| Revision as of 15:28, 28 January 2019 edit2601:602:880:5f76:88d2:e657:e20b:5cad (talk) numerous sources state albedo midway between Pluto and Charon and not near 0.83← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 00:17, 22 August 2024 edit undoInternetArchiveBot (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers5,382,355 edits Rescuing 3 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.9.5) (Hey man im josh - 20898 | ||
| (108 intermediate revisions by 48 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Moon of Pluto}} | |||
| {{Good article}} | |||
| {{Infobox planet | {{Infobox planet | ||
| | discoverer = ]<br>Pluto Companion Search Team | |||
| | pronounced = {{IPAc-en|ˈ|h|aɪ|d|r|ə}} | |||
| | named_after = ] | |||
| | period = {{val|38.20177|0.00003|u=d}} | |||
| | physical_characteristics = yes | |||
| | dimensions = ≈ {{val|65|x|45|x|25|u=km}}<ref name=LPSC>{{cite web|url=http://livestream.com/viewnow/LPSC2016|title=2016 Lunar & Planetary Science Conference by National Institute of Aerospace|publisher=}}</ref> | |||
| | density = | |||
| | name = Hydra | | name = Hydra | ||
| | image = Hydra |
| image = Hydra reprocessed.png | ||
| | caption = |
| caption = Near true-color image of Hydra, taken by '']'' on 14 July 2015 | ||
| | discovery_ref = <ref name="Nomenclature">{{cite web|title=Planet and Satellite Names and Discoverers|website=Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature|publisher=International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN)|url=https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Page/Planets|access-date=17 May 2021}}</ref> | |||
| | discovery = yes | |||
| | |
| discoverer = ] | ||
| | |
| discovered = 15 May 2005 | ||
| | alt_names = S/2005 P 1 | |||
| | mpc_name = Pluto III<ref name="Nomenclature"/> | |||
| | pronounced = {{IPAc-en|ˈ|h|aɪ|d|r|ə}}<ref>{{OED|hydra}}</ref> | |||
| | adjectives = Hydrian<ref>Davenport (1843) ''A new geographical, historical, and commercial grammar''</ref> {{IPAc-en|ˈ|h|aɪ|d|r|i|ən}}<ref>per {{Cite encyclopedia |url=http://www.lexico.com/definition/hydria |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200322184432/https://www.lexico.com/definition/hydria |url-status=dead |archive-date=March 22, 2020 |title=hydria |dictionary=] UK English Dictionary |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| | named_after = ] | |||
| | period = {{val|38.20177|0.00003|u=d}} | |||
| | dimensions = {{val|50.9|x|36.1|x|30.9|u=km}}<ref name="phasecurves" /><br/>(] of 38 km) | |||
| | note = yes | | note = yes | ||
| | orbit_ref = <ref name="ShowalterHamilton2015">{{cite journal|last1=Showalter|first1=M. R.|author1-link=Mark R. Showalter|last2=Hamilton|first2=D. P.|title=Resonant interactions and chaotic rotation of Pluto's small moons|journal=Nature|volume=522|issue=7554|date=3 June 2015|pages=45–49|doi=10.1038/nature14469|pmid=26040889|bibcode = 2015Natur.522...45S |s2cid=205243819}}</ref> | |||
| | adjectives = Hydrian | |||
| | orbit_ref = <ref name="ShowalterHamilton2015">{{cite journal|last1=Showalter|first1=M. R.|author1link=Mark R. Showalter|last2=Hamilton|first2=D. P.|title=Resonant interactions and chaotic rotation of Pluto’s small moons|journal=Nature|volume=522|issue=7554|date=3 June 2015|pages=45–49|doi=10.1038/nature14469|pmid=26040889|bibcode = 2015Natur.522...45S }}</ref> | |||
| | semimajor = {{val|64738|3|u=km}} | | semimajor = {{val|64738|3|u=km}} | ||
| | eccentricity = {{val|0.005862|0.000025}} | | eccentricity = {{val|0.005862|0.000025}} | ||
| | avg_speed = 0.123 km/s | |||
| | inclination = {{val|0.242|0.005|u=°}} | | inclination = {{val|0.242|0.005|u=°}} | ||
