| Revision as of 01:22, 6 June 2006 editTJive (talk | contribs)4,555 edits rv← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:17, 15 July 2024 edit undoCitation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,405,851 edits Alter: archive-url, template type. URLs might have been anonymized. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Whoop whoop pull up | Category:Opposition to Fidel Castro | #UCB_Category 103/131 | ||
| (154 intermediate revisions by 76 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Cuban writer, journalist, and political activist}} | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=February 2016}} | |||
| {{Infobox person | |||
| ⚫ | |name=Carlos Franqui | ||
| |birth_date= {{Birth date|1921|12|4}} | |||
| |birth_place= ] | |||
| |death_date= {{Death date and age|2010|04|16|1921|12|4}} | |||
| |death_place= ] | |||
| |image=CarlosFranquiThumb.jpg | |||
| |caption=Carlos Franqui, 2006<br/>in front of a painting with one of his poems | |||
| |other_names = | |||
| |movement= ] | |||
| |organization ='']'', ] | |||
| |monuments= | |||
| |awards= | |||
| |footnotes= | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Carlos Franqui''' (December 4, 1921 – April 16, 2010) was a ]n writer, poet, journalist, art critic, and political activist. After the ] coup in 1952, he became involved with the ] which was headed by ]. Upon the success of the ] in 1959, he was placed in charge of the rebellion's newspaper '']'', which became an official government publication. When he came to have political differences with the regime, he left Cuba with his family. In 1968 he broke with the Cuban government when he signed a letter condemning the ] invasion of ]. He became a vocal critic of the Castro government, writing frequently until his death on April 16, 2010. | |||
| ==Early years== | |||
| Born in a cane field, he |
Born in a cane field, he entered a ], where he joined the ]. He gave up the opportunity to enter the ] to become a professional organizer for the party at the age of 20. After successfully organizing the party in several small towns, he left the organization and became an unaffiliated leftist.<ref name="lieurac">{{cite web|year=2001 |url=http://www.lieurac.com/franqui_en.html |title=Carlos Franqui, the story of a revolution |format=MOVIE |publisher=lieurac |access-date=September 7, 2007 |first=Michel |last=Le Bayon |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070930010855/http://www.lieurac.com/franqui_en.html |archive-date=September 30, 2007 |df=mdy }}</ref> | ||
| He turned to journalism to make a living and became involved in several literary and artistic movements. He developed friendships with Cuban artists, including writer ] and painter ]. | |||
| He turned to journalism to make a living, where his voracious reading provided him with a much better education than he would have received in the university. After the ] coup in ], he became involved with the "]" which was directed by ]. He was jailed and tortured by the police. On his release, he went into exile in ] and ], but was soon drafted by Castro into the Sierra Maestra to head ''Revolución'', the guerrilla movement's clandestine newspaper and ''Radio Rebelde'', their clandestine radio station. | |||
| ==Role in the Cuban revolution== | |||
| Upon the success of the ] in ], he was placed in charge of ''Revolución'', which became an official paper. He maintained a degree of independence from the official line, which eventually caused him to leave for ]. There, he met artists and intellectuals, such as ], ], ], ]. Having resigned from ''Revolución'', he dedicated himself to art, organizing the famous "Salón de Mayo" exhibit in ] (]), where all leading artists in the world were represented. | |||
| After the ] coup in 1952, he became involved with the ] headed by Fidel Castro. He co-edited the underground newspaper ''Revolución'' in Havana, taking responsibility for public information. One article in particular reported the landing of the '']'' and confirmed that Castro was safe in the Sierra Maestra. For this he was jailed and tortured by the police. Upon his release, he went into exile first in Mexico and then in ], but was soon drafted by Castro into the Sierra Maestra to continue work on ''Revolución'' and also on ], the guerilla movement's clandestine radio station.<ref name="rebel1">{{cite web |date=April 1993 |url = http://donmoore.tripod.com/central/cuba/rebel1.html|title = Revolution! Clandestine Radio and the Rise of Fidel Castro|publisher = Monitoring Times| access-date = September 7, 2007 | first= Don | last=Moore }}</ref><ref>Carlos Franqui, ''Diary of the Cuban Revolutio'', NY: The Viking Press, 1980</ref>{{page needed|date=February 2016}} | |||
