| Revision as of 08:56, 16 March 2015 editEntropyandvodka (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,477 edits →Quintus Sertorius and Spartacus: Fixed link to wrong article on Consuls← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 17:34, 11 December 2024 edit undoGatemansgc (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers26,331 editsm Reverted edit by 165.166.60.34 (talk) to last version by DerMaxdorferTag: Rollback | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Roman general and statesman (106–48 BC)}} | |||
| {{about|Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, Pompey the Great, a Roman statesman|other Romans named "Gnaeus Pompeius"|Gnaeus Pompeius (disambiguation){{!}}Gnaeus Pompeius|other members of gens Pompeia|Pompeia (gens)|other uses}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=September 2024}} | |||
| {{distinguish|Pompeii (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{hatnote group| | |||
| {{Infobox politician | |||
| | |
{{Other uses|Pompey (disambiguation)|Gnaeus Pompeius (disambiguation)}} | ||
| {{Confuse|Pompeii|Pompei}} | |||
| | image = Hw-pompey.jpg | |||
| }} | |||
| | caption = Pompey the Great in middle age, ] in the ], ], ]. | |||
| {{Infobox person | |||
| | birth_date = September 29, 106 BC | |||
| | name = Pompey | |||
| | birth_place = ] (]), ] | |||
| | image = (Venice) Pompey the Great, Museo Archeologico Nazionale.jpg | |||
| | residence = | |||
| | image_upright = 1.15 | |||
| | death_date = September 29, 48 BC (aged 58) | |||
| | alt = White bust | |||
| | death_place = ], ] | |||
| | caption = Bust of Pompey, copy of an original from 70–60 BC, ] | |||
| | office = ] of the ] | |||
| | native_name = Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus | |||
| | term_start = 52 BC | |||
| | native_name_lang = la | |||
| | term_end = 51 BC | |||
| | birth_date = 29 September 106 BC | |||
| | alongside = ] | |||
| | birth_place = ], Italy | |||
| | predecessor = ] and ] | |||
| | death_date = {{nowrap|28 September 48 BC (aged 57)}} | |||
| | successor = ] and ] | |||
| | death_place = ], Egypt | |||
| | office2 = ] of the ] | |||
| | death_cause = ] | |||
| | term_start2 = 55 BC | |||
| | resting_place = ], Italy | |||
| | term_end2 = 54 BC | |||
| | |
| father = ] | ||
| | spouse = {{ubl|] (86–82 BC, divorced) |] (82 BC, her death) |] (79–61 BC, divorced) |] (59–54 BC, her death) |] (52–48 BC, his death)}} | |||
| | predecessor2 = ] and ] | |||
| | children = {{hlist|] |] |]}} | |||
| | successor2 = ] and ] | |||
| | relations = ] | |||
| | office3 = ] of the ] | |||
| | occupation = Military commander and politician | |||
| | term_start3 = 58 BC | |||
| | net_worth = <!-- Net worth should be supported with a citation from a reliable source --> | |||
| | term_end3 = 55 BC | |||
| | office = ] (70, 55, 52 BC) | |||
| | office4 = ] of the ] | |||
| | module = {{infobox military person |embed=yes | |||
| | term_start4 = 70 BC | |||
| | battles = | |||
| | term_end4 = 69 BC | |||
| {{tree list}} | |||
| | alongside4 = ] | |||
| *] | |||
| | predecessor4 = ] and ] | |||
| *] | |||
| | successor4 = ] and ] | |||
| *] | |||
| | constituency = | |||
| *] | |||
| | party = | |||
| *] | |||
| | religion = ] | |||
| *] | |||
| | occupation = Politician and military commander | |||
| *] | |||
| | majority = | |||
| *] | |||
| | spouse = ] (?- 82 BC)<br />] (82 BC - 79 BC)<br />] (79 BC - 61 BC)<br />] (59 BC - 54 BC)<br />] (52 BC - 48 BC) | |||
| {{tree list/end}} | |||
| | children = ]<br>]<br>] | |||
| | awards = 3 ]}} | |||
| | website = | |||
| | footnotes = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Ancient Rome and the fall of the Republic}} | {{Ancient Rome and the fall of the Republic}} | ||
| '''Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus''' ({{IPA|la|ˈŋnae̯ʊs pɔmˈpɛjjʊs ˈmaŋnʊs|lang}}; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as '''Pompey''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|p|ɒ|m|p|i}} {{respell|POM|pee}}) or '''Pompey the Great''', was a general and statesman of the ]. He played a significant role in the transformation of Rome from republic to ]. Early in his career, he was a partisan and protégé of the Roman general and ] ]; later, he became the political ally, and finally the enemy, of ]. | |||
| <!-- This article has been substantially rewritten, using British English. --> | |||
| '''Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus''' (official nomenclature <small>CN·POMPEIVS·CN·F·SEX·N·MAGNVS</small>;<ref>Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, son of Gnaeus, grandson of Sextus</ref> 29 September 106 BC – 29 September 48 BC), usually known in English as '''Pompey''' {{IPAc-en|ˈ|p|ɒ|m|p|iː}} or '''Pompey the Great''',<ref>William Smith, ''A New Classical Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography, Mythology and Geography'', 1851. (Under the tenth entry of ''Pompeius'').</ref> was a military and political leader of the late ]. He came from a wealthy ] background, and his father had been the first to establish the family among the ]. Pompey's immense success as a general while still very young enabled him to advance directly to his first ] without meeting the normal ]. Military success in ] led him to adopt the ] '']'', "the Great". He was consul three times and celebrated three ]. | |||
| A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving Sulla as a commander in ]. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first ] without following the traditional '']'' (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as consul on three occasions (70, 55, 52 BC). He celebrated three ], served as a commander in the ], the ], the ], and in various other military campaigns. Pompey's early success earned him the ] '']'' – "the Great" – after his boyhood hero ]. His adversaries gave him the nickname ''adulescentulus carnifex'' ("teenage butcher") for his ruthlessness.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=29}} | |||
| In the mid-60 BC, Pompey joined ] and ] in the unofficial military-political alliance known as the ], which Pompey's marriage to Caesar's daughter ] helped secure. After the deaths of Julia and Crassus, Pompey sided with the '']'', the conservative faction of the ]. Pompey and Caesar then contended for the leadership of the Roman state, leading to ]. When Pompey was defeated at the ], he sought refuge in Egypt, where he was assassinated. His career and defeat are significant in Rome's subsequent transformation from ] to ] and ]. | |||
| In 60 BC, Pompey joined ] and ] in the informal political alliance known as the ], cemented by Pompey's marriage with Caesar's daughter, ]. After the deaths of Julia and Crassus (in 54 and 53 BC), Pompey switched to the political faction known as the '']''—a conservative faction of the ]. Pompey and Caesar then began contending for leadership of the Roman state in its entirety, eventually leading to ]. Pompey was defeated at the ] in 48 BC, and he sought refuge in ], where he was assassinated by the courtiers of ]. | |||
| ==Early life and political debut== | |||
| Pompey's father, ], was a wealthy landed Italian provincial from ], one of the ''homines novi'' (new men). Pompeius Strabo ascended the traditional '']'', becoming '']'' in 104 BC, '']'' in 92 BC and '']'' in 89 BC, and acquired a reputation for greed, political double-dealing and military ruthlessness. He supported ]'s traditionalist '']'' against the ] general ] in the ] war.<ref name="penelope.uchicago.edu"></ref> | |||
| ==Early life and career== | |||
| He died during the Marian siege against Rome in 87 BC, either as a casualty of pandemic plague, or struck by lightning, or possibly both.<ref name="penelope.uchicago.edu"/> In Plutarch's account, his body was dragged from its ] by the mob.<ref>Plutarch, Life of Pompey, 1. (Loeb) at Thayer: :see also Velleius Paterculus,'' Roman History'' 2, 21. (Loeb) at Thayer: </ref> His twenty year-old son Pompey inherited his estates, his political leanings and the loyalty of his legions. | |||
| ], brought from Rome in 1627 by Galeazzo Arconati]] | |||
| Pompey was born in ] on 29 September 106 BC, eldest son of a provincial noble called ]. Although the dominant ] in Picenum, Strabo was the first of his branch to achieve senatorial status in ]; he completed the traditional '']'', becoming ] in 89 BC, and acquired a reputation for greed, political duplicity, and military ruthlessness. Pompey began his career serving with his father in the ].{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=13}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Pompey had served two years under his father's command, and had participated in the final acts of the ] against the Italians. He returned to Rome and was prosecuted for misappropriation of plunder: his betrothal to the judge's daughter, ], secured a rapid acquittal.<ref>Plutarch, Life of Pompey, pg 126</ref> | |||
| Strabo died in 87 BC during the short-lived civil war known as the {{Lang|la|]}}, although sources differ on whether he succumbed to disease, or was murdered by his own soldiers.{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=98}} Prior to his death, Strabo was accused of ]; as his legal heir, Pompey was held responsible for the alleged crime and put on trial.{{sfn|Beesley|1892|pp=167–170}} He was acquitted, supposedly after agreeing to marry the ] daughter, ].{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=100}} | |||
| For the next few years, the ] had possession of Italy.<ref>Boak, History of Rome, pgs 145-6</ref> When Sulla returned from campaigning against ] in ], Pompey raised three Picenean legions to support him against the Marian regime of ].<ref>Dio describes Pompey's troop levy as a "small band": Cassius Dio, 33, fragment 107 (Loeb) at Thayer:</ref> | |||
| One of the main issues at stake in 87 BC was the appointment of the ] ] as commander of the Roman army in the ongoing ], an opportunity to amass enormous wealth.{{sfn|Beard|2015|pp=241–242}} During his absence in the East, his political rivals led by ], ] and ] regained control of the ].{{sfn|Boak|1921|pp=145–146}} Sulla's return in 83 BC sparked ] within the Roman world.{{sfn|Beard|2015|p=272}} | |||
| Sulla and his allies displaced the Marians in Italy and Rome: Sulla, now ] of Rome, was impressed by the young Pompey's self-confident performance. He addressed him as '']'' and offered him his stepdaughter, ], in marriage. Aemilia – already married and pregnant – divorced her husband and Pompey divorced Antistia.<ref>Aemilia's first husband had offered Sulla unwelcome criticism.</ref> Though Aemilia died in childbirth soon after, the marriage confirmed Pompey's loyalty and greatly boosted his career.<ref>Plutarch, Life of Pompey, pg. 136</ref> | |||
| ==Pompey during Sulla's civil war== | |||
| ==Sicily and Africa== | |||
| {{main|Sulla's civil war}} | |||
| With the war in Italy over, Sulla sent Pompey against the ]s in Sicily and Africa.<ref>Plutarch, Life of Pompey, pg. 141</ref> In 82 BC, Pompey secured Sicily, guaranteeing ]. He executed Gnaeus Papirius Carbo and his supporters out of hand, which may have led to his dubbing as the ''adulescens carnifex'' (adolescent butcher).<ref>Valerius Maximus, </ref> In 81 BC, he moved on to the Roman province of ], where he defeated ] and the ]n king Hiarbas, after a hard-fought battle.<ref>Plutarch, Life of Pompey, pgs. 143-5</ref> | |||
| In the year prior to Sulla's return Pompey had raised and equipped a full ] from amongst his father's old clients and veterans in ]. In the spring of 83 Sulla landed in ]. As he marched north-west towards ], Pompey led his own legion south to join him. The government in Rome sent out three separate armies in an attempt to prevent the union between Pompey's and Sulla's army. Pompey attacked one of these armies and routed it. The three enemy commanders, unable to agree on a course of action, withdrew. Soon after Pompey arrived at Sulla's camp. He was greeted by Sulla with the official title of ] (General).{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=24–25}} | |||
| At some point in 83 BC, it is not clear when but definitely before the onset of winter, Sulla sent Pompey back to Picenum to raise more troops. When fighting broke out once more in 82 Sulla advanced towards Rome, while ] (one of his lieutenants), supported by Pompey, campaigned against the consul Gaius Papirius Carbo in ]. During this campaign Pompey acted as Metellus's cavalry commander.{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=25–26}} | |||
| After this string of victories, Pompey was proclaimed '']'' by his troops on the field in Africa; once back in Rome, he was given an enthusiastic popular reception and hailed by Sulla as ''Magnus'' (the Great) – probably in recognition of Pompey's undoubted victories and popularity. However, it seems that Sulla was reluctant to honor him. The young general was still officially a mere '']'' (private citizen) who had held no offices in the '']''. The title may have been meant to cut Pompey down to size; he himself used it only later in his career.<ref>Plutarch, Life of Pompey, pg 148 – 149.</ref> | |||
| Metellus and Pompey defeated Carbo's lieutenant, the ] ], in a six-hour battle at the river Aesis, only to be blockaded by Carbo himself. When word of Sulla's victory at the ] reached them, Carbo retreated to his base at ], severely harassed by Pompey's cavalry. Some time later Metellus defeated ], another of Carbo's lieutenants, Pompey's cavalry caught Censorinus's fleeing troops outside their base at ], defeating them and plundering the town. While Metellus remained in the north-west, Pompey seems to have transferred to Sulla's command in the south.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=26}} | |||
| When Pompey demanded a ] for his African victories, Sulla refused; it would be an unprecedented, even illegal, honour for a young privatus – he must disband his legions. Pompey refused, and presented himself expectantly at the gates of Rome. Sulla gave in.<ref>Plutarch, Life of Pompey, pg. 149</ref> However, Sulla had his own triumph first, then allowed ] his triumph, relegating Pompey to an extra-legal third place in a quick succession of triumphs.<ref>Pompey's age, his equestrian status and his victory over Roman foes should have disqualified him from a triumph. Sulla's consent (formalised by his obedient senate as a Republican permission) made it a "nontraditional" and strictly illegal triumph, but a triumph nevertheless. See Mary Beard, The Roman Triumph, The Belknapp Press, 2007. 16 – 17.</ref> | |||
| Pompey advanced south-west along the ] towards ], where he joined Marcus Licinius Crassus, together they defeated Carrinas once again. Pompey laid siege to Carrinas in Spoletium but the latter managed to escape. Pompey resumed his march to join Sulla's command. Not long afterwards Pompey successfully ambushed another large force under Censorinus, which was trying to get through to ] where Carbo's consular colleague, Marius the Younger (who was the figurehead of the struggle against Sulla), was blockaded. It was the failure of these attempts to get through the Sullan blockade in ] and ], added to Metellus's success in winning control of the north, which broke the back of the government's resistance.{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=26–27}} | |||
| On the day, Pompey attempted to upstage both his seniors in a triumphal chariot towed by an elephant, representing his exotic African conquests. The elephant would not fit through the city gate. Some hasty replanning was needed, much to the embarrassment of Pompey and amusement of those present.<ref>Plutarch, Life of Pompey, pg. 151</ref> His refusal to give in to his troops' near-mutinous demands for cash probably impressed his mentor and Rome's conservatives. | |||
| At the end of the campaigning season of 82, the government forces made one final effort to march to the relief of Praeneste. They mustered 10,000 legionaries and marched to join forces with the ] and the ], fierce enemies of Sulla, who had campaigned against them in the Social War.{{efn|] and ] had remained virtually neutral during the war, but now decided to throw their lot in with the Roman government – their hatred for Sulla probably being the deciding factor.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=27}}}} Pursued by Pompey they united their forces and made for Praeneste. Unable to break through Sulla's blockade, they marched for undefended Rome, only to be caught just in time and defeated by Sulla at the ]. Pompey, who was pursuing the government forces, arrived just after the battle.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=27}} | |||
| ==Quintus Sertorius and Spartacus== | |||
| ]]] | |||
| By the end of 82 BC, Sulla had expelled his opponents from Italy, and engineered his nomination as Dictator by the Senate.{{sfn|Beard|2015|p=245}} Either through admiration of his abilities, or concern at his ambition,{{sfn|Haley|1985|p=49}} Sulla sought to consolidate his alliance with Pompey by persuading him to divorce Antistia, and marry his stepdaughter Aemilia.{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=99}} ] claims she was already pregnant by her former husband, and died in childbirth soon after.{{sfn|Haley|1985|p=50}} | |||
| Pompey's career seems to have been driven by desire for military glory and disregard for traditional political constraints.<ref>Holland, Rubicon, pgs. 141-42</ref> In the consular elections of ], he supported ] against Sulla's wishes. In 78 BC, Sulla died; when Lepidus revolted, Pompey suppressed him on behalf of the Senate. Then he asked for ]ar '']'' in ]<ref>The Iberian peninsula, roughly comprising modern Spain and Portugal.</ref> to deal with the '']''' general ], who had held out for the past three years against ], one of Sulla's most able generals.<ref name="Plutarch, Life of Pompey, pg. 158">Plutarch, Life of Pompey, pg. 158</ref> | |||
| ==Sicily, Africa and Lepidus' rebellion== | |||
| The Roman aristocracy turned him down – they were beginning to fear the young, popular and successful general. Pompey resorted to his tried and tested persuasion; he refused to disband his legions until his request was granted.<ref name="Plutarch, Life of Pompey, pg. 158"/> The senate acceded, reluctantly granted him the title of proconsul and powers equal to those of Metellus, and sent him to Hispania.<ref>Boak, History of Rome, pg. 152</ref> | |||
| The surviving Marians escaped to Sicily, where their ally ] was ]. They were supported by a fleet under Carbo, while ] occupied the ]. Perperna abandoned Sicily after Pompey landed on the island with a large force,{{efn|Six legions and a navy of 120 warships and 800 transport ships. Both men and ships were immediately available: the men and ships from Sulla's armies{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=28}}}} while Carbo was captured and later executed. Pompey claimed this was justified by Carbo's alleged crimes against Roman citizens, but his opponents nicknamed him ''adulescentulus carnifex'', or "young butcher", as a result.{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=100}} | |||
| ] | |||
| On his way to Spain, Pompey spent one year subduing rebellious tribes in southern Gaul and organizing the province.<ref>''Pro lege Manilia'', Cicero</ref> | |||
| Pompey now sailed for Africa, leaving Sicily in the hands of his brother-in-law, ].{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=30}} After defeating and killing Ahenobarbus at the ], Pompey subdued ] and executed its king ], a Marian ally.{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=100}} He restored the deposed ] to the Numidian throne.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=30–31}} Around this time, his troops began referring to him as ''Magnus'', or "the Great", after ], a figure much admired by the Romans. Shortly thereafter, Pompey formally made this part of his ].{{sfn|Gray}} | |||
| Pompey remained in Hispania from 76 – 71 BC; he was for long unable to bring ] to an end due to Sertorius' guerrilla tactics. Though he was never able to decisively beat Sertorius (and he nearly met disaster at the battle of Sucro), he won several campaigns against Sertorius' junior officers and gradually took the advantage over his enemy in a war of attrition. Sertorius was significantly weakened, and by 74 BC, Metellus and Pompey were winning city after city.<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 153">Boak, History of Rome, pg. 153</ref> In 72 BC, the Sertorians controlled little more than Lusitania and many soldiers were deserting. | |||
| On returning to Rome, he asked for a triumph to celebrate his victories, an unprecedented demand for someone so young.{{sfn|Seager|2002|p=28}} Pompey refused to disband his army until Sulla agreed, although the latter tried to offset the impact by awarding simultaneous triumphs to ] and ].{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=31–32}} Sometime during this period, Pompey married Mucia Tertia, a member of the powerful ] family. They had three children before their divorce in 61 BC; ], usually known as Gnaeus, a daughter, ], and a younger son, ].{{sfn|Haley|1985|p=50}} | |||
| Finally, Pompey managed to crush the ''populares'' when Sertorius was murdered by his own officer, ], who was decisively defeated in 72 BC by the young general, at their first battle. By early 71 BC, the whole of Hispania was subdued.<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 153"/> Pompey showed a talent for efficient organisation and fair administration in the conquered province; this extended his patronage throughout Hispania and into southern ].<ref>Holland, Rubicon, pg. 142</ref> Some time in 71 BC, he set off for Italy, along with his army. | |||
| {{Location map many|Italy|caption =The Lepidan rebellion; key locations|relief=yes|border = black| width = 200| float = right | |||
| Meanwhile, ] was facing ] to end Rome's ]. Crassus defeated Spartacus, but in his march towards Rome, Pompey encountered the remnants of Spartacus' army; he captured five thousand of them and claimed the credit for finishing the revolt, which infuriated Crassus.<ref>Holland, Rubicon, pgs. 150-51</ref> | |||
| |label = Cosa|pos=left|coordinates={{coord|42|25|N|11|17|E}} | |||
| |label2 = Rome|pos2=right|coordinates2={{coord|41|52|N|12|29|E}} | |||
| |label3 = Mutina |pos3=right|coordinates3={{coord|44|39|N|10|56|E}} | |||
| |label5 = Sardinia|pos5=top|coordinates5={{coord|40|00|N|9|00|E}} | |||
| |label6 = Picenum|pos6=top|coordinates6={{coord|42|51|N|12|35|E}} | |||
| }} | |||
| Pompey supported ] as consul for 78 BC; Plutarch claims he did so against Sulla's advice, but most modern historians refute the idea.{{sfn|Rosenblitt|2014|pp=415–16}} When Sulla died in 78 BC, Lepidus sought to block his state funeral and roll back some of Sulla's laws, then became ] of Cisalpine and ] in January 77 BC.{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=101}} When the Senate ordered him back to Rome, Lepidus refused to comply unless granted another term as consul, a proposal that was rapidly rejected.{{sfn|Gruen|1995|p=15}} Assembling an army, he began marching on Rome; the Senate responded with a series of measures, one of which was to appoint Pompey to a military command.{{sfn|Gruen|1995|p=16}} | |||
