| Revision as of 15:12, 18 March 2015 editDoorknob747 (talk | contribs)1,222 edits added something.← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 17:18, 8 June 2024 edit undoGreenC bot (talk | contribs)Bots2,547,809 edits Move 2 urls. Wayback Medic 2.5 per WP:URLREQ#google.com/patents | ||
| (105 intermediate revisions by 27 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ]]] | |||
| This type of electric motor instead of using magnetism for it to revolve, it uses it to turn its cam up and down. It does this by a coil on the bottom of the motor and another on the top, both inside. The cam is usually magnetic. If the cam is magnetic north in the inside end of the motor usually for the cam to go inside the motor casing, the top coil is magnetized as south and the bottom is north. To go down the top becomes north and bottom becomes south. Although this is a good efficient way for an electric reciprocating engine, it usually requires a lot of power, and emits a lot of heat. Usually the life time of this type of engine is small. | |||
| A '''reciprocating electric motor''' is a motor in which the armature moves back and forth rather than circularly. Early ]s were sometimes of the reciprocating type, such as those made by ] in the 1840s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sparkmuseum.com/MOTORS.HTM|title=Motors|work=sparkmuseum.com|accessdate=30 March 2015}}</ref> Today, reciprocating electric motors are rare but they do have some ], e.g. in ]s for ]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.eng.ox.ac.uk/cryogenics/publications/abstracts/Preprint_ValvedComp.pdf/view|title=Preprint valved linear compressor|work=ox.ac.uk|accessdate=30 March 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.hymatic.co.uk/stirling.cryocooler.tp1.htm|title=ABSTRACT|work=hymatic.co.uk|accessdate=30 March 2015}}</ref> and as educational toys.<ref name="wondermagnet">. ''wondermagnet.com''. Retrieved on 31 March 2015.</ref> | |||
| <-----do not delete this page, delete if I do not place sources within a week, I am not home right now. -----> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| Daniel Davis<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.princetonmahistory.org/people-groups/residents/daniel-davis|title=Daniel Davis – PHS|work=princetonmahistory.org|accessdate=31 March 2015}}</ref> was an early maker of reciprocating electric motors.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://physics.kenyon.edu/EarlyApparatus/Daniel_Davis_Apparatus/Reciprocating_Armature_Engine/Reciprocating_Armature_Engine.html|title=Reciprocating Armature Engine|work=kenyon.edu |accessdate=31 March 2015}}</ref> | |||
| As can be seen in these examples, early motors of this type often followed the general layout of the ]s of the day, | |||
| simply replacing the piston-and-cylinder with an electromagnetic solenoid. | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| File:Motor Page.jpg|Page's reciprocating electric engine 1844 | |||
| File:Motor Grüel.jpg|Grüel elektromotor, 1873 | |||
| File:Motor Page LehrbuchPhysik S516.jpg|Bourbouce's electric engine, 1881 | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==Design== | |||
| {{more citations needed section|date=March 2015}} | |||
| <div style="float:right"> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| </div> | |||
| A reciprocating electric motor uses an alternating ] to move its ] back and forth, rather than circularly as in a conventional ]. A single ] may be placed at one end of the armature's possible movement, or a field coil may be used at each end. | |||
| The armature may be a ], in which case the coil or coils can exert both repulsive and attractive force on the armature. If there are two coils, they will be wound and connected so that their like poles face each other, so that when (for example) the poles facing the armature are both negative, one pole will attract the armature's south pole while the other will repel its north pole. When the armature reaches the extreme of its movement, polarity to the coils is reversed. | |||
| The armature may instead be made of ] material, as in an electromagnetic ]. In this case the current in the coils will alternate between on and off, rather than between polarities. A single-coil motor with a non-magnetic armature would require a ] or some other "return" mechanism to move the armature away from the coil upon completion of the "attract" cycle. An "interrupter"-style ] operates on this same principle. A dual-coil motor would alternately energize the two coils. Where the motor is adapted to produce rotary motion, the return mechanism consists of a ] and ]. | |||
| This is an extremely simple motor, such that demonstration models may be easily constructed for teaching purposes.<ref name="wondermagnet"/> As a practical motor it has several disadvantages. Magnetic field strength drops off rapidly with increasing distance. In the reciprocating electric motor the distance between armature and field coil must necessarily increase considerably over its minimum value; this reduces the motor's output power and starting force. Vibration is also an issue. | |||
| ==Applications== | |||
| ===Linear compressors=== | |||
| A design for a linear compressor of this type has been produced by the Cryogenic Engineering Group at the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.eng.ox.ac.uk/cryogenics/publications/abstracts/Preprint_ValvedComp.pdf/view|title=Preprint valved linear compressor|work=ox.ac.uk|accessdate=31 March 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.hymatic.co.uk/stirling.cryocooler.tp1.htm|title=ABSTRACT|work=hymatic.co.uk|accessdate=31 March 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ===Pumps=== | |||
| See ] | |||
| ===Electric shavers=== | |||
| Some ]s use reciprocating motors.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/education/clips/zvnw2hv|title=BBC Bitesize – GCSE Product Design – How does an electric shaver work?|work=bbc.co.uk|accessdate=30 March 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ===Toys=== | |||
| Educational toys can be built as ] projects.<ref name="wondermagnet"/> Some of them have even been patented (for e.g. one in 1929,<ref></ref> another in 1963<ref></ref>). | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| File:US1721447-Figure1.png|Figure 1 of Patent US1721447 - Reciprocating electric motor that simulates a steam engine | |||
| File:US3105162-Figure1.png|Figure 1 of Patent US3105162 | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{commons category|Reciprocating electric motor}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{reflist|30em}} | |||
| {{Piston engine configurations |expanded}} | {{Piston engine configurations |expanded}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:18, 8 June 2024

A reciprocating electric motor is a motor in which the armature moves back and forth rather than circularly. Early electric motors were sometimes of the reciprocating type, such as those made by Daniel Davis in the 1840s. Today, reciprocating electric motors are rare but they do have some niche applications, e.g. in linear compressors for cryogenics and as educational toys.
