. There are two particularly early records about Orca. In the centuries 200BC–1BC, the ] tribes of ] were known to paint Orca designs on their icons as a symbol of power and coverage. They also built temples to Orca deities. | |||
| The orca's use of dialects and the passing of other learned behaviours from generation to generation have been described as a form of ].<ref>{{Cite journal |doi=10.1371/journal.pbio.0050139 |last=Marino |first=Lori |title=Cetaceans Have Complex Brains for Complex Cognition |journal=] |year=2007 |page=e139 |volume=5 |issue=e139 |pmid=17503965 |pmc=1868071 |display-authors=etal |doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| The first description of an Orca is given in ]'s ''Natural History'' (written c.50BC). The aura of invincibility around the all-consuming Orca was well-established by this time. Having watched the public slaughtering of a whale stranded at a harbour near Rome, Pliny writes "A killer whale cannot be properly depicted or described except as an enormous mass of flesh armed with savage teeth... the enemy of other whales charge and pierce them like warships ramming." | |||
| {{blockquote|The complex and stable vocal and behavioural cultures of ] groups of killer whales (''Orcinus orca'') appear to have no parallel outside humans and represent an independent evolution of cultural faculties.<ref name=rendell>{{cite journal|last1=Rendell|first1= Luke|first2=Hal|last2= Whitehead|url=http://whitelab.biology.dal.ca/lr/bbs.htm|title=Culture in whales and dolphins|journal=Behavioral and Brain Sciences|year=2001|volume=24|issue=2|pages=309–324|access-date=March 7, 2010|pmid=11530544|doi=10.1017/S0140525X0100396X|s2cid=24052064|archive-date=May 30, 2010|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100530054246/http://whitelab.biology.dal.ca/lr/bbs.htm|url-status=live}}</ref>}} | |||
| == Orca and modern man == | |||
| ] | |||
| ==Life cycle== | |||
| Orca were targeted in commercial whaling for the middle part of the twentieth century once stocks or larger species had been depleted. Commercial hunting of Orca came to an abrupt halt in 1981 with the introduction of the moratorium on all whaling. (Although from a taxonomic point of view an Orca is a dolphin rather than a whale, it is sufficiently large to come under the purview of the ].) | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Female orcas begin to mature at around the age of 10 and reach peak fertility around 20,<ref name=Reproduction>{{cite journal |last1=Ward |first1=Eric J. |last2=Holmes |first2=Elizabeth E. |last3=Balcomb |first3=Ken C. |title=Quantifying the effects of prey abundance on killer whale reproduction |journal=Journal of Applied Ecology |date=June 2009 |volume=46 |issue=3 |pages=632–640 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2664.2009.01647.x|doi-access=free |bibcode=2009JApEc..46..632W }}</ref> experiencing periods of ] cycling separated by non-cycling periods of three to 16 months. Females can often breed until age 40, followed by a rapid decrease in fertility.<ref name=Reproduction /> Orcas are among the few ] and live for decades after they have finished breeding.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Bowden |first1=D. M. |last2=Williams |first2=D. D. |title=Aging |journal=Advances in Veterinary Science and Comparative Medicine |date=1984 |volume=28 |pages=305–341 |pmid=6395674 |doi=10.1016/B978-0-12-039228-5.50015-2 |isbn=9780120392285}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Physiological Basis of Aging and Geriatrics|edition= Fourth|first1=Paola S.|last1= Timiras|publisher= CRC Press|date= 2013| page= 161}}</ref> The lifespans of wild females average 50 to 80 years.<ref name="nationalgeographic.com">{{cite web |title=Orcas don't do well in captivity. Here's why. |url=https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/2019/03/orcas-captivity-welfare/ |website=Animals |access-date=31 May 2020 |language=en |date=25 March 2019 |archive-date=June 6, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200606082028/https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/2019/03/orcas-captivity-welfare/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> Some are claimed to have lived substantially longer: ] was estimated by some researchers to have been as old as 105 years at the time of her death, though a biopsy sample indicated her age as 65 to 80 years.{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|p=26}}<ref name=King>{{Cite news|url=http://www.king5.com/news/local/oldest-southern-resident-killer-whale-considered-dead/381349614|title=Oldest Southern Resident killer whale considered dead|last=TEGNA|newspaper=KING|language=en-US|access-date=January 3, 2017|archive-date=January 3, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170103094218/http://www.king5.com/news/local/oldest-southern-resident-killer-whale-considered-dead/381349614|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Orcazine">{{cite web|url=http://orcazine.com/granny-j2/|title=Orca Granny: was she really 105?|last=Podt|first=Annemieke|language=en-US|access-date=September 11, 2017|date=December 31, 2016|archive-date=October 15, 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181015152227/http://orcazine.com/granny-j2/|url-status=live}}</ref> It is thought that orcas held in captivity tend to have shorter lives than those in the wild, although this is subject to scientific debate.<ref name="nationalgeographic.com"/><ref name=robeck>{{cite journal |last1=Robeck |first1=Todd R. |last2=Willis |first2=Kevin |last3=Scarpuzzi |first3=Michael R. |last4=O'Brien |first4=Justine K. |title=Comparisons of life-history parameters between free-ranging and captive killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') populations for application toward species management |url=https://academic.oup.com/jmammal/article/96/5/1055/920547|journal=Journal of Mammalogy |pages=1055–1070 |language=en |doi=10.1093/jmammal/gyv113 |date=29 September 2015 |volume=96 |issue=5 |pmid=26937049 |pmc=4668992 |archive-date=April 23, 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190423085700/https://academic.oup.com/jmammal/article/96/5/1055/920547 |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Jett |first1=John |last2=Ventre |first2=Jeffrey |title=Captive killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') survival |journal=Marine Mammal Science |pages=1362–1377 |language=en |doi=10.1111/mms.12225 |date=2015 |volume=31|issue=4 |bibcode=2015MMamS..31.1362J }}</ref> | |||
| Males mate with females from other pods, which prevents ]. ] varies from 15 to 18 months.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=33}} Mothers usually calve a single offspring about once every five years. In resident pods, births occur at any time of year, although winter is the most common. Mortality is extremely high during the first seven months of life, when 37–50% of all calves die.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=35}} ] begins at about 12 months of age, and is complete by two years. According to observations in several regions, all male and female pod members participate in the care of the young.{{sfn|Heimlich|Boran|2001|p=35}} | |||
| The greatest hunter of Orca was ] which took an average of 56 animals per year from 1938 to 1981. Japan took an average of 43 animals from 1946 to 1981. (War year figures are not available but are likely to be far fewer). The ] took a few animals each in the Antarctic, with the extraordinary exception of the 1980 season where it took 916. | |||
| Males sexually mature at the age of 15, but do not typically reproduce until age 21. Wild males live around 29 years on average, with a maximum of about 60 years.{{sfn|Carwardine|2001|p=26}} One male, known as ], was reportedly spotted every winter between the 1840s and 1930 off ], Australia, which would have made him up to 90 years old. Examination of his teeth indicated he died around age 35,<ref>Mitchell, E. and Baker, A. N. (1980). Age of reputedly old Killer Whale, ''Orcinus orca'', 'Old Tom' from Eden, Twofold Bay, Australia, in: W. F. Perrin and A. C. Myrick Jr (eds.): Age determination of toothed whales and sirenians, pp. 143–154 Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. (Special Issue 3), cited in , The Dolphin's Encyclopaedia. Retrieved January 27, 2010</ref> but this method of age determination is now believed to be inaccurate for older animals.<ref>Olesiuk, Peter F.; Ellis, Graeme M. and Ford, John K. B. (2005). {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110419074348/http://www.pac.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/science/species-especes/cetacean-cetaces/CRP-publications/Olesiuk%20et%20al.%202005%20KW%20Pop%20Dyn.pdf |date=April 19, 2011 }}, Research Document 2005/045, Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat, Fisheries and Oceans Canada. p. 33. Retrieved January 27, 2010</ref> One male known to researchers in the ] (identified as J1) was estimated to have been 59 years old when he died in 2010.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091128230801/http://www.whaleresearch.com/orca_ID.html |date=November 28, 2009 }}, Center for Whale Research. Retrieved March 23, 2012</ref> Orcas are unique among cetaceans, as their caudal sections elongate with age, making their heads relatively shorter.{{sfn|Heptner|Nasimovich|Bannikov|Hoffmann|1996|p=681}} | |||
| Today, no country carries out a substantial hunt. Japan usually takes a few individuals each year as part of its controversial programme of scientific research. A similarly small of subsistence whaling is carried out by ] and ]. As well as hunting for their meat, Orca have also been killed because of their competition with fishermen. In the ] the ], at the request of the ] government used bombers and riflemen to slaughter Orca in Icelandic waters because they competed with humans for fish. The operation was considered a great success at the time by fishermen and the Icelandic Government. However many were unconvinced that Orca were responsible for the drop in fish stocks - blaming instead overfishing by humans. This debate has led to repeated studies of North Atlantic fish stocks, with neither side in the ] debate giving ground since that time. | |||
| ], once thought to occur only in captive orcas, was observed in wild populations by researchers off British Columbia on December 2, 2016. In this incident, an adult male killed the calf of a female within the same pod, with the adult male's mother also joining in the assault. It is theorized that the male killed the young calf in order to mate with its mother (something that ]), while the male's mother supported the breeding opportunity for her son. The attack ended when the calf's mother struck and injured the attacking male. Such behaviour matches that of many smaller dolphin species, such as the ].<ref>{{Cite web | url=http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/killer-whale-infanticide-1.4586867 | title='Horrified' scientists first to see killer whale infanticide | CBC News | access-date=March 22, 2018 | archive-date=March 23, 2018 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180323025412/http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/killer-whale-infanticide-1.4586867 | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The Orca is also occasionally killed out of fear. The species other common name - Killer Whale - and impressive rows of sharp teeth gave rise to a fearsome reputation. In fact no human has ever been attacked by an Orca in wildlife. Nevertheless fearful sailors in Alaska continue to resort to shooting the animal occasionally out of fear for their lives. This fear has generally dissipated in recent years, due to better education about the species. Part of this education has been the appearance of Orca in ]s and other aquatic attractions. The Orca's intelligence, trainability, striking appearance, playfulness in captivity and its sheer size have made it amongst the popular exhibits at such places. The first Orca capture and display took place in Vancouver in 1964. Over the next 15 years around 60–70 Orca were taken from Pacific waters for this purpose. In the late 70s and the first half of the 80s Orca were generally taken from Icelandic waters (50 in the five years to 1985). Since that time Orca have been successfully bred in captivity and wild specimens are considerably rarer. Orca in captivity may develop pathologies such as ] collapse, seen in 60–90% of captive males. | |||
| ==Conservation== | |||
| It must be noted that there have been incidents with Orcas in captivity attacking humans. A group of orcas killed a trainer in a Canadian aquarium, and in 1999 an orca killed a tourist who had sneaked into his pool at night. In late July 2004, an Orca attacked its trainer in a "]" park in Texas. During a show, the animal pushed its trainer under water and barred the way to the rim of the pool. The trainer, who could only be rescued from the raging animal by helpers after several minutes, already worked for ten years with this Orca. In another Sea World park, one orca killed another. Opponents of these shows see these incidents as supporting their criticisms. | |||
| ] | |||
| In 2008, the ] (International Union for Conservation of Nature) changed its assessment of the orca's ] from ] to ], recognizing that one or more orca types may actually be separate, ].<ref name="iucn status 19 November 2021" /> ], ], large-scale ]s, and ] caused by noise and conflicts with boats are the most significant worldwide threats.<ref name="iucn status 19 November 2021" /> In January 2020, the first orca in England and Wales since 2001 was found dead with a large fragment of plastic in its stomach.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-england-norfolk-51108830|title=First stranded Orca found in almost 20 years in the Wash|date=January 14, 2020|website=BBC News|url-status=live|archive-date=January 16, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200116204509/https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-england-norfolk-51108830}}</ref> | |||
| Like other animals at the highest ]s, the orca is particularly at risk of poisoning from ] of toxins, including ]s (PCBs).{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|Balcomb|2000|p=99}} European ]s have problems in reproductive and immune functions associated with high levels of PCBs and related contaminants, and a survey off the ] coast found PCB levels in orcas were higher than levels that had caused health problems in harbour seals.{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|Balcomb|2000|p=99}} Blubber samples in the ] show higher levels of PCBs, pesticides and ]s than in ]s. A 2018 study published in '']'' found that global orca populations are poised to dramatically decline due such toxic pollution.<ref>{{cite news |last=Carrington |first=Damian |date=September 27, 2018 |title=Orca 'apocalypse': half of killer whales doomed to die from pollution |url=https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2018/sep/27/orca-apocalypse-half-of-killer-whales-doomed-to-die-from-pollution |work=The Guardian |access-date=September 28, 2018 |archive-date=September 28, 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180928005643/https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2018/sep/27/orca-apocalypse-half-of-killer-whales-doomed-to-die-from-pollution |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Desforges|first1=J-P|last2=Hall|first2=A|last3=Mcconnell|first3=B|display-authors=etal|year=2018|title=Predicting global killer whale population collapse from PCB pollution|journal=Science|volume=361|issue=6409|pages=1373–1376|doi=10.1126/science.aat1953|pmid=30262502 |bibcode=2018Sci...361.1373D |hdl=10023/16189 |s2cid=52876312 |hdl-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| The movie '']'' (1993) focused on the quest for freedom for a captive orca and his human well-wishers. The whale starring in the movie, ], was originally caught in ]ic waters. After ] at the ] in ], he was later returned to the waters of the ], his native habitat, but continued to be dependent on humans until his death in December ]. | |||
| In the ], wild salmon stocks, a main resident food source, have declined dramatically in recent years.<ref name="iucn status 19 November 2021" /> In the ] region, only 75 whales remain with few births over the last few years.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2018/07/09/science/orcas-whales-endangered.html?rref=collection/sectioncollection/science&action=click&contentCollection=science®ion=rank&module=package&version=highlights&contentPlacement=1&pgtype=sectionfront|title=Orcas of the Pacific Northwest Are Starving and Disappearing|newspaper=The New York Times |date=July 9, 2018 |access-date=July 9, 2018|language=en|archive-date=July 10, 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180710011739/https://www.nytimes.com/2018/07/09/science/orcas-whales-endangered.html?rref=collection%2Fsectioncollection%2Fscience&action=click&contentCollection=science®ion=rank&module=package&version=highlights&contentPlacement=1&pgtype=sectionfront|url-status=live|last1=Robbins |first1=Jim }}</ref> On the west coast of Alaska and the ], seal and sea lion populations have also substantially declined.{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|Balcomb|2000|p=98}} | |||
| Other environmental pressures facing Orca include extensive ] which some research indicates changes whale behaviour. Heavy ship noise and "seal scarers" — small noise-emitting devices placed in coastal areas to scare seals away from salmon farms have caused some groups of Orca to change the frequencies of their "songs" and calls. | |||
| In 2005, the United States government listed the ] community as an endangered population under the ].<ref name=noaa/> This community comprises three pods which live mostly in the ] and ] and ] in ] and Washington. They do not breed outside of their community, which was once estimated at around 200 animals and later shrank to around 90.<ref name=Lyke>{{cite news|first=M. L.|last= Lyke|url=http://www.seattlepi.com/specials/brokenpromises/288674_granny614.html|title= Granny's Struggle: When Granny is gone, will her story be the last chapter?|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200915041546/https://www.seattlepi.com/news/article/Granny-s-Struggle-When-Granny-is-gone-will-her-1217200.php |archive-date=September 15, 2020|work=Seattle Post Intelligencer|date= October 14, 2006}}</ref> In October 2008, the annual survey revealed seven were missing and presumed dead, reducing the count to 83.<ref name=researchers/> This is potentially the largest decline in the population in the past 10 years. These deaths can be attributed to declines in ].<ref name=researchers>Le Phuong. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081028085210/http://www.usatoday.com/news/nation/environment/2008-10-25-orcas-puget-sound_N.htm |date=October 28, 2008 }}, Associated Press. USA Today, October 25, 2008</ref> | |||
| The '']'' oil spill had a particularly adverse effect on the Alaskan population. One pod was caught in the spill. Although the pod successfully swam through the oil to clear water, 14 of the pod (about half) died in the following days and weeks. The spill had a longer-term effect in reducing the amount of prey, such as salmon, available and thus was responsible for a local population decline. | |||
| Scientist ] has extensively studied orcas since 1976; he is the research biologist responsible for discovering ]. He studied orcas from the Center for Whale Research, located in ], Washington.<ref name = Pickrell>{{cite news|last=Pickrell|first=John|title=U.S. Navy Sonar May Harm Killer Whales, Expert Says.|url=http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2004/03/0331_040331_whalesincrisis.html|access-date=March 19, 2012|newspaper=National Geographic News|date=March 2004|archive-date=September 9, 2011|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110909000831/http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2004/03/0331_040331_whalesincrisis.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> He was also able to study orcas from "his home porch perched above Puget Sound, where the animals hunt and play in summer months".<ref name = Pickrell/> In May 2003, Balcomb (along with other ] near the Puget Sound coastline) noticed uncharacteristic behaviour displayed by the orcas. The whales seemed "agitated and were moving haphazardly, attempting to lift their heads free of the water" to escape the sound of the sonars.<ref name = Pickrell/> "Balcomb confirmed at the time that strange underwater pinging noises detected with underwater microphones were sonar. The sound originated from a U.S. Navy frigate 12 miles (19 kilometres) distant, Balcomb said."<ref name = Pickrell/> The impact of sonar waves on orcas is potentially life-threatening. Three years prior to Balcomb's discovery, research in the Bahamas showed 14 beaked whales washed up on the shore. These whales were beached on the day U.S. Navy destroyers were activated into sonar exercise.<ref name = Pickrell/> Of the 14 whales beached, six of them died. These six dead whales were studied, and ]s of two of the whale heads showed hemorrhaging around the brain and the ears, which is consistent with ].<ref name = Pickrell/> | |||
| Like other animals at the highest trophic levels of the ], the Orca is particularly susceptible to poisoning via accumulation of ]s in the body. A survey of animals off the Washington coast found that PCB levels in Orca were higher than those in ]s in Europe that have been proved to be made sick by the chemicals. However direct evidence of sickness in Orca has been found. The most likely effect, if any, would be a reduced rate of reproduction. | |||
| Another conservation concern was made public in September 2008 when the Canadian government decided it was not necessary to enforce further protections (including the ] in place to protect endangered animals along with their habitats) for orcas aside from the laws already in place. In response to this decision, six environmental groups sued the federal government, claiming orcas were facing many threats on the ] and the federal government did nothing to protect them from these threats.<ref name = CBC>{{cite news|title=Ottawa Sued over Lack of Legislation to Protect B.C. Killer Whales|url=https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/ottawa-sued-over-lack-of-legislation-to-protect-b-c-killer-whales-1.764491|access-date=March 19, 2012|newspaper=CBC News|date=October 9, 2008|archive-date=June 26, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120626200949/http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/story/2008/10/08/bc-killer-whale-lawsuit.html|url-status=live}}</ref> A legal and scientific nonprofit organization, ], led the lawsuit and represented the ], ], ], ], the ], and the ].<ref name = CBC/> Many scientists involved in this lawsuit, including Bill Wareham, a marine scientist with the David Suzuki Foundation, noted increased boat traffic, water toxic wastes, and low salmon population as major threats, putting approximately 87 orcas on the British Columbia Coast in danger.<ref name = CBC/> | |||
