| Revision as of 18:53, 24 April 2014 editHirabutor (talk | contribs)273 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 18:04, 1 November 2024 edit undoYue (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers71,764 editsm Reverted edit by 217.246.63.194 (talk) to last version by MonkbotTag: Rollback | ||
| (171 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Hungarian subgroup of Eastern Iranic descent}} | |||
| ⚫ | {{Distinguish| |
||
| {{Redirect|Jassi|the Indian |
{{Redirect|Jassi|the Indian drama|Jassi Jaissi Koi Nahin}} | ||
| ⚫ | {{Distinguish|Jassy (disambiguation){{!}}Jassy}} | ||
| {{refimprove|date=June 2015}} | |||
| {{Infobox ethnic group | {{Infobox ethnic group | ||
| |group=Jasz people | | group = Jasz people | ||
| |image= | | image = | ||
| |caption = | | caption = | ||
| | population = | |||
| |poptime= unknown | |||
| |popplace |
| popplace = ], ], ] | ||
| |langs=] |
| langs = ], ] (extinct) | ||
| |rels=] | | rels = Christianity (]) | ||
| |related= ], ] |
| related = ], ], other ], ] and ] | ||
| }} | |||
| ⚫ | ]]] | ||
| '''Jász''' is the ] name for a people previously known by the ] '''Iasi''' or '''Jassy''', an ethnic minority within ], who live mostly in the '']'' county. | |||
| The '''Jász''' ({{langx|la|Jazones}}) are a ] subgroup of ] descent who have lived in Hungary since the 13th century. They live mostly in a region known as '']'', which comprises the north-western part of ] county. They are sometimes known in English by the ] '''Jassic''' and are also known by the ]s '''''Iasi''''' and '''''Jassy'''''. They originated as a nomadic ] people from the ]. | |||
| ==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| {{Main|Jászság}} | {{Main|Jászság}} | ||
| ⚫ | ]]] | ||
| The Jasz people live in the region known as "'']''" (roughly translatable as Jász-land), which comprises the north-western part of the '']'' county. Their cultural and political center is the town of ]. | |||
| The cultural and political center of Jászság is the town of ]. | |||
| Jászság is sometimes, erroneously, known as "]", after a somewhat related ] people, the ], who lived in a similar area in ancient times. | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| The |
The Jász people descend from member of a nomadic people, the ], who originated on the ] and settled in the ] during the 13th century, following the Mongol invasions.<ref>{{cite book |last=Foltz|first=Richard|title=The Ossetes: Modern-Day Scythians of the Caucasus. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YZswEAAAQBAJ |year=2022 |location=London |publisher=Bloomsbury, p. 50 |isbn=9780755618453|author-link=Richard Foltz }}</ref> Their language, which belonged to the East Iranian group that includes modern ], had reportedly become extinct by the 16th century, when the Jász adopted ]. | ||
| Despite frequent claims to the contrary, their name is unrelated to that of the ], one of the ] tribes which, along with the ], reached the borders of ] during the late 1st century BC, over a thousand years before the Jasz accompanied the Cumans into Hungary. This confusion is motivated by a superficial resemblance in the names as they appear in Roman transliteration: Hungarian ''sz'' is merely a digraph representing a voiceless ''s'' sound, while Greek zeta represented originally a ''voiced'' affricate (dz), or a combination of fricative and stop (zd), and the initial ''j'' in Jasz isn't original to the word either. So then the two names actually have no more than an ''a'' in common. This confusion has a long history, as Medieval scholars with a knowledge of classical history and writing in Latin were already referring to the Jasz as Jazygians. | |||
| ⚫ | The Jász people came to the Kingdom of Hungary, together with the ] ({{langx|hu|Kun}} people) when their lands to the east, in some in the later ] (see ] or {{lang|hu|Jászvásár}}) were ] in the mid-13th century. They were admitted by the Hungarian king, ] ], who hoped that the Jászs would assist in resisting the ]. Shortly after their entry, the relationship worsened dramatically between the ] and the Cumanian-Jász tribes, which then abandoned the country. After the end of the Mongol-Tatar invasion they returned and settled in the central part of the ], near the rivers ] and Tarna. | ||
| Due to the circumstance that the Alans did not leave any linguistic relics, the Iranic origin of the Alano-As people is not definitively confirmed, and even, open to contra-theories. According to the account of ] the language of the Alans was a mixture of (]) ] and (]) ] languages. This situation is complicated by the fact that not the Iranian Ossetians, but the Turkic ]-], likely descending from the ], are called ''As''/''Alan'' both by their neighbors, and by themselves,<ref name="Karatay">Karatay O., '''', 2003, pp.13-14</ref> an ethnic name which is also found in the place names ] and ].<ref>Agustí Alemany, Sources on Alans, Brill, 2000, p.6.</ref> In Greek-Byzantine sources the Jassic language is described to be known to come from line of ], who live next to ] and ].<ref>Ios. Bell Jud. Book 7, p.244. In: Agustí Alemany, , Brill, 2000, pp.6-7. Quote: | |||
| *"''...языкъ же ясьский вeдом есть, яко отъ печенежьского рода родися, живуща подлe Тани и Меотьскаго моря...''"; where ''ясьский'' (= Greek '''') is an adjective derived from ''Ясы'', a form of the ethnic name ''*as-''.</ref> John Scylitzes (§ 5.28.1) also make reference to the Alan princess ''Áλδή'' (''Alsu''), widow of “] of ]“ and mother of a certain Demetrius. "]" happened to be a popular Turkic female name favoring the Turkic Pecheneg (Badjanak) evidence.<ref>Agustí Alemany, , Brill, 2000, pp.6-7.</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | The |
