| Revision as of 04:04, 17 August 2006 view sourceKober (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers46,985 editsm →See also← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 15:45, 8 November 2024 view source Monkbot (talk | contribs)Bots3,695,952 editsm Task 20: replace {lang-??} templates with {langx|??} ‹See Tfd› (Replaced 3; ignored 3: Lang-ka);Tag: AWB | ||
| (420 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Ethnographic group of Georgians}} | |||
| The '''Mingrelians''' (Megrelians) are an ethnographic group of ] that mostly live in ] region of ]. They speak both, the ] and ] language, but have only a ]. | |||
| {{pp-semi-protected|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Infobox ethnic group | |||
| | group = Mingrelians<br />{{langx|xmf|მარგალეფი}}<br />{{lang-ka|მეგრელები}} | |||
| | image = Kartvelian languages.svg | |||
| | image_caption = Distribution of Mingrelian in relation to the other Kartvelian languages | |||
| | population = {{circa|400,000}} | |||
| | popplace = Georgia 400,000{{efn|Including ], where ] live.}} | |||
| | languages = ], ] | |||
| | religions = Predominantly ] (]) | |||
| }} | |||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | {{Georgians}} | ||
| The '''Mingrelians'''{{efn|Also called ''Megrelians'', ''Mingrels'' or ''Megrels''}} ({{langx|xmf|მარგალეფი|margalepi}}; {{lang-ka|მეგრელები|tr}}) are an indigenous ]-speaking ] of ]<ref>Stuart J. Kaufman ::Modern Hatreds: The Symbolic Politics of Ethnic War''], p 86: "Additionally, the Georgian category includes an array of politically important subgroups especially Mingrelians, Svans and Ajarians" | |||
| </ref><ref>] . ].</ref><ref>Tunç Aybak , p 185: "... Georgians (Megrels) ..."</ref><ref>, p 116: "Georgia consists of three ethnics tribes: Imeretians, Kartvels, and Mingrelians."</ref><ref>''Small Nations and Great Powers: A Study of Ethnopolitical Conflict'', by Svante E. Cornell, p 142</ref><ref>''Political Construction Sites: Nation-building in Russia and the Post-Soviet World'', by Pål Kolstø, p. 8</ref> that mostly live in the ] ({{langx|xmf|სამარგალო|samargalo}}; {{lang-ka|სამეგრელო|tr}}) region of ]. They also live in considerable numbers in ] and ]. In the pre-1930 Soviet census, the Mingrelians were afforded their own ] category, alongside many other ethnic subgroups of Georgians.<ref>R. Wixman. (p.134)</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.demoscope.ru/weekly/ssp/ussr_nac_26.php?reg=5|title=Демоскоп Weekly - Приложение. Справочник статистических показателей.|website=www.demoscope.ru}}</ref> | |||
| The Mingrelians speak the ], and are typically bilingual also in ]. Both these languages belong to the ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.sorosoro.org/en/south-caucasian-language-family/|title=South Caucasian Languages « Sorosoro}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://id.loc.gov/vocabulary/iso639-5/ccs.html|title=LC Linked Data Service: Authorities and Vocabularies (Library of Congress)|first=The Library of|last=Congress|website=id.loc.gov}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=http://languageserver.uni-graz.at/ls/group?id=1059 |title=SOUTH CAUCASIAN - LanguageServer - University of Graz |access-date=2011-03-18 |archive-date=2016-03-04 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304191020/http://languageserver.uni-graz.at/ls/group?id=1059 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | ==History== | ||
| ⚫ | == History == | ||
| Until the ]s Mingrelians and ] had their own census grouping, but were classified under the broader category of Georgian thereafter. | |||
| In the 13th century ], the Kingdom of ] was formed as a result of the increasing consolidation of the tribes inhabiting the region, which covered modern western Georgia. The endonym ''margalepi'' (მარგალეფი) is presumably reflected in the Greek ''Manraloi'' (Μάνραλοι), recorded as a people of Colchis by ] in the 2nd century BC. | |||
| By the mid-3rd century, the Lazi tribe came to dominate most of Colchis, establishing the kingdom of Lazica (or ] in Georgian sources). In the 5th century, the first Christian king ] declared ] as a ] of Lazica. Locals began to have closer contact with the Greeks and acquired various ] cultural traits, including in some cases the language. From 542 to 562, Lazica was a scene of the protracted rivalry between the ] and ] empires, culminating in the ]. Emperor ]'s offensive in 628 AD brought victory over the Persians and ensured Roman predominance in Lazica until the invasion and conquest of the Caucasus by the ] in the second half of the 7th century. | |||
| ⚫ | The first President of an independent Georgia, |
||
| In the 7th century Lazica fell to the ]; however, in the 8th century combined Lazic and ] forces successfully repelled the Arab occupation. In 780 Lazica was incorporated into the ] as a result of dynastic succession, the latter led the ] in the 11th century. The nobility and clergy of Lazica switched from the Hellenic ecclesiastic tradition to the Georgian, and Georgian became the language of culture and education. After the fragmentation of the Kingdom of Georgia in the 15th century, Mingrelia was an autonomous principality within the ], until being annexed by the ] in the 19th century. | |||