| ] from shipping, drilling, and other human activities is a significant concern in some key orca habitats, including ] and ].{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|Balcomb|2000|p=100}} In the mid-1990s, loud underwater noises from ]s were used to deter seals. Orcas also avoided the surrounding waters.<ref> | |||
| {{webarchive|url=https://archive.today/20120911041805/http://www.raincoastresearch.org/orca.htm |date=September 11, 2012 }}, Raincoast Research Society. Retrieved February 18, 2010</ref> High-intensity sonar used by the ] disturbs orcas along with other marine mammals.<ref>{{Cite news|last=McClure|first=Robert|title=State expert urges Navy to stop sonar tests|url=http://www.seattlepi.com/local/article/State-expert-urges-Navy-to-stop-sonar-tests-1125871.php|work=Seattle Post Intelligencer|date=October 2, 2003|access-date=June 25, 2007|archive-date=October 4, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121004152333/http://www.seattlepi.com/local/article/State-expert-urges-Navy-to-stop-sonar-tests-1125871.php|url-status=live}}</ref> Orcas are popular with ], which may stress the whales and alter their behaviour, particularly if boats approach too closely or block their lines of travel.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Williams |first=Rob |title=Behavioural responses of male killer whales to a 'leapfrogging' vessel |journal=Journal of Cetacean Research and Management|volume=4 |issue=3 |pages=305–310 |year=2023 |doi=10.47536/jcrm.v4i3.844 |s2cid=55958971 |url=http://www.nwfsc.noaa.gov/research/divisions/cb/ecosystem/marinemammal/kwworkshops/boatpubs/leapfrogging_williamsetal.pdf |access-date=February 25, 2014 |archive-date=March 6, 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140306170841/http://www.nwfsc.noaa.gov/research/divisions/cb/ecosystem/marinemammal/kwworkshops/boatpubs/leapfrogging_williamsetal.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The ] adversely affected orcas in ] and Alaska's ] region. Eleven members (about half) of one resident pod disappeared in the following year. The spill damaged salmon and other prey populations, which in turn damaged local orcas. By 2009, scientists estimated the AT1 transient population (considered part of a larger population of 346 transients), numbered only seven individuals and had not reproduced since the spill. This population is expected to die out.<ref>{{cite magazine |url=https://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/03/valdezwhales/ |title=Unique Killer-Whale Pod Doomed by Exxon Valdez |magazine=Wired |access-date=December 31, 2009 |first=Brandon |last=Keim |date=March 24, 2009 |archive-date=January 6, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100106190509/http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/03/valdezwhales/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.whalesalaska.org/docs/m356p269.pdf |title=Marine Ecology Progress Series 356:269 |access-date=December 31, 2009 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110728174630/http://www.whalesalaska.org/docs/m356p269.pdf |archive-date=July 28, 2011 }}</ref> | |||
| Orcas are included in Appendix II of the ] (CITES), meaning international trade (including in parts/derivatives) is regulated.<ref name = "CITES"/> | |||
| ==Relationship with humans== | |||
| ===Indigenous cultures=== | |||
| {{see also|Animal worship}} | |||
| ] sculpture by ]|alt=Jade carving of a killer whale with exaggerated fins and bared teeth. Its body and fins are engraved with nested ovals and other patterns.]] | |||
| The ] feature orcas throughout ], history, spirituality and religion. The ] regarded orcas as the most powerful animals in the ocean, and their mythology tells of orcas living in houses and towns under the sea. According to these stories, they took on human form when submerged, and humans who drowned went to live with them.{{sfn|Francis|Hewlett|2007|pp=115–120}} For the ], the orca was regarded as the ruler of the undersea world, with ]s for slaves and dolphins for warriors.{{sfn|Francis|Hewlett|2007|pp=115–120}} In ] and ], orcas may embody the souls of deceased chiefs.{{sfn|Francis|Hewlett|2007|pp=115–120}} The ] of southeastern Alaska regarded the orca as custodian of the sea and a benefactor of humans.{{sfn|Ford|Ellis|Balcomb|2000|p=11}} | |||
| The ] consider orca to be people, referring to them as "qwe'lhol'mechen" which means "our relations under the waves".<ref>{{cite news |last1=Gibson |first1=Caitlin |title=The call of Tokitae |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/lifestyle/interactive/2023/tokitae-lolita-orca/ |newspaper=] |access-date=December 10, 2023 |date=December 5, 2023 |archive-date=December 5, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231205234228/https://www.washingtonpost.com/lifestyle/interactive/2023/tokitae-lolita-orca/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The ] people of ] also had great respect for orcas, as evidenced by stone carvings found in a 4,000-year-old burial at the ].<ref>Rollmann, Hans (1999). {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090504120020/http://www.heritage.nf.ca/society/religion.html |date=May 4, 2009 }}, Newfoundland and Labrador Heritage, Memorial University of Newfoundland. Retrieved January 26, 2010</ref><ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.2307/277719|author=Tuck|first1= James A.|year=1971 |title=An Archaic Cemetery at Port Au Choix, Newfoundland|journal=American Antiquity|volume=36|issue=3|pages=343–358|jstor=277719|s2cid=163391715 }}</ref> | |||
| In the tales and beliefs of the ] people, orcas are said to appear as ] in winter, and wolves as orcas in summer.<ref name=rubow>''The orphan boy with his sister'', p. 156 in Rubcova, E. S. (1954). ''Materials on the Language and Folklore of the Eskimoes, Vol. I, Chaplino Dialect''. Leningrad: ]. Original data: Е.С. Рубцова: Материалы по языку и фольклору эскимосов (чаплинский диалект). Академия Наук СССР. Москва-Ленинград, 1954</ref><ref name=menow>Menovshchikov, G. A. (1962). ''Grammar of the language of Asian Eskimos''. Vol. I., pp. 439, 441. Moscow and Leningrad: ]. Original data: Г. А. Меновщиков: Грамматиκа языка азиатских эскимосов. Часть первая. Академия Наук СССР. Москва-Ленинград, 1962</ref><ref name=ssipr>{{cite web|url=http://www.nsu.ru/ip/eskimos.php#3|title=Поддержка прав коренных народов Cибири - Spiritual culture subsection of the Eskimos page in the Support for Siberian Indigenous Peoples Rights|work=nsu.ru|language=ru|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070830162420/http://www.nsu.ru/ip/eskimos.php#3|archive-date=August 30, 2007}}</ref><ref name=submit>{{cite web |last=Vajda |first=Edward J |title=Siberian Yupik (Eskimo) |work=East Asian Studies |url=http://pandora.cii.wwu.edu/vajda/ea210/aleut.htm |access-date=August 7, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161028052901/http://pandora.cii.wwu.edu/vajda/ea210/aleut.htm |archive-date=October 28, 2016 |url-status=dead }}</ref> Orcas are believed to assist their hunters in driving walrus.<ref name=radio>{{cite serial |credits=Ковалева, Ирина & Богословская, Людмила |script-title=ru:Животные и отражение их прихода к человеку в самых разных текстах |network=Эхо Москвы |station=Арсенал |airdate=December 3, 2002 |url=http://echo.msk.ru/programs/beseda/20523/ |language=ru |access-date=April 29, 2008 |archive-date=May 5, 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080505005651/http://echo.msk.ru/programs/beseda/20523/ |url-status=live }} A radio interview with Russian scientists about man and animal, examples taken especially from Asian Eskimos</ref> Reverence is expressed in several forms: the boat represents the animal, and a wooden carving hung from the hunter's belt.<ref name=ssipr/> Small ]s such as tobacco or meat are strewn into the sea for them.<ref name=radio/><ref name=submit/> | |||
| The ] of ], the ], and southern ] often referred to orcas in their folklore and myth as '']'' (God of Sea/Offshore) to bring fortunes (whales) to the coasts, and there had been traditional funerals for stranded or deceased orcas akin to funerals for other animals such as ]s.<ref>{{cite news |last=Miyanaga |first=T. |year=2014 |script-title=ja:(北海道)「シャチ送り」の遺構か 礼文島の遺跡で出土 |newspaper=] |language=ja}}</ref> | |||
| ===Attacks by wild orcas on humans and animals=== | |||
| {{Further information|Orca attack}} | |||
| ], Germany, 1545<ref name="Greifswald church"/>|alt=Killer whale silhouette, with two projections above shown above the blowhole.]] | |||
| In ]s, orcas were historically feared as dangerous, savage predators.{{sfn|Obee|Ellis|1992|pp=Chapter 1}} The first written description of an orca was given by ] ''circa'' AD 70, who wrote, "Orcas (the appearance of which no image can express, other than an enormous mass of savage flesh with teeth) are the enemy of ... they charge and pierce them like warships ramming." (see citation in section ], above).<ref name=pliny1>]. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200915041547/http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/L/Roman/Texts/Pliny_the_Elder/9%2A.html#v |date=September 15, 2020 }} (Latin), in Bill Thayer's '' {{Webarchive|url=https://archive.today/20120524002003/http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/home.html |date=May 24, 2012 }}''. (See also an {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110604093248/http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.02.0137:book=9:chapter=5 |date=June 4, 2011 }} by ] and ], 1855.) Retrieved February 19, 2010.</ref> | |||
| Of the very few confirmed attacks on humans by wild orcas, none have been fatal.<ref name="3_News_71245">{{cite news |url=http://www.3news.co.nz/Orca-shares-the-waves-with-local-surfer/tabid/423/articleID/71245/Default.aspx |title=Orca shares the waves with local surfer |date=September 12, 2008 |work=] |access-date=October 13, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110724192551/http://www.3news.co.nz/Orca-shares-the-waves-with-local-surfer/tabid/423/articleID/71245/Default.aspx |archive-date=July 24, 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> In one instance, orcas tried to tip ice floes on which a dog team and ] of the ] were standing.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Cherry-Garrard|first=Apsley|title=The Worst Journey in the World: Antarctic 1910–1913|publisher=Globe Pequot|year=2004|page=92|isbn=978-1-59228-212-8}}</ref> The sled dogs' barking is speculated to have sounded enough like seal calls to trigger the orca's hunting curiosity. In the 1970s, a surfer in California was bitten, but the Orca then retreated,<ref>{{cite web |author=<!--not stated--> |date=1972-07-11 |title=Whale Takes Bite From Surfer's Leg |url=https://www.newspapers.com/article/the-los-angeles-times-kretschmer/141435593/ |work=Los Angeles Times |agency=UPI |location=MONTEREY |access-date=2024-03-23 |archive-date=February 18, 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240218211855/https://www.newspapers.com/article/the-los-angeles-times-kretschmer/141435593/ |url-status=live }}</ref> and in 2005, a boy in Alaska who was splashing in a region frequented by harbour seals was bumped by an orca that apparently misidentified him as prey.<ref name=ketchikan>{{cite news |agency=The ] |url=https://www.seattletimes.com/seattle-news/boy-survives-bump-from-killer-whale |title=Boy survives bump from killer whale |newspaper=] |date=August 18, 2005 |access-date=January 3, 2010 |archive-date=April 2, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110402062946/http://seattletimes.nwsource.com/html/localnews/2002444869_webwhale18.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| === Orca attacks on sailboats and small vessels === | |||
| {{main|Iberian orca attacks}} | |||
| Beginning around 2020, one or more pods of orcas began to attack sailing vessels off the southern tip of Europe, and a few were sunk. At least 15 interactions between orcas and boats off the Iberian coast were reported in 2020.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-05-23 |title=Scientists are puzzled by Orcas sinking boats in a string of abnormal attacks |url=https://www.nbcnews.com/science/science-news/orcas-sank-three-boats-coast-portugal-dont-call-killer-just-yet-rcna85678 |access-date=2023-07-04 |website=NBC News |language=en |archive-date=July 4, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230704125250/https://www.nbcnews.com/science/science-news/orcas-sank-three-boats-coast-portugal-dont-call-killer-just-yet-rcna85678 |url-status=live }}</ref> According to the Atlantic Orca Working Group (GTOA) as many as 500 vessels have been damaged between 2020 and 2023.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-05-29 |title=Gladis the killer whale and her gang of orcas out for revenge |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/gladis-whale-orca-boat-attacks-gibraltar-b2347572.html |access-date=2023-07-05 |website=The Independent |language=en |archive-date=June 20, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230620095318/https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/gladis-whale-orca-boat-attacks-gibraltar-b2347572.html |url-status=live }}</ref> In one video, an orca can be seen biting on one of the two rudders ripped from a catamaran near ]. The captain of the vessel reported this was the second attack on a vessel under his command and the orcas focused on the rudders. "Looks like they knew exactly what they are doing. They didn't touch anything else."<ref>{{Cite web |last=Dewan |first=Pandora |date=2023-06-09 |title=Orcas filmed destroying ship's rudder in shocking clip: "Surrounded" |url=https://www.newsweek.com/orcas-filmed-destroying-ship-rudder-shocking-clip-surrounded-1805644 |access-date=2023-07-05 |website=Newsweek |language=en |archive-date=July 5, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230705133639/https://www.newsweek.com/orcas-filmed-destroying-ship-rudder-shocking-clip-surrounded-1805644 |url-status=live }}</ref> After an orca repeatedly rammed a vessel off the coast of Norway in 2023, there is a concern the behavior is spreading to other areas.<ref>{{Cite news |last1=Hoare |first1=Philip |last2=Hoekendijk |first2=Jeroen |date=2023-06-21 |title=Orca rams into yacht off Shetland in first such incident in northern waters |language=en-GB |work=The Guardian |url=https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2023/jun/21/orca-rams-yacht-off-shetland-first-such-incident-northern-waters |access-date=2023-07-04 |issn=0261-3077}}</ref> This has led to recommendations that sailors now carry bags of sand.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-06-19 |title=Sprinkling sand 'deters orcas' according to Cruising Association |url=https://www.pbo.co.uk/news/orca-sand-deterrence-77513 |access-date=2023-07-04 |website=Practical Boat Owner |language=en-US |archive-date=July 4, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230704125251/https://www.pbo.co.uk/news/orca-sand-deterrence-77513 |url-status=live }}</ref> Dropping sand into the water near the rudder is thought to confuse the sonar signal.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Crisp |first=James |date=2023-05-27 |title=Sailors have a new way to stop killer whale attacks |language=en-GB |work=The Telegraph |url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/world-news/2023/05/27/orcas-killer-whales-attacking-boats-strait-gibraltar-sand/ |access-date=2023-07-04 |issn=0307-1235 |archive-date=July 4, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230704125250/https://www.telegraph.co.uk/world-news/2023/05/27/orcas-killer-whales-attacking-boats-strait-gibraltar-sand/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Experts were divided as to whether the behavior was some sort of revenge or protection response to a previous traumatic incident, or playful or frustrated attempts to get a boat's propeller to emit a stream of high-speed water.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.npr.org/2023/06/13/1181693759/orcas-killer-whales-boat-attacks |title=Orcas sank a yacht off Spain — the latest in a slew of such 'attacks' in recent years |date=May 15, 2024 |author=Scott Neuman |website=] |access-date=May 16, 2024 |archive-date=July 8, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230708083723/https://www.npr.org/2023/06/13/1181693759/orcas-killer-whales-boat-attacks |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Attacks on humans by captive orcas=== | |||
| Unlike wild orcas, captive orcas have made nearly two dozen ] since the 1970s, some of which have been fatal.<ref name=abc2006>{{cite web |url=https://abcnews.go.com/GMA/story?id=2690153 |title=ABC News: Killer Whale Attacks SeaWorld Trainer |publisher=ABC News |date=November 30, 2006 |access-date=January 3, 2010 |archive-date=February 28, 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100228172014/http://abcnews.go.com/GMA/story?id=2690153 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>"" {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100403195245/http://edition.cnn.com/2010/US/02/24/killer.whale.trainer.death/index.html |date=April 3, 2010}}, CNN, February 25, 2010, Retrieved September 9, 2010</ref> | |||
| ===Human attacks on orcas=== | |||
| Competition with fishermen also led to orcas being regarded as pests. In the waters of the ] and ], the shooting of orcas was accepted and even encouraged by governments.{{sfn|Obee|Ellis|1992|pp=Chapter 1}} As an indication of the intensity of shooting that occurred until fairly recently, about 25% of the orcas captured in ] for aquariums through 1970 bore bullet scars.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=41}} The U.S. Navy claimed to have deliberately killed hundreds of orcas in Icelandic waters in 1956 with machine guns, rockets, and ]s.<ref>Killer Whales Destroyed: VP-7 Accomplishes Special Task, ''Naval Aviation News'', December 1956, p. 19. Reproduced at {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100619230958/http://seaworld.org/infobooks/KillerWhale/deathkw.html |date=June 19, 2010 }}, SeaWorld/Busch Gardens ANIMALS. Retrieved January 11, 2010</ref><ref>{{cite journal |title=Naval War Declared Against Killer Whales|journal=The Science News-Letter|volume=69|issue=24|page=374|year=1956|jstor=3936619 |doi=10.2307/3936617}}</ref> | |||
| ===Modern Western attitudes=== | |||
| {{See also|Orcas in popular culture}} | |||
| ]'s research team filming orcas in New Zealand]] | |||
| Western attitudes towards orcas have changed dramatically in recent decades. In the mid-1960s and early 1970s, orcas came to much greater public and scientific awareness, starting with the live-capture and display of an orca known as ], a ] harpooned off ] in 1964.{{sfn|Obee|Ellis|1992|pp=Chapter 1}} He was the first ever orca to be studied at close quarters alive, not postmortem. ] at the time, including the first scientific studies of an orca's sound production, led to two articles about him in the journal ''Zoologica''.<ref name=Schevill&Watkins>{{cite journal |last1=Schevill |first1=William |last2=Watkins |first2=William |title=Sound Structure and Directionality in ''Orcinus'' (killer whale) |journal=Zoologica |date=Summer 1966 |volume=51 |issue=2 |pages=71–76 |publisher=]}}</ref><ref name=Newman&McGeer>{{cite journal |last1=Newman |first1=Murray |last2=McGeer |first2=Patrick |title=The Capture and Care of a Killer Whale, ''Orcinus orca'', in British Columbia |journal=Zoologica |date=Summer 1966 |volume=51 |issue=2 |pages=59–70 |publisher=]}}</ref> So little was known at the time, it was nearly two months before the whale's keepers discovered what food (fish) it was willing to eat. To the surprise of those who saw him, Moby Doll was a docile, non-aggressive whale who made no attempts to attack humans.{{sfn|Francis|Hewlett|2007|pp=58–59}} | |||
| ] was successfully returned to her family.|alt=Killer whale wrapped in white cloth on a boat, surrounded by four people. A board braces its dorsal fin.]] | |||
| Between 1964 and 1976, 50 orcas from the Pacific Northwest were captured for display in ], and public interest in the animals grew. In the 1970s, research pioneered by ] led to the discovery of the species' complex social structure, its use of vocal communication, and its extraordinarily stable mother–offspring bonds. Through ] techniques, individuals were named and tracked over decades.{{sfn|Baird|2002|pp=73–80}} | |||
| Bigg's techniques also revealed the Pacific Northwest population was in the low hundreds rather than the thousands that had been previously assumed.{{sfn|Obee|Ellis|1992|pp=Chapter 1}} The southern resident community alone had lost 48 of its members to captivity; by 1976, only 80 remained.{{sfn|Heimlich|Boran|2001|p=11}} In the Pacific Northwest, the species that had unthinkingly been targeted became a cultural icon within a few decades.<ref name=Lyke/> | |||
