| Revision as of 04:25, 8 May 2018 view sourceBearcat (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators1,566,301 editsm recat using AWB← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:36, 13 December 2023 view source Cortador (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users3,340 edits →Reception: There's nothing particularly "mainstream" about the critics.Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit | ||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|2010 book by Andrew Montford}} | |||
| {{pp-semi-indef}} | {{pp-semi-indef}} | ||
| {{Infobox book | {{Infobox book | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''''The Hockey Stick Illusion: Climategate and the Corruption of Science''''' is a book written by ] and published by ] in 2010 |
'''''The Hockey Stick Illusion: Climategate and the Corruption of Science''''' is a book written by ] and published by ] in 2010, which promotes ].<ref name="Hewitt" /><ref name="Joyner" /> | ||
| Montford, an ] and science ] who publishes a ] called 'Bishop Hill',<ref name="Ridley_2010-02-03_Spectator" /><ref>{{cite web|title=House of Commons Science and Technology Committee - Memorandum submitted by Andrew Montford (CRU 36) - The disclosure of climate data from the Climatic Research Unit at the University of East Anglia, Session 2009-2010 - Science and Technology Committee|website=UK Parliament|url=https://publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm200910/cmselect/cmsctech/387b/387we38.htm|access-date=23 May 2020}}</ref> writes about the "]" of global temperatures for the last 1000 years. The book has been criticized for its inaccuracies. | |||
| The book was ]'s second bestselling environment book of 2010.<ref> | |||
| ⚫ | {{cite |
||
| | url = https://www.theguardian.com/environment/damian-carrington-blog/2010/dec/17/bestselling-green-books-decade-2 | |||
| | date = 17 December 2010 | |||
| | title = Bestselling green books of the decade | |||
| | author = Damian Carrington | |||
| | work = ] | |||
| | accessdate = 12 July 2011 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| ==Background== | ==Background== | ||
| Line 42: | Line 35: | ||
| ==Synopsis== | ==Synopsis== | ||
| ] Figure 7.1.c (red) based on Lamb 1965 showing central England temperatures; central England temperatures to 2007 shown from Jones et al. 2009 (green dashed line).<ref name="Jones 09">P. D. Jones et al., The Holocene 19,1 (2009) pp. 3–49, High-resolution palaeoclimatology of the last millennium: a review of current status and future prospects Appendix A</ref> The high medieval temperatures contrast with the "hockey stick" MBH99 40 year average (blue, uncertainties omitted) and Moberg et al. 2005 low frequency signal (black).]] | ] Figure 7.1.c (red) based on Lamb 1965 showing central England temperatures; central England temperatures to 2007 shown from Jones et al. 2009 (green dashed line).<ref name="Jones 09">P. D. Jones et al., The Holocene 19,1 (2009) pp. 3–49, High-resolution palaeoclimatology of the last millennium: a review of current status and future prospects Appendix A</ref> The high medieval temperatures contrast with the "hockey stick" MBH99 40 year average (blue, uncertainties omitted) and Moberg et al. 2005 low frequency signal (black).]] | ||
| ]4 data from 1850 to 2013.]] | ]4 data from 1850 to 2013.]] | ||
| ''The Hockey Stick Illusion'' first outlines a brief ] with particular emphasis on the ] in 1990, with its inclusion of a schematic based on central England temperatures which Montford describes as a representation of common knowledge at that time. He then argues that a need to overturn this "well-embedded paradigm" was met by the 1998 publication by ], ] and ]' of their "]" in '']''.<ref name="Montford_2010_Stacey_p30" /> The book describes how ] first became interested in the graph in 2002 and the difficulties he found in replicating the results of "MBH98" (the original 1998 study) using available datasets, and further data which Mann gave him on request.<ref name="Montford_2010_Stacey_p57" /> It details the publication of a paper by McIntyre and ] in 2003 which criticized MBH98, and follows with Mann and his associates' rebuttals. The book recounts reactions to the dispute over the graph, including investigations by the ] and ] and hearings held on the graph before the ]. Efforts taken by other scientists to verify Mann's work and McIntyre's and others' responses to those efforts are described.<!