| | satellite_of = ] | | satellite_of = ] | ||
| | mass = {{val| |
| mass = {{val|3.01|0.30|e=16|u=kg}}<ref name="Porter2023"/>{{rp|page=10}} | ||
| | density = {{val|1.220|0.150|u=g/cm3}}<ref name="Porter2023"/>{{rp|page=10}} | |||
| | single_temperature = 33–55 ] | |||
| | single_temperature = 23 ]<ref name="Cook2018">{{cite journal|title=Composition of Pluto's small satellites: Analysis of ''New Horizons'' spectral images|first1=Jason C.|last1=Cook|first2=Cristina M.|last2=Dalle Ore|author2-link=Cristina Dalle Ore|first3=Silvia|last3=Protopapa|first4=Richard P.|last4=Binzel|first5=Richard|last5=Cartwright|first6=Dale P.|last6=Cruikshank|display-authors=etal|journal=Icarus|volume=315|issue=1964|pages=30–45|date=15 November 2018|doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2018.05.024|bibcode=2017LPI....48.2478C|s2cid=125374498}}</ref> | |||
| | rotation = 0.4295 ± 0.0008 d (chaotic)<ref name=LPSC/> | |||
| | rotation = 0.4295 d (10.31 h)<ref name=Lakdawalla2015/> (July 2015) | |||
| | axial_tilt = variable | |||
| | axial_tilt = {{val|110|u=deg}}<ref name="arxiv1604">{{cite journal |last1=Weaver |first1=H. A. |last2=Buie |first2=M. W. |last3=Showalter |first3=M. R. |last4=Stern |first4=S. A. |display-authors=etal|title=The Small Satellites of Pluto as Observed by New Horizons |journal=Science |volume=351 |issue=6279 |pages=aae0030 |date=18 April 2016|arxiv= 1604.05366|doi=10.1126/science.aae0030 |pmid=26989256 |bibcode=2016Sci...351.0030W |s2cid=206646188 }}</ref> | |||
| | albedo = 0.5 | |||
| | |
| albedo = 0.83 ± 0.08 (geometric)<ref name="scimag000">{{cite journal|last1=Stern|first1=S. A.|last2=Bagenal|first2=F.|last3=Ennico|first3=K.|last4=Gladstone|first4=G. R.|title=The Pluto system: Initial results from its exploration by New Horizons|journal=Science|date=15 October 2015|volume=350|issue=6258|pages=aad1815|doi=10.1126/science.aad1815|pmid=26472913|display-authors=etal|arxiv = 1510.07704 |bibcode = 2015Sci...350.1815S |s2cid=1220226}}</ref> | ||
| | surface_grav = {{val|0.00520055269|u=g}}<ref name="by-the-numbers">{{cite web|title=Hydra By the Numbers|url=https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/moons/pluto-moons/hydra/by-the-numbers/|publisher=NASA|website=solarsystem.nasa.gov|access-date=7 March 2019}}<br>(Original value of {{val|0.051|u=m/s2}} converted to g)</ref> | |||
| | magnitude = 22.9–23.3 (measured)<ref name="Stern06b">{{cite journal | author=Stern, S. A. |author2=Mutchler, M. J. |author3=Weaver, H. A. |author4= Steffl, A. J. |title=The Positions, Colors, and Photometric Variability of Pluto's Small Satellites from HST Observations 2005–2006 |journal=Astronomical Journal |date=2006 |pages=1405–1414 | issue=3 | doi=10.1086/506347 | volume=132 | bibcode=2006AJ....132.1405S|arxiv = astro-ph/0607507 |s2cid=14360964 }} ()</ref> | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Hydra''' is a ], with a diameter of approximately {{convert|51|km|mi|abbr=on}} across its longest dimension.<ref name="phasecurves">{{cite journal |last1=Verbiscer |first1=A. J. |last2=Porter |first2=S. B. |last3=Buratti |first3=B. J. |last4=Weaver |first4=H. A. |last5=Spencer |first5=J. R. |last6=Showalter |first6=M. R. |last7=Buie |first7=M. W. |last8=Hofgartner |first8=J. D. |last9=Hicks |first9=M. D. |last10=Ennico-Smith |first10=K. |last11=Olkin |first11=C. B. |last12=Stern |first12=S. A. |last13=Young |first13=L. A. |last14=Cheng |first14=A. |title=Phase Curves of Nix and Hydra from the ''New Horizons'' Imaging Cameras |journal=The Astrophysical Journal |date=2018 |volume=852 |issue=2 |pages=L35 |doi=10.3847/2041-8213/aaa486|doi-access=free |bibcode=2018ApJ...852L..35V }}</ref> It is the second-largest moon of ], being slightly larger than ]. Hydra was discovered along with Nix by astronomers using the ] on 15 May 2005,<ref name="Nomenclature"/> and was named after the ], the nine-headed underworld serpent in ].