| The public's growing appreciation also led to growing opposition to whale–keeping in aquarium. Only one whale has been taken in North American waters since 1976. In recent years, the extent of the public's interest in orcas has manifested itself in several high-profile efforts surrounding individuals. Following the success of the 1993 film '']'', the movie's captive star ] was returned to the coast of his native ] in 2002. The director of the International Marine Mammal Project for the ], David Phillips, led the efforts to return Keiko to the Iceland waters.<ref name = Wood>{{cite news|last=Wood|first=Daniel|title=Death of Sea World trainer: Do 'killer whales' belong in theme parks?|url=http://www.csmonitor.com/USA/2010/0224/Death-of-Sea-World-trainer-Do-killer-whales-belong-in-theme-parks|access-date=March 19, 2012|newspaper=The Christian Science Monitor|date=February 24, 2010|archive-date=May 13, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120513095029/http://www.csmonitor.com/USA/2010/0224/Death-of-Sea-World-trainer-Do-killer-whales-belong-in-theme-parks|url-status=live}}</ref> Keiko however did not adapt to the harsh climate of the ], and died a year into his release after contracting ], at the age of 27.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200607115808/https://apnews.com/f4012a2567261d6a6e661c1c636c128b |date=June 7, 2020 }} Associated Press. Published December 13, 2003. Retrieved June 7, 2020.</ref> In 2002, the orphan ] was discovered in ], Washington. She became the first whale to be successfully reintegrated into a wild pod after human intervention, crystallizing decades of research into the vocal behaviour and social structure of the region's orcas.<ref name=autogenerated2>{{Cite news|title=Orphaned orca's reunion with family celebrated|url=https://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/orphaned-orca-s-reunion-with-family-celebrated-1.634335|date=July 13, 2007|publisher=]|access-date=November 6, 2007|archive-date=November 6, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151106234637/http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/orphaned-orca-s-reunion-with-family-celebrated-1.634335|url-status=live}}</ref> The saving of Springer raised hopes that another young orca named ], which had become separated from his pod, could be returned to it. However, his case was marked by controversy about whether and how to intervene, and in 2006, Luna was killed by a boat propeller.<ref>{{Cite news |first=Robert |last=McClure |title=Luna the orca killed by tugboat |url=http://www.seattlepi.com/local/article/Luna-the-orca-killed-by-tugboat-1198168.php |work=Seattle Post-Intelligencer |publisher=Hearst Corporation |location=Seattle, Washington |date=March 11, 2006 |access-date=April 8, 2009 |archive-date=August 11, 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110811030505/http://www.seattlepi.com/local/article/Luna-the-orca-killed-by-tugboat-1198168.php |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Whaling=== | |||
| {{Main|Whaling}} | |||
| ] swims alongside a ], flanking a whale calf. The boat is being towed by a harpooned whale (not visible here), near Eden, Australia.|alt=A killer whale swims alongside a whaling boat, with a smaller whale in between. Two men are standing, the harpooner in the bow and a steersman on the aft rudder, while four oarsmen are seated.]] | |||
| The earliest known records of commercial hunting of orcas date to the 18th century in Japan. During the 19th and early 20th centuries, the global ] industry caught immense numbers of ] and sperm whales, but largely ignored orcas because of their limited amounts of ], their smaller populations, and the difficulty of taking them.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|p=39}} Once the stocks of larger species were depleted, orcas were targeted by commercial whalers in the mid-20th century. Between 1954 and 1997, Japan took 1,178 orcas (although the ] claims that there had been domestic catches of about 1,600 whales between late 1940s to 1960s<ref>{{cite journal|year=1998|title=海域自然環境保全基礎調査 - 海棲動物調査報告書, (2)- 19. シャチ ''Orcinus orca'' (Limaeus,1758)マイルカ科|url=http://www.biodic.go.jp/reports2/5th/kaisei_h10/5_kaisei_h10.pdf|page=54|journal=自然環境保全基礎調査|access-date=January 14, 2015|archive-date=July 17, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150717041428/http://www.biodic.go.jp/reports2/5th/kaisei_h10/5_kaisei_h10.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref>) and Norway took 987.{{sfn|Obee|Ellis|1992|p=34}} Extensive hunting of orcas, including an ] catch of 916 in 1979–80 alone, prompted the ] to recommend a ban on commercial hunting of the species pending further research.{{sfn|Obee|Ellis|1992|p=34}} Today, no country carries out a substantial hunt, although ] and ] permit small subsistence hunts (see ]). Other than commercial hunts, orcas were hunted along Japanese coasts out of public concern for potential conflicts with fisheries. Such cases include a semi-resident male-female pair in ] and ] being killed in the ] in 1957,<ref name=OSAKACEA>{{cite web|publisher=Osaka College of Eco & Animals|year=2011|script-title=ja:シャチ騒動|url=http://cblog-eco.oca.ac.jp/blog/2011/10/post-aa1b.html|access-date=December 24, 2014|language=ja|archive-date=December 24, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141224113540/http://cblog-eco.oca.ac.jp/blog/2011/10/post-aa1b.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|publisher=The Whale Laboratory of ]|year=2014|title=Stranding Base (1901–2012) for Hyogo Prefecture|url=http://whalelab.org/HyogoPRF.htm|access-date=December 24, 2014|archive-date=December 24, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141224112918/http://whalelab.org/HyogoPRF.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> the killing of five whales from a pod of 11 members that swam into ] in 1970,<ref>{{cite web|publisher=The Whale Laboratory of ]|year=2014|title=Stranding Date Base (1901-2012) for Chiba Prefecture|url=http://whalelab.org/ChibaPRF.htm|access-date=January 9, 2015|archive-date=January 9, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150109080045/http://whalelab.org/ChibaPRF.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> and a catch record in southern Taiwan in the 1990s.<ref name=SmallCetaceansChina>{{cite journal|author=Kaiya|first1= Z.|last2=Leatherwood|first2= S.|last3=Jefferson |first3=A. T.|title=Records of Small Cetaceans in Chinese Waters: A Review|journal=Asian Marine Biology|volume=12|year=1995|pages=119–139|url=https://swfsc.noaa.gov/uploadedFiles/Divisions/PRD/Publications/Zhouetal95(26).pdf|access-date=December 24, 2014|archive-date=July 17, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150717073608/https://swfsc.noaa.gov/uploadedFiles/Divisions/PRD/Publications/Zhouetal95(26).pdf|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|author=Kaiya|first1= Z.|last2=Leatherwood |first2=S.|last3=Jefferson|first3= A. T. |year=2002 |title=Report of the Second Workshop on The Biology and Conservation of Small Cetaceans and Dugongs of South-East Asia |journal=CMS Technical Series Publication Nº 9 at Convention on Migratory Species |url=http://www.iucn-csg.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/Perrinetal.0589.pdf |editor=Perrin F. W. |editor2=Reeves R. R. |editor3=Dolar L. L. M. |editor4=Jefferson A. T. |editor5=Marsh H. |editor6=Wang Y. J. |editor7=Estacion J. |access-date=December 24, 2014 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304045901/http://www.iucn-csg.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/Perrinetal.0589.pdf |archive-date=March 4, 2016 }}</ref> | |||
| ====Cooperation with humans==== | |||
| Orcas have helped humans hunting other whales.<ref name="scavenging">{{cite journal|last1=Reeves|first1=Randall|last2=Whitehead|first2=Hal|title=Killer whales and whaling: the scavenging hypothesis|journal=Biology Letters|volume=1|issue=4|pages=415–418|year=2005|pmid=17148221|pmc=1626385|doi=10.1098/rsbl.2005.0348}}</ref> One well-known example was the ], including the male known as ]. Whalers more often considered them a nuisance, however, as orcas would gather to scavenge meat from the whalers' catch.<ref name="scavenging"/> Some populations, such as in Alaska's ], may have been reduced significantly by whalers shooting them in retaliation.<ref name=baird/> | |||
| ===Whale watching=== | |||
| ] continues to increase in popularity, but may have some problematic impacts on orcas. Exposure to exhaust gases from large amounts of vessel traffic is causing concern for the overall health of the 75 remaining southern resident orcas (SRKWs) left as of early 2019.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.bewhalewise.org/|title=Home|website=Be Whale Wise|access-date=October 31, 2019|archive-date=October 31, 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191031050019/https://www.bewhalewise.org/|url-status=live}}</ref> This population is followed by approximately 20 vessels for 12 hours a day during the months May–September.<ref name="Lachmuth et al. 2011">{{cite journal |last1=Lachmuth |first1=Cara L. |last2=Barrett-Lennard |first2=Lance G. |last3=Steyn |first3=D. Q. |last4=Milsom |first4=William K. |title=Estimation of southern resident killer whale exposure to exhaust emissions from whale-watching vessels and potential adverse health effects and toxicity thresholds |journal=Marine Pollution Bulletin |date=April 2011 |volume=62 |issue=4 |pages=792–805 |doi=10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.01.002 |pmid=21276987|bibcode=2011MarPB..62..792L }}</ref> Researchers discovered that these vessels are in the line of sight for these whales for 98–99.5% of daylight hours.<ref name="Lachmuth et al. 2011"/> With so many vessels, the air quality around these whales deteriorates and impacts their health. Air pollutants that bind with exhaust fumes are responsible for the activation of the cytochrome P450 1A gene family.<ref name="Lachmuth et al. 2011"/> Researchers have successfully identified this gene in skin biopsies of live whales and also the lungs of deceased whales. A direct correlation between activation of this gene and the air pollutants can not be made because there are other known factors that will induce the same gene. Vessels can have either wet or dry exhaust systems, with wet exhaust systems leaving more pollutants in the water due to various gas solubility. A modelling study determined that the lowest-observed-adverse-effect-level (LOAEL) of exhaust pollutants was about 12% of the human dose.<ref name="Lachmuth et al. 2011"/> | |||
| As a response to this, in 2017 boats off the British Columbia coast now have a minimum approach distance of 200 metres compared to the previous 100 metres. This new rule complements Washington State's minimum approach zone of 180 metres that has been in effect since 2011. If a whale approaches a vessel it must be placed in neutral until the whale passes. The World Health Organization has set air quality standards in an effort to control the emissions produced by these vessels.<ref>{{Cite web|url = https://baleinesendirect.org/en/boats-to-maintain-greater-distance-from-killer-whales/|title = Boats to Maintain Greater Distance from Killer Whales | Whales online|date = November 8, 2017|access-date = March 14, 2019|archive-date = March 30, 2019|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20190330230118/https://baleinesendirect.org/en/boats-to-maintain-greater-distance-from-killer-whales/|url-status = live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Captivity=== | |||
| {{Main|Captive orcas}} | |||
| ], at the ], was one of the oldest orcas in captivity.]] | |||
| The orca's ], trainability, striking appearance, playfulness in captivity and sheer size have made it a popular exhibit at aquaria and ]s. From 1976 to 1997, 55 whales were taken from the wild in Iceland, 19 from Japan, and three from Argentina. These figures exclude animals that died during capture. Live captures fell dramatically in the 1990s, and by 1999, about 40% of the 48 animals on display in the world were captive-born.{{sfn|NMFS|2005|pp=43–44}} | |||
| Organizations such as ] and the ] campaign against the practice of keeping them in captivity. In captivity, they often develop pathologies, such as the ] collapse seen in 60–90% of captive males. Captives have vastly reduced life expectancies, on average only living into their 20s.{{efn|Although there are examples of killer whales living longer, including several over 30 years old, and two captive orcas (Corky II and Lolita) are in their mid-40s.}} That said, a 2015 study coauthored by staff at ] and the ] suggested no significant difference in survivorship between free-ranging and captive orcas.<ref name=robeck/> However, in the wild, females who survive infancy live 46 years on average, and up to 70–80 years in rare cases. Wild males who survive infancy live 31 years on average, and up to 50–60 years.<ref>{{cite web|author=Rose|first1= N. A.|year=2011|url=http://www.hsi.org/assets/pdfs/orca_white_paper.pdf|title=Killer Controversy: Why Orcas Should No Longer Be Kept in Captivity|publisher=Humane Society International and the Humane Society of the United States|access-date=December 21, 2014|archive-date=December 30, 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171230032203/http://www.hsi.org/assets/pdfs/orca_white_paper.pdf|url-status=live}}</ref> Captivity usually bears little resemblance to wild habitat, and captive whales' social groups are foreign to those found in the wild. Critics claim captive life is stressful due to these factors and the requirement to perform ]s that are not part of wild orca behaviour, see ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.wdcs.org/submissions_bin/cap-orc-glo-000016.pdf |title=Orcas in captivity |publisher=Whale and Dolphin Conservation Society |access-date=January 26, 2010 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100706134353/http://www.wdcs.org/submissions_bin/cap-orc-glo-000016.pdf |archive-date=July 6, 2010 }}</ref> Wild orcas may travel up to {{convert|160|km|mi|-1}} in a day, and critics say the animals are too big and intelligent to be suitable for captivity.<ref name=cbs2010>Associated Press. ''CBS News'', March 1, 2010. Retrieved March 7, 2010</ref> Captives occasionally act aggressively towards themselves, their tankmates, or humans, which critics say is a result of ].<ref name=abc2006 /> Between 1991 and 2010, the bull orca known as ] was involved in the death of three people, and was featured in the critically acclaimed 2013 film ].<ref name="RT review 1">{{cite web|url=http://www.rottentomatoes.com/m/blackfish_2013|title=Blackfish|website=]|access-date=November 23, 2013|archive-date=November 21, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131121215751/http://www.rottentomatoes.com/m/blackfish_2013/|url-status=live}}</ref> Tilikum lived at SeaWorld from 1992 until his death in 2017.<ref>{{cite book|chapter=The Killer in the Pool|first=Tim|last=Zimmerman|title=The Best American Sampler 2011|page=336|publisher=Houghton Mifflin Harcourt|year=2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/1999/07/07/us/corpse-is-found-on-whale.html|title=Corpse Is Found on Whale|newspaper=]|date=July 7, 1999|access-date=September 11, 2011|archive-date=June 13, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120613184958/http://www.nytimes.com/1999/07/07/us/corpse-is-found-on-whale.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| In March 2016, SeaWorld announced that they would be ending their orca breeding program and their theatrical shows.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://news.nationalgeographic.com/2016/03/160317-seaworld-orcas-killer-whales-captivity-breeding-shamu-tilikum/|title=SeaWorld to End Controversial Orca Shows and Breeding|date=March 17, 2016|website=National Geographic News|access-date=September 27, 2016|archive-date=April 20, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160420052351/http://news.nationalgeographic.com/2016/03/160317-seaworld-orcas-killer-whales-captivity-breeding-shamu-tilikum/|url-status=dead}}</ref> However, as of 2020, theatrical shows featuring orcas are still ongoing.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Stevens|first=Blair|date=2020-06-11|title=Even years after Blackfish, SeaWorld still has Orcas|url=https://8forty.ca/2020/06/10/even-years-after-blackfish-seaworld-still-has-orcas/|access-date=2020-12-23|language=en|archive-date=December 13, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201213055553/https://8forty.ca/2020/06/10/even-years-after-blackfish-seaworld-still-has-orcas/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Portal|Cetaceans|Mammals|Marine life|Oceans}} | |||
| *] | |||
| **] | |||
| ***''] melvillei'' – occupied a similar ecological niche | |||
| *] – a New Zealand biologist who swims with wild orcas | |||
| ==Footnotes== | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| {{Reflist|group=Note}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ===Works cited=== | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Baird |first=Robin W. |title=Killer Whales of the World |publisher=] |location=], ] |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Rjksm-5-ap4C&pg=PP1 |year=2002 |isbn=978-0-7603-2654-1}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=Carwardine |first=Mark |year=2001 |title=Killer Whales |location=London |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7894-8266-2|url=https://archive.org/details/killerwhales00carw}} | |||
| *{{Cite encyclopedia |last=Ford |first=John K. B. |year=2002 |chapter=Killer Whale |pages= |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2rkHQpToi9sC&pg=PP1 |encyclopedia=Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals |publisher=] |isbn=0-12-551340-2 |url=https://archive.org/details/encyclopediaofma2002unse/page/669 }} | |||
| *{{Cite book|last1=Ford |first1=John K. B. |last2=Ellis |first2=Graeme M. |last3=Balcomb |first3=Kenneth C. |title=Killer Whales |edition=Second|year=2000|publisher=UBC Press|location=Vancouver, BC|isbn=978-0-7748-0800-2|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yTmbu_CFomAC&pg=PP1}} | |||
| *{{Cite journal |last1=Ford |first1=John K. B. |last2=Ellis |first2=Graeme M. |year=2006 |pages=185–199 |title=Selective foraging by fish-eating killer whales ''Orcinus orca'' in British Columbia |journal=] |volume=316 |doi=10.3354/meps316185 |bibcode=2006MEPS..316..185F|doi-access=free }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last1=Francis |first1=Daniel |first2=Gil |last2=Hewlett |title=Operation Orca: Springer, Luna and the Struggle to Save West Coast Killer Whales |year=2007 |publisher=] |location=], ] |isbn=978-1-55017-426-7}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last1=Heimlich |first1=Sara |last2=Boran |first2=James |year=2001 |title=Killer Whales |location=], ] |publisher=] |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lQ9RUAQgEiIC&pg=PP1 |isbn=978-0-89658-545-4 }}{{Dead link|date=October 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last1=Heptner |first1=V. G. |last2=Nasimovich |first2=A. A. |last3=Bannikov |first3=A. G. |last4=Hoffmann |first4=Robert S. |url=https://archive.org/details/mammalsofsov231996gept |title=Mammals of the Soviet Union |volume=II, part 3 |year=1996 |publisher=] and National Science Foundation |location=] |isbn=978-1-886106-81-9}} | |||
| *{{cite web |publisher=] (NMFS) Northwest Regional Office |author=NMFS |year=2005 |url=http://www.nwr.noaa.gov/Marine-Mammals/Whales-Dolphins-Porpoise/Killer-Whales/Conservation-Planning/upload/SRKW-propConsPlan.pdf |title=Conservation Plan for Southern Resident Killer Whales (''Orcinus orca'') |location=], U.S. |access-date=January 2, 2009 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080626121719/http://www.nwr.noaa.gov/Marine-Mammals/Whales-Dolphins-Porpoise/Killer-Whales/Conservation-Planning/upload/SRKW-propConsPlan.pdf |archive-date=June 26, 2008 |url-status=dead}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |isbn=978-1-55110-034-0 |last1=Obee |first1=Bruce |first2=Graeme |last2=Ellis |title=Guardians of the Whales: The Quest to Study Whales in the Wild |editor=Elaine Jones |publisher=Whitecap Books |location=], ] |year=1992}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| *{{cite magazine|title=The Whales Called "Killer"|magazine=]|first=Erich|last=Hoyt|pages=220–237|volume=166|issue=2|date=August 1984|issn=0027-9358|oclc=643483454}} | |||
| *{{citation |last=Hoyt |first=Erich |year=1998 |title=Orca: The Whale Called Killer Camden House Publishing |publisher=Camden House |isbn=978-0-920656-25-9 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/orca00eric_0 }} | |||
| *{{Cite book |title=Behavioral Biology of Killer Whales |first1=B. C. |last1=Kirkevold |first2=J. S.|last2= Lockard |publisher=] |year=1986 |isbn=978-0-8451-3100-8}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| *''Orca: The Whale Called Killer'', Erich Hoyt, Camden House Publishing, ISBN 0920656250 | |||
| {{Wiktionary}} | |||
| *''Killer Whale'', John K.B. Ford, pp669–675 in the ''Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals'', Academic Press, ISBN 0125513402 | |||
| {{EB1911 poster|Grampus}} | |||
| *''National Audubon Society Guide to Marine Mammals of the World'', Reeves, Stewart, Clapham and Powell. Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 0375411410 | |||
| {{Commons|Orcinus orca}} | |||
| *''Kharakter vzaimootnoshenii kasatok i drugikh kitoobraznykh'' in ''Morskie mlekopitayushchie'' (in Russian, transliterations vary). "The nature of interrelationships between Killer Whales and Other Cetaceans" I.V.Shevchenko, 1975 pp173–175. (The author describes his discovery of Orca cannibalism). | |||
| {{Wikispecies|Orcinus orca}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20000815053430/http://www.orca-live.net/ |date=August 15, 2000 }} – Orcas in Johnstone Strait, British Columbia | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130709100220/http://www.orcasound.net/ |date=July 9, 2013 }} – Listen live to orcas in Washington State, U.S. | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230219193544/https://animals.howstuffworks.com/mammals/orca-killer-whale.htm |date=February 19, 2023 }}, HowStuffWorks.com, article by Jacob Silverman | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120405214004/http://www.gadling.com/2011/03/27/killer-whale-devours-great-white-shark/ |date=April 5, 2012 }} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210317071533/https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=1&v=IZTSd-CMEno&feature=emb_title |date=March 17, 2021 }}, off the coast of San Clemente | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200424035711/https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sRFp3kEBV-A&gl=US&hl=en |date=April 24, 2020 }} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191116062347/https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8KCQrLA3UKw&gl=US&hl=en |date=November 16, 2019 }} | ] | |||
| {{Cetacea|O.}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Taxonbar |from=Q26843}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{Featured article}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:05, 26 December 2024
Largest living species of dolphin For other uses, see Orca (disambiguation). "Killer Whale" redirects here. For The Avengers episode, see Killer Whale (The Avengers). For 1962 tokusatsu film, see Killer Whale (film).
