| Revision as of 07:10, 5 January 2014 editBon courage (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users66,177 edits →Natural products: cleanup← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 18:53, 23 December 2024 edit undoCitation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,406,828 edits Add: work, bibcode. Removed parameters. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Лисан аль-Гаиб | Category:Monoclonal antibodies for tumors | #UCB_Category 3/139 | ||
| (758 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Artificial stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer}} | |||
| {{multiple issues| | |||
| {{ |
{{Use dmy dates|date=December 2018}} | ||
| {{cs1 config|name-list-style=vanc|display-authors=6}} | |||
| {{Original research|date=March 2013}} | |||
| {{Infobox medical intervention | |||
| |name=Cancer immunotherapy | |||
| |synonym= | |||
| |image=Peptide bound to Rituximab FAB.png | |||
| |caption=] ] of ] bound to ] ] | |||
| |alt= | |||
| |pronounce= | |||
| |specialty=<!-- from Wikidata, can be overwritten --> | |||
| |synonyms= | |||
| |ICD10= | |||
| |ICD9= | |||
| |ICD9unlinked= | |||
| |CPT= | |||
| |MeshID= | |||
| |LOINC= | |||
| |other_codes= | |||
| |MedlinePlus= | |||
| |eMedicine= | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| ] ] of ] bound to ]'s ]]] | |||
| '''Cancer immunotherapy''' is the use of the ] to reject ]. The main premise is stimulating the patient's immune system to attack the malignant ] cells that are responsible for the disease. This can be either through ] of the patient (e.g., by administering a ], such as Dendreon's ]), in which case the patient's own immune system is trained to recognize tumor cells as targets to be destroyed, or through the administration of ] as drugs, in which case the patient's immune system is recruited to destroy tumor cells by the therapeutic antibodies. Cell based immunotherapy is another major entity of cancer immunotherapy. This involves immune cells such as the Natural killer Cells (NK cells), Lymphokine Activated killer cell(LAK), Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes(CTLs), Dendritic Cells (DC), etc., which are either activated in vivo by administering certain cytokines such as Interleukins or they are isolated, enriched and transfused to the patient to fight against cancer. | |||
| '''Cancer immunotherapy''' ('''immuno-oncotherapy''') is the stimulation of the ] to treat ], improving the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease.<ref>{{Cite web | vauthors = Biancalana M |date=December 14, 2022 |title=Harnessing the immune system to develop breakthrough cancer therapies |url=https://simbiosys.com/2022/12/14/harnessing-the-immune-system-to-develop-breakthrough-cancer-therapies/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231204135730/https://simbiosys.com/2022/12/14/harnessing-the-immune-system-to-develop-breakthrough-cancer-therapies/ |archive-date=December 4, 2023 |access-date=April 19, 2024}}</ref> It is an application of the ] of ] ('''immuno-oncology''') and a growing subspecialty of ]. | |||
| Since the immune system responds to the environmental factors it encounters on the basis of discrimination between self and non-self, many kinds of tumor ]s that arise as a result of the onset of cancer are more or less tolerated by the patient's own immune system since the tumor cells are essentially the patient's own cells that are growing, ] and spreading without proper regulatory control. | |||
| Cancer immunotherapy exploits the fact that ] often have ]s, molecules on their surface that can bind to ] proteins or ]s, triggering an immune system response. The tumor ] are often ]s or other macromolecules (e.g., ]s). Normal antibodies bind to external pathogens, but the modified ] antibodies bind to the tumor antigens marking and identifying the cancer cells for the immune system to inhibit or kill. The clinical success of cancer immunotherapy is highly variable between different forms of cancer; for instance, certain subtypes of ] react well to the approach whereas immunotherapy is not effective for other subtypes.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kodach LL, Peppelenbosch MP | title = Targeting the Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Compartment for Inducing Responsiveness to Immune Checkpoint Blockade Is Best Limited to Specific Subtypes of Gastric Cancers. | journal = Gastroenterology | volume = 161 | issue = 2 | pages = 727 | date = August 2021 | pmid = 33798523 | doi = 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.03.047 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| In spite of this fact, however, many kinds of tumor cells display unusual ]s that are either inappropriate for the cell type and/or its environment, or are only normally present during the organisms' development (e.g. ] antigens). Examples of such antigens include the ] ], a ] that is normally only expressed at a significant level on the outer surface membranes of ]al cells, where its exposure to the immune system is limited by the ]. GD2 is expressed on the surfaces of a wide range of tumor cells including ], ]s, ]s, ]s, ], ]s and other ]s. GD2 is thus a convenient tumor-specific target for immunotherapies. | |||
| In 2018, American immunologist ] and Japanese immunologist ] received the ] for their discovery of cancer therapy by inhibition of negative immune regulation.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2018/summary/|title=The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2018|website=NobelPrize.org|language=en-US|access-date=2019-08-04}}</ref> | |||
| Other kinds of tumor cells display ]s that are rare or absent on the surfaces of healthy cells, and which are responsible for activating cellular ] pathways that cause the unregulated growth and division of the tumor cell. Examples include ], a constitutively active cell surface receptor that is produced at abnormally high levels on the surface of ] tumor cells. | |||
| {{TOC limit}} | |||
| == History == | |||
| The use of some agents can lead to the re-activation of latent ] (TB) and this must be assessed for before those agents are used therapeutically.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.thedoctorschannel.com/go/reuters/2153.html |title=Elevated TB risk seen with anti-TNF antibody therapy - The Doctor's Channel |publisher=Thedoctorschannel.com |date= |accessdate=2013-08-25}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.brit-thoracic.org.uk/guidelines/tuberculosis-guidelines.aspx |title=Tuberculosis Guidelines |publisher=Brit-thoracic.org.uk |date= |accessdate=2013-08-25}}</ref> | |||
| "During the 17th and 18th centuries, various forms of immunotherapy in cancer became widespread... In the 18th and 19th centuries, septic dressings enclosing ulcerative tumours were used for the treatment of cancer. Surgical wounds were left open to facilitate the development of infection, and purulent sores were created deliberately... One of the most well-known effects of microorganisms on ... cancer was reported in 1891, when an American surgeon, ], inoculated patients having inoperable tumours with ]'' ]."<ref name=pmid26813865>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kucerova P, Cervinkova M | title = Spontaneous regression of tumour and the role of microbial infection--possibilities for cancer treatment | journal = Anti-Cancer Drugs | volume = 27 | issue = 4 | pages = 269–77 | date = April 2016 | pmid = 26813865 | pmc = 4777220 | doi = 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000337 }}</ref> "Coley thoroughly reviewed the literature available at that time and found 38 reports of cancer patients with accidental or ] feverish ]. In 12 patients, the sarcoma or carcinoma had completely disappeared; the others had substantially improved. Coley decided to attempt the therapeutic use of iatrogenic erysipelas..."<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kienle GS | title = Fever in Cancer Treatment: Coley's Therapy and Epidemiologic Observations | journal = Global Advances in Health and Medicine | volume = 1 | issue = 1 | pages = 92–100 | date = March 2012 | pmid = 24278806 | pmc = 3833486 | doi = 10.7453/gahmj.2012.1.1.016 }}</ref> "Coley developed a toxin that contained heat-killed bacteria ]'' ]. Until 1963, this treatment was used for the treatment of sarcoma."<ref name=pmid26813865/> "Coley injected more than 1000 cancer patients with bacteria or bacterial products."<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = McCarthy EF | title = The toxins of William B. Coley and the treatment of bone and soft-tissue sarcomas | journal = The Iowa Orthopaedic Journal | volume = 26 | pages = 154–8 | date = 2006 | pmid = 16789469 | pmc = 1888599 }}</ref> 51.9% of patients with inoperable soft-tissue sarcomas showed complete tumour regression and survived for more than 5 years, and 21.2% of the patients had no clinical evidence of tumour at least 20 years after this treatment..."<ref name=pmid26813865/> Research continued in the 20th century under Maria O'Connor Hornung at ].<ref>{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Z5QgAQAAMAAJ|title=Dissertation Abstracts International: Retrospective Index, Volumes I-XXIX.|date=1970|publisher=University Microfilms|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|title=Commencement speakers praise, advise local graduates . . .|language=en-US|newspaper=Washington Post|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/local/1977/06/16/commencement-speakers-praise-advise-local-graduates/7c57014b-90c9-4749-a9f0-8cd7dcf5ffd6/|access-date=2021-07-09|issn=0190-8286}}</ref> | |||
| == Types and categories == | |||
| ==History== | |||
| There are several types of immunotherapy used to treat cancer:<ref>{{cite web |title=Immunotherapy to Treat Cancer |url=https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types/immunotherapy |publisher=] |access-date=14 October 2023 |date=24 September 2019}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Immunotherapy for Cancer: An Overview |url=https://oncodaily.com/oncolibrary/immune-oncology/67103.html |archive-date= |access-date=29 May 2024 |website=Oncodaily.com|date=29 May 2024 }}</ref> | |||
| Cancer immunotherapy has arisen from advances in both ] and ] fields over the last few centuries. Immunotherapy began in 1796 when ] produced the first vaccine involving immunisation with ] to prevent ]. Towards the end of the 19th century ] and ] discovered that injecting animals with ] produced ] with anti-toxins to it. Following this ]'s research gave rise to the "]" concept; using antibodies to specifically target a disease. The production of pure ] for therapeutic use was not available until 1975 when ] and ] produced the ] technology, although it wasn't until 1997 when ], the first antibody treatment for cancer, was approved by the FDA for treatment of ]. Since this approval, 11 other antibodies have been approved for cancer; ] (1998), ] (2000), ] (2001), ] (2002), ] (2003), ] (2004), ] (2004), ] (2006), ] (2009), ] (2011) and ] (2011). The production of vaccines for cancer came later than the use of monoclonal antibodies. As our understanding of human immunology has improved, so has our potential to produce effective cancer vaccines. The first cell-based immunotherapy ], ], was approved in 2010 for the treatment of ].<ref>{{cite journal|last=Strebhardt|first=K|coauthors=Ullrich, A|title=Paul Ehrlich's magic bullet concept: 100 years of progress.|journal=Nature reviews. Cancer|date=June 2008|volume=8|issue=6|pages=473–80|pmid=18469827}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Waldmann|first=TA|title=Immunotherapy: past, present and future.|journal=Nature medicine|date=March 2003|volume=9|issue=3|pages=269–77|pmid=12612576}}</ref> | |||
| * ]s: drugs that block ] to allow immune cells to respond more strongly to the cancer. | |||
| * ]: a treatment that takes ]s from the tumor and selects or changes them in the lab to better attack cancer cells, then reintroduces them into the patient. | |||
| * ]: designed to bind to specific targets on cancer cells, marking cancer cells so that they will be better seen and destroyed by the immune system. | |||
| * ]: also known as therapeutic cancer vaccines, help the immune system learn to recognize and react to mutant proteins specific to the tumor and destroy cancer cells containing them. | |||
| * ]: agents that enhance the body’s immune response against cancer. | |||
| ] can be categorized as active or passive based on their ability to engage the host immune system against cancer.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Galluzzi L, Vacchelli E, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Buqué A, Senovilla L, Baracco EE, Bloy N, Castoldi F, Abastado JP, Agostinis P, Apte RN, Aranda F, Ayyoub M, Beckhove P, Blay JY, Bracci L, Caignard A, Castelli C, Cavallo F, Celis E, Cerundolo V, Clayton A, Colombo MP, Coussens L, Dhodapkar MV, Eggermont AM, Fearon DT, Fridman WH, Fučíková J, Gabrilovich DI, Galon J, Garg A, Ghiringhelli F, Giaccone G, Gilboa E, Gnjatic S, Hoos A, Hosmalin A, Jäger D, Kalinski P, Kärre K, Kepp O, Kiessling R, Kirkwood JM, Klein E, Knuth A, Lewis CE, Liblau R, Lotze MT, Lugli E, Mach JP, Mattei F, Mavilio D, Melero I, Melief CJ, Mittendorf EA, Moretta L, Odunsi A, Okada H, Palucka AK, Peter ME, Pienta KJ, Porgador A, Prendergast GC, Rabinovich GA, Restifo NP, Rizvi N, Sautès-Fridman C, Schreiber H, Seliger B, Shiku H, Silva-Santos B, Smyth MJ, Speiser DE, Spisek R, Srivastava PK, Talmadge JE, Tartour E, Van Der Burg SH, Van Den Eynde BJ, Vile R, Wagner H, Weber JS, Whiteside TL, Wolchok JD, Zitvogel L, Zou W, Kroemer G | title = Classification of current anticancer immunotherapies | journal = Oncotarget | volume = 5 | issue = 24 | pages = 12472–12508 | date = December 2014 | pmid = 25537519 | pmc = 4350348 | doi = 10.18632/oncotarget.2998 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Types of Biological Therapy |url=https://training.seer.cancer.gov/treatment/biotherapy/types.html |website=SEER Training Modules |publisher=] |access-date=14 October 2023}}</ref> Active immunotherapy specifically targets tumor cells via the immune system. Examples include therapeutic cancer vaccines (also known as treatment vaccines,<ref>{{Cite web|date=2013-09-30|title=What are Cancer Vaccines?|url=https://www.cancer.net/navigating-cancer-care/how-cancer-treated/immunotherapy-and-vaccines/what-are-cancer-vaccines|access-date=2021-08-15|website=Cancer.Net|language=en}}</ref> which are designed to boost the body's immune system to fight cancer), ], and targeted antibody therapies. In contrast, passive immunotherapy does not directly target tumor cells, but enhances the ability of the immune system to attack cancer cells. Examples include ]s and ]s. | |||
| ==Cell-Based immunotherapy== | |||
| Active cellular therapies aim to destroy cancer cells by recognition of distinct markers known as ]s. In cancer vaccines, the goal is to generate an immune response to these antigens through a vaccine. Currently, only one vaccine (] for prostate cancer) has been approved. In cell-mediated therapies like CAR-T cell therapy, immune cells are extracted from the patient, ]ed to recognize tumor-specific antigens, and returned to the patient. Cell types that can be used in this way are ]s, ]s, ]s, and ]s. Finally, specific antibodies can be developed that recognize cancer cells and target them for destruction by the immune system. Examples of such antibodies include ] (targeting CD-20), ] (targeting HER-2), and ] (targeting EGFR). | |||
| ===Adoptive T-cell therapy=== | |||
| ] | |||
| Adoptive T-cell therapy is form of ] by the transfusion of ]s, which are cells of the ]. They are found in ] and tissue and usually activate when they find foreign ]s. Specifically they activate when the T-cell's surface receptors encounter other cells that display small parts of foreign proteins on their surface ] molecules, known as ]s. These can be either infected cells, or specialised immune cells known as ]s (APCs). They are found in normal tissue and in tumor tissue, where they are known as ]s (TILs). They are activated by the presence of APCs, such as ]s that present ]s to the T-cells. Although these cells have the capability of attacking the tumor, the environment within the tumor is highly immunosuppressive, preventing immune-mediated tumour death. There are multiple ways of producing and obtaining tumour targeted T-cells. T-cells specific to a tumor antigen can either be removed from a tumor sample (TILs) or T-cells can be removed from the blood and genetically engineered to be tumor specific. Subsequent activation and expansion of these cells is performed outside the body ('']'') and then they are transfused into the recipient. Although research has made major advances in this form of therapy, there is no approved adoptive T-cell therapy as yet.<ref>{{cite journal|last=June|first=CH|title=Adoptive T cell therapy for cancer in the clinic.|journal=The Journal of clinical investigation|date=June 2007|volume=117|issue=6|pages=1466–76|pmid=17549249}}</ref><ref name="pmid2243739">{{cite journal|last=Restifo|first=NP|coauthors=Dudley, ME; Rosenberg, SA|title=Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer: harnessing the T cell response.|journal=Nature reviews. Immunology|date=Mar 22, 2012|volume=12|issue=4|pages=269–81|pmid=22437939}}</ref> | |||
| Passive antibody therapies aim to increase the activity of the immune system without specifically targeting cancer cells. For example, cytokines directly stimulate the immune system and increase immune activity. Checkpoint inhibitors target proteins (]s) that normally dampen the immune response. This enhances the ability of the immune system to attack cancer cells. Current research is identifying new potential targets to enhance immune function. Approved checkpoint inhibitors include antibodies such as ], ], and ]. | |||
| The tumor specific T-cells used for treatment will be specific for a particular antigen present within the tumor, or for the stroma or vasculature, which the tumor may be dependent on. Examples of T-cell targets are tissue differentiation antigens, mutant protein antigens, oncogenic ]s, ]s and vascular or stromal specific antigens. Tissue differentiation antigens are those that are specific to a certain type of tissue. T-cells specific to these antigens will target normal cells that contain these antigens as well as cancer cells (e.g. ]; CEA). Mutant protein antigens are likely to be much more specific to cancer cells because normal cells shouldn't contain these proteins. Normal cells will display the normal protein antigen on their MHC molecules, whereas cancer cells will display the mutant version. T-cells can differentiate between these two, selectively targeting the cancer cell. Some viral proteins are implicated in forming cancer (]), and therefore T-cells that are specific to viral antigens can be used to attack infected cells (which will include cancer cells). Cancer-testis antigens are antigens expressed primarily in the ]s of the ], but also in fetal ] and the ]. Some cancer cells aberrantly express these proteins and therefore present these antigens, allowing attack by T-cells specific to these antigens. Example antigens of this type are ] and ].<ref name="pmid2243739"/> | |||
| ] | |||
| ==Cellular immunotherapy== | |||
| ===Dendritic cell therapy=== | ===Dendritic cell therapy=== | ||
| ] | |||
| Dendritic cell therapy provokes anti-tumor responses by causing dendritic cells to present tumor antigens to lymphocytes, which activates them, priming them to kill other cells that present the antigen. Dendritic cells are ]s (APCs) in the mammalian immune system.<ref name="pmid11481463">{{cite journal | vauthors = Riddell SR | title = Progress in cancer vaccines by enhanced self-presentation | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | volume = 98 | issue = 16 | pages = 8933–35 | date = July 2001 | pmid = 11481463 | pmc = 55350 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.171326398 | bibcode = 2001PNAS...98.8933R | doi-access = free }}</ref> In cancer treatment, they aid cancer antigen targeting.<ref name="pmid23890062">{{cite journal | vauthors = Palucka K, Banchereau J|author-link2=Jacques Banchereau | title = Dendritic-cell-based therapeutic cancer vaccines | journal = Immunity | volume = 39 | issue = 1 | pages = 38–48 | date = July 2013 | pmid = 23890062 | pmc = 3788678 | doi = 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.004 }}</ref> The only approved cellular cancer therapy based on dendritic cells is ]. | |||
| One method of inducing dendritic cells to present tumor antigens is by vaccination with autologous tumor lysates<ref name="pmid27235694">{{cite journal | vauthors = Hirayama M, Nishimura Y | title = The present status and future prospects of peptide-based cancer vaccines | journal = International Immunology | volume = 28 | issue = 7 | pages = 319–28 | date = July 2016 | pmid = 27235694 | doi = 10.1093/intimm/dxw027 | doi-access = free }}</ref> or short peptides (small parts of the protein that correspond to the protein antigens on cancer cells). These peptides are often given in combination with ] (highly ] substances) to increase the immune and anti-tumor responses. Other adjuvants include proteins or other chemicals that attract and/or activate dendritic cells, such as ] (GM-CSF). The most common sources of antigens used for dendritic cell vaccine in ] (GBM) as an aggressive brain tumor were whole tumor lysate, CMV antigen RNA and tumor-associated peptides like ].<ref name = "Dastmalchi_2018">{{cite book | vauthors = Dastmalchi F, Karachi A, Mitchell D |chapter=Dendritic Cell Therapy |title=eLS |pages=1–27 |publisher=American Cancer Society |doi=10.1002/9780470015902.a0024243 |isbn=9780470015902 | date = June 2018 |s2cid=155185753 }}</ref> | |||
| ] therapy comprises a group of methods that provoke anti-tumor responses by causing dendritic cells to present tumor ]s. Dendritic cells present antigens to lymphocytes, which activates them, priming them to kill cells which also present the antigen. They are utilised in cancer treatment to specifically target cancer antigens.<ref name="pmid23890062">{{cite journal|last=Palucka|first=K|coauthors=Banchereau, J|title=Dendritic-cell-based therapeutic cancer vaccines.|journal=Immunity|date=Jul 25, 2013|volume=39|issue=1|pages=38–48|pmid=23890062}}</ref> This group of cell-based therapy boasts the only approved treatment for cancer, ]. | |||
| Dendritic cells can also be activated '']'' by making tumor cells express GM-CSF. This can be achieved by either genetically engineering tumor cells to produce GM-CSF or by infecting tumor cells with an ] that expresses GM-CSF. | |||
| One method of inducing dendritic cells to present tumor antigens is by vaccination with short ]s (small parts of protein that correspond to the protein antigens on cancer cells). These peptides on their own do not stimulate a strong immune response and may be given in combination with highly ] substances known as adjuvants. This provokes a strong response to the adjuvant being used, while also producing a (sometimes) robust anti-tumor response by the immune system. Other adjuvants being used are proteins or other chemicals that attract and/or activate dendritic cells, such as ] (GM-CSF). Dendritic cells can also be activated within the body (''in vivo'') by making tumour cells to express (GM-CSF). This can be achieved by either genetically engineering tumor cells that produce GM-CSF or by infecting tumor cells with an ] that expresses GM-CSF. Another strategy used in dendritic cell therapy is to remove dendritic cells from the blood of a person with cancer and activate them outside the body (''ex vivo''). The dendritic cells are activated in the presence of tumor antigens, which may be a single tumor specific peptide/protein or a tumor ] (a solution of broken down tumor cells). These activated dendritic cells are put back into the body where they provoke an immune response to the cancer cells. Adjuvants are sometimes used systemically to increase the anti-tumor response provided by ''ex vivo'' activated dendritic cells. More modern dendritic cell therapies include the use of antibodies that bind to receptors on the surface of dendritic cells. Antigens can be added to the antibody and can induce the dendritic cells to mature and provide immunity to the tumor. Dendritic cell receptors such as ], ], ] or ] have been used as targets by antibodies to produce immune responses.<ref name="pmid23890062"/> | |||
| Another strategy is to remove dendritic cells from the blood of a patient and activate them outside the body. The dendritic cells are activated in the presence of tumor antigens, which may be a single tumor-specific peptide/protein or a tumor ] (a solution of broken-down tumor cells). These cells (with optional adjuvants) are infused and provoke an immune response. | |||
| ====Sipuleucel-T==== | |||
| Dendritic cell therapies include the use of antibodies that bind to receptors on the surface of dendritic cells. Antigens can be added to the antibody and can induce the dendritic cells to mature and provide immunity to the tumor. Dendritic cell receptors such as ], ], ] or ] have been used as antibody targets.<ref name="pmid23890062" /> Dendritic cell-NK cell interface also has an important role in immunotherapy. The design of new dendritic cell-based vaccination strategies should also encompass NK cell-stimulating potency. It is critical to systematically incorporate NK cells monitoring as an outcome in antitumor DC-based clinical trials.{{Citation needed|date=December 2019|reason=removed citation to predatory publisher content}} | |||
| ] (Provenge) is the first approved cancer vaccine. It was approved for treatment of asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic metastatic castrate resistant ] in 2010. The treatment consists of removal of ]s from blood by ], and growing them with the ] P2024 made from ] and ] (PAP). These cells are infused back into the recipient to induce an immune response against the tumor because the PAP protein is prostate specific. This process is repeated three times.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Gardner|first=TA|coauthors=Elzey, BD; Hahn, NM|title=Sipuleucel-T (Provenge) autologous vaccine approved for treatment of men with asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic castrate-resistant metastatic prostate cancer.|journal=Human vaccines & immunotherapeutics|date=April 2012|volume=8|issue=4|pages=534–9|pmid=22832254}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Oudard|first=S|title=Progress in emerging therapies for advanced prostate cancer.|journal=Cancer treatment reviews|date=May 2013|volume=39|issue=3|pages=275–89|pmid=23107383}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Sims|first=RB|title=Development of sipuleucel-T: autologous cellular immunotherapy for the treatment of metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer.|journal=Vaccine|date=Jun 19, 2012|volume=30|issue=29|pages=4394–7|pmid=22122856}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Shore|first=ND|coauthors=Mantz, CA; Dosoretz, DE; Fernandez, E; Myslicki, FA; McCoy, C; Finkelstein, SE; Fishman, MN|title=Building on sipuleucel-T for immunologic treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer.|journal=Cancer control : journal of the Moffitt Cancer Center|date=January 2013|volume=20|issue=1|pages=7–16|pmid=23302902}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Drugs ==== | |||
| ==Monoclonal antibody therapy== | |||