| Back in Rome, Pompey was wildly popular. On December 31, 71 BC, he was given a triumph for his victories in Hispania – like his first, it was granted extralegally. To his admirers, he was the most brilliant general of the age, evidently favoured by the gods and a possible champion of the people's rights. He had successfully faced down Sulla and his Senate; he or his influence might restore the traditional plebeian rights and privileges lost under Sulla's dictatorship. | |||
| While Lepidus continued south, Pompey raised troops from among his veterans in Picenum, and moved north to besiege ], capital of Cisalpine Gaul. The town was held by Lepidus' ally ], who surrendered after a lengthy siege, and was assassinated next day, allegedly on Pompey's orders.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=42}} Catulus then defeated Lepidus outside Rome, while Pompey marched against his rear, catching him near Cosa. Lepidus and the remnants of his army retreated to ], where he died.{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=41–43}} | |||
| So Pompey was allowed to bypass another ancient Roman tradition; at only 35 years of age and while not even a senator, he was elected ] by an overwhelming majority vote, and served in 70 BC with Crassus as partner. Pompey's meteoric rise to the consulship was unprecedented; his tactics offended the traditionalist nobility whose values he claimed to share and defend. He had left them no option but to allow his consulship. | |||
| ==Sertorian War== | |||
| {{Main|Sertorian War}} | |||
| The Sertorian War began in 80 BC when ], a prominent ] Marian general, initiated a rebellion in ], where he was joined by other Roman exiles like Perperna. Supported by local ] tribes, he took control of ] and repeatedly defeated Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius through skillful use of ]. Sertorius defeated other Roman generals sent to oust him and soon conquered ] as well. Backed by his allies in the Senate, Pompey was appointed military commander in Spain with proconsular authority in order to defeat Sertorius. This act was technically illegal as he had yet to hold public office, illustrating Pompey's preference for military glory, and disregard for traditional political constraints.{{sfn|Holland|2004|pp=141–142}} | |||
| Pompey recruited 30,000 infantry and 1,000 cavalry, evidence of the threat posed by Sertorius.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=44}} En route to Hispania, he subdued a rebellion in ], after which his army entered winter quarters near ].{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=45}} In early 76 BC, he crossed the ] and entered the Iberian peninsula,{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=46}} where he would remain for the next five years. His arrival boosted the morale of Metellus' troops, while some rebels changed sides, but soon after he was defeated by Sertorius at the ],<ref>Appian, ''Bellum Civile'', 1.109</ref> losing one third of his army while inflicting next to no losses on Sertorius' army. This was a serious blow to Pompey's prestige, who spent the rest of the year re-organising his army.<ref name=":5">Plutarch, ''Life of Sertorius'', p. 18</ref> Metellus' failure to dislodge Sertorius and Pompey's defeat meant the senatorial generals made no progress in the year. | |||
| {{Location map many|Spain|caption =Sertorian War in Spain; key locations mentioned in article|relief=yes|border = black| width = 400| float = left | |||
| |label = Col de Portet|pos=top|coordinates={{coord|42|50|N|0|14|E}} | |||
| |label2 = Lauron|pos2=left|coordinates2={{coord|39|09|N|0|37|W}} | |||
| |label3 = Valencia |pos3=right|coordinates3={{coord|39|28|N|0|23|W}} | |||
| |label4 = Sucro|pos4=right|coordinates4={{coord|39|10|N|0|15|W}} | |||
| |label5 = Saguntum|pos5=top|coordinates5={{coord|39|41|N|0|17|W}} | |||
| |label6 = Clunia|pos6=top|coordinates6={{coord|41|47|N|3|22|W}} | |||
| |label7 = Italica|pos7=left|coordinates7={{coord|37|27|N|6|03|W}} | |||
| |label8 = Lusitania|pos8=left|coordinates8={{coord|38|46|N|7|13|W}} | |||
| |label9 = Narbo Martius|pos9=top|coordinates9={{coord|43|11|N|3|00|E}} | |||
| |label10 = Vaccaei|pos10=top|coordinates10={{coord|42|09|N|4|42|W}} | |||
| }} | |||
| In 75 BC, Sertorius led the campaign against Metellus, while Pompey defeated his subordinates Perperna and Gaius Herennius outside ].{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=48}}{{sfn|Matyszak|2013|pp=117-118}} When Sertorius took over operations against Pompey, Metellus defeated his deputy ] at the ].{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=47}}{{sfn|Matyszak|2013|p=118}} Pompey faced Sertorius in the indecisive ],{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=49}}{{sfn|Matyszak|2013|pp=121-122}} in which Sertorius defeated Pompey's right flank and nearly captured Pompey himself, but his legate ] defeated the Sertorian right. Sertorius withdrew inland, then turned to fight at ], where Pompey lost 6,000 men, including his brother-in-law Memmius, reputedly his most effective subordinate.{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=49-50}}{{sfn|Matyszak|2013|p=126}} Sertorius himself suffered 3,000 casualties, one of whom was Hirtuleius.<ref name=ApCW1.110>Appian, ''Bellum Civile'', 1.110</ref> | |||
| Although Metellus defeated Perperna in a separate battle, Sertorius was able to withdraw to ] late in the year, where he repaired the walls to lure his opponents into a siege, while forming garrisons from other towns into a new field army. Once this was ready, he escaped from Clunia and used it to disrupt Roman logistics on land and by sea. Lack of supplies forced Metellus to quarter his troops in ], while Pompey wintered among the ].<ref>Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives'', ''Life of Pompey'', 18–20.1.</ref><ref>Plutarch, ''Life of Sertorius'', pp. 19–21</ref> Dire straits caused by this stretch of the campaign and Sertorius' guerrilla warfare led Pompey to write a letter to the Senate asking for funds and men, and scolding their lack of support for him and Metellus.<ref>Sallust, ''Histories,'' 1.2.82</ref> | |||
| Pompey's letter had the effect of galvanizing the Senate into sending him more men and funds. Reinforced by two more legions, in 74 BC he and Metellus began a ] against their enemy. As his chief opponent had lost most of his Roman legionaries and could no longer match him in the field, Pompey, along with Metellus, gained the upper hand, conquering more and more Sertorian cities, slowly grinding down Sertorius' revolt. By now, Sertorius was being undermined by internal divisions.{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=102}} Discontent in Sertorius' coalition of Iberian and Roman forces came to a head in 72 or 73 BC when Perperna, leading a conspiracy with other prominent Sertorians, had Sertorius assassinated and assumed control of the rebel army. | |||
| Pompey engaged Perperna in battle and defeated him swiftly at the ]. Perperna was captured and attempted to persuade Pompey to spare him by giving over Sertorius' correspondence, allegedly containing proof of communications between the rebel leader and leading men in Rome. Pompey burned the letters unread and executed Perperna, and then spent some time restructuring the local Roman administration, showing a lack of animosity towards his former opponents, which extended his patronage throughout Hispania and into southern Gaul.{{sfn|Holland|2004|p=142}} Pompey and his army remained in Hispania for a few years conquering the Sertorian remnants, and then marched back to Rome. | |||
| ==First Consulship== | |||
| During Pompey's absence, Marcus Licinius Crassus was charged with suppressing the slave rebellion led by ] known as the ]. Pompey returned to Italy just before Crassus defeated the main rebel army in 71 BC, arriving in time to massacre 6,000 fugitives from the battle. His claim to have ended the war by doing so was a long-standing source of resentment for Crassus.<ref>Plutarch, ''Life of Crassus'', 11.7</ref><ref>Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives'', ''Life of Pompey'', 21.2.</ref> | |||
| ] minted by Pompey for his second triumph in 71 BC, featuring the head of Africa on the obverse (celebrating his victory against ]). The reverse shows Pompey in his triumphal chariot, with his son ] seated before and ] flying above.{{sfn|Crawford|1974|pp=412–413}}]] | |||
| Pompey was granted a second triumph for his victory in Hispania, and nominated for the consulship. Since he was both too young and technically ineligible, this required a special senatorial decree.<ref name="Livy, Periochae, 97.6">Livy, ''Periochae'', 97.6</ref> ] suggests Pompey supported Crassus as his co-consul in order to put him under an obligation.<ref name=":7">Plutarch, ''Life of Crassus'', 12.1</ref> The two men were elected consuls for 70 BC, but allegedly differed on almost every measure, rendering their term "politically barren and without achievement."<ref>Plutarch, ''Life of Crassus'', 12.2</ref> | |||
| However, their consulship did see the ] recover powers removed by Sulla. One of the most significant was the ability to veto Senatorial bills, an act often seen as a turning point in the politics of the late Republic. Although popular with the people, the measure must have been opposed by the ''optimates'', and thus passing it required support from both consuls, although most extant sources barely mention Crassus.<ref name="Livy, Periochae, 97.6"/> | |||
| ==Campaign against the pirates== | ==Campaign against the pirates== | ||
| {{Main articles|Pompey's campaign against the pirates}} | |||
| {{Further|Lex Gabinia}} | |||
| Pirates operated throughout the Mediterranean, while their fleets often formed temporary alliances with enemies of Rome, including Sertorius and Mithridates. Their power and range had increased over the past fifty years, partly because of the decline of traditional naval powers like ], while previous attempts to subdue them had been unsuccessful.{{sfn|Tröster|2009|pp=20–21}} However, Romans routinely referred to their opponents as "pirates" or "brigands", and some historians argue it is more accurate to see them as a conventional enemy, rather than disorganised outlaws.{{sfn|Tröster|2009|p=17}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Two years after his consulship, Pompey was offered command of a naval task force to deal with piracy in the ]. The conservative faction of the Senate remained suspicious and wary of him; this seemed yet another illegal or at least extraordinary appointment.<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 160">Boak, History of Rome, pg. 160</ref> Pompey's supporters for this command – including ] – were in the minority, but support was whipped up through his nomination by the ] of the Plebs ] who proposed a '']''; Pompey should have control over the sea and the coasts for 50 miles inland. This would set him above every military leader in the East – it was passed despite vehement opposition. | |||
| Principally based in ], in 68 BC they raided as far as ], Rome's port, and kidnapped two senators, to general outrage.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=66}}{{sfn|Seager|2002|pp=43–44}} Prompted by Pompey, ], tribune of the plebs in 67 BC, proposed the '']'', giving him a mandate for their suppression. It granted him proconsular authority for three years in any province within 50 miles of the Mediterranean, along with the power to appoint legates and significant financial resources.{{sfn|Flower|2014|pp=89–90}} Concerned by one man holding such wide-ranging powers, the Senate opposed the law but it was passed by the people.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=68}} Most of the difficulties Pompey faced came from officials who resented his authority. In Gaul, ] hampered his recruitment efforts, while in ], ] refused to comply with his instructions.{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=71,74}} | |||
| According to Rome's historians, ] had freely plundered the coastal cities of Greece, Asia and Italy itself. The extent and nature of their threat is questionable; anything that threatened Rome's grain supply was cause for panic. Roman public opinion and Pompey's supporters may have exaggerated the solution. Various settlements, peoples and city-states around the Mediterranean had coexisted several centuries and most had operated small fleets for war, or trade in commodities, including slaves. Their alliances might be loose and temporary or more-or-less permanent; some regarded themselves as nations.<ref name="books.google.co.uk">De Souza, 149 – 179, for background and detailed critique of primary sources on Pompey's commission and its fulfillment. Limited preview available from googlebooks </ref> | |||
| Pompey spread his forces throughout the Mediterranean to prevent the pirates escaping a Roman fleet by moving elsewhere.{{sfn|Seager|2002|p=47}} Fifteen legates were given specific areas to patrol, while he secured the grain route to Rome. These measures won him control of the western Mediterranean in just 40 days, after which his fleets moved to the east, forcing the pirates back to their bases in Cilicia. Pompey led the decisive assault on their stronghold in ], winning the ] and concluding the war in only three months.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=72}} | |||
| With Rome's increasing hegemony, the independent maritime economies of the Mediterranean would have been further marginalised; an increasing number would have resorted to piracy. As long as they met Rome's increasing requirement for slaves, left her allies and territories untouched and offered her enemies no support, they were tolerated. Some were subsidised.<ref name="books.google.co.uk"/> But fear of piracy was potent – and these same pirates, it was later alleged, had assisted Sertorius. | |||
| Most of his opponents surrendered without fighting, thanks to Pompey's reputation for clemency.{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=102}} They were granted lands in cities devastated during the Mithridatic War, notably ], renamed Pompeiopolis, and ] in Greece, with others sent to towns in Libya and ]. These communities retained a strong attachment to both Rome and Pompey.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=73}}{{Sfn|Seager|2002|pp=47–48}} | |||
| By the end of that winter, the preparations were complete. Pompey allocated one of thirteen areas to each of his ], and sent out their fleets. In forty days, the western Mediterranean was cleared.<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 160"/> Dio reported communication was restored between Hispania, Africa, and Italy;<ref>This probably refers to the grain supply; the extent of its interruption before Pompey's campaign is not known. The reference to Hispania might relate to Sertorius' revolt and resistance – abetted, in some accounts, by "Cilician pirates" – or its aftermath.</ref> and that Pompey then attended to the largest of these alliances, centered on the coast of "Rough ]".<ref>Approximate to Southern Turkey. Once a Seleucid province, in Pompey's day and for some time to come it was a semi-independent territory whose sovereignty was debated by neighbouring Greek polities. It resisted such claims, but was eventually absorbed into Rome's empire.</ref> After "defeating" its fleet, he induced its surrender with promises of pardon, and settled many of its people at ], which was henceforward called Pompeiopolis.<ref>Dio, Roman History, pg. 63</ref> | |||
| ==Third Mithridatic War and re-organisation of the east== | |||
| De Souza (2002) finds that Pompey had officially returned the Cilicians to their own cities, which were ideal bases for piracy and not – as Dio would have it – for the dignified reformation of pirates as farmers. Pompey's entire campaign is therefore in question; its description as "war" is hyperbole – some form of treaty or payoff is likely, with Pompey as chief negotiator. This was standard practice, but undignified and seldom acknowledged; Rome's generals were supposed to wage and win wars. A decade on, in the 50s BC, the Cilicians and pirates in general remained a nuisance to Rome's sea trade.<ref>De Souza, 176 ff.</ref> | |||
| === Third Mithridatic War === | |||
| In Rome, however, Pompey was hero; once again, he had guaranteed the grain supply. According to Plutarch, by the end of the summer of 66 BC, his forces had swept the Mediterranean clear of opposition. Pompey was hailed as the first man in Rome, '']'' (the first among equals). Cicero could not resist a ]:<ref>''pro Lege Manilia'', 12 or ''De Imperio Cn. Pompei'' (in favor of the Manilian Law on the command of Pompey), 66 BC.</ref> | |||
| {{main|Third Mithridatic War}} | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| ] | |||
| In 73 BC, ], formerly one of Sulla's chief lieutenants, was made proconsul of ], and commander in the Third Mithridatic War. The war began in 74 BC, when the last ruler of ] died and left his kingdom to Rome, sparking an invasion by ] of ], and ] of ]. Lucullus was a skilled general who won numerous victories, but claims he was protracting the war for "power and wealth" led to a Senate investigation, while by 69 BC his troops were weary and mutinous.<ref>Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives'', ''Life of Lucullus'', pp. 33–35.</ref> | |||
| "Pompey made his preparations for the war at the end of the winter, entered upon it at the commencement of spring, and finished it in the middle of the summer." | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| In 68 BC, ] replaced Lucullus in Cicilia, while ] received Bithynia. He also assumed leadership of the war against Mithridates, but failed to respond decisively when the latter re-occupied much of Pontus in 67 BC, then attacked ], a Roman ally.<ref>Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'', 36.14.4, 17.1.</ref> Seeing an opportunity, in 66 BC Pompey used the ] to pass the '']'', giving him extensive powers throughout Asia Minor in order to defeat Mithridates, in addition to those granted by the ''lex Gabinia''. The ''optimates'' were privately horrified that one man should hold so much influence, but fearful of his popularity allowed the measure to pass.<ref>Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives'', ''Life of Pompey'', 30.1–5.</ref> | |||
| The expedience of his campaign probably guaranteed Pompey his next and even more impressive command, this time in Rome's long-running war against Mithridates. By the 40s BC, Cicero could comment less favourably on the pirate campaign, and especially the funded "resettlement" at Soli/Pompeiopolis; "we give immunity to pirates and make our allies pay tribute."<ref>Cicero, On duties, 3.49; cited in De Souza, 177.</ref> | |||
| Incensed at being replaced, Lucullus called Pompey a "vulture" who profited from the work of others, a reference both to his new command and claim to have finished the war against Spartacus.{{sfn|Greenhalgh|1981|p=107}} Pompey agreed an alliance with ], king of ], whom he persuaded to invade Armenia. When Mithridates offered a truce, Lucullus argued the war was over, but Pompey demanded concessions which could not be accepted.<ref>Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'', 36.45–46.</ref> Outnumbered, Mithridates withdrew into Armenia, followed by Pompey, who defeated him at ] near the end of 66 BC.<ref>Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'', 36.47.</ref><ref>Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives'', ''Life of Pompey'', 32.1–3.</ref> | |||
| ==Pompey in the East== | |||
| {{further|Kingdom of Pontus|}} | |||
| ] of ] in the ], Paris]] | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Pompey spent the rest of that year and the beginning of the next visiting the cities of ] and ], and providing for the government of newly conquered territories. In his absence from Rome (66 BC), he was nominated to succeed Lucius Licinius ] as commander in the ] against ] in the East. Pompey's command was proposed by the tribune ], supported by Caesar and justified by ] in ''pro Lege Manilia''.<ref>Pompey, the Roman Alexander,P Greenhalg p101-4</ref> His brother-in-law ] served underneath him at this time and followed him in his exploits in the East. Like the Gabinian law, it was opposed by the aristocracy, but was carried nonetheless. | |||
| According to contemporary sources, Mithridates and a small contingent escaped the battle, outstripped their pursuers, and reached ] on the ].<ref>Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'', 36.48–50.</ref><ref>Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives'', ''Life of Pompey'', 32.3–7.</ref> While there, he took control of the ] from its Roman-backed ruler, his son ], who later committed suicide.<ref>Appian, ''The Mithridatic Wars'', pp. 101–102.</ref> Meanwhile, Pompey invaded Armenia supported by ], whose father quickly came to terms; in return for the restoration of Armenian territories taken by Lucullus, he paid a substantial cash indemnity{{efn|Reportedly 6,000 talents for Pompey, with ] getting 10,000 drachmas each, ] 1,000, and enlisted men 50}} and allowed Roman troops to be based on his territory. | |||
| Lucullus, a ] noble, was incensed at the prospect of his replacement by a "new man" such as Pompey. The outgoing commander and his replacements traded insults. Lucullus called Pompey a "vulture" who fed from the work of others. Lucullus was referring not merely to Pompey's new command against Mithridates, but also his claim to have finished the war against Spartacus.<ref>Pompey, the Roman Alexander,P Greenhalg p107</ref> | |||
| In 65 BC, Pompey set out to take Colchis, but to do so had first to ] various local tribes and allies of Mithridrates. After winning a series of battles, he reached ] and linked up with Servilius, admiral of his Euxine fleet, before a fresh revolt in ] forced him to retrace his steps. Victory at the ] enabled him to impose terms on the Albanians and agree truces with other tribes on the northern side of the Caucasus.<ref>Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'', 36.54, 37.2–5.1</ref> Pompey then wintered in Armenia, settling minor border contests and raids between his allies Phraates and Tigranes.<ref>Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'', 37.5.2–5, 6.</ref> | |||
| At Pompey's approach, Mithridates strategically withdrew his forces. However, Pompey managed to besiege his camp, but could not prevent his enemy from breaking the encirclement and retreating further east. But, afterward, near Armenia, Pompey managed to surprise the Pontic army by a daring nocturnal attack and all but destroyed it, leaving the king had no choice but to flee in disarray. ] refused him refuge, so he made his way to his own dominions in the ]. Pompey secured a treaty with Tigranes, and in 65 BC set out in pursuit of Mithridates, but ] from the Caucasian ] and ]. The Romans won a succession of decisive victories over these people on the Abas and the Cyrus rivers and at Seusamora, destroying their forces.<ref>''Pompey'', Eric Teyssier</ref> Pompey then advanced to ] in Colchis and liaised with his legate Servilius, admiral of his Euxine fleet, before decisively defeating Mithridates.<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 161">Boak, History of Rome, pg. 161</ref> | |||