| Orca Killer whale Temporal range: Pliocene to recent PreꞒ Ꞓ O S D C P T J K Pg N | |
|---|---|

| |
| Transient orcas near Unimak Island, eastern Aleutian Islands, Alaska | |

| |
| 5.4 meter (18 foot) female killer whale compared to 1.8 meter (5 foot 11 inches) human scuba diver | |
| Conservation status | |
 Data Deficient (IUCN 3.1) | |
| CITES Appendix II (CITES) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Infraorder: | Cetacea |
| Family: | Delphinidae |
| Genus: | Orcinus |
| Species: | O. orca |
| Binomial name | |
| Orcinus orca (Linnaeus, 1758) | |
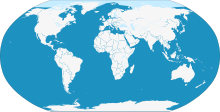
| |
| Orcinus orca range | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The orca (Orcinus orca), or killer whale, is a toothed whale and the largest member of the oceanic dolphin family. It is the only extant species in the genus Orcinus and is recognizable by its black-and-white patterned body. A cosmopolitan species, it is found in diverse marine environments, from Arctic to Antarctic regions to tropical seas.
Orcas are apex predators with a diverse diet. Individual populations often specialize in particular types of prey. This includes a variety of fish, sharks, rays, and marine mammals such as seals and other dolphins and whales. They are highly social; some populations are composed of highly stable matrilineal family groups (pods). Their sophisticated hunting techniques and vocal behaviors, often specific to a particular group and passed along from generation to generation, are considered to be manifestations of animal culture.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature assesses the orca's conservation status as data deficient because of the likelihood that two or more orca types are separate species. Some local populations are considered threatened or endangered due to prey depletion, habitat loss, pollution (by PCBs), capture for marine mammal parks, and conflicts with human fisheries. In late 2005, the southern resident orcas were placed on the U.S. Endangered Species list.
Orcas are not usually a threat to humans, and no fatal attack has ever been documented in their natural habitat. There have been cases of captive orcas killing or injuring their handlers at marine theme parks.
Naming
Orcas, despite being dolphins, are commonly called 'killer whales' due to a mistranslation of the Spanish 'asesino de ballenas' (literally 'whale killer'), reflecting their historical predation on whales. Since the 1960s, the use of "orca" instead of "killer whale" has steadily grown in common use.
The genus name Orcinus means 'of the kingdom of the dead', or 'belonging to Orcus'. Ancient Romans originally used orca (pl. orcae) for these animals, possibly borrowing Ancient Greek ὄρυξ (óryx), which referred (among other things) to a whale species, perhaps a narwhal. As part of the family Delphinidae, the species is more closely related to other oceanic dolphins than to other whales.
They are sometimes referred to as 'blackfish', a name also used for other whale species. 'Grampus' is a former name for the species, but is now seldom used. This meaning of 'grampus' should not be confused with the genus Grampus, whose only member is Risso's dolphin.
Taxonomy
 Orcinus citoniensis fossil, an extinct species of the same genus, Museo Capellini in Bologna
Orcinus citoniensis fossil, an extinct species of the same genus, Museo Capellini in Bologna Modern orca skeleton, Naturalis, Leiden
Modern orca skeleton, Naturalis, Leiden 3D model of skeleton
3D model of skeleton
Orcinus orca is the only recognized extant species in the genus Orcinus, and one of many animal species originally described by Carl Linnaeus in his landmark 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. Konrad Gessner wrote the first scientific description of an orca in his Piscium & aquatilium animantium natura of 1558, part of the larger Historia animalium, based on examination of a dead stranded animal in the Bay of Greifswald that had attracted a great deal of local interest.
The orca is one of 35 species in the oceanic dolphin family, which first appeared about 11 million years ago. The orca lineage probably branched off shortly thereafter. Although it has morphological similarities with the false killer whale, the pygmy killer whale and the pilot whales, a study of cytochrome b gene sequences indicates that its closest extant relatives are the snubfin dolphins of the genus Orcaella. However, a more recent (2018) study places the orca as a sister taxon to the Lissodelphininae, a clade that includes Lagenorhynchus and Cephalorhynchus. In contrast, a 2019 phylogenetic study found the orca to be the second most basal member of the Delphinidae, with only the Atlantic white-sided dolphin (Leucopleurus acutus) being more basal.
Types
Further information: Orca types and populationsThe three to five types of orcas may be distinct enough to be considered different races, subspecies, or possibly even species (see Species problem). The IUCN reported in 2008, "The taxonomy of this genus is clearly in need of review, and it is likely that O. orca will be split into a number of different species or at least subspecies over the next few years." Although large variation in the ecological distinctiveness of different orca groups complicate simple differentiation into types, research off the west coast of North America has identified fish-eating "residents", mammal-eating "transients" and "offshores". Other populations have not been as well studied, although specialized fish and mammal eating orcas have been distinguished elsewhere. Mammal-eating orcas in different regions were long thought likely to be closely related, but genetic testing has refuted this hypothesis.
A 2024 study supported the elevation of Eastern North American resident and transient orcas as distinct species, O. ater and O. rectipinnus respectively. The Society for Marine Mammalogy declined to recognize the two species, citing uncertainty as to whether the types constituted unique species or subspecies. "Pending a more complete global review and revision", the Society provisionally recognized them as subspecies Orcinus orca ater and O. o. rectipinnus, with O. o. orca as the nominate subspecies.
Four types have been documented in the Antarctic, Types A–D. Two dwarf species, named Orcinus nanus and Orcinus glacialis, were described during the 1980s by Soviet researchers, but most cetacean researchers are skeptical about their status. Complete mitochondrial sequencing indicates the two Antarctic groups (types B and C) should be recognized as distinct species, as should the North Pacific transients, leaving the others as subspecies pending additional data. A 2019 study of Type D orcas also found them to be distinct from other populations and possibly even a unique species.
Characteristics

Orcas are the largest extant members of the dolphin family. Males typically range from 6 to 8 m (20 to 26 ft) long and weigh in excess of 6 t (5.9 long tons; 6.6 short tons). Females are smaller, generally ranging from 5 to 7 m (16 to 23 ft) and weighing about 3 to 4 t (3.0 to 3.9 long tons; 3.3 to 4.4 short tons). Orcas may attain larger sizes as males have been recorded at 9.8 m (32 ft) and females at 8.5 m (28 ft). Large males can reach a weight of over 10 t (9.8 long tons; 11 short tons). Calves at birth weigh about 180 kg (400 lb) and are about 2.4 m (7 ft 10 in) long. The skeleton of the orca is typical for an oceanic dolphin, but more robust.
With their distinctive pigmentation, adult orcas are seldom confused with any other species. When seen from a distance, juveniles can be confused with false killer whales or Risso's dolphins. The orca is mostly black but with sharply bordered white areas. The entire lower jaw is white and from here, the colouration stretches across the underside to the genital area; narrowing and expanding some, and extending into lateral flank patches close to the end. The tail fluke (fin) is also white on the underside, while the eyes have white oval-shaped patches behind and above them, and a grey or white "saddle patch" exists behind the dorsal fin and across the back. Males and females also have different patterns of black and white skin in their genital areas. In newborns, the white areas are yellow or orange coloured. Antarctic orcas may have pale grey to nearly white backs. Some Antarctic orcas are brown and yellow due to diatoms in the water. Both albino and melanistic orcas have been documented.

Orca pectoral fins are large and rounded, resembling paddles, with those of males significantly larger than those of females. Dorsal fins also exhibit sexual dimorphism, with those of males about 1.8 m (5 ft 11 in) high, more than twice the size of the female's, with the male's fin more like an elongated isosceles triangle, whereas the female's is more curved. In the skull, adult males have longer lower jaws than females, as well as larger occipital crests. The snout is blunt and lacks the beak of other species. The orca's teeth are very strong, and its jaws exert a powerful grip; the upper teeth fall into the gaps between the lower teeth when the mouth is closed. The firm middle and back teeth hold prey in place, while the front teeth are inclined slightly forward and outward to protect them from powerful jerking movements.
Orcas have good eyesight above and below the water, excellent hearing, and a good sense of touch. They have exceptionally sophisticated echolocation abilities, detecting the location and characteristics of prey and other objects in the water by emitting clicks and listening for echoes, as do other members of the dolphin family. The mean body temperature of the orca is 36 to 38 °C (97 to 100 °F). Like most marine mammals, orcas have a layer of insulating blubber ranging from 7.6 to 10 cm (3.0 to 3.9 in) thick beneath the skin. The pulse is about 60 heartbeats per minute when the orca is at the surface, dropping to 30 beats/min when submerged.
An individual orca can often be identified from its dorsal fin and saddle patch. Variations such as nicks, scratches, and tears on the dorsal fin and the pattern of white or grey in the saddle patch are unique. Published directories contain identifying photographs and names for hundreds of North Pacific animals. Photographic identification has enabled the local population of orcas to be counted each year rather than estimated, and has enabled great insight into life cycles and social structures.
Range and habitat
Further information: Orca types and populations
Orcas are found in all oceans and most seas. Due to their enormous range, numbers, and density, relative distribution is difficult to estimate, but they clearly prefer higher latitudes and coastal areas over pelagic environments. Areas which serve as major study sites for the species include the coasts of Iceland, Norway, the Valdés Peninsula of Argentina, the Crozet Islands, New Zealand and parts of the west coast of North America, from California to Alaska. Systematic surveys indicate the highest densities of orcas (>0.40 individuals per 100 km) in the northeast Atlantic around the Norwegian coast, in the north Pacific along the Aleutian Islands, the Gulf of Alaska and in the Southern Ocean off much of the coast of Antarctica. They are considered "common" (0.20–0.40 individuals per 100 km) in the eastern Pacific along the coasts of British Columbia, Washington and Oregon, in the North Atlantic Ocean around Iceland and the Faroe Islands.

In the Antarctic, orcas range up to the edge of the pack ice and are believed to venture into the denser pack ice, finding open leads much like beluga whales in the Arctic. However, orcas are merely seasonal visitors to Arctic waters, and do not approach the pack ice in the summer. With the rapid Arctic sea ice decline in the Hudson Strait, their range now extends deep into the northwest Atlantic. Occasionally, orcas swim into freshwater rivers. They have been documented 100 mi (160 km) up the Columbia River in the United States. They have also been found in the Fraser River in Canada and the Horikawa River in Japan.
Migration patterns are poorly understood. Each summer, the same individuals appear off the coasts of British Columbia and Washington. Despite decades of research, where these animals go for the rest of the year remains unknown. Transient pods have been sighted from southern Alaska to central California.
Population
Worldwide population estimates are uncertain, but recent consensus suggests a minimum of 50,000 (2006). Local estimates include roughly 25,000 in the Antarctic, 8,500 in the tropical Pacific, 2,250–2,700 off the cooler northeast Pacific and 500–1,500 off Norway. Japan's Fisheries Agency estimated in the 2000s that 2,321 orcas were in the seas around Japan.
Feeding
 Tail-slapping in Vestfjorden, Norway
Tail-slapping in Vestfjorden, Norway Resident orca pursuing a chinook salmon
Resident orca pursuing a chinook salmon
Orcas are apex predators, meaning that they themselves have no natural predators. They are sometimes called "wolves of the sea", because they hunt in groups like wolf packs. Orcas hunt varied prey including fish, cephalopods, mammals, seabirds, and sea turtles. Different populations or ecotypes may specialize, and some can have a dramatic impact on prey species. However, whales in tropical areas appear to have more generalized diets due to lower food productivity. Orcas spend most of their time at shallow depths, but occasionally dive several hundred metres depending on their prey.
Fish
Fish-eating orcas prey on around 30 species of fish. Some populations in the Norwegian and Greenland sea specialize in herring and follow that fish's autumnal migration to the Norwegian coast. Salmon account for 96% of northeast Pacific residents' diet, including 65% of large, fatty Chinook. Chum salmon are also eaten, but smaller sockeye and pink salmon are not a significant food item. Depletion of specific prey species in an area is, therefore, cause for concern for local populations, despite the high diversity of prey. On average, an orca eats 227 kilograms (500 lb) each day. While salmon are usually hunted by an individual whale or a small group, herring are often caught using carousel feeding: the orcas force the herring into a tight ball by releasing bursts of bubbles or flashing their white undersides. They then slap the ball with their tail flukes, stunning or killing up to 15 fish at a time, then eating them one by one. Carousel feeding has been documented only in the Norwegian orca population, as well as some oceanic dolphin species.
In New Zealand, sharks and rays appear to be important prey, including eagle rays, long-tail and short-tail stingrays, common threshers, smooth hammerheads, blue sharks, basking sharks, and shortfin makos. With sharks, orcas may herd them to the surface and strike them with their tail flukes, while bottom-dwelling rays are cornered, pinned to the ground and taken to the surface. In other parts of the world, orcas have preyed on broadnose sevengill sharks, whale sharks, and even great white sharks. Competition between orcas and white sharks is probable in regions where their diets overlap. The arrival of orcas in an area can cause white sharks to flee and forage elsewhere. Orcas appear to target the liver of sharks. In one case a single orca was observed killing and eating a great white shark on its own.
Mammals and birds
Orcas are sophisticated and effective predators of marine mammals. They are recorded to prey on other cetacean species, usually smaller dolphins and porpoises such as common dolphins, bottlenose dolphins, Pacific white-sided dolphins, dusky dolphins, harbour porpoises and Dall's porpoises. While hunting these species, orcas usually have to chase them to exhaustion. For highly social species, orca pods try to separate an individual from its group. Larger groups have a better chance of preventing their prey from escaping, which is killed by being thrown around, rammed and jumped on. Arctic orcas may attack beluga whales and narwhals stuck in pools enclosed by sea ice, the former are also driven into shallower water where juveniles are grabbed. By contrast, orcas appear to be wary of pilot whales, which have been recorded to mob and chase them. Nevertheless, possible predation on long-finned pilot whales has been recorded in Iceland, and one study suggests short-finned pilot whales are among Caribbean Orcas' prey. Killer whales have been recorded attacking short-finned pilot whales in Peru as well.

Orcas also prey on larger species such as sperm whales, grey whales, humpback whales and minke whales. On three separate occasions in 2019 orcas were recorded to have killed blue whales off the south coast of Western Australia, including an estimated 18–22-meter (59–72 ft) individual. Large whales require much effort and coordination to kill and orcas often target calves. A hunt begins with a chase followed by a violent attack on the exhausted prey. Large whales often show signs of orca attack via tooth rake marks. Pods of female sperm whales sometimes protect themselves by forming a protective circle around their calves with their flukes facing outwards, using them to repel the attackers. There is also evidence that humpback whales will defend against or mob orcas who are attacking either humpback calves or juveniles as well as members of other species.
Prior to the advent of industrial whaling, great whales may have been the major food source for orcas. The introduction of modern whaling techniques may have aided orcas by the sound of exploding harpoons indicating the availability of prey to scavenge, and compressed air inflation of whale carcasses causing them to float, thus exposing them to scavenging. However, the devastation of great whale populations by unfettered whaling has possibly reduced their availability for orcas, and caused them to expand their consumption of smaller marine mammals, thus contributing to the decline of these as well.
