| Revision as of 00:40, 23 September 2012 edit206.255.121.244 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 11:31, 11 November 2024 edit undoGdimo (talk | contribs)139 edits Structure | ||
| (64 intermediate revisions by 45 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|1862 book by Jules Michelet}} | |||
| Satanism is a form of christian selfishness and self worship. Witchcraft has ABSOLUTELY NOTHING to do with the christian religion of Satanism. Witches don't believe in devils nor do they believe in worshipping a man called Yeshua. Yeshua, which translates to Joshua,(from Hebrew to English), was a man who taught the wisdom of King Solomon. Witchcraft is merely the practice of Wicca which only has one rule:Do what thou will and it harm none. | |||
| {{italic title}}__NOTOC__ | |||
| ⚫ | ==References== | ||
| ], of a '']'', in the 1911 edition of ''La Sorcière'', by ]]] | |||
| ⚫ | *English translation: ''Satanism and Witchcraft: A Study in Medieval Superstition''. Transl. ]. Lyle Stuart/Citadel Press, 1939. | ||
| '''''Satanism and Witchcraft''''' is a book by ] on the history of ]. Originally published in Paris as '''''La Sorcière''''' in 1862, the first English translation appeared in London a year later.<ref>''La Sorcière: The Witch of the Middle Ages'', translated by L. J. Teotter, "The only Authorized English Translation", London, 1863.</ref> Michelet portrays the life of witches and trials held for witchcraft, and argues that medieval witchcraft was a righteous act of rebellion by the lower classes against ] and the ]. | |||
| ⚫ | *''La Sorcière de Jules Michelet: l'envers de l'histoire'', ed. Paule Petitier. Paris, Champion, 2004. | ||
| Although his book is thought to be largely inaccurate, it is notable for being one of the first sympathetic histories of witchcraft. | |||
| ==Views== | |||
| ⚫ | {{reflist}} | ||
| According to Michelet, medieval witchcraft was an act of popular rebellion against the oppression of ] and the ]. This rebellion took the form of a secret religion inspired by ] and belief in ], organized by a woman who became its leader. The participants in the religion met regularly at ]s and ]s. Michelet's account dwells on the suffering of ]s and women in the Middle Ages, and writes that history should concentrate on ‘the people, and not only its leaders or its institutions’ put him ahead of his time as a writer of micro-history.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Sorceress - Jules Michelet|url=https://www.vamzzz.com/sorceress.html#.X9IQXy1h3x4|access-date=2020-12-10|website=www.vamzzz.com}}</ref> Michelet was one of the first people to attempt to give a sociological explanation of the Witch Trials, and interprets the source material very literally.<ref>{{Cite web|title=The Sorceress Index|url=https://www.sacred-texts.com/pag/sor/index.htm|access-date=2020-12-10|website=www.sacred-texts.com}}</ref> | |||
| According to Michelet, in a note added to the end of the book: | |||
| ==Sources Online== | |||
| ⚫ | * | ||
| ⚫ | * | ||
| ⚫ | * | ||
| * | |||
| ⚫ | * | ||
| {{quote|The object of my book was purely to give, not a history of Sorcery, but a simple and impressive formula of the Sorceress's way of life, which my learned predecessors darken by the very elaboration of their scientific methods and the excess of detail. My strong point is to start, not from the devil, from an empty conception, but from a living reality, the Sorceress, a warm, breathing reality, rich in results and possibilities.<ref>Michelet, p. 326</ref>}} | |||
| ⚫ | {{DEFAULTSORT:Satanism And Witchcraft}} | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ==Structure== | |||
| The book is divided into two parts, each constituted by twelve chapters. The first and most famous part is an imaginative reconstruction of the experience of a series of medieval witches who led the religion from its original form of social protest into decadence. The second part is a series of episodes in the ], including the ], the trials of the possessed women of ] and ], and the execution of ].<ref>{{Cite web|title=La Sorcière - Jules Michelet|url=https://www.universalis.fr/encyclopedie/la-sorciere-jules-michelet/#:~:text=Adoptant%20une%20approche%20et%20un,la%20lib%C3%A9ratrice)%20et%20de%20ceux%20%E2%80%93|access-date=October 30, 2024|website=www.universalis.fr}}</ref> Today, the book is regarded as being largely inaccurate, but still notable for being one of the first sympathetic histories of witchcraft, and as such it may have had an indirect influence on ].<ref>{{Cite web|title=How witches went on to become modern feminist icons|url=https://theconversation.com/how-witches-went-on-to-become-modern-feminist-icons-216705|access-date=November 2, 2024|website=www.theconversation.com}}</ref> Michelet uses a mix of scholarly research and imaginative storytelling that makes the book more accessible to readers. Had he opted for a more academic style it would perhaps be more widely regarded as a reputable study. The book often reads more like a novel or a tragedy than a typical historical treatise. | |||
| ==Media== | |||
| {{hist-book-stub}} | |||
| In the early 1970s, ''La Sorcière'' became the basis for ]'s film '']'' (starring ]) and the ] film '']'', by ]. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| ] | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * ] | |||
| ⚫ | ==References== | ||
| ⚫ | {{reflist}} | ||
| ==External links== | |||
| ⚫ | * | ||
| ⚫ | * | ||
| ⚫ | * | ||
| * {{Gutenberg|no=31420|name=La Sorcière: The Witch of the Middle Ages by Jules Michelet}} English translation | |||
| ⚫ | * | ||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| ⚫ | * English translation: ''Satanism and Witchcraft: A Study in Medieval Superstition''. Transl. ]. Lyle Stuart/Citadel Press, 1939. | ||
| ⚫ | * ''La Sorcière de Jules Michelet: l'envers de l'histoire'', ed. Paule Petitier. Paris, Champion, 2004. | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ⚫ | {{DEFAULTSORT:Satanism And Witchcraft}} | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:31, 11 November 2024
1862 book by Jules Michelet
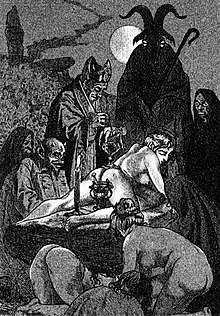
Satanism and Witchcraft is a book by Jules Michelet on the history of witchcraft. Originally published in Paris as La Sorcière in 1862, the first English translation appeared in London a year later. Michelet portrays the life of witches and trials held for witchcraft, and argues that medieval witchcraft was a righteous act of rebellion by the lower classes against feudalism and the Roman Catholic Church. Although his book is thought to be largely inaccurate, it is notable for being one of the first sympathetic histories of witchcraft.
Views
According to Michelet, medieval witchcraft was an act of popular rebellion against the oppression of feudalism and the Roman Catholic Church. This rebellion took the form of a secret religion inspired by paganism and belief in fairies, organized by a woman who became its leader. The participants in the religion met regularly at Witches' Sabbaths and Black Masses. Michelet's account dwells on the suffering of peasants and women in the Middle Ages, and writes that history should concentrate on ‘the people, and not only its leaders or its institutions’ put him ahead of his time as a writer of micro-history. Michelet was one of the first people to attempt to give a sociological explanation of the Witch Trials, and interprets the source material very literally.
According to Michelet, in a note added to the end of the book:
The object of my book was purely to give, not a history of Sorcery, but a simple and impressive formula of the Sorceress's way of life, which my learned predecessors darken by the very elaboration of their scientific methods and the excess of detail. My strong point is to start, not from the devil, from an empty conception, but from a living reality, the Sorceress, a warm, breathing reality, rich in results and possibilities.
Structure
The book is divided into two parts, each constituted by twelve chapters. The first and most famous part is an imaginative reconstruction of the experience of a series of medieval witches who led the religion from its original form of social protest into decadence. The second part is a series of episodes in the European witch trials, including the Louis Gaufridi affair, the trials of the possessed women of Loudun and Louviers, and the execution of Charlotte Cadière. Today, the book is regarded as being largely inaccurate, but still notable for being one of the first sympathetic histories of witchcraft, and as such it may have had an indirect influence on Wicca. Michelet uses a mix of scholarly research and imaginative storytelling that makes the book more accessible to readers. Had he opted for a more academic style it would perhaps be more widely regarded as a reputable study. The book often reads more like a novel or a tragedy than a typical historical treatise.
Media
In the early 1970s, La Sorcière became the basis for Alain Robbe-Grillet's film Glissements progressifs du plaisir (starring Jean-Louis Trintignant) and the anime film Kanashimi no Belladonna, by Mushi Production.
See also
References
- La Sorcière: The Witch of the Middle Ages, translated by L. J. Teotter, "The only Authorized English Translation", London, 1863.
- "Sorceress - Jules Michelet". www.vamzzz.com. Retrieved 2020-12-10.
- "The Sorceress Index". www.sacred-texts.com. Retrieved 2020-12-10.
- Michelet, p. 326
- "La Sorcière - Jules Michelet". www.universalis.fr. Retrieved October 30, 2024.
- "How witches went on to become modern feminist icons". www.theconversation.com. Retrieved November 2, 2024.
External links
- The full French text (various formats)
- The full French text, with internal links and pictures (MS Word format)
- Full text of "La Sorcière: The Witch in the Middle Ages" (1863 English translation)
- La Sorcière: The Witch of the Middle Ages by Jules Michelet at Project Gutenberg English translation
- Illustrations by Martin van Maële from 1911 edition
Further reading
- English translation: Satanism and Witchcraft: A Study in Medieval Superstition. Transl. A. R. Allinson. Lyle Stuart/Citadel Press, 1939.
- La Sorcière de Jules Michelet: l'envers de l'histoire, ed. Paule Petitier. Paris, Champion, 2004.