| Upon the success of the ] in 1959, he was placed in charge of ''Revolución'', which became an official organ of the government. During his tenure as editor, he maintained a degree of independence from the official line and emphasized the arts and literature, launching the literary supplement ''Lunes de Revolución'', which was directed by ] and featured high quality work by Cuban and international authors. His position allowed him to travel extensively outside of Cuba.<ref name=portrait>{{cite book | last = Carlos Franqui| title = Family Portrait with Fidel | year = 1985 | publisher = Random House UK Ltd. | isbn= 0-224-02268-7 |page= 65}}</ref> During his European travels, he met artists and intellectuals, including ], ], ], ], ], and ]. A significant number of these artists traveled to Cuba. One of the most memorable visits was that of Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir.<ref name=portrait/> | |||
| Because of his ] attitude, he continued to have problems with the Cuban government. Eventually, he was allowed to leave Cuba with his family and settled in ]. In ], he officially broke with the Castro regime when he signed a letter condemning the ] invasion of ]. | |||
| Franqui had frequent disagreements with the government, which eventually led to his resignation from "Revolución" in 1963. The paper was closed a few months later.{{when|date=February 2016}} After his resignation, Franqui dedicated himself to art projects. In 1967 he organized the '']'' exhibit in Havana, where many of the world's leading artists were represented. | |||
| After his definitive ], his literary production markedly increased. He has written several major historical accounts of the Cuban Revolution ("El Libro de los Doce", "Diario de la Revolución Cubana"). Another facet of his production are a number of poetry and graphic arts collections (for which he has collaborated with Miró, Tapies, Calder and others), several books of poetry, as well as several narrative works on art (some edited in Italian under pen names). | |||
| ==Exile from Cuba== | |||
| ⚫ | He |
||
| He continued to have problems with the Cuban government. He was allowed to leave Cuba with his family{{when|date=February 2016}}–an émigré rather than an exile–and settled in Italy where he worked as an unpaid cultural representative of Cuba. In 1968, he officially broke with the Cuban government when he signed a letter condemning the ] invasion of ].{{citation needed|date=February 2016}} Many ]s shunned Franqui because of the active role he had played in the Cuban revolution.{{citation needed|date=June 2012}} | |||
| Now definitively an exile, his literary production increased. Franqui authored several accounts of the Cuban Revolution, including, ''El Libro de los Doce'' (The Book about the Twelve) and ''Diario de la Revolución Cubana'' (The Diary of the Cuban Revolution). He collaborated with ], ], ], and others on graphic arts publications as well as other works about contemporary art, some of which he edited in Italian under pen names. He wrote several books of poetry as well. | |||
| In the early ] he moved to ], where he lives in semi-retirement. In ], he founded ''Carta de Cuba'', a quarterly journal featuring high-quality work produced in Cuba by independent journalists and writers. Franqui continues to edit the publication to this date. | |||
| ⚫ | He continued to campaign against repression in Cuba and other countries. He was officially branded a traitor by the Cuban government, which accused him of having ties to the U.S. ]. After breaking relations with Cuba the Cuban government began airbrushing Franqui's image from photographs that documented the revolution's early years. | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| Franqui responded with a poem:<ref>{{cite web|year = 2007|url = http://www.cs.dartmouth.edu/farid/research/digitaltampering/|title = digital tampering|access-date = September 7, 2007|first = Hany|last = Farid|archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20100804022639/http://www.cs.dartmouth.edu/farid/research/digitaltampering/|archive-date = August 4, 2010|url-status = dead|df = mdy-all}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| <poem>I discover my photographic death. | |||
| Do I exist? | |||
| I am a little black, | |||
| I am a little white, | |||
| I am a little shit, | |||
| On Fidel's vest.</poem> | |||
| In the early 1990s, he moved to ],<ref name="lieurac"/> where he lived in semi-retirement with his art collection from his years in Cuba and Europe. His artwork collection included works from Pablo Picasso, Joan Miro, Andy Warhol, and Frida Kahlo among others. In 1996, he founded '']'', a quarterly journal featuring work produced in Cuba by independent journalists and writers. He edited the publication until his death on April 16, 2010, in Puerto Rico.<ref>{{cite news |date= April 17, 2010|url = http://www.elpais.com/articulo/Necrologicas/Carlos/Franqui/escritor/critico/arte/cubano/elpeputec/20100417elpepinec_2/Tes |title = Carlos Franqui, writer and critic of Cuban art| work = El Pais | access-date = April 17, 2010 | last=Salas |first= Roger |language=es }}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ==Writings== | |||