||
| ⚫ | Initially, their main occupation was ]. Over the next two centuries they were assimilated into the Hungarian population; yet although their language disappeared, they preserved a distinct Jász identity. The Hungarian rulers granted the Jász people special privileges. Thus, the Jász were able to be more or less self-governing in an area known as Jászság in which Jászberény developed into the regional, cultural and administrative center. | ||
| ⚫ | In the 16th–17th centuries, areas populated by the Jász people were under ] administration, but at the end of the 17th century they were recaptured and returned to the ], which was then part of the ]. Habsburg Emperor ] sold the area to the ]. This saw the end of the privileged position of Jászberény. However, the Jász people did not want to accept this situation and started to collect money with which they could buy their freedom. By 1745, they had collected half a million Rhenish gold florins, a considerable sum for those days. However, in this time the famous 'Act of Redemption' took place: the Empress ] restored the Jász land and Jász hereditary privileges. From this point onwards, Jászberény flourished. The Jász regional autonomy was preserved until the year 1876, when the area populated by the Jász was administratively included into the Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok County. | ||
| ⚫ | ]) in the eighteenth century within the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary]] | ||
| ⚫ | Initially, their main occupation was ]. |
||
| ⚫ | In the 16th–17th centuries, areas populated by the |
||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| After dissolution of |
After dissolution of ] in 1918, areas populated by the Jasz people were included into an independent Hungary. Over a dozen settlements in the ] (e.g. the names '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'') still include a link to the Jász. In 1995, the 250th Anniversary of the Act of Redemption was celebrated in Jászberény with the President of Hungary as guest of honor as well as with numerous foreign dignitaries. | ||
| ==Language== | ==Language== | ||
| ⚫ | ] is the common name in English for the original language of the Jász. It was a dialect of ], an ]. Jassic became extinct and was replaced by Hungarian. The only literary record of the Jász language was found in the 1950s in the Hungarian '']''. The language was reconstructed with the help of various Ossetian analogies.{{cn|date=June 2017}} | ||
| == Genetics == | |||
| ⚫ | The only literary record of the Jász language was found in the 1950s in the Hungarian '']''. The language was reconstructed with the help of various Ossetian analogies. | ||
| Genetic studies on people from various Jász regions, have established a firm link towards other Hungarian ethnic groups, while simultaneously having shown a significant shift towards ], and especially ] ethnic groups with significant ]-related ancestry such as the ] of ].<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last=Guglielmino |first=C. R. |last2=Silvestri |first2=A. |last3=Beres |first3=J. |date=March 2000 |title=Probable ancestors of Hungarian ethnic groups: an admixture analysis |journal=Annals of Human Genetics |language=en |volume=64 |issue=2 |pages=145–159 |doi=10.1046/j.1469-1809.2000.6420145.x |issn=0003-4800|doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| Y-DNA haplogroups among people from Jász regions have been shown to be more diverse than those of other Hungarian people.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| ==Notable people of Jassic descent== | |||
| *] | |||
| * ]<ref>{{Cite web |title=Orbán Csányiról: "jász, az pedig kemény fajta" |url=https://hvg.hu/sport/20130804_Jasz_az_pedig_kemeny_fajta__Orban_Csanyi |first=HVG Kiadó|last=Zrt|date=August 4, 2013 |website=hvg.hu}}</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==Related articles and peoples== | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *]/] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 59: | Line 64: | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| * http://www.yazd.com/features/Jaszbereny/Jaszberenyyazd.htm | * | ||
| {{Iranian peoples}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Jassic People}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:04, 1 November 2024
Hungarian subgroup of Eastern Iranic descent "Jassi" redirects here. For the Indian drama, see Jassi Jaissi Koi Nahin. Not to be confused with Jassy.| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Jasz people" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Regions with significant populations | |
|---|---|
| Jászság, Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok County, Hungary | |
| Languages | |
| Hungarian, Jasz (extinct) | |
| Religion | |
| Christianity (Catholicism) | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Hungarians, Ossetians, other Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian peoples and Romanians |
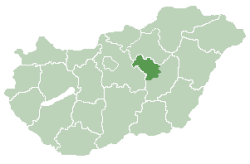
The Jász (Latin: Jazones) are a Hungarian subgroup of Eastern Iranic descent who have lived in Hungary since the 13th century. They live mostly in a region known as Jászság, which comprises the north-western part of Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county. They are sometimes known in English by the exonym Jassic and are also known by the endonyms Iasi and Jassy. They originated as a nomadic Alanic people from the Pontic steppe.