| Relying on his naval blockade to wear down Mithridates, Pompey spent 64 BC annexing the independent and wealthy cities of ], which were incorporated into a new Roman province. In the process, he acquired large amounts of money and prestige, as well as criticism from his opponents in Rome, who argued doing so exceeded his authority. Meanwhile, an ageing Mithridates had been cornered in ] by another of his sons, ]. An attempt to commit suicide by taking poison allegedly failed due to his habit of taking "precautionary antidotes", and he was killed by the rebels. Pharnaces sent his embalmed body to Pompey, in return for which he was granted the ] and made an ally of Rome.<ref>Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'', 37.11–14.2.</ref> | |||
| Pompey then retraced his steps, wintered at ], and made it into a Roman province. In 64 BC, he marched into ], deposed its king, ], and reconstituted this, too, as a Roman province.<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 161"/> In 63 BC, he moved south, and established Roman supremacy in ] and ].<ref>The Hellenized cities of the region, particularly the cities of the ], used a calendar that counted its dates from Pompey's conquest. See ].</ref> | |||
| ===Re-organisation of the East=== | |||
| In ], Pompey intervened in the civil war between ], who supported the ] faction and ], who supported the ]s. The armies of Pompey and Hyrcanus II ]. After three months, the city fell.<ref>Despite this, Aristobulus II would survive to briefly usurp Hyrcanus II, who was later (31 BC) executed by ].</ref> | |||
| {{details|Pompey's eastern settlement}} | |||
| The final collapse of the ] allowed Pompey to annex ] in 64 BC, but its dissolution destabilised the region, while many of its cities had used the power vacuum to achieve independence.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=93}} In early 63 BC, Pompey left ] and marched south, occupying coastal cities like ], before crossing the ] and capturing ] and ].{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=96}} | |||
| ] (blue) in 63 BC, after losing the ] (red) to the north]] | |||
| <blockquote>"Of the Jews there fell twelve thousand, but of the Romans very few.... and no small enormities were committed about the ] itself, which, in former ages, had been inaccessible, and seen by none; for Pompey went into it, and not a few of those that were with him also, and saw all that which it was unlawful for any other men to see but only for the high priests. There were in that temple the golden table, the holy candlestick, and the pouring vessels, and a great quantity of spices; and besides these there were among the treasures two thousand talents of sacred money: yet did Pompey touch nothing of all this, on account of his regard to religion; and in this point also he acted in a manner that was worthy of his virtue. The next day he gave order to those that had the charge of the temple to cleanse it, and to bring what offerings the law required to God; and restored the high priesthood to Hyrcanus, both because he had been useful to him in other respects, and because he hindered the Jews in the country from giving Aristobulus any assistance in his war against him." | |||
| (], '']'', book 14, chapter 4; tr. by William Whiston, available at Project Gutenberg.) | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| Pompey's incursion further south, into ], was occasioned on account of its inhabitants, under the leadership of ] and ], having ravaged ] and Pompey wanting to bring a stop to it.<ref>{{cite book |last=Cassius Dio |author-link=Cassius Dio|title=Dio's Roman History |publisher=Harvard University Press |editor=E.H. Warmington |series=The Loeb Classical Library |volume=3 |date=1969 |location=Cambridge |page=127 (book XXXVII)|language=en, Greek |oclc=264964964}}</ref> The initial onslaught was disrupted by the ], in which Pompey backed Hyrcanus II over his brother Aristobulus II. When he compelled the latter to surrender ], its defenders took refuge in the ], which the ], then looted. Judea became a client kingdom ruled by Hyrcanus, while its northern section was incorporated into the ], a league of semi-autonomous cities (see map). Both Judea and the League were made subordinate to the new province of Syria.<ref>Josephus, ''Jewish Antiquities'', 14.54.79</ref> | |||
| During the war in Judea, Pompey heard of Mithridates' suicide; his army had deserted him for his son ].<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 161"/> In all, Pompey had annexed four new provinces to the Republic: ], ], ], and ]. Rome's Asian protectorates now extended as far east as the ] and the ]. Pompey's military victories, political settlements and annexations in Asia created Rome's new frontier on the east. | |||
| Other organisational changes included creating the province of ], with the rest of Mithridates' territories distributed among Roman allies. Elsewhere, ] was restored to his throne, while Lesser Armenia was taken from Tigranes and incorporated into ], with Pompey's client ] becoming ruler of the new kingdom. Finally, Cilicia received the coastal region of ], previously a centre of piracy, along with other inland areas and reorganised into six parts.{{efn|These were Cilicia Aspera, Cilicia Campestris, Pamphylia, ], ], ], and ]}} These actions significantly increased Roman state income and presented Pompey with multiple opportunities to increase his personal wealth and patronage base.{{sfn|Morrill|2017|pp=57–97}} | |||
| ==Return to Rome, and third triumph== | |||
| News of Pompey's victories in the east – and probably of his divine honours there – reached Rome before he did. He had cult at Delos and was "saviour" in Samos and Mytelene. Plutarch quotes a wall-graffito in Athens, referring it to Pompey: "The more you know you're a man, the more you become a god". In Greece, these honours were standard fare for benefactors. In Rome, they would have seemed dangerously monarchic.<ref>In Beard, M., North, J., Price, S., ''Religions of Rome, Vol. 1, a history'', Cambridge University Press, 1998, 147.</ref> | |||
| ==Return to Rome and the First Triumvirate== | |||
| In Pompey's absence, his old supporter Cicero had risen to the consulship. His old enemy and colleague ] supported Caesar. In the Senate and behind its scenes, Pompey was probably equally admired, feared and excluded; on the streets he was as popular as ever. His eastern victories earned him his third triumph. On his 45th birthday, in 61 BC, he rode the triumphal chariot, a magnificent god-king, but one of Republican form, ritualistically reminded of his impermanence and mortality. Even so, he was accompanied by a gigantic portrait head of himself, studded with pearls.<ref name="ReferenceA">Beard, 16: for comments on Pompey's 3rd triumph, see also Plutarch, Sertorius, 18, 2, at Thayer : Cicero, Man. 61: Pliny, Nat. 7, 95.</ref><ref name="Mary Beard 2007, p9">Mary Beard, ''The Roman Triumph'', The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, 2007, p9. The traditional accounts exaggerate, certainly in the matter of gold, silver and military cash donatives. Appian's very doubtful "75,100,000" drachmae carried in the procession is 1.5 times his own estimate of Rome's total annual tax revenue: See Appian, ''Mithradates'', 116.</ref> | |||
| ]{{efn|The three wreaths on the reverse refer to the three triumphs of Pompey; the top wreath is the ] he received in 62; the globe in the center is a copy of the one paraded during the third triumph; the aplustre on the lower left alludes to his victory against the pirates}}<ref>{{harvnb|Crawford|1974|pp=449–451}}, though he only links the aplustre with Pompey's '']'' of 57.</ref>{{sfn|De Souza|2002|p=174}}]] | |||
| Before his return to Italy in 62 BC, Pompey paid his troops bonuses totalling around 16,000 ],{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=101}}{{efn|A Roman talent was roughly 32 kilograms of gold, making this distribution worth over $32 billion using 2023 prices}} but despite fears he intended to follow Sulla's example, they were dismissed upon arrival at Brundisium.{{sfn|Mitchell|1973|p=1}} His journey to Rome drew huge crowds wherever he stopped, showing that although opinion in the Senate was divided, Pompey remained as popular as ever with the masses. He was awarded a third triumph for his achievements in Asia Minor, celebrated on his 45th birthday in 61 BC.{{sfn|Beard|2015|p=273}} | |||
| His third triumph exceeded all others; an unprecedented two days were scheduled for its procession and games ('']''). Spoils, prisoners, army and banners depicting battle scenes wended the triumphal route between the ] and the Capitoline temple of ]. To conclude, he gave an immense triumphal banquet and money to the people of Rome, and promised them a new theatre.<ref name="ReferenceA"/><ref name="Mary Beard 2007, p9"/> Plutarch claimed this triumph represented Pompey's – and therefore Rome's – domination over the entire world, an achievement to outshine even Alexander's.<ref>Beard, 15–16: citing Plutarch, Pompey, 45, 5.</ref><ref>Beard, 16. For further elaboration on Pompey's 3rd triumph, see also Plutarch, ''Sertorius'', 18, 2, at Thayer : Cicero, Man. 61: Pliny, Nat. 7, 95.</ref> | |||
| Pompey claimed the new provinces established in the East had increased annual state income from 200 million to 340 million ], plus an additional payment of 480 million sesterces to the treasury.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=118}} He refused to provide details of his personal fortune, but given the amounts declared publicly, this must have been enormous. Some of it was used to build one of the most famous structures of Ancient Rome, the ].{{sfn|Kuritz|1987|p=48}} | |||
| In the meantime, Pompey promised his retiring veterans public lands to farm, then dismissed his armies. It was a reassuringly traditional gesture, but the Senate remained suspicious. They debated and delayed his eastern political settlements<ref>Dio, Roman History, pg. 178</ref> and the promised gifts of public land. From now on, Pompey seems to have toed a cautious line between his enthusiastic popular supporters and the conservatives who seemed so reluctant to acknowledge his solid achievements. It would lead him into unexpected political alliances. | |||
| However, the Senate then refused to ratify the treaties agreed by Pompey as part of his settlement of the East. Opposition was led by the ''optimates'' ] and ], whose sister Mucia had recently been divorced by Pompey, for reasons still disputed.{{sfn|Haley|1985|p=53}}{{efn|The divorce may also have been a factor in the defection of ], previously one of Pompey's main supporters, although the Metelli had their own political ambitions.{{sfn|Mitchell|1973|p=6}}}} They also defeated a bill to distribute farmland to his veterans, and landless members of the urban poor. A similar measure had been rejected in 63 BC, which arguably made the Senate over confident in their ability to control popular unrest.{{sfn|Mitchell|1973|p=2}} | |||
| ==Caesar and the First Triumvirate== | |||
| Although Pompey and Crassus distrusted each other, Crassus' ] clients were being rebuffed at the same time Pompey's veterans were being ignored, and by 61 BC, their grievances had pushed them both into an alliance with Caesar, six years younger than Pompey, returning from service in Hispania and ready to seek the ]ship for 59 BC. Their political alliance, known subsequently as the ], operated to the benefit of each. Pompey and Crassus would make Caesar Consul, and Caesar would use his consular power to promote their claims. | |||
| ]; left to right, ], ], and Pompey]] | |||
| Caesar's consulship of 59 BC brought Pompey land for his veterans, confirmation of his Asian political settlements and a new wife. She was Caesar's daughter, ]; Pompey was said to be besotted by her.<ref>Boak, History of Rome, pg. 167</ref> In the same year, ] renounced his patrician status, was adopted into a ] ''gens'' and was elected a ]. At the end of his consulship, Caesar secured proconsular command in Gaul. Pompey was given the ] of Hispania Ulterior, but remained in Rome to oversee ] as ''curator annonae''.<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 169">Boak, History of Rome, pg. 169</ref> | |||
| Although Pompey could not overcome ''optimate'' opposition on his own, the situation changed when Marius' nephew ] sought his endorsement for the consulship in 59 BC. A skilled, unscrupulous, and ambitious politician, Caesar used this alliance to harness Pompey's influence with the urban electorate.{{sfn|Mitchell|1973|p=3}} With additional support from Crassus, Caesar became one of the two consuls for 59 BC, the other being the ''optimate'' ]. This meant Caesar could help pass legislation sponsored by Pompey and Crassus, while it was in his interest to keep them aligned, an important factor given the rivalry between his two patrons.{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=120–121}} | |||
| Despite his preoccupation with his new wife, Pompey handled the grain issue well. His political acumen was less sure. When Clodius turned on him in turn, Pompey defended himself by supporting Cicero's recall from exile (57 BC). Once back in Rome, Cicero stepped back into his role as Pompey's defender and Clodius' antagonist, but Pompey himself retreated to his lovely young wife and his theatre plans; such behaviour was not expected of the once dazzling young general.<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 169"/> | |||
| Despite appearing to be the most junior, Caesar thus became central to the ], an informal political alliance designed to counter-balance the ''optimates''. Pompey's influence was based on his reputation as a military commander, and popularity with the Roman people.{{sfn|Mitchell|1973|p=17}} Crassus' wealth allowed him to construct extensive patronage networks, but he lacked the military clout essential for political success in the ].{{sfn|Beard|2015|p=275}} | |||
| Pompey might equally have been obsessed, exhausted and frustrated. His own party had not forgiven him for allowing Cicero's expulsion. Some tried to persuade him that Crassus was plotting his assassination. Meanwhile, Caesar seemed set on outstripping both his colleagues in generalship and popularity. | |||
| ], leader of ''optimate'' opposition to the triumvirate who became an ally of Pompey]] | |||
| By 56 BC, the bonds between the three men were fraying.<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 169"/> Caesar called first Crassus, then Pompey, to a secret meeting, the ], in the northern Italian town of ] to rethink their joint strategy. They agreed that Pompey and Crassus would again stand for the consulship in 55 BC. Once elected, they would extend Caesar's command in Gaul by five years. At the end of their joint consular year, Crassus would have the influential and lucrative governorship of Syria, and use this as a base to conquer Parthia. Pompey would keep Hispania ''in absentia''. | |||
| Once elected, Caesar secured the passage of a new agrarian bill, helped by Pompey's veterans, who filled the streets of Rome and allegedly intimidated the Senate. When Bibulus opposed the measure, he was attacked in the ], and spent the rest of his consulship under virtual house arrest.{{Sfn|Beard|2015|p=282}} Caesar then ensured ratification of Pompey's settlements in the east, while the '']'' made him governor of Gallia Cisalpina and ]. He was also assigned ] after its governor died in office, before leaving Rome to launch the ] in 58 BC. His alliance with Pompey was strengthened when the latter married Caesar's daughter Julia.{{sfn|Haley|1985|p=53}} | |||
| In 55 BC, Pompey and Crassus were elected as consuls, against a background of bribery, civil unrest and electioneering violence.<ref>Boak, History of Rome, pg. 170</ref> ] was inaugurated in the same year. It was Rome's first permanent theatre, a gigantic, architecturally daring, self-contained complex on the ], complete with shops, multi-service buildings, gardens and a temple to ]. The latter connected its donor to Aeneas, a son of Venus and ancestor of Rome itself. In its portico, the statuary, paintings and personal wealth of foreign kings could be admired at leisure. Pompey's triumph lived on.<ref>Beard, 22-3.</ref> His theatre made an ideal meeting place for his supporters. | |||
| Senatorial opposition to the triumvirate was led by ], a long-standing Pompeian ally. Despite this, the latter supported the populist politician ] in an attack on Cicero for executing Roman citizens without trial during the ].{{sfn|Holland|2004|pp=238–239}} Although Clodius succeeded in having Cicero exiled, he was recalled to Rome by Pompey eighteen months later in 58 BC.{{sfn|Holland|2004|p=254}} As a result, when shortages of grain caused popular unrest in 57 BC, a grateful Cicero backed Pompey's appointment as '']'', a temporary position set up for such occasions.{{sfn|Holland|2004|p=254}} | |||
| ==From confrontation to war== | |||
| In 54 BC, Julia, Caesar's only child and Pompey's wife, died in childbirth along with her baby. Pompey and Caesar shared their grief and condolences, but Julia's death broke their family bonds.<ref>Holland, Rubicon, pg. 287</ref> The following year, ], his son ] and most of his army were annihilated by the Parthians at ]. Caesar, not Pompey, was now Rome's great new general and the fragile balance of power between them was under threat. Public anxiety spilled over: rumours circulated that Pompey would be offered dictatorship for the sake of law and order. | |||
| Pompey and Crassus were competing for command of a new expedition to Asia Minor, and in 56 BC they ] with Caesar to resolve these issues. Although Crassus was a long-standing rival, there are also indications Pompey felt his status as the foremost soldier of the Republic was threatened by Caesar's success in ].{{sfn|Goldsworthy|2006|p=253}} With this in mind, Pompey set aside his differences with Crassus to promote their joint candidature as consuls for 55 BC. With Caesar's support, they were duly elected after prolonged periods of the violence which had become a feature of Roman political campaigns.{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=104}} | |||
| Caesar sought a second matrimonial alliance with Pompey, offering his grandniece ] (the sister of the future emperor ]). This time, though, Pompey refused. In 52 BC, he married ], the very young widow of Crassus's son Publius, and the daughter of ], one of Caesar’s greatest enemies. Pompey was drifting back toward the ''optimates''. It can be presumed that they thought him the lesser of two evils. | |||
| Once in office, they ensured passage of a law giving Crassus the province of Syria and command of a punitive expedition against Parthia, providing him opportunities for both military glory and loot. Pompey was assigned the restive provinces of Hispania, along with Africa, while Caesar's governorships in Gaul were extended. All three men were given these positions for a period of five years, as well as the right to levy troops and "make peace and war with whomsoever they pleased."{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=104}} | |||
| In the same year, ] was murdered. When his supporters burned down the ] in retaliation, the Senate appealed to Pompey. He reacted with ruthless efficiency. Cicero, defending the accused murderer ], was so shaken by a ] seething with armed soldiers, he was unable to complete his defense. | |||
| ==From confrontation to civil war== | |||
| Once order was restored, the Senate and ] avoided granting Pompey dictatorship – it recalled Sulla and his bloody proscriptions. Instead they made him sole Consul; this gave him sweeping, but limited, powers. A Dictator could not be lawfully punished for measures taken during his office. As sole Consul, Pompey would be answerable for his actions once out of office. | |||
| ] | |||
| In 54 BC, Caesar continued his conquest of Gaul, Crassus opened his campaign against the Parthians, and Pompey remained in Rome, where his wife Julia died in child birth in September. Contemporary sources suggest that combined with the death of Crassus and his son [[Publius Licinius Crassus (son of triumvir)| | |||
| While Caesar was fighting against ] in ], Pompey proceeded with a legislative agenda for Rome. Its details suggested covert alliance with Caesar's enemies: among his various legal and military reforms was a law allowing retrospective prosecution for electoral bribery. Caesar's allies correctly interpreted this as a threat to Caesar once his ''imperium'' ended. Pompey also prohibited Caesar from standing for the consulship ''in absentia'', though this had been permitted under past laws. | |||
| Publius]] at ] in May 53 BC, this removed any obstacle to direct confrontation between Caesar and Pompey.<ref>Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives'', ''Life of Caesar'', 23.5–6</ref><ref>Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives'', ''Life of Pompey'', 53.4–6.</ref>{{efn|Historian ] wrote "Pompey could not brook an equal, or Caesar a superior."<ref>Florus, ''Epitome of Roman History'', 2.13.14</ref>}} | |||
| Consular elections in 52 BC had to be suspended due to widespread violence. Seeking to end his alliance with Caesar, the ''optimate'' Bibulus proposed Pompey be elected sole consul, an unprecedented act backed by both Cato and the tribunate.{{sfn|Ramsey|2016|pp=307–308}} Having restored order, Pompey married Cornelia, widow of Publius Crassus and daughter of ], whom he appointed as his colleague for the last five months of the year.{{sfn|Ramsey|2016|p=299}} | |||
| This seemed to put paid to Caesar's plans after his term in Gaul expired. Finally, in 51 BC, Pompey was more forthright; Caesar would not be permitted to stand for Consul unless he relinquished his armies. This would, of course, leave Caesar defenseless before his enemies. As Cicero sadly noted, Pompey had been diminished by age, uncertainty, his fear of Caesar and the strain of being the chosen tool of a quarreling oligarchy of ''optimates''. The coming conflict seemed inevitable.<ref>Many historians have suggested Pompey was, in spite of everything, politically unaware of the fact that the optimates, including Cato, were merely using him against Caesar so that, with Caesar destroyed, they could then dispose of him.</ref> | |||
| As consul, Pompey helped enact legislation which some historians view as crucial to understanding the drift to war in 49 BC. Accused of using violence during his consulship in 59 BC, Caesar had previously been shielded by his proconsular immunity. With private support from Pompey, new laws made such prosecutions retrospective, which meant Caesar would probably be put on trial the moment he left Gaul and lost his '']''.{{sfn|Stanton|2003|p=73}} To avoid this, he had secured approval to stand for the consulship in 48 BC while still in Gaul, but another law backed by Pompey required electoral candidates to be physically present in Rome.{{sfn|Stanton|2003|p=75}} | |||
| ==Civil war and assassination== | |||
| Although the two continued to co-operate in public,{{sfn|Stanton|2003|p=67}} Pompey clearly viewed his colleague as a threat, as did much of the Senate. Both consuls for 50 BC, ] and ], were opponents of Caesar, as was ], a plebeian tribune. They initiated legislation to remove Caesar from his command in Gaul, who allegedly bypassed this by bribing Paullus and Curio.{{sfn|Drogula|2019|p=240}} For whatever reason, Curio came up with an alternative proposal; Caesar and Pompey should disarm at the same time, or be declared enemies of the state.{{sfn|Drogula|2019|pp=241–242}} | |||
| This was a clever move, since it was popular with those who wanted to avoid war, but unacceptable to the ''optimates'' who saw Caesar as a danger that had to be eliminated.{{sfn|Drogula|2019|p=243}} Rejection made open conflict more likely, and the Senate agreed to fund a consular army, organised by Pompey. When he fell ill while recruiting in ], the celebrations that followed his recovery allegedly convinced Pompey his popularity was sufficient to see off any opponent.{{sfn|Collins|1953|p=104}} In December, Caesar crossed the Alps with a single veteran legion and arrived at ], close to the border with the Roman Republic.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|p=558}}{{efn|Now in Northern Italy, Ravenna was then a federated ally of the ]}} | |||
| A significant number of senators opposed any concessions to Caesar, but many also mistrusted Pompey, who has been criticised for "weak and ineffectual leadership" in this period.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|pp=557–558}} On 1 January 49 BC, Caesar sent an ultimatum demanding acceptance of his compromise, failing which he would march on Rome "to avenge his country's wrongs". Confident their forces significantly outnumbered those available to Caesar, on 7 January the Senate declared him a public enemy; four days later, he crossed the ] into Italy.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|p=558}} | |||
| ==The Road to Pharsalus== | |||
| {{Main|Caesar's civil war}} | {{Main|Caesar's civil war}} | ||
| When the war began, Caesar was a rebel with no navy and three understrength legions, while Pompey was backed by all the resources of the Roman state and his clients in the East.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|p=557}} However, his position was weaker than it seemed, since he was simply an advisor to the Senate, many of whose members either preferred a negotiated solution, or regarded him with as much suspicion as Caesar. His military strategy had to be approved by the consuls, and he could only issue recommendations, which were not always followed. For example, Cicero rejected a request to help him with recruitment, and Cato refused to take command of Sicily, vital for control of Rome's grain supply.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|pp=558–559}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| In the beginning, Pompey claimed he could defeat Caesar and raise armies merely by stamping his foot on the soil of Italy, but by the spring of 49 BC, with Caesar ] and his invading legions sweeping down the peninsula, Pompey ordered the abandonment of Rome. His legions retreated south towards ], where Pompey intended to find renewed strength by waging war against Caesar in the east. In the process, neither Pompey nor the Senate thought of taking the vast treasury with them, probably thinking Caesar would not dare take it for himself. It was left conveniently in the ] when Caesar and his forces entered Rome. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Barely eluding Caesar in Brundisium, Pompey crossed over into ], where, during Caesar's Spanish campaign, Pompey had gathered a large force in Macedonia, comprising nine legions reinforced by contingents from the Roman allies in the east.<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 176">Boak, History of Rome, pg. 176</ref> His fleet, recruited from the maritime cities in the east, controlled the ]. Nevertheless, Caesar managed to cross over into Epirus in November 49 BC, and proceeded to capture ].<ref name="Boak, History of Rome, pg. 176"/> | |||
| Plans to defend Italy were undone by the speed with which Caesar moved, advancing directly on Rome with minimal resistance. Although outnumbered, his troops were experienced veterans, while many of Pompey's were new recruits, a weakness made worse by lack of co-ordination. Cato's brother-in-law, the ''optimate'' leader ], was cut off and captured in a hopeless defence of ], and his 13,000 men incorporated into Caesar's army.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|pp=558–559}} Led by ], they were later used to occupy Sicily.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=183}} | |||
| Pompey managed to arrive in time to save ], and he then attempted to wait Caesar out during the ], scoring a victory. Yet, by failing to pursue at the critical moment of Caesar's defeat, Pompey threw away the chance to destroy Caesar's much smaller army. As Caesar himself said, "Today the enemy would have won, if they had a commander who was a winner" (Plutarch, 65E). | |||
| Pompey had abandoned Rome, ordering all senators and public officials to accompany him as he withdrew south to ]. From there, he transported his troops across the ] to ] in ], an operation performed with almost complete success.{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=173–185}} Lacking ships to pursue him, Caesar first secured his rear by subduing Pompeian forces in Hispania, before returning to Rome in December 49 BC. This gave Pompey time to build an army nearly twice the size of his opponents, while his navy destroyed two fleets being built for Caesar, ensuring the Pompeians retained control of the sea lanes.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|p=559}} | |||
| According to ], it was at this point that Caesar said that "that man (Pompey) does not know how to win a war." With Caesar on their backs, the conservatives led by Pompey fled to Greece. Caesar and Pompey had their final showdown at the ] in 48 BC. The fighting was bitter for both sides, and although Pompey was expected to win, due to advantage in numbers, the brilliant tactics and the superior fighting abilities of Caesar's veterans led to a victory for Caesar. Pompey met his wife Cornelia and his son ] on the island of ]. He then wondered where to go next. The decision of running to one of the eastern kingdoms was overruled in favour of ]. | |||
| Despite this, in January 48 BC Caesar managed to cross the Adriatic with seven legions and land in southern ].{{sfn|Boak|1921|p=176}}{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=192}} After capturing ] and ], he advanced on Pompey's main supply base at ]. The latter arrived in time to ] the attempt, and establish a fortified camp on the other side of the River ], where the two armies remained until spring.{{efn|Pompey was based at ],{{sfn|Wylle|1992|p=560}} a small port north of Dyrrhachium, roughly on the site of modern ] in Albania}} Neither commander was anxious to begin hostilities, since Caesar was too weak militarily, while as with Mithridates, Pompey preferred to starve his opponent into submission.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|p=560}} | |||
| After his arrival in Egypt, Pompey's fate was decided by the counselors of the young king ]. While Pompey waited offshore, they argued the cost of offering him refuge with Caesar already en route to Egypt; the king's eunuch ] won out. In the final dramatic passages of his biography, Plutarch had Cornelia watch anxiously from the trireme as Pompey left in a small boat with a few sullen, silent comrades, and headed for what appeared to be a welcoming party on the Egyptian shore at ]. As Pompey rose to disembark, he was stabbed to death by his betrayers, ], ] and Salvius.<ref name="Plutarch, Pompey, 79–80">Plutarch, Pompey, 79–80</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Plutarch has him meet his fate with great dignity, one day after his 59th birthday. His body remained on the shoreline, to be cremated by his loyal freeman Philip on the rotten planks of a fishing boat. His head and seal were presented to Caesar, who, according to Plutarch, mourned this insult to the greatness of his former ally and son-in-law, and punished his assassins and their Egyptian co-conspirators, putting both Achillas and Pothinus to death. Pompey's ashes were eventually returned to Cornelia, who carried them to his country house near ].<ref name="Plutarch, Pompey, 79–80"/> | |||
| In late March the stalemate was broken when ] finally managed to cross the Adriatic with four more legions and land at ], some 57 kilometres north of Dyrrachium. Pompey tried to prevent the two Caesarian armies from linking up, by marching north-east and laying an ambush for Antony. The ambush, however, was revealed to Antony by some local Caesarian sympathisers, and he stayed in camp until Caesar approached. Pompey not willing to be caught between the two Caesarian forces withdrew.{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=192–193}} | |||
| ] describes Caesar's reactions with skepticism, and considers Pompey's own political misjudgments, rather than treachery, as instrumental in his downfall.<ref></ref> In Appian's account of the civil war, Caesar has Pompey's severed head interred in Alexandria, in ground reserved for a new temple to the goddess ], whose divine functions included the punishment of ].<ref>Appian, Bella Civilia, II 90, cited in Michael B. Hornum, ''Nemesis, the Roman state and the games'', Brill, 1993, p.15.</ref> For ], the humiliation of Pompey's end is anticipated by the vaunting pride of his oversized portrait-head, studded entirely with pearls, and carried in procession during his greatest Triumph.<ref>Pliny, ''Historia Naturalis,'' 37, 14–16.</ref> ], however, states of Caesar "He even restored to their position the statues of Lucius Sulla and of Pompey which had been broken up by the common people." <ref> Suetonius, "Lives of the Caesars: Translated by Catherine Edwards", 34. </ref> | |||
| Caesar, his army now united with Antony's force, redeployed his forces by sending one-and-a-half legion to win support and gather supplies in ] and ], and a further two legions under ] to intercept ] in Macedonia. Meanwhile, ], Pompey's oldest son, managed to destroy Caesar's fleet at Oricum and ], making sure no more reinforcements and supplies would reach Caesar from Italy. Caesar tried to lure Pompey into a ] at Asparagium, but the latter refused. The next day Caesar outmaneuvred Pompey and marched for Dyrrachium again. When Pompey arrived at the city Caesar had already set up camp.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=193}} | |||
| ] the head of Pompey; etching, 1820]] | |||
| Caesar lacked the siege equipment needed to take Dyrrhachium, and could not risk leaving Pompey to threaten his rear. He solved this by ].{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=194}} Although the latter had enough food, water was scarce because Caesar had dammed the local rivers, and the Pompeian cavalry lacked forage for their horses. Ending the stalemate became a matter of urgency, and in late July Pompey finally managed to break through part of Caesar's defensive lines. Since this made the blockade pointless, Caesar cut his losses and withdrew to Apollonia.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|p=560}}{{sfn|Leach|1978|pp=193–198}} | |||
| ==Generalship== | |||
| At this point Metellus Scipio arrived in Thessaly. Caesar moved south to confront this threat and link up with Domitius Calvinus, allowing his men to sack ] en route. Pursued by Pompey, he then withdrew to the area near ], but failed to tempt Pompey into giving battle.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|p=561}}{{efn|The exact location of the battle is still disputed}} Although it was later claimed Pompey only did so after being pressured by his subordinates, the delay may simply have been a reflection of his natural caution.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|p=562}} | |||
| Pompey's military glory was second to none for a few decades. Yet, his skills were occasionally criticized by some of his peers. Sertorius or Lucullus, for instance, were especially critical.<ref>Plutarch</ref> Pompey's tactics were usually efficient, albeit not particularly innovative or imaginative. They could prove insufficient against greater tacticians. However, Pharsalus was his only decisive defeat.<ref>''Pompey the great'', John Leach</ref> At times, he was reluctant to risk an open battle. While not hugely charismatic, Pompey could display tremendous bravery and fighting skills on the battlefield, something which provided inspiration to his men.<ref name="Pompey the great, John Leach">Pompey the great, John Leach</ref> | |||
| Regardless, Pompey's army of around 38,000 outnumbered the 22,000 men commanded by Caesar,{{efn|these numbers refer to legionaries and do not include the light-armed troops provided by allied rulers and nations{{sfn|Leach|1978|p=204}}}} with 7,000 cavalry to 1,000.{{sfn|Keppie|1984|p=109}} On 9 August he deployed his men in battle formation, planning to use his superior cavalry to outflank his opponent on his left. Caesar had anticipated this, and repulsed the cavalry which fled in confusion, exposing the infantry behind them. Under pressure from the left and in front, the Pompeian army collapsed.{{sfn|Wylle|1992|p=563}} | |||
| On the other hand, Pompey is usually considered an outstanding strategist and organizer, who could win campaigns without displaying genius on the battlefield, but simply by constantly outmaneuvering his opponents and gradually pushing them into a desperate situation.<ref>John Leach</ref> Pompey was a great forward planner, and had tremendous organizational skill, which allowed him to devise grand strategies and operate effectively with large armies.<ref>''Pharsalus'', Si Sheppard</ref> During his campaigns in the east, he acted like a sledgehammer, relentlessly pursuing his enemies, and choosing the ground for his battles. | |||
| ==Death== | |||
| Above all, he was often able to adapt to his enemies. On many occasions, he acted very swiftly and decisively, as he did during his campaigns in Sicily and Africa, or against the Cilician pirates. During the Sertorian war, on the other hand, Pompey was beaten several times by Sertorius. Therefore, he decided to resort to a war of attrition, in which he would avoid open battles against his chief opponent but instead try to gradually regain the strategic advantage by capturing his fortresses and cities and defeating his junior officers.<ref name="Pompey the great, John Leach"/> In some instances, Sertorius showed up and forced Pompey to abandon a siege, only to see him strike somewhere else.<ref>Appian</ref> This strategy was not spectacular but it led to constant territorial gains and did much to demoralize the Sertorian forces. By 72 BC, the year of his assassination, Sertorius was already in a desperate situation and his troops were deserting. Against Perpernna, a far inferior tactician than his former commander in chief, Pompey decided to revert to a more aggressive strategy and he scored a decisive victory that effectively ended the war. | |||
| ] | |||
| Against Caesar too, his strategy was sound. During the campaign of Greece, he managed to regain the initiative, join his forces to that of Metellus Scipio (something that Caesar wanted to avoid) and trap his enemy. His strategic position was hence much better than that of Caesar and could have starved his army to death. However, he was finally compelled to fight an open battle by his allies and his conventional tactics proved no match to that of Caesar and his better-trained troops. | |||
| Pompey escaped from the battlefield and made his way to ], where he was reunited with his wife Cornelia. Most of his Eastern allies were present at Pharsalus and had either been killed or captured. The main absentee was 14-year-old ], ruler of the wealthy and strategically important kingdom of ], making it an obvious destination. Cato announced his intention to continue the war from Africa, although most of his senatorial colleagues, including Cicero and ], made their peace with Caesar and returned to Rome.{{sfn|Holland|2004|p=323}} | |||
| ==Later portrayals and reputation== | |||
| For the historians of his own and later Roman periods, Pompey fit the trope of the great man who achieved extraordinary triumphs through his own efforts, yet fell from power and was, in the end, murdered through treachery. | |||
| Pompey sailed from ] with a small fleet, and on 28 September 48 BC arrived at ] in Egypt, where Ptolemy was engaged in a bitter civil war with his co-ruler and elder sister, ]. When he went ashore to greet an official delegation, Pompey was killed by ], a Roman officer and former colleague serving in the Egyptian army. His body was cremated by two servants, while the head was kept as evidence.{{sfn|Beard|2015|p=290}} | |||
| He was a hero of the Republic, who seemed once to hold the Roman world in his palm, only to be brought low by Caesar. Pompey was idealized as a tragic hero almost immediately after Pharsalus and his murder. Plutarch portrayed him as a Roman ], pure of heart and mind, destroyed by the cynical ambitions of those around him. This portrayal of him survived into the ] and ] periods, for example in ]'s play '']'' (1642). In spite of his war against Caesar, Pompey was still widely celebrated during the imperial period, as the conqueror of the orient. At Augustus' funeral procession, pictures of him were carried as he was still widely considered as the great conqueror of the Orient. As a triumphator, he also had numerous statues in Rome, one of which was on the forum of Augustus. Though the imperial power did not honor him as much as his archenemy, who was considered a god, his reputation among many aristocrats and historians was equal or even superior to that of Caesar.<ref>Pompey, Eric Teyssier</ref> | |||
| One suggestion is that Ptolemy and his advisors feared Pompey planned to seize control of Egypt, especially since many Egyptian army officers were Roman mercenaries like Septimius who had previously served with him. At the same time, it seemed an easy way to win Caesar's support against Cleopatra, although ultimately this proved not to be the case.{{sfn|Holland|2004|p=327}} Pompey's head was later returned to Cornelia for burial at his villa in the ], while his ignominious death prompted Cicero to write "his life outlasted his power".{{sfn|Beard|2015|p=290}} | |||
| Pompey has appeared as a character in several modern novels, plays, motion pictures, and other media. | |||
| == |
==Marriages and issue== | ||
| {{main|Wives of Pompey the Great}} | |||
| *A theatrical portrayal was ]'s play '']'' (1910). | |||
| Pompey had five wives:{{sfn|Haley|1985}}<ref>Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives'', ''Life of Pompey'', 5, 9, 15, 48.</ref> | |||
| *In the opening scene of the 1961 film '']'', he is played by actor ]. | |||
| * ]. They married in 86 BC and divorced in 82 BC. By her he had no issue. | |||
| *In the television series '']'', he is portrayed by actor ]. | |||
| * ]. When they married in 82 BC, Aemilia was pregnant by her former husband and died in childbirth in the same year. | |||
| *] portrays Pompey in the 2002 miniseries '']''. | |||
| * ]. They married in 79 BC and divorced in 61 BC. By her he had two sons and a daughter: | |||
| *He appears as a ] in the first season of the ], in which he is portrayed by ]. | |||
| ** ] | |||
| *In 2006 he was played by ] in the BBC docu-drama ]''. | |||
| ** ] | |||
| *In the television series '']'', he is portrayed by actor ]. | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * ], the daughter of ]. They married in 59 BC and she died in childbirth in 54 BC. The child died a few days after birth. | |||
| * ]. They married in 52 BC and had no children together. | |||
| == |
==Generalship== | ||
| *In ]'s '']'' series of historical novels, Pompey's youthful exploits are depicted in '']'', the formation of the First Triumvirate and his marriage to Julia is a large part of '']'' and his loss of Julia, the dissolution of the First Triumvirate, his later political career, the civil war between him and Caesar and his eventual defeat and his betrayal and murder in Egypt are all told in '']''. | |||
| *In comics, he appears as Julius Caesar's foe throughout the '']'' series. | |||
| *Pompey is a recurring character in the '']'' series of novels by ], portraying his role in the Civil War with Caesar. His final appearance is in Saylor's novel '']'', graphically depicting his murder by Ptolemy in Egypt. | |||
| *Pompey also appears frequently in the ] by ], narrated by Senator ], a fictional nephew of Caecilius ]. Decius despises Pompey as a glory-seeker and credit-grabber, while acknowledging that he is a political dunce who was eventually swept up into the ''optimates'' feud with Caesar. | |||
| Pompey's military glory was second to none for two decades, yet his skills were occasionally criticized by some of his contemporaries. Sertorius or Lucullus, for instance, were especially critical.<ref>Plutarch, ''Life of Sertorius'' and ''Life of Lucullus''</ref> Pompey's tactics were usually efficient, albeit not particularly innovative or imaginative, and they could prove insufficient against greater tacticians. However, Pharsalus was his only decisive defeat.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p={{pn|date=September 2023}}}} At times, he was reluctant to risk an open battle. While not extremely charismatic, Pompey could display tremendous bravery and fighting skills on the battlefield, which inspired his men.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p={{pn|date=September 2023}}}} While being a superb commander, Pompey also earned a reputation for stealing other generals' victories.{{sfn|Brice|2014|p=145}} | |||
| ==Marriages and offspring== | |||
| * First wife, ] | |||
| * Second wife, ] (Sulla's stepdaughter) | |||
| * Third wife, ] (whom he divorced for adultery, according to ]'s letters) | |||
| ** ], ] in 45 BC, after the ] | |||
| ** ], married to ]; ancestor of ] | |||
| ** ], who would rebel in ] against ] | |||
| * Fourth wife ] (daughter of Caesar) | |||
| * Fifth wife, ] (daughter of Metellus Scipio) | |||
| On the other hand, Pompey is usually considered an outstanding strategist and organizer, who could win campaigns without displaying genius on the battlefield, but simply by constantly outmaneuvering his opponents and gradually pushing them into a desperate situation.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p={{pn|date=September 2023}}}} Pompey was a great forward planner, and had tremendous organizational skill, which allowed him to devise grand strategies and operate effectively with large armies.<ref name=":8">Si Sheppard, ''Pharsalus''</ref> During his campaigns in the east, he relentlessly pursued his enemies, choosing the ground for his battles.<ref>{{Cite book |title=History of the Ancient & Medieval World Vol. 6 |publisher=Marshall Cavendish Corporation |year=1996 |isbn=0761403574 |edition=Revised |location=Tarrytown, NY |pages=731 |language=English}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Hazel |first=John |title=Who's Who in the Roman World |publisher=Routledge Taylor & Francis Group |year=2001 |isbn=0415224101 |edition=2nd |location=New York |pages=247–248 |language=English}}</ref> | |||
| ==Chronology of Pompey's life and career== | |||
| *106 BC September 29– Born in ] | |||
| *83 BC– Aligns with ], after his return from the ] against King ]; Marriage to ] | |||
| *82–81 BC– Defeats ]'s allies in Sicily and Africa | |||
| *81 BC– Returns to Rome and celebrates First triumph | |||
| *76–71 BC– Campaign in ] against ] | |||
| *71 BC– Returns to Italy and participates in the suppression of a ] led by ]; Second triumph | |||
| *70 BC– First consulship (with ]) | |||
| *67 BC– Defeats the pirates and goes to Asia province | |||
| *66–61 BC– Defeats King Mithridates of Pontus; end of the Third Mithridatic War | |||
| *64–63 BC– Pompey's March through Syria, the Levant, and Judea | |||
| *61 BC September 29– Third triumph | |||
| *59 BC April– The first ] is constituted; Pompey allies to ] and Licinius Crassus; marriage to ] | |||
| *58–55 BC– Governs Hispania Ulterior by proxy, construction of Pompey's Theater | |||
| *55 BC– Second consulship (with M. Licinius Crassus), Dedication of the Theatre of Pompey | |||
| *54 BC– ] dies; the first triumvirate ends | |||
| *52 BC– Serves as sole consul for ],<ref>See Abbott, 114</ref> third ordinary consulship with Metellus Scipio for the rest of the year; marriage to ] | |||
| *51 BC– Forbids Caesar (in Gaul) to stand for consulship in absentia | |||
| *50 BC– Falls dangerously ill with fever in Campania, but is saved 'by public prayers'<ref>Juvenal, Satire X, 283</ref> | |||
| *49 BC– Caesar crosses the Rubicon River and invades Italy; Pompey retreats to Greece with the conservatives | |||
| *48 BC– Caesar defeats Pompey's army near Pharsalus, Greece. Pompey retreats to Egypt and is killed at ]. | |||
| Above all, he was often able to adapt to his enemies and showed determination. On many occasions, he acted very swiftly and decisively, as he did during his campaigns in Sicily and Africa, or against the Cilician pirates. During the Sertorian war, on the other hand, Pompey was beaten several times by Sertorius. Despite an abysmal first year of the war for Pompey in 76 BC, he continued to campaign vigorously and as a result defeated many of Sertorius' subordinates. After Sertorius' army was greatly diminished, Pompey then decided to conduct a ], in which he would avoid open battles against his chief opponent but instead tried to gradually regain the strategic advantage by capturing his fortresses and cities and defeating his junior officers.{{sfn|Leach|1978|p={{pn|date=September 2023}}}} This strategy was unspectacular, but it led to constant territorial gains and did much to demoralize the Sertorian forces. By 73 or 72 BC, when he was assassinated, Sertorius was already in a desperate situation and his troops were deserting. Against Perperna, a tactician far inferior to his former commander-in-chief, Pompey decided to revert to a more aggressive strategy and he scored a decisive victory that effectively ended the war. | |||
| {{s-start}} | |||
| {{s-off}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=] and ]}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=] of the ]|years=''with ]''<br/>70 BC}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=] and ]}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=] and ]}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=] of the ]|years=''with ]''<br/>55 BC}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=] and ]}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=] and ]}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=] of the ]|years=''Without Colleague''<br/>], 52 BC<ref name="Abbott, 114">Abbott (1901), 114</ref>}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=Gnaeus Pompey Magnus and ]}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=Gnaeus Pompey Magnus}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=] of the ]|years=''with ]''<br/>52 BC}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=] and ]}} | |||
| {{s-end}} | |||
| Against Caesar too, his strategy was sound. During the campaign in Greece, he managed to regain the initiative, join his forces to that of Metellus Scipio (something that Caesar wanted to avoid) and trap his enemy. His strategic position was hence much better than that of Caesar and he could have starved Caesar's army to death.<ref name=":8"/> However, he was finally compelled to fight an open battle by his allies, and his conventional tactics proved no match to those of Caesar (who also commanded the more experienced troops). | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{reflist|2}} | |||
| == Literary heritage == | |||
| Pompey was so striking a figure, and his fall so dramatic, that his story became the subject of frequent literary treatment. In the century after his death, the civil war between himself and Caesar was retold in ]'s epic ''De Bello Civili'', now known as the '']'' after the culminating battle. In the poem's final sections, however, Pompey's vengeful ghost returns to possess those responsible for his murder in Egypt and bring about their death.<ref>Sean Easton, "Why Pompey Is better off dead", ''The Classical Journal'' 107.2 (2011), </ref> | |||
| In ] Britain, too, several plays returned to the subject of "Caesar and Pompey", including ]'s ''The Wars of Pompey and Caesar'' (c. 1604). Another contemporary treatment by ], ''Cornelia, or Pompey the Great, his faire Cornelia's tragedy'' (1594), was a translation from the French of ].<ref>''A Manual of Old English Plays'' (1892), </ref> Later in France, Pompey's story was told without the character appearing onstage in ]'s ''La Mort de Pompée'' (1643) and this too had English adaptations: as ''Pompey'' (1663) by ], as ''Pompey the Great'' by ] and others in 1664,<ref>Andrew Shifflett, ''Stoicism, Politics and Literature in the Age of Milton'', Cambridge University 1998, </ref> and later as '']'' (1724) by ]. | |||
| Later in the 18th century, Pompey is made the recipient of a ] in rhyming couplets from a supposed former lover in ]'s "Flora to Pompey".<ref>Joseph Wharton, ''An Essay on the Genius and Writings of Pope'', (London, 1756), </ref><ref>Robert Dodsley, ''A Collection of Poems by Several Hands'', (London 1755), </ref> He also figures in narrative poems of the 19th century. ]'s "The Vale of Tempe" records the fugitive's desperate appearance as glimpsed by a bystander in the Greek valley;<ref>''The Broken Heart, with other poems'', London 1825, </ref> his arrival in Egypt is related by ] in "The Death of Pompey the Great",<ref>Alaric A. Watts, ''Lyrics of the Heart'', London 1851, </ref> and the ruined column raised to mark the site of his killing outside Alexandria is described by ] in ''Ruins of Many Lands''.<ref> "Pompey’s Pillar", ''Ruins of Many Lands'', London 1849, </ref> These were followed by ]'s prose drama '']'' of 1910, covering the period from his decision to fight Caesar to his assassination in Egypt.<ref>, London, 1910</ref> The play was later filmed for television in 1950 for the '']''.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://explore.bfi.org.uk/4ce2b7f3044be |title=The Tragedy of Pompey the Great |website=BFI Film Forever |publisher=British Film Institute|date=20 July 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120720043235/http://explore.bfi.org.uk/4ce2b7f3044be |archive-date=20 July 2012}}</ref> | |||
| Pompey's career is recapitulated a century later in series of historical novels. In ]'s '']'', Pompey is mainly featured in Books III-V, covering his rise to prominence through to his betrayal and murder in Egypt.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Rocío Gordillo Hervás |title=Historical Fiction and Ancient Rome: Colleen McCullough's ''Masters Of Rome'' Series |journal=Collection de l'Institut des Sciences et Techniques de l'Antiquité |date=9 February 2024 |volume=1476 |issue=1 |pages=206 ff |url=https://www.persee.fr/doc/ista_0000-0000_2019_ant_1476_1_3780#ista_0000-0000_2019_ant_1476_1_T11_0198_0000}}</ref> Pompey is also a recurring character in ]'s '']'' crime fiction novels, where he brushes shoulders with Gordianus, the main protagonist of the series.<ref>{{cite web |website=Crime Fiction Lover |url=https://crimefictionlover.com/2014/10/interview-steven-saylor |title=Interview: Steven Saylor |author=Keith Nixon |date=19 October 2014}}</ref> Another fiction series in which Pompey plays a part in the historical background is ] trilogy of the life of ].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.thebookseller.com/author-interviews/robert-harris-interview-312032 |title=Robert Harris {{!}} 'Cicero had very good relations with Caesar but he was absolutely delighted to see him murdered before his own eyes' |website=The Bookseller |author=Benedicte Page |date=11 September 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ==Chronology of Pompey's life and career== | |||
| * 29 September 106 BC – Born in ]; | |||
| * 86 BC – Marriage to Antistia; | |||
| * 89 BC – Serves under his father at Asculum (during the ]); | |||
| * 83 BC – Aligns with ], after his return from the ] against King ], raising a legion and cavalry in hopes of joining him;{{sfn|Goldsworthy|2004|p=174}} | |||
| * 83–82 BC – Fights for Sulla during the war in Italy. First as cavalry commander then joint-commands and finally commanding an independent army. | |||
| * 82 BC – Divorce by Antistia and marriage to Aemilia at the behest of Sulla, but Aemilia is already pregnant and eventually dies during childbirth;{{sfn|Goldsworthy|2004|p=179}} | |||
| * 82–81 BC – Defeats ]' allies in Sicily and Africa; | |||
| * 81 BC – Returns to Rome and celebrates first triumph; | |||
| * 79 BC – Pompey marries ], of the ] family;{{sfn|Goldsworthy|2004|p=179}} | |||
| * 79 BC – Pompey supports the election of ], who openly revolts against the Senate a few months later. Pompey suppresses the rebellion with an army raised from ] and puts down the rebellion, killing the rebel ], father of ], who would go on to assassinate ];{{sfn|Goldsworthy|2004|p=180, 181}} | |||
| * 76–71 BC – Campaign in ] against ]; | |||
| * 71 BC – Returns to Italy and participates in the suppression of a ] led by ], obtaining his second triumph; | |||
| * 70 BC – First consulship (with ]); | |||
| * 67 BC – Defeats the pirates and goes to the province of Asia; | |||
| * 66–61 BC – Defeats King Mithridates of Pontus, ending the Third Mithridatic War; | |||
| * 64–63 BC – Marches through Syria, the Levant, and Judea; | |||
| * 61 BC – Divorce by Mucia Tertia; | |||
| * 29 September 61 BC – Third triumph; | |||
| * April 59 BC – The so-called first ] is constituted. Pompey allies with ] and Crassus, marrying Caesar's daughter ]; | |||
| * 58–55 BC – Governs Hispania Ulterior by proxy, while the Theater of Pompey is constructed; | |||
| * 55 BC – Second consulship (with Marcus Licinius Crassus), and the Theater of Pompey is finally inaugurated; | |||
| * 54 BC – ] dies in childbirth, and the first triumvirate ends; | |||
| * 52 BC – Serves as sole consul for an ],{{sfn|Abbott|1963|p=114}} but has a third ordinary consulship with Metellus Scipio for the rest of the year, marrying his daughter ]; | |||
| * 51 BC – Forbids Caesar (in Gaul) to stand for consulship ''in absentia''; | |||
| * 50 BC – Falls dangerously ill with fever in Campania, but is saved "by public prayers";<ref>Juvenal, ''Satire X'', p. 283</ref> | |||
| * 49 BC – Caesar crosses the Rubicon river and invades Italy, while Pompey retreats to Greece with the conservatives; | |||
| * 48 BC – Caesar defeats Pompey's army near Pharsalus, Greece. Pompey retreats to Egypt and is killed at ]. | |||
| ==Footnotes== | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist|20em}} | |||
| {{Wikiquotepar|Pompey the Great}} | |||
| {{Commons category|Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus}} | |||
| ==Bibliography== | |||
| * Abbott, Frank Frost (1901). ''A History and Description of Roman Political Institutions''. Elibron Classics (ISBN 0-543-92749-0). | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * Boak, Arthur E.R. ''A History of Rome to 565 A.D.'' (MacMillan, New York, 1922) | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Abbott |first1=Frank Frost |title=A History and Description of Roman Political Institutions |date=1963 |publisher=Biblo and Tannen |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3aQgAQAAIAAJ |language=en}} | |||
| * De Souza, P., ''Piracy in the Graeco-Roman World'', Cambridge University Press, 2002. ISBN 978-0-521-01240-9 | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Beard|first=Mary|title=SPQR: A History of Ancient Rome|publisher=Profile Press |year=2015|edition=2016|isbn=978-1846683817}} | |||
| * Cassius Dio, ''Roman History, Volume 3'' (Loeb Classical Library, 1914) | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Beesley|first=A.|title=The Gracchi Marius and Sulla Epochs of Ancient History |publisher=Pinnacle Press|year=1892 |edition=2017|isbn=978-1374894761}} | |||
| * ]. ''In the name of Rome: The Men Who Won the Roman Empire''. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 2004 (hardcopy, ISBN 0-297-84666-3); New York: Phoenix Press, (paperback, ISBN 0-7538-1789-6). | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Boak|first=Edward|title=A History of Rome to 565 AD|publisher=Wentworth Publishing |year=1921|edition=2016|isbn=978-1363094448}} | |||
| * Greenhalgh, Peter. ''Pompey The Republican Prince'', George Weidenfield and Nicolson Ltd, 1981, ISBN 0-297-77881-1 | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Brice |first1=Lee |title=Warfare in the Roman Republic: from the Etruscan Wars to the Battle of Actium |date=2014 |publisher=ABC-CLIO |location=Santa Barbara, Calif. |isbn=978-1610692991}} | |||
| * Hillman, Thomas P. ''The Reputation of Cn. Pompeius Magnus among His Contemporaries from 83 to 59 B.C.'', Diss. New York 1989. | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Collins|first=H.P. |title=Decline and Fall of Pompey the Great |journal=Greece and Rome|volume=22|issue=66 |year=1953|jstor=641489|pages=98–106 |doi=10.1017/S0017383500011888 |s2cid=161450990}} | |||
| * Holland, Tom. ''Rubicon – The Triumph and Tragedy of the Roman Republic'', Abacus, London, 2004, ISBN 0-349-11563-X | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Crawford |first=Michael H. |title=Roman Republican coinage |publisher=Cambridge University Press |publication-place=London |date=1974 |isbn=0-521-07492-4 |oclc=1288923 |author-link=Michael Crawford (historian)}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=De Souza |first1=Philip |title=Piracy in the Graeco-Roman World |date=2002 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |location=Cambridge |isbn=978-0-521-01240-9 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SOK-Jh1Zuk4C |language=en}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Drogula|first=Fred K. |title=Cato the Younger: Life and death at the end of the Roman Republic |date=2019|isbn=978-0190869021|publisher=Oxford University Press}} | |||
| * {{Cite book|last=Flower|first=Harriet |title=The Cambridge Companion to the Roman Republic |date=2014 |publisher=CUP|isbn=978-1107032248}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Goldsworthy|first=Adrian |title=In the name of Rome: The Men Who Won the Roman Empire |publisher=Phoenix |place=London |year=2004|isbn=978-0753817896}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Goldsworthy|first=Adrian |title=Caesar; The Life of a Colossus |publisher=Orion |year=2006|edition=2013 |isbn=978-0297864004}} | |||
| * {{cite web|last=Gray|first=Eric William |title=Pompey the Great|website=Encyclopaedia Britannica |url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Pompey-the-Great|access-date=16 March 2023}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Greenhalgh|first=P. |title=Pompey: The Republican Prince|publisher=Littlehampton Book Services Ltd|year=1981|isbn=978-0297778813}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Gruen|first=Erich |title=The Last Generation of the Roman Republic|year=1995 |publisher=University of California|isbn=978-0520022386}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Haley|first=Shelley|author-link=Shelley Haley|date=April 1985|title=The Five Wives of Pompey the Great |journal=Greece and Rome|volume=32|issue=1 |pages=49–59 |doi=10.1017/S0017383500030138 |jstor=642299 |s2cid=154822339 |issn=1477-4550}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Holland|first=Tom |title=Rubicon, The Triumph and Tragedy of the Roman Republic |publisher=Abacus|year=2004|isbn=978-0349115634}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Keppie|first=Lawrence |title=The Making of the Roman Army: From Republic to Empire |publisher=Routledge |date=1984|edition=2015|isbn=978-1138129139}} | |||
| * {{cite book |title =The Making of Theatre History |last=Kuritz| first=Paul |publisher=] |year=1987|isbn=978-0-13-547861-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Leach|first=John |title=Pompey the Great|publisher=Biddles Ltd|year=1978 |isbn=0-8476-6035-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Matyszak|first=Philip |title=Sertorius and the Struggle for Spain|year=2013 |publisher=Pen and Sword|isbn=978-1848847873}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Mitchell|first=Thomas |title=Cicero, Pompey and the Rise of the First Triumvirate |journal=Traditio|volume=29 |year=1973|pages=1–26|jstor=641489 |doi=10.1017/S0362152900008953 |s2cid=152020610}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Morrill|first=Kit |title=Pompey, Cato, and the Governance of the Roman Empire|year=2017 |publisher=OUP|isbn=978-0198755142}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Ramsey|first=John |title=How and why was Pompey Made Sole Consul in 52 BC? |journal=Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte|volume=65|issue=3|year=2016 |pages=298–324 |jstor=45019234}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Rosenblitt|first=Alison |title=The Turning Tide: The Politics of the Year 79 B.C.E. |journal=Transactions of the American Philological Association |year=2014|pages=415–431|volume=144|issue=2 |doi=10.1353/apa.2014.0008 |jstor=43830445|s2cid=144556938}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Seager|first=R|title=Pompey the Great: A Political Biography|publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |year=2002|isbn=978-0826203564}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Stanton|first=John |title=Why Did Caesar Cross the Rubicon?|journal=Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte|volume=52|issue=1|year=2003|pages=67–94|jstor=4436678}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Tröster|first=Manuel |title=Roman Hegemony and Non-State Violence: A Fresh Look at Pompey's Campaign against the Pirates|journal=Greece and Rome|volume=56 |issue=1|year=2009|jstor=40388852 |pages=14–33 |doi=10.1017/S0017383508000673 |s2cid=154000527}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Wylle|first=Graham |title=The Road to Pharsalus|journal=Latomus|volume=51|issue=3 |year=1992|jstor=41541372|pages=557–565}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| * Christ, Karl (2004). ''Pompeius. Der Feldherr Roms. Eine Biographie'' . Munich: C. H. Beck, {{ISBN|3-406-51543-6}}. | |||
| * Dingmann, Matthias (2007). ''Pompeius Magnus. Machtgrundlagen eines spätrepublikanischen Politikers'' . Rahden: Leidorf, {{ISBN|978-3-89646-733-1}}. | |||
| * Hillman, T., P., ''The Reputation of Cn. Pompeius Magnus among His Contemporaries from 83 to 59 B.C.'', Diss. New York 1989. | |||
| * Nicols, Marianne Schoenlin. ''Appearance and Reality. A Study of the Clientele of Pompey the Great'', Diss. Berkeley/Cal. 1992. | * Nicols, Marianne Schoenlin. ''Appearance and Reality. A Study of the Clientele of Pompey the Great'', Diss. Berkeley/Cal. 1992. | ||
| * Southern, P., Pompey the Great: Caesar's Friend and Foe, The History Press, 2003; {{ISBN|978-0752425214}} | |||
| * Plutarch, '''' (Loeb Classical Library, 1917) | |||
| * Stockton, D., ''The First Consulship of Pompey'', ''Historia'' 22 (1973), 205–18. | |||
| * Seager, Robin. ''Pompey the Great: A Political Biography''. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2002 (hardcover, ISBN 0-631-22720-2; paperback, ISBN 0-631-22721-0). | |||
| * Van Ooteghem, J., ''Pompée le Grand. Bâtisseur d’Empire''. Brussels 1954. | |||
| * Southern, Pat. ''Pompey the Great: Caesar's Friend and Foe''. Stroud, Gloucestershire, UK: Tempus Publishing, 2002 (paperback, ISBN 0-7524-2521-8). | |||
| * |
* Wylie, G., J., ''Pompey Megalopsychos'', ''Klio'' 72 (1990), 445–456. | ||
| * Tröster, Manuel. ''Roman Hegemony and Non-State Violence. A Fresh Look at Pompey’s Campaign against the Pirates'', ''Greece & Rome'' 56 (2009), 14-33. | |||
| * Van Ooteghem, J. ''Pompée le Grand. Bâtisseur d’Empire''. Brussels 1954. | |||
| * Wylie, Graham J. ''Pompey Megalopsychos'', ''Klio'' 72 (1990), 445-456. | |||
| {{s-start}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{s-off}} | |||
| * - Jona Lendering details Pompey's conquest of Judea | |||
| {{s-bef|before=]|before2=]}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=70 BC|with=]}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=]|after2=]}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=]|before2=]}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=] II|years=55 BC|with=] II}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=]|after2=]}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=]|before2=]}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=] III|years=], 52 BC<br />''without colleague''}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=Himself|after2=]}} | |||
| {{s-bef|before=Himself}} | |||
| {{s-ttl|title=]|years=52 BC|with=]}} | |||
| {{s-aft|after=]|after2=]}} | |||
| {{s-end}} | |||
| {{Pompey}} | |||
| {{Plutarch}} | {{Plutarch}} | ||
| {{Pirates}} | {{Pirates}} | ||
| {{Ancient Greek and Roman Wars}} | |||
| {{authority control}} | |||
| <!-- Metadata: see ] --> | |||
| {{Persondata | |||
| ] | |||
| |NAME = Pompey | |||
| |ALTERNATIVE NAMES = Pompeius Magnus, Gnaeus; CN·POMPEIVS·CN·F·SEX·N·MAGNVS | |||
| |SHORT DESCRIPTION = Roman general | |||
| |DATE OF BIRTH = September 29 106 BC | |||
| |PLACE OF BIRTH = Rome | |||
| |DATE OF DEATH = September 29 48 BC | |||
| |PLACE OF DEATH = Pelusium | |||
| }} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:34, 11 December 2024
Roman general and statesman (106–48 BC)For other uses, see Pompey (disambiguation) and Gnaeus Pompeius (disambiguation). Not to be confused with Pompeii or Pompei.
| Pompey | |
|---|---|
| Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus | |
 Bust of Pompey, copy of an original from 70–60 BC, Venice National Archaeological Museum Bust of Pompey, copy of an original from 70–60 BC, Venice National Archaeological Museum | |
| Born | 29 September 106 BC Picenum, Italy |
| Died | 28 September 48 BC (aged 57) Pelusium, Egypt |
| Cause of death | Assassination |
| Resting place | Albanum, Italy |
| Occupation(s) | Military commander and politician |
| Office | Consul (70, 55, 52 BC) |
| Spouses |
|
| Children | |
| Father | Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo |
| Relatives | Pompeia gens |
| Military career | |
| Battles / wars | |
| Awards | 3 Triumphs |
 |
| Part of a series on |
| Ancient Rome and the fall of the Republic |
|---|
|
People
Events
Places |
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (Latin: [ˈŋnae̯ʊs pɔmˈpɛjjʊs ˈmaŋnʊs]; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey (/ˈpɒmpi/ POM-pee) or Pompey the Great, was a general and statesman of the Roman Republic. He played a significant role in the transformation of Rome from republic to empire. Early in his career, he was a partisan and protégé of the Roman general and dictator Sulla; later, he became the political ally, and finally the enemy, of Julius Caesar.
A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving Sulla as a commander in the civil war of 83–81 BC. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first consulship without following the traditional cursus honorum (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as consul on three occasions (70, 55, 52 BC). He celebrated three triumphs, served as a commander in the Sertorian War, the Third Servile War, the Third Mithridatic War, and in various other military campaigns. Pompey's early success earned him the cognomen Magnus – "the Great" – after his boyhood hero Alexander the Great. His adversaries gave him the nickname adulescentulus carnifex ("teenage butcher") for his ruthlessness.
In 60 BC, Pompey joined Crassus and Caesar in the informal political alliance known as the First Triumvirate, cemented by Pompey's marriage with Caesar's daughter, Julia. After the deaths of Julia and Crassus (in 54 and 53 BC), Pompey switched to the political faction known as the optimates—a conservative faction of the Roman Senate. Pompey and Caesar then began contending for leadership of the Roman state in its entirety, eventually leading to Caesar's Civil War. Pompey was defeated at the Battle of Pharsalus in 48 BC, and he sought refuge in Ptolemaic Egypt, where he was assassinated by the courtiers of Ptolemy XIII.
Early life and career

Pompey was born in Picenum on 29 September 106 BC, eldest son of a provincial noble called Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo. Although the dominant family in Picenum, Strabo was the first of his branch to achieve senatorial status in Rome; he completed the traditional cursus honorum, becoming consul in 89 BC, and acquired a reputation for greed, political duplicity, and military ruthlessness. Pompey began his career serving with his father in the Social War (91–87 BC).
Strabo died in 87 BC during the short-lived civil war known as the Bellum Octavianum, although sources differ on whether he succumbed to disease, or was murdered by his own soldiers. Prior to his death, Strabo was accused of embezzlement; as his legal heir, Pompey was held responsible for the alleged crime and put on trial. He was acquitted, supposedly after agreeing to marry the judge's daughter, Antistia.
One of the main issues at stake in 87 BC was the appointment of the consul Lucius Cornelius Sulla as commander of the Roman army in the ongoing First Mithridatic War, an opportunity to amass enormous wealth. During his absence in the East, his political rivals led by Lucius Cornelius Cinna, Gnaeus Papirius Carbo and Gaius Marius the Younger regained control of the Roman Senate. Sulla's return in 83 BC sparked a civil war within the Roman world.
Pompey during Sulla's civil war
Main article: Sulla's civil warIn the year prior to Sulla's return Pompey had raised and equipped a full legion from amongst his father's old clients and veterans in Picenum. In the spring of 83 Sulla landed in Brundusium. As he marched north-west towards Campania, Pompey led his own legion south to join him. The government in Rome sent out three separate armies in an attempt to prevent the union between Pompey's and Sulla's army. Pompey attacked one of these armies and routed it. The three enemy commanders, unable to agree on a course of action, withdrew. Soon after Pompey arrived at Sulla's camp. He was greeted by Sulla with the official title of Imperator (General).
At some point in 83 BC, it is not clear when but definitely before the onset of winter, Sulla sent Pompey back to Picenum to raise more troops. When fighting broke out once more in 82 Sulla advanced towards Rome, while Metellus (one of his lieutenants), supported by Pompey, campaigned against the consul Gaius Papirius Carbo in Cisalpine Gaul. During this campaign Pompey acted as Metellus's cavalry commander.
Metellus and Pompey defeated Carbo's lieutenant, the praetor Gaius Carrinas, in a six-hour battle at the river Aesis, only to be blockaded by Carbo himself. When word of Sulla's victory at the Battle of Sacriportus reached them, Carbo retreated to his base at Ariminium, severely harassed by Pompey's cavalry. Some time later Metellus defeated Gaius Marcius Censorinus, another of Carbo's lieutenants, Pompey's cavalry caught Censorinus's fleeing troops outside their base at Sena Gallica, defeating them and plundering the town. While Metellus remained in the north-west, Pompey seems to have transferred to Sulla's command in the south.
Pompey advanced south-west along the Via Flaminia towards Spoletium, where he joined Marcus Licinius Crassus, together they defeated Carrinas once again. Pompey laid siege to Carrinas in Spoletium but the latter managed to escape. Pompey resumed his march to join Sulla's command. Not long afterwards Pompey successfully ambushed another large force under Censorinus, which was trying to get through to Praeneste where Carbo's consular colleague, Marius the Younger (who was the figurehead of the struggle against Sulla), was blockaded. It was the failure of these attempts to get through the Sullan blockade in Umbria and Etruria, added to Metellus's success in winning control of the north, which broke the back of the government's resistance.
At the end of the campaigning season of 82, the government forces made one final effort to march to the relief of Praeneste. They mustered 10,000 legionaries and marched to join forces with the Samnites and the Lucanians, fierce enemies of Sulla, who had campaigned against them in the Social War. Pursued by Pompey they united their forces and made for Praeneste. Unable to break through Sulla's blockade, they marched for undefended Rome, only to be caught just in time and defeated by Sulla at the Battle of the Colline Gate. Pompey, who was pursuing the government forces, arrived just after the battle.
By the end of 82 BC, Sulla had expelled his opponents from Italy, and engineered his nomination as Dictator by the Senate. Either through admiration of his abilities, or concern at his ambition, Sulla sought to consolidate his alliance with Pompey by persuading him to divorce Antistia, and marry his stepdaughter Aemilia. Plutarch claims she was already pregnant by her former husband, and died in childbirth soon after.
Sicily, Africa and Lepidus' rebellion
The surviving Marians escaped to Sicily, where their ally Marcus Perperna was propraetor. They were supported by a fleet under Carbo, while Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus occupied the Roman province of Africa. Perperna abandoned Sicily after Pompey landed on the island with a large force, while Carbo was captured and later executed. Pompey claimed this was justified by Carbo's alleged crimes against Roman citizens, but his opponents nicknamed him adulescentulus carnifex, or "young butcher", as a result.
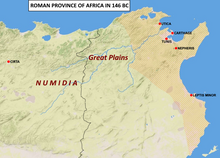
Pompey now sailed for Africa, leaving Sicily in the hands of his brother-in-law, Gaius Memmius. After defeating and killing Ahenobarbus at the Battle of Utica, Pompey subdued Numidia and executed its king Hiarbas, a Marian ally. He restored the deposed Hiempsal to the Numidian throne. Around this time, his troops began referring to him as Magnus, or "the Great", after Alexander the Great, a figure much admired by the Romans. Shortly thereafter, Pompey formally made this part of his name.
On returning to Rome, he asked for a triumph to celebrate his victories, an unprecedented demand for someone so young. Pompey refused to disband his army until Sulla agreed, although the latter tried to offset the impact by awarding simultaneous triumphs to Lucius Licinius Murena and Gaius Valerius Flaccus. Sometime during this period, Pompey married Mucia Tertia, a member of the powerful Metellus family. They had three children before their divorce in 61 BC; Pompey the younger, usually known as Gnaeus, a daughter, Pompeia Magna, and a younger son, Sextus.

Pompey supported Marcus Aemilius Lepidus as consul for 78 BC; Plutarch claims he did so against Sulla's advice, but most modern historians refute the idea. When Sulla died in 78 BC, Lepidus sought to block his state funeral and roll back some of Sulla's laws, then became proconsul of Cisalpine and Transalpine Gaul in January 77 BC. When the Senate ordered him back to Rome, Lepidus refused to comply unless granted another term as consul, a proposal that was rapidly rejected. Assembling an army, he began marching on Rome; the Senate responded with a series of measures, one of which was to appoint Pompey to a military command.
While Lepidus continued south, Pompey raised troops from among his veterans in Picenum, and moved north to besiege Mutina, capital of Cisalpine Gaul. The town was held by Lepidus' ally Marcus Junius Brutus, who surrendered after a lengthy siege, and was assassinated next day, allegedly on Pompey's orders. Catulus then defeated Lepidus outside Rome, while Pompey marched against his rear, catching him near Cosa. Lepidus and the remnants of his army retreated to Sardinia, where he died.
Sertorian War
Main article: Sertorian WarThe Sertorian War began in 80 BC when Quintus Sertorius, a prominent proscribed Marian general, initiated a rebellion in Hispania, where he was joined by other Roman exiles like Perperna. Supported by local Iberian tribes, he took control of Hispania Ulterior and repeatedly defeated Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius through skillful use of guerrilla warfare. Sertorius defeated other Roman generals sent to oust him and soon conquered Hispania Citerior as well. Backed by his allies in the Senate, Pompey was appointed military commander in Spain with proconsular authority in order to defeat Sertorius. This act was technically illegal as he had yet to hold public office, illustrating Pompey's preference for military glory, and disregard for traditional political constraints.
Pompey recruited 30,000 infantry and 1,000 cavalry, evidence of the threat posed by Sertorius. En route to Hispania, he subdued a rebellion in Gallia Narbonensis, after which his army entered winter quarters near Narbo Martius. In early 76 BC, he crossed the Col de Portet and entered the Iberian peninsula, where he would remain for the next five years. His arrival boosted the morale of Metellus' troops, while some rebels changed sides, but soon after he was defeated by Sertorius at the Battle of Lauron, losing one third of his army while inflicting next to no losses on Sertorius' army. This was a serious blow to Pompey's prestige, who spent the rest of the year re-organising his army. Metellus' failure to dislodge Sertorius and Pompey's defeat meant the senatorial generals made no progress in the year.

In 75 BC, Sertorius led the campaign against Metellus, while Pompey defeated his subordinates Perperna and Gaius Herennius outside Valencia. When Sertorius took over operations against Pompey, Metellus defeated his deputy Lucius Hirtuleius at the Battle of Italica. Pompey faced Sertorius in the indecisive Battle of Sucro, in which Sertorius defeated Pompey's right flank and nearly captured Pompey himself, but his legate Lucius Afranius defeated the Sertorian right. Sertorius withdrew inland, then turned to fight at Saguntum, where Pompey lost 6,000 men, including his brother-in-law Memmius, reputedly his most effective subordinate. Sertorius himself suffered 3,000 casualties, one of whom was Hirtuleius.
Although Metellus defeated Perperna in a separate battle, Sertorius was able to withdraw to Clunia late in the year, where he repaired the walls to lure his opponents into a siege, while forming garrisons from other towns into a new field army. Once this was ready, he escaped from Clunia and used it to disrupt Roman logistics on land and by sea. Lack of supplies forced Metellus to quarter his troops in Gaul, while Pompey wintered among the Vaccaei. Dire straits caused by this stretch of the campaign and Sertorius' guerrilla warfare led Pompey to write a letter to the Senate asking for funds and men, and scolding their lack of support for him and Metellus.
Pompey's letter had the effect of galvanizing the Senate into sending him more men and funds. Reinforced by two more legions, in 74 BC he and Metellus began a war of attrition against their enemy. As his chief opponent had lost most of his Roman legionaries and could no longer match him in the field, Pompey, along with Metellus, gained the upper hand, conquering more and more Sertorian cities, slowly grinding down Sertorius' revolt. By now, Sertorius was being undermined by internal divisions. Discontent in Sertorius' coalition of Iberian and Roman forces came to a head in 72 or 73 BC when Perperna, leading a conspiracy with other prominent Sertorians, had Sertorius assassinated and assumed control of the rebel army.
Pompey engaged Perperna in battle and defeated him swiftly at the Battle near Osca. Perperna was captured and attempted to persuade Pompey to spare him by giving over Sertorius' correspondence, allegedly containing proof of communications between the rebel leader and leading men in Rome. Pompey burned the letters unread and executed Perperna, and then spent some time restructuring the local Roman administration, showing a lack of animosity towards his former opponents, which extended his patronage throughout Hispania and into southern Gaul. Pompey and his army remained in Hispania for a few years conquering the Sertorian remnants, and then marched back to Rome.
First Consulship
During Pompey's absence, Marcus Licinius Crassus was charged with suppressing the slave rebellion led by Spartacus known as the Third Servile War. Pompey returned to Italy just before Crassus defeated the main rebel army in 71 BC, arriving in time to massacre 6,000 fugitives from the battle. His claim to have ended the war by doing so was a long-standing source of resentment for Crassus.

Pompey was granted a second triumph for his victory in Hispania, and nominated for the consulship. Since he was both too young and technically ineligible, this required a special senatorial decree. Plutarch suggests Pompey supported Crassus as his co-consul in order to put him under an obligation. The two men were elected consuls for 70 BC, but allegedly differed on almost every measure, rendering their term "politically barren and without achievement."
However, their consulship did see the plebeian tribune recover powers removed by Sulla. One of the most significant was the ability to veto Senatorial bills, an act often seen as a turning point in the politics of the late Republic. Although popular with the people, the measure must have been opposed by the optimates, and thus passing it required support from both consuls, although most extant sources barely mention Crassus.
Campaign against the pirates
Main article: Pompey's campaign against the piratesPirates operated throughout the Mediterranean, while their fleets often formed temporary alliances with enemies of Rome, including Sertorius and Mithridates. Their power and range had increased over the past fifty years, partly because of the decline of traditional naval powers like Rhodes, while previous attempts to subdue them had been unsuccessful. However, Romans routinely referred to their opponents as "pirates" or "brigands", and some historians argue it is more accurate to see them as a conventional enemy, rather than disorganised outlaws.
Principally based in Cilicia, in 68 BC they raided as far as Ostia, Rome's port, and kidnapped two senators, to general outrage. Prompted by Pompey, Aulus Gabinius, tribune of the plebs in 67 BC, proposed the Lex Gabinia, giving him a mandate for their suppression. It granted him proconsular authority for three years in any province within 50 miles of the Mediterranean, along with the power to appoint legates and significant financial resources. Concerned by one man holding such wide-ranging powers, the Senate opposed the law but it was passed by the people. Most of the difficulties Pompey faced came from officials who resented his authority. In Gaul, Piso hampered his recruitment efforts, while in Crete, Quintus Metellus refused to comply with his instructions.
Pompey spread his forces throughout the Mediterranean to prevent the pirates escaping a Roman fleet by moving elsewhere. Fifteen legates were given specific areas to patrol, while he secured the grain route to Rome. These measures won him control of the western Mediterranean in just 40 days, after which his fleets moved to the east, forcing the pirates back to their bases in Cilicia. Pompey led the decisive assault on their stronghold in Coracaesium, winning the Battle of Korakesion and concluding the war in only three months.
Most of his opponents surrendered without fighting, thanks to Pompey's reputation for clemency. They were granted lands in cities devastated during the Mithridatic War, notably Soli, renamed Pompeiopolis, and Dyme in Greece, with others sent to towns in Libya and Calabria. These communities retained a strong attachment to both Rome and Pompey.
Third Mithridatic War and re-organisation of the east
Third Mithridatic War
Main article: Third Mithridatic War
In 73 BC, Lucius Licinius Lucullus, formerly one of Sulla's chief lieutenants, was made proconsul of Cilicia, and commander in the Third Mithridatic War. The war began in 74 BC, when the last ruler of Bithynia died and left his kingdom to Rome, sparking an invasion by Mithridates VI of Pontus, and Tigranes the Great of Armenia. Lucullus was a skilled general who won numerous victories, but claims he was protracting the war for "power and wealth" led to a Senate investigation, while by 69 BC his troops were weary and mutinous.
In 68 BC, Quintus Marcius Rex replaced Lucullus in Cicilia, while Manius Acilius Glabrio received Bithynia. He also assumed leadership of the war against Mithridates, but failed to respond decisively when the latter re-occupied much of Pontus in 67 BC, then attacked Cappadocia, a Roman ally. Seeing an opportunity, in 66 BC Pompey used the tribunate to pass the lex Manilia, giving him extensive powers throughout Asia Minor in order to defeat Mithridates, in addition to those granted by the lex Gabinia. The optimates were privately horrified that one man should hold so much influence, but fearful of his popularity allowed the measure to pass.
Incensed at being replaced, Lucullus called Pompey a "vulture" who profited from the work of others, a reference both to his new command and claim to have finished the war against Spartacus. Pompey agreed an alliance with Phraates III, king of Parthia, whom he persuaded to invade Armenia. When Mithridates offered a truce, Lucullus argued the war was over, but Pompey demanded concessions which could not be accepted. Outnumbered, Mithridates withdrew into Armenia, followed by Pompey, who defeated him at Lycus near the end of 66 BC.

According to contemporary sources, Mithridates and a small contingent escaped the battle, outstripped their pursuers, and reached Colchis on the Black Sea. While there, he took control of the Cimmerian Bosporus from its Roman-backed ruler, his son Machares, who later committed suicide. Meanwhile, Pompey invaded Armenia supported by Tigranes the Younger, whose father quickly came to terms; in return for the restoration of Armenian territories taken by Lucullus, he paid a substantial cash indemnity and allowed Roman troops to be based on his territory.
In 65 BC, Pompey set out to take Colchis, but to do so had first to subdue various local tribes and allies of Mithridrates. After winning a series of battles, he reached Phasis and linked up with Servilius, admiral of his Euxine fleet, before a fresh revolt in Caucasian Albania forced him to retrace his steps. Victory at the Abas enabled him to impose terms on the Albanians and agree truces with other tribes on the northern side of the Caucasus. Pompey then wintered in Armenia, settling minor border contests and raids between his allies Phraates and Tigranes.
Relying on his naval blockade to wear down Mithridates, Pompey spent 64 BC annexing the independent and wealthy cities of Syria, which were incorporated into a new Roman province. In the process, he acquired large amounts of money and prestige, as well as criticism from his opponents in Rome, who argued doing so exceeded his authority. Meanwhile, an ageing Mithridates had been cornered in Panticapaeum by another of his sons, Pharnaces II of Pontus. An attempt to commit suicide by taking poison allegedly failed due to his habit of taking "precautionary antidotes", and he was killed by the rebels. Pharnaces sent his embalmed body to Pompey, in return for which he was granted the Bosporan Kingdom and made an ally of Rome.
Re-organisation of the East
Further information: Pompey's eastern settlementThe final collapse of the Seleucid Empire allowed Pompey to annex Syria in 64 BC, but its dissolution destabilised the region, while many of its cities had used the power vacuum to achieve independence. In early 63 BC, Pompey left Antioch and marched south, occupying coastal cities like Apamea, before crossing the Anti-Lebanon Mountains and capturing Pella, Jordan and Damascus.

Pompey's incursion further south, into Judea, was occasioned on account of its inhabitants, under the leadership of Hyrcanus II and Aristobulus II, having ravaged Phoenicia and Pompey wanting to bring a stop to it. The initial onslaught was disrupted by the Hasmonean Civil War, in which Pompey backed Hyrcanus II over his brother Aristobulus II. When he compelled the latter to surrender Jerusalem, its defenders took refuge in the Temple, which the Romans first stormed, then looted. Judea became a client kingdom ruled by Hyrcanus, while its northern section was incorporated into the Decapolis, a league of semi-autonomous cities (see map). Both Judea and the League were made subordinate to the new province of Syria.
Other organisational changes included creating the province of Bithynia and Pontus, with the rest of Mithridates' territories distributed among Roman allies. Elsewhere, Ariobarzanes I of Cappadocia was restored to his throne, while Lesser Armenia was taken from Tigranes and incorporated into Galatia, with Pompey's client Deiotarus becoming ruler of the new kingdom. Finally, Cilicia received the coastal region of Pamphylia, previously a centre of piracy, along with other inland areas and reorganised into six parts. These actions significantly increased Roman state income and presented Pompey with multiple opportunities to increase his personal wealth and patronage base.
Return to Rome and the First Triumvirate

Before his return to Italy in 62 BC, Pompey paid his troops bonuses totalling around 16,000 talents, but despite fears he intended to follow Sulla's example, they were dismissed upon arrival at Brundisium. His journey to Rome drew huge crowds wherever he stopped, showing that although opinion in the Senate was divided, Pompey remained as popular as ever with the masses. He was awarded a third triumph for his achievements in Asia Minor, celebrated on his 45th birthday in 61 BC.
Pompey claimed the new provinces established in the East had increased annual state income from 200 million to 340 million sesterces, plus an additional payment of 480 million sesterces to the treasury. He refused to provide details of his personal fortune, but given the amounts declared publicly, this must have been enormous. Some of it was used to build one of the most famous structures of Ancient Rome, the Theatre of Pompey.
However, the Senate then refused to ratify the treaties agreed by Pompey as part of his settlement of the East. Opposition was led by the optimates Cato the Younger and Metellus Celer, whose sister Mucia had recently been divorced by Pompey, for reasons still disputed. They also defeated a bill to distribute farmland to his veterans, and landless members of the urban poor. A similar measure had been rejected in 63 BC, which arguably made the Senate over confident in their ability to control popular unrest.

Although Pompey could not overcome optimate opposition on his own, the situation changed when Marius' nephew Julius Caesar sought his endorsement for the consulship in 59 BC. A skilled, unscrupulous, and ambitious politician, Caesar used this alliance to harness Pompey's influence with the urban electorate. With additional support from Crassus, Caesar became one of the two consuls for 59 BC, the other being the optimate Marcus Calpurnius Bibulus. This meant Caesar could help pass legislation sponsored by Pompey and Crassus, while it was in his interest to keep them aligned, an important factor given the rivalry between his two patrons.
Despite appearing to be the most junior, Caesar thus became central to the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance designed to counter-balance the optimates. Pompey's influence was based on his reputation as a military commander, and popularity with the Roman people. Crassus' wealth allowed him to construct extensive patronage networks, but he lacked the military clout essential for political success in the late Republican era.

Once elected, Caesar secured the passage of a new agrarian bill, helped by Pompey's veterans, who filled the streets of Rome and allegedly intimidated the Senate. When Bibulus opposed the measure, he was attacked in the forum, and spent the rest of his consulship under virtual house arrest. Caesar then ensured ratification of Pompey's settlements in the east, while the Lex Vatinia made him governor of Gallia Cisalpina and Illyricum. He was also assigned Gallia Transalpina after its governor died in office, before leaving Rome to launch the Gallic Wars in 58 BC. His alliance with Pompey was strengthened when the latter married Caesar's daughter Julia.
Senatorial opposition to the triumvirate was led by Cicero, a long-standing Pompeian ally. Despite this, the latter supported the populist politician Publius Clodius Pulcher in an attack on Cicero for executing Roman citizens without trial during the Catilinarian conspiracy. Although Clodius succeeded in having Cicero exiled, he was recalled to Rome by Pompey eighteen months later in 58 BC. As a result, when shortages of grain caused popular unrest in 57 BC, a grateful Cicero backed Pompey's appointment as praefectus annonae, a temporary position set up for such occasions.
Pompey and Crassus were competing for command of a new expedition to Asia Minor, and in 56 BC they met with Caesar to resolve these issues. Although Crassus was a long-standing rival, there are also indications Pompey felt his status as the foremost soldier of the Republic was threatened by Caesar's success in Gaul. With this in mind, Pompey set aside his differences with Crassus to promote their joint candidature as consuls for 55 BC. With Caesar's support, they were duly elected after prolonged periods of the violence which had become a feature of Roman political campaigns.
Once in office, they ensured passage of a law giving Crassus the province of Syria and command of a punitive expedition against Parthia, providing him opportunities for both military glory and loot. Pompey was assigned the restive provinces of Hispania, along with Africa, while Caesar's governorships in Gaul were extended. All three men were given these positions for a period of five years, as well as the right to levy troops and "make peace and war with whomsoever they pleased."
From confrontation to civil war

In 54 BC, Caesar continued his conquest of Gaul, Crassus opened his campaign against the Parthians, and Pompey remained in Rome, where his wife Julia died in child birth in September. Contemporary sources suggest that combined with the death of Crassus and his son Publius at Carrhae in May 53 BC, this removed any obstacle to direct confrontation between Caesar and Pompey.
Consular elections in 52 BC had to be suspended due to widespread violence. Seeking to end his alliance with Caesar, the optimate Bibulus proposed Pompey be elected sole consul, an unprecedented act backed by both Cato and the tribunate. Having restored order, Pompey married Cornelia, widow of Publius Crassus and daughter of Metellus Scipio Nasica, whom he appointed as his colleague for the last five months of the year.
As consul, Pompey helped enact legislation which some historians view as crucial to understanding the drift to war in 49 BC. Accused of using violence during his consulship in 59 BC, Caesar had previously been shielded by his proconsular immunity. With private support from Pompey, new laws made such prosecutions retrospective, which meant Caesar would probably be put on trial the moment he left Gaul and lost his Imperium. To avoid this, he had secured approval to stand for the consulship in 48 BC while still in Gaul, but another law backed by Pompey required electoral candidates to be physically present in Rome.
Although the two continued to co-operate in public, Pompey clearly viewed his colleague as a threat, as did much of the Senate. Both consuls for 50 BC, Paullus and Gaius Claudius, were opponents of Caesar, as was Curio, a plebeian tribune. They initiated legislation to remove Caesar from his command in Gaul, who allegedly bypassed this by bribing Paullus and Curio. For whatever reason, Curio came up with an alternative proposal; Caesar and Pompey should disarm at the same time, or be declared enemies of the state.
This was a clever move, since it was popular with those who wanted to avoid war, but unacceptable to the optimates who saw Caesar as a danger that had to be eliminated. Rejection made open conflict more likely, and the Senate agreed to fund a consular army, organised by Pompey. When he fell ill while recruiting in Naples, the celebrations that followed his recovery allegedly convinced Pompey his popularity was sufficient to see off any opponent. In December, Caesar crossed the Alps with a single veteran legion and arrived at Ravenna, close to the border with the Roman Republic.
A significant number of senators opposed any concessions to Caesar, but many also mistrusted Pompey, who has been criticised for "weak and ineffectual leadership" in this period. On 1 January 49 BC, Caesar sent an ultimatum demanding acceptance of his compromise, failing which he would march on Rome "to avenge his country's wrongs". Confident their forces significantly outnumbered those available to Caesar, on 7 January the Senate declared him a public enemy; four days later, he crossed the Rubicon into Italy.
The Road to Pharsalus
Main article: Caesar's civil warWhen the war began, Caesar was a rebel with no navy and three understrength legions, while Pompey was backed by all the resources of the Roman state and his clients in the East. However, his position was weaker than it seemed, since he was simply an advisor to the Senate, many of whose members either preferred a negotiated solution, or regarded him with as much suspicion as Caesar. His military strategy had to be approved by the consuls, and he could only issue recommendations, which were not always followed. For example, Cicero rejected a request to help him with recruitment, and Cato refused to take command of Sicily, vital for control of Rome's grain supply.

Plans to defend Italy were undone by the speed with which Caesar moved, advancing directly on Rome with minimal resistance. Although outnumbered, his troops were experienced veterans, while many of Pompey's were new recruits, a weakness made worse by lack of co-ordination. Cato's brother-in-law, the optimate leader Lucius Domitius, was cut off and captured in a hopeless defence of Corfinium, and his 13,000 men incorporated into Caesar's army. Led by Asinius Pollio, they were later used to occupy Sicily.
Pompey had abandoned Rome, ordering all senators and public officials to accompany him as he withdrew south to Brundisium. From there, he transported his troops across the Adriatic to Dyrrhachium in Thessaly, an operation performed with almost complete success. Lacking ships to pursue him, Caesar first secured his rear by subduing Pompeian forces in Hispania, before returning to Rome in December 49 BC. This gave Pompey time to build an army nearly twice the size of his opponents, while his navy destroyed two fleets being built for Caesar, ensuring the Pompeians retained control of the sea lanes.
Despite this, in January 48 BC Caesar managed to cross the Adriatic with seven legions and land in southern Albania. After capturing Oricum and Apollonia, he advanced on Pompey's main supply base at Dyrrhachium. The latter arrived in time to block the attempt, and establish a fortified camp on the other side of the River Apus, where the two armies remained until spring. Neither commander was anxious to begin hostilities, since Caesar was too weak militarily, while as with Mithridates, Pompey preferred to starve his opponent into submission.

In late March the stalemate was broken when Mark Antony finally managed to cross the Adriatic with four more legions and land at Nymphaeum, some 57 kilometres north of Dyrrachium. Pompey tried to prevent the two Caesarian armies from linking up, by marching north-east and laying an ambush for Antony. The ambush, however, was revealed to Antony by some local Caesarian sympathisers, and he stayed in camp until Caesar approached. Pompey not willing to be caught between the two Caesarian forces withdrew.
Caesar, his army now united with Antony's force, redeployed his forces by sending one-and-a-half legion to win support and gather supplies in Aetolia and Thessaly, and a further two legions under Domitius Calvinus to intercept Metellus Scipio in Macedonia. Meanwhile, Gnaeus, Pompey's oldest son, managed to destroy Caesar's fleet at Oricum and Lissus, making sure no more reinforcements and supplies would reach Caesar from Italy. Caesar tried to lure Pompey into a pitched battle at Asparagium, but the latter refused. The next day Caesar outmaneuvred Pompey and marched for Dyrrachium again. When Pompey arrived at the city Caesar had already set up camp.
Caesar lacked the siege equipment needed to take Dyrrhachium, and could not risk leaving Pompey to threaten his rear. He solved this by besieging Pompey in his camp. Although the latter had enough food, water was scarce because Caesar had dammed the local rivers, and the Pompeian cavalry lacked forage for their horses. Ending the stalemate became a matter of urgency, and in late July Pompey finally managed to break through part of Caesar's defensive lines. Since this made the blockade pointless, Caesar cut his losses and withdrew to Apollonia.
At this point Metellus Scipio arrived in Thessaly. Caesar moved south to confront this threat and link up with Domitius Calvinus, allowing his men to sack Gomphi en route. Pursued by Pompey, he then withdrew to the area near Pharsalus, but failed to tempt Pompey into giving battle. Although it was later claimed Pompey only did so after being pressured by his subordinates, the delay may simply have been a reflection of his natural caution.
Regardless, Pompey's army of around 38,000 outnumbered the 22,000 men commanded by Caesar, with 7,000 cavalry to 1,000. On 9 August he deployed his men in battle formation, planning to use his superior cavalry to outflank his opponent on his left. Caesar had anticipated this, and repulsed the cavalry which fled in confusion, exposing the infantry behind them. Under pressure from the left and in front, the Pompeian army collapsed.
Death

Pompey escaped from the battlefield and made his way to Mytilene, where he was reunited with his wife Cornelia. Most of his Eastern allies were present at Pharsalus and had either been killed or captured. The main absentee was 14-year-old Ptolemy XIII, ruler of the wealthy and strategically important kingdom of Egypt, making it an obvious destination. Cato announced his intention to continue the war from Africa, although most of his senatorial colleagues, including Cicero and Marcus Junius Brutus, made their peace with Caesar and returned to Rome.
Pompey sailed from Cyprus with a small fleet, and on 28 September 48 BC arrived at Pelusium in Egypt, where Ptolemy was engaged in a bitter civil war with his co-ruler and elder sister, Cleopatra VII. When he went ashore to greet an official delegation, Pompey was killed by Lucius Septimius, a Roman officer and former colleague serving in the Egyptian army. His body was cremated by two servants, while the head was kept as evidence.
One suggestion is that Ptolemy and his advisors feared Pompey planned to seize control of Egypt, especially since many Egyptian army officers were Roman mercenaries like Septimius who had previously served with him. At the same time, it seemed an easy way to win Caesar's support against Cleopatra, although ultimately this proved not to be the case. Pompey's head was later returned to Cornelia for burial at his villa in the Alban Hills, while his ignominious death prompted Cicero to write "his life outlasted his power".
Marriages and issue
Main article: Wives of Pompey the GreatPompey had five wives:
- Antistia. They married in 86 BC and divorced in 82 BC. By her he had no issue.
- Aemilia Scaura. When they married in 82 BC, Aemilia was pregnant by her former husband and died in childbirth in the same year.
- Mucia Tertia. They married in 79 BC and divorced in 61 BC. By her he had two sons and a daughter:
- Julia, the daughter of Julius Caesar. They married in 59 BC and she died in childbirth in 54 BC. The child died a few days after birth.
- Cornelia Metella. They married in 52 BC and had no children together.
Generalship
Pompey's military glory was second to none for two decades, yet his skills were occasionally criticized by some of his contemporaries. Sertorius or Lucullus, for instance, were especially critical. Pompey's tactics were usually efficient, albeit not particularly innovative or imaginative, and they could prove insufficient against greater tacticians. However, Pharsalus was his only decisive defeat. At times, he was reluctant to risk an open battle. While not extremely charismatic, Pompey could display tremendous bravery and fighting skills on the battlefield, which inspired his men. While being a superb commander, Pompey also earned a reputation for stealing other generals' victories.
On the other hand, Pompey is usually considered an outstanding strategist and organizer, who could win campaigns without displaying genius on the battlefield, but simply by constantly outmaneuvering his opponents and gradually pushing them into a desperate situation. Pompey was a great forward planner, and had tremendous organizational skill, which allowed him to devise grand strategies and operate effectively with large armies. During his campaigns in the east, he relentlessly pursued his enemies, choosing the ground for his battles.
Above all, he was often able to adapt to his enemies and showed determination. On many occasions, he acted very swiftly and decisively, as he did during his campaigns in Sicily and Africa, or against the Cilician pirates. During the Sertorian war, on the other hand, Pompey was beaten several times by Sertorius. Despite an abysmal first year of the war for Pompey in 76 BC, he continued to campaign vigorously and as a result defeated many of Sertorius' subordinates. After Sertorius' army was greatly diminished, Pompey then decided to conduct a war of attrition, in which he would avoid open battles against his chief opponent but instead tried to gradually regain the strategic advantage by capturing his fortresses and cities and defeating his junior officers. This strategy was unspectacular, but it led to constant territorial gains and did much to demoralize the Sertorian forces. By 73 or 72 BC, when he was assassinated, Sertorius was already in a desperate situation and his troops were deserting. Against Perperna, a tactician far inferior to his former commander-in-chief, Pompey decided to revert to a more aggressive strategy and he scored a decisive victory that effectively ended the war.
Against Caesar too, his strategy was sound. During the campaign in Greece, he managed to regain the initiative, join his forces to that of Metellus Scipio (something that Caesar wanted to avoid) and trap his enemy. His strategic position was hence much better than that of Caesar and he could have starved Caesar's army to death. However, he was finally compelled to fight an open battle by his allies, and his conventional tactics proved no match to those of Caesar (who also commanded the more experienced troops).
Literary heritage
Pompey was so striking a figure, and his fall so dramatic, that his story became the subject of frequent literary treatment. In the century after his death, the civil war between himself and Caesar was retold in Lucan's epic De Bello Civili, now known as the Pharsalia after the culminating battle. In the poem's final sections, however, Pompey's vengeful ghost returns to possess those responsible for his murder in Egypt and bring about their death.
In Renaissance Britain, too, several plays returned to the subject of "Caesar and Pompey", including George Chapman's The Wars of Pompey and Caesar (c. 1604). Another contemporary treatment by Thomas Kyd, Cornelia, or Pompey the Great, his faire Cornelia's tragedy (1594), was a translation from the French of Robert Garnier. Later in France, Pompey's story was told without the character appearing onstage in Pierre Corneille's La Mort de Pompée (1643) and this too had English adaptations: as Pompey (1663) by Catherine Philips, as Pompey the Great by Edmund Waller and others in 1664, and later as The Death of Pompey (1724) by Colley Cibber.
Later in the 18th century, Pompey is made the recipient of a 'heroical epistle' in rhyming couplets from a supposed former lover in John Hervey's "Flora to Pompey". He also figures in narrative poems of the 19th century. John Edmund Reade's "The Vale of Tempe" records the fugitive's desperate appearance as glimpsed by a bystander in the Greek valley; his arrival in Egypt is related by Alaric Watts in "The Death of Pompey the Great", and the ruined column raised to mark the site of his killing outside Alexandria is described by Nicholas Michell in Ruins of Many Lands. These were followed by John Masefield's prose drama The Tragedy of Pompey the Great of 1910, covering the period from his decision to fight Caesar to his assassination in Egypt. The play was later filmed for television in 1950 for the BBC Sunday Night Theatre.
Pompey's career is recapitulated a century later in series of historical novels. In Colleen McCullough's Masters of Rome, Pompey is mainly featured in Books III-V, covering his rise to prominence through to his betrayal and murder in Egypt. Pompey is also a recurring character in Steven Saylor's Roma Sub Rosa crime fiction novels, where he brushes shoulders with Gordianus, the main protagonist of the series. Another fiction series in which Pompey plays a part in the historical background is Robert Harris's trilogy of the life of Cicero.
Chronology of Pompey's life and career
- 29 September 106 BC – Born in Picenum;
- 86 BC – Marriage to Antistia;
- 89 BC – Serves under his father at Asculum (during the Social War);
- 83 BC – Aligns with Sulla, after his return from the First Mithridatic War against King Mithridates VI of Pontus, raising a legion and cavalry in hopes of joining him;
- 83–82 BC – Fights for Sulla during the war in Italy. First as cavalry commander then joint-commands and finally commanding an independent army.
- 82 BC – Divorce by Antistia and marriage to Aemilia at the behest of Sulla, but Aemilia is already pregnant and eventually dies during childbirth;
- 82–81 BC – Defeats Gaius Marius' allies in Sicily and Africa;
- 81 BC – Returns to Rome and celebrates first triumph;
- 79 BC – Pompey marries Mucia Tertia, of the Mucii Scaevolae family;
- 79 BC – Pompey supports the election of Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, who openly revolts against the Senate a few months later. Pompey suppresses the rebellion with an army raised from Picenum and puts down the rebellion, killing the rebel Marcus Junius Brutus, father of Brutus, who would go on to assassinate Julius Caesar;
- 76–71 BC – Campaign in Hispania against Sertorius;
- 71 BC – Returns to Italy and participates in the suppression of a slave rebellion led by Spartacus, obtaining his second triumph;
- 70 BC – First consulship (with Marcus Licinius Crassus);
- 67 BC – Defeats the pirates and goes to the province of Asia;
- 66–61 BC – Defeats King Mithridates of Pontus, ending the Third Mithridatic War;
- 64–63 BC – Marches through Syria, the Levant, and Judea;
- 61 BC – Divorce by Mucia Tertia;
- 29 September 61 BC – Third triumph;
- April 59 BC – The so-called first triumvirate is constituted. Pompey allies with Julius Caesar and Crassus, marrying Caesar's daughter Julia;
- 58–55 BC – Governs Hispania Ulterior by proxy, while the Theater of Pompey is constructed;
- 55 BC – Second consulship (with Marcus Licinius Crassus), and the Theater of Pompey is finally inaugurated;
- 54 BC – Julia dies in childbirth, and the first triumvirate ends;
- 52 BC – Serves as sole consul for an intercalary month, but has a third ordinary consulship with Metellus Scipio for the rest of the year, marrying his daughter Cornelia Metella;
- 51 BC – Forbids Caesar (in Gaul) to stand for consulship in absentia;
- 50 BC – Falls dangerously ill with fever in Campania, but is saved "by public prayers";
- 49 BC – Caesar crosses the Rubicon river and invades Italy, while Pompey retreats to Greece with the conservatives;
- 48 BC – Caesar defeats Pompey's army near Pharsalus, Greece. Pompey retreats to Egypt and is killed at Pelusium.
Footnotes
- Samnium and Lucania had remained virtually neutral during the war, but now decided to throw their lot in with the Roman government – their hatred for Sulla probably being the deciding factor.
- Six legions and a navy of 120 warships and 800 transport ships. Both men and ships were immediately available: the men and ships from Sulla's armies
- Reportedly 6,000 talents for Pompey, with tribunes getting 10,000 drachmas each, centurions 1,000, and enlisted men 50
- These were Cilicia Aspera, Cilicia Campestris, Pamphylia, Pisidia, Isauria, Lycaonia, and Phrygia
- The three wreaths on the reverse refer to the three triumphs of Pompey; the top wreath is the corona aurea he received in 62; the globe in the center is a copy of the one paraded during the third triumph; the aplustre on the lower left alludes to his victory against the pirates
- A Roman talent was roughly 32 kilograms of gold, making this distribution worth over $32 billion using 2023 prices
- The divorce may also have been a factor in the defection of Metellus Nepos, previously one of Pompey's main supporters, although the Metelli had their own political ambitions.
- Historian Florus wrote "Pompey could not brook an equal, or Caesar a superior."
- Now in Northern Italy, Ravenna was then a federated ally of the Roman Republic
- Pompey was based at Petra, a small port north of Dyrrhachium, roughly on the site of modern Shkëmbi i Kavajës in Albania
- The exact location of the battle is still disputed
- these numbers refer to legionaries and do not include the light-armed troops provided by allied rulers and nations
References
- Leach 1978, p. 29.
- Leach 1978, p. 13.
- Collins 1953, p. 98.
- Beesley 1892, pp. 167–170.
- ^ Collins 1953, p. 100.
- Beard 2015, pp. 241–242.
- Boak 1921, pp. 145–146.
- Beard 2015, p. 272.
- Leach 1978, pp. 24–25.
- Leach 1978, pp. 25–26.
- Leach 1978, p. 26.
- Leach 1978, pp. 26–27.
- ^ Leach 1978, p. 27.
- Beard 2015, p. 245.
- Haley 1985, p. 49.
- Collins 1953, p. 99.
- ^ Haley 1985, p. 50.
- Leach 1978, p. 28.
- Leach 1978, p. 30.
- Leach 1978, p. 30–31.
- Gray.
- Seager 2002, p. 28.
- Leach 1978, pp. 31–32.
- Rosenblitt 2014, pp. 415–16.
- Collins 1953, p. 101.
- Gruen 1995, p. 15.
- Gruen 1995, p. 16.
- Leach 1978, p. 42.
- Leach 1978, pp. 41–43.
- Holland 2004, pp. 141–142.
- Leach 1978, p. 44.
- Leach 1978, p. 45.
- Leach 1978, p. 46.
- Appian, Bellum Civile, 1.109
- Plutarch, Life of Sertorius, p. 18
- Leach 1978, p. 48.
- Matyszak 2013, pp. 117–118.
- Leach 1978, p. 47.
- Matyszak 2013, p. 118.
- Leach 1978, p. 49.
- Matyszak 2013, pp. 121–122.
- Leach 1978, pp. 49–50.
- Matyszak 2013, p. 126.
- Appian, Bellum Civile, 1.110
- Plutarch, Parallel Lives, Life of Pompey, 18–20.1.
- Plutarch, Life of Sertorius, pp. 19–21
- Sallust, Histories, 1.2.82
- ^ Collins 1953, p. 102.
- Holland 2004, p. 142.
- Plutarch, Life of Crassus, 11.7
- Plutarch, Parallel Lives, Life of Pompey, 21.2.
- Crawford 1974, pp. 412–413.
- ^ Livy, Periochae, 97.6
- Plutarch, Life of Crassus, 12.1
- Plutarch, Life of Crassus, 12.2
- Tröster 2009, pp. 20–21.
- Tröster 2009, p. 17.
- Leach 1978, p. 66.
- Seager 2002, pp. 43–44.
- Flower 2014, pp. 89–90.
- Leach 1978, p. 68.
- Leach 1978, pp. 71, 74.
- Seager 2002, p. 47.
- Leach 1978, p. 72.
- Leach 1978, p. 73.
- Seager 2002, pp. 47–48.
- Plutarch, Parallel Lives, Life of Lucullus, pp. 33–35.
- Cassius Dio, Roman History, 36.14.4, 17.1.
- Plutarch, Parallel Lives, Life of Pompey, 30.1–5.
- Greenhalgh 1981, p. 107.
- Cassius Dio, Roman History, 36.45–46.
- Cassius Dio, Roman History, 36.47.
- Plutarch, Parallel Lives, Life of Pompey, 32.1–3.
- Cassius Dio, Roman History, 36.48–50.
- Plutarch, Parallel Lives, Life of Pompey, 32.3–7.
- Appian, The Mithridatic Wars, pp. 101–102.
- Cassius Dio, Roman History, 36.54, 37.2–5.1
- Cassius Dio, Roman History, 37.5.2–5, 6.
- Cassius Dio, Roman History, 37.11–14.2.
- Leach 1978, p. 93.
- Leach 1978, p. 96.
- Cassius Dio (1969). E.H. Warmington (ed.). Dio's Roman History. The Loeb Classical Library (in English and Greek). Vol. 3. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. p. 127 (book XXXVII). OCLC 264964964.
- Josephus, Jewish Antiquities, 14.54.79
- Morrill 2017, pp. 57–97.
- Crawford 1974, pp. 449–451, though he only links the aplustre with Pompey's cura annonae of 57.
- De Souza 2002, p. 174.
- Leach 1978, p. 101.
- Mitchell 1973, p. 1.
- Beard 2015, p. 273.
- Leach 1978, p. 118.
- Kuritz 1987, p. 48.
- ^ Haley 1985, p. 53.
- Mitchell 1973, p. 6.
- Mitchell 1973, p. 2.
- Mitchell 1973, p. 3.
- Leach 1978, pp. 120–121.
- Mitchell 1973, p. 17.
- Beard 2015, p. 275.
- Beard 2015, p. 282.
- Holland 2004, pp. 238–239.
- ^ Holland 2004, p. 254.
- Goldsworthy 2006, p. 253.
- ^ Collins 1953, p. 104.
- Plutarch, Parallel Lives, Life of Caesar, 23.5–6
- Plutarch, Parallel Lives, Life of Pompey, 53.4–6.
- Florus, Epitome of Roman History, 2.13.14
- Ramsey 2016, pp. 307–308.
- Ramsey 2016, p. 299.
- Stanton 2003, p. 73.
- Stanton 2003, p. 75.
- Stanton 2003, p. 67.
- Drogula 2019, p. 240.
- Drogula 2019, pp. 241–242.
- Drogula 2019, p. 243.
- ^ Wylle 1992, p. 558.
- Wylle 1992, pp. 557–558.
- Wylle 1992, p. 557.
- ^ Wylle 1992, pp. 558–559.
- Leach 1978, p. 183.
- Leach 1978, pp. 173–185.
- Wylle 1992, p. 559.
- Boak 1921, p. 176.
- Leach 1978, p. 192.
- ^ Wylle 1992, p. 560.
- Leach 1978, pp. 192–193.
- Leach 1978, p. 193.
- Leach 1978, p. 194.
- Leach 1978, pp. 193–198.
- Wylle 1992, p. 561.
- Wylle 1992, p. 562.
- Leach 1978, p. 204.
- Keppie 1984, p. 109.
- Wylle 1992, p. 563.
- Holland 2004, p. 323.
- ^ Beard 2015, p. 290.
- Holland 2004, p. 327.
- Haley 1985.
- Plutarch, Parallel Lives, Life of Pompey, 5, 9, 15, 48.
- Plutarch, Life of Sertorius and Life of Lucullus
- ^ Leach 1978, p. .
- Brice 2014, p. 145.
- ^ Si Sheppard, Pharsalus
- History of the Ancient & Medieval World Vol. 6 (Revised ed.). Tarrytown, NY: Marshall Cavendish Corporation. 1996. p. 731. ISBN 0761403574.
- Hazel, John (2001). Who's Who in the Roman World (2nd ed.). New York: Routledge Taylor & Francis Group. pp. 247–248. ISBN 0415224101.
- Sean Easton, "Why Pompey Is better off dead", The Classical Journal 107.2 (2011), pp. 212–23
- A Manual of Old English Plays (1892), pp. 33, 50
- Andrew Shifflett, Stoicism, Politics and Literature in the Age of Milton, Cambridge University 1998, pp. 76 ff
- Joseph Wharton, An Essay on the Genius and Writings of Pope, (London, 1756), vol. 1, p. 296
- Robert Dodsley, A Collection of Poems by Several Hands, (London 1755), vol. 4, pp. 90–94
- The Broken Heart, with other poems, London 1825, pp. 56–60
- Alaric A. Watts, Lyrics of the Heart, London 1851, pp. 209–213
- "Pompey’s Pillar", Ruins of Many Lands, London 1849, pp. 61–2
- The Tragedy of Pompey the Great, London, 1910
- "The Tragedy of Pompey the Great". BFI Film Forever. British Film Institute. 20 July 2012. Archived from the original on 20 July 2012.
- Rocío Gordillo Hervás (9 February 2024). "Historical Fiction and Ancient Rome: Colleen McCullough's Masters Of Rome Series". Collection de l'Institut des Sciences et Techniques de l'Antiquité. 1476 (1): 206 ff.
- Keith Nixon (19 October 2014). "Interview: Steven Saylor". Crime Fiction Lover.
- Benedicte Page (11 September 2015). "Robert Harris | 'Cicero had very good relations with Caesar but he was absolutely delighted to see him murdered before his own eyes'". The Bookseller.
- Goldsworthy 2004, p. 174.
- ^ Goldsworthy 2004, p. 179.
- Goldsworthy 2004, p. 180, 181.
- Abbott 1963, p. 114.
- Juvenal, Satire X, p. 283
Bibliography
- Abbott, Frank Frost (1963). A History and Description of Roman Political Institutions. Biblo and Tannen.
- Beard, Mary (2015). SPQR: A History of Ancient Rome (2016 ed.). Profile Press. ISBN 978-1846683817.
- Beesley, A. (1892). The Gracchi Marius and Sulla Epochs of Ancient History (2017 ed.). Pinnacle Press. ISBN 978-1374894761.
- Boak, Edward (1921). A History of Rome to 565 AD (2016 ed.). Wentworth Publishing. ISBN 978-1363094448.
- Brice, Lee (2014). Warfare in the Roman Republic: from the Etruscan Wars to the Battle of Actium. Santa Barbara, Calif.: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1610692991.
- Collins, H.P. (1953). "Decline and Fall of Pompey the Great". Greece and Rome. 22 (66): 98–106. doi:10.1017/S0017383500011888. JSTOR 641489. S2CID 161450990.
- Crawford, Michael H. (1974). Roman Republican coinage. London: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-07492-4. OCLC 1288923.
- De Souza, Philip (2002). Piracy in the Graeco-Roman World. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-01240-9.
- Drogula, Fred K. (2019). Cato the Younger: Life and death at the end of the Roman Republic. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0190869021.
- Flower, Harriet (2014). The Cambridge Companion to the Roman Republic. CUP. ISBN 978-1107032248.
- Goldsworthy, Adrian (2004). In the name of Rome: The Men Who Won the Roman Empire. London: Phoenix. ISBN 978-0753817896.
- Goldsworthy, Adrian (2006). Caesar; The Life of a Colossus (2013 ed.). Orion. ISBN 978-0297864004.
- Gray, Eric William. "Pompey the Great". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 16 March 2023.
- Greenhalgh, P. (1981). Pompey: The Republican Prince. Littlehampton Book Services Ltd. ISBN 978-0297778813.
- Gruen, Erich (1995). The Last Generation of the Roman Republic. University of California. ISBN 978-0520022386.
- Haley, Shelley (April 1985). "The Five Wives of Pompey the Great". Greece and Rome. 32 (1): 49–59. doi:10.1017/S0017383500030138. ISSN 1477-4550. JSTOR 642299. S2CID 154822339.
- Holland, Tom (2004). Rubicon, The Triumph and Tragedy of the Roman Republic. Abacus. ISBN 978-0349115634.
- Keppie, Lawrence (1984). The Making of the Roman Army: From Republic to Empire (2015 ed.). Routledge. ISBN 978-1138129139.
- Kuritz, Paul (1987). The Making of Theatre History. Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-547861-5.
- Leach, John (1978). Pompey the Great. Biddles Ltd. ISBN 0-8476-6035-4.
- Matyszak, Philip (2013). Sertorius and the Struggle for Spain. Pen and Sword. ISBN 978-1848847873.
- Mitchell, Thomas (1973). "Cicero, Pompey and the Rise of the First Triumvirate". Traditio. 29: 1–26. doi:10.1017/S0362152900008953. JSTOR 641489. S2CID 152020610.
- Morrill, Kit (2017). Pompey, Cato, and the Governance of the Roman Empire. OUP. ISBN 978-0198755142.
- Ramsey, John (2016). "How and why was Pompey Made Sole Consul in 52 BC?". Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte. 65 (3): 298–324. JSTOR 45019234.
- Rosenblitt, Alison (2014). "The Turning Tide: The Politics of the Year 79 B.C.E.". Transactions of the American Philological Association. 144 (2): 415–431. doi:10.1353/apa.2014.0008. JSTOR 43830445. S2CID 144556938.
- Seager, R (2002). Pompey the Great: A Political Biography. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-0826203564.
- Stanton, John (2003). "Why Did Caesar Cross the Rubicon?". Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte. 52 (1): 67–94. JSTOR 4436678.
- Tröster, Manuel (2009). "Roman Hegemony and Non-State Violence: A Fresh Look at Pompey's Campaign against the Pirates". Greece and Rome. 56 (1): 14–33. doi:10.1017/S0017383508000673. JSTOR 40388852. S2CID 154000527.
- Wylle, Graham (1992). "The Road to Pharsalus". Latomus. 51 (3): 557–565. JSTOR 41541372.
Further reading
- Christ, Karl (2004). Pompeius. Der Feldherr Roms. Eine Biographie . Munich: C. H. Beck, ISBN 3-406-51543-6.
- Dingmann, Matthias (2007). Pompeius Magnus. Machtgrundlagen eines spätrepublikanischen Politikers . Rahden: Leidorf, ISBN 978-3-89646-733-1.
- Hillman, T., P., The Reputation of Cn. Pompeius Magnus among His Contemporaries from 83 to 59 B.C., Diss. New York 1989.
- Nicols, Marianne Schoenlin. Appearance and Reality. A Study of the Clientele of Pompey the Great, Diss. Berkeley/Cal. 1992.
- Southern, P., Pompey the Great: Caesar's Friend and Foe, The History Press, 2003; ISBN 978-0752425214
- Stockton, D., The First Consulship of Pompey, Historia 22 (1973), 205–18.
- Van Ooteghem, J., Pompée le Grand. Bâtisseur d’Empire. Brussels 1954.
- Wylie, G., J., Pompey Megalopsychos, Klio 72 (1990), 445–456.
| Political offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded byP. Cornelius Lentulus Sura Cn. Aufidius Orestes |
Roman consul 70 BC With: M. Licinius Crassus |
Succeeded byQ. Hortensius Hortalus Q. Caecilius Metellus Creticus |
| Preceded byCn. Cornelius Lentulus Marcellinus L. Marcius Philippus |
Roman consul II 55 BC With: M. Licinius Crassus II |
Succeeded byL. Domitius Ahenobarbus Ap. Claudius Pulcher |
| Preceded byCn. Domitius Calvinus M. Valerius Messalla Rufus |
Roman consul III Intercalary Month, 52 BC without colleague |
Succeeded byHimself Metellus Scipio |
| Preceded byHimself | Roman consul 52 BC With: Metellus Scipio |
Succeeded bySer. Sulpicius Rufus M. Claudius Marcellus |
| Pompey | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Military career |
| ||||||||||
| Legislative activity | |||||||||||
| Buildings | |||||||||||
| Cities | |||||||||||
| Family |
| ||||||||||
| Legacy | |||||||||||
| Works of Plutarch | |
|---|---|
| Works | |
| Lives |
|
| Translators and editors | |
| |
- Pompey
- 106 BC births
- 48 BC deaths
- 1st-century BC Roman augurs
- 1st-century BC Roman consuls
- 1st-century BC Roman generals
- People involved in anti-piracy efforts
- Assassinated ancient Roman politicians
- Correspondents of Cicero
- Deaths by stabbing in Egypt
- First Triumvirate
- Julius Caesar
- People from le Marche
- People murdered in Egypt
- Pompeii (Romans)
- Roman governors of Hispania
- Supporters of Sulla
- People of Sulla's civil war
- People of the Sertorian War
- Ancient Roman triumphators
- People of the Mithridatic Wars