| ⚫ | ==Notable Mingrelians == | ||
| *], one of the most influential ] writers of the 20th century | |||
| *], first president of post-Soviet Georgia | |||
| *Stalin's chief of secret police, ] | |||
| In several censuses under the Russian Empire and the early ], Mingrelian were considered a separate group, largely because at the time of the annexation Mingrelia was politically separate from eastern Georgia, the historical political and cultural centers of the Medieval Georgian Kingdoms. They were reclassified under the broader category of Georgian in the 1930s. Currently, most Mingrelian identify themselves as a subgroup of the Georgian nation and have preserved many characteristic cultural features – including the Mingrelian language – that date back to the pre-Christian ] era. | |||
| ⚫ | ==See also== | ||
| *] | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ], the Chief of ]'s secret police, was a Mingrelian. (As is well known, Stalin himself was a Georgian.) | |||
| {{ethno-group-stub}} | |||
| ⚫ | The first President of an independent Georgia, ] (1939–1993), was a Mingrelian and also a creator of ].<ref name="McCauley, Martin 1900. pg. 1">McCauley, Martin. ''Who's who in Russia since 1900''. Psychology Press, 1997: p. 1</ref> Therefore, after the violent coup d'état of December 21, 1991 – January 6, 1992, Mingrelia became the centre of a ], which ended with the defeat of Gamsakhurdia's supporters. | ||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| Approximately 180,000–200,000 Mingrelian and other subgroups of ] have been expelled from Abkhazia as a result of the ] in the early 1990s and the ensuing ] in this separatist region. | |||
| ⚫ | == Notable Mingrelians == | ||
| * ] (1893–1975), one of the most influential Georgian writers of the 20th century<ref>Rayfield, Donald. ''Stalin and His Hangmen: The Tyrant and Those Who Killed for Him''. Random House Digital, Inc., 2005: p. 354</ref> | |||
| * ] (1939–1993), the first ]<ref name="McCauley, Martin 1900. pg. 1"/> (in office: 1991–1992) | |||
| * ] (1899–1953), Soviet chief of secret police in the later ] era<ref name="McCauley, Martin 1900. pg. 1"/> | |||
| * ] (1939–1989), Georgian ], ], ], ]<ref>Hoiris, Ole. Yurukel, Sefa. ''Contrasts and solutions in the Caucasus''. Aarhus University Press, 1998: p. 187</ref> | |||
| * ] (1861–1927) ] | |||
| * ] (1868-1956), Georgian ethnographer, lexicologist, folklore scientist, translator, opinion journalist and educator | |||
| * ] (1868-1956), Georgian entrepreneur, socialite, and philanthropist | |||
| *] ({{circa|1825}} – 1889), Ottoman ] in 1876 | |||
| *] (1947–1993) ] | |||
| *] (1944–1993) National Hero of Georgia | |||
| *] (1936–1993) National Hero of Georgia | |||
| *] – Georgian army corporal, National Hero of Georgia | |||
| *] (1945–1993) was awarded Vakhtang Gorgasali First grade order for his courage and heroism in the fight for the protection of the homeland and its territorial integrity | |||
| *] (1920-1993) was a Georgian sergeant of the ] credited with having ] ] over the ] | |||
| *] (1907-1988) was a Georgian artist | |||
| *Dutu Megreli (1867-1938) - Georgian writer, poet and public figure, a member of the society for spreading literacy among Georgians | |||
| *Nikoloz Dadiani (1878-1939) - Georgian poet, writer and publicist. | |||
| *] (born 1997), a professional mixed martial artist | |||
| *] (born 2001), a football player | |||
| *] (born 1991), a basketball player | |||
| *] (born 1984), a basketball player | |||
| *] (1943-1993) National hero of Georgia | |||
| ⚫ | == See also == | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| == Bibliography == | |||
| * ]. . ''World Culture Encyclopedia''. | |||
| {{Commons category|Mingrelians}} | |||
| ⚫ | {{Ethnographic groups of ethnic Georgians}} | ||
| {{Peoples of the Caucasus}} | |||
| {{Ethnic groups in Georgia}} | |||
| {{Eastern Christianity footer}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:45, 8 November 2024
Ethnographic group of GeorgiansEthnic group
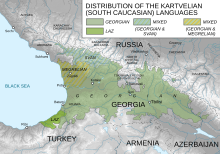 Distribution of Mingrelian in relation to the other Kartvelian languages Distribution of Mingrelian in relation to the other Kartvelian languages | |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| c. 400,000 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Georgia 400,000 | |
| Languages | |
| Mingrelian, Georgian | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Eastern Orthodox Christianity (Georgian Orthodox Church) |

| Part of a series on |
| Georgians ქართველები |
|---|
 The The Kartvelian people |
| Nation |
| Georgia |
| Ancient Kartvelian people |
| Subgroups |
| Culture |
| Languages |
| Religion |
| Symbols |
| History of Georgia |
The Mingrelians (Mingrelian: მარგალეფი, romanized: margalepi; Georgian: მეგრელები, romanized: megrelebi) are an indigenous Kartvelian-speaking ethnic subgroup of Georgians that mostly live in the Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti (Mingrelian: სამარგალო, romanized: samargalo; Georgian: სამეგრელო, romanized: samegrelo) region of Georgia. They also live in considerable numbers in Abkhazia and Tbilisi. In the pre-1930 Soviet census, the Mingrelians were afforded their own ethnic group category, alongside many other ethnic subgroups of Georgians.