| *{{cite book | last = Franqui, Carlos | title = Diary of the Cuban Revolution | date = June 18, 1980| publisher = Library of America | isbn= 0-670-27217-5}} | |||
| *{{cite book | last = Franqui, Carlos | title = Cuba, La Revolucion/ Cuba, the Revolution: Mito O Realidad/ Myth or Reality (El Ojo Infalible) |date=October 2006| publisher = Peninsular Publishing Company | isbn= 970-777-137-2}} | |||
| *{{cite book | last = Franqui | first = Carlos | title = Family Portrait With Fidel: A Memoir | url = https://archive.org/details/familyportraitwi0000fran | url-access = registration | year = 1984 | publisher = Random House, New York | isbn= 0-224-02268-7 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Franqui | first= Carlos| title = Camilo, el Héroe Desaparecido | publisher=Planeta | year= 2001 | language= es| isbn=0-9715256-3-3 }} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Franqui|first=Carlos Franqui| author-link = Carlos Franqui| title = Cuba, la revolución, mito o realidad?: memorias de un fantasma socialista|year=2006| publisher = Ediciones Península| isbn= 9788483077252|language=Spanish}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{commons category|Carlos Franqui}} | |||
| * by '']'' | |||
| * | |||
| *The {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200716123255/https://findingaids.princeton.edu/collections/C0644.pdf |date=July 16, 2020 }} is held at Princeton University Library, Special Collections. | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Franqui, Carlos}} | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:17, 15 July 2024
Cuban writer, journalist, and political activist
| Carlos Franqui | |
|---|---|
 Carlos Franqui, 2006 Carlos Franqui, 2006in front of a painting with one of his poems | |
| Born | (1921-12-04)December 4, 1921 Cifuentes, Cuba |
| Died | April 16, 2010(2010-04-16) (aged 88) San Juan, Puerto Rico |
| Organization(s) | Revolución, Radio Rebelde |
| Movement | 26th of July Movement |
Carlos Franqui (December 4, 1921 – April 16, 2010) was a Cuban writer, poet, journalist, art critic, and political activist. After the Fulgencio Batista coup in 1952, he became involved with the 26th of July Movement which was headed by Fidel Castro. Upon the success of the Cuban Revolution in 1959, he was placed in charge of the rebellion's newspaper Revolución, which became an official government publication. When he came to have political differences with the regime, he left Cuba with his family. In 1968 he broke with the Cuban government when he signed a letter condemning the Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia. He became a vocal critic of the Castro government, writing frequently until his death on April 16, 2010.
Early years
Born in a cane field, he entered a vocational school, where he joined the Communist Party of Cuba. He gave up the opportunity to enter the University of Havana to become a professional organizer for the party at the age of 20. After successfully organizing the party in several small towns, he left the organization and became an unaffiliated leftist.
He turned to journalism to make a living and became involved in several literary and artistic movements. He developed friendships with Cuban artists, including writer Guillermo Cabrera Infante and painter Wifredo Lam.
Role in the Cuban revolution
After the Fulgencio Batista coup in 1952, he became involved with the 26th of July Movement headed by Fidel Castro. He co-edited the underground newspaper Revolución in Havana, taking responsibility for public information. One article in particular reported the landing of the Granma and confirmed that Castro was safe in the Sierra Maestra. For this he was jailed and tortured by the police. Upon his release, he went into exile first in Mexico and then in Florida, but was soon drafted by Castro into the Sierra Maestra to continue work on Revolución and also on Radio Rebelde, the guerilla movement's clandestine radio station.
Upon the success of the Cuban Revolution in 1959, he was placed in charge of Revolución, which became an official organ of the government. During his tenure as editor, he maintained a degree of independence from the official line and emphasized the arts and literature, launching the literary supplement Lunes de Revolución, which was directed by Guillermo Cabrera Infante and featured high quality work by Cuban and international authors. His position allowed him to travel extensively outside of Cuba. During his European travels, he met artists and intellectuals, including Pablo Picasso, Miró, Calder, Jean-Paul Sartre, Simone de Beauvoir, and Julio Cortázar. A significant number of these artists traveled to Cuba. One of the most memorable visits was that of Sartre and Simone de Beauvoir.