| Sipuleucel-T (Provenge) was approved for treatment of asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic metastatic castration-resistant ] in 2010. The treatment consists of removal of ]s from blood by ] and growing them with the ] PA2024 made from GM-CSF and prostate-specific ] (PAP) and reinfused. This process is repeated three times.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gardner TA, Elzey BD, Hahn NM | title = Sipuleucel-T (Provenge) autologous vaccine approved for treatment of men with asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic castrate-resistant metastatic prostate cancer | journal = Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics | volume = 8 | issue = 4 | pages = 534–39 | date = April 2012 | pmid = 22832254 | doi = 10.4161/hv.19795 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Oudard S | title = Progress in emerging therapies for advanced prostate cancer | journal = Cancer Treatment Reviews | volume = 39 | issue = 3 | pages = 275–89 | date = May 2013 | pmid = 23107383 | doi = 10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.09.005 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sims RB | title = Development of sipuleucel-T: autologous cellular immunotherapy for the treatment of metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer | journal = Vaccine | volume = 30 | issue = 29 | pages = 4394–97 | date = June 2012 | pmid = 22122856 | doi = 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.11.058 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Shore ND, Mantz CA, Dosoretz DE, Fernandez E, Myslicki FA, McCoy C, Finkelstein SE, Fishman MN | title = Building on sipuleucel-T for immunologic treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer | journal = Cancer Control | volume = 20 | issue = 1 | pages = 7–16 | date = January 2013 | pmid = 23302902 | doi = 10.1177/107327481302000103 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| {{main|Monoclonal antibody therapy}} | |||
| ] are a key component of the ], playing a central role in both in the recognition of foreign antigens and the stimulation of an immune response to them. It is not surprising therefore, that many immunotherapeutic approaches involve the use of antibodies. The advent of ] technology has made it possible to raise antibodies against specific antigens such as the unusual antigens that are presented on the surfaces of tumors. | |||
| === Adoptive T-cell therapy === | |||
| ===Types of monoclonal antibodies=== | |||
| ]{{Main|Adoptive cell transfer}} | |||
| Two types of monoclonal antibodies are used in cancer treatments:<ref name="pmid22437872"/> | |||
| Adoptive T cell therapy is a form of ] by the transfusion of T-cells. They are found in blood and tissue and typically activate when they find foreign ]s. Activation occurs when the T-cell's surface receptors encounter cells that display parts of foreign proteins (either on their surface or intracellularly). These can be either infected cells or other ]s (APCs). The latter are found in normal tissue and in tumor tissue, where they are known as ] (TILs). They are activated by the presence of APCs such as dendritic cells that present ]s. Although these cells can attack tumors, the ] is highly immunosuppressive, interfering with immune-mediated tumour death.<ref name="NatureRev2012">{{cite journal | vauthors = Restifo NP, Dudley ME, Rosenberg SA | title = Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer: harnessing the T cell response | journal = Nature Reviews. Immunology | volume = 12 | issue = 4 | pages = 269–81 | date = March 2012 | pmid = 22437939 | pmc = 6292222 | doi = 10.1038/nri3191 }}</ref> | |||
| * Naked monoclonal antibodies are antibodies without modification. Most of the currently used antibodies therapies fall into this category. | |||
| * Conjugated monoclonal antibodies are joined to another molecule, which is either toxic to cells or radioactive. The toxic chemicals are usually routinely used chemotherapy drugs but other toxins can be used. The antibody binds to specific antigens on the surface of cancer cells and directs the drug or radiation to the tumor. Radioactive compound-linked antibodies are referred to as radiolabelled. If the antibodies are labelled with chemotherapy or toxins, they are known as chemolabelled or immunotoxins, respectively. | |||
| Multiple ways of producing tumour-destroying T-cells have been developed. Most commonly, T-cells specific to a tumor antigen can be removed from a tumor sample (TILs) or filtered from blood. The T-cells can optionally be modified in various ways, cultured and infused into patients. T cells can be modified via genetic engineering, producing CAR-T cell or TCR T cells or by exposing the T cells to tumor antigens in a non-immunosuppressive environment, that they recognize as foreign and learn to attack. | |||
| Antibodies are also referred to as murine, chimeric, humanized and human. Murine antibodies were the first type of antibody to be produced, and they carry a great risk of immune reaction by the recipient because the antibodies are from a different species. Chimeric antibodies were the first attempt to reduce the ] of these antibodies. They are murine antibodies with a specific part of the antibody replaced with the corresponding human counterpart, known as the constant region. Humanized antibodies are almost completely human; only the ] of the ]s are derived from murine antibodies. Human antibodies have a completely human ] sequence.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Harding|first=FA|coauthors=Stickler, MM; Razo, J; DuBridge, RB|title=The immunogenicity of humanized and fully human antibodies: residual immunogenicity resides in the CDR regions.|journal=mAbs|date=2010 May-Jun|volume=2|issue=3|pages=256–65|pmid=20400861}}</ref> | |||
| Another approach is transfer of haploidentical ] or ] from a healthy donor.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Barros MS, de Araújo ND, Magalhães-Gama F, Pereira Ribeiro TL, Alves Hanna FS, Tarragô AM, Malheiro A, Costa AG | title = γδ T Cells for Leukemia Immunotherapy: New and Expanding Trends | journal = Frontiers in Immunology | volume = 12 | pages = 729085 | date = 22 September 2021 | pmid = 34630403 | doi = 10.3389/fimmu.2021.729085 | pmc = 8493128 | doi-access = free }}</ref> The major advantage of this approach is that these cells do not cause ]. The disadvantage is that transferred cells frequently have impaired function.<ref name="pmid = 24528541">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wilhelm M, Smetak M, Schaefer-Eckart K, Kimmel B, Birkmann J, Einsele H, Kunzmann V | title = Successful adoptive transfer and in vivo expansion of haploidentical γδ T cells | journal = Journal of Translational Medicine | volume = 12 | pages = 45 | date = February 2014 | pmid = 24528541 | pmc = 3926263 | doi = 10.1186/1479-5876-12-45 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| === |
==== Tumor-derived T cell therapy ==== | ||
| The simplest example involves removing TILs from a tumor, culturing but not modifying them, and infusing the result back into the tumour. The first therapy of this type, ], achieved US ] (FDA) approval in February 2024. | |||
| ==== CAR-T cell therapy ==== | |||
| {{main|Chimeric antigen receptor T cell}} | |||
| The premise of CAR-T immunotherapy is to modify T cells to recognize cancer cells in order to target and destroy them. Scientists harvest T cells from people, genetically alter them to add a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) that specifically recognizes cancer cells, then infuse the resulting CAR-T cells into patients to attack their tumors. | |||
| ] (Kymriah), a ] (CAR-T) therapy, was approved by the FDA in 2017 to treat ] (ALL).<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm574058.htm|title=Press Announcements – FDA approval brings first gene therapy to the United States | author = Office of the Commissioner|website=fda.gov|access-date=13 December 2017}}</ref> This treatment removes ] positive cells (B-cells) from the body (including the diseased cells, but also normal antibody-producing cells). | |||
| ] (Yescarta) is another CAR-T therapeutic, approved in 2017 for treatment of ] (DLBCL).<ref name="fda.gov">{{cite web|url=https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm581216.htm|title=FDA approves CAR-T cell therapy to treat adults with certain types of large B-cell lymphoma|publisher=fda.gov|date=18 October 2017|access-date=8 November 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Multifunctional alginate scaffolds ==== | |||
| Multifunctional alginate scaffolds for T cell engineering and release (MASTER) is a technique for ''in situ'' engineering, replication and release of genetically engineered T cells. It is an evolution of ] therapy. T cells are extracted from the patient and mixed with a genetically engineered virus that contains a cancer-targeting gene (as with CAR T). The mixture is then added to a MASTER (scaffold), which absorbs them. The MASTER contains ] that activate the T cells and ] that trigger cell proliferation. The MASTER is then implanted into the patient. The activated T cells interact with the viruses to become CAR T cells. The interleukins stimulate these CAR T cells to proliferate, and the CAR T cells exit the MASTER to attack the cancer. The technique takes hours instead of weeks. And because the cells are younger, they last longer in the body, show stronger potency against cancer, and display fewer markers of exhaustion. These features were demonstrated in mouse models. The treatment was more effective and longer-lasting against ].<ref>{{Cite web | vauthors = Irving M |date=2022-03-29 |title=Implantable immunotherapy "factory" fights cancer faster, more effectively |url=https://newatlas.com/medical/cancer-immunotherapy-master-implant-car-t-cells/ |access-date=2022-03-29 |website=New Atlas |language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Agarwalla P, Ogunnaike EA, Ahn S, Froehlich KA, Jansson A, Ligler FS, Dotti G, Brudno Y | title = Bioinstructive implantable scaffolds for rapid in vivo manufacture and release of CAR-T cells | journal = Nature Biotechnology | pages = 1250–1258 | date = March 2022 | volume = 40 | issue = 8 | pmid = 35332339 | doi = 10.1038/s41587-022-01245-x | pmc = 9376243 }}</ref> | |||
| ==== T cell receptor T cell therapy ==== | |||
| {{Excerpt|T cell receptor T cell therapy}} | |||
| == Antibody therapy == | |||
| ] | |||
| {{excerpt|Monoclonal antibody therapy|paragraphs=1|this=This paragraph is}} | |||
| ===Antibody types === | |||
| ==== Conjugation ==== | |||
| Two types are used in cancer treatments:<ref name="pmid22437872" /> | |||
| * Naked monoclonal antibodies are antibodies without added elements. Most antibody therapies use this antibody type. | |||
| * Conjugated monoclonal antibodies are joined to another molecule, which is either cytotoxic or ]. The toxic chemicals are those typically used as ] drugs, but other toxins can be used. The antibody binds to specific antigens on cancer cell surfaces, directing the therapy to the tumor. Radioactive compound-linked antibodies are referred to as radiolabelled. Chemolabelled or immunotoxins antibodies are tagged with chemotherapeutic molecules or toxins, respectively.<ref name=":0" /> Research has also demonstrated conjugation of a ] to an anti-tumor monoclonal antibody.<ref name="GaddGrecoCobbEdwards2015">{{cite journal | vauthors = Gadd AJ, Greco F, Cobb AJ, Edwards AD | title = Targeted Activation of Toll-Like Receptors: Conjugation of a Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist to a Monoclonal Antibody Maintains Antigen Binding and Specificity | language = en | journal = Bioconjugate Chemistry | volume = 26 | issue = 8 | pages = 1743–52 | date = August 2015 | pmid = 26133029 | doi = 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00302 | s2cid = 26307107 | url = http://centaur.reading.ac.uk/41984/1/TLR7-Ritux%20conjug%20Revised%20FINAL%20CentAUR.pdf | quote = We demonstrate here for the first time the successful conjugation of a small molecule TLR7 agonist to an antitumor mAb (the anti-hCD20 rituximab) without compromising antigen specificity. }}</ref> | |||
| ==== Fc regions ==== | |||
| Fc's ability to bind ] is important because it allows antibodies to activate the immune system. Fc regions are varied: they exist in numerous subtypes and can be further modified, for example with the addition of sugars in a process called ]. Changes in the ] can alter an antibody's ability to engage Fc receptors and, by extension, will determine the type of immune response that the antibody triggers.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Pincetic A, Bournazos S, DiLillo DJ, Maamary J, Wang TT, Dahan R, Fiebiger BM, Ravetch JV | title = Type I and type II Fc receptors regulate innate and adaptive immunity | journal = Nature Immunology | volume = 15 | issue = 8 | pages = 707–16 | date = August 2014 | pmid = 25045879 | doi = 10.1038/ni.2939 | pmc = 7430760 }}</ref> For example, ] blockers targeting PD-1 are antibodies designed to bind PD-1 expressed by T cells and reactivate these cells to eliminate ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD, Sosman JA, Atkins MB, Leming PD, Spigel DR, Antonia SJ, Horn L, Drake CG, Pardoll DM, Chen L, Sharfman WH, Anders RA, Taube JM, McMiller TL, Xu H, Korman AJ, Jure-Kunkel M, Agrawal S, McDonald D, Kollia GD, Gupta A, Wigginton JM, Sznol M | title = Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer | journal = The New England Journal of Medicine | volume = 366 | issue = 26 | pages = 2443–54 | date = June 2012 | pmid = 22658127 | pmc = 3544539 | doi = 10.1056/NEJMoa1200690 }}</ref> ] contain not only a Fab region that binds PD-1 but also an Fc region. Experimental work indicates that the Fc portion of cancer immunotherapy drugs can affect the outcome of treatment. For example, anti-PD-1 drugs with Fc regions that bind inhibitory Fc receptors can have decreased therapeutic efficacy.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Dahan R, Sega E, Engelhardt J, Selby M, Korman AJ, Ravetch JV | title = FcγRs Modulate the Anti-tumor Activity of Antibodies Targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 Axis | journal = Cancer Cell | volume = 28 | issue = 4 | pages = 543 | date = October 2015 | pmid = 28854351 | doi = 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.09.011 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Imaging studies have further shown that the Fc region of anti-PD-1 drugs can bind Fc receptors expressed by tumor-associated macrophages. This process removes the drugs from their intended targets (i.e. PD-1 molecules expressed on the surface of T cells) and limits therapeutic efficacy.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Arlauckas SP, Garris CS, Kohler RH, Kitaoka M, Cuccarese MF, Yang KS, Miller MA, Carlson JC, Freeman GJ, Anthony RM, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ | title = In vivo imaging reveals a tumor-associated macrophage-mediated resistance pathway in anti-PD-1 therapy | journal = Science Translational Medicine | volume = 9 | issue = 389 | pages = eaal3604 | date = May 2017 | pmid = 28490665 | pmc = 5734617 | doi = 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3604 }}</ref> Furthermore, antibodies targeting the co-stimulatory protein ] require engagement with selective Fc receptors for optimal therapeutic efficacy.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Dahan R, Barnhart BC, Li F, Yamniuk AP, Korman AJ, Ravetch JV | title = Therapeutic Activity of Agonistic, Human Anti-CD40 Monoclonal Antibodies Requires Selective FcγR Engagement | journal = Cancer Cell | volume = 29 | issue = 6 | pages = 820–31 | date = July 2016 | pmid = 27265505 | pmc = 4975533 | doi = 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.05.001 }}</ref> Together, these studies underscore the importance of Fc status in antibody-based ] targeting strategies. | |||
| ==== Human/non-human antibodies ==== | |||
| Antibodies can come from a variety of sources, including human cells, mice, and a combination of the two (chimeric antibodies). Different sources of antibodies can provoke different kinds of immune responses. For example, the human immune system can recognize mouse antibodies (also known as murine antibodies) and trigger an immune response against them. This could reduce the effectiveness of the antibodies as a treatment and cause an immune reaction. Chimeric antibodies attempt to reduce murine antibodies' ] by replacing part of the antibody with the corresponding human counterpart. Humanized antibodies are almost completely human; only the ] of the ]s are derived from murine sources. Human antibodies have been produced using unmodified human DNA.<ref name=":0">{{cite journal | vauthors = Harding FA, Stickler MM, Razo J, DuBridge RB | title = The immunogenicity of humanized and fully human antibodies: residual immunogenicity resides in the CDR regions | journal = mAbs | volume = 2 | issue = 3 | pages = 256–65 | date = May–Jun 2010 | pmid = 20400861 | pmc = 2881252 | doi = 10.4161/mabs.2.3.11641 }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Mechanism of action=== | |||
| ====Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)==== | ====Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)==== | ||
| ] (ADCC) |
] (ADCC) requires antibodies to bind to target cell surfaces. Antibodies are formed of a binding region (Fab) and the Fc region that can be detected by immune system cells via their ]. Fc receptors are found on many immune system cells, including NK cells. When NK cells encounter antibody-coated cells, the latter's Fc regions interact with their Fc receptors, releasing ] and ] to kill the tumor cell. Examples include ], ], ], and ]. Antibodies under development have altered Fc regions that have higher affinity for a specific type of Fc receptor, FcγRIIIA, which can dramatically increase effectiveness.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Weiner LM, Surana R, Wang S | title = Monoclonal antibodies: versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy | journal = Nature Reviews. Immunology | volume = 10 | issue = 5 | pages = 317–27 | date = May 2010 | pmid = 20414205 | pmc = 3508064 | doi = 10.1038/nri2744 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Seidel UJ, Schlegel P, Lang P | title = Natural killer cell mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in tumor immunotherapy with therapeutic antibodies | journal = Frontiers in Immunology | volume = 4 | pages = 76 | year = 2013 | pmid = 23543707 | pmc = 3608903 | doi = 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00076 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | ||
| ===Anti-CD47 therapy=== | |||
| Many tumor cells overexpress ] to escape ] of host immune system. CD47 binds to its receptor ] (SIRPα) and downregulate ] of tumor cell.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Jaiswal S, Chao MP, Majeti R, Weissman IL | title = Macrophages as mediators of tumor immunosurveillance | journal = Trends in Immunology | volume = 31 | issue = 6 | pages = 212–19 | date = June 2010 | pmid = 20452821 | doi = 10.1016/j.it.2010.04.001 | pmc = 3646798 }}</ref> Therefore, anti-CD47 therapy aims to restore clearance of tumor cells. Additionally, growing evidence supports the employment of tumor antigen-specific ] in response to anti-CD47 therapy.<ref name=":1">{{cite journal | vauthors = Weiskopf K | title = Cancer immunotherapy targeting the CD47/SIRPα axis | journal = European Journal of Cancer | volume = 76 | pages = 100–09 | date = May 2017 | pmid = 28286286 | doi = 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.02.013 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Matlung HL, Szilagyi K, Barclay NA, van den Berg TK | title = The CD47-SIRPα signaling axis as an innate immune checkpoint in cancer | journal = Immunological Reviews | volume = 276 | issue = 1 | pages = 145–64 | date = March 2017 | pmid = 28258703 | doi = 10.1111/imr.12527 | s2cid = 6275163 }}</ref> A number of therapeutics are being developed, including anti-CD47 ], engineered ], anti-SIRPα ] and bispecific agents.<ref name=":1" /> As of 2017, wide range of solid and hematologic malignancies were being clinically tested.<ref name=":1" /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Veillette A, Chen J | title = SIRPα-CD47 Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Anticancer Therapy | journal = Trends in Immunology | volume = 39 | issue = 3 | pages = 173–84 | date = March 2018 | pmid = 29336991 | doi = 10.1016/j.it.2017.12.005 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Anti-GD2 antibodies=== | |||
| ] | |||
| Carbohydrate ]s on the surface of cells can be used as targets for immunotherapy. ] is a ] found on the surface of many types of cancer cell including ], ], ], ], ]s, ], ], ], ], ], ] and other ]s. It is not usually expressed on the surface of normal tissues, making it a good target for immunotherapy. As of 2014, clinical trials were underway.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ahmed M, Cheung NK | title = Engineering anti-GD2 monoclonal antibodies for cancer immunotherapy | journal = FEBS Letters | volume = 588 | issue = 2 | pages = 288–97 | date = January 2014 | pmid = 24295643 | doi = 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.11.030 | doi-access = free | bibcode = 2014FEBSL.588..288A }}</ref> | |||
| ====Complement==== | ====Complement Activation==== | ||
| The ] |
The ] includes blood proteins that can cause cell death after an antibody binds to the cell surface (the ], among the ways of complement activation). Generally, the system deals with foreign pathogens but can be activated with therapeutic antibodies in cancer. The system can be triggered if the antibody is chimeric, humanized, or human; as long as it contains the ] ]. Complement can lead to cell death by activation of the ], known as complement-dependent ]; enhancement of ]; and CR3-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Complement-dependent cytotoxicity occurs when antibodies bind to the cancer cell surface, the C1 complex binds to these antibodies and subsequently, protein pores are formed in cancer ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gelderman KA, Tomlinson S, Ross GD, Gorter A | title = Complement function in mAb-mediated cancer immunotherapy | journal = Trends in Immunology | volume = 25 | issue = 3 | pages = 158–64 | date = March 2004 | pmid = 15036044 | doi = 10.1016/j.it.2004.01.008 }}</ref> | ||
| '''Blocking''' | |||
| ====Cell signalling==== | |||
| ] or ]s]] | |||
| Antibodies that bind to molecules on the surface of the cancer cells, or bind to molecules in the blood can affect cell signalling in various ways. The antibodies can bind to a receptor and prevent binding from external proteins, peptides or small molecules that would normally bind to the receptor (called ]). Receptors that have been extensively researched for antibody targeting are ]s (targeted by ] and ]). Antibodies can also bind the ligands themselves such as ] (VEGF); involved in blood vessel formation. ] is a clinically used antibody that binds VEGF. These receptor-ligand interactions may be essential for the cancer cell to survive, so blocking them can induce the death of these cancer cells. Antibodies like these are known as antagonists, but antibodies can also activate signalling by binding to receptors, then they are known as agonists. One signalling pathway that is activated by antibodies is the programmed cell death (]) pathway.<ref name="pmid22437872"/> | |||
| Antibody therapies can also function by binding to proteins and physically blocking them from interacting with other proteins. Checkpoint inhibitors (CTLA-4, PD-1, and PD-L1) operate by this mechanism. Briefly, checkpoint inhibitors are proteins that normally help to slow immune responses and prevent the immune system from attacking normal cells. Checkpoint inhibitors bind these proteins and prevent them from functioning normally, which increases the activity of the immune system. Examples include ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| ====Payload==== | |||
| Conjugated antibodies carry a payload that is either a drug (usually a ]), ], ] or ]. ] is the term used with the use of antibodies conjugated to a ] against cellular antigens. Most research currently involves their application to ], as these are highly radio-sensitive malignancies.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Sharkey|first=RM|coauthors=Goldenberg, DM|title=Cancer radioimmunotherapy.|journal=Immunotherapy|date=March 2011|volume=3|issue=3|pages=349–70|pmid=21395378}}</ref> Out of the 12 approved antibodies used in cancer, two use toxic compounds (] - ] and ] - ]) and two are radiolabelled (] - ] and ] - ]). These antibodies specifically bind to their targets on the surface of cancer cells and the payloads they are attached to lead to cancer cell death.<ref name="pmid22437872"/> | |||
| === |
===FDA-approved antibodies=== | ||
| {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto" width="600px" align="right" | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto" width="600px" align="right" | ||
| |+ '''Cancer immunotherapy:Monoclonal antibodies'''<ref name="pmid22437872">{{cite journal| |
|+ '''Cancer immunotherapy:Monoclonal antibodies'''<ref name="pmid22437872">{{cite journal | vauthors = Scott AM, Wolchok JD, Old LJ | title = Antibody therapy of cancer | journal = Nature Reviews. Cancer | volume = 12 | issue = 4 | pages = 278–87 | date = March 2012 | pmid = 22437872 | doi = 10.1038/nrc3236 | s2cid = 205469234 }}</ref><ref name="Waldmann">{{cite journal | vauthors = Waldmann TA | title = Immunotherapy: past, present and future | journal = Nature Medicine | volume = 9 | issue = 3 | pages = 269–77 | date = March 2003 | pmid = 12612576 | doi = 10.1038/nm0303-269 | s2cid = 9745527 | url = https://zenodo.org/record/1233435 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | ||
| ! Antibody |
! Antibody | ||
| !Brand name | |||
| !Type | |||
| ! Target | |||
| !Approval date | |||
| ! Approved treatment(s) | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| | ] || Campath|| humanized || ]|| 2001 || ] ] (CLL)<ref>{{cite journal|last=Demko|first=S|coauthors=Summers, J; Keegan, P; Pazdur, R|title=FDA drug approval summary: alemtuzumab as single-agent treatment for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia.|journal=The oncologist|date=February 2008|volume=13|issue=2|pages=167–74|pmid=18305062}}</ref> | |||
| | Campath | |||
| | humanized | |||
| | ]|| 2001 || ] ] (CLL)<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Demko S, Summers J, Keegan P, Pazdur R | title = FDA drug approval summary: alemtuzumab as single-agent treatment for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia | journal = The Oncologist | volume = 13 | issue = 2 | pages = 167–74 | date = February 2008 | pmid = 18305062 | doi = 10.1634/theoncologist.2007-0218 | citeseerx = 10.1.1.503.6960 }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |rowspan=4|] ||rowspan=4 | Avastin ||rowspan=4 | humanized ||rowspan=4 | ]|| 2004||metastatic ] <ref>{{cite journal|last=Cohen|first=MH|coauthors=Gootenberg, J; Keegan, P; Pazdur, R|title=FDA drug approval summary: bevacizumab plus FOLFOX4 as second-line treatment of colorectal cancer.|journal=The oncologist|date=March 2007|volume=12|issue=3|pages=356–61|pmid=17405901}}</ref> | |||
| | Tecentriq | |||
| | humanized | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 2016 | |||
| | ]<ref name="FDA-BC-2016">{{cite news|url=https://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm501762.htm|title=FDA approves new, targeted treatment for bladder cancer|date=18 May 2016|publisher=FDA|access-date=20 May 2016}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |2006 ||]<ref>{{cite journal|last=Cohen|first=MH|coauthors=Gootenberg, J; Keegan, P; Pazdur, R|title=FDA drug approval summary: bevacizumab (Avastin) plus Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as first-line treatment of advanced/metastatic recurrent nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer.|journal=The oncologist|date=June 2007|volume=12|issue=6|pages=713–8|pmid=17602060}}</ref> | |||
| | Tecentriq Hybreza | |||
| | humanized | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 2024 | |||