 Orca beaching to capture sea lion along Valdes Peninsula
Orca beaching to capture sea lion along Valdes Peninsula Orcas swimming in close synchronization to create a wave to wash the crabeater seal off the floe
Orcas swimming in close synchronization to create a wave to wash the crabeater seal off the floe
Other marine mammal prey includes seal species such as harbour seals, elephant seals, California sea lions, Steller sea lions, South American sea lions and walruses. Often, to avoid injury, orcas disable their prey before killing and eating it. This may involve throwing it in the air, slapping it with their tails, ramming it, or breaching and landing on it. In steeply banked beaches off Península Valdés, Argentina, and the Crozet Islands, orcas feed on South American sea lions and southern elephant seals in shallow water, even beaching temporarily to grab prey before wriggling back to the sea. Beaching, usually fatal to cetaceans, is not an instinctive behaviour, and can require years of practice for the young. Orcas can then release the animal near juvenile whales, allowing the younger whales to practice the difficult capture technique on the now-weakened prey. In the Antarctic, type B orcas hunt Weddell seals and other prey by "wave-hunting". They "spy-hop" to locate them on resting on ice floes, and then swim in groups to create waves that wash over the floe. This washes the prey into the water, where other orcas lie in wait.
In the Aleutian Islands, a decline in sea otter populations in the 1990s was controversially attributed by some scientists to orca predation, although with no direct evidence. The decline of sea otters followed a decline in seal populations, which in turn may be substitutes for their original prey, now decimated by industrial whaling. Orcas have been observed preying on terrestrial mammals, such as moose swimming between islands off the northwest coast of North America. Orca cannibalism has also been reported based on analysis of stomach contents, but this is likely to be the result of scavenging remains dumped by whalers. One orca was also attacked by its companions after being shot. Although resident orcas have never been observed to eat other marine mammals, they occasionally harass and kill porpoises and seals for no apparent reason. Some dolphins recognize resident orcas as harmless and remain in the same area.
Orcas do consume seabirds but are more likely to kill and leave them uneaten. Penguin species recorded as prey in Antarctic and sub-Antarctic waters include gentoo penguins, chinstrap penguins, king penguins and rockhopper penguins. Orcas in many areas may prey on cormorants and gulls. A captive orca at Marineland of Canada discovered it could regurgitate fish onto the surface, attracting sea gulls, and then eat the birds. Four others then learned to copy the behaviour.
Behaviour

Day-to-day orca behaviour generally consists of foraging, travelling, resting and socializing. Orcas frequently engage in surface behaviour such as breaching (jumping completely out of the water) and tail-slapping. These activities may have a variety of purposes, such as courtship, communication, dislodging parasites, or play. Spyhopping is a behaviour in which a whale holds its head above water to view its surroundings. Resident orcas swim alongside porpoises and other dolphins.
Orcas will engage in surplus killing, that is, killing that is not designed to be for food. As an example, a BBC film crew witnessed orca in British Columbia playing with a male Steller sea lion to exhaustion, but not eating it.
Some orcas have been observed swimming with dead salmon on their heads, resembling hats.
Social structure
Orcas are notable for their complex societies. Only elephants and higher primates live in comparably complex social structures. Due to orcas' complex social bonds, many marine experts have concerns about how humane it is to keep them in captivity.
Resident orcas in the eastern North Pacific live in particularly complex and stable social groups. Unlike any other known mammal social structure, resident whales live with their mothers for their entire lives. These family groups are based on matrilines consisting of the eldest female (matriarch) and her sons and daughters, and the descendants of her daughters, etc. The average size of a matriline is 5.5 animals. Because females can reach age 90, as many as four generations travel together. These matrilineal groups are highly stable. Individuals separate for only a few hours at a time, to mate or forage. With one exception, an orca named Luna, no permanent separation of an individual from a resident matriline has been recorded.

Closely related matrilines form loose aggregations called pods, usually consisting of one to four matrilines. Unlike matrilines, pods may separate for weeks or months at a time. DNA testing indicates resident males nearly always mate with females from other pods. Clans, the next level of resident social structure, are composed of pods with similar dialects, and common but older maternal heritage. Clan ranges overlap, mingling pods from different clans. The highest association layer is the community, which consists of pods that regularly associate with each other but share no maternal relations or dialects.
Transient pods are smaller than resident pods, typically consisting of an adult female and one or two of her offspring. Males typically maintain stronger relationships with their mothers than other females. These bonds can extend well into adulthood. Unlike residents, extended or permanent separation of transient offspring from natal matrilines is common, with juveniles and adults of both sexes participating. Some males become "rovers" and do not form long-term associations, occasionally joining groups that contain reproductive females. As in resident clans, transient community members share an acoustic repertoire, although regional differences in vocalizations have been noted.
As with residents and transients, the lifestyle of these whales appears to reflect their diet; fish-eating orcas off Norway have resident-like social structures, while mammal-eating orcas in Argentina and the Crozet Islands behave more like transients.
Orcas of the same sex and age group may engage in physical contact and synchronous surfacing. These behaviours do not occur randomly among individuals in a pod, providing evidence of "friendships".
Vocalizations
| Multimedia relating to the orca |
 Orca calls at a distance Vocalizations of an orca Problems playing these files? See media help. |
Like all cetaceans, orcas depend heavily on underwater sound for orientation, feeding, and communication. They produce three categories of sounds: clicks, whistles, and pulsed calls. Clicks are believed to be used primarily for navigation and discriminating prey and other objects in the surrounding environment, but are also commonly heard during social interactions.
Northeast Pacific resident groups tend to be much more vocal than transient groups in the same waters. Residents feed primarily on Chinook and chum salmon, which are insensitive to orca calls (inferred from the audiogram of Atlantic salmon). In contrast, the marine mammal prey of transients hear whale calls well and thus transients are typically silent. Vocal behaviour in these whales is mainly limited to surfacing activities and milling (slow swimming with no apparent direction) after a kill.
All members of a resident pod use similar calls, known collectively as a dialect. Dialects are composed of specific numbers and types of discrete, repetitive calls. They are complex and stable over time. Call patterns and structure are distinctive within matrilines. Newborns produce calls similar to their mothers, but have a more limited repertoire. Individuals likely learn their dialect through contact with pod members. Family-specific calls have been observed more frequently in the days following a calf's birth, which may help the calf learn them. Dialects are probably an important means of maintaining group identity and cohesiveness. Similarity in dialects likely reflects the degree of relatedness between pods, with variation growing over time. When pods meet, dominant call types decrease and subset call types increase. The use of both call types is called biphonation. The increased subset call types may be the distinguishing factor between pods and inter-pod relations.
Dialects also distinguish types. Resident dialects contain seven to 17 (mean = 11) distinctive call types. All members of the North American west coast transient community express the same basic dialect, although minor regional variation in call types is evident. Preliminary research indicates offshore orcas have group-specific dialects unlike those of residents and transients.
Norwegian and Icelandic herring-eating orcas appear to have different vocalizations for activities like hunting. A population that live in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica have 28 complex burst-pulse and whistle calls.
Intelligence
Main article: Cetacean intelligenceOrcas have the second-heaviest brains among marine mammals (after sperm whales, which have the largest brain of any animal). Orcas have more gray matter and more cortical neurons than any mammal, including humans. They can be trained in captivity and are often described as intelligent, although defining and measuring "intelligence" is difficult in a species whose environment and behavioural strategies are very different from those of humans. Orcas imitate others, and seem to deliberately teach skills to their kin. Off the Crozet Islands, mothers push their calves onto the beach, waiting to pull the youngster back if needed. In March 2023, a female orca was spotted with a newborn pilot whale in Snæfellsnes.

People who have interacted closely with orcas offer numerous anecdotes demonstrating the whales' curiosity, playfulness, and ability to solve problems. Alaskan orcas have not only learned how to steal fish from longlines, but have also overcome a variety of techniques designed to stop them, such as the use of unbaited lines as decoys. Once, fishermen placed their boats several miles apart, taking turns retrieving small amounts of their catch, in the hope that the whales would not have enough time to move between boats to steal the catch as it was being retrieved. The tactic worked initially, but the orcas figured it out quickly and split into groups.
In other anecdotes, researchers describe incidents in which wild orcas playfully tease humans by repeatedly moving objects the humans are trying to reach, or suddenly start to toss around a chunk of ice after a human throws a snowball.
The orca's use of dialects and the passing of other learned behaviours from generation to generation have been described as a form of animal culture.
The complex and stable vocal and behavioural cultures of sympatric groups of killer whales (Orcinus orca) appear to have no parallel outside humans and represent an independent evolution of cultural faculties.
Life cycle

Female orcas begin to mature at around the age of 10 and reach peak fertility around 20, experiencing periods of polyestrous cycling separated by non-cycling periods of three to 16 months. Females can often breed until age 40, followed by a rapid decrease in fertility. Orcas are among the few animals that undergo menopause and live for decades after they have finished breeding. The lifespans of wild females average 50 to 80 years. Some are claimed to have lived substantially longer: Granny (J2) was estimated by some researchers to have been as old as 105 years at the time of her death, though a biopsy sample indicated her age as 65 to 80 years. It is thought that orcas held in captivity tend to have shorter lives than those in the wild, although this is subject to scientific debate.
Males mate with females from other pods, which prevents inbreeding. Gestation varies from 15 to 18 months. Mothers usually calve a single offspring about once every five years. In resident pods, births occur at any time of year, although winter is the most common. Mortality is extremely high during the first seven months of life, when 37–50% of all calves die. Weaning begins at about 12 months of age, and is complete by two years. According to observations in several regions, all male and female pod members participate in the care of the young.
Males sexually mature at the age of 15, but do not typically reproduce until age 21. Wild males live around 29 years on average, with a maximum of about 60 years. One male, known as Old Tom, was reportedly spotted every winter between the 1840s and 1930 off New South Wales, Australia, which would have made him up to 90 years old. Examination of his teeth indicated he died around age 35, but this method of age determination is now believed to be inaccurate for older animals. One male known to researchers in the Pacific Northwest (identified as J1) was estimated to have been 59 years old when he died in 2010. Orcas are unique among cetaceans, as their caudal sections elongate with age, making their heads relatively shorter.
Infanticide, once thought to occur only in captive orcas, was observed in wild populations by researchers off British Columbia on December 2, 2016. In this incident, an adult male killed the calf of a female within the same pod, with the adult male's mother also joining in the assault. It is theorized that the male killed the young calf in order to mate with its mother (something that occurs in other carnivore species), while the male's mother supported the breeding opportunity for her son. The attack ended when the calf's mother struck and injured the attacking male. Such behaviour matches that of many smaller dolphin species, such as the bottlenose dolphin.
Conservation

In 2008, the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) changed its assessment of the orca's conservation status from conservation dependent to data deficient, recognizing that one or more orca types may actually be separate, endangered species. Depletion of prey species, pollution, large-scale oil spills, and habitat disturbance caused by noise and conflicts with boats are the most significant worldwide threats. In January 2020, the first orca in England and Wales since 2001 was found dead with a large fragment of plastic in its stomach.
Like other animals at the highest trophic levels, the orca is particularly at risk of poisoning from bioaccumulation of toxins, including Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). European harbour seals have problems in reproductive and immune functions associated with high levels of PCBs and related contaminants, and a survey off the Washington coast found PCB levels in orcas were higher than levels that had caused health problems in harbour seals. Blubber samples in the Norwegian Arctic show higher levels of PCBs, pesticides and brominated flame-retardants than in polar bears. A 2018 study published in Science found that global orca populations are poised to dramatically decline due such toxic pollution.
In the Pacific Northwest, wild salmon stocks, a main resident food source, have declined dramatically in recent years. In the Puget Sound region, only 75 whales remain with few births over the last few years. On the west coast of Alaska and the Aleutian Islands, seal and sea lion populations have also substantially declined.
In 2005, the United States government listed the southern resident community as an endangered population under the Endangered Species Act. This community comprises three pods which live mostly in the Georgia and Haro Straits and Puget Sound in British Columbia and Washington. They do not breed outside of their community, which was once estimated at around 200 animals and later shrank to around 90. In October 2008, the annual survey revealed seven were missing and presumed dead, reducing the count to 83. This is potentially the largest decline in the population in the past 10 years. These deaths can be attributed to declines in Chinook salmon.
Scientist Ken Balcomb has extensively studied orcas since 1976; he is the research biologist responsible for discovering U.S. Navy sonar may harm orcas. He studied orcas from the Center for Whale Research, located in Friday Harbor, Washington. He was also able to study orcas from "his home porch perched above Puget Sound, where the animals hunt and play in summer months". In May 2003, Balcomb (along with other whale watchers near the Puget Sound coastline) noticed uncharacteristic behaviour displayed by the orcas. The whales seemed "agitated and were moving haphazardly, attempting to lift their heads free of the water" to escape the sound of the sonars. "Balcomb confirmed at the time that strange underwater pinging noises detected with underwater microphones were sonar. The sound originated from a U.S. Navy frigate 12 miles (19 kilometres) distant, Balcomb said." The impact of sonar waves on orcas is potentially life-threatening. Three years prior to Balcomb's discovery, research in the Bahamas showed 14 beaked whales washed up on the shore. These whales were beached on the day U.S. Navy destroyers were activated into sonar exercise. Of the 14 whales beached, six of them died. These six dead whales were studied, and CAT scans of two of the whale heads showed hemorrhaging around the brain and the ears, which is consistent with decompression sickness.
Another conservation concern was made public in September 2008 when the Canadian government decided it was not necessary to enforce further protections (including the Species at Risk Act in place to protect endangered animals along with their habitats) for orcas aside from the laws already in place. In response to this decision, six environmental groups sued the federal government, claiming orcas were facing many threats on the British Columbia Coast and the federal government did nothing to protect them from these threats. A legal and scientific nonprofit organization, Ecojustice, led the lawsuit and represented the David Suzuki Foundation, Environmental Defence, Greenpeace Canada, International Fund for Animal Welfare, the Raincoast Conservation Foundation, and the Wilderness Committee. Many scientists involved in this lawsuit, including Bill Wareham, a marine scientist with the David Suzuki Foundation, noted increased boat traffic, water toxic wastes, and low salmon population as major threats, putting approximately 87 orcas on the British Columbia Coast in danger.
Underwater noise from shipping, drilling, and other human activities is a significant concern in some key orca habitats, including Johnstone Strait and Haro Strait. In the mid-1990s, loud underwater noises from salmon farms were used to deter seals. Orcas also avoided the surrounding waters. High-intensity sonar used by the Navy disturbs orcas along with other marine mammals. Orcas are popular with whale watchers, which may stress the whales and alter their behaviour, particularly if boats approach too closely or block their lines of travel.
The Exxon Valdez oil spill adversely affected orcas in Prince William Sound and Alaska's Kenai Fjords region. Eleven members (about half) of one resident pod disappeared in the following year. The spill damaged salmon and other prey populations, which in turn damaged local orcas. By 2009, scientists estimated the AT1 transient population (considered part of a larger population of 346 transients), numbered only seven individuals and had not reproduced since the spill. This population is expected to die out.
Orcas are included in Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES), meaning international trade (including in parts/derivatives) is regulated.
Relationship with humans
Indigenous cultures
See also: Animal worship
The indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast feature orcas throughout their art, history, spirituality and religion. The Haida regarded orcas as the most powerful animals in the ocean, and their mythology tells of orcas living in houses and towns under the sea. According to these stories, they took on human form when submerged, and humans who drowned went to live with them. For the Kwakwaka'wakw, the orca was regarded as the ruler of the undersea world, with sea lions for slaves and dolphins for warriors. In Nuu-chah-nulth and Kwakwaka'wakw mythology, orcas may embody the souls of deceased chiefs. The Tlingit of southeastern Alaska regarded the orca as custodian of the sea and a benefactor of humans. The Lummi consider orca to be people, referring to them as "qwe'lhol'mechen" which means "our relations under the waves".
The Maritime Archaic people of Newfoundland also had great respect for orcas, as evidenced by stone carvings found in a 4,000-year-old burial at the Port au Choix Archaeological Site.
In the tales and beliefs of the Siberian Yupik people, orcas are said to appear as wolves in winter, and wolves as orcas in summer. Orcas are believed to assist their hunters in driving walrus. Reverence is expressed in several forms: the boat represents the animal, and a wooden carving hung from the hunter's belt. Small sacrifices such as tobacco or meat are strewn into the sea for them.
The Ainu people of Hokkaido, the Kuril Islands, and southern Sakhalin often referred to orcas in their folklore and myth as Repun Kamuy (God of Sea/Offshore) to bring fortunes (whales) to the coasts, and there had been traditional funerals for stranded or deceased orcas akin to funerals for other animals such as brown bears.
Attacks by wild orcas on humans and animals
Further information: Orca attack
In Western cultures, orcas were historically feared as dangerous, savage predators. The first written description of an orca was given by Pliny the Elder circa AD 70, who wrote, "Orcas (the appearance of which no image can express, other than an enormous mass of savage flesh with teeth) are the enemy of ... they charge and pierce them like warships ramming." (see citation in section "Naming", above).
Of the very few confirmed attacks on humans by wild orcas, none have been fatal. In one instance, orcas tried to tip ice floes on which a dog team and photographer of the Terra Nova Expedition were standing. The sled dogs' barking is speculated to have sounded enough like seal calls to trigger the orca's hunting curiosity. In the 1970s, a surfer in California was bitten, but the Orca then retreated, and in 2005, a boy in Alaska who was splashing in a region frequented by harbour seals was bumped by an orca that apparently misidentified him as prey.
Orca attacks on sailboats and small vessels
Main article: Iberian orca attacksBeginning around 2020, one or more pods of orcas began to attack sailing vessels off the southern tip of Europe, and a few were sunk. At least 15 interactions between orcas and boats off the Iberian coast were reported in 2020. According to the Atlantic Orca Working Group (GTOA) as many as 500 vessels have been damaged between 2020 and 2023. In one video, an orca can be seen biting on one of the two rudders ripped from a catamaran near Gibraltar. The captain of the vessel reported this was the second attack on a vessel under his command and the orcas focused on the rudders. "Looks like they knew exactly what they are doing. They didn't touch anything else." After an orca repeatedly rammed a vessel off the coast of Norway in 2023, there is a concern the behavior is spreading to other areas. This has led to recommendations that sailors now carry bags of sand. Dropping sand into the water near the rudder is thought to confuse the sonar signal. Experts were divided as to whether the behavior was some sort of revenge or protection response to a previous traumatic incident, or playful or frustrated attempts to get a boat's propeller to emit a stream of high-speed water.
Attacks on humans by captive orcas
Unlike wild orcas, captive orcas have made nearly two dozen attacks on humans since the 1970s, some of which have been fatal.