Franqui had frequent disagreements with the government, which eventually led to his resignation from "Revolución" in 1963. The paper was closed a few months later. After his resignation, Franqui dedicated himself to art projects. In 1967 he organized the Salón de Mayo exhibit in Havana, where many of the world's leading artists were represented.
Exile from Cuba
He continued to have problems with the Cuban government. He was allowed to leave Cuba with his family–an émigré rather than an exile–and settled in Italy where he worked as an unpaid cultural representative of Cuba. In 1968, he officially broke with the Cuban government when he signed a letter condemning the Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia. Many Cuban exiles shunned Franqui because of the active role he had played in the Cuban revolution.
Now definitively an exile, his literary production increased. Franqui authored several accounts of the Cuban Revolution, including, El Libro de los Doce (The Book about the Twelve) and Diario de la Revolución Cubana (The Diary of the Cuban Revolution). He collaborated with Joan Miró, Antoni Tàpies, Alexander Calder, and others on graphic arts publications as well as other works about contemporary art, some of which he edited in Italian under pen names. He wrote several books of poetry as well.
He continued to campaign against repression in Cuba and other countries. He was officially branded a traitor by the Cuban government, which accused him of having ties to the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency. After breaking relations with Cuba the Cuban government began airbrushing Franqui's image from photographs that documented the revolution's early years.
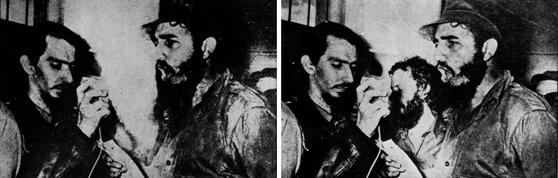
Franqui responded with a poem:
I discover my photographic death.
Do I exist?
I am a little black,
I am a little white,
I am a little shit,
On Fidel's vest.
In the early 1990s, he moved to Puerto Rico, where he lived in semi-retirement with his art collection from his years in Cuba and Europe. His artwork collection included works from Pablo Picasso, Joan Miro, Andy Warhol, and Frida Kahlo among others. In 1996, he founded Carta de Cuba, a quarterly journal featuring work produced in Cuba by independent journalists and writers. He edited the publication until his death on April 16, 2010, in Puerto Rico.
References
- ^ Le Bayon, Michel (2001). "Carlos Franqui, the story of a revolution". lieurac. Archived from the original (MOVIE) on September 30, 2007. Retrieved September 7, 2007.
- Moore, Don (April 1993). "Revolution! Clandestine Radio and the Rise of Fidel Castro". Monitoring Times. Retrieved September 7, 2007.
- Carlos Franqui, Diary of the Cuban Revolutio, NY: The Viking Press, 1980
- ^ Carlos Franqui (1985). Family Portrait with Fidel. Random House UK Ltd. p. 65. ISBN 0-224-02268-7.
- Farid, Hany (2007). "digital tampering". Archived from the original on August 4, 2010. Retrieved September 7, 2007.
- Salas, Roger (April 17, 2010). "Carlos Franqui, writer and critic of Cuban art". El Pais (in Spanish). Retrieved April 17, 2010.
Writings
- Franqui, Carlos (June 18, 1980). Diary of the Cuban Revolution. Library of America. ISBN 0-670-27217-5.
- Franqui, Carlos (October 2006). Cuba, La Revolucion/ Cuba, the Revolution: Mito O Realidad/ Myth or Reality (El Ojo Infalible). Peninsular Publishing Company. ISBN 970-777-137-2.
- Franqui, Carlos (1984). Family Portrait With Fidel: A Memoir. Random House, New York. ISBN 0-224-02268-7.
- Franqui, Carlos (2001). Camilo, el Héroe Desaparecido (in Spanish). Planeta. ISBN 0-9715256-3-3.
- Franqui, Carlos Franqui (2006). Cuba, la revolución, mito o realidad?: memorias de un fantasma socialista (in Spanish). Ediciones Península. ISBN 9788483077252.
External links
- Obituary: Carlos Franqui by The Daily Telegraph
- Info on web.archive.org
- The Carlos Franqui Collection Archived July 16, 2020, at the Wayback Machine is held at Princeton University Library, Special Collections.