| | non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma<ref name="FDA 20240912">{{cite web | title=FDA approves atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs | website=U.S. Food and Drug Administration | date=12 September 2024 | url=https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-atezolizumab-and-hyaluronidase-tqjs-subcutaneous-injection | access-date=14 September 2024 | archive-date=14 September 2024 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240914055712/https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-atezolizumab-and-hyaluronidase-tqjs-subcutaneous-injection | url-status=live }} {{PD-notice}}</ref><ref>{{cite press release | title=FDA Approves Genentech's Tecentriq Hybreza, the First and Only Subcutaneous Anti-PD-(L)1 Cancer Immunotherapy | website=Genentech | date=12 September 2024 | url=https://www.gene.com/media/press-releases/15035/2024-09-12/fda-approves-genentechs-tecentriq-hybrez | access-date=14 September 2024 | archive-date=13 September 2024 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240913041829/https://www.gene.com/media/press-releases/15035/2024-09-12/fda-approves-genentechs-tecentriq-hybrez | url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite press release | title=Halozyme Announces FDA Approval of Roche's Tecentriq Hybreza With Enhanze for Multiple Types of Cancer | publisher=Halozyme Therapeutics | via=PR Newswire | date=12 September 2024 | url=https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/halozyme-announces-fda-approval-of-roches-tecentriq-hybreza-with-enhanze-for-multiple-types-of-cancer-302247280.html | access-date=14 September 2024 | archive-date=13 September 2024 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240913013612/https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/halozyme-announces-fda-approval-of-roches-tecentriq-hybreza-with-enhanze-for-multiple-types-of-cancer-302247280.html | url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |2009 ||]<ref>{{cite journal|last=Summers|first=J|coauthors=Cohen, MH; Keegan, P; Pazdur, R|title=FDA drug approval summary: bevacizumab plus interferon for advanced renal cell carcinoma.|journal=The oncologist|year=2010|volume=15|issue=1|pages=104–11|pmid=20061402}}</ref> | |||
| | Bavencio | |||
| | human | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 2017 | |||
| | metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/761049s000lbl.pdf|title=US Food and Drug Administration – Avelumab Prescribing Label}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | |||
| |2009 ||]<ref>{{cite journal|last=Cohen|first=MH|coauthors=Shen, YL; Keegan, P; Pazdur, R|title=FDA drug approval summary: bevacizumab (Avastin) as treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme.|journal=The oncologist|date=November 2009|volume=14|issue=11|pages=1131–8|pmid=19897538}}</ref> | |||
| |Imfinzi | |||
| |human | |||
| |PD-L1 | |||
| |2017 | |||
| |bladder cancer<ref>{{Cite web| title = Approved Drugs – Durvalumab (Imfinzi) |url=https://www.fda.gov/drugs/informationondrugs/approveddrugs/ucm555930.htm | author = Center for Drug Evaluation and Research|website=fda.gov|access-date=6 May 2017}}</ref> non-small cell lung cancer<ref>{{Cite journal|url=https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm597248.htm|title=FDA approves durvalumab after chemoradiation for unresectable stage III NSCLC|journal=FDA|date=9 February 2019}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |rowspan=2|] ||rowspan=2|Adcetris || rowspan=2|chimeric ||rowspan=2|]|| 2011||relapsed ]<ref name ="pmid22962441">{{cite journal|last=de Claro|first=RA|coauthors=McGinn, K; Kwitkowski, V; Bullock, J; Khandelwal, A; Habtemariam, B; Ouyang, Y; Saber, H; Lee, K; Koti, K; Rothmann, M; Shapiro, M; Borrego, F; Clouse, K; Chen, XH; Brown, J; Akinsanya, L; Kane, R; Kaminskas, E; Farrell, A; Pazdur, R|title=U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval summary: brentuximab vedotin for the treatment of relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma or relapsed systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma.|journal=Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research|date=Nov 1, 2012|volume=18|issue=21|pages=5845–9|pmid=22962441}}</ref> | |||
| | Empliciti | |||
| | humanized | |||
| | ]|| 2015 || ]<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://news.bms.com/news/r-and-d/2014/Bristol-Myers-Squibb-and-AbbVie-Receive-US-FDA-Breakthrough-Therapy-Designation-for-Elotuzumab-an-Investigational-Humanized-Monoclonal-Antibody-for-Multiple-Myeloma/default.aspx |title = Bristol-Myers Squibb and AbbVie Receive U.S. FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation for Elotuzumab, an Investigational Humanized Monoclonal Antibody for Multiple Myeloma | BMS Newsroom}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |] | |||
| |2011||relapsed ]<ref name ="pmid22962441"/> | |||
| | Yervoy | |||
| | human | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 2011 | |||
| |metastatic ]<ref>{{cite web|vauthors=Pazdur R|title=FDA approval for Ipilimumab|url=http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/druginfo/fda-ipilimumab|access-date=7 November 2013|archive-date=6 April 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150406011836/http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/druginfo/fda-ipilimumab|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |rowspan=4| ] ||rowspan=4|Erbitux ||rowspan=4|chimeric ||rowspan=4|] || 2004||]<ref name="FDA cetuximab">{{cite web|last=Pazdur|first=Richard|title=FDA approval for Cetuximab|url=http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/druginfo/fda-cetuximab|accessdate=7 November 2013}}</ref> | |||
| | Opdivo | |||
| | human | |||
| | ] | |||
| | 2014 | |||
| | ] or ], ], Renal cell carcinoma, colorectal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, classical hodgkin lymphoma<ref name="sa15">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sharma P, Allison JP | title = The future of immune checkpoint therapy | journal = Science | volume = 348 | issue = 6230 | pages = 56–61 | date = April 2015 | pmid = 25838373 | doi = 10.1126/science.aaa8172 | bibcode = 2015Sci...348...56S | s2cid = 4608450 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.drugs.com/history/opdivo.html|title=Opdivo (nivolumab) FDA Approval History|website=Drugs.com}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |2006||advanced ] of the head and neck (SCCHN)<ref name="FDA cetuximab"/> | |||
| | Arzerra | |||
| | human | |||
| | ] | |||
| |2009 | |||
| | refractory ]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lemery SJ, Zhang J, Rothmann MD, Yang J, Earp J, Zhao H, McDougal A, Pilaro A, Chiang R, Gootenberg JE, Keegan P, Pazdur R | title = U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval: ofatumumab for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab | journal = Clinical Cancer Research | volume = 16 | issue = 17 | pages = 4331–38 | date = September 2010 | pmid = 20601446 | doi = 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0570 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |2011|| recurrent locoregional or metastatic ]<ref>{{cite journal|last=Cohen|first=MH|coauthors=Chen, H; Shord, S; Fuchs, C; He, K; Zhao, H; Sickafuse, S; Keegan, P; Pazdur, R|title=Approval summary: Cetuximab in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin and 5-fluorouracil for the first-line treatment of patients with recurrent locoregional or metastatic squamous cell head and neck cancer.|journal=The oncologist|year=2013|volume=18|issue=4|pages=460–6|pmid=23576486}}</ref> | |||
| |Keytruda | |||
| |humanized | |||
| | ] | |||
| |2014 | |||
| |] or ], ] (NSCLC),<ref>{{cite journal|url=https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm624659.htm|title=FDA approves pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy for first-line treatment of metastatic squamous NSCLC|journal=FDA|date=20 December 2019}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite journal|url=https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm546893.htm|title=Pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA) for classical Hodgkin lymphoma|journal=FDA|date=9 February 2019}}</ref> ] (MCC),<ref>{{cite journal|url=https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm628867.htm|title=FDA approves pembrolizumab for Merkel cell carcinoma|journal=FDA|date=20 December 2019}}</ref> ] (PMBCL),<ref>{{cite journal|url=https://www.fda.gov/drugs/informationondrugs/approveddrugs/ucm610670.htm|title=FDA approves pembrolizumab for treatment of relapsed or refractory PMBCL|journal=FDA|date=9 February 2019}}</ref> ], ]<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/pembrolizumab|title=National Cancer Institute - Pembrolizumab Use in Cancer|date=18 September 2014}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |2012|| EGFR-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer<ref name="FDA cetuximab"/> | |||
| | Rituxan, Mabthera | |||
| |- | |||
| | chimeric | |||
| | ] || Mylotarg || humanized|| ] ||2000 ||] (with ])<ref>{{cite journal|last=Bross|first=PF|coauthors=Beitz, J; Chen, G; Chen, XH; Duffy, E; Kieffer, L; Roy, S; Sridhara, R; Rahman, A; Williams, G; Pazdur, R|title=Approval summary: gemtuzumab ozogamicin in relapsed acute myeloid leukemia.|journal=Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research|date=June 2001|volume=7|issue=6|pages=1490–6|pmid=11410481}}</ref> | |||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1997 | |||
| | ] || Zevalin || murine || ]|| 2002||] (with ])<ref>{{cite web|title=FDA - Ibritumomab Tiuxetan|url=http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/druginfo/ibritumomabtiuxetan|accessdate=7 November 2013}}</ref> | |||
| |]<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = James JS, Dubs G | title = FDA approves new kind of lymphoma treatment. Food and Drug Administration | journal = AIDS Treatment News | issue = 284 | pages = 2–3 | date = December 1997 | pmid = 11364912 }}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |- | |||
| |] || Yervoy || human || ] || 2011 ||metastatic ]<ref>{{cite web|last=Pazdur|first=Richard|title=FDA approval for Ipilimumab|url=http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/druginfo/fda-ipilimumab|accessdate=7 November 2013}}</ref> | |||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | Rituxan Hycela | |||
| | ] || Arzerra || human || ] ||2009|| refractory ]<ref>{{cite journal|last=Lemery|first=SJ|coauthors=Zhang, J; Rothmann, MD; Yang, J; Earp, J; Zhao, H; McDougal, A; Pilaro, A; Chiang, R; Gootenberg, JE; Keegan, P; Pazdur, R|title=U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval: ofatumumab for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab.|journal=Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research|date=Sep 1, 2010|volume=16|issue=17|pages=4331–8|pmid=20601446}}</ref> | |||
| | chimeric | |||
| |- | |||
| | ] | |||
| | ] || Vectibix ||human||] || 2006|| metastatic ]<ref>{{cite journal|last=Giusti|first=RM|coauthors=Cohen, MH; Keegan, P; Pazdur, R|title=FDA review of a panitumumab (Vectibix) clinical trial for first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.|journal=The oncologist|date=March 2009|volume=14|issue=3|pages=284–90|pmid=19282350}}</ref> | |||
| | 2017 | |||
| |- | |||
| | follicular lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia<ref>{{cite web | title=Rituxan Hycela- rituximab and hyaluronidase injection, solution | website=DailyMed | date=8 July 2024 | url=https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=3e5b7e82-f018-4eaf-ae78-d6145a906b20 | access-date=15 September 2024}}</ref> | |||
| |rowspan=2 |] ||rowspan=2 | Rituxan, Mabthera ||rowspan=2 | chimeric ||rowspan=2|] || 1997||]<ref>{{cite journal|last=James|first=JS|coauthors=Dubs, G|title=FDA approves new kind of lymphoma treatment. Food and Drug Administration.|journal=AIDS treatment news|date=Dec 5, 1997|issue= 284|pages=2–3|pmid=11364912}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | |||
| |2010||]<ref>{{cite journal|last=Casak|first=SJ|coauthors=Lemery, SJ; Shen, YL; Rothmann, MD; Khandelwal, A; Zhao, H; Davis, G; Jarral, V; Keegan, P; Pazdur, R|title=U.S. Food and drug administration approval: rituximab in combination with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.|journal=The oncologist|year=2011|volume=16|issue=1|pages=97–104|pmid=21212432}}</ref> | |||
| | Rituxan Hycela | |||
| |- | |||
| | humanized | |||
| |Tositumomab || Bexxar|| murine || CD20 || 2003 || ]<ref>{{cite web|last=Pazdur|first=Richard|title=FDA Approval for Tositumomab and Iodine I 131 Tositumomab|url=http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/druginfo/fda-tositumomab-I131iodine-tositumomab|accessdate=7 November 2013}}</ref> | |||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | 1998 | |||
| | ] || Herceptin || humanized ||]|| 1998||]<ref>{{cite web|title=FDA Expands Use of Herceptin for Early Stage Breast Cancer After Primary Therapy|url=http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/2006/ucm108788.htm|accessdate=7 November 2013}}</ref> | |||
| | breast cancer, gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma | |||
| |- | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| ====Alemtuzumab==== | ====Alemtuzumab==== | ||
| ] ( |
] (Campath-1H) is an anti-] humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody indicated for the treatment of ]-refractory ] (CLL), ], ] and ]. CD52 is found on >95% of peripheral blood ]s (both T-cells and B-cells) and ]s, but its function in lymphocytes is unknown. It binds to CD52 and initiates its cytotoxic effect by complement fixation and ADCC mechanisms. Due to the antibody target (cells of the immune system), common complications of alemtuzumab therapy are infection, toxicity and ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Byrd JC, Stilgenbauer S, Flinn IW | title = Chronic lymphocytic leukemia | journal = Hematology. American Society of Hematology. Education Program | volume = 2004 | issue = 1 | pages = 163–83 | date = 1 January 2004 | pmid = 15561682 | doi = 10.1182/asheducation-2004.1.163 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Domagała A, Kurpisz M | title = CD52 antigen--a review | journal = Medical Science Monitor | volume = 7 | issue = 2 | pages = 325–31 | date = 2001 | pmid = 11257744 | url = https://www.medscimonit.com/download/index/idArt/421140 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Dearden C | title = How I treat prolymphocytic leukemia | journal = Blood | volume = 120 | issue = 3 | pages = 538–51 | date = July 2012 | pmid = 22649104 | doi = 10.1182/blood-2012-01-380139 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | ||
| ==== |
====Atezolizumab==== | ||
| {{Excerpt|Atezolizumab}} | |||
| ] (Avastin) is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody which binds to ]-A (VEGF-A), referred to commonly as VEGF without a suffix. Normally VEGF will bind to the ] on the cell's surface, activating signalling pathways within blood vessel ]s. A marked increase in VEGF expression within the tumor environment stimulates the production of blood vessels, a process known as ], which is essential for growth of a tumor. These blood vessels, however, are not formed well and lead to poor blood flow in the tumor, which also affects drug delivery to cancer cells.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Lenz|first=HJ|title=Antiangiogenic agents in cancer therapy.|journal=Oncology (Williston Park, N.Y.)|date=April 2005|volume=19|issue=4 Suppl 3|pages=17–25|pmid=15934499}}</ref><ref name="pmid15705858">{{cite journal|last=Gerber|first=HP|coauthors=Ferrara, N|title=Pharmacology and pharmacodynamics of bevacizumab as monotherapy or in combination with cytotoxic therapy in preclinical studies.|journal=Cancer research|date=Feb 1, 2005|volume=65|issue=3|pages=671–80|pmid=15705858}}</ref><ref name="pmid23057939">{{cite journal|last=Sun|first=W|title=Angiogenesis in metastatic colorectal cancer and the benefits of targeted therapy.|journal=Journal of hematology & oncology|date=Oct 11, 2012|volume=5|pages=63|pmid=23057939}}</ref> | |||
| ====Atezolizumab/hyaluronidase==== | |||
| Bevacizumab binds to and physically blocks VEGF, preventing ] activation, known as ] interference. Bevacizumab's action on VEGF has three possible effects on tumor vasculature: it may cause microvessels to regress; it can normalise tumor blood vessels, allowing better delivery of other drugs to the tumor; and it can prevent the formation of new vasculature. Normalisation of faulty vessels may be the reason why Bevacizumab is particularly effective in combination with conventional drugs.<ref name="pmid15705858"/><ref name="pmid23057939"/><ref name="pmid20037132"/> | |||
| {{Excerpt|Atezolizumab/hyaluronidase}} | |||
| ====Avelumab==== | |||
| Bevacizumab is licensed for ], ], ], ], ] and ], although licenses may vary between countries. Bevacizumab increases the duration of survival, progression-free survival, the rate of response and the duration of response in these cancers, but because of its mechanism of action does not cure them.<ref name="pmid23057939"/><ref name="pmid20037132">{{cite journal|last=Mukherji|first=SK|title=Bevacizumab (Avastin).|journal=AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology|date=February 2010|volume=31|issue=2|pages=235–6|pmid=20037132}}</ref><ref name="pmid24204124">{{cite journal|last=Cheng|first=YD|coauthors=Yang, H; Chen, GQ; Zhang, ZC|title=Molecularly targeted drugs for metastatic colorectal cancer.|journal=Drug design, development and therapy|date=Nov 1, 2013|volume=7|pages=1315–1322|pmid=24204124}}</ref> | |||
| {{Excerpt|Avelumab}} | |||
| ==== |
====Durvalumab==== | ||
| {{Main|Durvalumab}} | |||
| ] (Erbitux) is a chimeric IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets the extracellular domain (part of the receptor outside the cell) of the ] (EGFR). It is used in the treatment of ] and ]. Once a ] binds to the EGFR on the surface of the cell, signalling pathways are activated inside the cell that are associated with malignant characteristics. These include the ]/] and ]/]/] pathways that cause cancer cell ], invasion, ] and cancer stem cell renewal.<ref name="pmid22576456">{{cite journal|last=Kirkwood|first=JM|coauthors=Butterfield, LH; Tarhini, AA; Zarour, H; Kalinski, P; Ferrone, S|title=Immunotherapy of cancer in 2012.|journal=CA: a cancer journal for clinicians|date=2012 Sep-Oct|volume=62|issue=5|pages=309–35|pmid=22576456}}</ref><ref name="pmid24204124"/><ref>{{cite journal|last=Bou-Assaly|first=W|coauthors=Mukherji, S|title=Cetuximab (erbitux).|journal=AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology|date=April 2010|volume=31|issue=4|pages=626–7|pmid=20167650}}</ref> | |||
| ] (Imfinzi) is a human immunoglobulin G1 kappa (IgG1κ) monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) with the PD-1 and CD80 (B7.1) molecules. Durvalumab is approved for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who: | |||
| Cetuximab functions by competitively inhibiting ] binding, thereby preventing EGFR activation and subsequent cellular signalling. It also induces ADCC and leads to increased levels of a protein known as ], which activates programmed cell death (]). ], a down-stream protein of the EGFR, may be mutated in some cases of cancer and remains constitutively active, irrespective of EGFR blocking. Cetuximab is only effective in the treatment of colorectal cancers with ] (unmutated) KRAS ]s, which includes approximately 40% of cases.<ref name="pmid22576456"/><ref name="pmid24204124"/> | |||
| * have disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy. | |||
| * have disease progression within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy. | |||
| On 16 February 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved durvalumab for patients with unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy.<ref>{{Cite journal | url=https://www.fda.gov/drugs/informationondrugs/approveddrugs/ucm597248.htm | title=FDA approves durvalumab after chemoradiation for unresectable stage III NSCLC| journal=FDA| date=9 February 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ====Elotuzumab==== | |||
| Other anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in development include: ], hR3, and ]. Although they hold significant promise for the future, none of the agents are currently beyond phase I ]s. | |||
| {{Excerpt|Elotuzumab}} | |||
| ==== |
====Ipilimumab==== | ||
| ] (Yervoy) is a human ] antibody that binds the surface protein ]. In normal physiology T-cells are activated by two signals: the ] binding to an ]-] and T-cell surface receptor CD28 binding to ] or ] proteins. CTLA4 binds to CD80 or CD86, preventing the binding of CD28 to these surface proteins and therefore negatively regulates the activation of T-cells.<ref name="pmid21629286">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sondak VK, Smalley KS, Kudchadkar R, Grippon S, Kirkpatrick P | title = Ipilimumab | journal = Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery | volume = 10 | issue = 6 | pages = 411–12 | date = June 2011 | pmid = 21629286 | doi = 10.1038/nrd3463 }}</ref><ref name="pmid21900389">{{cite journal | vauthors = Lipson EJ, Drake CG | title = Ipilimumab: an anti-CTLA-4 antibody for metastatic melanoma | journal = Clinical Cancer Research | volume = 17 | issue = 22 | pages = 6958–62 | date = November 2011 | pmid = 21900389 | pmc = 3575079 | doi = 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1595 }}</ref><ref name="pmid21294471">{{cite journal | vauthors = Thumar JR, Kluger HM | title = Ipilimumab: a promising immunotherapy for melanoma | journal = Oncology | volume = 24 | issue = 14 | pages = 1280–88 | date = December 2010 | pmid = 21294471 }}</ref><ref name="pmid11244047">{{cite journal | vauthors = Chambers CA, Kuhns MS, Egen JG, Allison JP | title = CTLA-4-mediated inhibition in regulation of T cell responses: mechanisms and manipulation in tumor immunotherapy | journal = Annual Review of Immunology | volume = 19 | pages = 565–94 | year = 2001 | pmid = 11244047 | doi = 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.565 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| ] is an “immuno-conjugate” of an ] anti-] antibody chemically linked to a ] ] derivative.<ref name="pmid22003069">{{cite journal|last=Ricart|first=AD|title=Antibody-drug conjugates of calicheamicin derivative: gemtuzumab ozogamicin and inotuzumab ozogamicin.|journal=Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research|date=Oct 15, 2011|volume=17|issue=20|pages=6417–27|pmid=22003069}}</ref> It was used for the treatment of ] (AML) after ] by the ] in May 2000, but in June 2010 it was withdrawn from the market regarding safety concerns.<ref>{{cite web|last=Food and Drug Administration|title=Mylotarg (gemtuzumab ozogamicin): Market Withdrawal|url=http://www.fda.gov/safety/medwatch/safetyinformation/safetyalertsforhumanmedicalproducts/ucm216458.htm|accessdate=23 November 2013}}</ref> Further research and clinical trials indicate that gemtuzumab ozogamicin might be safe and effective in a subset of AML with favourable prognoses.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Ravandi|first=F|coauthors=Estey, EH; Appelbaum, FR; Lo-Coco, F; Schiffer, CA; Larson, RA; Burnett, AK; Kantarjian, HM|title=Gemtuzumab ozogamicin: time to resurrect?|journal=Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology|date=Nov 10, 2012|volume=30|issue=32|pages=3921–3|pmid=22987091}}</ref> | |||
| Active ]s are required for the immune system to attack melanoma cells. Normally inhibited active melanoma-specific cytotoxic T-cells can produce an effective anti-tumor response. Ipilimumab can cause a shift in the ratio of ] to cytotoxic T-cells to increase the anti-tumor response. Regulatory T-cells inhibit other T-cells, which may benefit the tumor.<ref name="pmid21629286" /><ref name="pmid21900389" /><ref name="pmid21294471" /><ref name="pmid11244047" /> | |||
| The antibody binds to the ] antigen, which is found on the surface of immature precursor cells (]s) in AML in approximately 80% of cases. The antibody is liked to a chemical derivative of ], (''N''-acetyl-''γ'' calicheamicin 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine dichloride) which is highly toxic to cells due to its ability to bind to ]. Because the antibody is an IgG4 ], it doesn't activate ] or complement-mediated cytotoxicity, but instead is internalised into the cancer cells. Inside ]s within the cell, the pH is very acidic (approximately pH 4) causing the release of the calicheamicin from the antibody. Once released it is activated and free to bind to DNA, which leads to breakage of DNA and subsequent cell death.<ref name="pmid22003069"/> | |||
| ==== |
==== Nivolumab ==== | ||
| {{Main|Nivolumab}}] is a human ] antibody that prevents T-cell inactivation by blocking the binding of ] or programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (PD-L1 or PD-L2), a protein expressed by cancer cells, with ], a protein found on the surface of activated T-cells.<ref name=":4" /><ref name="pmid22437870"/> Nivolumab is used in advanced melanoma, metastatic renal cell carcinoma, advanced lung cancer, advanced head and neck cancer, and Hodgkin's lymphoma.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M, Floudas CS, Soni P, Chandra AB | title = Current Diagnosis and Management of Immune Related Adverse Events (irAEs) Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy | journal = Frontiers in Pharmacology | volume = 8 | pages = 49 | date = 2017 | pmid = 28228726 | pmc = 5296331 | doi = 10.3389/fphar.2017.00049 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| ==== Ofatumumab ==== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] is a second generation human ] antibody that binds to ]. It is used in the treatment of ] (CLL) because the cancerous cells of CLL are usually CD20-expressing B-cells. Unlike ], which binds to a large loop of the CD20 protein, ofatumumab binds to a separate, small loop. This may explain their different characteristics. Compared to rituximab, ofatumumab induces complement-dependent cytotoxicity at a lower dose with less ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Castillo J, Perez K | title = The role of ofatumumab in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia resistant to previous therapies | journal = Journal of Blood Medicine | volume = 1 | pages = 1–8 | year = 2010 | pmid = 22282677 | pmc = 3262337 | doi = 10.2147/jbm.s7284 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Zhang B | title = Ofatumumab | journal = mAbs | volume = 1 | issue = 4 | pages = 326–31 | date = Jul–Aug 2009 | pmid = 20068404 | pmc = 2726602 | doi = 10.4161/mabs.1.4.8895 }}</ref> | |||
| ] (Zevalin) is a murine anti-] antibody chemically linked to a ] that binds the ] ] (<sup>90</sup>Y). It is used to treat a specific type of ], ], which is a tumor of ]s. The antibody target, CD20, is primarily expressed on the surface of B-cells which allows the <sup>90</sup>Y to emit a targeted dose of ] to the tumor. <sup>90</sup>Y has a ] of 64 hours (2.67 days) and a tissue penetration of 1-5 millimetres (90% of its energy is absorbed within a 5.3mm sphere). Ibritumomab tiuxetan and the radioisotope are obtained separately and mixed shortly before administration. The tiuxetan chelating agent attached to the antibody binds the radioisotope forming the active drug.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Tennvall|first=J|coauthors=Fischer, M; Bischof Delaloye, A; Bombardieri, E; Bodei, L; Giammarile, F; Lassmann, M; Oyen, W; Brans, B; Therapy Committee,, EANM; Oncology Committee,, EANM; Dosimetry Committee,, EANM|title=EANM procedure guideline for radio-immunotherapy for B-cell lymphoma with 90Y-radiolabelled ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin).|journal=European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging|date=April 2007|volume=34|issue=4|pages=616–22|pmid=17323056}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Maloney|first=DG|title=Anti-CD20 antibody therapy for B-cell lymphomas.|journal=The New England journal of medicine|date=May 24, 2012|volume=366|issue=21|pages=2008–16|pmid=22621628}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Pembrolizumab ==== | |||