The Mingrelians speak the Mingrelian language, and are typically bilingual also in Georgian. Both these languages belong to the Kartvelian language family.
History
In the 13th century BC, the Kingdom of Colchis was formed as a result of the increasing consolidation of the tribes inhabiting the region, which covered modern western Georgia. The endonym margalepi (მარგალეფი) is presumably reflected in the Greek Manraloi (Μάνραλοι), recorded as a people of Colchis by Ptolemy in the 2nd century BC.
By the mid-3rd century, the Lazi tribe came to dominate most of Colchis, establishing the kingdom of Lazica (or Egrisi in Georgian sources). In the 5th century, the first Christian king Gubazes I declared Christianity as a state religion of Lazica. Locals began to have closer contact with the Greeks and acquired various Hellenic cultural traits, including in some cases the language. From 542 to 562, Lazica was a scene of the protracted rivalry between the Eastern Roman and Sassanid empires, culminating in the Lazic War. Emperor Heraclius's offensive in 628 AD brought victory over the Persians and ensured Roman predominance in Lazica until the invasion and conquest of the Caucasus by the Arabs in the second half of the 7th century.
In the 7th century Lazica fell to the Muslim conquest; however, in the 8th century combined Lazic and Abasgian forces successfully repelled the Arab occupation. In 780 Lazica was incorporated into the Kingdom of Abkhazia as a result of dynastic succession, the latter led the unification of the Georgian monarchy in the 11th century. The nobility and clergy of Lazica switched from the Hellenic ecclesiastic tradition to the Georgian, and Georgian became the language of culture and education. After the fragmentation of the Kingdom of Georgia in the 15th century, Mingrelia was an autonomous principality within the Kingdom of Imereti, until being annexed by the Russian Empire in the 19th century.
In several censuses under the Russian Empire and the early Soviet Union, Mingrelian were considered a separate group, largely because at the time of the annexation Mingrelia was politically separate from eastern Georgia, the historical political and cultural centers of the Medieval Georgian Kingdoms. They were reclassified under the broader category of Georgian in the 1930s. Currently, most Mingrelian identify themselves as a subgroup of the Georgian nation and have preserved many characteristic cultural features – including the Mingrelian language – that date back to the pre-Christian Colchian era.
Lavrentiy Beria, the Chief of Stalin's secret police, was a Mingrelian. (As is well known, Stalin himself was a Georgian.)
The first President of an independent Georgia, Zviad Gamsakhurdia (1939–1993), was a Mingrelian and also a creator of Georgian nationalism. Therefore, after the violent coup d'état of December 21, 1991 – January 6, 1992, Mingrelia became the centre of a civil war, which ended with the defeat of Gamsakhurdia's supporters.
Approximately 180,000–200,000 Mingrelian and other subgroups of Georgian people have been expelled from Abkhazia as a result of the Abkhaz–Georgian conflict in the early 1990s and the ensuing ethnic cleansing of Georgians in this separatist region.
Notable Mingrelians
- Konstantine Gamsakhurdia (1893–1975), one of the most influential Georgian writers of the 20th century
- Zviad Gamsakhurdia (1939–1993), the first President of Georgia (in office: 1991–1992)
- Lavrentiy Beria (1899–1953), Soviet chief of secret police in the later Stalin era
- Merab Kostava (1939–1989), Georgian dissident, poet, musician, National Hero of Georgia
- Ambrosi Khelaia (1861–1927) Catholicos-Patriarch of all Georgia
- Tedo Sakhokia (1868-1956), Georgian ethnographer, lexicologist, folklore scientist, translator, opinion journalist and educator
- Akaki Khoshtaria (1868-1956), Georgian entrepreneur, socialite, and philanthropist
- Şevkefza Sultan (c. 1825 – 1889), Ottoman Valide sultan in 1876
- Guram Gabiskiria (1947–1993) National Hero of Georgia
- Zhiuli Shartava (1944–1993) National Hero of Georgia
- Geno Adamia (1936–1993) National Hero of Georgia
- Zaza Damenia – Georgian army corporal, National Hero of Georgia
- Alexander Berulava (1945–1993) was awarded Vakhtang Gorgasali First grade order for his courage and heroism in the fight for the protection of the homeland and its territorial integrity
- Meliton Kantaria (1920-1993) was a Georgian sergeant of the Soviet Army credited with having hoisted a Soviet flag over the Reichstag
- Vera Pagava (1907-1988) was a Georgian artist
- Dutu Megreli (1867-1938) - Georgian writer, poet and public figure, a member of the society for spreading literacy among Georgians
- Nikoloz Dadiani (1878-1939) - Georgian poet, writer and publicist.
- Ilia Topuria (born 1997), a professional mixed martial artist
- Khvicha Kvaratskhelia (born 2001), a football player
- Tornike Shengelia (born 1991), a basketball player
- Zaza Pachulia (born 1984), a basketball player
- Mamia Alasania (1943-1993) National hero of Georgia
See also
Notes
- Including Abkhazia, where 46,000 Mingrelians and Georgians live.
- Also called Megrelians, Mingrels or Megrels
References
- Stuart J. Kaufman Modern Hatreds: The Symbolic Politics of Ethnic War ::Modern Hatreds: The Symbolic Politics of Ethnic War], p 86: "Additionally, the Georgian category includes an array of politically important subgroups especially Mingrelians, Svans and Ajarians"
- Kevin Tuite "The Meaning of Dæl. Symbolic and Spatial Associations of the South Caucasian Goddess of Game Animals". Université de Montréal.
- Tunç Aybak Politics of the Black Sea: Dynamics of Cooperation and Conflict, p 185: "... Georgians (Megrels) ..."
- Andropov, New Challenge to the West, by Arnold Beichman, Mikhail S. Bernstam, p 116: "Georgia consists of three ethnics tribes: Imeretians, Kartvels, and Mingrelians."
- Small Nations and Great Powers: A Study of Ethnopolitical Conflict, by Svante E. Cornell, p 142
- Political Construction Sites: Nation-building in Russia and the Post-Soviet World, by Pål Kolstø, p. 8
- R. Wixman. The Peoples of the USSR: An Ethnographic Handbook (p.134)
- "Демоскоп Weekly - Приложение. Справочник статистических показателей". www.demoscope.ru.
- "South Caucasian Languages « Sorosoro".
- Congress, The Library of. "LC Linked Data Service: Authorities and Vocabularies (Library of Congress)". id.loc.gov.
- "SOUTH CAUCASIAN - LanguageServer - University of Graz". Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2011-03-18.
- ^ McCauley, Martin. Who's who in Russia since 1900. Psychology Press, 1997: p. 1
- Rayfield, Donald. Stalin and His Hangmen: The Tyrant and Those Who Killed for Him. Random House Digital, Inc., 2005: p. 354
- Hoiris, Ole. Yurukel, Sefa. Contrasts and solutions in the Caucasus. Aarhus University Press, 1998: p. 187
Bibliography
- Stephen F. Jones. Mingrelians. World Culture Encyclopedia.
| Ethnic Georgians | |
|---|---|
| See Also: Ethnic groups in the Caucasus | |
| Ethnic groups in the Caucasus | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caucasian (areal) |
|  | ||||||||||||||||
| Indo- European |
| |||||||||||||||||
| Turkic |
| |||||||||||||||||
| Others | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ethnic groups in Georgia | |
|---|---|
| Kartvelians | |
| Ethnic minorities | |
| Ethnic minorities in Georgia | |
| Eastern Christianity | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural area of Christian traditions that developed since Early Christianity in the Middle East, Eastern Europe, North and East Africa, Asia Minor, South India, and parts of the Far East. | ||||||||
| Main divisions |
| Christ Pantocrator (circa 1261) in Hagia Sophia | ||||||
| History |
| |||||||
| Scriptures | ||||||||
| Theology | ||||||||
| Worship | ||||||||