History
Daniel Davis was an early maker of reciprocating electric motors.
As can be seen in these examples, early motors of this type often followed the general layout of the steam engines of the day, simply replacing the piston-and-cylinder with an electromagnetic solenoid.
-
 Page's reciprocating electric engine 1844
Page's reciprocating electric engine 1844
-
 Grüel elektromotor, 1873
Grüel elektromotor, 1873
-
 Bourbouce's electric engine, 1881
Bourbouce's electric engine, 1881
Design
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (March 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |


A reciprocating electric motor uses an alternating magnetic field to move its armature back and forth, rather than circularly as in a conventional electric motor. A single field coil may be placed at one end of the armature's possible movement, or a field coil may be used at each end.
The armature may be a permanent magnet, in which case the coil or coils can exert both repulsive and attractive force on the armature. If there are two coils, they will be wound and connected so that their like poles face each other, so that when (for example) the poles facing the armature are both negative, one pole will attract the armature's south pole while the other will repel its north pole. When the armature reaches the extreme of its movement, polarity to the coils is reversed.
The armature may instead be made of ferromagnetic material, as in an electromagnetic solenoid. In this case the current in the coils will alternate between on and off, rather than between polarities. A single-coil motor with a non-magnetic armature would require a spring or some other "return" mechanism to move the armature away from the coil upon completion of the "attract" cycle. An "interrupter"-style electromechanical buzzer operates on this same principle. A dual-coil motor would alternately energize the two coils. Where the motor is adapted to produce rotary motion, the return mechanism consists of a crankshaft and flywheel.
This is an extremely simple motor, such that demonstration models may be easily constructed for teaching purposes. As a practical motor it has several disadvantages. Magnetic field strength drops off rapidly with increasing distance. In the reciprocating electric motor the distance between armature and field coil must necessarily increase considerably over its minimum value; this reduces the motor's output power and starting force. Vibration is also an issue.
Applications
Linear compressors
A design for a linear compressor of this type has been produced by the Cryogenic Engineering Group at the University of Oxford.
Pumps
See Plunger pump
Electric shavers
Some electric shavers use reciprocating motors.
Toys
Educational toys can be built as DIY projects. Some of them have even been patented (for e.g. one in 1929, another in 1963).
-
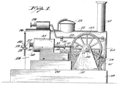 Figure 1 of Patent US1721447 - Reciprocating electric motor that simulates a steam engine
Figure 1 of Patent US1721447 - Reciprocating electric motor that simulates a steam engine
-
 Figure 1 of Patent US3105162
Figure 1 of Patent US3105162
See also
References
- "Motors". sparkmuseum.com. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- "Preprint valved linear compressor". ox.ac.uk. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- "ABSTRACT". hymatic.co.uk. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- ^ "WONDERMAGNET.COM – NdFeB Magnets, Magnet Wire, Books, Weird Science, Needful Things". wondermagnet.com. Retrieved on 31 March 2015.
- "Daniel Davis – PHS". princetonmahistory.org. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- "Reciprocating Armature Engine". kenyon.edu. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- "Preprint valved linear compressor". ox.ac.uk. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- "ABSTRACT". hymatic.co.uk. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- "BBC Bitesize – GCSE Product Design – How does an electric shaver work?". bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- Patent US1721447
- Patent US3105162
| Engine configurations for piston engines | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | |||||||||||
| Stroke cycles | |||||||||||
| Cylinder layouts |
| ||||||||||