| As of 2019, ], which blocks ], programmed cell death protein 1, has been used via intravenous infusion to treat inoperable or metastatic ], metastatic ] (NSCLC) in certain situations, as a second-line treatment for ] (HNSCC), after ], and for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with refractory classic ] (cHL).<ref name=USlabel2016>{{cite web|title=Pembrolizumab label |url=https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/125514s014lbl.pdf|publisher=FDA|date=May 2017}} linked from November 2016</ref><ref name=UKlabel2016>{{cite web|title=Pembrolizumab label at eMC|url=https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/30602|publisher=UK Electronic Medicines Compendium|date=27 January 2017|access-date=4 October 2018|archive-date=13 December 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171213010050/https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/medicine/30602|url-status=dead}}</ref> It is also indicated for certain patients with ], ] and ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/125514s034lbl.pdf|title=HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION - KEYTRUDA (Pembrolizumab)|date=June 2018|website=fda.gov|access-date=27 February 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ==== Rituximab ==== | ==== Rituximab ==== | ||
| ] is a chimeric monoclonal IgG1 antibody specific for CD20, developed from its parent antibody ]. As with ibritumomab, rituximab targets CD20, making it effective in treating certain B-cell malignancies. These include aggressive and indolent lymphomas such as ] and follicular lymphoma and ]s such as B-cell ]. Although the function of CD20 is relatively unknown, CD20 may be a ] involved in B-cell activation. The antibody's mode of action is primarily through the induction of ADCC and ] Other mechanisms include apoptosis{{Clarify|reason=Vague|date=April 2016}} and cellular growth arrest. Rituximab also increases the sensitivity of cancerous B-cells to chemotherapy.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Keating GM | title = Rituximab: a review of its use in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, low-grade or follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | journal = Drugs | volume = 70 | issue = 11 | pages = 1445–76 | date = July 2010 | pmid = 20614951 | doi = 10.2165/11201110-000000000-00000 }}</ref><ref name="Plosker 2003 803–43">{{cite journal | vauthors = Plosker GL, Figgitt DP | title = Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia | journal = Drugs | volume = 63 | issue = 8 | pages = 803–43 | year = 2003 | pmid = 12662126 | doi = 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cerny T, Borisch B, Introna M, Johnson P, Rose AL | title = Mechanism of action of rituximab | journal = Anti-Cancer Drugs | volume = 13 | issue = Suppl 2 | pages = S3–10 | date = November 2002 | pmid = 12710585 | doi = 10.1097/00001813-200211002-00002 | s2cid = 25061294 }}</ref><ref name="Janeway">{{cite book | vauthors = Janeway C, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik M |author-link1 = Charles Janeway |title=Immunobiology | edition = Fifth |publisher=Garland Science |year=2001 |location=New York and London |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowTOC&rid=imm.TOC&depth=10 |isbn=978-0-8153-4101-7}}{{page needed|date=February 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Weiner GJ | title = Rituximab: mechanism of action | journal = Seminars in Hematology | volume = 47 | issue = 2 | pages = 115–23 | date = April 2010 | pmid = 20350658 | pmc = 2848172 | doi = 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2010.01.011 }}</ref> | |||
| ] is a chimeric monoclonal antibody specific for ]. CD20 is widely expressed on B-cells. Although the function of CD20 is relatively unknown it has been suggested that CD20 could play a role in ] influx across ], maintaining intracellular calcium concentration and allowing for the activation of ].<ref name=Janeway>{{cite book | last = Janeway | first = Charles | authorlink = Charles Janeway | coauthors = Paul Travers, Mark Walport, and Mark Shlomchik | title = Immunobiology; Fifth Edition | publisher = Garland Science | year = 2001 | location = New York and London| pages = | url = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowTOC&rid=imm.TOC&depth=10| doi = | isbn = 0-8153-4101-6}}</ref> The exact mode of action of rituximab is also unclear, but it has been found to have a general regulatory effect on the ] and on immune-receptor expression.<ref name=Waldmann/> Experiments involving ]s showed that treatment with anti-CD20 reduced peripheral B-cells by 98%, and peripheral ] and ] B-cells by up to 95%.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Reff | first1 = ME | last2 = Carner | first2 = K | last3 = Chambers | first3 = KS | author-separator =, | last4 = Chinn | author-name-separator= | year = 1994 | first4 = PC | last5 = Leonard | first5 = JE | last6 = Raab | first6 = R | last7 = Newman | first7 = RA | last8 = Hanna | first8 = N | last9 = Anderson | first9 = DR | title = Depletion of B cells ''in vivo'' by a chimeric mouse human monoclonal antibody to CD20 | url = | journal = Blood | volume = 83 | issue = 2| pages = 435–445 | pmid = 7506951 }}</ref> | |||
| ====Trastuzumab==== | |||
| ====Tositumomab/iodine (<sup>131</sup>I) tositumomab regimen==== | |||
| {{Excerpt|Trastuzumab}} | |||
| ] is a murine IgG2a anti-] antibody. Iodine (<sup>131</sup>I) tositumomab is covalently bound to ] 131. <sup>131</sup>I emits both ] and ], and is broken down rapidly in the body.<ref>{{cite journal | doi = 10.3121/cmr.3.3.157 | last1 = Rao | first1 = AV | last2 = Akabani | first2 = G | last3 = Rizzieri | first3 = DA. | author-separator =, | author-name-separator= | year = 2005 | title = Radioimmunotherapy for Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma | url = | journal = Clin Med Res | volume = 3 | issue = 3| pages = 157–165 | pmid = 16160070 | pmc = 1237157 }}</ref> Clinical trials have established the efficacy of a sequential application of tositumomab and iodine (<sup>131</sup>I) tositumomab in patients with ]d ].<ref>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1056/NEJMoa041511 | last1 = Kaminski | first1 = MS | last2 = Tuck | first2 = M | last3 = Estes | first3 = J | author-separator =, | last4 = Kolstad | author-name-separator= | first4 = A| year = 2005 | last5 = Ross | first5 = CW | last6 = Zasadny | first6 = K | last7 = Regan | first7 = D | last8 = Kison | first8 = P | last9 = Fisher | first9 = S | title = 131I-tositumomab therapy as initial treatment for follicular lymphoma | url = | journal = N Engl J Med | volume = 352 | issue = 5| pages = 441–449 | pmid = 15689582 }}</ref> | |||
| == {{anchor|Immune checkpoint blockade}} Immune checkpoint antibody therapy or immune checkpoint blockade == <!--"Checkpoint inhibitor" redirects here--> | |||
| ==== Trastuzumab ==== | |||
| {{Main|Immune checkpoint|Immunotherapy}} | |||
| ] and ]s of the ] ] binding region (]) bound the ] protein.]] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] is a monoclonal IgG1 humanized antibody specific for the ] 2 protein (]). It received FDA-approval in 1998, and is clinically used for the treatment of ]. The use of Trastuzumab is restricted to patients whose tumours over-express HER-2, as assessed by ] (IHC) and either chromogenic or ] ] ] (]), as well as numerous ]-based methodologies. | |||
| ] | |||
| ]s affect the immune system function. Immune checkpoints can be stimulatory or inhibitory. Tumors can use these checkpoints to protect themselves from immune system attacks. Checkpoint therapies approved as of 2012 block inhibitory checkpoint receptors. Blockade of negative feedback signaling to immune cells thus results in an enhanced immune response against tumors.<ref name="pmid22437870">{{cite journal | vauthors = Pardoll DM | title = The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy | journal = Nature Reviews. Cancer | volume = 12 | issue = 4 | pages = 252–64 | date = March 2012 | pmid = 22437870 | pmc = 4856023 | doi = 10.1038/nrc3239 }}</ref> As of 2020, immune checkpoint blockade therapies have varied effectiveness. In ] and natural killer ], response rates are high, at 50–60%. Response rates are quite low for breast and prostate cancers, however.<ref>{{Cite journal| vauthors = Ganesan S, Mehnert J |date=2020-03-09|title=Biomarkers for Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockade |journal=Annual Review of Cancer Biology |volume=4|issue=1|pages=331–351|doi=10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030419-033604 |doi-access=free}}</ref> A major challenge are the large variations in responses to immunocheckpoint inhibitors, some patients showing spectacular clinical responses while no positive effects are seen in others. A plethora of possible reasons for the absence of efficacy in many patients have been proposed, but the biomedical community has still to begin to find consensus in this respect. For instance, a recent paper documented that infection with ] would negatively influence the effects of immunocheckpoint inhibitors in ].,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Magahis PT, Maron SB, Cowzer D, King S, Schattner M, Janjigian Y, Faleck D, Laszkowska M | title = Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection status on outcomes among patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. | journal = J Immunother Cancer | date = October 2023 | volume = 11 | issue = 10 | pages = e007699 | pmid = 37899129| pmc = 10619027 | doi = 10.1136/jitc-2023-007699 | doi-access = free }}</ref> but this notion was quickly challenged by others.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Yu B, Peppelenbosch M, Fuhler G| title = Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection status on outcomes among patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.| journal = J Immunother Cancer | date = January 2024 | volume = 12| issue = 1| pages = e008422| pmid = 38242721| pmc = 10806497 | doi = 10.1136/jitc-2023-008422 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| One ligand-receptor interaction under investigation is the interaction between the transmembrane ] protein (PDCD1, PD-1; also known as CD279) and its ligand, ] (PD-L1, CD274). PD-L1 on the cell surface binds to PD1 on an immune cell surface, which inhibits immune cell activity. Among PD-L1 functions is a key regulatory role on T cell activities. It appears that (cancer-mediated) upregulation of PD-L1 on the cell surface may inhibit T cells that might otherwise attack. PD-L1 on cancer cells also inhibits FAS- and interferon-dependent apoptosis, protecting cells from cytotoxic molecules produced by T cells. Antibodies that bind to either PD-1 or PD-L1 and therefore block the interaction may allow the T-cells to attack the tumor.<ref name="ReferenceA">{{cite journal | vauthors = Granier C, De Guillebon E, Blanc C, Roussel H, Badoual C, Colin E, Saldmann A, Gey A, Oudard S, Tartour E | title = Mechanisms of action and rationale for the use of checkpoint inhibitors in cancer | journal = ESMO Open | volume = 2 | issue = 2 | pages = e000213 |year = 2017 | pmid = 28761757 | pmc = 5518304 | doi = 10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000213 }}</ref> | |||
| HER-2 is a member of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family of transmembrane ], and is normally involved in regulation of ] and ].<ref>{{cite journal | pmid = 10376526 | author-separator =, | last1 = Jones | author-name-separator= | first1 = FE| doi=10.1038/sj.onc.1202698 | last2 = Stern | first2 = DF | title = Expression of dominant-negative ErbB2 in the mammary gland of transgenic mice reveals a role in lobuloalveolar development and lactation. | journal = Oncogene | volume=18 | issue=23 | year=1999 | month=June | pages=3481–90}}</ref> Amplification or overexpression of HER-2 is present in 25-30% of breast carcinomas and has been associated with aggressive tumour phenotype, poor ], non-responsiveness to ] and reduced sensitivity to conventional chemotherapeutic agents.<ref>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1126/science.2470152 | last1 = Slamon | first1 = DJ | last2 = Godolphin | first2 = W | last3 = Jones | first3 = LA | author-separator =, | last4 = Holt | author-name-separator= | first4 = JA| year = 1989 | last5 = Wong | first5 = SG | last6 = Keith | first6 = DE | last7 = Levin | first7 = WJ | last8 = Stuart | first8 = SG | last9 = Udove | first9 = J | title = Studies of the HER-2/neu proto oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer | url = | journal = Science | volume = 244 | issue = 4905| pages = 707–712 | pmid = 2470152 }}</ref> | |||
| === CTLA-4 blockade === | |||
| ==Interferon== | |||
| ]s are proteins produced by the immune system. There are three groups of ]s (IFNs): ] (IFNα and IFNβ), ] (IFNγ) and the relatively newly discovered ] (IFNλ). IFNα has been approved for use in ], ]-related ], ], ] and ]. Type I and II IFNs have been researched extensively and although both types promote the anti-tumor effects of the immune system, only type I IFNs have been shown to be clinically effective in cancer treatment. IFNλ has been tested for its anti-tumor effects in ]s, and shows promise.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Dunn|first=GP|coauthors=Koebel, CM; Schreiber, RD|title=Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting.|journal=Nature reviews. Immunology|date=November 2006|volume=6|issue=11|pages=836–48|pmid=17063185}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last=Lasfar|first=A|coauthors=Abushahba, W; Balan, M; Cohen-Solal, KA|title=Interferon lambda: a new sword in cancer immunotherapy.|journal=Clinical & developmental immunology|year=2011|volume=2011|pages=349575|pmid=22190970}}</ref> | |||
| The first checkpoint antibody approved by the FDA was ], approved in 2011 to treat melanoma.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cameron F, Whiteside G, Perry C | title = Ipilimumab: first global approval | journal = Drugs | volume = 71 | issue = 8 | pages = 1093–104 | date = May 2011 | pmid = 21668044 | doi = 10.2165/11594010-000000000-00000 }}</ref> It blocks the immune checkpoint molecule ]. As of 2012, clinical trials have also shown some benefits of anti-CTLA-4 therapy on lung cancer or ], specifically in combination with other drugs.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lynch TJ, Bondarenko I, Luft A, Serwatowski P, Barlesi F, Chacko R, Sebastian M, Neal J, Lu H, Cuillerot JM, Reck M | title = Ipilimumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line treatment in stage IIIB/IV non-small-cell lung cancer: results from a randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase II study | journal = Journal of Clinical Oncology | volume = 30 | issue = 17 | pages = 2046–54 | date = June 2012 | pmid = 22547592 | doi = 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.4032 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Le DT, Lutz E, Uram JN, Sugar EA, Onners B, Solt S, Zheng L, Diaz LA, Donehower RC, Jaffee EM, Laheru DA | title = Evaluation of ipilimumab in combination with allogeneic pancreatic tumor cells transfected with a GM-CSF gene in previously treated pancreatic cancer | journal = Journal of Immunotherapy | volume = 36 | issue = 7 | pages = 382–89 | date = September 2013 | pmid = 23924790 | pmc = 3779664 | doi = 10.1097/CJI.0b013e31829fb7a2 }}</ref> In on-going trials the combination of CTLA-4 blockade with PD-1 or ]s is tested on different types of cancer.<ref>{{ClinicalTrialsGov|NCT01928394|A Study of Nivolumab by Itself or Nivolumab Combined With Ipilimumab in Patients With Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors}}</ref> | |||
| ==Advances in immunotherapy== | |||
| The development and testing of second generation immunotherapies are already under way. While antibodies targeted to disease-causing antigens can be effective under certain circumstances, in many cases, their efficacy may be limited by other factors. In the case of cancer tumors, the microenvironment is ], allowing even those tumors that present unusual antigens to survive and flourish in spite of the immune response generated by the cancer patient, against his or her own tumor tissue. Certain members of a group of molecules known as ]s, such as ] also play a key role in modulating the immune response, and have been tried in conjunction with antibodies in order to generate an even more devastating immune response against the tumor. While the therapeutic administration of such cytokines may cause systemic inflammation, resulting in serious ]s and ], a new generation of ] molecules consisting of an immune-stimulatory cytokine attached to an antibody that targets the cytokine's activity to a specific environment such as a tumor, are able to generate a very effective yet localized immune response against the tumor tissue, destroying the cancer-causing cells without the unwanted side-effects. A different type of chimeric molecule is an ]. | |||
| However, as of 2015 it is known that patients treated with checkpoint blockade (specifically CTLA-4 blocking antibodies), or a combination of check-point blocking antibodies, are at high risk of having immune-related adverse events such as dermatologic, gastrointestinal, endocrine, or hepatic ] reactions.<ref name=":4">{{cite journal | vauthors = Postow MA, Callahan MK, Wolchok JD | title = Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy | journal = Journal of Clinical Oncology | volume = 33 | issue = 17 | pages = 1974–82 | date = June 2015 | pmid = 25605845 | pmc = 4980573 | doi = 10.1200/JCO.2014.59.4358 }}</ref> These are most likely due to the breadth of the induced T-cell activation when anti-CTLA-4 antibodies are administered by injection in the bloodstream. | |||
| The targeted delivery of cytokines by anti-tumor antibodies is one example of using antibodies to deliver payloads rather than simply relying on the antibody to trigger an immune response against the target cell. | |||
| Another strategy is to deliver a lethal radioactive dose directly to the target cell, which has been utilized in the case of the ] therapeutic. | |||
| A third strategy is to deliver a lethal chemical dose to the target, as used in the ] therapeutic (an ]). Engineering the antibody-payload pair in such a way that they separate after entry into a cell by ] can potentially increase the efficacy of the payload. One strategy to accomplish this is the use of a ] which could be severed by the ] conditions in the cellular interior. However, recent evidence suggests that the actual intracellular trafficking of the antibody-payload after endocytosis is such to make this strategy not generally applicable. Other potentially useful linkage types include ] and ] linkages.<ref>{{cite journal | |||
| |author=Austin C.D. | |||
| |title=Oxidizing potential of endosomes and lysosomes limits intracellular cleavage of disulfide-based antibody–drug conjugates | |||
| |journal=Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A | |||
| |year=2005 | |||
| |volume=102 | |||
| |issue=50 | |||
| |pages= 17987–17992 | |||
| |doi=10.1073/pnas.0509035102 | |||
| |pmid=16322102 | |||
| |pmc=1298180 | |||
| |author-separator=, | |||
| |display-authors=1 | |||
| |last2=Wen | |||
| |first2=X | |||
| |last3=Gazzard | |||
| |first3=L | |||
| |last4=Nelson | |||
| |first4=C | |||
| |last5=Scheller | |||
| |first5=RH | |||
| |last6=Scales | |||
| |first6=SJ | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| A 2024 cohort study of ICI use during pregnancy showed no overreporting of specific adverse effects on pregnancy, fetal, and/or newborn outcomes, interestingly.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gougis P, Hamy AS, Jochum F, Bihan K, Carbonnel M, Salem JE, Dumas E, Kabirian R, Grandal B, Barraud S, Coussy F, Hotton J, Savarino R, Marabelle A, Cadranel J, Spano JP, Laas E, Reyal F, Abbar B | title = Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Use During Pregnancy and Outcomes in Pregnant Individuals and Newborns | journal = JAMA Network Open | volume = 7 | issue = 4 | pages = e245625 | date = April 2024 | pmid = 38630478 | pmc = 11024778 | doi = 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5625 }}</ref> | |||
| Anti-CD47 antibodies, which block the protein CD47 from telling the cancer's host human immune system not to attack it, have been shown to eliminate or inhibit the growth of a wide range of cancers and tumors because CD47 is present on all known cancer cells (it is also present on many healthy cells of the body). After the cancer cells have been engulfed by macrophages, the host immune system's CD8+ T Cells become mobilized against the cancer and attack it on their own in addition to the macrophages, producing a personalized attack on virtually any form of cancer. When the immunotherapy technique was tested on human tumors transplanted in to mice, it stopped the spread of cancer 90 percent of the time and often eliminated all signs of the cancer. Phase 1 human trials are set to begin in 2014.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://med.stanford.edu/ism/2013/may/cd47.html |title=Anti-CD47 antibody may offer new route to successful cancer vaccination - Office of Communications & Public Affairs - Stanford University School of Medicine |publisher=Med.stanford.edu |date=2013-05-20 |accessdate=2013-08-25}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last=Blaustein |first=Michael |url=http://www.nypost.com/p/news/national/testing_starts_creates_homegrown_4jSHWpWFBEkczPTFque7VM |title=New wonder drug matches and kills all kinds of cancer — human testing starts 2014 |publisher=NYPOST.com |date=2013-07-11 |accessdate=2013-08-25}}</ref> | |||
| Using a mouse model of bladder cancer, researchers have found that a local injection of a low dose anti-CTLA-4 in the tumour area had the same tumour inhibiting capacity as when the antibody was delivered in the blood.<ref name=":3">{{cite journal | vauthors = van Hooren L, Sandin LC, Moskalev I, Ellmark P, Dimberg A, Black P, Tötterman TH, Mangsbo SM | title = Local checkpoint inhibition of CTLA-4 as a monotherapy or in combination with anti-PD1 prevents the growth of murine bladder cancer | journal = European Journal of Immunology | volume = 47 | issue = 2 | pages = 385–93 | date = February 2017 | pmid = 27873300 | doi = 10.1002/eji.201646583 | s2cid = 2463514 | doi-access = free }}</ref> At the same time the levels of circulating antibodies were lower, suggesting that local administration of the anti-CTLA-4 therapy might result in fewer adverse events.<ref name=":3" /> | |||
| === Immune checkpoint blockade === | |||
| <!-- initial text copied from PD-L1#Cancer --> | |||
| It appears that upregulation of ] may allow cancers to evade the host immune system. PD-L1 on the tumor cell surface inhibits T cells that might otherwise attack the tumor cell. | |||
| An analysis of 196 tumor specimens from patients with ] found that high tumor expression of PD-L1 was associated with increased tumor aggressiveness and a 4.5-fold increased risk of death.<ref name="pmid15569934">{{cite journal | author = Thompson RH, Gillett MD, Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Dong H, Webster WS, Krejci KG, Lobo JR, Sengupta S, Chen L, Zincke H, Blute ML, Strome SE, Leibovich BC, Kwon ED | title = Costimulatory B7-H1 in renal cell carcinoma patients: Indicator of tumor aggressiveness and potential therapeutic target | journal = Proc Natl Acad Sci USA | volume = 101 | issue = 49 | pages = 17174–9 | year = 2004 | month = December | pmid = 15569934 | pmc = 534606 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.0406351101| url = }}</ref> ] patients with higher expression of PD-L1 had a significantly poorer prognosis than those with lower expression. PD-L1 expression correlated inversely with intraepithelial CD8+ T-lymphocyte count, suggesting that PD-L1 on tumor cells may suppress antitumor CD8+ T cells.<ref name="pmid17360651">{{cite journal | author = Hamanishi J, Mandai M, Iwasaki M, Okazaki T, Tanaka Y, Yamaguchi K, Higuchi T, Yagi H, Takakura K, Minato N, Honjo T, Fujii S. | |||
| | title = Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes are prognostic factors of human ovarian cancer | journal = Proc Natl Acad Sci USA | volume = 104 | issue = 9 | pages = 3360–5 | year = 2007 | month = February | pmid = 17360651 | pmc = 1805580 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.0611533104| url = }}</ref> This has encouraged development of ]s (a type of ]) which {{as of|2013|4}} have started clinical trials.<ref></ref> | |||
| === PD-1 inhibitors === | |||
| Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (]) antibodies were the first of this class of immunotherapeutics to achieve US FDA approval.<ref name=Pardoll2012>{{cite journal |title=The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. |author=Pardoll |year=2012 |pmid=22437870 |doi=10.1038/nrc3239 |volume=12 |issue=4 |journal=Nat Rev Cancer |pages=252–64}}</ref> ] was approved by US FDA for melanoma in 2011. | |||
| {{main|PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors}} | |||
| Initial clinical trial results with IgG4 PD1 antibody ] were published in 2010.<ref name="pmid22437870" /> It was approved in 2014. Nivolumab is approved to treat melanoma, lung cancer, kidney cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, and ].<ref name=":2">{{Cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2016/05/19/business/food-and-drug-administration-immunotherapy-bladder-cancer.html|title=F.D.A. Approves an Immunotherapy Drug for Bladder Cancer|access-date=21 May 2016| vauthors = Pollack A |date=18 May 2016|newspaper=The New York Times|issn=0362-4331}}</ref> A 2016 clinical trial for non-small cell lung cancer failed to meet its primary endpoint for treatment in the first-line setting, but is FDA-approved in subsequent lines of therapy.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/bristol-myers-opdivo-failed-to-meet-endpoint-in-key-lung-cancer-study-1470400926|title=Bristol Myers: Opdivo Failed to Meet Endpoint in Key Lung-Cancer Study| vauthors = Steele A |date=5 August 2016|newspaper=The Wall Street Journal|issn=0099-9660|access-date=5 August 2016}}</ref> | |||
| ] (Keytruda) is another PD1 inhibitor that was approved by the FDA in 2014. Pembrolizumab is approved to treat melanoma and lung cancer.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
| ==Natural products== | |||
| {{Main|Medicinal mushrooms}} | |||
| Some types of natural products have shown promise to stimulate the immune system. Research suggests that mushrooms like ] and '']'', (often mistakenly called ''Agaricus blazei'') may be able to stimulate the immune system. Research has shown that '']'' may be a potent stimulator of ].<ref name="Studies on the Effect of Lentinan on Human Immune System. II. In Vivo Effect on NK Activity, MLR | |||
| Induced Killer Activity and PHA Induced Blastic Response of Lymphocytes in Cancer Patients."> | |||
| {{Cite journal | |||
| | last1 = Amino | |||
| | first1 = M | |||
| | title = Studies On the Effect of Lentinan on Human Immune System. II. In Vivo Effect on NK Activity, MLR Induced Killer Activity and PHA Induced Blastic Response of Lymphocytes in Cancer Patients | |||
| | journal = Gan to Kagaku Ryoho | |||
| | volume = 10 | |||
| | pages = 2000–6 | |||
| | publisher = | |||
| | location = | |||
| | year = 1983 | |||
| | url = | |||
| | doi = | |||
| | id = | |||
| | accessdate = | |||
| | pmid = 6225393 | |||
| | last2 = Noguchi | |||
| | first2 = R | |||
| | last3 = Yata | |||
| | first3 = J | |||
| | last4 = Matsumura | |||
| | first4 = J | |||
| | last5 = Hirayama | |||
| | first5 = R | |||
| | last6 = Abe | |||
| | first6 = O | |||
| | last7 = Enomoto | |||
| | first7 = K | |||
| | last8 = Asato | |||
| | first8 = Y | |||
| | issue = 9 | |||
| | postscript = <!--None--> }}</ref> | |||
| '']'' is rich in proteoglucans and ], which are potent stimulators of ].<ref name="b-1,3-glucan reduces growth of Mycobacterium | |||
| bovis in macrophage cultures."> | |||
| {{Cite journal | |||
| | last1 = Hetland | |||
| | first1 = G | |||
| | title = b-1,3-glucan reduces growth of Mycobacterium bovis in macrophage cultures | |||
| | journal = FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol | |||
