| Revision as of 16:55, 30 September 2018 editTravelmite (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,504 edits Revert anonymous user as per talk page explanation← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:25, 19 December 2024 edit undoRsk6400 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users15,264 edits Undid revision 1263734778 by AngelusVastator3456 (talk) - not relevantTag: Undo | ||
| (716 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Outdated grouping of human beings}} | |||
| '''Australoid''' is an outdated ] introduced by ] in 1870 to refer to certain peoples indigenous to ] and ] and ].<ref>{{cite book|last1=Pearson|first1=Roger|title=Anthropological Glossary|date=1985|publisher=Krieger Publishing Company|pages=20, 128, 267|url=https://www.google.com/books?id=HjANAAAAYAAJ|accessdate=2 February 2018}}</ref>. It holds oppressive and persecutory connotations<ref>{{cite book|last1=Black|first1=Sue|last2=Ferguson|first2=Eilidh|title=Forensic Anthropology: 2000 to 2010|date=2011|publisher=Taylor and Francis Group|page=127|url=https://books.google.com.sg/books?id=306ruTniZmcC&pg=PA127|accessdate=3 July 2018}}</ref> and used in support of ].<ref name="Racism">{{cite book |last=Fluehr-Lobban |first=C. |title=Race and racism : an Introduction |publisher=Lanham : Rowman & Littlefield |date=2005 |page=131-133 |url= https://books.google.it/books?id=3lq3XDz39pIC&pg=PA132&lpg=PA131}}</ref> | |||
| {{EngvarB|date=October 2023}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=October 2023}} | |||
| '''Australo-Melanesians''' (also known as '''Australasians''' or the '''Australomelanesoid''', '''Australoid''' or '''Australioid race''') is an outdated ] of various people indigenous to ] and ]. Controversially, some groups found in parts of ] and ] were also sometimes included. | |||
| While most authors included ], ] and ] (mainly from ], ], ] and ]), there was controversy about the inclusion of the various Southeast Asian populations grouped as "]", or a number of ] tribal populations of the ].<ref name="p. 26" /><ref name="Kulatilake">{{Cite journal |last=Kulatilake |first=Samanti |title=Cranial Morphology of the Vedda people - the indigenes of Sri Lanka|url= https://www.academia.edu/9637404}}</ref> | |||
| The concept of dividing humankind into three, four or five races (often called ], ], ], and Australoid) was introduced in the 18th century and further developed by Western scholars in the context of "]"<ref name="AAPARace" /> during the age of ].<ref name="AAPARace">{{cite web|author=American Association of Physical Anthropologists|title=AAPA Statement on Race and Racism |website=American Association of Physical Anthropologists|access-date=19 June 2020 |date=27 March 2019 |url=https://physanth.org/about/position-statements/aapa-statement-race-and-racism-2019/}}</ref> With the rise of modern ], the concept of distinct human races in a biological sense has become obsolete. In 2019, the ] stated: "The belief in “races” as natural aspects of human biology, and the structures of inequality (racism) that emerge from such beliefs, are among the most damaging elements in the human experience both today and in the past."<ref name="AAPARace" /> | |||
| The Australoid type was theorised by some early anthropologists to have been common among ], ], the populations grouped as "]" (the ], the ] and ], the ], the ], the ], and various other ]), as well as certain ], the ] of ], and a number of tribal populations in the interior of the ]<ref>T. Pullaiah, K. V. Krishnamurthy, Bir Bahadur, ''Ethnobotany of India, Volume 5: The Indo-Gangetic Region and Central India'' (2017), names: the tribes of Chota Nagpur, the Baiga, Gond, Bhil, Santal and Oroan tribes; counted as of partial Australoid and partial ] ancestry are certain Munda-speaking groups (Munda, Gadaba, Santals) and certain Dravidian-speaking groups (Maria, Muria, Gond, Oroan).</ref>. One hypothesis derives ] as from an originally Australoid stock, | |||
| ⚫ | <ref>{{cite book|last1=Sarat Chandra Roy (Ral Bahadur)|title=Man in India - Volume 80|date=2000|publisher=A. K. Bose|page=59|url=https:// |
||
| ==Terminological history== | |||