Human attacks on orcas
Competition with fishermen also led to orcas being regarded as pests. In the waters of the Pacific Northwest and Iceland, the shooting of orcas was accepted and even encouraged by governments. As an indication of the intensity of shooting that occurred until fairly recently, about 25% of the orcas captured in Puget Sound for aquariums through 1970 bore bullet scars. The U.S. Navy claimed to have deliberately killed hundreds of orcas in Icelandic waters in 1956 with machine guns, rockets, and depth charges.
Modern Western attitudes
See also: Orcas in popular cultureWestern attitudes towards orcas have changed dramatically in recent decades. In the mid-1960s and early 1970s, orcas came to much greater public and scientific awareness, starting with the live-capture and display of an orca known as Moby Doll, a southern resident orca harpooned off Saturna Island in 1964. He was the first ever orca to be studied at close quarters alive, not postmortem. Moby Doll's impact in scientific research at the time, including the first scientific studies of an orca's sound production, led to two articles about him in the journal Zoologica. So little was known at the time, it was nearly two months before the whale's keepers discovered what food (fish) it was willing to eat. To the surprise of those who saw him, Moby Doll was a docile, non-aggressive whale who made no attempts to attack humans.

Between 1964 and 1976, 50 orcas from the Pacific Northwest were captured for display in aquaria, and public interest in the animals grew. In the 1970s, research pioneered by Michael Bigg led to the discovery of the species' complex social structure, its use of vocal communication, and its extraordinarily stable mother–offspring bonds. Through photo-identification techniques, individuals were named and tracked over decades.
Bigg's techniques also revealed the Pacific Northwest population was in the low hundreds rather than the thousands that had been previously assumed. The southern resident community alone had lost 48 of its members to captivity; by 1976, only 80 remained. In the Pacific Northwest, the species that had unthinkingly been targeted became a cultural icon within a few decades.
The public's growing appreciation also led to growing opposition to whale–keeping in aquarium. Only one whale has been taken in North American waters since 1976. In recent years, the extent of the public's interest in orcas has manifested itself in several high-profile efforts surrounding individuals. Following the success of the 1993 film Free Willy, the movie's captive star Keiko was returned to the coast of his native Iceland in 2002. The director of the International Marine Mammal Project for the Earth Island Institute, David Phillips, led the efforts to return Keiko to the Iceland waters. Keiko however did not adapt to the harsh climate of the Arctic Ocean, and died a year into his release after contracting pneumonia, at the age of 27. In 2002, the orphan Springer was discovered in Puget Sound, Washington. She became the first whale to be successfully reintegrated into a wild pod after human intervention, crystallizing decades of research into the vocal behaviour and social structure of the region's orcas. The saving of Springer raised hopes that another young orca named Luna, which had become separated from his pod, could be returned to it. However, his case was marked by controversy about whether and how to intervene, and in 2006, Luna was killed by a boat propeller.
Whaling
Main article: Whaling
The earliest known records of commercial hunting of orcas date to the 18th century in Japan. During the 19th and early 20th centuries, the global whaling industry caught immense numbers of baleen and sperm whales, but largely ignored orcas because of their limited amounts of recoverable oil, their smaller populations, and the difficulty of taking them. Once the stocks of larger species were depleted, orcas were targeted by commercial whalers in the mid-20th century. Between 1954 and 1997, Japan took 1,178 orcas (although the Ministry of the Environment claims that there had been domestic catches of about 1,600 whales between late 1940s to 1960s) and Norway took 987. Extensive hunting of orcas, including an Antarctic catch of 916 in 1979–80 alone, prompted the International Whaling Commission to recommend a ban on commercial hunting of the species pending further research. Today, no country carries out a substantial hunt, although Indonesia and Greenland permit small subsistence hunts (see Aboriginal whaling). Other than commercial hunts, orcas were hunted along Japanese coasts out of public concern for potential conflicts with fisheries. Such cases include a semi-resident male-female pair in Akashi Strait and Harimanada being killed in the Seto Inland Sea in 1957, the killing of five whales from a pod of 11 members that swam into Tokyo Bay in 1970, and a catch record in southern Taiwan in the 1990s.
Cooperation with humans
Orcas have helped humans hunting other whales. One well-known example was the orcas of Eden, Australia, including the male known as Old Tom. Whalers more often considered them a nuisance, however, as orcas would gather to scavenge meat from the whalers' catch. Some populations, such as in Alaska's Prince William Sound, may have been reduced significantly by whalers shooting them in retaliation.
Whale watching
Whale watching continues to increase in popularity, but may have some problematic impacts on orcas. Exposure to exhaust gases from large amounts of vessel traffic is causing concern for the overall health of the 75 remaining southern resident orcas (SRKWs) left as of early 2019. This population is followed by approximately 20 vessels for 12 hours a day during the months May–September. Researchers discovered that these vessels are in the line of sight for these whales for 98–99.5% of daylight hours. With so many vessels, the air quality around these whales deteriorates and impacts their health. Air pollutants that bind with exhaust fumes are responsible for the activation of the cytochrome P450 1A gene family. Researchers have successfully identified this gene in skin biopsies of live whales and also the lungs of deceased whales. A direct correlation between activation of this gene and the air pollutants can not be made because there are other known factors that will induce the same gene. Vessels can have either wet or dry exhaust systems, with wet exhaust systems leaving more pollutants in the water due to various gas solubility. A modelling study determined that the lowest-observed-adverse-effect-level (LOAEL) of exhaust pollutants was about 12% of the human dose.
As a response to this, in 2017 boats off the British Columbia coast now have a minimum approach distance of 200 metres compared to the previous 100 metres. This new rule complements Washington State's minimum approach zone of 180 metres that has been in effect since 2011. If a whale approaches a vessel it must be placed in neutral until the whale passes. The World Health Organization has set air quality standards in an effort to control the emissions produced by these vessels.
Captivity
Main article: Captive orcas
The orca's intelligence, trainability, striking appearance, playfulness in captivity and sheer size have made it a popular exhibit at aquaria and aquatic theme parks. From 1976 to 1997, 55 whales were taken from the wild in Iceland, 19 from Japan, and three from Argentina. These figures exclude animals that died during capture. Live captures fell dramatically in the 1990s, and by 1999, about 40% of the 48 animals on display in the world were captive-born.
Organizations such as World Animal Protection and the Whale and Dolphin Conservation campaign against the practice of keeping them in captivity. In captivity, they often develop pathologies, such as the dorsal fin collapse seen in 60–90% of captive males. Captives have vastly reduced life expectancies, on average only living into their 20s. That said, a 2015 study coauthored by staff at SeaWorld and the Minnesota Zoo suggested no significant difference in survivorship between free-ranging and captive orcas. However, in the wild, females who survive infancy live 46 years on average, and up to 70–80 years in rare cases. Wild males who survive infancy live 31 years on average, and up to 50–60 years. Captivity usually bears little resemblance to wild habitat, and captive whales' social groups are foreign to those found in the wild. Critics claim captive life is stressful due to these factors and the requirement to perform circus tricks that are not part of wild orca behaviour, see above. Wild orcas may travel up to 160 kilometres (100 mi) in a day, and critics say the animals are too big and intelligent to be suitable for captivity. Captives occasionally act aggressively towards themselves, their tankmates, or humans, which critics say is a result of stress. Between 1991 and 2010, the bull orca known as Tilikum was involved in the death of three people, and was featured in the critically acclaimed 2013 film Blackfish. Tilikum lived at SeaWorld from 1992 until his death in 2017.
In March 2016, SeaWorld announced that they would be ending their orca breeding program and their theatrical shows. However, as of 2020, theatrical shows featuring orcas are still ongoing.
See also
- List of marine mammal species
- List of cetaceans
- Livyatan melvillei – occupied a similar ecological niche
- List of cetaceans
- Ingrid Visser (researcher) – a New Zealand biologist who swims with wild orcas
Footnotes
- According to Baird, killer whales prefer harbour seals to sea lions and porpoises in some areas.
- Although there are examples of killer whales living longer, including several over 30 years old, and two captive orcas (Corky II and Lolita) are in their mid-40s.
References
- Mead, J. G.; Brownell, R. L. Jr. (2005). "Order Cetacea". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 723–743. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- "Orcinus orca Linnaeus 1758". Fossilworks. Archived from the original on December 12, 2021. Retrieved December 17, 2021.
- ^ Reeves, R.; Pitman, R. L.; Ford, J. K. B. (2017). "Orcinus orca". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T15421A50368125. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T15421A50368125.en. Retrieved November 19, 2021.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Archived from the original on December 5, 2017. Retrieved January 14, 2022.
- "Orcinus orca (Linnaeus, 1758)". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved March 9, 2011.
- Fisheries, NOAA (February 5, 2024). "Southern Resident Killer Whale (Orcinus orca) | NOAA Fisheries". NOAA. Retrieved December 9, 2024.
- "Facts about orcas (killer whales)". Whales.org. Whale & Dolphin Conservation USA. Archived from the original on February 8, 2022. Retrieved February 8, 2022.
- Price, Mary (July 22, 2013). "Orcas: How Science Debunked Superstition". National Wildlife Federation. Archived from the original on January 31, 2017. Retrieved July 30, 2020.
- Ford, Ellis & Balcomb 2000, p. 69.
- Killer Whales. Scientific Classification Archived August 15, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Seaworld.org, September 23, 2010, Retrieved September 9, 2010.
- Lewis, Charlton T.; Short, Charles (1879). "orca". A Latin Dictionary. Perseus Digital Library. Archived from the original on October 7, 2022. Retrieved October 7, 2022.
- Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert (1940). "ὄρυξ". A Greek-English Lexicon. Perseus Digital Library. Archived from the original on May 26, 2024. Retrieved October 9, 2023.
- Best, P. B. (2007). Whales and Dolphins of the Southern African Subregion. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-89710-5.
- Leatherwood, Stephen; Hobbs, Larry J. (1988). Whales, dolphins, and porpoises of the eastern North Pacific and adjacent Arctic waters: a guide to their identification. Courier Dover Publications. p. 118. ISBN 0-486-25651-0. Retrieved January 28, 2010.
- Linnaeus, C. (1758). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I (in Latin). Vol. v.1 (10th ed.). Holmiae. (Laurentii Salvii). p. 824. Archived from the original on March 25, 2017. Retrieved January 14, 2018.
- ^ Zum Wal in der Marienkirche (in German). St. Mary's Church, Greifswald. Retrieved February 16, 2010
- Carwardine 2001, p. 19.
- LeDuc, R. G.; Perrin, W. F.; Dizon, A. E. (1999). "Phylogenetic relationships among the delphinid cetaceans based on full cytochrome b sequences". Marine Mammal Science. 15 (3): 619–648. Bibcode:1999MMamS..15..619L. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1999.tb00833.x. ISSN 0824-0469.
- Horreo, Jose L. (2018). "New insights into the phylogenetic relationships among the oceanic dolphins (Cetacea: Delphinidae)". Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research. 57 (2): 476–480. doi:10.1111/jzs.12255. S2CID 91933816.
- McGowen, Michael R.; Tsagkogeorga, Georgia; Álvarez-Carretero, Sandra; dos Reis, Mario; Struebig, Monika; Deaville, Robert; Jepson, Paul D.; Jarman, Simon; Polanowski, Andrea; Morin, Phillip A.; Rossiter, Stephen J. (October 21, 2019). "Phylogenomic Resolution of the Cetacean Tree of Life Using Target Sequence Capture". Systematic Biology. 69 (3): 479–501. doi:10.1093/sysbio/syz068. ISSN 1063-5157. PMC 7164366. PMID 31633766.
- ^ (Baird 2002). Status of Killer Whales in Canada Archived November 8, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Contract report to the Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada, Ottawa, ON, Canada. Also published as Status of Killer Whales, Orcinus orca, in Canada Archived July 14, 2010, at the Wayback Machine The Canadian Field-Naturalist 115 (4) (2001), 676–701. Retrieved January 26, 2010.
- ^ Pitman, Robert L.; Ensor, Paul (2003). "Three forms of killer whales (Orcinus orca) in Antarctic waters" (PDF). Journal of Cetacean Research and Management. 5 (2): 131–139. doi:10.47536/jcrm.v5i2.813. S2CID 52257732. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 27, 2020. Retrieved January 9, 2010.
- De Bruyn, P. J. N.; Tosh, C. A.; Terauds, A. (2013). "Killer whale ecotypes: Is there a global model?". Biological Reviews. 88 (1): 62–80. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.2012.00239.x. hdl:2263/21531. PMID 22882545. S2CID 6336624.
- Ford, Ellis & Balcomb 2000, pp. 16–21.
- ^ Jefferson, T. A.; Stacey, P. J.; Baird, R. W. (1991). "A review of killer whale interactions with other marine mammals: predation to co-existence" (PDF). Mammal Review. 21 (4): 151–180. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2907.1991.tb00291.x. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 22, 2011. Retrieved February 23, 2010.
- Schrope, Mark (2007). "Food chains: Killer in the kelp". Nature. 445 (7129): 703–705. Bibcode:2007Natur.445..703S. doi:10.1038/445703a. PMID 17301765. S2CID 4421362.
- Josh D. McInnes; Andrew W. Trites; Chelsea R. Mathieson; Marilyn E. Dahlheim; Jeffrey E. Moore; Paula A. Olson; Kevin M. Lester (2024). "Evidence for an Oceanic Population of Killer Whales (Orcinus orca) in Offshore Waters of California and Oregon". Aquatic Mammals. 50 (2 }): 93–106. doi:10.1578/am.50.2.2024.93. Retrieved March 22, 2024.
- Morin, P. A.; McCarthy, M. L.; Fung, C. W.; Durban, J. W.; Parsons, K. M.; Perrin, W. F.; Taylor, B. L.; Jefferson, T. A.; Archer, F. I. (2024). "Revised taxonomy of eastern North Pacific killer whales (Orcinus orca): Bigg's and resident ecotypes deserve species status". Royal Society Open Science. 11 (3). Bibcode:2024RSOS...1131368M. doi:10.1098/rsos.231368. PMC 10966402. PMID 38545612.
- "List of Marine Mammal Species and Subspecies". MarineMammalScience.org. Society for Marine Mammalogy. June 2024.
- Morin, Phillip A.; Archer, Frederick; Foote, Andrew D.; Vilstrup, Julia; Allen, Eric E.; Wade, Paul; Durban, John; Parsons, Kim; Pitman, Robert (2010). "Complete mitochondrial genome phylogeographic analysis of killer whales (Orcinus orca) indicates multiple species". Genome Research. 20 (7): 908–916. doi:10.1101/gr.102954.109. PMC 2892092. PMID 20413674.
- Pitman, Robert L.; Durban, John W.; Greenfelder, Michael; Guinet, Christophe; Jorgensen, Morton; Olson, Paula A.; Plana, Jordi; Tixier, Paul; Towers, Jared R. (August 7, 2010). "Observations of a distinctive morphotype of killer whale (Orcinus orca), type D, from subantarctic waters". Polar Biology. 34 (2): 303–306. doi:10.1007/s00300-010-0871-3. S2CID 20734772.
- Baird 2002, p. 129.
- ^ Heyning, J. E.; Dahlheim, M. E. (1988). "Orcinus orca" (PDF). Mammalian Species (304): 1–9. doi:10.2307/3504225. JSTOR 3504225. S2CID 253914153. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 18, 2012.
- Webber, Marc A.; Jefferson, Thomas Allen; Pitman, Robert L. (July 28, 2015). Marine Mammals of the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Identification. Academic Press. p. 189. ISBN 978-0-12-409592-2.
- Anderson, Robert; Waayers, Robyn; Knight, Andrew (August 2016). "Orca Behavior and Subsequent Aggression Associated with Oceanarium Confinement". Animals. 6 (8): 49. doi:10.3390/ani6080049. ISSN 2076-2615. PMC 4997274. PMID 27548232.
- Olsen, Ken (2006). "Orcas on the edge". National Wildlife. Vol. 44, no. 6. pp. 22–30. ISSN 0028-0402.
- Stewart, Doug (2001). "Tales of two orcas". National Wildlife. Vol. 39, no. 1. pp. 54–59. ISSN 0028-0402.
- ^ Carwardine 2001, p. 20.
- "Wild Whales". Vancouver Aquarium. Archived from the original on April 5, 2012. Retrieved March 23, 2012.
- ^ Ford, John K. B. (2009). "Killer Whale". In Perrin, William F.; Wursig, Bernd; Thewissen, J. G. M. 'Hans' (eds.). Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals. Academic Press. pp. 550–556. ISBN 978-0-08-091993-5.
- Ford, Ellis & Balcomb 2000, p. 45.
- Orca (Killer whale). American Cetacean Society. Retrieved January 2, 2009
- ^ Heptner et al. 1996, p. 681.
- Heptner et al. 1996, p. 683.
- Carwardine 2001, pp. 30–32.
- ^ "Killer Whales — Adaptations for an Aquatic Environment". Seaworld.org. Archived from the original on September 4, 2013. Retrieved September 14, 2013.
- N. W. Kasting, S. A. L. Adderly, T. Safford, K. G. Hewlett (1989). "Thermoregulation in Beluga (Delphinapterus luecas) and Killer (Orcinus orca) Whales"
- Spencer, M. P.; Gornall 3rd, T. A.; Poulter, T. C. (1967). "Respiratory and cardiac activity of killer whales". Journal of Applied Physiology. 22 (5): 974–981. doi:10.1152/jappl.1967.22.5.974. PMID 6025756.
- Obee & Ellis 1992, pp. 1–27.
- ^ Forney, K. A.; Wade, P. (2007). "Worldwide distribution and abundance of killer whales" (PDF). In Estes, James A.; DeMaster, Douglas P.; Doak, Daniel F.; Williams, Terrie M.; Brownell, Robert L. Jr. (eds.). Whales, whaling and ocean ecosystems. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 145–162. ISBN 978-0-520-24884-7. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 7, 2020. Retrieved February 25, 2014.
- Carwardine 2001, p. 21.
- Baird 2002, p. 128.
- Kwan, Jennifer (January 22, 2007). "Canada Finds Killer Whales Drawn to Warmer Arctic". Reuters. Archived from the original on August 17, 2017.
- ^ Baird 2002, p. 10.
- "Southern Resident Killer Whale Research" (PDF). Northwest Fisheries Science Center. February 14, 2007 . Archived from the original (PDF) on March 6, 2014. Retrieved January 26, 2010.
- NMFS 2005, pp. 24–29.
- ^ Ford & Ellis 2006.
- ^ "Killer whale (Orcinus orca)". NOAA Fisheries. Office of Protected Resources, National Marine Fisheries Service. Archived from the original on July 9, 2017. Retrieved August 15, 2017.
- NMFS 2005, p. 46.
- Ecology of Japanese Coastal Orcas Archived August 22, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, sha-chi.jp. Retrieved February 17, 2010
- Ten Years after Taiji Orca Capture Archived March 1, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, January 28, 2007. Iruka (dolphin) and Kujira (whale) Action Network (IKAN): Iruma, Saitama Prefecture, Japan. Retrieved February 17, 2010
- "Orcinus orca – Orca (Killer Whale)". Marinebio.org. Archived from the original on July 13, 2012. Retrieved June 26, 2007.