| | volume = 33 | |||
| | pages = 41–45 | |||
| | publisher = | |||
| | location = | |||
| | year = 2002 | |||
| | url = | |||
| | doi = 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2002.tb00570.x | |||
| | id = | |||
| | accessdate = | |||
| | pmid = 11985967 | |||
| | last2 = Sandven | |||
| | first2 = P | |||
| | issue = 1 | |||
| | postscript = <!--None--> }}</ref> | |||
| Antibody ] is a PD-1 inhibitor (designed to not bind Fc gamma receptor I) in early clinical trials.<ref>{{cite press release|url=https://globenewswire.com/news-release/2016/06/05/846118/0/en/BeiGene-Presents-Initial-Clinical-Data-on-PD-1-Antibody-BGB-A317-at-the-2016-American-Society-of-Clinical-Oncology-Annual-Meeting.html|title=BeiGene Presents Initial Clinical Data on PD-1 Antibody BGB-A317 at the 2016 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting|author=BeiGene, Ltd.|year=2016|publisher=Globe Newswire}}</ref> | |||
| Research on the compounds in ] most responsible for up-regulating the immune system and providing an anti-cancer effect, are a diverse collection of ] compounds, particularly ]. Beta-glucans are known as "biological response modifiers", and their ability to activate the immune system is well documented. Specifically, beta-glucans stimulate the ] branch of the immune system. Research has shown beta-glucans have the ability to stimulate ], ], ], and immune system ]. The mechanisms in which beta-glucans stimulate the immune system is only partially understood. One mechanism in which beta-glucans are able to activate the immune system, is by interacting with the ] (]) ] on immune cells.<ref name=pmid15084502>{{cite pmid|15084502}} (review)</ref> | |||
| === PD-L1 inhibitors === | |||
| Highly purified compounds isolated from medicinal mushrooms such as ] (isolated from ]), and ], (isolated from '']''), have become incorporated into the health care system of a few countries, such as ].<ref name="psk"> | |||
| {{main|PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors}} | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| In May 2016, PD-L1 inhibitor ]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.roche.com/investors/updates/inv-update-2016-04-11.htm|title=FDA grants priority review for Roche's cancer immunotherapy atezolizumab in specific type of lung cancer|last1=Roche}}</ref> was approved for treating bladder cancer. | |||
| | title = Coriolus Versicolor | |||
| | url = http://www.cancer.org/docroot/ETO/content/ETO_5_3X_Coriolous_Versicolor.asp | |||
| | postscript = <!--None--> | |||
| }}</ref> Japan's ] approved the use of ] in the 1980s, to stimulate the immune systems of patients undergoing chemotherapy. In ], a pharmaceutical based on a mixture of several mycological extracts including lentinan and Polysaccharide-K is sold commercially as ]. | |||
| Anti-PD-L1 antibodies currently in development include ]<ref>{{cite web|last1=Merck Group|title=Immuno-oncology Avelumab|url=http://www.merckgroup.com/en/innovation/research_activities/immuno_oncology/immuno_oncology.html}}</ref> and ],<ref>{{cite web|last1=Cure today|title=Durvalumab continues to progress in treatment of advanced bladder cancer.|date=April 2016 |url=http://www.curetoday.com/articles/durvalumab-continues-to-progress-in-treatment-of-advanced-bladder-cancer}}</ref> in addition to an inhibitory affimer.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Avacta Life Sciences|title=Affimer biotherapeutics target cancer's off-switch with PD-L1 inhibitor|url=https://www.avactalifesciences.com/blogs/affimer-biotherapeutics-target-cancer-s-switch-pd-l1-inhibitor|access-date=16 May 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160806162015/https://www.avactalifesciences.com/blogs/affimer-biotherapeutics-target-cancer-s-switch-pd-l1-inhibitor|archive-date=6 August 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| ==Public awareness== | |||
| Starting with the FDA approval in 2010 of the therapeutic vaccine sipuleucel-T (Provenge) for prostate cancer and, in 2011, of ipilimumab (Yervoy) for melanoma, public awareness of cancer immunotherapy has increased thanks to a growing number of mainstream news articles covering this field of cancer therapy.<ref>http://www.nytimes.com/2013/05/16/business/melanoma-treatment-harnesses-immune-system-to-combat-cancer-cells.html</ref><ref>{{cite web|last=Winslow |first=Ron |url=http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323398204578485401089823868.html |title=New Cancer Drugs Harness Power of Immune System - WSJ.com |publisher=Online.wsj.com |date=2013-05-15 |accessdate=2013-08-25}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cnn.com/2013/05/16/health/cancer-research/index.html |title=A workout a day may keep cancer away |publisher=CNN.com |date= |accessdate=2013-08-25}}</ref><ref>http://www.nytimes.com/2012/12/10/health/a-breakthrough-against-leukemia-using-altered-t-cells.html?pagewanted=all</ref> In light of these developments, in 2013 the Cancer Research Institute, a nonprofit organization dedicated to cancer immunotherapy, proclaimed June Cancer Immunotherapy Awareness Month.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cancerresearch.org/news-publications/news-at-cri/2013/may/cancer-research-institute-announces-june-cancer-immunotherapy-awareness-month |title=News at CRI - CRI |publisher=Cancerresearch.org |date=2013-05-07 |accessdate=2013-08-25}}</ref> The goal of this month is to raise public awareness of the potential for immunotherapy to transform cancer treatment as well as the need for the public to support research to bring immunotherapies to more cancer patients sooner. | |||
| == |
=== CISH === | ||
| {{Excerpt|Adoptive cell transfer#Intrinsic (Intracellular) checkpoint blockade}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| === Combinations === | |||
| Many cancer patients do not respond to immune checkpoint blockade. Response rate may be improved by combining that with additional therapies, including those that stimulate T cell infiltration. For example, targeted therapies such as radiotherapy, vasculature targeting agents, and immunogenic chemotherapy<ref>{{cite journal |vauthors=Pfirschke C, Engblom C, Rickelt S, Cortez-Retamozo V, Garris C, Pucci F, Yamazaki T, Poirier-Colame V, Newton A, Redouane Y, Lin YJ, Wojtkiewicz G, Iwamoto Y, Mino-Kenudson M, Huynh TG, Hynes RO, Freeman GJ, Kroemer G, Zitvogel L, Weissleder R, Pittet MJ |date=February 2016 |title=Immunogenic Chemotherapy Sensitizes Tumors to Checkpoint Blockade Therapy |journal=Immunity |volume=44 |issue=2 |pages=343–54 |doi=10.1016/j.immuni.2015.11.024 |pmc=4758865 |pmid=26872698}}</ref> can improve immune checkpoint blockade response in animal models. | |||
| Combining immunotherapies such as PD1 and CTLA4 inhibitors can create to durable responses.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ott PA, Hodi FS, Kaufman HL, Wigginton JM, Wolchok JD | title = Combination immunotherapy: a road map | journal = Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer | volume = 5 | pages = 16 | year = 2017 | pmid = 28239469 | pmc = 5319100 | doi = 10.1186/s40425-017-0218-5 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mahoney KM, Rennert PD, Freeman GJ | title = Combination cancer immunotherapy and new immunomodulatory targets | journal = Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery | volume = 14 | issue = 8 | pages = 561–84 | date = August 2015 | pmid = 26228759 | doi = 10.1038/nrd4591 | s2cid = 2220735 }}</ref> | |||
| ] enhances the immunostimulating response and has synergistic effects for metastatic cancer treatment.<ref name="hindawi9251375">{{cite journal | vauthors = Mehta A, Oklu R, Sheth RA | title = Thermal Ablative Therapies and Immune Checkpoint Modulation: Can Locoregional Approaches Effect a Systemic Response? | journal = Gastroenterology Research and Practice | volume = 2016 | pages = 9251375 | year = 2015 | pmid = 27051417 | pmc = 4802022 | doi = 10.1155/2016/9251375 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| Combining checkpoint immunotherapies with pharmaceutical agents has the potential to improve response, and as of 2018 were a target of clinical investigation.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Tang J, Shalabi A, Hubbard-Lucey VM | title = Comprehensive analysis of the clinical immuno-oncology landscape | journal = Annals of Oncology | volume = 29 | issue = 1 | pages = 84–91 | date = January 2018 | pmid = 29228097 | doi = 10.1093/annonc/mdx755 | doi-access = free }}</ref> Immunostimulatory drugs such as ] inhibitors and ] agonists have been effective.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Perry CJ, Muñoz-Rojas AR, Meeth KM, Kellman LN, Amezquita RA, Thakral D, Du VY, Wang JX, Damsky W, Kuhlmann AL, Sher JW, Bosenberg M, Miller-Jensen K, Kaech SM | title = Myeloid-targeted immunotherapies act in synergy to induce inflammation and antitumor immunity | journal = The Journal of Experimental Medicine | volume = 215 | issue = 3 | pages = 877–93 | date = March 2018 | pmid = 29436395 | pmc = 5839759 | doi = 10.1084/jem.20171435 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal| vauthors = Rodell CB, Arlauckas SP, Cuccarese MF, Garris CS, Li R, Ahmed MS, Kohler RH, Pittet MJ, Weissleder R |date=21 May 2018|title=TLR7/8-agonist-loaded nanoparticles promote the polarization of tumour-associated macrophages to enhance cancer immunotherapy |journal=Nature Biomedical Engineering |volume=2|issue=8|pages=578–588|doi=10.1038/s41551-018-0236-8 |pmid=31015631|pmc=6192054|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| Two independent 2024 clinical trials reported that combinations of ] with anti–PD-1 immunotherapy could improve efficacy. A phase 2 trial investigated the combination as a first-line therapy for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Administration of itacitinib after treatment with pembrolizumab improved therapeutic response. A separate phase 1/2 trial with patients with relapsed/refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma combined ] and ], yielding improved clinical efficacy in patients who had previously failed checkpoint blockade immunotherapy.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Zak J, Pratumchai I, Marro BS, Marquardt KL, Zavareh RB, Lairson LL, Oldstone MB, Varner JA, Hegerova L, Cao Q, Farooq U, Kenkre VP, Bachanova V, Teijaro JR | title = JAK inhibition enhances checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma | journal = Science | volume = 384 | issue = 6702 | pages = eade8520 | date = June 2024 | pmid = 38900864 | doi = 10.1126/science.ade8520 | pmc = 11283877 | bibcode = 2024Sci...384e8520Z }}</ref> | |||
| ==Cytokine therapy== | |||
| ]s are proteins produced by many types of cells present within a tumor. They can modulate immune responses. The tumor often employs them to allow it to grow and reduce the immune response. These immune-modulating effects allow them to be used as drugs to provoke an immune response. Two commonly used cytokines are interferons and interleukins.<ref name="pmid14708024">{{cite journal | vauthors = Dranoff G | title = Cytokines in cancer pathogenesis and cancer therapy | journal = Nature Reviews. Cancer | volume = 4 | issue = 1 | pages = 11–22 | date = January 2004 | pmid = 14708024 | doi = 10.1038/nrc1252 | s2cid = 42092046 }}</ref> | |||
| ] and ]-α are cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behavior of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as passive cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of ], AIDS-related ], ], ] and ]. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of ] and ].<ref>{{Cite web | url=https://ibiotherapy.com/immunotherapy/| title=Immunotherapy For Cancer | accessdate=2023-05-12}}</ref> | |||
| ===Interferon=== | |||
| ]s are produced by the immune system. They are usually involved in anti-viral response, but also have use for cancer. They fall in three groups: ] (IFNα and IFNβ), ] (IFNγ) and ] (IFNλ). IFNα has been approved for use in ], AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, ] and melanoma. Type I and II IFNs have been researched extensively and although both types promote anti-tumor immune system effects, only type I IFNs have been shown to be clinically effective. IFNλ shows promise for its anti-tumor effects in ]s.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Dunn GP, Koebel CM, Schreiber RD | title = Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting | journal = Nature Reviews. Immunology | volume = 6 | issue = 11 | pages = 836–48 | date = November 2006 | pmid = 17063185 | doi = 10.1038/nri1961 | s2cid = 223082 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lasfar A, Abushahba W, Balan M, Cohen-Solal KA | title = Interferon lambda: a new sword in cancer immunotherapy | journal = Clinical & Developmental Immunology | volume = 2011 | pages = 349575 | year = 2011 | pmid = 22190970 | pmc = 3235441 | doi = 10.1155/2011/349575 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| Unlike type I IFNs, ] is not approved yet for the treatment of any cancer. However, improved survival was observed when ] was administered to patients with ] and ] cancers. The most promising result was achieved in patients with stage 2 and 3 of ]. The '']'' study of IFN-gamma in cancer cells is more extensive and results indicate anti-proliferative activity of IFN-gamma leading to the growth inhibition or cell death, generally induced by ] but sometimes by ].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Razaghi A, Owens L, Heimann K | title = Review of the recombinant human interferon gamma as an immunotherapeutic: Impacts of production platforms and glycosylation | journal = Journal of Biotechnology | volume = 240 | pages = 48–60 | date = December 2016 | pmid = 27794496 | doi = 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.10.022 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Interleukin=== | |||
| ]s have an array of immune system effects. ] is used in the treatment of ] and ]. In normal physiology it promotes both effector T cells and T-regulatory cells, but its exact mechanism of action is unknown.<ref name="pmid14708024" /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Coventry BJ, Ashdown ML | title = The 20th anniversary of interleukin-2 therapy: bimodal role explaining longstanding random induction of complete clinical responses | journal = Cancer Management and Research | volume = 4 | pages = 215–21 | year = 2012 | pmid = 22904643 | pmc = 3421468 | doi = 10.2147/cmar.s33979 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| ==Genetic pre-treatment testing for therapeutic significance== | |||
| Because of the high cost of many of immunotherapy medications and the reluctance of medical insurance companies to prepay for their prescriptions various test methods have been proposed, to attempt to forecast the effectiveness of these medications. In some cases the FDA has approved genetic tests for medication specific to certain genetic markers. For example, the FDA approved ]-associated medication for metastatic melanoma, to be administered to patients after testing for the BRAF genetic mutation.<ref>{{cite web | url = https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm611981.htm | title = FDA approves Encorafenib and Binimetinib in combination for unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF mutations | date = 27 June 2018 | publisher = U.S. Food and Drug Administration }}</ref> | |||
| As of 2018, the detection of ] protein seemed to be an indication of cancer susceptible to several immunotherapy medications, but research found that both the lack of this protein or its inclusion in the cancerous tissue was inconclusive, due to the little-understood varying quantities of the protein during different times and locations within the infected cells and tissue.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cancergenetics.com/cancer-genetics-offers-the-fda-approved-dako-pd-l1-ihc-22c3-pharmdx-companion-diagnostic-test-for-keytruda/|title=Cancer Genetics offers the FDA-approved DAKO PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx companion diagnostic test for KEYTRUDA®|work=Cancer Genetics Inc. |date=3 February 2016}}</ref><ref name="pmid29426340">{{cite journal | vauthors = Udall M, Rizzo M, Kenny J, Doherty J, Dahm S, Robbins P, Faulkner E | title = PD-L1 diagnostic tests: a systematic literature review of scoring algorithms and test-validation metrics | journal = Diagnostic Pathology | volume = 13 | issue = 1 | pages = 12 | date = February 2018 | pmid = 29426340 | pmc = 5807740 | doi = 10.1186/s13000-018-0689-9 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name="pmid29688334">{{cite journal | vauthors = Dacic S | title = Time is up for PD-L1 testing standardization in lung cancer | journal = Annals of Oncology | volume = 29 | issue = 4 | pages = 791–792 | date = April 2018 | pmid = 29688334 | doi = 10.1093/annonc/mdy069 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| In 2018, some genetic indications such as ] (TMB, the number of mutations within a targeted genetic region in the cancerous cell's DNA), and ] (MSI, the quantity of impaired DNA mismatch leading to probable mutations), have been approved by the FDA as good indicators for the probability of effective treatment of immunotherapy medication for certain cancers, but research is still in progress.<ref name="pmid28835386">{{cite journal | vauthors = Goodman AM, Kato S, Bazhenova L, Patel SP, Frampton GM, Miller V, Stephens PJ, Daniels GA, Kurzrock R | title = Tumor Mutational Burden as an Independent Predictor of Response to Immunotherapy in Diverse Cancers | journal = Molecular Cancer Therapeutics | volume = 16 | issue = 11 | pages = 2598–2608 | date = November 2017 | pmid = 28835386 | pmc = 5670009 | doi = 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0386 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.ascopost.com/News/59015 | title = FDA Accepts sBLA for First-Line Nivolumab Plus Low-Dose Ipilimumab in NSCLC With Tumor Mutational Burden ≥ 10 mut/mb | date = 7 February 2018 | publisher = ] | work = ASCO Post }}</ref> As of 2020, the patient prioritization for immunotherapy based on TMB was still highly controversial.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Liu D, Schilling B, Liu D, Sucker A, Livingstone E, Jerby-Arnon L, Zimmer L, Gutzmer R, Satzger I, Loquai C, Grabbe S, Vokes N, Margolis CA, Conway J, He MX, Elmarakeby H, Dietlein F, Miao D, Tracy A, Gogas H, Goldinger SM, Utikal J, Blank CU, Rauschenberg R, von Bubnoff D, Krackhardt A, Weide B, Haferkamp S, Kiecker F, Izar B, Garraway L, Regev A, Flaherty K, Paschen A, Van Allen EM, Schadendorf D | title = Integrative molecular and clinical modeling of clinical outcomes to PD1 blockade in patients with metastatic melanoma | journal = Nature Medicine | volume = 25 | issue = 12 | pages = 1916–1927 | date = December 2019 | pmid = 31792460 | pmc = 6898788 | doi = 10.1038/s41591-019-0654-5 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Motzer RJ, Robbins PB, Powles T, Albiges L, Haanen JB, Larkin J, Mu XJ, Ching KA, Uemura M, Pal SK, Alekseev B, Gravis G, Campbell MT, Penkov K, Lee JL, Hariharan S, Wang X, Zhang W, Wang J, Chudnovsky A, di Pietro A, Donahue AC, Choueiri TK | title = Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in advanced renal cell carcinoma: biomarker analysis of the phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 trial | journal = Nature Medicine | pages = 1733–1741 | date = September 2020 | volume = 26 | issue = 11 | pmid = 32895571 | doi = 10.1038/s41591-020-1044-8 | pmc = 8493486 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| Tests of this sort are being widely advertised for general cancer treatment and are expensive. In the past, some ] for cancer treatment has been involved in scams such as the ], or claimed to be hoaxes.<ref>{{Cite news | vauthors = Flam F |date=2015-01-22 |title=Duke U Cancer Fraud Scandal: A Cautionary Tale For Obama's Precision Medicine Push |url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/fayeflam/2015/01/22/investigator-offers-lessons-from-precision-medicines-cancer-scandal/ |access-date=2024-04-21 |work=Forbes |language=en}}</ref><ref> David Gorski, 28 September 2015, ] website</ref><ref> from 2011 on the melanoma.org website shows costs and claims.</ref> | |||
| ==Research== | |||
| <!--- need research Introduction/summary statement(s) here ---> | |||
| {{Further|topic=the Autologous Lymphoid Effector Cells Specific Against Tumor cells technology|ALECSAT}}<!--- Place here for now. ---> | |||
| ===Oncolytic virus=== | |||
| An ] is a virus that preferentially infects and kills cancer cells. As the infected cancer cells are destroyed by ], they release new infectious virus particles or virions to help destroy the remaining tumour. Oncolytic viruses are thought not only to cause direct destruction of the tumour cells, but also to stimulate host anti-tumour immune responses for long-term immunotherapy.<ref name=pmid27486853>{{cite journal | vauthors = Fukuhara H, Ino Y, Todo T | title = Oncolytic virus therapy: A new era of cancer treatment at dawn | journal = Cancer Science | volume = 107 | issue = 10 | pages = 1373–79 | date = October 2016 | pmid = 27486853 | pmc = 5084676 | doi = 10.1111/cas.13027 }}</ref><ref name=pmid28589082>{{cite journal | vauthors = Haddad D | title = Genetically Engineered Vaccinia Viruses As Agents for Cancer Treatment, Imaging, and Transgene Delivery | journal = Frontiers in Oncology | volume = 7 | pages = 96 | year = 2017 | pmid = 28589082 | pmc = 5440573 | doi = 10.3389/fonc.2017.00096 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref name=pmid29329556>{{cite journal | vauthors = Marin-Acevedo JA, Soyano AE, Dholaria B, Knutson KL, Lou Y | title = Cancer immunotherapy beyond immune checkpoint inhibitors | journal = Journal of Hematology & Oncology | volume = 11 | issue = 1 | pages = 8 | date = January 2018 | pmid = 29329556 | pmc = 5767051 | doi = 10.1186/s13045-017-0552-6 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| The potential of viruses as anti-cancer agents was first realized in the early twentieth century, although coordinated research efforts did not begin until the 1960s. A number of viruses including ], ], ], ], ] virus and ] have now been clinically tested as oncolytic agents. T-Vec is the first FDA-approved ] for the treatment of melanoma. A number of other oncolytic viruses are in Phase II-III development.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lawler SE, Speranza MC, Cho CF, Chiocca EA | title = Oncolytic Viruses in Cancer Treatment: A Review | journal = JAMA Oncology | volume = 3 | issue = 6 | pages = 841–849 | date = June 2017 | pmid = 27441411 | doi = 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.2064 | s2cid = 39321536 | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| ===Polysaccharides=== | |||
| Certain compounds found in ], primarily ]s, can up-regulate the immune system and may have anti-cancer properties. For example, ]s such as ] have been shown in laboratory studies to stimulate ], ], ] and immune system ] and have been investigated in clinical trials as ]s.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Aleem E | title = β-Glucans and their applications in cancer therapy: focus on human studies | journal = Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry | volume = 13 | issue = 5 | pages = 709–19 | date = June 2013 | pmid = 23293888 | doi = 10.2174/1871520611313050007 }}</ref> | |||
| === Neoantigens === | |||
| {{Main|Neoantigen}}Many tumors express mutations. These mutations potentially create new targetable antigens (neoantigens) for use in T-cell immunotherapy. The presence of CD8+ T cells in cancer lesions, as identified using RNA sequencing data, is higher in tumors with a high ]. The level of transcripts associated with the cytolytic activity of natural killer cells and T cells positively correlates with mutational load in many human tumors. In non–small cell lung cancer patients treated with lambrolizumab, mutational load shows a strong correlation with clinical response. In melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab, the long-term benefit is also associated with a higher mutational load, although less significantly. The predicted MHC binding neoantigens in patients with a long-term clinical benefit were enriched for a series of ] motifs that were not found in tumors of patients with no or minimal clinical benefit.<ref name="SnyderMakarov2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Snyder A, Makarov V, Merghoub T, Yuan J, Zaretsky JM, Desrichard A, Walsh LA, Postow MA, Wong P, Ho TS, Hollmann TJ, Bruggeman C, Kannan K, Li Y, Elipenahli C, Liu C, Harbison CT, Wang L, Ribas A, Wolchok JD, Chan TA | title = Genetic basis for clinical response to CTLA-4 blockade in melanoma | journal = The New England Journal of Medicine | volume = 371 | issue = 23 | pages = 2189–99 | date = December 2014 | pmid = 25409260 | pmc = 4315319 | doi = 10.1056/NEJMoa1406498 }}</ref> However, human neoantigens identified in other studies do not show the bias toward tetrapeptide signatures.<ref name="ss15">{{cite journal | vauthors = Schumacher TN, Schreiber RD | title = Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy | journal = Science | volume = 348 | issue = 6230 | pages = 69–74 | date = April 2015 | pmid = 25838375 | doi = 10.1126/science.aaa4971 | bibcode = 2015Sci...348...69S | doi-access = free }}</ref> | |||
| ===Polysaccharide-K=== | |||
| In the 1980s, Japan's ] approved ] extracted from the mushroom, '']'', to stimulate the immune systems of patients undergoing chemotherapy. It is a ] in the US and other jurisdictions.<ref name="CoriolusVersicolor">{{cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060215064239/http://www.cancer.org/docroot/ETO/content/ETO_5_3X_Coriolous_Versicolor.asp|url=http://www.cancer.org/docroot/ETO/content/ETO_5_3X_Coriolous_Versicolor.asp|archive-date=15 February 2006|url-status=dead|title=Coriolus Versicolor|publisher=American Cancer Society}}</ref> | |||
| == See also == | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == |
== References == | ||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| == External links == | |||
| * | |||
| * , NIH | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170404222913/https://www.cancer.gov/research/areas/treatment/immunotherapy-using-immune-system |date=4 April 2017 }} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | * | ||
| * {{cite news |url=https://www.economist.com/news/science-and-technology/21653602-doctors-are-tryingwith-some-successto-recruit-immune-system-help|title=And Then There Were Five|work=Economist}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite web|url=http://www.immunooncology.com/home.aspx|title=Discover the Science of Immuno-Oncology|publisher=]|access-date=13 March 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141010230254/http://www.immunooncology.com/home.aspx|archive-date=10 October 2014|url-status=dead}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{cite journal | vauthors = Eggermont A, Finn O | title = Advances in immuno-oncology. Foreword | journal = Annals of Oncology | volume = 23 | issue = Suppl 8 | pages = viii5 | date = September 2012 | pmid = 22918929 | doi = 10.1093/annonc/mds255 | doi-access = free }} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist|2}} | |||
| {{Tumors}} | {{Tumors}} | ||
| {{Chemotherapeutic agents}} | {{Chemotherapeutic agents}} | ||
| {{Breakthrough of the Year}} | {{Breakthrough of the Year}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:53, 23 December 2024
Artificial stimulation of the immune system to treat cancerMedical intervention
| Cancer immunotherapy | |
|---|---|
 Peptide epitope of CD20 bound to rituximab's FAB Peptide epitope of CD20 bound to rituximab's FAB | |
| Specialty | Immuno-oncology |
| [edit on Wikidata] | |
Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncotherapy) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the fundamental research of cancer immunology (immuno-oncology) and a growing subspecialty of oncology.