-- Passive voice, could be rewritten --><ref name="Montford_2010_Stacey_p151-401" /> | ''The Hockey Stick Illusion'' first outlines a brief ] with particular emphasis on the ] in 1990, with its inclusion of a schematic based on central England temperatures which Montford describes as a representation of common knowledge at that time. He then argues that a need to overturn this "well-embedded paradigm" was met by the 1998 publication by ], ] and ]' of their "]" in '']''.<ref name="Montford_2010_Stacey_p30" /> The book describes how ] first became interested in the graph in 2002 and the difficulties he found in replicating the results of "MBH98" (the original 1998 study) using available datasets, and further data which Mann gave him on request.<ref name="Montford_2010_Stacey_p57" /> It details the publication of a paper by McIntyre and ] in 2003 which criticized MBH98, and follows with Mann and his associates' rebuttals. The book recounts reactions to the dispute over the graph, including investigations by the ] and ] and hearings held on the graph before the ]. Efforts taken by other scientists to verify Mann's work and McIntyre's and others' responses to those efforts are described.<!-- Passive voice, could be rewritten --><ref name="Montford_2010_Stacey_p151-401" /> | ||
| The last chapter of the book deals with what the book calls ]. Here, the author compares several e-mails to the evidence he presents in ''The Hockey Stick Illusion.'' Montford focuses on those e-mails dealing with the ] process and how these pertained to Stephen McIntyre's efforts to obtain the data and methodology from Mann's and other ]' published works.<ref name="Montford_2010_Stacey_p402-449" /> | The last chapter of the book deals with what the book calls ]. Here, the author compares several e-mails to the evidence he presents in ''The Hockey Stick Illusion.'' Montford focuses on those e-mails dealing with the ] process and how these pertained to Stephen McIntyre's efforts to obtain the data and methodology from Mann's and other ]' published works.<ref name="Montford_2010_Stacey_p402-449" /> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 43: | ||
| ==Reception== | ==Reception== | ||
| Montford had set out to provide a more detailed explanation than the primers ] had written describing the case he and McIntyre had produced against the MBH climate reconstructions,{{sfn|Montford|2010|p=13}} and when McKitrick contributed to a 2014 compilation published by the ] think-tank, he opened with a sentence saying the "best place to start when learning about the hockey stick is Andrew Montford's superb book".<ref></ref><ref name="IPA">{{cite book|author1=John Roskam|author2=Alan J. Moran|title=Climate Change: The Facts 2014|url=https://ipa.org.au/publications-ipa/books/climate-change-facts-2014|year=2014|publisher=Institute of Public Affairs|isbn=978-0-986398-30-8}}</ref> ] discussed it in '']'',<ref name="Ridley_2010-02-03_Spectator" /> and in '']'' magazine said the book was "written with grace and flair" and deserved to win prizes, while conceding that he had financial interests in coal mining.<ref name="prospect"/> | |||
| Other reviewers criticized the book as providing cover for individuals opposing ]. ] in '']'' described how "Montford's entertaining conspiracy yarn" presented arguments based on "glaring inaccuracies".<ref name="Ward_2010-08-25_Guardian" /> In '']'', Ward said Montford's "incredible yarn is based on a misleading and one-sided version of events, littered with inaccuracies".<ref name="Ward GeoS">{{cite news|url=http://www.geolsoc.org.uk/gsl/site/GSL/lang/en/page8394.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101007062942/http://www.geolsoc.org.uk/gsl/site/GSL/lang/en/page8394.html|archive-date=2010-10-07|title=Not so jolly hockey stick|last=Ward|first=Bob|date=October 2010|work=]|access-date=8 April 2011}}</ref> Nick Hewitt in '']'' outlined the basic physics of climate change, and said that, unable to dispute this, ], "(or sceptics as they are disingenuously described in this book) have made sustained attempts to discredit climate scientists and the way they work", concluding that "Readers of ''Chemistry World'' will have far better things to do than read this pedantic book."<ref name="Hewitt">{{citation|last=Hewitt|first=Nick|url=http://www.rsc.org/chemistryworld/Issues/2010/September/Reviews/ClimateChangeScepticism.asp| title=The hockey stick illusion: climategate and the corruption of science|journal=Chemistry World|year=2010|volume=7|issue=9}}</ref> Richard Joyner, writing in '']'', described it as "a McCarthyite book that uses the full range of smear tactics to peddle climate change denial."<ref name="Joyner">{{cite web|last=Joyner|first=Richard|title=Mean-spirited scepticism|url=http://www.prospectmagazine.co.uk/2010/08/mean-spirited-scepticism-montford-hockey-stic/|date=2010-08-23}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 51: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 66: | Line 58: | ||