- NMFS 2005, p. 17.
- Morell, Virginia (2011). "Killer Whales Earn Their Name". Science. 331 (6015): 274–276. Bibcode:2011Sci...331..274M. doi:10.1126/science.331.6015.274. PMID 21252323.
- Baird, R. W.; et al. (2006). "Killer whales in Hawaiian waters: information on population identity and feeding habits" (PDF). Pacific Science. 60 (4): 523–530. doi:10.1353/psc.2006.0024. hdl:10125/22585. S2CID 16788148. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 23, 2017. Retrieved October 23, 2017.
- Weir, C. R.; Collins, T.; Carvalho, I.; Rosenbaum, H. C. (2010). "Killer whales (Orcinus orca) in Angolan and Gulf of Guinea waters, tropical West Africa" (PDF). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 90 (8): 1601–1611. Bibcode:2010JMBUK..90.1601W. doi:10.1017/S002531541000072X. S2CID 84721171. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 30, 2014.
- Miller, Patrick James O'Malley; Shapiro, Ari Daniel; Deecke, Volker Bernt (November 2010). "The diving behaviour of mammal-eating killer whales : variations with ecological not physiological factors" (PDF). Canadian Journal of Zoology. 88 (11): 1103–1112. doi:10.1139/Z10-080. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 20, 2018. Retrieved August 23, 2020.
Overall, the whales spent 50% of their time 8 m or shallower and 90% of their time 40 m or shallower
- Reisinger, Ryan R.; Keith, Mark; Andrews, Russel D.; de Bruyn, P. J. N. (December 2015). "Movement and diving of killer whales (Orcinus orca) at a Southern Ocean archipelago". Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology. 473: 90–102. Bibcode:2015JEMBE.473...90R. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2015.08.008. hdl:2263/49986. Archived from the original on June 30, 2022. Retrieved December 6, 2021.
maximum dive depths were 767.5 and 499.5 m
- Towers, Jared R; Tixier, Paul; Ross, Katherine A; Bennett, John; Arnould, John P Y; Pitman, Robert L; Durban, John W; Northridge, Simon (January 2019). "Movements and dive behaviour of a toothfish-depredating killer and sperm whale". ICES Journal of Marine Science. 76 (1): 298–311. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsy118. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30120094. S2CID 91256980.
The killer whale dove >750 m on five occasions while depredating (maximum: 1087 m), but these deep dives were always followed by long periods (3.9–4.6 h) of shallow (<100 m) diving.
- NMFS 2005, p. 18.
- Hughes, Catherine D. (March 2014). "National Geographic creature feature". Archived from the original on June 2, 2023. Retrieved July 25, 2007.
- Similä, T.; Ugarte, F. (1993). "Surface and underwater observations of cooperatively feeding killer whales in Northern Norway". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 71 (8): 1494–1499. Bibcode:1993CaJZ...71.1494S. doi:10.1139/z93-210.
- ^ Visser, Ingrid N. (2005). "First Observations of Feeding on Thresher (Alopias vulpinus) and Hammerhead (Sphyrna zygaena) Sharks by Killer Whales (Orcinus orca) Specialising on Elasmobranch Prey". Aquatic Mammals. 31 (1): 83–88. doi:10.1578/AM.31.1.2005.83.
- Visser, Ingrid N.; Berghan, Jo; van Meurs, Rinie; Fertl, Dagmar (2000). "Killer Whale (Orcinus orca) Predation on a Shortfin Mako Shark (Isurus oxyrinchus) in New Zealand Waters" (PDF). Aquatic Mammals. 26 (3): 229–231. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 26, 2012. Retrieved May 3, 2014.
- Visser, Ingrid N. (1999). "Benthic foraging on stingrays by killer whales (Orcinus orca) in New Zealand waters". Marine Mammal Science. 15 (1): 220–227. Bibcode:1999MMamS..15..220V. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1999.tb00793.x.
- ^ Engelbrecht, T. M.; Kock, A. A.; O'Riain, M. J. (2019). "Running scared: when predators become prey". Ecosphere. 10 (1): e02531. Bibcode:2019Ecosp..10E2531E. doi:10.1002/ecs2.2531.
- O'Sullivan, J. B. (2000). "A fatal attack on a whale shark Rhincodon typus, by killer whales Orcinus orca off Bahia de Los Angeles, Baja California". American Elasmobranch Society 16th Annual Meeting, June 14–20, 2000. La Paz, B.C.S., México. Archived from the original on February 28, 2010. Retrieved February 18, 2010.
- Pancaldi, Francesca; Ayres, Kathryn A.; Gallagher, Austin J.; Moskito, James; Williamson, Kelsey C.; Higuera Rivas, Jesús Erick (November 29, 2024). "Killer whales (Orcinus orca) hunt, kill and consume the largest fish on Earth, the whale shark (Rhincodon typus)". Frontiers in Marine Science. 11. doi:10.3389/fmars.2024.1448254. ISSN 2296-7745.
- ^ Pyle, Peter; Schramm, Mary Jane; Keiper, Carol; Anderson, Scot D. (1999). "Predation on a white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) by a killer whale (Orcinus orca) and a possible case of competitive displacement" (PDF). Marine Mammal Science. 15 (2): 563–568. Bibcode:1999MMamS..15..563P. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1999.tb00822.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 22, 2012. Retrieved April 28, 2014.
- Heithaus, Michael (2001). "Predator–prey and competitive interactions between sharks (order Selachii) and dolphins (suborder Odontoceti): a review" (PDF). Journal of Zoology. 253 (1): 53–68. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.404.130. doi:10.1017/S0952836901000061. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 15, 2016. Retrieved January 18, 2010.
- Jorgensen, S. J.; et al. (2019). "Killer whales redistribute white shark foraging pressure on seals". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 6153. Bibcode:2019NatSR...9.6153J. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-39356-2. PMC 6467992. PMID 30992478.
- Towner, AV; Watson, RGA; Kock, AA; Papastamatiou, Y; Sturup, M; Gennari, E; Baker, K; Booth, T; Dicken, M; Chivell, W; Elwen, S (April 3, 2022). "Fear at the top: killer whale predation drives white shark absence at South Africa's largest aggregation site". African Journal of Marine Science. 44 (2): 139–152. Bibcode:2022AfJMS..44..139T. doi:10.2989/1814232X.2022.2066723. ISSN 1814-232X. S2CID 250118179.
- Towner, A; Micarelli, P; Hurwitz, D; Smale, Mj; Booth, Aj; Stopforth, C; Jacobs, E; Reinero, Fr; Ricci, V; Di Bari, A; Gavazzi, S; Carugno, G; Mahrer, M; Gennari, E (2024). "Further insights into killer whales Orcinus orca preying on white sharks Carcharodon carcharias in South Africa". African Journal of Marine Science. 46 (1): 1–5. Bibcode:2024AfJMS..46....1T. doi:10.2989/1814232X.2024.2311272. ISSN 1814-232X.
- ^ Weller, D. W. (2009). "Predation on marine mammals". In Perrin, William F.; Wursig, Bernd; Thewissen, J. G. M. 'Hans' (eds.). Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals. Academic Press. pp. 927–930. ISBN 978-0-08-091993-5.
- Selbmann, A.; et al. (2022). "Occurrence of long-finned pilot whales (Globicephala melas) and killer whales (Orcinus orca) in Icelandic coastal waters and their interspecific interactions". Acta Ethol. 25 (3): 141–154. doi:10.1007/s10211-022-00394-1. PMC 9170559. PMID 35694552. S2CID 249487897.
- Samarra, Filipa (2018). "Prey of killer whales (Orcinus orca) in Iceland". PLOS ONE. 13 (12): 6. Bibcode:2018PLoSO..1307287S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0207287. hdl:20.500.11815/1095. PMC 6291266. PMID 30540762.
- Kiszka, Jeremy (2021). "Feeding Ecology of Elusive Caribbean Killer Whales Inferred From Bayesian Stable Isotope Mixing Models and Whalers' Ecological Knowledge". Frontiers in Marine Science. 8. doi:10.3389/fmars.2021.648421.
- Gonzalez-Pestana, Adriana (2019). "Killer whale (Orcinus Orca) occurrence and interactions with marine mammals off Peru". Pacific Science. 73 (2): 262-273. doi:10.2984/73.2.7.
- Totterdell, J. A.; Wellard, R.; Reeves, I. M.; Elsdon, B.; Markovic, P.; Yoshida, M.; Fairchild, A.; Sharp, G.; Pitman, R. (2022). "The first three records of killer whales (Orcinus orca) killing and eating blue whales (Balaenoptera musculus)". Marine Mammal Science. 38 (3): 1286–1301. Bibcode:2022MMamS..38.1286T. doi:10.1111/mms.12906. S2CID 246167673.
- Pitman, Robert L.; et al. (2001). "Killer Whale Predation on Sperm Whales: Observations and Implications". Marine Mammal Science. 17 (3): 494–507. Bibcode:2001MMamS..17..494P. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2001.tb01000.x. Archived from the original on December 11, 2015. Retrieved February 25, 2014.
- Pitman, Robert L. (2016). "Humpback whales interfering when mammal-eating killer whales attack other species: Mobbing behavior and interspecific altruism?". Marine Mammal Science. 33: 7–58. doi:10.1111/mms.12343.
- Estes, James (February 26, 2009). "Ecological effects of marine mammals". In Perrin, William F. (ed.). Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals. Wursig, Bernd & Thewissen, J. G. M. Academic Press. pp. 357–361. ISBN 978-0-08-091993-5. Archived from the original on May 9, 2016. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- ^ Heimlich & Boran 2001, p. 45.
- Carwardine 2001, p. 29.
- ^ Baird 2002, pp. 61–62.
- Pitman, R. L.; Durban, J. W. (2011). "Cooperative hunting behavior, prey selectivity and prey handling by pack ice killer whales (Orcinus orca), type B, in Antarctic Peninsula waters". Marine Mammal Science. 28 (1): 16–36. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2010.00453.x. Archived from the original on August 2, 2023. Retrieved July 27, 2023.
- Visser, Ingrid N.; Smith, Thomas G.; Bullock, Ian D.; Green, Geoffrey D.; Carlsson, Olle G. L.; Imberti, Santiago (2008). "Antarctic peninsula killer whales (Orcinus orca) hunt seals and a penguin on floating ice" (PDF). Marine Mammal Science. 24 (1): 225–234. Bibcode:2008MMamS..24..225V. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2007.00163.x. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 31, 2011.
- Pinell, Nadine, et al. "Transient Killer Whales – Culprits in the Decline of Sea Otters in Western Alaska? Archived June 30, 2017, at the Wayback Machine" B.C. Cetacean Sightings Network, June 1, 2004. Retrieved March 13, 2010
- ^ Baird 2002, p. 23.
- Killer Whales Develop a Taste For Sea Otters Archived November 7, 2015, at the Wayback Machine Ned Rozell, Article #1418, Alaska Science Forum, December 10, 1998. Retrieved February 26, 2010
- Springer, A. M. (2003). "Sequential megafaunal collapse in the North Pacific Ocean: An ongoing legacy of industrial whaling?". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 100 (21): 12223–12228. Bibcode:2003PNAS..10012223S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1635156100. PMC 218740. PMID 14526101.
- Demaster, D.; Trites, A.; Clapham, P.; Mizroch, S.; Wade, P.; Small, R.; Hoef, J. (2006). "The sequential megafaunal collapse hypothesis: Testing with existing data". Progress in Oceanography. 68 (2–4): 329–342. Bibcode:2006PrOce..68..329D. doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2006.02.007.
- Estes, J. A.; Doak, D. F.; Springer, A. M.; Williams, T. M. (2009). "Causes and consequences of marine mammal population declines in southwest Alaska: a food-web perspective". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 364 (1524): 1647–1658. doi:10.1098/rstb.2008.0231. PMC 2685424. PMID 19451116.
- Baird, Robert W.; Baird, Robin W. (August 31, 2006). Killer Whales of the World: Natural History and Conservation. Voyageur Press. pp. 23–. ISBN 978-0-7603-2654-1. Archived from the original on July 21, 2011. Retrieved February 2, 2011.
- Baird 2002, p. 124.
- Ford, Ellis & Balcomb 2000, p. 19.
- Chung, Emily (February 18, 2019). "Killer whales eat dolphins. So why are these dolphins tempting fate?". CBC News. Archived from the original on August 7, 2023. Retrieved August 7, 2023.
- Pitman, R. L.; Durban, J. W. (2010). "Killer whale predation on penguins in Antarctica". Polar Biology. 33 (11): 1589–1594. Bibcode:2010PoBio..33.1589P. doi:10.1007/s00300-010-0853-5. S2CID 44055219.
- Baird 2002, p. 14.
- "Whale uses fish as bait to catch seagulls then shares strategy with fellow orcas". Associated Press. September 7, 2005. Archived from the original on March 22, 2010. Retrieved February 18, 2010.
- Carwardine 2001, p. 64.
- Connelly, Laylan (July 30, 2019). "Videos show killer whales frantically hunting for dolphins off San Clemente". The OCR. Archived from the original on December 10, 2019. Retrieved November 24, 2019.
- "Orcas Kill, But Not Just for Food (2:06)". YouTube. April 19, 2022. Archived from the original on June 2, 2023. Retrieved June 2, 2023.
- "Why orcas wear dead salmon as 'hats' remains a mystery, scientists say". CBC. November 30, 2024. Retrieved December 1, 2024.
- ^ Heimlich & Boran 2001, p. 35.
- "Keep Whales Wild". Keep Whales Wild. January 14, 2011. Archived from the original on December 16, 2010. Retrieved February 16, 2011.
- ^ NMFS 2005, p. 12.
- ^ NMFS 2005, p. 39.
- Ford, J. K. B.; Ellis, G. M.; Balcomb, K. C. (1999). Killer Whales: The Natural History and Genealogy of Orcinus orca in British Columbia and Washington State. University of British Columbia Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-0774804691.
- NMFS 2005, p. 13.
- ^ NMFS 2005, p. 14.
- Ford, Ellis & Balcomb 2000, p. 27.
- Weiss, M. N.; et al. (2021). "Age and sex influence social interactions, but not associations, within a killer whale pod". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 288 (1953). doi:10.1098/rspb.2021.0617. hdl:10871/125706. PMC 8206696. PMID 34130498.
- Lesté-Lasserre, Christa (June 17, 2021). "Killer whales form killer friendships, new drone footage suggests". Science. Archived from the original on December 5, 2022. Retrieved June 18, 2021.
- ^ NMFS 2005, p. 20.
- Deeck, V. B.; Ford, J. K. B.; Slater, P. J. B. (2005). "The vocal behaviour of mammal-eating killer whales: communicating with costly calls". Animal Behaviour. 69 (2): 395–405. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2004.04.014. S2CID 16899659.
- Foote, A. D.; Osborne, R. W.; Hoelzel, A. (2008). "Temporal and contextual patterns of killer whale (Orcinus orca) call type production". Ethology. 114 (6): 599–606. Bibcode:2008Ethol.114..599F. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0310.2008.01496.x.
- ^ Kremers, D.; Lemasson, A.; Almunia, J.; Wanker, R. (2012). "Vocal sharing and individual acoustic distinctiveness within a group of captive orcas (Orcinus orca)". Journal of Comparative Psychology. 126 (4): 433–445. doi:10.1037/a0028858. PMID 22866769.
- Filatova, Olga A.; Fedutin, Ivan D.; Burdin, Alexandr M.; Hoyt, Erich (2007). "The structure of the discrete call repertoire of killer whales Orcinus orca from Southeast Kamchatka" (PDF). Bioacoustics. 16 (3): 261–280. Bibcode:2007Bioac..16..261F. doi:10.1080/09524622.2007.9753581. S2CID 56304541. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 15, 2011. Retrieved February 23, 2010.
- Weiß, Brigitte M.; Ladich, Friedrich; Spong, Paul; Symonds, Helena (2006). "Vocal behaviour of resident killer whale matrilines with newborn calves: The role of family signatures" (PDF). The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 119 (1): 627–635. Bibcode:2006ASAJ..119..627W. doi:10.1121/1.2130934. PMID 16454316. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 27, 2011.
- ^ NMFS 2005, pp. 15–16.
- Simon, M.; McGregor, P. K.; Ugarte, F. (2007). "The relationship between the acoustic behaviour and surface activity of killer whales (Orcinus orca) that feed on herring (Clupea harengus)". Acta Ethologica. 10 (2): 47–53. doi:10.1007/s10211-007-0029-7. S2CID 29828311.
- Szondy, David (February 26, 2020). "The smallest killer whale has a large musical repertoire". New Atlas. Archived from the original on February 27, 2020. Retrieved February 27, 2020.
- Spear, Kevin (March 7, 2010). "Killer whales: How smart are they?". Orlando Sentinel. Archived from the original on September 8, 2015. Retrieved March 7, 2010.
- Dunham, Will (October 16, 2017). "Big and brilliant: complex whale behavior tied to brain size". Reuters. Archived from the original on July 19, 2021. Retrieved December 23, 2020.
- Ridgway, Sam H.; Brownson, Robert H.; Van Alstyne, Kaitlin R.; Hauser, Robert A. (December 16, 2019). Li, Songhai (ed.). "Higher neuron densities in the cerebral cortex and larger cerebellums may limit dive times of delphinids compared to deep-diving toothed whales". PLOS ONE. 14 (12): e0226206. Bibcode:2019PLoSO..1426206R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0226206. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 6914331. PMID 31841529.
- ^ Associated Press. Whale Attack Renews Captive Animal Debate CBS News, March 1, 2010. Retrieved March 7, 2010
- ^ Carwardine 2001, p. 67.
- Weston, Phoebe (March 10, 2023). "'Extraordinary' sighting of orca with baby pilot whale astounds scientists". The Guardian.
- ^ Obee & Ellis 1992, p. 42.
- "Killer whale games" (PDF). Blackfish Sounder. 13: 5. 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 11, 2007.
- Pitman, Robert L. Scientist Has 'Snowball Fight' With a Killer Whale Archived September 15, 2020, at the Wayback Machine. Live Science, February 6, 2009. Retrieved March 7, 2010
- Marino, Lori; et al. (2007). "Cetaceans Have Complex Brains for Complex Cognition". PLOS Biology. 5 (e139): e139. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050139. PMC 1868071. PMID 17503965.
- Rendell, Luke; Whitehead, Hal (2001). "Culture in whales and dolphins". Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 24 (2): 309–324. doi:10.1017/S0140525X0100396X. PMID 11530544. S2CID 24052064. Archived from the original on May 30, 2010. Retrieved March 7, 2010.
- ^ Ward, Eric J.; Holmes, Elizabeth E.; Balcomb, Ken C. (June 2009). "Quantifying the effects of prey abundance on killer whale reproduction". Journal of Applied Ecology. 46 (3): 632–640. Bibcode:2009JApEc..46..632W. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2009.01647.x.