Cancer immunotherapy exploits the fact that cancer cells often have tumor antigens, molecules on their surface that can bind to antibody proteins or T-cell receptors, triggering an immune system response. The tumor antigens are often proteins or other macromolecules (e.g., carbohydrates). Normal antibodies bind to external pathogens, but the modified immunotherapy antibodies bind to the tumor antigens marking and identifying the cancer cells for the immune system to inhibit or kill. The clinical success of cancer immunotherapy is highly variable between different forms of cancer; for instance, certain subtypes of gastric cancer react well to the approach whereas immunotherapy is not effective for other subtypes.
In 2018, American immunologist James P. Allison and Japanese immunologist Tasuku Honjo received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery of cancer therapy by inhibition of negative immune regulation.
History
"During the 17th and 18th centuries, various forms of immunotherapy in cancer became widespread... In the 18th and 19th centuries, septic dressings enclosing ulcerative tumours were used for the treatment of cancer. Surgical wounds were left open to facilitate the development of infection, and purulent sores were created deliberately... One of the most well-known effects of microorganisms on ... cancer was reported in 1891, when an American surgeon, William Coley, inoculated patients having inoperable tumours with ." "Coley thoroughly reviewed the literature available at that time and found 38 reports of cancer patients with accidental or iatrogenic feverish erysipelas. In 12 patients, the sarcoma or carcinoma had completely disappeared; the others had substantially improved. Coley decided to attempt the therapeutic use of iatrogenic erysipelas..." "Coley developed a toxin that contained heat-killed bacteria . Until 1963, this treatment was used for the treatment of sarcoma." "Coley injected more than 1000 cancer patients with bacteria or bacterial products." 51.9% of patients with inoperable soft-tissue sarcomas showed complete tumour regression and survived for more than 5 years, and 21.2% of the patients had no clinical evidence of tumour at least 20 years after this treatment..." Research continued in the 20th century under Maria O'Connor Hornung at Tulane Medical School.
Types and categories
There are several types of immunotherapy used to treat cancer:
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors: drugs that block immune system checkpoints to allow immune cells to respond more strongly to the cancer.
- T-cell transfer therapy: a treatment that takes T-cells from the tumor and selects or changes them in the lab to better attack cancer cells, then reintroduces them into the patient.
- Monoclonal antibodies: designed to bind to specific targets on cancer cells, marking cancer cells so that they will be better seen and destroyed by the immune system.
- Treatment vaccines: also known as therapeutic cancer vaccines, help the immune system learn to recognize and react to mutant proteins specific to the tumor and destroy cancer cells containing them.
- Immune system modulators: agents that enhance the body’s immune response against cancer.
Immunotherapies can be categorized as active or passive based on their ability to engage the host immune system against cancer. Active immunotherapy specifically targets tumor cells via the immune system. Examples include therapeutic cancer vaccines (also known as treatment vaccines, which are designed to boost the body's immune system to fight cancer), CAR-T cells, and targeted antibody therapies. In contrast, passive immunotherapy does not directly target tumor cells, but enhances the ability of the immune system to attack cancer cells. Examples include checkpoint inhibitors and cytokines.
Active cellular therapies aim to destroy cancer cells by recognition of distinct markers known as antigens. In cancer vaccines, the goal is to generate an immune response to these antigens through a vaccine. Currently, only one vaccine (sipuleucel-T for prostate cancer) has been approved. In cell-mediated therapies like CAR-T cell therapy, immune cells are extracted from the patient, genetically engineered to recognize tumor-specific antigens, and returned to the patient. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer (NK) cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells, and dendritic cells. Finally, specific antibodies can be developed that recognize cancer cells and target them for destruction by the immune system. Examples of such antibodies include rituximab (targeting CD-20), trastuzumab (targeting HER-2), and cetuximab (targeting EGFR).
Passive antibody therapies aim to increase the activity of the immune system without specifically targeting cancer cells. For example, cytokines directly stimulate the immune system and increase immune activity. Checkpoint inhibitors target proteins (immune checkpoints) that normally dampen the immune response. This enhances the ability of the immune system to attack cancer cells. Current research is identifying new potential targets to enhance immune function. Approved checkpoint inhibitors include antibodies such as ipilimumab, nivolumab, and pembrolizumab.
Cellular immunotherapy
Dendritic cell therapy

Dendritic cell therapy provokes anti-tumor responses by causing dendritic cells to present tumor antigens to lymphocytes, which activates them, priming them to kill other cells that present the antigen. Dendritic cells are antigen-presenting cells (APCs) in the mammalian immune system. In cancer treatment, they aid cancer antigen targeting. The only approved cellular cancer therapy based on dendritic cells is sipuleucel-T.
One method of inducing dendritic cells to present tumor antigens is by vaccination with autologous tumor lysates or short peptides (small parts of the protein that correspond to the protein antigens on cancer cells). These peptides are often given in combination with adjuvants (highly immunogenic substances) to increase the immune and anti-tumor responses. Other adjuvants include proteins or other chemicals that attract and/or activate dendritic cells, such as granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). The most common sources of antigens used for dendritic cell vaccine in glioblastoma (GBM) as an aggressive brain tumor were whole tumor lysate, CMV antigen RNA and tumor-associated peptides like EGFRvIII.
Dendritic cells can also be activated in vivo by making tumor cells express GM-CSF. This can be achieved by either genetically engineering tumor cells to produce GM-CSF or by infecting tumor cells with an oncolytic virus that expresses GM-CSF.
Another strategy is to remove dendritic cells from the blood of a patient and activate them outside the body. The dendritic cells are activated in the presence of tumor antigens, which may be a single tumor-specific peptide/protein or a tumor cell lysate (a solution of broken-down tumor cells). These cells (with optional adjuvants) are infused and provoke an immune response.
Dendritic cell therapies include the use of antibodies that bind to receptors on the surface of dendritic cells. Antigens can be added to the antibody and can induce the dendritic cells to mature and provide immunity to the tumor. Dendritic cell receptors such as TLR3, TLR7, TLR8 or CD40 have been used as antibody targets. Dendritic cell-NK cell interface also has an important role in immunotherapy. The design of new dendritic cell-based vaccination strategies should also encompass NK cell-stimulating potency. It is critical to systematically incorporate NK cells monitoring as an outcome in antitumor DC-based clinical trials.
Drugs
Sipuleucel-T (Provenge) was approved for treatment of asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in 2010. The treatment consists of removal of antigen-presenting cells from blood by leukapheresis and growing them with the fusion protein PA2024 made from GM-CSF and prostate-specific prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) and reinfused. This process is repeated three times.
Adoptive T-cell therapy

Adoptive T cell therapy is a form of passive immunization by the transfusion of T-cells. They are found in blood and tissue and typically activate when they find foreign pathogens. Activation occurs when the T-cell's surface receptors encounter cells that display parts of foreign proteins (either on their surface or intracellularly). These can be either infected cells or other antigen-presenting cells (APCs). The latter are found in normal tissue and in tumor tissue, where they are known as tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). They are activated by the presence of APCs such as dendritic cells that present tumor antigens. Although these cells can attack tumors, the tumor microenvironment is highly immunosuppressive, interfering with immune-mediated tumour death.
Multiple ways of producing tumour-destroying T-cells have been developed. Most commonly, T-cells specific to a tumor antigen can be removed from a tumor sample (TILs) or filtered from blood. The T-cells can optionally be modified in various ways, cultured and infused into patients. T cells can be modified via genetic engineering, producing CAR-T cell or TCR T cells or by exposing the T cells to tumor antigens in a non-immunosuppressive environment, that they recognize as foreign and learn to attack.
Another approach is transfer of haploidentical γδ T cells or natural killer cells from a healthy donor. The major advantage of this approach is that these cells do not cause graft-versus-host disease. The disadvantage is that transferred cells frequently have impaired function.
Tumor-derived T cell therapy
The simplest example involves removing TILs from a tumor, culturing but not modifying them, and infusing the result back into the tumour. The first therapy of this type, Lifileucel, achieved US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval in February 2024.
CAR-T cell therapy
Main article: Chimeric antigen receptor T cellThe premise of CAR-T immunotherapy is to modify T cells to recognize cancer cells in order to target and destroy them. Scientists harvest T cells from people, genetically alter them to add a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) that specifically recognizes cancer cells, then infuse the resulting CAR-T cells into patients to attack their tumors.
Tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR-T) therapy, was approved by the FDA in 2017 to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). This treatment removes CD19 positive cells (B-cells) from the body (including the diseased cells, but also normal antibody-producing cells).
Axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) is another CAR-T therapeutic, approved in 2017 for treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Multifunctional alginate scaffolds
Multifunctional alginate scaffolds for T cell engineering and release (MASTER) is a technique for in situ engineering, replication and release of genetically engineered T cells. It is an evolution of CAR T cell therapy. T cells are extracted from the patient and mixed with a genetically engineered virus that contains a cancer-targeting gene (as with CAR T). The mixture is then added to a MASTER (scaffold), which absorbs them. The MASTER contains antibodies that activate the T cells and interleukins that trigger cell proliferation. The MASTER is then implanted into the patient. The activated T cells interact with the viruses to become CAR T cells. The interleukins stimulate these CAR T cells to proliferate, and the CAR T cells exit the MASTER to attack the cancer. The technique takes hours instead of weeks. And because the cells are younger, they last longer in the body, show stronger potency against cancer, and display fewer markers of exhaustion. These features were demonstrated in mouse models. The treatment was more effective and longer-lasting against lymphoma.
T cell receptor T cell therapy
This section is an excerpt from T cell receptor T cell therapy.T cell receptor T cell therapy (TCR-T) is a type of adoptive T-cell therapy that targets some cancers. TCR-T therapies use heterodimers made of alpha and beta peptide chains to recognize MHC-presented polypeptide fragment molecules. Unlike CAR-T, which uses cell surface antigens, TCR-T can recognize MHC's larger set of intracellular antigen fragments. However, TCR-T cell therapy depends on MHC molecules, limiting its usefulness.
Each T cell's TCR is specific to one antigen and sits on the T cell's surface. The affinity of human TCRs to tumor antigens is relatively low, rendering them unable to recognize and kill tumor cells effectively. The modified T cell has much higher affinity, which enhances both recognition and affinity supporting the recognition of tumor cells.Antibody therapy

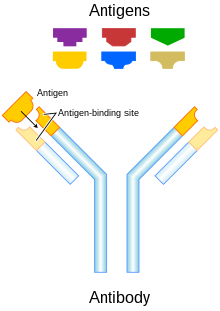
Antibody types
Conjugation
Two types are used in cancer treatments:
- Naked monoclonal antibodies are antibodies without added elements. Most antibody therapies use this antibody type.
- Conjugated monoclonal antibodies are joined to another molecule, which is either cytotoxic or radioactive. The toxic chemicals are those typically used as chemotherapy drugs, but other toxins can be used. The antibody binds to specific antigens on cancer cell surfaces, directing the therapy to the tumor. Radioactive compound-linked antibodies are referred to as radiolabelled. Chemolabelled or immunotoxins antibodies are tagged with chemotherapeutic molecules or toxins, respectively. Research has also demonstrated conjugation of a TLR agonist to an anti-tumor monoclonal antibody.
Fc regions
Fc's ability to bind Fc receptors is important because it allows antibodies to activate the immune system. Fc regions are varied: they exist in numerous subtypes and can be further modified, for example with the addition of sugars in a process called glycosylation. Changes in the Fc region can alter an antibody's ability to engage Fc receptors and, by extension, will determine the type of immune response that the antibody triggers. For example, immune checkpoint blockers targeting PD-1 are antibodies designed to bind PD-1 expressed by T cells and reactivate these cells to eliminate tumors. Anti-PD-1 drugs contain not only a Fab region that binds PD-1 but also an Fc region. Experimental work indicates that the Fc portion of cancer immunotherapy drugs can affect the outcome of treatment. For example, anti-PD-1 drugs with Fc regions that bind inhibitory Fc receptors can have decreased therapeutic efficacy. Imaging studies have further shown that the Fc region of anti-PD-1 drugs can bind Fc receptors expressed by tumor-associated macrophages. This process removes the drugs from their intended targets (i.e. PD-1 molecules expressed on the surface of T cells) and limits therapeutic efficacy. Furthermore, antibodies targeting the co-stimulatory protein CD40 require engagement with selective Fc receptors for optimal therapeutic efficacy. Together, these studies underscore the importance of Fc status in antibody-based immune checkpoint targeting strategies.
Human/non-human antibodies
Antibodies can come from a variety of sources, including human cells, mice, and a combination of the two (chimeric antibodies). Different sources of antibodies can provoke different kinds of immune responses. For example, the human immune system can recognize mouse antibodies (also known as murine antibodies) and trigger an immune response against them. This could reduce the effectiveness of the antibodies as a treatment and cause an immune reaction. Chimeric antibodies attempt to reduce murine antibodies' immunogenicity by replacing part of the antibody with the corresponding human counterpart. Humanized antibodies are almost completely human; only the complementarity determining regions of the variable regions are derived from murine sources. Human antibodies have been produced using unmodified human DNA.

Mechanism of action
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) requires antibodies to bind to target cell surfaces. Antibodies are formed of a binding region (Fab) and the Fc region that can be detected by immune system cells via their Fc surface receptors. Fc receptors are found on many immune system cells, including NK cells. When NK cells encounter antibody-coated cells, the latter's Fc regions interact with their Fc receptors, releasing perforin and granzyme B to kill the tumor cell. Examples include rituximab, ofatumumab, elotuzumab, and alemtuzumab. Antibodies under development have altered Fc regions that have higher affinity for a specific type of Fc receptor, FcγRIIIA, which can dramatically increase effectiveness.
Anti-CD47 therapy
Many tumor cells overexpress CD47 to escape immunosurveilance of host immune system. CD47 binds to its receptor signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) and downregulate phagocytosis of tumor cell. Therefore, anti-CD47 therapy aims to restore clearance of tumor cells. Additionally, growing evidence supports the employment of tumor antigen-specific T cell response in response to anti-CD47 therapy. A number of therapeutics are being developed, including anti-CD47 antibodies, engineered decoy receptors, anti-SIRPα antibodies and bispecific agents. As of 2017, wide range of solid and hematologic malignancies were being clinically tested.
Anti-GD2 antibodies
Carbohydrate antigens on the surface of cells can be used as targets for immunotherapy. GD2 is a ganglioside found on the surface of many types of cancer cell including neuroblastoma, retinoblastoma, melanoma, small cell lung cancer, brain tumors, osteosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, liposarcoma, fibrosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma and other soft tissue sarcomas. It is not usually expressed on the surface of normal tissues, making it a good target for immunotherapy. As of 2014, clinical trials were underway.
Complement Activation
The complement system includes blood proteins that can cause cell death after an antibody binds to the cell surface (the classical complement pathway, among the ways of complement activation). Generally, the system deals with foreign pathogens but can be activated with therapeutic antibodies in cancer. The system can be triggered if the antibody is chimeric, humanized, or human; as long as it contains the IgG1 Fc region. Complement can lead to cell death by activation of the membrane attack complex, known as complement-dependent cytotoxicity; enhancement of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; and CR3-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Complement-dependent cytotoxicity occurs when antibodies bind to the cancer cell surface, the C1 complex binds to these antibodies and subsequently, protein pores are formed in cancer cell membrane.
Blocking
Antibody therapies can also function by binding to proteins and physically blocking them from interacting with other proteins. Checkpoint inhibitors (CTLA-4, PD-1, and PD-L1) operate by this mechanism. Briefly, checkpoint inhibitors are proteins that normally help to slow immune responses and prevent the immune system from attacking normal cells. Checkpoint inhibitors bind these proteins and prevent them from functioning normally, which increases the activity of the immune system. Examples include durvalumab, ipilimumab, nivolumab, and pembrolizumab.
FDA-approved antibodies
| Antibody | Brand name | Type | Target | Approval date | Approved treatment(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alemtuzumab | Campath | humanized | CD52 | 2001 | B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) |
| Atezolizumab | Tecentriq | humanized | PD-L1 | 2016 | bladder cancer |
| Atezolizumab/hyaluronidase | Tecentriq Hybreza | humanized | PD-L1 | 2024 | non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma |
| Avelumab | Bavencio | human | PD-L1 | 2017 | metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma |
| Durvalumab | Imfinzi | human | PD-L1 | 2017 | bladder cancer non-small cell lung cancer |
| Elotuzumab | Empliciti | humanized | SLAMF7 | 2015 | multiple myeloma |
| Ipilimumab | Yervoy | human | CTLA4 | 2011 | metastatic melanoma |
| Nivolumab | Opdivo | human | PD-1 | 2014 | unresectable or metastatic melanoma, squamous non-small cell lung cancer, Renal cell carcinoma, colorectal cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, classical hodgkin lymphoma |
| Ofatumumab | Arzerra | human | CD20 | 2009 | refractory CLL |
| Pembrolizumab | Keytruda | humanized | PD-1 | 2014 | unresectable or metastatic melanoma, squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), Hodgkin's lymphoma, Merkel-cell carcinoma (MCC), primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), stomach cancer, cervical cancer |
| Rituximab | Rituxan, Mabthera | chimeric | CD20 | 1997 | non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| Rituximab/hyaluronidase | Rituxan Hycela | chimeric | CD20 | 2017 | follicular lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| Trastuzumab | Rituxan Hycela | humanized | HER2/neu | 1998 | breast cancer, gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma |
Alemtuzumab
Alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) is an anti-CD52 humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody indicated for the treatment of fludarabine-refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, peripheral T-cell lymphoma and T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia. CD52 is found on >95% of peripheral blood lymphocytes (both T-cells and B-cells) and monocytes, but its function in lymphocytes is unknown. It binds to CD52 and initiates its cytotoxic effect by complement fixation and ADCC mechanisms. Due to the antibody target (cells of the immune system), common complications of alemtuzumab therapy are infection, toxicity and myelosuppression.
Atezolizumab
This section is an excerpt from Atezolizumab.
Atezolizumab, sold under the brand name Tecentriq among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat urothelial carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), small cell lung cancer (SCLC), hepatocellular carcinoma and alveolar soft part sarcoma, but discontinued for use in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). It is a fully humanized, engineered monoclonal antibody of IgG1 isotype against the protein programmed cell death-ligand 1 (PD-L1).
The most common side effects when used on its own include tiredness, reduced appetite, nausea, vomiting, cough, difficulty breathing, diarrhea, rash, fever, pain in the back, joints, muscles and bones, weakness, itching and urinary tract infection. The most common side effects when used with other cancer medicines include peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage in the hands and feet), nausea, anemia (low red blood cell counts), neutropenia (low white blood cell counts), thrombocytopenia (low platelet counts), rash, tiredness, constipation, reduced appetite, diarrhea, and cough.
Atezolizumab was the first PD-L1 inhibitor approved by the U.S. for bladder cancer. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
In the European Union, atezolizumab is the first PD-(L)1 cancer immunotherapy for subcutaneous injection.Atezolizumab/hyaluronidase
This section is an excerpt from Atezolizumab/hyaluronidase.
Atezolizumab/hyaluronidase, sold under the brand name Tecentriq Hybreza, is a fixed-dose combination medication used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, melanoma, and alveolar soft part sarcoma. It contains atezolizumab, a programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) blocking monoclonal antibody; and hyaluronidase (human recombinant), an endoglycosidase. It is taken by subcutaneous injection.
The most common adverse reactions include fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite.
Atezolizumab/hyaluronidase was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2024.Avelumab
This section is an excerpt from Avelumab.
Avelumab, sold under the brand name Bavencio, is a fully human monoclonal antibody medication for the treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma, urothelial carcinoma, and renal cell carcinoma.
Common side effects include fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, nausea, infusion-related reactions, rash, decreased appetite and swelling of the limbs (peripheral edema).
Avelumab targets the protein programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). It has received orphan drug designation by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the treatment of gastric cancer in January 2017. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved it in March 2017, for the treatment of Merkel-cell carcinoma, an aggressive type of skin cancer. The EMA approved it in September 2017, for the same indication. This is the first FDA-approved treatment for metastatic Merkel-cell carcinoma, a rare, aggressive form of skin cancer. Avelumab was developed by Merck KGaA and Pfizer.Durvalumab
Main article: DurvalumabDurvalumab (Imfinzi) is a human immunoglobulin G1 kappa (IgG1κ) monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) with the PD-1 and CD80 (B7.1) molecules. Durvalumab is approved for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma who:
- have disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy.
- have disease progression within 12 months of neoadjuvant or adjuvant treatment with platinum-containing chemotherapy.
On 16 February 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved durvalumab for patients with unresectable stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease has not progressed following concurrent platinum-based chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Elotuzumab
This section is an excerpt from Elotuzumab. Pharmaceutical compound| Monoclonal antibody | |
|---|---|
| Type | Whole antibody |
| Source | Humanized |
| Target | SLAMF7 (CD319) |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Empliciti |
| Other names | HuLuc63 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% (IV) |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6476H9982N1714O2016S42 |
| Molar mass | 145453.59 g·mol |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Elotuzumab, sold under the brand name Empliciti, is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody medication used in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, for adults that have received 1 to 3 prior therapies for the treatment of multiple myeloma. It is also indicated for adult patients in combination with pomalidomide and dexamethasone, who have received 2 prior therapies including lenalidomide and a protease inhibitor. Administration of elotuzumab is done intravenously. Each intravenous injection of elotuzumab should be premedicated with dexamethasone, diphenhydramine, ranitidine and acetaminophen. It is being developed by Bristol Myers Squibb and AbbVie.
Common side effects of elotuzumab with lenalidomide and dexamethasone includes fatigue, diarrhea, pyrexia, constipation, cough, peripheral neuropathy, nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased appetite, and pneumonia. The most common side effects of elotuzumab with pomalidomide and dexamethasone includes constipation and hyperglycemia. There is no available information for the use of elotuzumab in pregnant women.
Elotuzumab is an immunostimulatory antibody that targets the Signaling Lymphocytic Activation Molecule Family member 7 (SLAMF7) through two mechanisms.
In May 2014, it was granted breakthrough therapy designation by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (for multiple myeloma). The initial FDA approval of elotuzumab in 2015 in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone was carried out through the results illustrated in the ELOQUENT 2 study. In May 2016 the EC/EU gave a similar approval. Furthermore, the results of the ELOQUENT 3 study led to the FDA approval of elotuzumab in combination with pomalidomide and dexamethasone in 2018.Ipilimumab
Ipilimumab (Yervoy) is a human IgG1 antibody that binds the surface protein CTLA4. In normal physiology T-cells are activated by two signals: the T-cell receptor binding to an antigen-MHC complex and T-cell surface receptor CD28 binding to CD80 or CD86 proteins. CTLA4 binds to CD80 or CD86, preventing the binding of CD28 to these surface proteins and therefore negatively regulates the activation of T-cells.
Active cytotoxic T-cells are required for the immune system to attack melanoma cells. Normally inhibited active melanoma-specific cytotoxic T-cells can produce an effective anti-tumor response. Ipilimumab can cause a shift in the ratio of regulatory T-cells to cytotoxic T-cells to increase the anti-tumor response. Regulatory T-cells inhibit other T-cells, which may benefit the tumor.
Nivolumab
Main article: NivolumabNivolumab is a human IgG4 antibody that prevents T-cell inactivation by blocking the binding of programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 or programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 (PD-L1 or PD-L2), a protein expressed by cancer cells, with PD-1, a protein found on the surface of activated T-cells. Nivolumab is used in advanced melanoma, metastatic renal cell carcinoma, advanced lung cancer, advanced head and neck cancer, and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Ofatumumab
Ofatumumab is a second generation human IgG1 antibody that binds to CD20. It is used in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) because the cancerous cells of CLL are usually CD20-expressing B-cells. Unlike rituximab, which binds to a large loop of the CD20 protein, ofatumumab binds to a separate, small loop. This may explain their different characteristics. Compared to rituximab, ofatumumab induces complement-dependent cytotoxicity at a lower dose with less immunogenicity.
Pembrolizumab
As of 2019, pembrolizumab, which blocks PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1, has been used via intravenous infusion to treat inoperable or metastatic melanoma, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in certain situations, as a second-line treatment for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), after platinum-based chemotherapy, and for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with refractory classic Hodgkin's lymphoma (cHL). It is also indicated for certain patients with urothelial carcinoma, stomach cancer and cervical cancer.
Rituximab
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal IgG1 antibody specific for CD20, developed from its parent antibody Ibritumomab. As with ibritumomab, rituximab targets CD20, making it effective in treating certain B-cell malignancies. These include aggressive and indolent lymphomas such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma and leukemias such as B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Although the function of CD20 is relatively unknown, CD20 may be a calcium channel involved in B-cell activation. The antibody's mode of action is primarily through the induction of ADCC and complement-mediated cytotoxicity. Other mechanisms include apoptosis and cellular growth arrest. Rituximab also increases the sensitivity of cancerous B-cells to chemotherapy.
Trastuzumab
This section is an excerpt from Trastuzumab.
Pharmaceutical compound
 Trastuzumab Fab region (cyan) binding HER2/neu (gold) Trastuzumab Fab region (cyan) binding HER2/neu (gold) | |
| Monoclonal antibody | |
|---|---|
| Type | Whole antibody |
| Source | Humanized (from mouse) |
| Target | HER2/neu |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Herceptin, Herceptin SC, others |
| Biosimilars | trastuzumab-anns, trastuzumab-dkst, trastuzumab-dttb, trastuzumab-pkrb, trastuzumab-qyyp, trastuzumab-strf, Adheroza, Hercessi, Herzuma, Herwenda, Kanjinti, Ogivri, Ontruzant, Trastucip, Trazimera, Tuznue, Tuzucip, Zercepac |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, subcutaneous |
| Drug class | Antineoplastic agent |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Unknown, possibly reticuloendothelial system |
| Elimination half-life | 2-12 days |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem SID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6470H10012N1726O2013S42 |
| Molar mass | 145531.86 g·mol |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Trastuzumab, sold under the brand name Herceptin among others, is a monoclonal antibody used to treat breast cancer and stomach cancer. It is specifically used for cancer that is HER2 receptor positive. It may be used by itself or together with other chemotherapy medication. Trastuzumab is given by slow injection into a vein and injection just under the skin.