| <!-- order by Author_date_publisher--> | <!-- order by Author_date_publisher--> | ||
| <ref name="Curry_2010-09-25_judithcurry"> by ], September 25, 2010.</ref> | |||
| <ref name="Montford_2008_Bishophill">{{Harvnb|Montford|2008}}</ref> | <ref name="Montford_2008_Bishophill">{{Harvnb|Montford|2008}}</ref> | ||
| Line 85: | Line 74: | ||
| | date = 2010-03-10 | | date = 2010-03-10 | ||
| | title = The case against the hockey stick | | title = The case against the hockey stick | ||
| | author = |
| author = Matt Ridley | ||
| | author-link = Matt Ridley | |||
| | work = ] (]) | | work = ] (]) | ||
| | |
| access-date = 2010-04-03 | ||
| }}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| Line 93: | Line 83: | ||
| |url=http://www.spectator.co.uk/2010/02/the-global-warming-guerrillas/ | |url=http://www.spectator.co.uk/2010/02/the-global-warming-guerrillas/ | ||
| |title=The global warming guerrillas | |title=The global warming guerrillas | ||
| |author = |
|author = Matt Ridley | ||
| |author-link = Matt Ridley | |||
| |date=2010-02-03 | |date=2010-02-03 | ||
| |publisher=] (]) | |publisher=] (]) | ||
| | |
|access-date=2017-01-08 | ||
| }}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| Line 102: | Line 93: | ||
| | url = https://www.theguardian.com/environment/cif-green/2010/aug/19/climate-sceptics-mislead-public | | url = https://www.theguardian.com/environment/cif-green/2010/aug/19/climate-sceptics-mislead-public | ||
| | title = Did climate sceptics mislead the public over the significance of the hacked emails? | | title = Did climate sceptics mislead the public over the significance of the hacked emails? | ||
| | author = |
| author = Bob Ward | ||
| | author-link = Bob Ward (communications director) | |||
| | work = ] | | work = ] | ||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20100825121029/http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/cif-green/2010/aug/19/climate-sceptics-mislead-public | |||
| | archiveurl = https://www.webcitation.org/5sHNPBO1d | |||
| | |
| archive-date = 2010-08-25 | ||
| | |
| url-status = live | ||
| | access-date = 2010-08-19 | |||
| | quote = ''This article was amended on 20 August 2010 following a complaint from Andrew Montford to make it clear that we did not mean to imply that Andrew Montford deliberately published false information in order to support the arguments made in his book. We apologise if such a false impression was given. '' | | quote = ''This article was amended on 20 August 2010 following a complaint from Andrew Montford to make it clear that we did not mean to imply that Andrew Montford deliberately published false information in order to support the arguments made in his book. We apologise if such a false impression was given. '' | ||
| | location=London | | location=London | ||
| Line 117: | Line 110: | ||
| | url = https://www.theguardian.com/environment/cif-green/2010/aug/19/climate-sceptics-mislead-public | | url = https://www.theguardian.com/environment/cif-green/2010/aug/19/climate-sceptics-mislead-public | ||
| | title = Did climate sceptics mislead the public over the significance of the hacked emails? | | title = Did climate sceptics mislead the public over the significance of the hacked emails? | ||
| | author = |
| author = Bob Ward | ||
| | author-link = Bob Ward | |||
| | work = ] | | work = ] | ||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20100825121029/http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/cif-green/2010/aug/19/climate-sceptics-mislead-public | |||
| | archiveurl = https://www.webcitation.org/5sESwSkX3 | |||
| | |
| archive-date = 2010-08-25 | ||
| | |
| url-status = live | ||
| | access-date = 2010-08-19 | |||
| | quote = Montford's entertaining conspiracy yarn reaches two apparently devastating conclusions about the work of climate scientists, partly based on his analysis of the hacked email messages. | | quote = Montford's entertaining conspiracy yarn reaches two apparently devastating conclusions about the work of climate scientists, partly based on his analysis of the hacked email messages. | ||
| | location=London | | location=London | ||
| Line 133: | Line 128: | ||
| |date=2010-03-25 | |date=2010-03-25 | ||
| |work=Times Higher Education | |work=Times Higher Education | ||
| | |
|access-date=26 April 2010 | ||
| }}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| Line 147: | Line 142: | ||
| | date=2010-02-27 | | date=2010-02-27 | ||
| | title =A perfect storm is brewing for the IPCC | | title =A perfect storm is brewing for the IPCC | ||
| | author= |
| author=Christopher Booker | ||
| | author-link=Christopher Booker | |||
| | publisher=www.telegraph.co.uk | | publisher=www.telegraph.co.uk | ||
| | |
| access-date= 2010-04-03 | ||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20100523101234/http://www.telegraph.co.uk/comment/columnists/christopherbooker/7332803/A-perfect-storm-is-brewing-for-the-IPCC.html | |||
| | archiveurl = https://www.webcitation.org/5sHRm8vhl | |||
| | |
| archive-date = 2010-05-23 | ||
| | url-status=live | |||
| | location=London}}</ref> | | location=London}}</ref> | ||
| <ref name="Fisher_2010_JofEL">{{Cite journal | <ref name="Fisher_2010_JofEL">{{Cite journal | ||
| Line 160: | Line 157: | ||
| | coauthors= Pasky Pascual and Wendy Wagner | | coauthors= Pasky Pascual and Wendy Wagner | ||
| | title = Understanding Environmental Models in Their Legal and Regulatory Context | | title = Understanding Environmental Models in Their Legal and Regulatory Context | ||
| | journal = Journal of Environmental Law |
| journal = Journal of Environmental Law | ||
| | volume = 22 | | volume = 22 | ||
| | issue = 2 | | issue = 2 | ||
| Line 166: | Line 163: | ||
| | year = 2010 | | year = 2010 | ||
| | url = http://jel.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/22/2/251 | | url = http://jel.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/22/2/251 | ||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20100807174246/http://jel.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/22/2/251 | |||
| | archiveurl = https://www.webcitation.org/5rFIPyTmx | |||
| | |
| archive-date = 2010-08-07 | ||
| | url-status = live | |||
| | doi = 10.1093/jel/eqq012 | | doi = 10.1093/jel/eqq012 | ||
| | quote = 1.1 The Prevalence of Models in Environmental Regulation In the policy sphere many of these disputes have been in relation to policy-catalyst models. This is not surprising. As such models are establishing the premises for potential state action, it is obvious they will be controversial with different actors arguing for and against such action.36 Moreover, these disputes will also involve a range of public and private institutions as the models in question are derived from a range of sources.37 Notes 37 A W Montford, The Hockey Stick Illusion: Climategate and the Corruption of Science (Stacey International, London 2010). | | quote = 1.1 The Prevalence of Models in Environmental Regulation In the policy sphere many of these disputes have been in relation to policy-catalyst models. This is not surprising. As such models are establishing the premises for potential state action, it is obvious they will be controversial with different actors arguing for and against such action.36 Moreover, these disputes will also involve a range of public and private institutions as the models in question are derived from a range of sources.37 Notes 37 A W Montford, The Hockey Stick Illusion: Climategate and the Corruption of Science (Stacey International, London 2010). | ||
| Line 182: | Line 180: | ||
| | month = 05 | | month = 05 | ||
| | url = http://eprints.lse.ac.uk/27939/1/HartwellPaper_English_version.pdf | | url = http://eprints.lse.ac.uk/27939/1/HartwellPaper_English_version.pdf | ||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20100705000455/http://eprints.lse.ac.uk/27939/1/HartwellPaper_English_version.pdf | |||
| | archiveurl = https://www.webcitation.org/5rFHmwWwi | |||
| | |
| url-status = live | ||
| | archive-date = 2010-07-05 | |||
| }}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| --> | --> | ||
| Line 197: | Line 196: | ||
| | publisher=Continuum International Publishing Group Ltd | | publisher=Continuum International Publishing Group Ltd | ||
| | year=2009 | | year=2009 | ||
| | isbn=1-4411-1052- |
| isbn=978-1-4411-1052-7 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ⚫ | * {{cite web | ||
| * {{cite journal|last=Montford|first=Andrew|title=Caspar and the Jesus paper|journal=Bishop Hill|date=August 11, 2008|url=http://bishophill.squarespace.com/blog/2008/8/11/caspar-and-the-jesus-paper.html |ref=harv}}<!-- {{cite web | |||
| | ref=Montford2008 | |||
| | last = Montford | | last = Montford | ||
| | first = Andrew | | first = Andrew | ||
| Line 206: | Line 204: | ||
| | title=Caspar and the Jesus paper | | title=Caspar and the Jesus paper | ||
| | date=2008-08-11 | | date=2008-08-11 | ||
| | |
| access-date=2010-04-01 | ||
| }} | |||
| * {{cite book | * {{cite book | ||
| | ref=CITEREFMontford2010 | |||
| | last=Montford | | last=Montford | ||
| | first=Andrew | | first=Andrew | ||
| Line 215: | Line 213: | ||
| | publisher=Stacey International | | publisher=Stacey International | ||
| | pages=482 | | pages=482 | ||
| | isbn=1-906768-35- |
| isbn=978-1-906768-35-5 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| * {{cite journal |author=PAGES 2k Consortium| title=A global multiproxy database for temperature reconstructions of the Common Era - Scientific Data | journal=Scientific Data | date=11 July 2017 | volume=4 | issue=1 | page=170088 | doi=10.1038/sdata.2017.88 | pmid=28696409 | pmc=5505119}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| Line 222: | Line 221: | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Hockey Stick Illusion}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Hockey Stick Illusion}} | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:36, 13 December 2023
2010 book by Andrew Montford
 | |
| Author | A.W. Montford |
|---|---|
| Language | English |
| Subject | Climate change |
| Publisher | Stacey International |
| Publication date | 2010 |
| Publication place | United Kingdom |
| Pages | 482 |
| ISBN | 978-1-906768-35-5 |
The Hockey Stick Illusion: Climategate and the Corruption of Science is a book written by Andrew Montford and published by Stacey International in 2010, which promotes climate change denial.
Montford, an accountant and science publisher who publishes a blog called 'Bishop Hill', writes about the "hockey stick graph" of global temperatures for the last 1000 years. The book has been criticized for its inaccuracies.
Background
According to Montford, in 2005 he followed a link from a British political blog to the Climate Audit website. While perusing the site, Montford noticed that new readers often asked if there was an introduction to the site and the story of the hockey stick controversy. In 2008, after the story of Caspar Ammann's "purported" replication of the hockey stick became public, Montford wrote his own summary of the controversy.
Montford published the summary on his Bishop Hill blog and called it Caspar and the Jesus paper. Montford states that word of his article caused the traffic to his blog to surge from several hundred hits a day to 30,000 in just three days. Montford adds that there was also an attempt to use his article as a source in Misplaced Pages. After Montford saw the hockey stick graph used in a science book manuscript he was reviewing, he decided to expand his article into book form.
Synopsis
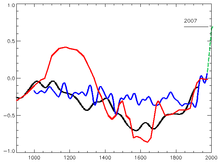
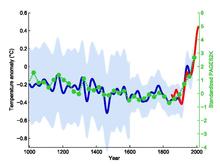
The Hockey Stick Illusion first outlines a brief history of climate change science with particular emphasis on the description of the Medieval Warm Period in the first IPCC report in 1990, with its inclusion of a schematic based on central England temperatures which Montford describes as a representation of common knowledge at that time. He then argues that a need to overturn this "well-embedded paradigm" was met by the 1998 publication by Michael E. Mann, Raymond S. Bradley and Malcolm K. Hughes' of their "hockey stick graph" in Nature. The book describes how Steve McIntyre first became interested in the graph in 2002 and the difficulties he found in replicating the results of "MBH98" (the original 1998 study) using available datasets, and further data which Mann gave him on request. It details the publication of a paper by McIntyre and Ross McKitrick in 2003 which criticized MBH98, and follows with Mann and his associates' rebuttals. The book recounts reactions to the dispute over the graph, including investigations by the National Academy of Sciences and Edward Wegman and hearings held on the graph before the United States House Energy Subcommittee on Oversight and Investigations. Efforts taken by other scientists to verify Mann's work and McIntyre's and others' responses to those efforts are described.
The last chapter of the book deals with what the book calls "Climategate". Here, the author compares several e-mails to the evidence he presents in The Hockey Stick Illusion. Montford focuses on those e-mails dealing with the peer review process and how these pertained to Stephen McIntyre's efforts to obtain the data and methodology from Mann's and other paleoclimatologists' published works.
Reception
Montford had set out to provide a more detailed explanation than the primers Ross McKitrick had written describing the case he and McIntyre had produced against the MBH climate reconstructions, and when McKitrick contributed to a 2014 compilation published by the Institute of Public Affairs think-tank, he opened with a sentence saying the "best place to start when learning about the hockey stick is Andrew Montford's superb book". Matt Ridley discussed it in The Spectator, and in Prospect magazine said the book was "written with grace and flair" and deserved to win prizes, while conceding that he had financial interests in coal mining.
Other reviewers criticized the book as providing cover for individuals opposing action on climate change. Bob Ward in The Guardian described how "Montford's entertaining conspiracy yarn" presented arguments based on "glaring inaccuracies". In Geoscientist, Ward said Montford's "incredible yarn is based on a misleading and one-sided version of events, littered with inaccuracies". Nick Hewitt in Chemistry World outlined the basic physics of climate change, and said that, unable to dispute this, climate deniers, "(or sceptics as they are disingenuously described in this book) have made sustained attempts to discredit climate scientists and the way they work", concluding that "Readers of Chemistry World will have far better things to do than read this pedantic book." Richard Joyner, writing in Prospect, described it as "a McCarthyite book that uses the full range of smear tactics to peddle climate change denial."
See also
- Climatic Research Unit email controversy
- Historical climatology
- Medieval warm period
- Global warming controversy
References
- ^ Hewitt, Nick (2010), "The hockey stick illusion: climategate and the corruption of science", Chemistry World, 7 (9)
- ^ Joyner, Richard (2010-08-23). "Mean-spirited scepticism".
- ^ Matt Ridley (2010-02-03). "The global warming guerrillas". The Spectator (spectator.co.uk). Retrieved 2017-01-08.
- "House of Commons Science and Technology Committee - Memorandum submitted by Andrew Montford (CRU 36) - The disclosure of climate data from the Climatic Research Unit at the University of East Anglia, Session 2009-2010 - Science and Technology Committee". UK Parliament. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ^ Montford 2010, p. 13
- Montford 2008
- P. D. Jones et al., The Holocene 19,1 (2009) pp. 3–49, High-resolution palaeoclimatology of the last millennium: a review of current status and future prospects Appendix A
- Montford 2010, pp. 19–30
- Montford 2010, pp. 57–87
- Montford 2010, pp. 151–401
- Montford 2010, pp. 402–49
- Montford 2010, p. 13.
- preprint from Climate Change: The Facts 2014, Institute for Policy Analysis, Australia.
- John Roskam; Alan J. Moran (2014). Climate Change: The Facts 2014. Institute of Public Affairs. ISBN 978-0-986398-30-8.
- Matt Ridley (2010-03-10). "The case against the hockey stick". Prospect (prospectmagazine.co.uk). Retrieved 2010-04-03.
- Bob Ward (2010-08-19). "Did climate sceptics mislead the public over the significance of the hacked emails?". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 2010-08-25. Retrieved 2010-08-19.
This article was amended on 20 August 2010 following a complaint from Andrew Montford to make it clear that we did not mean to imply that Andrew Montford deliberately published false information in order to support the arguments made in his book. We apologise if such a false impression was given.
- Ward, Bob (October 2010). "Not so jolly hockey stick". Geoscientist. Archived from the original on 2010-10-07. Retrieved 8 April 2011.
Bibliography and further reading
- Booker, Christopher (2009). The Real Global Warming Disaster. Continuum International Publishing Group Ltd. ISBN 978-1-4411-1052-7.
- Montford, Andrew (2008-08-11). "Caspar and the Jesus paper". Retrieved 2010-04-01.
- Montford, Andrew (2010). The Hockey Stick Illusion. Stacey International. p. 482. ISBN 978-1-906768-35-5.
- PAGES 2k Consortium (11 July 2017). "A global multiproxy database for temperature reconstructions of the Common Era - Scientific Data". Scientific Data. 4 (1): 170088. doi:10.1038/sdata.2017.88. PMC 5505119. PMID 28696409.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)