| The term Australoid belongs to a set of terms introduced by 19th-century anthropologists attempting to categorize human races. Such terms are associated with potentially offensive notions of racial types.<ref name="oxford">{{cite web| title = Ask Oxford – Definition of Australoid| publisher = ]|year=2018| url = https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/australoid| accessdate = 2018-06-28}}</ref> Terms such as Australasian, Australo-Melanesian and Veddoid appear in other works.<ref name=LCS1994>Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza, Paolo Menozzi, Alberto Piazza, ''The History and Geography of Human Genes'' (1994), . R. P. Pathak, ''Education in the Emerging India'' (2007), .</ref> | |||
| The term "Australoid" was coined in ethnology in the mid 19th century, describing tribes or populations "of the type of native Australians".<ref>J.R. Logan (ed.), ''The Journal of the Indian archipelago and eastern Asia'' (1859), .</ref> The term "Australioid race" was introduced by ] in 1870 to refer to certain peoples indigenous to ] and ] and ].<ref>{{cite book|last1=Pearson|first1=Roger|title=Anthropological Glossary|date=1985|publisher=Krieger Publishing Company|pages=20, 128, 267|isbn=9780898745108 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HjANAAAAYAAJ|access-date=2 February 2018}}</ref> In ], ''Australoid'' is used for morphological features characteristic of Aboriginal Australians by ] in his ''Text-book of Anatomy'' (1902). An ''Australioid'' (''sic'', with an additional ''-i-'') racial group was first proposed by ] in an essay ''On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind'' (1870), in which he divided humanity into four principal groups (Xanthochroic, ], ], and Australioid).<ref></ref> His original model included the native inhabitants of ] in ] under the Australoid category, specifically "in a well-marked form" among the hill tribes of the Deccan Plateau. Huxley further classified the ] (Peoples of the ]) as a mixture of the ] (northern Europeans) and Australioids.<ref>Huxley, Thomas. On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind. 1870. 14 August 2006. </ref> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| ]'' (1885-90)]] | |||
| The ''Australioid'' racial group was created by ] in an essay 'On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind' (1870), in which he divided humanity into four principal groups (Xanthochroic, ], ], and Australioid).<ref></ref> Huxley's original model included the native inhabitants of ] under the Australoid category. | |||
| Huxley further classified the ] (Peoples of the ]) as a mixture of the ] (northern Europeans) and Australioids.<ref>Huxley, Thomas. On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind. 1870. August 14, 2006. <http://aleph0.clarku.edu/huxley/SM3/GeoDis.html></ref> Later writers dropped the first "i" in Australioid. | |||
| ⚫ | Huxley (1870) described Australioids as ]; their hair as usually silky, black and wavy or curly, with large, heavy jaws and ], with skin the color of chocolate and irises which are dark brown or black.<ref name="aleph0.clarku.edu">] "" (1870) ''Journal of the Ethnological Society of London''</ref> | ||
| The term "Proto-Australoid" was used by ] in his ''Racial History of Man'' (1923). | |||
| ⚫ | The term "Proto-Australoid" was used by ] in his ''Racial History of Man'' (1923). In ''The Origin of Races'' (1962), ] expounded his system of five races (Australoid, Caucasoid, Mongoloid, Congoid and Capoid) with separate origins. Based on such evidence as claiming Australoids had the largest, megadont teeth, this group was assessed by Coon as being the most archaic and therefore the most primitive and backward. Coon's methods and conclusions were later discredited and show either a "poor understanding of human cultural history and ] or his use of ] for a racialist agenda."<ref name="Fluehr-Lobban2011">{{cite book |last=Fluehr-Lobban |first=C. |title=Race and racism : an Introduction |publisher=Lanham : Rowman & Littlefield |date=2005 |pages=131–133 |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=3lq3XDz39pIC&pg=PA132|isbn=9780759107953 }}</ref> | ||
| In a 1962 publication, Australoid was described as one of the five major human races alongside ], ], Congoid and Capoid.<ref>Moore, Ruth ''Evolution'' (Life Nature Library) New York:1962 Time, Inc. Chapter 8: "The Emergence of Modern ''Homo sapiens''" Page 173 – First page of picture section "Man and His Genes": "The ''Australoid'' race is identified as one of the five major races of mankind, along with the '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']'' races (pictures of a person typical of each race are shown)"</ref> However, under the three race paradigm of Caucasoid, Negroid and Mongoloid, no Australoid category existed.<ref name="Dennis2006">O'Neil, Dennis. "Biological Anthropology Terms." 2006. May 13, 2007. Palomar College.{{cite web|url=http://anthro.palomar.edu/tutorials/pglossary.htm |title=Archived copy |accessdate=2007-05-14 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070612085927/http://anthro.palomar.edu/tutorials/pglossary.htm |archivedate=2007-06-12 |df= }}</ref> | |||
| Terms associated with outdated notions of racial types, such as those ending in "-oid" have come to be seen as potentially offensive<ref name="Black2011">{{cite book|last1=Black|first1=Sue|last2=Ferguson|first2=Eilidh|title=Forensic Anthropology: 2000 to 2010|date=2011|publisher=Taylor and Francis Group|page=127|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=306ruTniZmcC&pg=PA127|access-date=3 July 2018|isbn=9781439845899}} "There are considered to be four basic ancestry groups into which an individual can be placed by physical appearance, not accounting for admixture: the sub-Saharan African group ("Negroid"), the European group ("Caucasoid"), the Central Asian group ("Mongoloid"), and the Australasian group ("Australoid"). The rather outdated names of all but one of these groups were originally derived from geography"</ref> and related to ].<ref name="Fluehr-Lobban2011"/><ref name="oxford">{{cite web| title = Ask Oxford – Definition of Australoid| publisher = ]|year=2018| url = https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/australoid| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20180627202220/https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/australoid| url-status = dead| archive-date = 27 June 2018| access-date = 28 June 2018}}</ref> | |||
| In 1985, Archaeologist Peter Bellwood used the words "Australoid", "Australomelanesoid" and "Australo-Melanesians" to describe the genetic heritage of "the Southern ] populations of ] and ]". <ref>{{cite book|last=Bellwood|first=Peter|title=Prehistory of the Indo-Malaysian Archipelago|publisher=Australian National University|year=1985|isbn=978-1-921313-11-0|url=https://books.google.com/?id=4obAfGBGKY0C&pg=RA1-PA346&lpg=RA1-PA346&dq=australomelanesoid}}</ref> | |||
| == Controversies == | |||
| ==Racial depiction== | |||
| {{MeyersLexikonEthnographicMap}} | |||
| ] (1962). | |||
| The populations grouped as "]", such as the ] (from the Andaman Islands in the Indian Ocean), the ] and ] peoples (from Malaysia), the ] (from Thailand), the ], the ], and certain other ], the ] of Sri Lanka and a number of ] tribal populations in the interior of the ] (some ] tribes and ] ]) were also suggested by some to belong to the Australo-Melanesian group,<ref name="p. 26">{{cite book|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=ErE0DwAAQBAJ&pg=PP26 |first1=T |last1=Pullaiah |first2=KV |last2=Krishnamurthy |first3=Bir |last3=Bahadur |title=Ethnobotany of India, Volume 5: The Indo-Gangetic Region and Central India |year=2017 |page=26|publisher=CRC Press |isbn=9781351741316 }} names the tribes of Chota Nagpur, the Baiga, Gond, Bhil, Santal and Oroan tribes; counted as of partial Australoid and partial ] ancestry are certain Munda-speaking groups (Munda, Bonda, Gadaba, Santals) and certain Dravidian-speaking groups (Maria, Muria, Gond, Oroan).</ref><ref name="Coon 1939 425–431">{{cite book |last=Coon |first=Carleton Stevens |year=1939 |location=] |publisher=] |title=The Races of Europe|url= https://archive.org/details/racesofeurope031695mbp |author-link=Carleton S. Coon |pages=–431}}</ref> but there were controversies about this inclusion. | |||
| {| | |||
| | style="background-color:lime; width:1.0em" | | |||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="background-color:yellow" | | |||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="background-color:magenta" | | |||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="background-color:#5998ff" | | |||
| | ] | |||
| |-| | |||
| | style="background-color:tomato" | | |||
| | ] | |||
| |}]] | |||
| ⚫ | Huxley |
||
| The inclusion of Indian tribes in the group was not well-defined, and was closely related to the question of the original ], and the possible shared ancestry between Indian, Andamanese, and ] populations of the Upper Paleolithic.{{Citation needed|date=June 2024}} | |||
| ⚫ | In ''The Origin of Races'' (1962), ] |
||
| <ref name="Racism"/> | |||
| The suggested Australo-Melanesian ancestry of the original South Asian populations has long remained an open question. It was embraced by Indian anthropologists as emphasising the deep antiquity of Indian prehistory. Australo-Melanesian hunter-gatherer and fisherman tribes of the interior of India were identified with the ] described in the ]. ] (1923) following Vincenzo Giuffrida-Ruggeri (1913) recognises a Pre-Dravidian ''Australo-Veddaic'' stratum in India.<ref>P. Mitra, ''Prehistoric India'' (1923), p. 48.</ref> | |||
| Forensic anthropologist Caroline Wilkenson wrote in 2004 that Australoids have the largest brow ridges "with moderate to large supraorbital arches"<!--pg87-->.<ref name=Wilkenson /> Caucasoids have the second largest brow ridges with "moderate supraorbital ridges"<!--pg 84-->.<ref name=Wilkenson /> Negroids have the third largest brow ridges with an "undulating ]".<ref name=Wilkenson /> Mongoloids are absent of brow ridges<!--pg86-->, so they have the smallest brow ridges.<ref name=Wilkenson>Wilkenson, Caroline. Forensic Facial Reconstruction. Cambridge University Press. 2004. {{ISBN|0-521-82003-0}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | Alternatively, the ] themselves have been claimed as originally of Australo-Melanesian stock,<ref>{{cite book|last1=Sarat Chandra Roy (Ral Bahadur)|title=Man in India - Volume 80|date=2000|publisher=A. K. Bose|page=59|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wPhEAQAAIAAJ|access-date=21 May 2018}}</ref> a view held by ] among others.<ref>R. R. Bhattacharya et al. (eds., ''Anthropology of B.S. Guha: a centenary tribute'' (1996), p. 50.</ref> | ||
| ==Possible early presence in the Americas== | |||
| {{main|Pleistocene peopling of the Americas}} | |||
| {{see also|Genetic_history_of_indigenous_peoples_of_the_Americas#Paleoamericans|Fuegians|Pericúes}} | |||
| ]'s skull]] | |||
| South Indian tribes specifically described as having Australo-Melanesian affinities include the ], ], ], ], ], the ] of Kerala, the ] and ] of the ], the ] of Malabar, the ], ], ] and ].<ref>Mhaiske, Vinod M., Patil, Vinayak K., Narkhede, S. S., ''Forest Tribology And Anthropology'' (2016), . Bhuban Mohan Das, ''The Peoples of Assam'' (1987), .</ref> | |||
| A speculative theory of ] in the 1990s proposes that an early Australoid population may have been the earliest occupants of the New World. The theory was based on an analysis of the ] fossil found in Brazil, and found tentative academic support.<ref></ref> | |||
| In 1953, the Australoid race were believed to be part of the "Archaic Caucasoid race", along with ], Dravidians and ].<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Beals |first1=Ralph L. |title=An Introduction to Anthropology |last2=Hoijer |first2=Harry |publisher=The Macmillan Company |year=1953 |place=New York}}</ref> | |||
| If this hypothesis is correct, it would mean that some Australoid groups continued the ] beyond ], along the continental shelf north in ] and across the ], reaching the ] by about 50,000 years ago.{{cn|date=June 2018}} | |||
| == Criticism based on modern genetics == | |||
| ===Genetic evidence=== | |||
| {{See also|Genetic studies on Indigenous Australians|Race and genetics}} | |||
| In 2015, two major studies{{cn|date=May 2018}} of the DNA of living and ancient people detect in modern Native Americans a trace of DNA related to that of native people from ] and ]. Australasian admixture in some living Native Americans, including those of the ] and the ] of Amazonian Brazil. | |||
| After discussing various criteria used in biology to define subspecies or races, ] concludes in 2016: "he answer to the question whether races exist in humans is clear and unambiguous: no."<ref name="Templeton2016"> {{cite book |last1= Templeton |first1= A. |chapter= Evolution and Notions of Human Race |editor1-last= Losos |editor1-first= J. |editor2-last= Lenski |editor2-first= R. |title= How Evolution Shapes Our Lives: Essays on Biology and Society |date=2016 |pages=346–361 |doi=10.2307/j.ctv7h0s6j.26 |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctv7h0s6j.26 |access-date= |publisher=Princeton University Press |location=Princeton, Oxford |jstor= j.ctv7h0s6j.26 |isbn=978-1-4008-8138-3}}</ref>{{rp|360}}<ref>That this view reflects the consensus among American anthropologists is stated in: {{cite journal |last1=Wagner |first1=Jennifer K. |last2=Yu |first2=Joon-Ho |last3=Ifekwunigwe |first3=Jayne O. |last4=Harrell |first4=Tanya M. |last5=Bamshad |first5=Michael J. |last6=Royal |first6=Charmaine D. |date=February 2017 |title=Anthropologists' views on race, ancestry, and genetics |journal=American Journal of Physical Anthropology |volume=162 |issue=2 |pages=318–327 |doi=10.1002/ajpa.23120 |issn=0002-9483 |pmc=5299519 |pmid=27874171}} See also: {{cite web |author=American Association of Physical Anthropologists |author-link=American Association of Physical Anthropologists |date=27 March 2019 |title=AAPA Statement on Race and Racism |url=https://physanth.org/about/position-statements/aapa-statement-race-and-racism-2019/ |access-date=19 June 2020 |website=American Association of Physical Anthropologists}}</ref> | |||
| Evidence of Australasian admixture in Amazonian populations was found by Skoglund and Reich (2016).<ref name=Skoglund2016>P. Skoglund, D. Reich, "A genomic view of the peopling of the Americas", ''Curr Opin Genet Dev.'' 2016 Dec; 41: 27–35, doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.06.016. | |||
| "Recently, we carried out a stringent test of the null hypothesis of a single founding population of Central and South Americans using genome-wide data from diverse Native Americans. We detected a statistically clear signal linking Native Americans in the Amazonian region of Brazil to present-day Australo-Melanesians and Andaman Islanders (‘Australasians’). Specifically, we found that Australasians share significantly more genetic variants with some Amazonian populations—including ones speaking Tupi languages—than they do with other Native Americans. We called this putative ancient Native American lineage “Population Y” after Ypykuéra, which means ‘ancestor’ in the Tupi language family."</ref> | |||
| The Pan-Asian genome project concluded that Negrito populations in Malaysia and the Negrito populations in the Philippines were more closely related to non-Negrito local populations, rather than to each other, highlighting the non-existence of a distinct Australo-Melanesian grouping.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Stoneking |first1=Mark |last2=Delfin |first2=Frederick |date=23 February 2010 |title=The Human Genetic History of East Asia: Weaving a Complex Tapestry |journal=Current Biology |language=English |volume=20 |issue=4 |pages=R188–R193 |doi=10.1016/j.cub.2009.11.052 |issn=0960-9822 |pmid=20178766|s2cid=18777315 |doi-access=free |bibcode=2010CBio...20.R188S }}</ref> | |||
| Walter Neves and Mark Hubbe argue that these people descended from an early wave of migration that was separate from the one that gave rise to today’s Native Americans, and drew on a different source population in Asia.<ref> by Michael Balter published in the "American Association for the Advancement of Science" on July 21, 2015</ref> | |||
| ===Morphology=== | |||
| Christy Turner notes that "cranial analyses of some South American crania have suggested that there might have been some early migration of "Australoids."<ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RI32r548fUwC|last=Turner|first=Christy|chapter=Teeth, Needles, Dogs and Siberia: Bioarchaeological Evidence for the Colonization of the New World|title=The First Americans: The Pleistocene Colonization of the New World'|publisher=University of California Press|year=2002|page=138 | isbn=978-0-940228-50-4}}</ref> | |||
| However, Turner argues that cranial morphology suggests ] in all the populations he has studied. | |||
| One of the earliest skulls discovered in the Americas by archaeologists is an Upper Paleolithic specimen named the ]. According to Neves, Luzia's ] predecessors lived in South East Asia for tens of thousands of years, after ] from ], and began arriving in the ], as early as 15,000 years ago. Some anthropologists have hypothesized that Paleo-Indians migrated along the coast of ] and ] in small watercraft, before or during the LGM. | |||
| Neves' conclusions have been challenged researchers who argued that the cranio-facial variability could just be due to genetic drift and other factors affecting cranio-facial plasticity in Native Americans.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://docs.google.com/Doc?docid=0AVJyLBsGC0mKZGZucHhrNTRfMTRjd20zbnBkOQ&hl=en|title=THE KENNEWICK FOLLIES: "New" Theories about the Peopling of the Americas|author=Stuart J. Fiedel|year=2004|accessdate=2008-02-15}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{ |
{{Reflist|30em}} | ||
| {{Historical definitions of race}} | {{Historical definitions of race}} | ||
| ] | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Australoid Race}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:25, 19 December 2024
Outdated grouping of human beingsAustralo-Melanesians (also known as Australasians or the Australomelanesoid, Australoid or Australioid race) is an outdated historical grouping of various people indigenous to Melanesia and Australia. Controversially, some groups found in parts of Southeast Asia and South Asia were also sometimes included.
While most authors included Papuans, Aboriginal Australians and Melanesians (mainly from Fiji, New Caledonia, Solomon Islands and Vanuatu), there was controversy about the inclusion of the various Southeast Asian populations grouped as "Negrito", or a number of dark-skinned tribal populations of the Indian subcontinent.
The concept of dividing humankind into three, four or five races (often called Caucasoid, Mongoloid, Negroid, and Australoid) was introduced in the 18th century and further developed by Western scholars in the context of "racist ideologies" during the age of colonialism. With the rise of modern genetics, the concept of distinct human races in a biological sense has become obsolete. In 2019, the American Association of Biological Anthropologists stated: "The belief in “races” as natural aspects of human biology, and the structures of inequality (racism) that emerge from such beliefs, are among the most damaging elements in the human experience both today and in the past."
Terminological history
The term "Australoid" was coined in ethnology in the mid 19th century, describing tribes or populations "of the type of native Australians". The term "Australioid race" was introduced by Thomas Huxley in 1870 to refer to certain peoples indigenous to South and Southeast Asia and Oceania. In physical anthropology, Australoid is used for morphological features characteristic of Aboriginal Australians by Daniel John Cunningham in his Text-book of Anatomy (1902). An Australioid (sic, with an additional -i-) racial group was first proposed by Thomas Huxley in an essay On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind (1870), in which he divided humanity into four principal groups (Xanthochroic, Mongoloid, Negroid, and Australioid). His original model included the native inhabitants of Deccan in India under the Australoid category, specifically "in a well-marked form" among the hill tribes of the Deccan Plateau. Huxley further classified the Melanochroi (Peoples of the Mediterranean race) as a mixture of the Xanthochroi (northern Europeans) and Australioids.
Huxley (1870) described Australioids as dolichocephalic; their hair as usually silky, black and wavy or curly, with large, heavy jaws and prognathism, with skin the color of chocolate and irises which are dark brown or black.
The term "Proto-Australoid" was used by Roland Burrage Dixon in his Racial History of Man (1923). In The Origin of Races (1962), Carleton Coon expounded his system of five races (Australoid, Caucasoid, Mongoloid, Congoid and Capoid) with separate origins. Based on such evidence as claiming Australoids had the largest, megadont teeth, this group was assessed by Coon as being the most archaic and therefore the most primitive and backward. Coon's methods and conclusions were later discredited and show either a "poor understanding of human cultural history and evolution or his use of ethnology for a racialist agenda."
Terms associated with outdated notions of racial types, such as those ending in "-oid" have come to be seen as potentially offensive and related to scientific racism.
Controversies
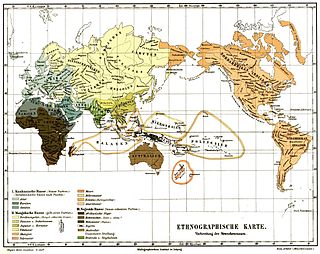
| Caucasoid: Aryans Semitic Hamitic Negroid: African Negro Khoikhoi Melanesian Negrito Australoid Uncertain: Dravida & Sinhalese | Mongoloid: North Mongol Chinese & Indochinese Korean & Japanese Tibetan & Burmese Malay Polynesian Maori Micronesian Eskimo & Inuit American |
The populations grouped as "Negrito", such as the Andamanese (from the Andaman Islands in the Indian Ocean), the Semang and Batek peoples (from Malaysia), the Maniq people (from Thailand), the Aeta people, the Ati people, and certain other ethnic groups in the Philippines, the Vedda people of Sri Lanka and a number of dark-skinned tribal populations in the interior of the Indian subcontinent (some Dravidian-speaking tribes and Austroasiatic-speaking Munda peoples) were also suggested by some to belong to the Australo-Melanesian group, but there were controversies about this inclusion.
The inclusion of Indian tribes in the group was not well-defined, and was closely related to the question of the original peopling of India, and the possible shared ancestry between Indian, Andamanese, and Sahulian populations of the Upper Paleolithic.
The suggested Australo-Melanesian ancestry of the original South Asian populations has long remained an open question. It was embraced by Indian anthropologists as emphasising the deep antiquity of Indian prehistory. Australo-Melanesian hunter-gatherer and fisherman tribes of the interior of India were identified with the Nishada Kingdom described in the Mahabharata. Panchanan Mitra (1923) following Vincenzo Giuffrida-Ruggeri (1913) recognises a Pre-Dravidian Australo-Veddaic stratum in India.
Alternatively, the Dravidians themselves have been claimed as originally of Australo-Melanesian stock, a view held by Biraja Sankar Guha among others.
South Indian tribes specifically described as having Australo-Melanesian affinities include the Oraon, Munda, Santal, Bhil, Gondi, the Kadars of Kerala, the Kurumba and Irula of the Nilgiris, the Paniyans of Malabar, the Uralis, Kannikars, Muthuvan and Chenchus.
In 1953, the Australoid race were believed to be part of the "Archaic Caucasoid race", along with Ainus, Dravidians and Veddas.
Criticism based on modern genetics
See also: Genetic studies on Indigenous Australians and Race and geneticsAfter discussing various criteria used in biology to define subspecies or races, Alan R. Templeton concludes in 2016: "he answer to the question whether races exist in humans is clear and unambiguous: no."
The Pan-Asian genome project concluded that Negrito populations in Malaysia and the Negrito populations in the Philippines were more closely related to non-Negrito local populations, rather than to each other, highlighting the non-existence of a distinct Australo-Melanesian grouping.
See also
References
- ^ Pullaiah, T; Krishnamurthy, KV; Bahadur, Bir (2017). Ethnobotany of India, Volume 5: The Indo-Gangetic Region and Central India. CRC Press. p. 26. ISBN 9781351741316. names the tribes of Chota Nagpur, the Baiga, Gond, Bhil, Santal and Oroan tribes; counted as of partial Australoid and partial Mongoloid ancestry are certain Munda-speaking groups (Munda, Bonda, Gadaba, Santals) and certain Dravidian-speaking groups (Maria, Muria, Gond, Oroan).
- Kulatilake, Samanti. "Cranial Morphology of the Vedda people - the indigenes of Sri Lanka".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ American Association of Physical Anthropologists (27 March 2019). "AAPA Statement on Race and Racism". American Association of Physical Anthropologists. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- J.R. Logan (ed.), The Journal of the Indian archipelago and eastern Asia (1859), p. 68.
- Pearson, Roger (1985). Anthropological Glossary. Krieger Publishing Company. pp. 20, 128, 267. ISBN 9780898745108. Retrieved 2 February 2018.
- Huxley, Thomas On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind. 1870. August 14, 2006
- Huxley, Thomas. On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind. 1870. 14 August 2006.
- Huxley, T. H. "On the Geographical Distribution of the Chief Modifications of Mankind" (1870) Journal of the Ethnological Society of London
- ^ Fluehr-Lobban, C. (2005). Race and racism : an Introduction. Lanham : Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 131–133. ISBN 9780759107953.
- Black, Sue; Ferguson, Eilidh (2011). Forensic Anthropology: 2000 to 2010. Taylor and Francis Group. p. 127. ISBN 9781439845899. Retrieved 3 July 2018. "There are considered to be four basic ancestry groups into which an individual can be placed by physical appearance, not accounting for admixture: the sub-Saharan African group ("Negroid"), the European group ("Caucasoid"), the Central Asian group ("Mongoloid"), and the Australasian group ("Australoid"). The rather outdated names of all but one of these groups were originally derived from geography"
- "Ask Oxford – Definition of Australoid". Oxford Dictionary of English. 2018. Archived from the original on 27 June 2018. Retrieved 28 June 2018.
- Coon, Carleton Stevens (1939). The Races of Europe. New York: The Macmillan Company. pp. 425–431.
- P. Mitra, Prehistoric India (1923), p. 48.
- Sarat Chandra Roy (Ral Bahadur) (2000). Man in India - Volume 80. A. K. Bose. p. 59. Retrieved 21 May 2018.
- R. R. Bhattacharya et al. (eds., Anthropology of B.S. Guha: a centenary tribute (1996), p. 50.
- Mhaiske, Vinod M., Patil, Vinayak K., Narkhede, S. S., Forest Tribology And Anthropology (2016), p. 5. Bhuban Mohan Das, The Peoples of Assam (1987), p. 78.
- Beals, Ralph L.; Hoijer, Harry (1953). An Introduction to Anthropology. New York: The Macmillan Company.
- Templeton, A. (2016). "Evolution and Notions of Human Race". In Losos, J.; Lenski, R. (eds.). How Evolution Shapes Our Lives: Essays on Biology and Society. Princeton, Oxford: Princeton University Press. pp. 346–361. doi:10.2307/j.ctv7h0s6j.26. ISBN 978-1-4008-8138-3. JSTOR j.ctv7h0s6j.26.
- That this view reflects the consensus among American anthropologists is stated in: Wagner, Jennifer K.; Yu, Joon-Ho; Ifekwunigwe, Jayne O.; Harrell, Tanya M.; Bamshad, Michael J.; Royal, Charmaine D. (February 2017). "Anthropologists' views on race, ancestry, and genetics". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 162 (2): 318–327. doi:10.1002/ajpa.23120. ISSN 0002-9483. PMC 5299519. PMID 27874171. See also: American Association of Physical Anthropologists (27 March 2019). "AAPA Statement on Race and Racism". American Association of Physical Anthropologists. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- Stoneking, Mark; Delfin, Frederick (23 February 2010). "The Human Genetic History of East Asia: Weaving a Complex Tapestry". Current Biology. 20 (4): R188 – R193. Bibcode:2010CBio...20.R188S. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2009.11.052. ISSN 0960-9822. PMID 20178766. S2CID 18777315.