Common side effects include fever, infection, cough, headache, trouble sleeping, and rash. Other severe side effects include heart failure, allergic reactions, and lung disease. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Trastuzumab works by binding to the HER2 receptor and slowing down cell replication.
Trastuzumab was approved for medical use in the United States in September 1998, and in the European Union in August 2000. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.Immune checkpoint antibody therapy or immune checkpoint blockade
Main articles: Immune checkpoint and Immunotherapy
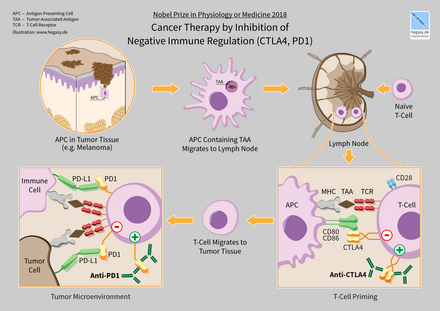
Immune checkpoints affect the immune system function. Immune checkpoints can be stimulatory or inhibitory. Tumors can use these checkpoints to protect themselves from immune system attacks. Checkpoint therapies approved as of 2012 block inhibitory checkpoint receptors. Blockade of negative feedback signaling to immune cells thus results in an enhanced immune response against tumors. As of 2020, immune checkpoint blockade therapies have varied effectiveness. In Hodgkin lymphoma and natural killer T-cell lymphoma, response rates are high, at 50–60%. Response rates are quite low for breast and prostate cancers, however. A major challenge are the large variations in responses to immunocheckpoint inhibitors, some patients showing spectacular clinical responses while no positive effects are seen in others. A plethora of possible reasons for the absence of efficacy in many patients have been proposed, but the biomedical community has still to begin to find consensus in this respect. For instance, a recent paper documented that infection with Helicobacter pylori would negatively influence the effects of immunocheckpoint inhibitors in gastric cancer., but this notion was quickly challenged by others.
One ligand-receptor interaction under investigation is the interaction between the transmembrane programmed cell death 1 protein (PDCD1, PD-1; also known as CD279) and its ligand, PD-1 ligand 1 (PD-L1, CD274). PD-L1 on the cell surface binds to PD1 on an immune cell surface, which inhibits immune cell activity. Among PD-L1 functions is a key regulatory role on T cell activities. It appears that (cancer-mediated) upregulation of PD-L1 on the cell surface may inhibit T cells that might otherwise attack. PD-L1 on cancer cells also inhibits FAS- and interferon-dependent apoptosis, protecting cells from cytotoxic molecules produced by T cells. Antibodies that bind to either PD-1 or PD-L1 and therefore block the interaction may allow the T-cells to attack the tumor.
CTLA-4 blockade
The first checkpoint antibody approved by the FDA was ipilimumab, approved in 2011 to treat melanoma. It blocks the immune checkpoint molecule CTLA-4. As of 2012, clinical trials have also shown some benefits of anti-CTLA-4 therapy on lung cancer or pancreatic cancer, specifically in combination with other drugs. In on-going trials the combination of CTLA-4 blockade with PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors is tested on different types of cancer.
However, as of 2015 it is known that patients treated with checkpoint blockade (specifically CTLA-4 blocking antibodies), or a combination of check-point blocking antibodies, are at high risk of having immune-related adverse events such as dermatologic, gastrointestinal, endocrine, or hepatic autoimmune reactions. These are most likely due to the breadth of the induced T-cell activation when anti-CTLA-4 antibodies are administered by injection in the bloodstream.
A 2024 cohort study of ICI use during pregnancy showed no overreporting of specific adverse effects on pregnancy, fetal, and/or newborn outcomes, interestingly.
Using a mouse model of bladder cancer, researchers have found that a local injection of a low dose anti-CTLA-4 in the tumour area had the same tumour inhibiting capacity as when the antibody was delivered in the blood. At the same time the levels of circulating antibodies were lower, suggesting that local administration of the anti-CTLA-4 therapy might result in fewer adverse events.
PD-1 inhibitors
Main article: PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitorsInitial clinical trial results with IgG4 PD1 antibody nivolumab were published in 2010. It was approved in 2014. Nivolumab is approved to treat melanoma, lung cancer, kidney cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, and Hodgkin's lymphoma. A 2016 clinical trial for non-small cell lung cancer failed to meet its primary endpoint for treatment in the first-line setting, but is FDA-approved in subsequent lines of therapy.
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) is another PD1 inhibitor that was approved by the FDA in 2014. Pembrolizumab is approved to treat melanoma and lung cancer.
Antibody BGB-A317 is a PD-1 inhibitor (designed to not bind Fc gamma receptor I) in early clinical trials.
PD-L1 inhibitors
Main article: PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitorsIn May 2016, PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab was approved for treating bladder cancer.
Anti-PD-L1 antibodies currently in development include avelumab and durvalumab, in addition to an inhibitory affimer.
CISH
This section is an excerpt from Adoptive cell transfer § Intrinsic (Intracellular) checkpoint blockade. Other modes of enhancing immuno-therapy include targeting so-called intrinsic immune checkpoint blockades. Many of these intrinsic regulators include molecules with ubiquitin ligase activity, including CBLB. More recently, CISH, a molecule with ubiquitin ligase activity, was found to be induced by T cell receptor ligation (TCR) and suppressed by targeting the critical signaling intermediate PLC-gamma-1. The deletion of CISH in effector T cells dramatically augments TCR signaling and subsequent effector cytokine release, proliferation and survival. The adoptive transfer of tumor-specific effector T cells knocked out or knocked down CISH, resulting in a significant increase in functional avidity and sustained tumor immunity. Surprisingly no changes in activity of STAT5, CISH's purported target. Thus CISH represents a new class of T-cell intrinsic immunologic checkpoints with the potential to enhance adoptive immunotherapies.Combinations
Many cancer patients do not respond to immune checkpoint blockade. Response rate may be improved by combining that with additional therapies, including those that stimulate T cell infiltration. For example, targeted therapies such as radiotherapy, vasculature targeting agents, and immunogenic chemotherapy can improve immune checkpoint blockade response in animal models.
Combining immunotherapies such as PD1 and CTLA4 inhibitors can create to durable responses.
Combinatorial ablation and immunotherapy enhances the immunostimulating response and has synergistic effects for metastatic cancer treatment.
Combining checkpoint immunotherapies with pharmaceutical agents has the potential to improve response, and as of 2018 were a target of clinical investigation. Immunostimulatory drugs such as CSF-1R inhibitors and TLR agonists have been effective.
Two independent 2024 clinical trials reported that combinations of JAK inhibitors with anti–PD-1 immunotherapy could improve efficacy. A phase 2 trial investigated the combination as a first-line therapy for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Administration of itacitinib after treatment with pembrolizumab improved therapeutic response. A separate phase 1/2 trial with patients with relapsed/refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma combined ruxolitinib and nivolumab, yielding improved clinical efficacy in patients who had previously failed checkpoint blockade immunotherapy.
Cytokine therapy
Cytokines are proteins produced by many types of cells present within a tumor. They can modulate immune responses. The tumor often employs them to allow it to grow and reduce the immune response. These immune-modulating effects allow them to be used as drugs to provoke an immune response. Two commonly used cytokines are interferons and interleukins.
Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behavior of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as passive cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.
Interferon
Interferons are produced by the immune system. They are usually involved in anti-viral response, but also have use for cancer. They fall in three groups: type I (IFNα and IFNβ), type II (IFNγ) and type III (IFNλ). IFNα has been approved for use in hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and melanoma. Type I and II IFNs have been researched extensively and although both types promote anti-tumor immune system effects, only type I IFNs have been shown to be clinically effective. IFNλ shows promise for its anti-tumor effects in animal models.
Unlike type I IFNs, Interferon gamma is not approved yet for the treatment of any cancer. However, improved survival was observed when Interferon gamma was administered to patients with bladder carcinoma and melanoma cancers. The most promising result was achieved in patients with stage 2 and 3 of ovarian carcinoma. The in vitro study of IFN-gamma in cancer cells is more extensive and results indicate anti-proliferative activity of IFN-gamma leading to the growth inhibition or cell death, generally induced by apoptosis but sometimes by autophagy.
Interleukin
Interleukins have an array of immune system effects. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma. In normal physiology it promotes both effector T cells and T-regulatory cells, but its exact mechanism of action is unknown.
Genetic pre-treatment testing for therapeutic significance
Because of the high cost of many of immunotherapy medications and the reluctance of medical insurance companies to prepay for their prescriptions various test methods have been proposed, to attempt to forecast the effectiveness of these medications. In some cases the FDA has approved genetic tests for medication specific to certain genetic markers. For example, the FDA approved BRAF-associated medication for metastatic melanoma, to be administered to patients after testing for the BRAF genetic mutation.
As of 2018, the detection of PD-L1 protein seemed to be an indication of cancer susceptible to several immunotherapy medications, but research found that both the lack of this protein or its inclusion in the cancerous tissue was inconclusive, due to the little-understood varying quantities of the protein during different times and locations within the infected cells and tissue.
In 2018, some genetic indications such as Tumor Mutational Burden (TMB, the number of mutations within a targeted genetic region in the cancerous cell's DNA), and microsatellite instability (MSI, the quantity of impaired DNA mismatch leading to probable mutations), have been approved by the FDA as good indicators for the probability of effective treatment of immunotherapy medication for certain cancers, but research is still in progress. As of 2020, the patient prioritization for immunotherapy based on TMB was still highly controversial.
Tests of this sort are being widely advertised for general cancer treatment and are expensive. In the past, some genetic testing for cancer treatment has been involved in scams such as the Duke University Cancer Fraud scandal, or claimed to be hoaxes.
Research
Further information on the Autologous Lymphoid Effector Cells Specific Against Tumor cells technology: ALECSATOncolytic virus
An oncolytic virus is a virus that preferentially infects and kills cancer cells. As the infected cancer cells are destroyed by oncolysis, they release new infectious virus particles or virions to help destroy the remaining tumour. Oncolytic viruses are thought not only to cause direct destruction of the tumour cells, but also to stimulate host anti-tumour immune responses for long-term immunotherapy.
The potential of viruses as anti-cancer agents was first realized in the early twentieth century, although coordinated research efforts did not begin until the 1960s. A number of viruses including adenovirus, reovirus, measles, herpes simplex, Newcastle disease virus and vaccinia have now been clinically tested as oncolytic agents. T-Vec is the first FDA-approved oncolytic virus for the treatment of melanoma. A number of other oncolytic viruses are in Phase II-III development.
Polysaccharides
Certain compounds found in mushrooms, primarily polysaccharides, can up-regulate the immune system and may have anti-cancer properties. For example, beta-glucans such as lentinan have been shown in laboratory studies to stimulate macrophage, NK cells, T cells and immune system cytokines and have been investigated in clinical trials as immunologic adjuvants.
Neoantigens
Main article: NeoantigenMany tumors express mutations. These mutations potentially create new targetable antigens (neoantigens) for use in T-cell immunotherapy. The presence of CD8+ T cells in cancer lesions, as identified using RNA sequencing data, is higher in tumors with a high mutational burden. The level of transcripts associated with the cytolytic activity of natural killer cells and T cells positively correlates with mutational load in many human tumors. In non–small cell lung cancer patients treated with lambrolizumab, mutational load shows a strong correlation with clinical response. In melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab, the long-term benefit is also associated with a higher mutational load, although less significantly. The predicted MHC binding neoantigens in patients with a long-term clinical benefit were enriched for a series of tetrapeptide motifs that were not found in tumors of patients with no or minimal clinical benefit. However, human neoantigens identified in other studies do not show the bias toward tetrapeptide signatures.
Polysaccharide-K
In the 1980s, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare approved polysaccharide-K extracted from the mushroom, Coriolus versicolor, to stimulate the immune systems of patients undergoing chemotherapy. It is a dietary supplement in the US and other jurisdictions.
See also
- Cancer vaccine
- Antigen 5T4
- Coley's toxins
- Combinatorial ablation and immunotherapy
- Cryoimmunotherapy
- Photoimmunotherapy
- Radioimmunotherapy
References
- Biancalana M (14 December 2022). "Harnessing the immune system to develop breakthrough cancer therapies". Archived from the original on 4 December 2023. Retrieved 19 April 2024.
- Kodach LL, Peppelenbosch MP (August 2021). "Targeting the Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Compartment for Inducing Responsiveness to Immune Checkpoint Blockade Is Best Limited to Specific Subtypes of Gastric Cancers". Gastroenterology. 161 (2): 727. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.03.047. PMID 33798523.
- "The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2018". NobelPrize.org. Retrieved 4 August 2019.
- ^ Kucerova P, Cervinkova M (April 2016). "Spontaneous regression of tumour and the role of microbial infection--possibilities for cancer treatment". Anti-Cancer Drugs. 27 (4): 269–77. doi:10.1097/CAD.0000000000000337. PMC 4777220. PMID 26813865.
- Kienle GS (March 2012). "Fever in Cancer Treatment: Coley's Therapy and Epidemiologic Observations". Global Advances in Health and Medicine. 1 (1): 92–100. doi:10.7453/gahmj.2012.1.1.016. PMC 3833486. PMID 24278806.
- McCarthy EF (2006). "The toxins of William B. Coley and the treatment of bone and soft-tissue sarcomas". The Iowa Orthopaedic Journal. 26: 154–8. PMC 1888599. PMID 16789469.
- Dissertation Abstracts International: Retrospective Index, Volumes I-XXIX. University Microfilms. 1970.
- "Commencement speakers praise, advise local graduates . . ". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- "Immunotherapy to Treat Cancer". National Cancer Institute. 24 September 2019. Retrieved 14 October 2023.
- "Immunotherapy for Cancer: An Overview". Oncodaily.com. 29 May 2024. Retrieved 29 May 2024.
- Galluzzi L, Vacchelli E, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Buqué A, Senovilla L, Baracco EE, et al. (December 2014). "Classification of current anticancer immunotherapies". Oncotarget. 5 (24): 12472–12508. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.2998. PMC 4350348. PMID 25537519.
- "Types of Biological Therapy". SEER Training Modules. National Cancer Institute. Retrieved 14 October 2023.
- "What are Cancer Vaccines?". Cancer.Net. 30 September 2013. Retrieved 15 August 2021.
- Riddell SR (July 2001). "Progress in cancer vaccines by enhanced self-presentation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (16): 8933–35. Bibcode:2001PNAS...98.8933R. doi:10.1073/pnas.171326398. PMC 55350. PMID 11481463.
- ^ Palucka K, Banchereau J (July 2013). "Dendritic-cell-based therapeutic cancer vaccines". Immunity. 39 (1): 38–48. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.004. PMC 3788678. PMID 23890062.
- Hirayama M, Nishimura Y (July 2016). "The present status and future prospects of peptide-based cancer vaccines". International Immunology. 28 (7): 319–28. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxw027. PMID 27235694.
- Dastmalchi F, Karachi A, Mitchell D (June 2018). "Dendritic Cell Therapy". eLS. American Cancer Society. pp. 1–27. doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0024243. ISBN 9780470015902. S2CID 155185753.
- Gardner TA, Elzey BD, Hahn NM (April 2012). "Sipuleucel-T (Provenge) autologous vaccine approved for treatment of men with asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic castrate-resistant metastatic prostate cancer". Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 8 (4): 534–39. doi:10.4161/hv.19795. PMID 22832254.
- Oudard S (May 2013). "Progress in emerging therapies for advanced prostate cancer". Cancer Treatment Reviews. 39 (3): 275–89. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.09.005. PMID 23107383.
- Sims RB (June 2012). "Development of sipuleucel-T: autologous cellular immunotherapy for the treatment of metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer". Vaccine. 30 (29): 4394–97. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.11.058. PMID 22122856.
- Shore ND, Mantz CA, Dosoretz DE, Fernandez E, Myslicki FA, McCoy C, et al. (January 2013). "Building on sipuleucel-T for immunologic treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer". Cancer Control. 20 (1): 7–16. doi:10.1177/107327481302000103. PMID 23302902.
- Restifo NP, Dudley ME, Rosenberg SA (March 2012). "Adoptive immunotherapy for cancer: harnessing the T cell response". Nature Reviews. Immunology. 12 (4): 269–81. doi:10.1038/nri3191. PMC 6292222. PMID 22437939.
- Barros MS, de Araújo ND, Magalhães-Gama F, Pereira Ribeiro TL, Alves Hanna FS, Tarragô AM, et al. (22 September 2021). "γδ T Cells for Leukemia Immunotherapy: New and Expanding Trends". Frontiers in Immunology. 12: 729085. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.729085. PMC 8493128. PMID 34630403.
- Wilhelm M, Smetak M, Schaefer-Eckart K, Kimmel B, Birkmann J, Einsele H, et al. (February 2014). "Successful adoptive transfer and in vivo expansion of haploidentical γδ T cells". Journal of Translational Medicine. 12: 45. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-12-45. PMC 3926263. PMID 24528541.
- Office of the Commissioner. "Press Announcements – FDA approval brings first gene therapy to the United States". fda.gov. Retrieved 13 December 2017.
- "FDA approves CAR-T cell therapy to treat adults with certain types of large B-cell lymphoma". fda.gov. 18 October 2017. Retrieved 8 November 2017.
- Irving M (29 March 2022). "Implantable immunotherapy "factory" fights cancer faster, more effectively". New Atlas. Retrieved 29 March 2022.
- Agarwalla P, Ogunnaike EA, Ahn S, Froehlich KA, Jansson A, Ligler FS, et al. (March 2022). "Bioinstructive implantable scaffolds for rapid in vivo manufacture and release of CAR-T cells". Nature Biotechnology. 40 (8): 1250–1258. doi:10.1038/s41587-022-01245-x. PMC 9376243. PMID 35332339.
- ^ Zhao L, Cao YJ (2019). "Engineered T Cell Therapy for Cancer in the Clinic". Frontiers in Immunology. 10: 2250. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02250. PMC 6798078. PMID 31681259.
- "TCR Vs. CAR-T: What is CAR-T Cell, TCR Therapy, and What are They Used For?". Akadeum Life Sciences. 23 November 2020. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ^ Yao S, Zhu Y, Chen L (February 2013). "Advances in targeting cell surface signalling molecules for immune modulation". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 12 (2): 130–146. doi:10.1038/nrd3877. PMC 3698571. PMID 23370250.
- ^ Scott AM, Wolchok JD, Old LJ (March 2012). "Antibody therapy of cancer". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 12 (4): 278–87. doi:10.1038/nrc3236. PMID 22437872. S2CID 205469234.
- ^ Harding FA, Stickler MM, Razo J, DuBridge RB (May–June 2010). "The immunogenicity of humanized and fully human antibodies: residual immunogenicity resides in the CDR regions". mAbs. 2 (3): 256–65. doi:10.4161/mabs.2.3.11641. PMC 2881252. PMID 20400861.
- Gadd AJ, Greco F, Cobb AJ, Edwards AD (August 2015). "Targeted Activation of Toll-Like Receptors: Conjugation of a Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist to a Monoclonal Antibody Maintains Antigen Binding and Specificity" (PDF). Bioconjugate Chemistry. 26 (8): 1743–52. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00302. PMID 26133029. S2CID 26307107.
We demonstrate here for the first time the successful conjugation of a small molecule TLR7 agonist to an antitumor mAb (the anti-hCD20 rituximab) without compromising antigen specificity.
- Pincetic A, Bournazos S, DiLillo DJ, Maamary J, Wang TT, Dahan R, et al. (August 2014). "Type I and type II Fc receptors regulate innate and adaptive immunity". Nature Immunology. 15 (8): 707–16. doi:10.1038/ni.2939. PMC 7430760. PMID 25045879.
- Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, et al. (June 2012). "Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer". The New England Journal of Medicine. 366 (26): 2443–54. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1200690. PMC 3544539. PMID 22658127.
- Dahan R, Sega E, Engelhardt J, Selby M, Korman AJ, Ravetch JV (October 2015). "FcγRs Modulate the Anti-tumor Activity of Antibodies Targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 Axis". Cancer Cell. 28 (4): 543. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2015.09.011. PMID 28854351.
- Arlauckas SP, Garris CS, Kohler RH, Kitaoka M, Cuccarese MF, Yang KS, et al. (May 2017). "In vivo imaging reveals a tumor-associated macrophage-mediated resistance pathway in anti-PD-1 therapy". Science Translational Medicine. 9 (389): eaal3604. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3604. PMC 5734617. PMID 28490665.
- Dahan R, Barnhart BC, Li F, Yamniuk AP, Korman AJ, Ravetch JV (July 2016). "Therapeutic Activity of Agonistic, Human Anti-CD40 Monoclonal Antibodies Requires Selective FcγR Engagement". Cancer Cell. 29 (6): 820–31. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2016.05.001. PMC 4975533. PMID 27265505.
- Weiner LM, Surana R, Wang S (May 2010). "Monoclonal antibodies: versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy". Nature Reviews. Immunology. 10 (5): 317–27. doi:10.1038/nri2744. PMC 3508064. PMID 20414205.
- Seidel UJ, Schlegel P, Lang P (2013). "Natural killer cell mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in tumor immunotherapy with therapeutic antibodies". Frontiers in Immunology. 4: 76. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00076. PMC 3608903. PMID 23543707.
- Jaiswal S, Chao MP, Majeti R, Weissman IL (June 2010). "Macrophages as mediators of tumor immunosurveillance". Trends in Immunology. 31 (6): 212–19. doi:10.1016/j.it.2010.04.001. PMC 3646798. PMID 20452821.
- ^ Weiskopf K (May 2017). "Cancer immunotherapy targeting the CD47/SIRPα axis". European Journal of Cancer. 76: 100–09. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2017.02.013. PMID 28286286.
- Matlung HL, Szilagyi K, Barclay NA, van den Berg TK (March 2017). "The CD47-SIRPα signaling axis as an innate immune checkpoint in cancer". Immunological Reviews. 276 (1): 145–64. doi:10.1111/imr.12527. PMID 28258703. S2CID 6275163.
- Veillette A, Chen J (March 2018). "SIRPα-CD47 Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Anticancer Therapy". Trends in Immunology. 39 (3): 173–84. doi:10.1016/j.it.2017.12.005. PMID 29336991.
- Ahmed M, Cheung NK (January 2014). "Engineering anti-GD2 monoclonal antibodies for cancer immunotherapy". FEBS Letters. 588 (2): 288–97. Bibcode:2014FEBSL.588..288A. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.11.030. PMID 24295643.
- Gelderman KA, Tomlinson S, Ross GD, Gorter A (March 2004). "Complement function in mAb-mediated cancer immunotherapy". Trends in Immunology. 25 (3): 158–64. doi:10.1016/j.it.2004.01.008. PMID 15036044.
- Waldmann TA (March 2003). "Immunotherapy: past, present and future". Nature Medicine. 9 (3): 269–77. doi:10.1038/nm0303-269. PMID 12612576. S2CID 9745527.
- Demko S, Summers J, Keegan P, Pazdur R (February 2008). "FDA drug approval summary: alemtuzumab as single-agent treatment for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia". The Oncologist. 13 (2): 167–74. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.503.6960. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2007-0218. PMID 18305062.
- "FDA approves new, targeted treatment for bladder cancer". FDA. 18 May 2016. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
- "FDA approves atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 12 September 2024. Archived from the original on 14 September 2024. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "FDA Approves Genentech's Tecentriq Hybreza, the First and Only Subcutaneous Anti-PD-(L)1 Cancer Immunotherapy". Genentech (Press release). 12 September 2024. Archived from the original on 13 September 2024. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
- "Halozyme Announces FDA Approval of Roche's Tecentriq Hybreza With Enhanze for Multiple Types of Cancer" (Press release). Halozyme Therapeutics. 12 September 2024. Archived from the original on 13 September 2024. Retrieved 14 September 2024 – via PR Newswire.
- "US Food and Drug Administration – Avelumab Prescribing Label" (PDF).
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. "Approved Drugs – Durvalumab (Imfinzi)". fda.gov. Retrieved 6 May 2017.
- "FDA approves durvalumab after chemoradiation for unresectable stage III NSCLC". FDA. 9 February 2019.
- "Bristol-Myers Squibb and AbbVie Receive U.S. FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation for Elotuzumab, an Investigational Humanized Monoclonal Antibody for Multiple Myeloma | BMS Newsroom".
- Pazdur R. "FDA approval for Ipilimumab". Archived from the original on 6 April 2015. Retrieved 7 November 2013.
- Sharma P, Allison JP (April 2015). "The future of immune checkpoint therapy". Science. 348 (6230): 56–61. Bibcode:2015Sci...348...56S. doi:10.1126/science.aaa8172. PMID 25838373. S2CID 4608450.
- "Opdivo (nivolumab) FDA Approval History". Drugs.com.
- Lemery SJ, Zhang J, Rothmann MD, Yang J, Earp J, Zhao H, et al. (September 2010). "U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval: ofatumumab for the treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia refractory to fludarabine and alemtuzumab". Clinical Cancer Research. 16 (17): 4331–38. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0570. PMID 20601446.
- "FDA approves pembrolizumab in combination with chemotherapy for first-line treatment of metastatic squamous NSCLC". FDA. 20 December 2019.
- "Pembrolizumab (KEYTRUDA) for classical Hodgkin lymphoma". FDA. 9 February 2019.
- "FDA approves pembrolizumab for Merkel cell carcinoma". FDA. 20 December 2019.
- "FDA approves pembrolizumab for treatment of relapsed or refractory PMBCL". FDA. 9 February 2019.
- "National Cancer Institute - Pembrolizumab Use in Cancer". 18 September 2014.
- James JS, Dubs G (December 1997). "FDA approves new kind of lymphoma treatment. Food and Drug Administration". AIDS Treatment News (284): 2–3. PMID 11364912.
- "Rituxan Hycela- rituximab and hyaluronidase injection, solution". DailyMed. 8 July 2024. Retrieved 15 September 2024.
- Byrd JC, Stilgenbauer S, Flinn IW (1 January 2004). "Chronic lymphocytic leukemia". Hematology. American Society of Hematology. Education Program. 2004 (1): 163–83. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2004.1.163. PMID 15561682.
- Domagała A, Kurpisz M (2001). "CD52 antigen--a review". Medical Science Monitor. 7 (2): 325–31. PMID 11257744.
- Dearden C (July 2012). "How I treat prolymphocytic leukemia". Blood. 120 (3): 538–51. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-01-380139. PMID 22649104.
- "Tecentriq- atezolizumab injection, solution". DailyMed. 3 June 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2020.
- "FDA grants approval to atezolizumab for alveolar soft part sarcoma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 9 December 2022. Retrieved 20 December 2022.
- Madhusoodanan J (9 August 2023). "How a controversial US drug policy could be harming cancer patients worldwide". Nature. 620 (7973): 264–267. Bibcode:2023Natur.620..264M. doi:10.1038/d41586-023-02492-x. PMID 37558845. Retrieved 21 August 2023.
- "Genentech Presents Positive Results of Atezolizumab in Advanced Bladder Cancer". 2 October 2015.
- ^ "Tecentriq EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 29 September 2017. Retrieved 31 July 2020. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- "FDA approves new, targeted treatment for bladder cancer" (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 18 May 2016. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "European Commission approves Roche's Tecentriq SC, the EU's first PD-(L)1 cancer immunotherapy subcutaneous injection for multiple cancer types – Company Announcement - FT.com". markets.ft.com. Retrieved 5 March 2024.
- ^ "Tecentriq Hybreza- atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs injection". DailyMed. 25 September 2024. Retrieved 5 October 2024.
- ^ "FDA approves atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 12 September 2024. Archived from the original on 14 September 2024. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "FDA Approves Genentech's Tecentriq Hybreza, the First and Only Subcutaneous Anti-PD-(L)1 Cancer Immunotherapy". Genentech (Press release). 12 September 2024. Archived from the original on 13 September 2024. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
- "Halozyme Announces FDA Approval of Roche's Tecentriq Hybreza With Enhanze for Multiple Types of Cancer" (Press release). Halozyme Therapeutics. 12 September 2024. Archived from the original on 13 September 2024. Retrieved 14 September 2024 – via PR Newswire.
- "Bavencio- avelumab injection, solution, concentrate". DailyMed. 2 July 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ "FDA approves first treatment for rare form of skin cancer". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 23 March 2017. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- "Public summary of opinion on orphan designation: Avelumab for the treatment of gastric cancer" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 9 January 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 August 2017. Retrieved 29 April 2017.
- "Bavencio: EPAR - Product Information" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 18 September 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 June 2018. Retrieved 23 February 2018.
- Merck-Pfizer Alliance. "Merck-Pfizer Alliance Avelumab Fact Sheet" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 May 2017. Retrieved 2 December 2015.
- "FDA approves durvalumab after chemoradiation for unresectable stage III NSCLC". FDA. 9 February 2019.
- "Prescription medicines: registration of new chemical entities in Australia, 2016". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 10 April 2023.
- "Health Canada New Drug Authorizations: 2016 Highlights". Health Canada. 14 March 2017. Retrieved 7 April 2024.
- ^ "Elotuzumab Package Insert" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 December 2015.
- "Empliciti (elotuzumab) for Injection, for Intravenous Use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Empliciti (elotuzumab) for US Healthcare Professionals. Princeton, New Jersey: Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 December 2015.
- "Bristol Myers Squibb Reports Primary Results of ELOQUENT-1 Study Evaluating Empliciti (elotuzumab) Plus Revlimid (lenalidomide) and Dexamethasone in Patients with Newly Diagnosed, Untreated Multiple Myeloma". news.bms.com. Retrieved 18 March 2021.
- "Bristol-Myers Squibb and AbbVie Receive U.S. FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation for Elotuzumab, an Investigational Humanized Monoclonal Antibody for Multiple Myeloma" (Press release). Princeton, New Jersey and North Chicago, Illinois: Bristol-Myers Squibb. 19 May 2014. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- "Bristol-Myers Squibb and AbbVie Receive FDA Approval of Empliciti™ (elotuzumab) for the Treatment of Patients with Multiple Myeloma Who Have Received One to Three Prior Therapies". news.bms.com. Retrieved 18 March 2021.
- BMS gets two new cancer approvals in Europe. May 2016
- "U.S. Food and Drug Administration Approves Empliciti® (elotuzumab) Plus Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone, a New Immunotherapy Combination for Certain Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma". news.bms.com. Retrieved 18 March 2021.
- ^ Sondak VK, Smalley KS, Kudchadkar R, Grippon S, Kirkpatrick P (June 2011). "Ipilimumab". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 10 (6): 411–12. doi:10.1038/nrd3463. PMID 21629286.
- ^ Lipson EJ, Drake CG (November 2011). "Ipilimumab: an anti-CTLA-4 antibody for metastatic melanoma". Clinical Cancer Research. 17 (22): 6958–62. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1595. PMC 3575079. PMID 21900389.
- ^ Thumar JR, Kluger HM (December 2010). "Ipilimumab: a promising immunotherapy for melanoma". Oncology. 24 (14): 1280–88. PMID 21294471.
- ^ Chambers CA, Kuhns MS, Egen JG, Allison JP (2001). "CTLA-4-mediated inhibition in regulation of T cell responses: mechanisms and manipulation in tumor immunotherapy". Annual Review of Immunology. 19: 565–94. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.565. PMID 11244047.
- ^ Postow MA, Callahan MK, Wolchok JD (June 2015). "Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 33 (17): 1974–82. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.59.4358. PMC 4980573. PMID 25605845.
- ^ Pardoll DM (March 2012). "The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 12 (4): 252–64. doi:10.1038/nrc3239. PMC 4856023. PMID 22437870.
- Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M, Floudas CS, Soni P, Chandra AB (2017). "Current Diagnosis and Management of Immune Related Adverse Events (irAEs) Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 8: 49. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00049. PMC 5296331. PMID 28228726.
- Castillo J, Perez K (2010). "The role of ofatumumab in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia resistant to previous therapies". Journal of Blood Medicine. 1: 1–8. doi:10.2147/jbm.s7284. PMC 3262337. PMID 22282677.
- Zhang B (July–August 2009). "Ofatumumab". mAbs. 1 (4): 326–31. doi:10.4161/mabs.1.4.8895. PMC 2726602. PMID 20068404.
- "Pembrolizumab label" (PDF). FDA. May 2017. linked from Index page at FDA website November 2016
- "Pembrolizumab label at eMC". UK Electronic Medicines Compendium. 27 January 2017. Archived from the original on 13 December 2017. Retrieved 4 October 2018.
- "HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION - KEYTRUDA (Pembrolizumab)" (PDF). fda.gov. June 2018. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- Keating GM (July 2010). "Rituximab: a review of its use in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, low-grade or follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma". Drugs. 70 (11): 1445–76. doi:10.2165/11201110-000000000-00000. PMID 20614951.
- Plosker GL, Figgitt DP (2003). "Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia". Drugs. 63 (8): 803–43. doi:10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. PMID 12662126.
- Cerny T, Borisch B, Introna M, Johnson P, Rose AL (November 2002). "Mechanism of action of rituximab". Anti-Cancer Drugs. 13 (Suppl 2): S3–10. doi:10.1097/00001813-200211002-00002. PMID 12710585. S2CID 25061294.
- Janeway C, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik M (2001). Immunobiology (Fifth ed.). New York and London: Garland Science. ISBN 978-0-8153-4101-7.
- Weiner GJ (April 2010). "Rituximab: mechanism of action". Seminars in Hematology. 47 (2): 115–23. doi:10.1053/j.seminhematol.2010.01.011. PMC 2848172. PMID 20350658.
- "Trastuzumab - Drugs.com". www.drugs.com. Archived from the original on 7 April 2017. Retrieved 21 December 2016.
- ^ "Kanjinti- trastuzumab-anns injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution; Kanjinti- trastuzumab-anns kit". DailyMed. 13 October 2022. Archived from the original on 5 December 2021. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- ^ "Ogivri- trastuzumab kit; Ogivri- trastuzumab injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution". DailyMed. 8 February 2021. Archived from the original on 7 December 2022. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- ^ "Ontruzant- trastuzumab injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution; Ontruzant- ontruzant kit". DailyMed. 31 January 2023. Archived from the original on 13 August 2022. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- ^ "Trazimera- trastuzumab-qyyp kit; Trazimera- trastuzumab-qyyp injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution". DailyMed. 14 February 2022. Archived from the original on 7 December 2022. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- ^ "Highlights of prescribing information" (PDF). www.accessdata.fda.gov.
- "Regulatory Decision Summary for Adheroza". Drug and Health Products Portal. 20 August 2024. Retrieved 27 December 2024.
- "Herzuma- trastuzumab kit; Herzuma- trastuzumab injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution". DailyMed. 6 February 2023. Archived from the original on 16 May 2021. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- "Herzuma EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 8 November 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- "Herzuma PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 13 February 2018. Retrieved 30 September 2024.
- "Herwenda EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 15 November 2023. Archived from the original on 3 December 2023. Retrieved 11 December 2023. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- "Herwenda Product information". Union Register of medicinal products. 16 November 2023. Archived from the original on 26 November 2023. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- "Kanjinti EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 31 October 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- "Kanjinti PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 18 May 2018. Retrieved 30 September 2024.
- "Ogivri- trastuzumab kit; Ogivri- trastuzumab injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution". DailyMed. 28 July 2023. Archived from the original on 10 March 2024. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- "Ontruzant EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 4 August 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- "Ontruzant PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 17 November 2017. Retrieved 30 September 2024.
- ^ "Trastucip and Tuzucip APMDS". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 29 July 2022. Archived from the original on 30 July 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- "Tuznue EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 26 July 2024. Retrieved 29 July 2024. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- "Tuznue PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 24 September 2024. Retrieved 27 September 2024.
- "Zercepac EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 26 May 2020. Archived from the original on 28 July 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- "Zercepac PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 28 July 2020. Retrieved 30 September 2024.
- ^ "Trastuzumab Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 3 December 2019. Retrieved 3 December 2019.
- "Herceptin (trastuzumab) powder for injection". Roche Products Pty Limited. 7 May 2021. Archived from the original on 8 March 2023. Retrieved 8 January 2023.
- "Trastuzumab". Roche Products Pty Limited. 7 April 2022. Archived from the original on 8 January 2023.
- "Summary Basis of Decision - Ontruzant". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Archived from the original on 6 August 2022. Retrieved 6 August 2022.
- ^ "Herceptin- trastuzumab kit Herceptin- trastuzumab injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution". DailyMed. 30 September 2019. Archived from the original on 4 August 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- "Ogivri EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 24 March 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- "Ogivri PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 14 December 2018. Retrieved 30 September 2024.
- ^ "Trastuzumab". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- "FDA approves first biosimilar for the treatment of certain breast and stomach cancers". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 10 September 2019. Archived from the original on 15 December 2019. Retrieved 18 February 2020.
- ^ "Herceptin EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 28 July 2020. Retrieved 28 July 2020.
- British national formulary : BNF 69 (69 ed.). British Medical Association. 2015. p. 626. ISBN 978-0-85711-156-2.
- "Trastuzumab Product Approval Information - Licensing Action 9/25/98". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 18 December 2015. Archived from the original on 28 January 2017. Retrieved 3 December 2019.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- Ganesan S, Mehnert J (9 March 2020). "Biomarkers for Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockade". Annual Review of Cancer Biology. 4 (1): 331–351. doi:10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030419-033604.
- Magahis PT, Maron SB, Cowzer D, King S, Schattner M, Janjigian Y, et al. (October 2023). "Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection status on outcomes among patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors". J Immunother Cancer. 11 (10): e007699. doi:10.1136/jitc-2023-007699. PMC 10619027. PMID 37899129.
- Yu B, Peppelenbosch M, Fuhler G (January 2024). "Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection status on outcomes among patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors". J Immunother Cancer. 12 (1): e008422. doi:10.1136/jitc-2023-008422. PMC 10806497. PMID 38242721.
- Granier C, De Guillebon E, Blanc C, Roussel H, Badoual C, Colin E, et al. (2017). "Mechanisms of action and rationale for the use of checkpoint inhibitors in cancer". ESMO Open. 2 (2): e000213. doi:10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000213. PMC 5518304. PMID 28761757.
- Cameron F, Whiteside G, Perry C (May 2011). "Ipilimumab: first global approval". Drugs. 71 (8): 1093–104. doi:10.2165/11594010-000000000-00000. PMID 21668044.
- Lynch TJ, Bondarenko I, Luft A, Serwatowski P, Barlesi F, Chacko R, et al. (June 2012). "Ipilimumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line treatment in stage IIIB/IV non-small-cell lung cancer: results from a randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase II study". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 30 (17): 2046–54. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.38.4032. PMID 22547592.
- Le DT, Lutz E, Uram JN, Sugar EA, Onners B, Solt S, et al. (September 2013). "Evaluation of ipilimumab in combination with allogeneic pancreatic tumor cells transfected with a GM-CSF gene in previously treated pancreatic cancer". Journal of Immunotherapy. 36 (7): 382–89. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e31829fb7a2. PMC 3779664. PMID 23924790.
- Clinical trial number NCT01928394 for "A Study of Nivolumab by Itself or Nivolumab Combined With Ipilimumab in Patients With Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Gougis P, Hamy AS, Jochum F, Bihan K, Carbonnel M, Salem JE, et al. (April 2024). "Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Use During Pregnancy and Outcomes in Pregnant Individuals and Newborns". JAMA Network Open. 7 (4): e245625. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5625. PMC 11024778. PMID 38630478.
- ^ van Hooren L, Sandin LC, Moskalev I, Ellmark P, Dimberg A, Black P, et al. (February 2017). "Local checkpoint inhibition of CTLA-4 as a monotherapy or in combination with anti-PD1 prevents the growth of murine bladder cancer". European Journal of Immunology. 47 (2): 385–93. doi:10.1002/eji.201646583. PMID 27873300. S2CID 2463514.
- ^ Pollack A (18 May 2016). "F.D.A. Approves an Immunotherapy Drug for Bladder Cancer". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 21 May 2016.
- Steele A (5 August 2016). "Bristol Myers: Opdivo Failed to Meet Endpoint in Key Lung-Cancer Study". The Wall Street Journal. ISSN 0099-9660. Retrieved 5 August 2016.
- BeiGene, Ltd. (2016). "BeiGene Presents Initial Clinical Data on PD-1 Antibody BGB-A317 at the 2016 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting" (Press release). Globe Newswire.
- Roche. "FDA grants priority review for Roche's cancer immunotherapy atezolizumab in specific type of lung cancer".
- Merck Group. "Immuno-oncology Avelumab".
- Cure today (April 2016). "Durvalumab continues to progress in treatment of advanced bladder cancer".
- Avacta Life Sciences. "Affimer biotherapeutics target cancer's off-switch with PD-L1 inhibitor". Archived from the original on 6 August 2016. Retrieved 16 May 2016.
- Palmer DC, Guittard GC, Franco Z, Crompton JG, Eil RL, Patel SJ, et al. (November 2015). "Cish actively silences TCR signaling in CD8+ T cells to maintain tumor tolerance". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 212 (12): 2095–2113. doi:10.1084/jem.20150304. PMC 4647263. PMID 26527801.
- Guittard G, Dios-Esponera A, Palmer DC, Akpan I, Barr VA, Manna A, et al. (March 2018). "The Cish SH2 domain is essential for PLC-γ1 regulation in TCR stimulated CD8 T cells". Scientific Reports. 8 (1): 5336. Bibcode:2018NatSR...8.5336G. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-23549-2. PMC 5871872. PMID 29593227.
- Palmer DC, Guittard GC, Franco Z, Crompton JG, Eil RL, Patel SJ, et al. (November 2015). "Cish actively silences TCR signaling in CD8+ T cells to maintain tumor tolerance". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 212 (12): 2095–2113. doi:10.1084/jem.20150304. PMC 4647263. PMID 26527801.
- Palmer DC, Webber BR, Patel Y, Johnson MJ, Kariya CM, Lahr WS, et al. (25 September 2020). "Internal checkpoint regulates T cell neoantigen reactivity and susceptibility to PD1 blockade". bioRxiv 10.1101/2020.09.24.306571.
- Pfirschke C, Engblom C, Rickelt S, Cortez-Retamozo V, Garris C, Pucci F, et al. (February 2016). "Immunogenic Chemotherapy Sensitizes Tumors to Checkpoint Blockade Therapy". Immunity. 44 (2): 343–54. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2015.11.024. PMC 4758865. PMID 26872698.
- Ott PA, Hodi FS, Kaufman HL, Wigginton JM, Wolchok JD (2017). "Combination immunotherapy: a road map". Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer. 5: 16. doi:10.1186/s40425-017-0218-5. PMC 5319100. PMID 28239469.
- Mahoney KM, Rennert PD, Freeman GJ (August 2015). "Combination cancer immunotherapy and new immunomodulatory targets". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 14 (8): 561–84. doi:10.1038/nrd4591. PMID 26228759. S2CID 2220735.
- Mehta A, Oklu R, Sheth RA (2015). "Thermal Ablative Therapies and Immune Checkpoint Modulation: Can Locoregional Approaches Effect a Systemic Response?". Gastroenterology Research and Practice. 2016: 9251375. doi:10.1155/2016/9251375. PMC 4802022. PMID 27051417.
- Tang J, Shalabi A, Hubbard-Lucey VM (January 2018). "Comprehensive analysis of the clinical immuno-oncology landscape". Annals of Oncology. 29 (1): 84–91. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdx755. PMID 29228097.
- Perry CJ, Muñoz-Rojas AR, Meeth KM, Kellman LN, Amezquita RA, Thakral D, et al. (March 2018). "Myeloid-targeted immunotherapies act in synergy to induce inflammation and antitumor immunity". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 215 (3): 877–93. doi:10.1084/jem.20171435. PMC 5839759. PMID 29436395.
- Rodell CB, Arlauckas SP, Cuccarese MF, Garris CS, Li R, Ahmed MS, et al. (21 May 2018). "TLR7/8-agonist-loaded nanoparticles promote the polarization of tumour-associated macrophages to enhance cancer immunotherapy". Nature Biomedical Engineering. 2 (8): 578–588. doi:10.1038/s41551-018-0236-8. PMC 6192054. PMID 31015631.
- Zak J, Pratumchai I, Marro BS, Marquardt KL, Zavareh RB, Lairson LL, et al. (June 2024). "JAK inhibition enhances checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma". Science. 384 (6702): eade8520. Bibcode:2024Sci...384e8520Z. doi:10.1126/science.ade8520. PMC 11283877. PMID 38900864.
- ^ Dranoff G (January 2004). "Cytokines in cancer pathogenesis and cancer therapy". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 4 (1): 11–22. doi:10.1038/nrc1252. PMID 14708024. S2CID 42092046.
- "Immunotherapy For Cancer". Retrieved 12 May 2023.
- Dunn GP, Koebel CM, Schreiber RD (November 2006). "Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting". Nature Reviews. Immunology. 6 (11): 836–48. doi:10.1038/nri1961. PMID 17063185. S2CID 223082.
- Lasfar A, Abushahba W, Balan M, Cohen-Solal KA (2011). "Interferon lambda: a new sword in cancer immunotherapy". Clinical & Developmental Immunology. 2011: 349575. doi:10.1155/2011/349575. PMC 3235441. PMID 22190970.
- Razaghi A, Owens L, Heimann K (December 2016). "Review of the recombinant human interferon gamma as an immunotherapeutic: Impacts of production platforms and glycosylation". Journal of Biotechnology. 240: 48–60. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.10.022. PMID 27794496.
- Coventry BJ, Ashdown ML (2012). "The 20th anniversary of interleukin-2 therapy: bimodal role explaining longstanding random induction of complete clinical responses". Cancer Management and Research. 4: 215–21. doi:10.2147/cmar.s33979. PMC 3421468. PMID 22904643.
- "FDA approves Encorafenib and Binimetinib in combination for unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF mutations". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 27 June 2018.
- "Cancer Genetics offers the FDA-approved DAKO PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx companion diagnostic test for KEYTRUDA®". Cancer Genetics Inc. 3 February 2016.
- Udall M, Rizzo M, Kenny J, Doherty J, Dahm S, Robbins P, et al. (February 2018). "PD-L1 diagnostic tests: a systematic literature review of scoring algorithms and test-validation metrics". Diagnostic Pathology. 13 (1): 12. doi:10.1186/s13000-018-0689-9. PMC 5807740. PMID 29426340.
- Dacic S (April 2018). "Time is up for PD-L1 testing standardization in lung cancer". Annals of Oncology. 29 (4): 791–792. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdy069. PMID 29688334.
- Goodman AM, Kato S, Bazhenova L, Patel SP, Frampton GM, Miller V, et al. (November 2017). "Tumor Mutational Burden as an Independent Predictor of Response to Immunotherapy in Diverse Cancers". Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 16 (11): 2598–2608. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0386. PMC 5670009. PMID 28835386.
- "FDA Accepts sBLA for First-Line Nivolumab Plus Low-Dose Ipilimumab in NSCLC With Tumor Mutational Burden ≥ 10 mut/mb". ASCO Post. American Society of Clinical Oncology. 7 February 2018.
- Liu D, Schilling B, Liu D, Sucker A, Livingstone E, Jerby-Arnon L, et al. (December 2019). "Integrative molecular and clinical modeling of clinical outcomes to PD1 blockade in patients with metastatic melanoma". Nature Medicine. 25 (12): 1916–1927. doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0654-5. PMC 6898788. PMID 31792460.
- Motzer RJ, Robbins PB, Powles T, Albiges L, Haanen JB, Larkin J, et al. (September 2020). "Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in advanced renal cell carcinoma: biomarker analysis of the phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 trial". Nature Medicine. 26 (11): 1733–1741. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1044-8. PMC 8493486. PMID 32895571.
- Flam F (22 January 2015). "Duke U Cancer Fraud Scandal: A Cautionary Tale For Obama's Precision Medicine Push". Forbes. Retrieved 21 April 2024.
- "Liquid biopsies" for cancer screening: Life-saving tests, or overdiagnosis and overtreatment taken to a new level? David Gorski, 28 September 2015, Science-Based Medicine website
- A public discussion by cancer patients from 2011 on the melanoma.org website shows costs and claims.
- Fukuhara H, Ino Y, Todo T (October 2016). "Oncolytic virus therapy: A new era of cancer treatment at dawn". Cancer Science. 107 (10): 1373–79. doi:10.1111/cas.13027. PMC 5084676. PMID 27486853.
- Haddad D (2017). "Genetically Engineered Vaccinia Viruses As Agents for Cancer Treatment, Imaging, and Transgene Delivery". Frontiers in Oncology. 7: 96. doi:10.3389/fonc.2017.00096. PMC 5440573. PMID 28589082.
- Marin-Acevedo JA, Soyano AE, Dholaria B, Knutson KL, Lou Y (January 2018). "Cancer immunotherapy beyond immune checkpoint inhibitors". Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 11 (1): 8. doi:10.1186/s13045-017-0552-6. PMC 5767051. PMID 29329556.
- Lawler SE, Speranza MC, Cho CF, Chiocca EA (June 2017). "Oncolytic Viruses in Cancer Treatment: A Review". JAMA Oncology. 3 (6): 841–849. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.2064. PMID 27441411. S2CID 39321536.
- Aleem E (June 2013). "β-Glucans and their applications in cancer therapy: focus on human studies". Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry. 13 (5): 709–19. doi:10.2174/1871520611313050007. PMID 23293888.
- Snyder A, Makarov V, Merghoub T, Yuan J, Zaretsky JM, Desrichard A, et al. (December 2014). "Genetic basis for clinical response to CTLA-4 blockade in melanoma". The New England Journal of Medicine. 371 (23): 2189–99. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1406498. PMC 4315319. PMID 25409260.
- Schumacher TN, Schreiber RD (April 2015). "Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy". Science. 348 (6230): 69–74. Bibcode:2015Sci...348...69S. doi:10.1126/science.aaa4971. PMID 25838375.
- "Coriolus Versicolor". American Cancer Society. Archived from the original on 15 February 2006.
External links
- A primer on "Immunotherapy to Treat Cancer", NIH
- Immunotherapy – Using the Immune System to Treat Cancer Archived 4 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- Cancer Research Institute – What is Cancer Immunotherapy
- Association for Immunotherapy of Cancer
- Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer
- "And Then There Were Five". Economist.
- "Discover the Science of Immuno-Oncology". Bristol-Myers Squibb. Archived from the original on 10 October 2014. Retrieved 13 March 2014.
- Eggermont A, Finn O (September 2012). "Advances in immuno-oncology. Foreword". Annals of Oncology. 23 (Suppl 8): viii5. doi:10.1093/annonc/mds255. PMID 22918929.
- "Cancer Immunotherapy in Gujarat"
| Overview of tumors, cancer and oncology | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conditions |
| ||||||||||
| Staging/grading | |||||||||||
| Carcinogenesis | |||||||||||
| Misc. | |||||||||||
| Science Breakthroughs of the Year | |
|---|---|
| Science journal |
|