- Bowden, D. M.; Williams, D. D. (1984). "Aging". Advances in Veterinary Science and Comparative Medicine. 28: 305–341. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-039228-5.50015-2. ISBN 9780120392285. PMID 6395674.
- Timiras, Paola S. (2013). Physiological Basis of Aging and Geriatrics (Fourth ed.). CRC Press. p. 161.
- ^ "Orcas don't do well in captivity. Here's why". Animals. March 25, 2019. Archived from the original on June 6, 2020. Retrieved May 31, 2020.
- ^ Carwardine 2001, p. 26.
- TEGNA. "Oldest Southern Resident killer whale considered dead". KING. Archived from the original on January 3, 2017. Retrieved January 3, 2017.
- Podt, Annemieke (December 31, 2016). "Orca Granny: was she really 105?". Archived from the original on October 15, 2018. Retrieved September 11, 2017.
- ^ Robeck, Todd R.; Willis, Kevin; Scarpuzzi, Michael R.; O'Brien, Justine K. (September 29, 2015). "Comparisons of life-history parameters between free-ranging and captive killer whale (Orcinus orca) populations for application toward species management". Journal of Mammalogy. 96 (5): 1055–1070. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyv113. PMC 4668992. PMID 26937049. Archived from the original on April 23, 2019.
- Jett, John; Ventre, Jeffrey (2015). "Captive killer whale (Orcinus orca) survival". Marine Mammal Science. 31 (4): 1362–1377. Bibcode:2015MMamS..31.1362J. doi:10.1111/mms.12225.
- NMFS 2005, p. 33.
- NMFS 2005, p. 35.
- Mitchell, E. and Baker, A. N. (1980). Age of reputedly old Killer Whale, Orcinus orca, 'Old Tom' from Eden, Twofold Bay, Australia, in: W. F. Perrin and A. C. Myrick Jr (eds.): Age determination of toothed whales and sirenians, pp. 143–154 Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. (Special Issue 3), cited in Know the Killer Whale, The Dolphin's Encyclopaedia. Retrieved January 27, 2010
- Olesiuk, Peter F.; Ellis, Graeme M. and Ford, John K. B. (2005). Life History and Population Dynamics of Northern Resident Killer Whales (Orcinus orca) in British Columbia Archived April 19, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Research Document 2005/045, Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat, Fisheries and Oceans Canada. p. 33. Retrieved January 27, 2010
- How Southern Resident Killer Whales are Identified Archived November 28, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, Center for Whale Research. Retrieved March 23, 2012
- "'Horrified' scientists first to see killer whale infanticide | CBC News". Archived from the original on March 23, 2018. Retrieved March 22, 2018.
- "First stranded Orca found in almost 20 years in the Wash". BBC News. January 14, 2020. Archived from the original on January 16, 2020.
- ^ Ford, Ellis & Balcomb 2000, p. 99.
- Carrington, Damian (September 27, 2018). "Orca 'apocalypse': half of killer whales doomed to die from pollution". The Guardian. Archived from the original on September 28, 2018. Retrieved September 28, 2018.
- Desforges, J-P; Hall, A; Mcconnell, B; et al. (2018). "Predicting global killer whale population collapse from PCB pollution". Science. 361 (6409): 1373–1376. Bibcode:2018Sci...361.1373D. doi:10.1126/science.aat1953. hdl:10023/16189. PMID 30262502. S2CID 52876312.
- Robbins, Jim (July 9, 2018). "Orcas of the Pacific Northwest Are Starving and Disappearing". The New York Times. Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 9, 2018.
- Ford, Ellis & Balcomb 2000, p. 98.
- ^ Lyke, M. L. (October 14, 2006). "Granny's Struggle: When Granny is gone, will her story be the last chapter?". Seattle Post Intelligencer. Archived from the original on September 15, 2020.
- ^ Le Phuong. Researchers: 7 Orcas Missing from Puget Sound Archived October 28, 2008, at the Wayback Machine, Associated Press. USA Today, October 25, 2008
- ^ Pickrell, John (March 2004). "U.S. Navy Sonar May Harm Killer Whales, Expert Says". National Geographic News. Archived from the original on September 9, 2011. Retrieved March 19, 2012.
- ^ "Ottawa Sued over Lack of Legislation to Protect B.C. Killer Whales". CBC News. October 9, 2008. Archived from the original on June 26, 2012. Retrieved March 19, 2012.
- Ford, Ellis & Balcomb 2000, p. 100.
- Research on Orcas Archived September 11, 2012, at archive.today, Raincoast Research Society. Retrieved February 18, 2010
- McClure, Robert (October 2, 2003). "State expert urges Navy to stop sonar tests". Seattle Post Intelligencer. Archived from the original on October 4, 2012. Retrieved June 25, 2007.
- Williams, Rob (2023). "Behavioural responses of male killer whales to a 'leapfrogging' vessel" (PDF). Journal of Cetacean Research and Management. 4 (3): 305–310. doi:10.47536/jcrm.v4i3.844. S2CID 55958971. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 6, 2014. Retrieved February 25, 2014.
- Keim, Brandon (March 24, 2009). "Unique Killer-Whale Pod Doomed by Exxon Valdez". Wired. Archived from the original on January 6, 2010. Retrieved December 31, 2009.
- "Marine Ecology Progress Series 356:269" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 28, 2011. Retrieved December 31, 2009.
- ^ Francis & Hewlett 2007, pp. 115–120.
- Ford, Ellis & Balcomb 2000, p. 11.
- Gibson, Caitlin (December 5, 2023). "The call of Tokitae". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on December 5, 2023. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- Rollmann, Hans (1999). Religion in Newfoundland and Labrador Archived May 4, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, Newfoundland and Labrador Heritage, Memorial University of Newfoundland. Retrieved January 26, 2010
- Tuck, James A. (1971). "An Archaic Cemetery at Port Au Choix, Newfoundland". American Antiquity. 36 (3): 343–358. doi:10.2307/277719. JSTOR 277719. S2CID 163391715.
- The orphan boy with his sister, p. 156 in Rubcova, E. S. (1954). Materials on the Language and Folklore of the Eskimoes, Vol. I, Chaplino Dialect. Leningrad: Academy of Sciences of the USSR. Original data: Е.С. Рубцова: Материалы по языку и фольклору эскимосов (чаплинский диалект). Академия Наук СССР. Москва-Ленинград, 1954
- Menovshchikov, G. A. (1962). Grammar of the language of Asian Eskimos. Vol. I., pp. 439, 441. Moscow and Leningrad: Academy of Sciences of the USSR. Original data: Г. А. Меновщиков: Грамматиκа языка азиатских эскимосов. Часть первая. Академия Наук СССР. Москва-Ленинград, 1962
- ^ "Поддержка прав коренных народов Cибири - Spiritual culture subsection of the Eskimos page in the Support for Siberian Indigenous Peoples Rights". nsu.ru (in Russian). Archived from the original on August 30, 2007.
- ^ Vajda, Edward J. "Siberian Yupik (Eskimo)". East Asian Studies. Archived from the original on October 28, 2016. Retrieved August 7, 2013.
- ^ Ковалева, Ирина & Богословская, Людмила (December 3, 2002). Животные и отражение их прихода к человеку в самых разных текстах (in Russian). Эхо Москвы. Арсенал. Archived from the original on May 5, 2008. Retrieved April 29, 2008. A radio interview with Russian scientists about man and animal, examples taken especially from Asian Eskimos
- Miyanaga, T. (2014). (北海道)「シャチ送り」の遺構か 礼文島の遺跡で出土. Asahi Shimbun (in Japanese).
- ^ Obee & Ellis 1992, pp. Chapter 1.
- Gaius Plinius Secundus. Historia Naturalis 9.5.12 Archived September 15, 2020, at the Wayback Machine (Latin), in Bill Thayer's LacusCurtius: Into the Roman World Archived May 24, 2012, at archive.today. (See also an English translation Archived June 4, 2011, at the Wayback Machine by John Bostock and Henry Thomas Riley, 1855.) Retrieved February 19, 2010.
- "Orca shares the waves with local surfer". 3 News. September 12, 2008. Archived from the original on July 24, 2011. Retrieved October 13, 2011.
- Cherry-Garrard, Apsley (2004). The Worst Journey in the World: Antarctic 1910–1913. Globe Pequot. p. 92. ISBN 978-1-59228-212-8.
- "Whale Takes Bite From Surfer's Leg". Los Angeles Times. MONTEREY. UPI. July 11, 1972. Archived from the original on February 18, 2024. Retrieved March 23, 2024.
- "Boy survives bump from killer whale". The Seattle Times. The Associated Press. August 18, 2005. Archived from the original on April 2, 2011. Retrieved January 3, 2010.
- "Scientists are puzzled by Orcas sinking boats in a string of abnormal attacks". NBC News. May 23, 2023. Archived from the original on July 4, 2023. Retrieved July 4, 2023.
- "Gladis the killer whale and her gang of orcas out for revenge". The Independent. May 29, 2023. Archived from the original on June 20, 2023. Retrieved July 5, 2023.
- Dewan, Pandora (June 9, 2023). "Orcas filmed destroying ship's rudder in shocking clip: "Surrounded"". Newsweek. Archived from the original on July 5, 2023. Retrieved July 5, 2023.
- Hoare, Philip; Hoekendijk, Jeroen (June 21, 2023). "Orca rams into yacht off Shetland in first such incident in northern waters". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved July 4, 2023.
- "Sprinkling sand 'deters orcas' according to Cruising Association". Practical Boat Owner. June 19, 2023. Archived from the original on July 4, 2023. Retrieved July 4, 2023.
- Crisp, James (May 27, 2023). "Sailors have a new way to stop killer whale attacks". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on July 4, 2023. Retrieved July 4, 2023.
- Scott Neuman (May 15, 2024). "Orcas sank a yacht off Spain — the latest in a slew of such 'attacks' in recent years". NPR. Archived from the original on July 8, 2023. Retrieved May 16, 2024.
- ^ "ABC News: Killer Whale Attacks SeaWorld Trainer". ABC News. November 30, 2006. Archived from the original on February 28, 2010. Retrieved January 3, 2010.
- "SeaWorld trainer killed by killer whale" Archived April 3, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, CNN, February 25, 2010, Retrieved September 9, 2010
- NMFS 2005, p. 41.
- Killer Whales Destroyed: VP-7 Accomplishes Special Task, Naval Aviation News, December 1956, p. 19. Reproduced at Longevity and Causes of Death Archived June 19, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, SeaWorld/Busch Gardens ANIMALS. Retrieved January 11, 2010
- "Naval War Declared Against Killer Whales". The Science News-Letter. 69 (24): 374. 1956. doi:10.2307/3936617. JSTOR 3936619.
- Schevill, William; Watkins, William (Summer 1966). "Sound Structure and Directionality in Orcinus (killer whale)". Zoologica. 51 (2). New York Zoological Society: 71–76.
- Newman, Murray; McGeer, Patrick (Summer 1966). "The Capture and Care of a Killer Whale, Orcinus orca, in British Columbia". Zoologica. 51 (2). New York Zoological Society: 59–70.
- Francis & Hewlett 2007, pp. 58–59.
- Baird 2002, pp. 73–80.
- Heimlich & Boran 2001, p. 11.
- Wood, Daniel (February 24, 2010). "Death of Sea World trainer: Do 'killer whales' belong in theme parks?". The Christian Science Monitor. Archived from the original on May 13, 2012. Retrieved March 19, 2012.
- Movie-Star Whale Keiko Dies of Pneumonia. Archived June 7, 2020, at the Wayback Machine Associated Press. Published December 13, 2003. Retrieved June 7, 2020.
- "Orphaned orca's reunion with family celebrated". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. July 13, 2007. Archived from the original on November 6, 2015. Retrieved November 6, 2007.
- McClure, Robert (March 11, 2006). "Luna the orca killed by tugboat". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Seattle, Washington: Hearst Corporation. Archived from the original on August 11, 2011. Retrieved April 8, 2009.
- "海域自然環境保全基礎調査 - 海棲動物調査報告書, (2)- 19. シャチ Orcinus orca (Limaeus,1758)マイルカ科" (PDF). 自然環境保全基礎調査: 54. 1998. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 17, 2015. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- ^ Obee & Ellis 1992, p. 34.
- シャチ騒動 (in Japanese). Osaka College of Eco & Animals. 2011. Archived from the original on December 24, 2014. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- "Stranding Base (1901–2012) for Hyogo Prefecture". The Whale Laboratory of Shimonoseki. 2014. Archived from the original on December 24, 2014. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- "Stranding Date Base (1901-2012) for Chiba Prefecture". The Whale Laboratory of Shimonoseki. 2014. Archived from the original on January 9, 2015. Retrieved January 9, 2015.
- Kaiya, Z.; Leatherwood, S.; Jefferson, A. T. (1995). "Records of Small Cetaceans in Chinese Waters: A Review" (PDF). Asian Marine Biology. 12: 119–139. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 17, 2015. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- Kaiya, Z.; Leatherwood, S.; Jefferson, A. T. (2002). Perrin F. W.; Reeves R. R.; Dolar L. L. M.; Jefferson A. T.; Marsh H.; Wang Y. J.; Estacion J. (eds.). "Report of the Second Workshop on The Biology and Conservation of Small Cetaceans and Dugongs of South-East Asia" (PDF). CMS Technical Series Publication Nº 9 at Convention on Migratory Species. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ^ Reeves, Randall; Whitehead, Hal (2005). "Killer whales and whaling: the scavenging hypothesis". Biology Letters. 1 (4): 415–418. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2005.0348. PMC 1626385. PMID 17148221.
- "Home". Be Whale Wise. Archived from the original on October 31, 2019. Retrieved October 31, 2019.
- ^ Lachmuth, Cara L.; Barrett-Lennard, Lance G.; Steyn, D. Q.; Milsom, William K. (April 2011). "Estimation of southern resident killer whale exposure to exhaust emissions from whale-watching vessels and potential adverse health effects and toxicity thresholds". Marine Pollution Bulletin. 62 (4): 792–805. Bibcode:2011MarPB..62..792L. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.01.002. PMID 21276987.
- "Boats to Maintain Greater Distance from Killer Whales | Whales online". November 8, 2017. Archived from the original on March 30, 2019. Retrieved March 14, 2019.
- NMFS 2005, pp. 43–44.
- Rose, N. A. (2011). "Killer Controversy: Why Orcas Should No Longer Be Kept in Captivity" (PDF). Humane Society International and the Humane Society of the United States. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 30, 2017. Retrieved December 21, 2014.
- "Orcas in captivity" (PDF). Whale and Dolphin Conservation Society. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 6, 2010. Retrieved January 26, 2010.
- "Blackfish". Rotten Tomatoes. Archived from the original on November 21, 2013. Retrieved November 23, 2013.
- Zimmerman, Tim (2011). "The Killer in the Pool". The Best American Sampler 2011. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 336.
- "Corpse Is Found on Whale". The New York Times. July 7, 1999. Archived from the original on June 13, 2012. Retrieved September 11, 2011.
- "SeaWorld to End Controversial Orca Shows and Breeding". National Geographic News. March 17, 2016. Archived from the original on April 20, 2016. Retrieved September 27, 2016.
- Stevens, Blair (June 11, 2020). "Even years after Blackfish, SeaWorld still has Orcas". Archived from the original on December 13, 2020. Retrieved December 23, 2020.
Works cited
- Baird, Robin W. (2002). Killer Whales of the World. Stillwater, MN.: Voyageur Press. ISBN 978-0-7603-2654-1.
- Carwardine, Mark (2001). Killer Whales. London: BBC Worldwide. ISBN 978-0-7894-8266-2.
- Ford, John K. B. (2002). "Killer Whale". Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals. Academic Press. pp. 669–675. ISBN 0-12-551340-2.
- Ford, John K. B.; Ellis, Graeme M.; Balcomb, Kenneth C. (2000). Killer Whales (Second ed.). Vancouver, BC: UBC Press. ISBN 978-0-7748-0800-2.
- Ford, John K. B.; Ellis, Graeme M. (2006). "Selective foraging by fish-eating killer whales Orcinus orca in British Columbia". Marine Ecology Progress Series. 316: 185–199. Bibcode:2006MEPS..316..185F. doi:10.3354/meps316185.
- Francis, Daniel; Hewlett, Gil (2007). Operation Orca: Springer, Luna and the Struggle to Save West Coast Killer Whales. Madeira Park, B.C.: Harbour Publishing. ISBN 978-1-55017-426-7.
- Heimlich, Sara; Boran, James (2001). Killer Whales. Stillwater, MN: Voyageur Press. ISBN 978-0-89658-545-4.
- Heptner, V. G.; Nasimovich, A. A.; Bannikov, A. G.; Hoffmann, Robert S. (1996). Mammals of the Soviet Union. Vol. II, part 3. Washington D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Libraries and National Science Foundation. ISBN 978-1-886106-81-9.
- NMFS (2005). "Conservation Plan for Southern Resident Killer Whales (Orcinus orca)" (PDF). Seattle, U.S.: National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) Northwest Regional Office. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 26, 2008. Retrieved January 2, 2009.
- Obee, Bruce; Ellis, Graeme (1992). Elaine Jones (ed.). Guardians of the Whales: The Quest to Study Whales in the Wild. North Vancouver, British Columbia: Whitecap Books. ISBN 978-1-55110-034-0.
Further reading
- Hoyt, Erich (August 1984). "The Whales Called "Killer"". National Geographic. Vol. 166, no. 2. pp. 220–237. ISSN 0027-9358. OCLC 643483454.
- Hoyt, Erich (1998), Orca: The Whale Called Killer Camden House Publishing, Camden House, ISBN 978-0-920656-25-9
- Kirkevold, B. C.; Lockard, J. S. (1986). Behavioral Biology of Killer Whales. Alan R. Liss Inc. ISBN 978-0-8451-3100-8.
External links
- Orca-Live Archived August 15, 2000, at the Wayback Machine – Orcas in Johnstone Strait, British Columbia
- Salish Sea Hydrophone Network Archived July 9, 2013, at the Wayback Machine – Listen live to orcas in Washington State, U.S.
- Keep Whales Wild
- Why are orca called killer whales? Archived February 19, 2023, at the Wayback Machine, HowStuffWorks.com, article by Jacob Silverman
- Voices in the Sea - Sounds of the Orca (Killer Whale)
- Orca devours great white shark Archived April 5, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- Orcas Preying On Dolphins (Caught On Drone) Archived March 17, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, off the coast of San Clemente
- Orcas vs Sperm Whales Archived April 24, 2020, at the Wayback Machine
- Watch: Killer Whales Charge Blue Whale (Rare Drone Footage) Archived November 16, 2019, at the Wayback Machine | National Geographic
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Orcinus orca |
|
| Delphinus orca | |
Categories: