| Revision as of 18:44, 4 July 2013 editOsamaK (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers19,183 editsm fix img← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 13:03, 31 December 2024 edit undoHarukaAmaranth (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users15,704 edits →Notable residents: grammar fixes | ||
| (488 intermediate revisions by 97 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Prefecture-level city in Jiangxi, China}} | |||
| {{other uses}} | {{other uses}} | ||
| {{Refimprove|date=July 2011}} | |||
| {{Infobox settlement | {{Infobox settlement | ||
| <!-- Basic info ----------------> | <!-- Basic info ----------------> | ||
| |name = |
|name = Jiujiang | ||
| |official_name = |
|official_name = | ||
| |other_name = | |other_name = Kiukiang | ||
| |native_name = |
|native_name = 九江市 | ||
| |native_name_lang = zh | |||
| |nickname = | |nickname = | ||
| |settlement_type =] | |settlement_type =] | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
| |motto = | |motto = | ||
| <!-- images and maps -----------> | <!-- images and maps -----------> | ||
| |image_skyline = |
|image_skyline = {{multiple image | ||
| | |
| border = infobox | ||
| | |
| total_width = 290 | ||
| | |
| image_style = border:1; | ||
| | |
| perrow = 1/2/2 | ||
| | image1 = Jiujiang_Culture_and_Art_Center_3.jpg | |||
| | image2 = Pagoda_of_Suojiang_Pavilion_0.jpg | |||
| | image3 = Jiu_Jiang_Victory_Monument.jpg | |||
| | image4 = 庐山含鄱口看五老峰.jpg | |||
| | image5 = Suojiang_Pavilion.jpg | |||
| | image6 = 八里湖南湖.jpg | |||
| | image7 = Ruqin_Lake.jpg | |||
| }} | |||
| |imagesize = 290 | |||
| |image_caption = '''Top to bottom, left to right:''' Jiujiang Culture and Art Center, Pagoda of Suojiang Pavilion, Jiu Jiang victory monument, looking at Wulaofeng from Mount Lushan's Pokou, Suojiang pavilion, Bali Hunan lake, Ruqin lake | |||
| |image_seal = | |image_seal = | ||
| |seal_size = | |seal_size = | ||
| Line 41: | Line 52: | ||
| --> | --> | ||
| <!-- Location ------------------> | <!-- Location ------------------> | ||
| |coordinates_region = CN-36 | |||
| |subdivision_type = Country | |subdivision_type = Country | ||
| |subdivision_name = People's Republic of China | |subdivision_name = People's Republic of China | ||
| Line 49: | Line 59: | ||
| |subdivision_name2 = | |subdivision_name2 = | ||
| |seat_type = | |seat_type = | ||
| |seat = | |seat = Municipal seat | ||
| |parts_type = | |parts_type = ] | ||
| |parts_style = <!-- =list (for list), coll (for collapsed list), para (for paragraph format) | |parts_style = <!-- =list (for list), coll (for collapsed list), para (for paragraph format) | ||
| Default is list if up to 5 items, coll if more than 5--> | Default is list if up to 5 items, coll if more than 5--> | ||
| Line 59: | Line 69: | ||
| |government_footnotes = | |government_footnotes = | ||
| |government_type = | |government_type = | ||
| |leader_title = | |leader_title =] | ||
| |leader_name = | |leader_name =Liu Wenhua | ||
| |leader_title1 = | |leader_title1 =] | ||
| |leader_name1 = | |leader_name1 =Yang Wenbin | ||
| |leader_title2 = | |leader_title2 = | ||
| |leader_name2 = | |leader_name2 = | ||
| Line 92: | Line 102: | ||
| |area_blank1_km2 = | |area_blank1_km2 = | ||
| <!-- Elevation --------------------------> | <!-- Elevation --------------------------> | ||
| |elevation_footnotes = <ref name="geo intro">{{cite web |url=http://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/zjjj/jjgk/dljt/201506/t20150614_1217090.htm |script-title=zh:地理交通 |trans-title=Geography and transport |publisher=Jiujiang People's Government |language=zh-hans |access-date=1 June 2018 |archive-date=18 November 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191118081802/http://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/zjjj/jjgk/dljt/201506/t20150614_1217090.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| |elevation_footnotes = <!--for references: use <ref> tags--> | |||
| |elevation_m = | |elevation_m = 20 | ||
| |elevation_ft = | |elevation_ft = | ||
| |elevation_max_m = | |elevation_max_m = 1794 | ||
| | |
|elevation_max_point = ] | ||
| |elevation_min_m = | |elevation_min_m = | ||
| |elevation_min_ft = | |elevation_min_ft = | ||
| <!-- Population -----------------------> | <!-- Population -----------------------> | ||
| |population_as_of = |
|population_as_of =2020 census | ||
| |population_footnotes = | |population_footnotes = | ||
| |population_note = | |population_note = | ||
| |population_total = |
|population_total =4600276 | ||
| |population_density_km2 =auto <!--For automatic calculation, any density field may contain: auto --> | |population_density_km2 =auto <!--For automatic calculation, any density field may contain: auto --> | ||
| |population_metro = |
|population_metro =1164268 | ||
| |population_density_metro_km2 =auto | |population_density_metro_km2 =auto | ||
| |population_urban = |
|population_urban =2814240 | ||
| |population_density_urban_km2 =auto | |population_density_urban_km2 =auto | ||
| |population_blank1_title = | |population_blank1_title = | ||
| |population_blank1 = | |population_blank1 = | ||
| |population_density_blank1_km2 = | |population_density_blank1_km2 = | ||
| | demographics_type2 = GDP<ref>{{cite book |author=江西省统计局、国家统计局江西调查总队 |title=《江西统计年鉴-2016》 |date=August 2016 |publisher=中国统计出版社 |isbn=978-7-5037-7809-4 |url=http://www.jxstj.gov.cn/resource/nj/2016CD/indexch.htm |access-date=2017-06-05 |archive-date=2018-05-11 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180511215556/http://www.jxstj.gov.cn/resource/nj/2016CD/indexch.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| | demographics2_title1 = ] | |||
| | demographics2_info1 = ] 190.3 billion<br />] 30.5 billion | |||
| | demographics2_title2 = Per capita | |||
| | demographics2_info2 = CN¥ 39,505<br />US$ 6,343 | |||
| <!-- General information ---------------> | <!-- General information ---------------> | ||
| |timezone = ] | |timezone = ] | ||
| |utc_offset = +8 | |utc_offset = +8 | ||
| |coor_pinpoint = Jiujiang municipal government | |||
| |latd= 29 |latm= 44 |lats= 17 |latNS=N | |||
| |coordinates = {{coord|29.661|N|115.954|E|type:adm2nd_region:CN-36_source:Gaode|format=dms|display=it}} | |||
| |longd=115 |longm=59 |longs=14 |longEW=E | |||
| <!-- Area/postal codes & others --------> | <!-- Area/postal codes & others --------> | ||
| |postal_code_type = ] <!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... --> | |postal_code_type = ] <!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... --> | ||
| |postal_code = | |postal_code = | ||
| |area_code = | |area_code = | ||
| |iso_code = ] | |||
| |blank_name = | |||
| |website = {{URL|https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/english/}} | |||
| |blank_info = | |||
| |blank1_name = | |||
| |blank1_info = | |||
| |blank2_name = | |||
| |blank2_info = | |||
| |blank3_name = | |||
| |blank3_info = | |||
| |blank4_name = | |||
| |blank4_info = | |||
| |blank5_name = | |||
| |blank5_info = | |||
| |blank6_name = | |||
| |blank6_info = | |||
| |website = {{URL|jiujiang.gov.cn}} | |||
| |footnotes = | |footnotes = | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Infobox Chinese | |||
| '''Jiujiang''' ({{zh|c=九江 |p=Jiǔjiāng}}), formerly transliterated '''Kiukiang''' or '''Kew Keang''', is a ] located on the southern shores of the ] in northwest ] Province, People's Republic of China. It is the second-largest prefecture-level city in Jiangxi province{{Citation needed|date=August 2008}}, after the provincial capital ]. ''Jiujiang'' literally means "nine rivers". | |||
| |c={{linktext|lang=zh|九江}} | |||
| |p=Jiǔjiāng | |||
| |w=Chiu-chiang | |||
| |psp=Kiukang | |||
| |mi={{IPAc-cmn|j|iu|3|j|iang|1}} | |||
| |j=Gau<sup>2</sup>-gong<sup>1</sup> | |||
| |y=Gáu-gōng | |||
| |tl=Káu-kang | |||
| |l=Nine Rivers | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Jiujiang'''<!--Chinese in infoboxes; see ]-->, formerly transliterated '''Kiukiang''' and '''Kew-Keang''', is a ] located on the southern shores of the ] in northwest ] in the ]. It is the second-largest prefecture-level city in Jiangxi and its borders include ], the largest freshwater ] in China. Jiujiang is the fourth largest port on the Yangtze River<ref>{{cite web |title=改革开放40年:九江港成为名副其实的"亿吨大港" |url=https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1620381053261144241&wfr=spider&for=pc |website=Jiujiang News Network |access-date=22 July 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title="百年老港"江西九江港稳固亿吨大港地位 |url=https://www.sohu.com/a/126891057_119778 |website=Sohu.com |access-date=22 July 2021}}</ref> and was one of the first five cities that were opened to foreign trade along the Yangtze River following the implementation of ]'s ]. It is ]'s only international trade port city. | |||
| Its population is 4,728,763 inhabitants at the 2010 census whom 545,616 in the built up area made of 2 urban districts (] and ]). | |||
| Its population was 4,600,276 inhabitants at the ], 1,164,268 of whom resided in the built-up area (metro) made up of three urban districts (aka ], ], and ]).<ref name="aoi">{{cite web |title=九江市第七次全国人口普查公报 |url=http://tjj.jiujiang.gov.cn/zwgk/zdly/tjgb/202106/P020210611315177788811.pdf |website=Jiujiang Statistics Bureau Website |access-date=22 July 2021 |archive-date=3 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211103131902/http://tjj.jiujiang.gov.cn/zwgk/zdly/tjgb/202106/P020210611315177788811.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref> In 2007, the city was named China's top ten livable cities by the Chinese Cities Brand Value Report, which was released at 2007 Beijing Summit of China Cities Forum.<ref>{{cite web | |||
| == Administrative divisions == | |||
| |title=China's Top 10 Most Livable Cities | |||
| * ]: | |||
| |url=http://eng.hnloudi.gov.cn/engld%5Caboutloudi/Loudicity/Loudihonor/2011/1_327/default.shtml | |||
| :*] | |||
| |archive-url=https://archive.today/20130410050946/http://eng.hnloudi.gov.cn/engld%5Caboutloudi/Loudicity/Loudihonor/2011/1_327/default.shtml | |||
| * ]: | |||
| |url-status=dead | |||
| :*] | |||
| |archive-date=2013-04-10 | |||
| :*] | |||
| |website=hnloudi.gov.cn | |||
| :*] | |||
| |publisher=Hunan Loudi Official Government | |||
| :*] | |||
| |date=2012-03-28 | |||
| :*] | |||
| |access-date=2014-08-04 | |||
| :*] | |||
| }}</ref> In 2022, the State Council of China granted Jiujiang the title of Famed National Historical and Cultural City for its rich history and multiculture background in the ] era. | |||
| :*] | |||
| :*] | |||
| ==Administrative divisions== | |||
| :*] | |||
| ], 1954)]] | |||
| * ]: | * ]: | ||
| :*] (浔阳) | :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|浔阳区}}) | ||
| :*] | :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|濂溪区}}) | ||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|柴桑区}}) | |||
| * ]: | |||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|武宁县}}) | |||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|修水县}}) | |||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|永修县}}) | |||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|德安县}}) | |||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|都昌县}}) | |||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|湖口县}}) | |||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|彭泽县}}) | |||
| * ]: | |||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-Hans-CN|瑞昌市}}) | |||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-Hans-CN|共青城市}}). Directly administered as a ] since 1 July 2014.<ref name="直管县改革">{{cite web |url=http://jx.people.com.cn/n/2014/0529/c359142-21311620.html |script-title=zh:共青城市被列入省直管县改革试点 |publisher=] |date=29 May 2014 |language=zh-hans |access-date=7 June 2018 |archive-date=12 June 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180612142128/http://jx.people.com.cn/n/2014/0529/c359142-21311620.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| :*] ({{lang|zh-hans|庐山市}}) | |||
| * Others: | |||
| :* Bureau and Administration Committees | |||
| ::* Mount Lu Scenic Area Administration Bureau | |||
| ::* Mount Lu West Sea Scenic Area Management Committee | |||
| ::* Bali Lake New Area Management Committee | |||
| ::* Poyang Lake Ecological Science and Technology City Management Committee | |||
| :* Towns and Sub-district Offices | |||
| * Others | |||
| ::* There are 235 towns and 11 sub-district offices | |||
| :* Bureau | |||
| ::* Lushan Cultural Sites Administrative Bureau | |||
| :* Development regions: | |||
| ::* Jiujiang Open Development Region, Gongqing Open Development Region | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| There are 235 towns and 11 sub-district offices. | |||
| ! Map | |||
| |- | |||
| | <div style="position: relative" class="center"> | |||
| {{Image label begin|image=Administrative Division Jiujiang 2.png|width=800|link=}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1400|y=270|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1490|y=220|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1380|y=350|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1190|y=340|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=710|y=610|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=300|y=790|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1120|y=730|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1090|y=480|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1580|y=500|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1550|y=300|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1760|y=180|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=960|y=350|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1175|y=615|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1340|y=490|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label|x=1480|y=710|scale=800/2000|text=]}} | |||
| {{Image label end}}</div> | |||
| |} | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The city suffered only slight damage in the ], but there were several deaths reported in outlying areas. | |||
| ===Ancient history=== | |||
| In ancient times it was told that nine rivers converged near where Jiujiang sprang up to become Jiangxi’s main water port today. During the Xia through the Shang Dynasties Jiujiang was a capital of several states. In the Spring & Autumn Period (770-476 BCE) Jiujiang bordered between the states of Wu (downstream, to the east) and Chu (upstream, to the west). ] (365-429 CE) a famous Chinese philosopher lived at the base of Lushan. He was once appointed magistrate of nearby Pengze County and after 83 days resigned due to the politics involved in administering justice. He retreated back to his village to pen an essay called Peach Flower Garden. In 757 ] (701-762 CE) was implicated in An Lushan’s rebellion and imprisoned at Jiujiang. ] (772-846 CE) wrote a poem called "Lute Song", which is about his sadness and isolation of forced exile as a middle rank official to reside in such a small town. In the 13th century ] was a Confucian philosopher who practiced at the ], on Lushan’s eastern flanks. | |||
| In ancient times it was told that nine rivers converged near where Jiujiang sprang up to become Jiangxi's main water port today. From the ] to the ] dynasty, the capitals of several states were located in area of Jiujiang.{{citation needed|date=August 2019}} In the ] (770–476 BCE) Jiujiang bordered between the states of ] (downstream, to the east) and ] (upstream, to the west). | |||
| ===Imperial history=== | |||
| Jiujiang has also been known as Jiangzhou and Xunyang in former times. During the Qin Dynasty (265-420 CE) it was known as Sin Yang, the Liang dynasty (502-557 CE) it was called Jiang Zhou. The Sui Dynasty saw its name as Jiujiang and the Song Dynasty (960-1127) called it Ting Jiang. The Ming dynasty (1368–1644), gave it Jiujiang which has retained its name to this day. It was a Taiping stronghold for five years (1850–64) after they devastated the town to only leave one street with buildings intact. | |||
| ] (365–429 CE), a famous Chinese philosopher, ] and poet, lived at the base of ]. He was once appointed magistrate of nearby ] and after 83 days resigned owing to the politics involved in administering justice. He retired back to his village to pen an essay called "]". In 757, ] (701–762 CE) was implicated in the ] and exiled at Jiujiang. ] (772–846 CE) wrote a poem called "Lute Song", which is about his sadness and isolation of ] as a middle rank official to reside in such a small and remote town. In the 13th century ] was a Confucian philosopher who practiced at the ], on Mount Lu's eastern flanks. | |||
| Jiujiang has also been known as Jiangzhou (江州) and Xunyang (浔阳) in former times. During the ] it was known as Sin Yang{{citation needed|date=August 2019}}, the ] (502–557) of ] it was called Jiangzhou. After reunification, the ] saw its name as Jiujiang, and the Song dynasty (960–1127) called it Ting Jiang. The ] (1368–1644), gave it Jiujiang which has retained its name to this day. It was a ] stronghold for five years (1850–1864) after they{{who|date=August 2019}} devastated the town to only leave one street with buildings intact. The city served as the capital of Taiping's Jiangxi province during this time. | |||
| A member of Lord Elgin’s committee arriving in 1858 to survey Chinese ports for treaty status noted: “We found it to the last degree deplorable. A single dilapidated street, composed only of a few mean shops, was all that existed of this once thriving populous city. The remainder of the vast area composed within its massive walls 9-10 kilometers in circumference, contained nothing but ruins, weeds and kitchen gardens. After becoming an open treaty port in 1862, it was exporting Jiangxi’s vast rice crop. In 1904, more than 160,000 kilos of opium were moved through its customs house. | |||
| ===British concession and European settlement history=== | |||
| It became one of the three centers of the tea trade in China along with Hankou and Fuzhou. The Russians had two brick tea producing factories, but ceased operations after 1917. The British surrendered their concession in 1927 after being robbed and its Chinese workers mutineered their posts to the marauding crowds. An economic recession had set in over the decades as Indian and Chelonian teas made for greater competition. A military advance was being staged upriver in Wuhan by the ] in 1927 and all the remaining expatriate community fled on British and American warships towards safer waters of Shanghai, to never return. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ====The arrival of the Europeans==== | |||
| Jiujiang languished as a port and much of its export trade was siphoned off with the connecting Nanchang to coastal rail lines built in 1936-37. Until 1949 Jiujiang had very little industry except for local handicrafts. Manufacturing is Jiujiang’s backbone today with auto, machinery, petrochemical, shipbuilding and textiles as its cornerstones. After the completion of the Yangtze River Bridge in 1992 and the Beijing to Kowloon (Hong Kong) - Wuhan to Shanghai rail system laid, a convenient ground corridor was provided and a regional airport now serves most of China’s capital cities. | |||
| A member of ]'s committee arriving in 1858 to survey Chinese ports for treaty status noted: "We found it to the last degree deplorable." A single dilapidated street, composed only of a few mean shops, was all that existed of this once thriving populous city. The remainder of the vast area composed within its massive walls 9–10 kilometers in circumference, contained nothing but ruins, weeds and kitchen gardens. After Jiujiang becoming an open treaty port in 1862, it was exporting Jiangxi's vast rice crop. In 1904, more than 160,000 kilos of opium were moved through its customs house. The New York Methodist Mission Society's superintendent, Virgil C. Hart, arrived in Kiukiang in 1866 and bought a piece of property just east of the city wall. This is where the city's first Methodist church and Western hospital was built, with the hospital renamed the No. 1 Hospital, and the oldest/continuous operating hospital in Jiangxi Province.<ref>"Man On A Mission" by Stanley Crawford</ref> In 1896 Drs. ] and Ida Kahn (Kahn Cheng) arrived back in Jiujiang, being China's first two native female Western-educated doctors; having graduated from the ] Medical School. They were provided with funds collected by Dr. I. N. Danforth (from Chicago residents), to build the Elizabeth Skelton Danforth Hospital and administered entirely by the native Chinese. This was later renamed Jiujiang Women's and Children's Hospital, and the nursing education by Drs. Stone and Kahn would later be the impetus for the founding of ] and Jiujiang Medical School.<ref>"The Middle Kingdom's Miracle Maidens" by Stanley Crawford</ref> | |||
| It became one of the three centers of the tea trade in China along with ] and ]. The Russians had two brick tea producing factories, but ceased operations after 1917. On October 16, 1927, there was an explosion of ammunition on the Chinese troopship ''Kuang Yuang'' near Jiujiang.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=FB0E1FF83C581B7A93C5A8178BD95F428285F9|title=1,200 Die as Yangtse Troopship Blows Up|newspaper=]|date=October 17, 1926}}</ref> The British surrendered their concession in 1927 after being robbed and its Chinese workers mutineered their posts to the marauding crowds. An economic recession had set in over the decades as Indian and Chelonian tea made for greater competition. A military advance was being staged upriver in Wuhan by the ] in 1927 and all the remaining expatriate community fled on British and American warships towards safer waters of Shanghai, to never return.{{citation needed|date=August 2019}} Jiujiang languished as a port and much of its export trade was siphoned off with the connecting of ] to coastal rail lines built in 1936–37. | |||
| ==Demography== | |||
| The city administers a total population of approximately 4,500,000, of whom approximately 650,000 are urban. The population density is 235 per km². ] make up 99.8% of the population, but registered residents include representatives of 25 minority nationalities, including six with a local population of more than 100: ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| ====The establishment of the British concession==== | |||
| Unlike the ] dialects typical of Jiangxi, the local speech of Jiujiang is a variety of ]. | |||
| {{Further|British Concession of Jiujiang}}] | |||
| After China's defeat in the Second Opium War, China and Britain signed the ]. At the beginning of the eleventh year of Xianfeng (1861), the British counsellor, ], went to the new port on the Yangtse River by naval vessel according to the treaty to investigate the situation and select the site of concession to be opened. After the concession sites of Zhenjiang and Hankou were delimit, on March 22, ] returned to Jiujiang from Hankou and decided to open up a commercial port in Jiujiang.<ref>Bickers, R., & Jackson, I. (2016). Introduction: law, land and power: treaty ports and concessions in modern China. In Treaty Ports in Modern China (pp. 11–32). Routledge.</ref> | |||
| In the 11th year of xianfeng (1861), Zhang Jixin, general minister of Jiangxi province, signed with Harry Parkers the treaty of opening up the British concession in Jiujiang, the Treaty of Land Lease in Jiujiang. The concession was located in a narrow area on the west of Jiujiang, between the Yangtze River and Gantang Lake, to the west of Longkai River, with a length of 150 zhang from east to west and a depth of 60 zhang from south to north, covering an area of 150 acres. The southern part of the concession includes part of PenPu Port.<ref name="aoii">Bickers, R. (2013). 8. British Concessions and Chinese Cities, 1910s–1930s. In New Narratives of Urban Space in Republican Chinese Cities (pp. 155–195). Brill.</ref> | |||
| == Climate == | |||
| ====The development of Kuling in Mount Lu==== | |||
| {{Weather box | |||
| ] | |||
| |location = Jiujiang | |||
| In the early 20th century, ] on top of ] became the summer resort for international residents because of its beautiful geological landscape and nice climate. At the golden age, over 4000 foreigners from America and European countries lived in this small town in summer time.<ref>Nield, R. (2015). China’s Foreign Places: The Foreign Presence in China in the Treaty Port Era, 1840–1943. Hong Kong University Press.</ref> | |||
| |single line = Y | |||
| |metric first = Y | |||
| Kuling, on the slopes of a wide valley of Mount Lu, was established in 1895 by the missionaries ], ] and three others, as a sanitarium and rest resort for Western missionaries in southern China. They built their houses in the colonial style of architecture, and added churches, schools, and sports facilities. It was named by Little, as a pun: it is wonderfully ''cooling'' after the summer heat in the plains below. It was also a word that sounded conveniently Chinese to the local people, and has been adopted by them. Kuling was run by the missionaries in a Kuling Council that sold the plots of the land and with the proceeds paid for local services and security. In 1910, Caroline Maddock Hart and four others met to found the Nurses Association of China; with Caroline Maddock Hart being its first president. | |||
| |Jan mean C = 4.5 | |||
| |Feb mean C = 5.8 | |||
| ]]] | |||
| |Mar mean C = 10.2 | |||
| |Apr mean C = 16.6 | |||
| ===Modern history=== | |||
| |May mean C = 21.7 | |||
| In 1938, Jiujiang was occupied by Japanese forces during the ]. Following its capture, the city was the site of a "mini-]," where male residents were executed and women raped.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Mitter |first=Rana |title=Forgotten Ally: China's World War II, 1937-1945 |date=2013 |publisher=Houghton Mifflin Harcourt |pages=165}}</ref> Many of the city's urban districts and suburban villages were razed, including the city's ceramics factories and boats used for transportation.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Harmsen |first=Peter |title=Storm Clouds Over the Pacific, 1931–1941 (War in the Far East) |date=2018 |publisher=Casemate |pages=150–151}}</ref> | |||
| |Jun mean C = 25.6 | |||
| |Jul mean C = 29.3 | |||
| Until 1949 Jiujiang had very little industry except for local handicrafts. Manufacturing is Jiujiang's backbone today with auto, machinery, petrochemical, shipbuilding and textiles as its cornerstones. After the completion of the ] in 1992 and the ] and Wuhan to Shanghai rail systems laid, a convenient ground corridor was provided and a regional airport now serves most of China's capital cities. | |||
| |Aug mean C = 28.8 | |||
| |Sep mean C = 23.9 | |||
| In 2005, an earthquake hit ]. ] donated 200 sets of desks and chairs and more than 50 sets of Oxford English-Chinese Dictionary to a local primary school near Ruichang.<ref>{{cite web |title=牯岭芝罘学校外籍校友阔别60多年重游庐山 |url=https://jj.jxnews.com.cn/system/2012/07/23/012050366.shtml |website=Jiujiang News Network |access-date=22 July 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Kuling American School Association美国学堂 |url=http://www.kulingamericanschool.com/index.html |website=Kuling American School Association Website |access-date=22 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| |Oct mean C = 18.6 | |||
| |Nov mean C = 12.5 | |||
| ==Economy== | |||
| |Dec mean C = 6.8 | |||
| ===Economic and Technological Development Zones=== | |||
| :*Jiujiang Free Trade (Tariff-free) Zone<ref>{{cite web |title=九江综合保税区 |url=http://bsq.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |website=Jiujiang Free Trade Zone Website |access-date=20 July 2021 |archive-date=20 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210720063114/http://bsq.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| :*Jiujiang National Economical and Technological Development Zone<ref>{{cite web |title=九江国家级经济技术开发区 |url=http://jkq.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |website=Jiujiang National Economical and Technological Development Zone Website |access-date=20 July 2021 |archive-date=22 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210722230112/http://jkq.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| :*Jiujiang Gongqingcheng National High-tech Industrial Development Zone<ref>{{cite web |title=九江共青城国家高新技术产业开发区 |url=http://www.gongqing.gov.cn/zwzx/ztzl/gqcgxq/ |website=Jiujiang Gongqingcheng National High-tech Industrial Development Zone |access-date=20 July 2021 |archive-date=20 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210720063656/http://www.gongqing.gov.cn/zwzx/ztzl/gqcgxq/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ===Latest Ranking in the Chinese Cities=== | |||
| In 2021, Jiujiang's GDP is 373.528 Billion Yuan. Jiujiang's GDP ranks 70th among all Chinese cities.<ref>{{cite web |title=2021年中国城市GDP百强榜 |url=https://new.qq.com/omn/20210721/20210721A0D9Z800.html |website=tencent.com |access-date=22 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| ==Demography== | |||
| The city administers a total population of approximately 4,600,276 at the 2020 census of whom approximately 2,814,240 are urban living in the urban area.<ref name="aoi"/> The population density is 240 per km<sup>2</sup>. ] make up 99.8% of the population. Registered residents include 25 ethnic minorities. Six of them are major minorities in Jiujiang. They are: ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| Jiujiang dialect is unlike typical ] dialect of Jiangxi. Jiujiang dialect is a variety of ] and is close to Wu languages.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Lin |first=Xianlian |date=2019-03-26 |title=zh:九江方言的前世今生 |trans-title=The Past and Present Life of Jiujiang Dialect |url=http://www.zgdazxw.com.cn/culture/2019-03/26/content_272765.htm |access-date=2024-06-08 |website=www.zgdazxw.com.cn |language=zh}}</ref> | |||
| ==Climate== | |||
| Jiujiang a ] (] ''Cfa''). Extremes since 1951 have ranged from as low as {{convert|-6.7|°C|1}} (though an unofficially has reached as low as {{convert|-10|°C|1}} on 10 January 1931)<ref>{{Cite web |last=网易 |date=2018-12-08 |title=这两天根本不算冷 看看全国各大城市历史极端最低温度是几度? |url=https://www.163.com/dy/article/E2HHPSS305444WQP.html |access-date=2024-09-16 |website=www.163.com}}</ref> to as high as {{convert|40.9|°C|1}}.{{Weather box|width=auto | |||
| |metric first=y | |||
| |single line=y | |||
| |collapsed = Y | |||
| |location = Jiujiang (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||
| |Jan high C = 8.0 | |||
| |Feb high C = 11.0 | |||
| |Mar high C = 15.5 | |||
| |Apr high C = 22.1 | |||
| |May high C = 27.1 | |||
| |Jun high C = 29.8 | |||
| |Jul high C = 33.7 | |||
| |Aug high C = 32.6 | |||
| |Sep high C = 28.7 | |||
| |Oct high C = 23.5 | |||
| |Nov high C = 17.2 | |||
| |Dec high C = 10.9 | |||
| |Jan mean C = 4.9 | |||
| |Feb mean C = 7.5 | |||
| |Mar mean C = 11.5 | |||
| |Apr mean C = 17.8 | |||
| |May mean C = 22.8 | |||
| |Jun mean C = 26.1 | |||
| |Jul mean C = 29.8 | |||
| |Aug mean C = 28.7 | |||
| |Sep mean C = 24.8 | |||
| |Oct mean C = 19.6 | |||
| |Nov mean C = 13.3 | |||
| |Dec mean C = 7.3 | |||
| |Jan low C = 2.6 | |||
| |Feb low C = 5.0 | |||
| |Mar low C = 8.6 | |||
| |Apr low C = 14.5 | |||
| |May low C = 19.5 | |||
| |Jun low C = 23.3 | |||
| |Jul low C = 26.7 | |||
| |Aug low C = 25.9 | |||
| |Sep low C = 22.1 | |||
| |Oct low C = 16.7 | |||
| |Nov low C = 10.4 | |||
| |Dec low C = 4.8 | |||
| |Jan record high C = 21.3 |Jan record low C = -4.2 | |||
| |Feb record high C = 29.1 |Feb record low C = -5.3 | |||
| |Mar record high C = 31.8 |Mar record low C = -1.0 | |||
| |Apr record high C = 34.1 |Apr record low C = 3.6 | |||
| |May record high C = 37.0 |May record low C = 10.0 | |||
| |Jun record high C = 38.6 |Jun record low C = 14.5 | |||
| |Jul record high C = 40.9 |Jul record low C = 19.8 | |||
| |Aug record high C = 40.9 |Aug record low C = 17.8 | |||
| |Sep record high C = 38.9 |Sep record low C = 14.3 | |||
| |Oct record high C = 35.6 |Oct record low C = 5.6 | |||
| |Nov record high C = 29.7 |Nov record low C = -0.7 | |||
| |Dec record high C = 22.8 |Dec record low C = -6.7 | |||
| |year high C= |year low C= | |||
| |year high F = |year low F = | |||
| |precipitation colour = green | |precipitation colour = green | ||
| | |
|Jan precipitation mm = 80.7 | ||
| | |
|Feb precipitation mm = 99.2 | ||
| | |
|Mar precipitation mm = 147.6 | ||
| | |
|Apr precipitation mm = 166.6 | ||
| | |
|May precipitation mm = 186.0 | ||
| | |
|Jun precipitation mm = 229.3 | ||
| | |
|Jul precipitation mm = 170.0 | ||
| | |
|Aug precipitation mm = 123.3 | ||
| | |
|Sep precipitation mm = 74.3 | ||
| | |
|Oct precipitation mm = 73.5 | ||
| | |
|Nov precipitation mm = 73.5 | ||
| | |
|Dec precipitation mm = 54.0 | ||
| |Jan humidity = 76 | |||
| |year precipitation mm = | |||
| |Feb humidity = 75 | |||
| |unit precipitation days = 0.1 mm | |||
| |Mar humidity = 75 | |||
| | Jan precipitation days = 10.7 | |||
| |Apr humidity = 74 | |||
| | Feb precipitation days = 12.7 | |||
| |May humidity = 74 | |||
| | Mar precipitation days = 16.2 | |||
| |Jun humidity = 79 | |||
| | Apr precipitation days = 15.7 | |||
| |Jul humidity = 74 | |||
| | May precipitation days = 15.2 | |||
| |Aug humidity = 77 | |||
| | Jun precipitation days = 13.8 | |||
| |Sep humidity = 76 | |||
| | Jul precipitation days = 10.5 | |||
| |Oct humidity = 72 | |||
| | Aug precipitation days = 9.1 | |||
| |Nov humidity = 74 | |||
| | Sep precipitation days = 10.0 | |||
| |Dec humidity = 72 | |||
| | Oct precipitation days = 9.6 | |||
| | |
|unit precipitation days = 0.1 mm | ||
| | |
|Jan precipitation days = 12.6 | ||
| |Feb precipitation days = 12.4 | |||
| |source 1 = | |||
| |Mar precipitation days = 15.9 | |||
| |Apr precipitation days = 14.5 | |||
| |May precipitation days = 13.9 | |||
| |Jun precipitation days = 14.1 | |||
| |Jul precipitation days = 10.7 | |||
| |Aug precipitation days = 11.2 | |||
| |Sep precipitation days = 8.1 | |||
| |Oct precipitation days = 8.5 | |||
| |Nov precipitation days = 10.3 | |||
| |Dec precipitation days = 9.4 | |||
| |year precipitation days = | |||
| |Jan sun = 86.0 | |||
| |Feb sun = 90.3 | |||
| |Mar sun = 109.6 | |||
| |Apr sun = 135.3 | |||
| |May sun = 148.8 | |||
| |Jun sun = 133.9 | |||
| |Jul sun = 197.0 | |||
| |Aug sun = 188.7 | |||
| |Sep sun = 158.0 | |||
| |Oct sun = 152.5 | |||
| |Nov sun = 124.4 | |||
| |Dec sun = 113.0 | |||
| |year sun = | |||
| | Jan percentsun = 26 | |||
| | Feb percentsun = 29 | |||
| | Mar percentsun = 29 | |||
| | Apr percentsun = 35 | |||
| | May percentsun = 35 | |||
| | Jun percentsun = 32 | |||
| | Jul percentsun = 46 | |||
| | Aug percentsun = 47 | |||
| | Sep percentsun = 43 | |||
| | Oct percentsun = 43 | |||
| | Nov percentsun = 39 | |||
| | Dec percentsun = 36 | |||
| | year percentsun = | |||
| |Jan snow days = 3.6 | |||
| |Feb snow days = 2.2 | |||
| |Mar snow days = 0.6 | |||
| |Apr snow days = 0 | |||
| |May snow days = 0 | |||
| |Jun snow days = 0 | |||
| |Jul snow days = 0 | |||
| |Aug snow days = 0 | |||
| |Sep snow days = 0 | |||
| |Oct snow days = 0 | |||
| |Nov snow days = 0.1 | |||
| |Dec snow days = 1.5 | |||
| |year snow days = | |||
| |source 1 = ]<ref name="cma graphical">{{cite web |url=http://data.cma.cn/data/weatherBk.html |script-title=zh:中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data |publisher=] |language = zh-hans |access-date=28 June 2023}}</ref><ref> | |||
| {{cite web|url=https://experience.arcgis.com/template/e724038fda394e9d9b7921f10fd1aa55/page/%E7%BA%AF%E8%A1%A8%E6%A0%BC%E7%BB%9F%E8%AE%A1-(%E5%AF%B9%E6%AF%948110%E5%8F%98%E5%8C%96)/?org=UQmaps |script-title=zh:中国气象数据网|publisher=] |language = zh-hans | access-date =28 June 2023 |title=Experience Template }}</ref> | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| ==Industry== | ==Industry== | ||
| Primary industries and tertiary sector include:<ref>{{cite web |title=产业 |url=https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |website=Jiujiang People's Government Website |access-date=21 July 2021 |archive-date=21 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210721002539/https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| Primary industries include | |||
| * Manufacturing | |||
| * Petrochemical |
* Petrochemical Refinement | ||
| * Tourism | |||
| * Agricultural chemical production | |||
| * Import/ |
* Import/Export (through river port) | ||
| * Agricultural Chemical Production | |||
| ==Transport== | ==Transport== | ||
| === Road === | |||
| Source:<ref>{{cite web |title=公路 |url=https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |website=Jiujiang Government Website |access-date=22 July 2021 |archive-date=21 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210721002539/https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *Jiujiang Ring Expressway | |||
| *Chang-Jiu Expressway | |||
| *Jiu-Rui Expressway | |||
| *G45 Daguang Expressway | |||
| *Yongwu Expressway | |||
| *Penghu Expressway | |||
| *Xiu-ping Expressway | |||
| *Du-Jiu Expressway | |||
| *Dong-jiu Expressway | |||
| ===Rail=== | ===Rail=== | ||
| <ref>{{cite web |title=铁路 |url=https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |website=Jiujiang Government Website |access-date=22 July 2021 |archive-date=21 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210721002539/https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| Jiujiang is served by the ], ], ] and ] Railways. | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *Chang-jiu intercity railway | |||
| *Wu-jiu high speed railway | |||
| *Jiujing-qu railway | |||
| *He-an-Jiu passenger dedicated line | |||
| *Fu-gang-jiu passenger dedicated line | |||
| *Chang-jiu high speed railway. | |||
| ===Air=== | ===Air=== | ||
| <ref>{{cite web |title=机场 |url=https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |website=Jiujiang Government Website |access-date=22 July 2021 |archive-date=21 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210721002539/https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ] (JIU) | |||
| *] (JIU) | |||
| === |
===Port=== | ||
| Jiujiang Port is the largest port in Jiangxi Province located at the junction of the Yangtze River, Poyang Lake and the Beijing-Kowloon Railway. From west to east, this port consists of five docks namely Ruichang, Chengxi, Chengqu, Hukou and Pengze. As an important port situated on the lower and middle reaches of Yangtze River and one of the 5 main ports on the river, many domestic and international marine routes have been established, In the main, the freight handled consists of mineral building materials, coals, metal and nonmetal ores and petroleum. | |||
| The ] is used heavily for shipping. There is currently one bridge, the ], that carries road and rail over the river. A second bridge, the ], is under construction that will carry traffic on the ]. | |||
| <ref>{{cite web |title=港口 |url=https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |website=Jiujiang Government Website |access-date=22 July 2021 |archive-date=21 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210721002539/https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ===Yangtze Bridges=== | |||
| At present, Jiujiang has two Bridges built across the Yangtze River. They are ] and ]. The third bridge across the Yangtze River in Jiujiang is under construction. The fourth bridge across the Yangtze River in Jiujiang is being designed | |||
| <ref>{{cite web |title=大桥 |url=https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |website=Jiujiang Government Website |access-date=22 July 2021 |archive-date=21 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210721002539/https://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| <ref>{{cite web |title=九江长江大桥 |url=http://www.china-qiao.com/ql35/ksql060.htm |website=China-qiao.com |access-date=23 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| ==Colleges and universities== | ==Colleges and universities== | ||
| ] | |||
| * ]: A small picturesque college located right by the lake and next to Walmart, this college is well situated within the city. | |||
| * ]: a university located in ]. The location is most easily reached by the 101 bus from the city center.<ref>{{cite web |title=九江学院 |url=https://www.jju.edu.cn/ |website=Jiujiang University Website |access-date=19 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| * ]: a small picturesque college located right by the lake. This college is well situated within the city.<ref>{{cite web |title=江西财经职业学院 |url=https://www.jxvc.jx.cn/ |website=Jiangxi Vocational College of Finance & Economics Website |access-date=19 July 2021 |archive-date=19 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210719210930/https://www.jxvc.jx.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| * ]: a vocational college located in ] near ].<ref>{{cite web |title=九江职业技术学院 |url=https://www.jvtc.jx.cn/ |website=Jiujiang Vocational and Technical College Website |access-date=2021-07-19 |archive-date=2022-05-01 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220501183601/https://www.jvtc.jx.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| * ]: a vocational college located in ] near ].<ref>{{cite web |title=九江职业大学 |url=https://www.jxvc.jx.cn/ |website=Jiujiang Vocational University Website |access-date=19 July 2021 |archive-date=19 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210719210930/https://www.jxvc.jx.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| * ]: Located farther out from the city center, it is most easily reached by the 101 bus from the center. If you are one of the 15 or so native English speaking foreigners in the city, it is a good idea to go to Freedom Bar, located across from the university's main entrance on the second floor of the shopping mall, to meet fellow foreigners, most of whom are English teachers. | |||
| * ]: a vocational college located in Yongxiu county. Yongxiu county belongs to Jiujiang.<ref>{{cite web |title=江西枫林涉外经贸职业学院 |url=http://www.jxfte.com/ |website=Jiangxi Fenglin College of Foreign Economy & Trade Website |access-date=19 July 2021 |archive-date=27 January 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210127014309/http://www.jxfte.com/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| * ]: a vocational college located in Jiujiang Economic and Technological Development Zone.<ref>{{cite web |title=九江理工职业技术学院 |url=http://www.jjvsp.cn/ |website=Jiujiang Vocational College of Polytechnic Website |access-date=19 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| * ]: a vocational college located in ]. Gongqingcheng belongs to Jiujiang.<ref>{{cite web |title=共青职业技术学院 |url=http://www.gqkj.com.cn/ |website=Gongqing Institute of Science and Technology Website |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| * ]: a local college located in Gongqingcheng.<ref>{{cite web |title=南昌大学共青学院 |url=http://www.ndgy.cn/ |website=Gongqing College of Nanchang Website |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| * ]: a local college located in Gongqingcheng.<ref>{{cite web |title=江西师范大学科学技术学院 |url=https://kjxy.jxnu.edu.cn/ |website=Science and Technology College of Jiangxi Normal University |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| * ]: a local college located in Gongqingcheng.<ref>{{cite web |title=江西财经大学现代经济管理学院 |url=http://xjg.jxufe.cn |website=Modern Economics and Management College of Jiangxi Finance and Economics University Website |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| * ]: a vocational college located in Gongqingcheng.<ref>{{cite web |title=南昌航空大学科学技术学院 |url=http://kjxy.nchu.edu.cn/ |website=Science and Technology College of Nanchang Aviation University Website |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| * ]: a local college located in Gongqingcheng.<ref>{{cite web |title=南昌大学共青学院 |url=http://www.ndkj.com.cn/ |website=Science and Technology College of Nanchang University Website |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| * ]: a local vocational college located in Gongqingcheng.<ref>{{cite web |title=江西农业大学南昌商学院 |url=http://ncsxy.jxau.edu.cn |website=Nanchang Business College of Jiangxi Agriculture University Website |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| ==International relations== | |||
| ===Former Diplomatic Representatives in Jiujiang=== | |||
| *] was established in 1861 | |||
| *] was established on July 16, 1915 | |||
| ===Twin towns — Sister cities=== | |||
| {{See also|List of twin towns and sister cities in China}} | |||
| Jiujiang is ] with: | |||
| <ref>{{cite web|title=Sister Cities|url=http://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/english/en_jiujiang_174/201911/t20191101_2114824.html|website=jiujiang.gov.cn|publisher=Jiujiang|access-date=2020-07-12|archive-date=2020-07-14|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200714180830/http://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/english/en_jiujiang_174/201911/t20191101_2114824.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=20em}} | |||
| *{{flagicon|AUS}} ], Australia | |||
| *{{flagicon|GRC}} ], Greece | |||
| *{{flagicon|KOR}} ], South Korea | |||
| *{{flagicon|FIN}} ], Finland | |||
| *{{flagicon|SVN}} ], Slovenia | |||
| *{{flagicon|POL}} ], Poland | |||
| *{{flagicon|USA}} ], United States | |||
| *{{flagicon|ARG}} ], Argentina | |||
| *{{flagicon|BRA}} ], Brazil | |||
| *{{flagicon|ENG}} ], England, United Kingdom | |||
| *{{flagicon|USA}} ], United States | |||
| *{{flagicon|BOT}} ], Botswana | |||
| *{{flagicon|JPN}} ], Japan | |||
| <!--Würselen - not twinning--> | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ==Tourism== | ==Tourism== | ||
| ] | |||
| Picturesque ], located in the south of the urban center, is listed as a ] site. | |||
| *]: one of the most famous mountains in China. It is located in the south of the urban center and listed as a ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Mount Lu Scenic Area |url=https://au.trip.com/travel-guide/gspoi/lushan/mount-lu-scenic-area-101223 |website=Trip.com |access-date=19 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *]: is located on Mount Lu. In 1996, Mount Lu became a UNESCO ]. In 2004, the Mount Lu Geopark became a member of ]. Mount Lu Geopark is a place of striking beauty. It has spectacular peaks, lakes, cliffs, waterfalls and important Buddhist and Taoist temples.<ref>{{cite web |title=Mt. Lushan National Park |url=https://www.tripadvisor.com.au/Attraction_Review-g494935-d319118-Reviews-Mt_Lushan_National_Park-Jiujiang_Jiangxi.html |website=Tripadvisory.com |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *]: as a homonym for cooling. It is a mountain town in the Mount Lu National Park. It was established in 1895 by the missionaries ], Dr. ] and three others, as a sanitarium and summer resort for Western missionaries in southern China.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Kuling, Peake's Birthplace |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/24776512 |journal=Peake Studies |jstor=24776512 |access-date=20 July 2021|last1=Winnington |first1=G. Peter |last2=Stauber |first2=Max |year=2006 |volume=9 |issue=4 |pages=9–22 }}</ref> | |||
| *]: located on Binjiang road. It was established by local government from transforming buildings left from the former ].<ref>]</ref>{{Circular reference|date=April 2022}} | |||
| *]: a street combines Chinese and Western cultures. Beside the street are:<ref>{{cite web |title=Xunyang District "13th Five-Year" Historical and Cultural Block Construction Documentation |url=http://www.xunyang.gov.cn/zwzx/xyyw/202101/t20210112_4738127.html |website=Xunyang People's Government Website |access-date=19 July 2021 |archive-date=19 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210719222655/http://www.xunyang.gov.cn/zwzx/xyyw/202101/t20210112_4738127.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| **the old Catholic school | |||
| **the old monastery | |||
| **the Catholic church | |||
| **Taling Park | |||
| **the old Perkins Villa | |||
| **Nengren temple | |||
| **Western Goods Exhibition Window | |||
| *]: located in Hotspring town, ]. ] is a county-level city belong to Jiujiang.<ref>{{cite web |title=Lushan Hot Spring – Jiujiang |url=https://www.visitourchina.com/jiujiang/hotel/lushan-hot-spring-jiujiang.html |website=Visit Our China |access-date=19 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *]: located in Balihu Park. It is the only high standard man-made beach in ] Province. It is a famous scenic spot and entertainment resort in Jiujiang.<ref>{{cite web |title=Haiyun Sand Beach |url=https://au.trip.com/travel-guide/gspoi/jiujiang/haiyun-sand-beach-39520705 |website=Trip.com |access-date=19 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *]: located on Binjiang Road in ]. It is near shoreline of the Yangtze River. Covering an area of some 765 acres (around 509,490 sqm), with distance of 5.2 km long from east to west. It is only 4.5 km away from Jiujiang Station, 1.6 km away from Fuzhou-Yinchuan Expressway, and about an hour's drive from Changbei Airport. Its rich tourism resources include river, ancient building, garden and museum as follows:<ref>{{cite web |title=Xunyang River Scenic Area |url=https://xunyangjiang.net/english/ |website=Xunyang River Scenic Area Website |access-date=19 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| **Pipa Pavilion | |||
| **Xunyang Tower | |||
| **Suojiang Pagoda | |||
| **] | |||
| **Baishui Lake Park | |||
| **Xunyang River Cruise Ship | |||
| *]: is located about 90 kilometers to the south of Mount Lu. It is National 5-Star Scenic Spot. There are thousands of islands in the area just like Maldives. In 2007, between June and August, American reality program Survivor filmed its fifteenth season, '']'', in the area. The program host Jeff Probst claimed that this was the first American television series filmed entirely in China.<ref>{{cite web |title=庐山西海 |url=http://lsxh.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |website=Mountain Lu West Sea Website |access-date=2021-07-21 |archive-date=2021-07-21 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210721013331/http://lsxh.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| *Nanshan Park ({{zh|labels=no|s=南山公园}}): completed in early 2013. This park, home to a new pagoda, is covered in flora and lights up the Jiujiang sky at night.<ref>{{cite web |title=Nanshan Park |url=https://au.trip.com/travel-guide/gspoi/jiujiang/nanshan-park-20920706 |website=Trip.com |access-date=19 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *Yanshui Pavilion: located in city center, near Gantang lake. It is a well known scenic spot in Jiujiang.<ref>{{cite web |title=Yanshui Pavilion |url=https://en.tripadvisor.com.hk/Attraction_Review-g494935-d505767-Reviews-Yanshui_Pavilion-Jiujiang_Jiangxi.html |website=Tripadvisor |access-date=19 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *]: a Buddhist temple located at foot of Mount Lu. It is built by ], founder of ]. Pure Land Buddhism later spread to Japan and gained its prominence there. In 1175, ] established Pure Land Buddhism as an independent sect in Japan known as ]. Pure Land schools have nearly 40 percent of Japanese Buddhism practitioners, only second to ] schools.<ref>{{cite web |title=Donglin Temple |url=https://au.trip.com/travel-guide/gspoi/lushan/donglin-temple-82188 |website=Trip.com |access-date=19 July 2021}}</ref><ref name="东林祖庭">{{cite web |title=东林祖庭 |url=http://www.donglin.org/ |website=Donglin Temple Website |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| **The temple provide free vegetarian lunch and free guest house. Visitors can stay at guest house in temple for free up to three days. The guest house is gender separated, and visitors have to share room with others.<ref name="东林祖庭"/> | |||
| *]: the world's tallest statue of ]. Total cost is about 1 billion Yuan. Surface of the Buddha is plated with 48 kilograms of gold. Buddha height is 48 meters tall, representing the forty-eighth vows of Amitabha Buddha. Total height is 81 meters.<ref>{{cite web |title=Donglin Buddha |url=https://uk.trip.com/travel-guide/gspoi/lushan/donglin-buddha-18257332/ |website=Trip.com |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=东林大佛 |url=http://www.donglin.org/dafo/fuxiangzhuzao/ |website=Donglin Temple Website |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *Mount Lu Four Seasons Flower City (Botanical Garden): located in Bali lake New Area. It is Jiujiang's largest flower plant park.<ref>{{cite web |title=九江四季花城 |url=http://www.0535-0411.com/article/39906.html |website=Jiujiang News Network |access-date=20 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *Stone Bell Hill: just downriver from Jiujiang is Hukou where the Yangtze River and waters of Boyang Lake converge with an abrupt color change. People have been coming here for centuries to listen to the stone-bell sound resonating from the cliffs overlooking this spot. A few theories are provided why this rare geographical phenomenon happens. Li Daoyuan from the Northern Wei period (386–534) theorizes that it is because the hill has a bell-shaped appearance and hollow inside, thus providing the sound when struck. Or it may be because of the water lapping within the limestone nooks and fissures around its base, as famous litterateur from the same time Su Shui discovered. Su Dongpo also did three trips around its perimeter, before settling on this last explanation for its unique sound also. Many Chinese literati's have left more than twenty calligraphy masterpieces carved upon its rocks, with some dating back to the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE).<ref>{{cite web |title=Stone Bell HIll (Shizhong shan) |url=https://en.tripadvisor.com.hk/Attraction_Review-g1409077-d505764-Reviews-Stone_Bell_Hill_Shizhong_Shan-Hukou_County_Jiangxi.html |website=tripadvisor.com |access-date=19 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| ==Notable residents== | |||
| Stone Bell Hill | |||
| *] (1873–1954), one of the first western trained Chinese female physicians. Founder of Elizabeth Skelton Danforth Hospital (now called Jiujiang Women and Children's Hospital) in Jiujiang.<ref name=James_Tobin>{{cite web|last=Tobin|first=James|title=The New Women of China|url=http://www.medicineatmichigan.org/archive/2010/fall|work=Medicine at Michigan, Fall'10, Volume 12, Number 3|publisher=University of Michigan|access-date=15 February 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160328212527/http://www.medicineatmichigan.org/archive/2010/fall|archive-date=28 March 2016|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite web|url=https://womenofchristianity.com/shi-meiyu-mary-stone/|title=Shi Meiyu (Mary Stone) {{!}}|language=en-US|access-date=2020-04-27|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200428182012/http://womenofchristianity.com/shi-meiyu-mary-stone/|archive-date=2020-04-28|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| *Lo-Yi Chang (1907–1988), was born in ], ]. She was spouse of ], then Premier of the Republic of China. She has made a significant contribution to the promotion of China overseas.<ref>{{cite web |title=国内名人传记丛书(套装共6册) |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hvY0CgAAQBAJ&dq=%E5%BC%A0%E4%B9%90%E6%80%A1%E4%BD%9C%E5%87%BA%E8%B4%A1%E7%8C%AE&pg=PT851 |website=books.google |access-date=22 July 2021|author1 = 池昕鸿|date = 22 July 2015}}</ref> | |||
| *] (1892–1973), was the first American woman to win the Nobel Prize in Literature, for her rich and truly epic descriptions of peasant life in China, in 1938. She also won Pulitzer Prize in 1932. She spent her childhood with her family in ] in summer time. Her father built a stone villa in Kuling in 1897, and lived there until his death in 1931.<ref>{{cite web |title=赛兆祥墓碑 |url=http://www.mylushan.com/Stone/2009108/200910819545821.html |website=mylushan.com |access-date=22 July 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Pearl S. Buck house in Zhenjiang |url=http://www.sexualfables.com/Pearl-Buck-house-in-Zhenjiang.php |access-date=22 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *{{ill|Masato Matsuura|ja|松浦正人}} (松浦正人) (1942– ), born in Jiujiang. He was a Japanese politician. He served as ] mayor and president of National Mayors Association of Japan.<ref>{{cite web |title=松浦正人 |url=https://www.zhz.wiki/blog/ja/%E6%9D%BE%E6%B5%A6%E6%AD%A3%E4%BA%BA |website=ZHZ.wiki |access-date=22 July 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=7/30 日本全國市長會會長松浦正人就任祝賀會 |url=https://www.roc-taiwan.org/jpfuk/post/7545.html |website=Fukuoka Branch, Taipei Economic and Cultural Office in Osaka Website |access-date=22 July 2021}}</ref> In 2018, then ] mayor and president of National Mayors Association of Japan (NMAJ), Masato Matsuura (松浦正人), led a delegation of NMAJ visited ]. Masato Matsuura said :''I was born in the former Japanese consulate of Jiujiang. Jiujiang is my second hometown. I am deeply attached to the beautiful landscape here''.<ref>{{cite web |title=日本全国市长会代表团来访九江租界旧址 |url=http://www.jjwenlv.com/detail.php?wzid=787&lbid=1264 |website=Jiujiang Cultural and Tourism Development Group Website |access-date=21 July 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *] (1903–1977), born in Jiujiang. He was a Chinese poet, author, painter and calligrapher. His translation of ''Coca Cola'' is remembered by all Chinese.<ref>Huang, Shuchen S., "Chiang Yee", in ''Asian-American Autobiographers: a bio-bibliographical critical sourcebook'', edited by Guiyou Huang, Greenwood Press, 2001. {{ISBN|0-313-31408-X}}.</ref> | |||
| Just downriver from Jiujiang is Hukou where the Yangtze River and waters of Boyang Lake converge with an abrupt color change. People have been coming here for centuries to listen to the stone-bell sound resonating from the cliffs overlooking this spot. A few theories are provided why this rare geographical phenomenon happens Li Dao Yuan writes from the Northern Wei period (386-534), is due to the hill having a bell-shaped appearance and hollow inside, thus providing the sound when struck or water lapping within the limestone nooks and fissures around its base, as famous litterateur from the same time Su Shui discovered. Su Dong Po also did three trips around its perimeter, before settling on this last explanation for its unique sound also. | |||
| *] (1911–1968), born in ], ]. He was an English writer, artist, poet, and illustrator. He was well known for being the illustrator of ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''.<ref>{{cite book |title=Alice's Adventures in Wonderland |isbn = 1582341745|last1 = Carroll|first1 = Lewis|date = 12 October 2001| publisher=Bloomsbury Publishing USA }}</ref> | |||
| Many Chinese literati's have left more than twenty calligraphy masterpieces carved upon its rocks, with some dating back to the Tang dynasty (618-907 CE). | |||
| * ] (2000- ), born in Jiujiang and adopted to Canada at an early age<ref>{{cite web|last=Tang|first=Didi|url=https://www.thetimes.co.uk/article/maggie-mac-neils-olympic-gold-for-canada-thrusts-chinas-one-child-policy-back-into-spotlight-5753w9h53|title=Maggie Mac Neil's Olympic gold for Canada thrusts China's one-child policy back into spotlight|newspaper=]|date=2021-07-27|access-date=2021-08-01}}</ref> | |||
| *] (1915–2022), born in Kiukiang and later became a Los Angeles restaurateur and a writer. | |||
| *] (died 1920), Methodist missionary educator born in Jiujiang<ref>Honsinger, Welthy B., ''Woman's Missionary Friend'' 52(20)(August 1920): 285.</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| 南山公园 (Nanshan Gongyuan) Nanshan Park | |||
| Completed in early 2013, this brand new pagoda and surrounding park are a relaxing get away from the center of the city. The pagoda itself should be open rather soon (as of March 2013 residents are not permitted to enter the pagoda), and the park itself is covered in flora and lights up the Jiujiang sky at night. | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| File:Nanshan Park.JPG|Nanshan Park | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| * ] | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{Commons category|Jiujiang}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{ |
{{Reflist|30em}} | ||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{Commons category|Jiujiang}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070228211856/http://www.jiujiang.gov.cn/ |date=2007-02-28 }} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110703032300/http://www.china-lushan.com/ |date=2011-07-03 }} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210720171402/http://www.jjxw.cn/ |date=2021-07-20 }} | |||
| * | |||
| {{Jiangxi topics}} | {{Jiangxi topics}} | ||
| {{Jiangxi}} | {{Jiangxi}} | ||
| {{Prefectural-level divisions of the People's Republic of China}} | |||
| {{Major cities along the Yangtze River}} | {{Major cities along the Yangtze River}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:03, 31 December 2024
Prefecture-level city in Jiangxi, China For other uses, see Jiujiang (disambiguation). Prefecture-level city in Jiangxi, People's Republic of China| Jiujiang 九江市Kiukiang | |
|---|---|
| Prefecture-level city | |
       Top to bottom, left to right: Jiujiang Culture and Art Center, Pagoda of Suojiang Pavilion, Jiu Jiang victory monument, looking at Wulaofeng from Mount Lushan's Pokou, Suojiang pavilion, Bali Hunan lake, Ruqin lake Top to bottom, left to right: Jiujiang Culture and Art Center, Pagoda of Suojiang Pavilion, Jiu Jiang victory monument, looking at Wulaofeng from Mount Lushan's Pokou, Suojiang pavilion, Bali Hunan lake, Ruqin lake | |
 Location of Jiujiang City jurisdiction in Jiangxi Location of Jiujiang City jurisdiction in Jiangxi | |
| Coordinates (Jiujiang municipal government): 29°39′40″N 115°57′14″E / 29.661°N 115.954°E / 29.661; 115.954 | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Jiangxi |
| Seat | Municipal seat |
| Government | |
| • Party Secretary | Liu Wenhua |
| • Mayor | Yang Wenbin |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 18,823 km (7,268 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 598 km (231 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 598 km (231 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 20 m (70 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 1,794 m (5,886 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,600,276 |
| • Density | 240/km (630/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,814,240 |
| • Urban density | 4,700/km (12,000/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,164,268 |
| • Metro density | 1,900/km (5,000/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Prefecture-level city | CN¥ 190.3 billion US$ 30.5 billion |
| • Per capita | CN¥ 39,505 US$ 6,343 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-JX-04 |
| Website | www |
| Jiujiang | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 九江 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Kiukang | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Nine Rivers | ||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Jiujiang, formerly transliterated Kiukiang and Kew-Keang, is a prefecture-level city located on the southern shores of the Yangtze River in northwest Jiangxi Province in the People's Republic of China. It is the second-largest prefecture-level city in Jiangxi and its borders include Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Jiujiang is the fourth largest port on the Yangtze River and was one of the first five cities that were opened to foreign trade along the Yangtze River following the implementation of Deng Xiaoping's Opening-Up Policy. It is Jiangxi's only international trade port city.
Its population was 4,600,276 inhabitants at the 2020 census, 1,164,268 of whom resided in the built-up area (metro) made up of three urban districts (aka Xunyang, Lianxi, and Chaisang). In 2007, the city was named China's top ten livable cities by the Chinese Cities Brand Value Report, which was released at 2007 Beijing Summit of China Cities Forum. In 2022, the State Council of China granted Jiujiang the title of Famed National Historical and Cultural City for its rich history and multiculture background in the Republic of China era.
Administrative divisions

- Xunyang District (浔阳区)
- Lianxi District (濂溪区)
- Chaisang District (柴桑区)
- Wuning County (武宁县)
- Xiushui County (修水县)
- Yongxiu County (永修县)
- De'an County (德安县)
- Duchang County (都昌县)
- Hukou County (湖口县)
- Pengze County (彭泽县)
- Ruichang (瑞昌市)
- Gongqingcheng (共青城市). Directly administered as a sub-prefecture-level city since 1 July 2014.
- Lushan (庐山市)
- Others:
- Bureau and Administration Committees
- Mount Lu Scenic Area Administration Bureau
- Mount Lu West Sea Scenic Area Management Committee
- Bali Lake New Area Management Committee
- Poyang Lake Ecological Science and Technology City Management Committee
- Towns and Sub-district Offices
- There are 235 towns and 11 sub-district offices
| Map |
|---|
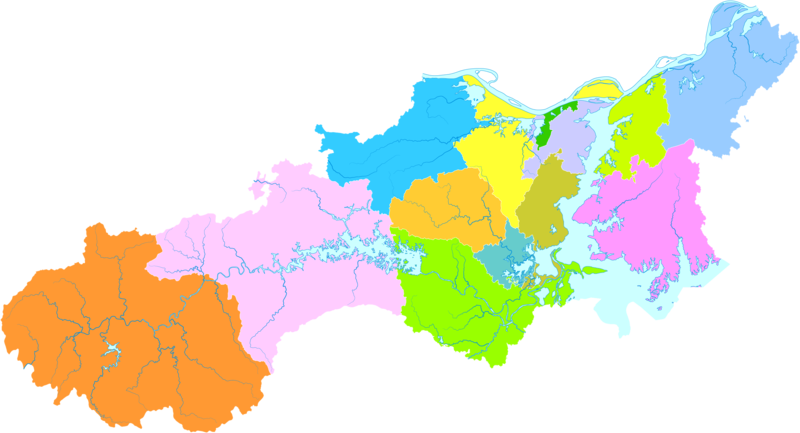 Xunyang
*
Lianxi
Chaisang
Xunyang
*
Lianxi
Chaisang* Wuning County Xiushui County Yongxiu County De'an County Duchang County Hukou County Pengze County Ruichang (city) Gongqingcheng (city) Lushan (city) Poyang Lake |
History

Ancient history
In ancient times it was told that nine rivers converged near where Jiujiang sprang up to become Jiangxi's main water port today. From the Xia to the Shang dynasty, the capitals of several states were located in area of Jiujiang. In the Spring and Autumn period (770–476 BCE) Jiujiang bordered between the states of Wu (downstream, to the east) and Chu (upstream, to the west).
Imperial history
Tao Yuanming (365–429 CE), a famous Chinese philosopher, recluse and poet, lived at the base of Mount Lu. He was once appointed magistrate of nearby Pengze County and after 83 days resigned owing to the politics involved in administering justice. He retired back to his village to pen an essay called "Peach Blossom Spring". In 757, Li Bai (701–762 CE) was implicated in the An–Shi disturbances and exiled at Jiujiang. Bai Juyi (772–846 CE) wrote a poem called "Lute Song", which is about his sadness and isolation of forced exile as a middle rank official to reside in such a small and remote town. In the 13th century Zhu Xi was a Confucian philosopher who practiced at the White Deer Grotto Academy, on Mount Lu's eastern flanks.
Jiujiang has also been known as Jiangzhou (江州) and Xunyang (浔阳) in former times. During the Jin dynasty (266–420) it was known as Sin Yang, the Liang dynasty (502–557) of Southern and Northern Dynasties era it was called Jiangzhou. After reunification, the Sui dynasty saw its name as Jiujiang, and the Song dynasty (960–1127) called it Ting Jiang. The Ming dynasty (1368–1644), gave it Jiujiang which has retained its name to this day. It was a Taiping rebellion stronghold for five years (1850–1864) after they devastated the town to only leave one street with buildings intact. The city served as the capital of Taiping's Jiangxi province during this time.
British concession and European settlement history





The arrival of the Europeans
A member of Lord Elgin's committee arriving in 1858 to survey Chinese ports for treaty status noted: "We found it to the last degree deplorable." A single dilapidated street, composed only of a few mean shops, was all that existed of this once thriving populous city. The remainder of the vast area composed within its massive walls 9–10 kilometers in circumference, contained nothing but ruins, weeds and kitchen gardens. After Jiujiang becoming an open treaty port in 1862, it was exporting Jiangxi's vast rice crop. In 1904, more than 160,000 kilos of opium were moved through its customs house. The New York Methodist Mission Society's superintendent, Virgil C. Hart, arrived in Kiukiang in 1866 and bought a piece of property just east of the city wall. This is where the city's first Methodist church and Western hospital was built, with the hospital renamed the No. 1 Hospital, and the oldest/continuous operating hospital in Jiangxi Province. In 1896 Drs. Mary Stone (Shi Meiyu) and Ida Kahn (Kahn Cheng) arrived back in Jiujiang, being China's first two native female Western-educated doctors; having graduated from the University of Michigan Medical School. They were provided with funds collected by Dr. I. N. Danforth (from Chicago residents), to build the Elizabeth Skelton Danforth Hospital and administered entirely by the native Chinese. This was later renamed Jiujiang Women's and Children's Hospital, and the nursing education by Drs. Stone and Kahn would later be the impetus for the founding of Jiujiang University and Jiujiang Medical School.
It became one of the three centers of the tea trade in China along with Hankou and Fuzhou. The Russians had two brick tea producing factories, but ceased operations after 1917. On October 16, 1927, there was an explosion of ammunition on the Chinese troopship Kuang Yuang near Jiujiang. The British surrendered their concession in 1927 after being robbed and its Chinese workers mutineered their posts to the marauding crowds. An economic recession had set in over the decades as Indian and Chelonian tea made for greater competition. A military advance was being staged upriver in Wuhan by the Kuomintang in 1927 and all the remaining expatriate community fled on British and American warships towards safer waters of Shanghai, to never return. Jiujiang languished as a port and much of its export trade was siphoned off with the connecting of Nanchang to coastal rail lines built in 1936–37.
The establishment of the British concession
Further information: British Concession of Jiujiang
After China's defeat in the Second Opium War, China and Britain signed the Treaty of Tientsin. At the beginning of the eleventh year of Xianfeng (1861), the British counsellor, Harry Parkes, went to the new port on the Yangtse River by naval vessel according to the treaty to investigate the situation and select the site of concession to be opened. After the concession sites of Zhenjiang and Hankou were delimit, on March 22, Harry Parkes returned to Jiujiang from Hankou and decided to open up a commercial port in Jiujiang.
In the 11th year of xianfeng (1861), Zhang Jixin, general minister of Jiangxi province, signed with Harry Parkers the treaty of opening up the British concession in Jiujiang, the Treaty of Land Lease in Jiujiang. The concession was located in a narrow area on the west of Jiujiang, between the Yangtze River and Gantang Lake, to the west of Longkai River, with a length of 150 zhang from east to west and a depth of 60 zhang from south to north, covering an area of 150 acres. The southern part of the concession includes part of PenPu Port.
The development of Kuling in Mount Lu

In the early 20th century, Kuling on top of Mount Lu became the summer resort for international residents because of its beautiful geological landscape and nice climate. At the golden age, over 4000 foreigners from America and European countries lived in this small town in summer time.
Kuling, on the slopes of a wide valley of Mount Lu, was established in 1895 by the missionaries Edward Selby Little, Dr. Edgerton Haskell Hart and three others, as a sanitarium and rest resort for Western missionaries in southern China. They built their houses in the colonial style of architecture, and added churches, schools, and sports facilities. It was named by Little, as a pun: it is wonderfully cooling after the summer heat in the plains below. It was also a word that sounded conveniently Chinese to the local people, and has been adopted by them. Kuling was run by the missionaries in a Kuling Council that sold the plots of the land and with the proceeds paid for local services and security. In 1910, Caroline Maddock Hart and four others met to found the Nurses Association of China; with Caroline Maddock Hart being its first president.

Modern history
In 1938, Jiujiang was occupied by Japanese forces during the Wuhan campaign. Following its capture, the city was the site of a "mini-Nanjing Massacre," where male residents were executed and women raped. Many of the city's urban districts and suburban villages were razed, including the city's ceramics factories and boats used for transportation.
Until 1949 Jiujiang had very little industry except for local handicrafts. Manufacturing is Jiujiang's backbone today with auto, machinery, petrochemical, shipbuilding and textiles as its cornerstones. After the completion of the Yangtze River Bridge in 1992 and the Beijing to Kowloon (Hong Kong) and Wuhan to Shanghai rail systems laid, a convenient ground corridor was provided and a regional airport now serves most of China's capital cities.
In 2005, an earthquake hit Ruichang. Kuling American School Association donated 200 sets of desks and chairs and more than 50 sets of Oxford English-Chinese Dictionary to a local primary school near Ruichang.
Economy
Economic and Technological Development Zones
- Jiujiang Free Trade (Tariff-free) Zone
- Jiujiang National Economical and Technological Development Zone
- Jiujiang Gongqingcheng National High-tech Industrial Development Zone
Latest Ranking in the Chinese Cities
In 2021, Jiujiang's GDP is 373.528 Billion Yuan. Jiujiang's GDP ranks 70th among all Chinese cities.
Demography
The city administers a total population of approximately 4,600,276 at the 2020 census of whom approximately 2,814,240 are urban living in the urban area. The population density is 240 per km. Han Chinese make up 99.8% of the population. Registered residents include 25 ethnic minorities. Six of them are major minorities in Jiujiang. They are: Hui, Miao, Zhuang, Tujia, and She.
Jiujiang dialect is unlike typical Gan dialect of Jiangxi. Jiujiang dialect is a variety of Lower Yangtze Mandarin and is close to Wu languages.
Climate
Jiujiang a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa). Extremes since 1951 have ranged from as low as −6.7 °C (19.9 °F) (though an unofficially has reached as low as −10 °C (14.0 °F) on 10 January 1931) to as high as 40.9 °C (105.6 °F).
| Climate data for Jiujiang (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 21.3 (70.3) |
29.1 (84.4) |
31.8 (89.2) |
34.1 (93.4) |
37.0 (98.6) |
38.6 (101.5) |
40.9 (105.6) |
40.9 (105.6) |
38.9 (102.0) |
35.6 (96.1) |
29.7 (85.5) |
22.8 (73.0) |
40.9 (105.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 8.0 (46.4) |
11.0 (51.8) |
15.5 (59.9) |
22.1 (71.8) |
27.1 (80.8) |
29.8 (85.6) |
33.7 (92.7) |
32.6 (90.7) |
28.7 (83.7) |
23.5 (74.3) |
17.2 (63.0) |
10.9 (51.6) |
21.7 (71.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.9 (40.8) |
7.5 (45.5) |
11.5 (52.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
26.1 (79.0) |
29.8 (85.6) |
28.7 (83.7) |
24.8 (76.6) |
19.6 (67.3) |
13.3 (55.9) |
7.3 (45.1) |
17.8 (64.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 2.6 (36.7) |
5.0 (41.0) |
8.6 (47.5) |
14.5 (58.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
23.3 (73.9) |
26.7 (80.1) |
25.9 (78.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
16.7 (62.1) |
10.4 (50.7) |
4.8 (40.6) |
15.0 (59.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −4.2 (24.4) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
3.6 (38.5) |
10.0 (50.0) |
14.5 (58.1) |
19.8 (67.6) |
17.8 (64.0) |
14.3 (57.7) |
5.6 (42.1) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 80.7 (3.18) |
99.2 (3.91) |
147.6 (5.81) |
166.6 (6.56) |
186.0 (7.32) |
229.3 (9.03) |
170.0 (6.69) |
123.3 (4.85) |
74.3 (2.93) |
73.5 (2.89) |
73.5 (2.89) |
54.0 (2.13) |
1,478 (58.19) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 12.6 | 12.4 | 15.9 | 14.5 | 13.9 | 14.1 | 10.7 | 11.2 | 8.1 | 8.5 | 10.3 | 9.4 | 141.6 |
| Average snowy days | 3.6 | 2.2 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 76 | 75 | 75 | 74 | 74 | 79 | 74 | 77 | 76 | 72 | 74 | 72 | 75 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 86.0 | 90.3 | 109.6 | 135.3 | 148.8 | 133.9 | 197.0 | 188.7 | 158.0 | 152.5 | 124.4 | 113.0 | 1,637.5 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 26 | 29 | 29 | 35 | 35 | 32 | 46 | 47 | 43 | 43 | 39 | 36 | 37 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration | |||||||||||||
Industry
Primary industries and tertiary sector include:
- Manufacturing
- Petrochemical Refinement
- Tourism
- Import/Export (through river port)
- Agricultural Chemical Production
Transport
Road
Source:
- G56 Hangzhou–Ruili Expressway
- G70 Fuzhou–Yinchuan Expressway
- Jiujiang Ring Expressway
- Chang-Jiu Expressway
- Jiu-Rui Expressway
- G45 Daguang Expressway
- Yongwu Expressway
- Penghu Expressway
- Xiu-ping Expressway
- Du-Jiu Expressway
- Dong-jiu Expressway
Rail
- Beijing-Kowloon
- Tongling–Jiujiang
- Hefei–Jiujiang
- Wuhan–Jiujiang
- Nanchang–Jiujiang Intercity Railway
- Chang-jiu intercity railway
- Wu-jiu high speed railway
- Jiujing-qu railway
- He-an-Jiu passenger dedicated line
- Fu-gang-jiu passenger dedicated line
- Chang-jiu high speed railway.
Air
- Jiujiang Lushan Airport (JIU)
Port
Jiujiang Port is the largest port in Jiangxi Province located at the junction of the Yangtze River, Poyang Lake and the Beijing-Kowloon Railway. From west to east, this port consists of five docks namely Ruichang, Chengxi, Chengqu, Hukou and Pengze. As an important port situated on the lower and middle reaches of Yangtze River and one of the 5 main ports on the river, many domestic and international marine routes have been established, In the main, the freight handled consists of mineral building materials, coals, metal and nonmetal ores and petroleum.
Yangtze Bridges
At present, Jiujiang has two Bridges built across the Yangtze River. They are Jiujiang Yangtze River Bridge and Jiujiang Yangtze River Expressway Bridge. The third bridge across the Yangtze River in Jiujiang is under construction. The fourth bridge across the Yangtze River in Jiujiang is being designed
Colleges and universities

- University of Jiujiang: a university located in Lianxi District. The location is most easily reached by the 101 bus from the city center.
- Jiangxi Vocational College of Finance and Economics: a small picturesque college located right by the lake. This college is well situated within the city.
- Jiujiang Vocational and Technical College: a vocational college located in Lianxi District near University of Jiujiang.
- Jiujiang Vocational University: a vocational college located in Lianxi District near University of Jiujiang.
- Jiangxi Fenglin College: a vocational college located in Yongxiu county. Yongxiu county belongs to Jiujiang.
- Jiujiang Vocational College of Polytechnic: a vocational college located in Jiujiang Economic and Technological Development Zone.
- Gongqing Institute of Science and Technology: a vocational college located in Gongqingcheng. Gongqingcheng belongs to Jiujiang.
- Gongqing College of Nanchang University: a local college located in Gongqingcheng.
- Science and Technology College of Jiangxi Normal University: a local college located in Gongqingcheng.
- Modern Economics and Management College of Jiangxi Finance and Economics University: a local college located in Gongqingcheng.
- Science and Technology College of Nanchang Aviation University: a vocational college located in Gongqingcheng.
- Science and Technology College of Nanchang University: a local college located in Gongqingcheng.
- Nanchang Business College of Jiangxi Agriculture University: a local vocational college located in Gongqingcheng.
International relations
Former Diplomatic Representatives in Jiujiang
- British Consulate General Jiujiang was established in 1861
- Japanese Consulate General Jiujiang was established on July 16, 1915
Twin towns — Sister cities
See also: List of twin towns and sister cities in ChinaJiujiang is twinned with:
 Baw Baw, Australia
Baw Baw, Australia Chios, Greece
Chios, Greece Jeongseon, South Korea
Jeongseon, South Korea Kajaani, Finland
Kajaani, Finland Koper, Slovenia
Koper, Slovenia Legionowo, Poland
Legionowo, Poland Louisville, United States
Louisville, United States La Plata, Argentina
La Plata, Argentina Queimados, Brazil
Queimados, Brazil Redbridge, England, United Kingdom
Redbridge, England, United Kingdom Savannah, United States
Savannah, United States Serowe, Botswana
Serowe, Botswana Tamano, Japan
Tamano, Japan
Tourism

- Mount Lu: one of the most famous mountains in China. It is located in the south of the urban center and listed as a World Heritage Site.
- Mount Lu Geopark: is located on Mount Lu. In 1996, Mount Lu became a UNESCO World Heritage Site. In 2004, the Mount Lu Geopark became a member of Global Geoparks Network. Mount Lu Geopark is a place of striking beauty. It has spectacular peaks, lakes, cliffs, waterfalls and important Buddhist and Taoist temples.
- Kuling: as a homonym for cooling. It is a mountain town in the Mount Lu National Park. It was established in 1895 by the missionaries Edward Selby Little, Dr. Edgerton Haskell Hart and three others, as a sanitarium and summer resort for Western missionaries in southern China.
- British Concession Museum: located on Binjiang road. It was established by local government from transforming buildings left from the former British Concession of Jiujiang.
- Yuliang South Road Historical and Cultural Block: a street combines Chinese and Western cultures. Beside the street are:
- the old Catholic school
- the old monastery
- the Catholic church
- Taling Park
- the old Perkins Villa
- Nengren temple
- Western Goods Exhibition Window
- Lushan Hotspring: located in Hotspring town, Lushan City. Lushan City is a county-level city belong to Jiujiang.
- Haiyun Sand Beach: located in Balihu Park. It is the only high standard man-made beach in Jiangxi Province. It is a famous scenic spot and entertainment resort in Jiujiang.
- Xunyang River Scenic Area: located on Binjiang Road in Xunyang District. It is near shoreline of the Yangtze River. Covering an area of some 765 acres (around 509,490 sqm), with distance of 5.2 km long from east to west. It is only 4.5 km away from Jiujiang Station, 1.6 km away from Fuzhou-Yinchuan Expressway, and about an hour's drive from Changbei Airport. Its rich tourism resources include river, ancient building, garden and museum as follows:
- Pipa Pavilion
- Xunyang Tower
- Suojiang Pagoda
- British Concession Museum
- Baishui Lake Park
- Xunyang River Cruise Ship
- Mount Lu West Sea: is located about 90 kilometers to the south of Mount Lu. It is National 5-Star Scenic Spot. There are thousands of islands in the area just like Maldives. In 2007, between June and August, American reality program Survivor filmed its fifteenth season, Survivor: China, in the area. The program host Jeff Probst claimed that this was the first American television series filmed entirely in China.
- Nanshan Park (南山公园): completed in early 2013. This park, home to a new pagoda, is covered in flora and lights up the Jiujiang sky at night.
- Yanshui Pavilion: located in city center, near Gantang lake. It is a well known scenic spot in Jiujiang.
- Donglin Temple: a Buddhist temple located at foot of Mount Lu. It is built by Huiyuan (Buddhist), founder of Pure Land Buddhism. Pure Land Buddhism later spread to Japan and gained its prominence there. In 1175, Hōnen established Pure Land Buddhism as an independent sect in Japan known as Jōdo-shū. Pure Land schools have nearly 40 percent of Japanese Buddhism practitioners, only second to Chan schools.
- The temple provide free vegetarian lunch and free guest house. Visitors can stay at guest house in temple for free up to three days. The guest house is gender separated, and visitors have to share room with others.
- Donglin Buddha: the world's tallest statue of Amitabha Buddha. Total cost is about 1 billion Yuan. Surface of the Buddha is plated with 48 kilograms of gold. Buddha height is 48 meters tall, representing the forty-eighth vows of Amitabha Buddha. Total height is 81 meters.
- Mount Lu Four Seasons Flower City (Botanical Garden): located in Bali lake New Area. It is Jiujiang's largest flower plant park.
- Stone Bell Hill: just downriver from Jiujiang is Hukou where the Yangtze River and waters of Boyang Lake converge with an abrupt color change. People have been coming here for centuries to listen to the stone-bell sound resonating from the cliffs overlooking this spot. A few theories are provided why this rare geographical phenomenon happens. Li Daoyuan from the Northern Wei period (386–534) theorizes that it is because the hill has a bell-shaped appearance and hollow inside, thus providing the sound when struck. Or it may be because of the water lapping within the limestone nooks and fissures around its base, as famous litterateur from the same time Su Shui discovered. Su Dongpo also did three trips around its perimeter, before settling on this last explanation for its unique sound also. Many Chinese literati's have left more than twenty calligraphy masterpieces carved upon its rocks, with some dating back to the Tang dynasty (618–907 CE).
Notable residents
- Mary Stone (Shi Meiyu) (1873–1954), one of the first western trained Chinese female physicians. Founder of Elizabeth Skelton Danforth Hospital (now called Jiujiang Women and Children's Hospital) in Jiujiang.
- Lo-Yi Chang (1907–1988), was born in Kuling, Mount Lu. She was spouse of T.V. Soong, then Premier of the Republic of China. She has made a significant contribution to the promotion of China overseas.
- Pearl S. Buck (1892–1973), was the first American woman to win the Nobel Prize in Literature, for her rich and truly epic descriptions of peasant life in China, in 1938. She also won Pulitzer Prize in 1932. She spent her childhood with her family in Kuling in summer time. Her father built a stone villa in Kuling in 1897, and lived there until his death in 1931.
- Masato Matsuura [ja] (松浦正人) (1942– ), born in Jiujiang. He was a Japanese politician. He served as Hōfu mayor and president of National Mayors Association of Japan. In 2018, then Hōfu mayor and president of National Mayors Association of Japan (NMAJ), Masato Matsuura (松浦正人), led a delegation of NMAJ visited former Japanese consulate of Jiujiang. Masato Matsuura said :I was born in the former Japanese consulate of Jiujiang. Jiujiang is my second hometown. I am deeply attached to the beautiful landscape here.
- Chiang Yee (1903–1977), born in Jiujiang. He was a Chinese poet, author, painter and calligrapher. His translation of Coca Cola is remembered by all Chinese.
- Mervyn Peake (1911–1968), born in Kuling, Mount Lu. He was an English writer, artist, poet, and illustrator. He was well known for being the illustrator of Alice's Adventures in Wonderland.
- Maggie Mac Neil (2000- ), born in Jiujiang and adopted to Canada at an early age
- Sylvia Wu (1915–2022), born in Kiukiang and later became a Los Angeles restaurateur and a writer.
- Ilien Tang (died 1920), Methodist missionary educator born in Jiujiang
See also
References
- 地理交通 [Geography and transport] (in Simplified Chinese). Jiujiang People's Government. Archived from the original on 18 November 2019. Retrieved 1 June 2018.
- 江西省统计局、国家统计局江西调查总队 (August 2016). 《江西统计年鉴-2016》. 中国统计出版社. ISBN 978-7-5037-7809-4. Archived from the original on 2018-05-11. Retrieved 2017-06-05.
- "改革开放40年:九江港成为名副其实的"亿吨大港"". Jiujiang News Network. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- ""百年老港"江西九江港稳固亿吨大港地位". Sohu.com. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- ^ "九江市第七次全国人口普查公报" (PDF). Jiujiang Statistics Bureau Website. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 November 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "China's Top 10 Most Livable Cities". hnloudi.gov.cn. Hunan Loudi Official Government. 2012-03-28. Archived from the original on 2013-04-10. Retrieved 2014-08-04.
- 共青城市被列入省直管县改革试点 (in Simplified Chinese). People.com.cn. 29 May 2014. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 7 June 2018.
- "Man On A Mission" by Stanley Crawford
- "The Middle Kingdom's Miracle Maidens" by Stanley Crawford
- "1,200 Die as Yangtse Troopship Blows Up". The New York Times. October 17, 1926.
- Bickers, R., & Jackson, I. (2016). Introduction: law, land and power: treaty ports and concessions in modern China. In Treaty Ports in Modern China (pp. 11–32). Routledge.
- Bickers, R. (2013). 8. British Concessions and Chinese Cities, 1910s–1930s. In New Narratives of Urban Space in Republican Chinese Cities (pp. 155–195). Brill.
- Nield, R. (2015). China’s Foreign Places: The Foreign Presence in China in the Treaty Port Era, 1840–1943. Hong Kong University Press.
- Mitter, Rana (2013). Forgotten Ally: China's World War II, 1937-1945. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 165.
- Harmsen, Peter (2018). Storm Clouds Over the Pacific, 1931–1941 (War in the Far East). Casemate. pp. 150–151.
- "牯岭芝罘学校外籍校友阔别60多年重游庐山". Jiujiang News Network. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "Kuling American School Association美国学堂". Kuling American School Association Website. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "九江综合保税区". Jiujiang Free Trade Zone Website. Archived from the original on 20 July 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "九江国家级经济技术开发区". Jiujiang National Economical and Technological Development Zone Website. Archived from the original on 22 July 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "九江共青城国家高新技术产业开发区". Jiujiang Gongqingcheng National High-tech Industrial Development Zone. Archived from the original on 20 July 2021. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "2021年中国城市GDP百强榜". tencent.com. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- Lin, Xianlian (2019-03-26). "zh:九江方言的前世今生" [The Past and Present Life of Jiujiang Dialect]. www.zgdazxw.com.cn (in Chinese). Retrieved 2024-06-08.
- 网易 (2018-12-08). "这两天根本不算冷 看看全国各大城市历史极端最低温度是几度?". www.163.com. Retrieved 2024-09-16.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 June 2023.
- "Experience Template" 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 June 2023.
- "产业". Jiujiang People's Government Website. Archived from the original on 21 July 2021. Retrieved 21 July 2021.
- "公路". Jiujiang Government Website. Archived from the original on 21 July 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "铁路". Jiujiang Government Website. Archived from the original on 21 July 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "机场". Jiujiang Government Website. Archived from the original on 21 July 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "港口". Jiujiang Government Website. Archived from the original on 21 July 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "大桥". Jiujiang Government Website. Archived from the original on 21 July 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "九江长江大桥". China-qiao.com. Retrieved 23 July 2021.
- "九江学院". Jiujiang University Website. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "江西财经职业学院". Jiangxi Vocational College of Finance & Economics Website. Archived from the original on 19 July 2021. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "九江职业技术学院". Jiujiang Vocational and Technical College Website. Archived from the original on 2022-05-01. Retrieved 2021-07-19.
- "九江职业大学". Jiujiang Vocational University Website. Archived from the original on 19 July 2021. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "江西枫林涉外经贸职业学院". Jiangxi Fenglin College of Foreign Economy & Trade Website. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "九江理工职业技术学院". Jiujiang Vocational College of Polytechnic Website. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "共青职业技术学院". Gongqing Institute of Science and Technology Website. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "南昌大学共青学院". Gongqing College of Nanchang Website. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "江西师范大学科学技术学院". Science and Technology College of Jiangxi Normal University. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "江西财经大学现代经济管理学院". Modern Economics and Management College of Jiangxi Finance and Economics University Website. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "南昌航空大学科学技术学院". Science and Technology College of Nanchang Aviation University Website. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "南昌大学共青学院". Science and Technology College of Nanchang University Website. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "江西农业大学南昌商学院". Nanchang Business College of Jiangxi Agriculture University Website. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "Sister Cities". jiujiang.gov.cn. Jiujiang. Archived from the original on 2020-07-14. Retrieved 2020-07-12.
- "Mount Lu Scenic Area". Trip.com. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "Mt. Lushan National Park". Tripadvisory.com. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- Winnington, G. Peter; Stauber, Max (2006). "Kuling, Peake's Birthplace". Peake Studies. 9 (4): 9–22. JSTOR 24776512. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- British Concession in Jiujiang
- "Xunyang District "13th Five-Year" Historical and Cultural Block Construction Documentation". Xunyang People's Government Website. Archived from the original on 19 July 2021. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "Lushan Hot Spring – Jiujiang". Visit Our China. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "Haiyun Sand Beach". Trip.com. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "Xunyang River Scenic Area". Xunyang River Scenic Area Website. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "庐山西海". Mountain Lu West Sea Website. Archived from the original on 2021-07-21. Retrieved 2021-07-21.
- "Nanshan Park". Trip.com. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "Yanshui Pavilion". Tripadvisor. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- "Donglin Temple". Trip.com. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ^ "东林祖庭". Donglin Temple Website. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "Donglin Buddha". Trip.com. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "东林大佛". Donglin Temple Website. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "九江四季花城". Jiujiang News Network. Retrieved 20 July 2021.
- "Stone Bell HIll (Shizhong shan)". tripadvisor.com. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- Tobin, James. "The New Women of China". Medicine at Michigan, Fall'10, Volume 12, Number 3. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on 28 March 2016. Retrieved 15 February 2014.
- "Shi Meiyu (Mary Stone) |". Archived from the original on 2020-04-28. Retrieved 2020-04-27.
- 池昕鸿 (22 July 2015). "国内名人传记丛书(套装共6册)". books.google. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "赛兆祥墓碑". mylushan.com. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "Pearl S. Buck house in Zhenjiang". Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "松浦正人". ZHZ.wiki. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "7/30 日本全國市長會會長松浦正人就任祝賀會". Fukuoka Branch, Taipei Economic and Cultural Office in Osaka Website. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- "日本全国市长会代表团来访九江租界旧址". Jiujiang Cultural and Tourism Development Group Website. Retrieved 21 July 2021.
- Huang, Shuchen S., "Chiang Yee", in Asian-American Autobiographers: a bio-bibliographical critical sourcebook, edited by Guiyou Huang, Greenwood Press, 2001. ISBN 0-313-31408-X.
- Carroll, Lewis (12 October 2001). Alice's Adventures in Wonderland. Bloomsbury Publishing USA. ISBN 1582341745.
- Tang, Didi (2021-07-27). "Maggie Mac Neil's Olympic gold for Canada thrusts China's one-child policy back into spotlight". The Times. Retrieved 2021-08-01.
- Honsinger, Welthy B., "Ilien Tang" Woman's Missionary Friend 52(20)(August 1920): 285.
External links
- People's Government of Jiujiang (Chinese language) Archived 2007-02-28 at the Wayback Machine
- Mount Lu Website (Chinese language) Archived 2011-07-03 at the Wayback Machine
- Jiujiang News Network (Chinese language) Archived 2021-07-20 at the Wayback Machine
- Kuling American School Association
| Jiangxi topics | |
|---|---|
| Nanchang (capital) | |
| General | |
| Geography | |
| Education | |
| Culture | |
| Visitor attractions | |
| County-level divisions of Jiangxi Province | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanchang (capital) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Prefecture-level cities |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cities along the Yangtze | |
|---|---|
| Province-level | Cities (from upper reaches to lower reaches) |
| Yunnan | |
| Sichuan | |
| Chongqing | |
| Hubei | |
| Hunan | |
| Jiangxi | |
| Anhui | |
| Jiangsu | |
| Shanghai | |
| Major cities along the Pearl River · Major cities along the Yellow River | |