Geography
Main article: Jászság
The cultural and political center of Jászság is the town of Jászberény.
Jászság is sometimes, erroneously, known as "Jazygia", after a somewhat related Sarmatian people, the Iazyges, who lived in a similar area in ancient times.
History
The Jász people descend from member of a nomadic people, the Alans, who originated on the Eurasian steppe and settled in the Kingdom of Hungary during the 13th century, following the Mongol invasions. Their language, which belonged to the East Iranian group that includes modern Ossetian, had reportedly become extinct by the 16th century, when the Jász adopted Hungarian.
Despite frequent claims to the contrary, their name is unrelated to that of the Jazyges, one of the Sarmatian tribes which, along with the Roxolani, reached the borders of Dacia during the late 1st century BC, over a thousand years before the Jasz accompanied the Cumans into Hungary. This confusion is motivated by a superficial resemblance in the names as they appear in Roman transliteration: Hungarian sz is merely a digraph representing a voiceless s sound, while Greek zeta represented originally a voiced affricate (dz), or a combination of fricative and stop (zd), and the initial j in Jasz isn't original to the word either. So then the two names actually have no more than an a in common. This confusion has a long history, as Medieval scholars with a knowledge of classical history and writing in Latin were already referring to the Jasz as Jazygians.
The Jász people came to the Kingdom of Hungary, together with the Cumanians (Hungarian: Kun people) when their lands to the east, in some in the later Moldavia (see Iași or Jászvásár) were invaded by the Mongol Empire in the mid-13th century. They were admitted by the Hungarian king, Béla IV Árpád, who hoped that the Jászs would assist in resisting the Mongol-Tatar invasion. Shortly after their entry, the relationship worsened dramatically between the Hungarian nobility and the Cumanian-Jász tribes, which then abandoned the country. After the end of the Mongol-Tatar invasion they returned and settled in the central part of the Pannonian Plain, near the rivers Zagyva and Tarna.

Initially, their main occupation was animal husbandry. Over the next two centuries they were assimilated into the Hungarian population; yet although their language disappeared, they preserved a distinct Jász identity. The Hungarian rulers granted the Jász people special privileges. Thus, the Jász were able to be more or less self-governing in an area known as Jászság in which Jászberény developed into the regional, cultural and administrative center.
In the 16th–17th centuries, areas populated by the Jász people were under Ottoman administration, but at the end of the 17th century they were recaptured and returned to the Kingdom of Hungary, which was then part of the Habsburg monarchy. Habsburg Emperor Leopold I sold the area to the Knights of the Teutonic Order. This saw the end of the privileged position of Jászberény. However, the Jász people did not want to accept this situation and started to collect money with which they could buy their freedom. By 1745, they had collected half a million Rhenish gold florins, a considerable sum for those days. However, in this time the famous 'Act of Redemption' took place: the Empress Maria Theresa restored the Jász land and Jász hereditary privileges. From this point onwards, Jászberény flourished. The Jász regional autonomy was preserved until the year 1876, when the area populated by the Jász was administratively included into the Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok County.

After dissolution of Austria-Hungary in 1918, areas populated by the Jasz people were included into an independent Hungary. Over a dozen settlements in the Great Hungarian Plain (e.g. the names Jászberény, Jászárokszállás, Jászfényszaru, Jászalsószentgyörgy) still include a link to the Jász. In 1995, the 250th Anniversary of the Act of Redemption was celebrated in Jászberény with the President of Hungary as guest of honor as well as with numerous foreign dignitaries.
Language
Jassic is the common name in English for the original language of the Jász. It was a dialect of Ossetian, an Eastern Iranian language. Jassic became extinct and was replaced by Hungarian. The only literary record of the Jász language was found in the 1950s in the Hungarian National Széchényi Library. The language was reconstructed with the help of various Ossetian analogies.
Genetics
Genetic studies on people from various Jász regions, have established a firm link towards other Hungarian ethnic groups, while simultaneously having shown a significant shift towards Iranian peoples, and especially Turkic ethnic groups with significant Sarmatian-related ancestry such as the Bashkirs of Bashkortostan.
Y-DNA haplogroups among people from Jász regions have been shown to be more diverse than those of other Hungarian people.
Notable people of Jassic descent
Related articles and peoples
References
- Foltz, Richard (2022). The Ossetes: Modern-Day Scythians of the Caucasus. London: Bloomsbury, p. 50. ISBN 9780755618453.
- ^ Guglielmino, C. R.; Silvestri, A.; Beres, J. (March 2000). "Probable ancestors of Hungarian ethnic groups: an admixture analysis". Annals of Human Genetics. 64 (2): 145–159. doi:10.1046/j.1469-1809.2000.6420145.x. ISSN 0003-4800.
- Zrt, HVG Kiadó (August 4, 2013). "Orbán Csányiról: "jász, az pedig kemény fajta"". hvg.hu.
External links
| Iranian peoples | |
|---|---|
| Ethnic groups | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Ancient peoples | |
| Origin | |
| Languages | |
| Iranian religions | |