<ref name="ChasingNH">{{cite book |last1=Stern |first1=Alan |last2=Grinspoon |first2=David |title=]: Inside the Epic First Mission to Pluto |publisher=Picador |date=May 1, 2018 |chapter=Chapter 7: Bringing It All Together|isbn=9781250098962}}</ref> By distance, Hydra is the fifth and outermost moon of Pluto, orbiting beyond Pluto's fourth moon ].<ref name="scimag000"/> | |||
| '''Hydra''' is the outermost known ]. It was discovered along with ] in June 2005, and was visited along with Pluto by '']'' in July 2015. Hydra's surface is probably covered with water ice. It is irregularly shaped, and measures 50 kilometers (31 miles) along its longest dimension<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.nasa.gov/feature/pluto-s-icy-moon-hydra|title=Pluto’s Icy Moon Hydra|last=Keeter|first=Bill|date=2016-05-05|work=NASA|access-date=2018-02-20|language=en}}</ref>. Hydra's reflectivity (the percentage of incident light reflected from the surface) is intermediate between those of Pluto and ].<ref name="HydraEmerges">{{cite web |title=Hydra Emerges from the Shadows |author=NASA |date=15 July 2015 |accessdate=16 July 2015 |url=http://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/hydra-emerges-from-the-shadows}}</ref><ref Name=universeToday>{{cite web|title=Pluto's Moon Hydra|author=NASA/APL | date=2008| url=http://imgur.com/2IqsLTt/}}</ref> | |||
| Hydra has a highly ] surface caused by the presence of ], similar to other Plutonian moons.<ref name="IcyMoon">{{Cite web|url=https://www.nasa.gov/feature/pluto-s-icy-moon-hydra|title=Pluto's Icy Moon Hydra|last=Keeter|first=Bill|date=5 May 2016|work=NASA|access-date=20 February 2018|language=en|archive-date=22 January 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180122173535/https://www.nasa.gov/feature/pluto-s-icy-moon-hydra/|url-status=dead}}</ref> Hydra's reflectivity is intermediate, in between those of Pluto and ].<ref name="HydraEmerges">{{cite web |title=Hydra Emerges from the Shadows |author=NASA |date=15 July 2015 |access-date=16 July 2015 |url=http://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/hydra-emerges-from-the-shadows}}</ref> The '']'' spacecraft imaged Pluto and its moons in July 2015 and returned multiple images of Hydra.<ref name="CapturesTwo">{{cite web |title=New Horizons 'Captures' Two of Pluto's Smaller Moons|publisher=Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory |date=21 July 2015 |access-date=22 July 2015 |url=http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/News-Center/News-Article.php?page=20150721}}</ref> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| == Discovery == | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| Members of the ''New Horizons'' team suspected that Pluto and Charon might be accompanied by other small, distant moons, weakly bound to the Pluto system. They used the ] to test this hypothesis. This led to the discovery of Nix and Hydra – both surprisingly close to Pluto/Charon – and that no significant moons existed in Pluto's extended sphere of influence. | |||
| Hydra was discovered by the ]'s "Pluto Companion Search Team", consisting of Hal A. Weaver, ], Max J. Mutchler, Andrew J. Steffl, ], William J. Merline, John R. Spencer, Eliot F. Young, and Leslie A. Young. The discovery images were taken on 15 May 2005, and 18 May 2005; Nix and Hydra were independently discovered by Max J. Mutchler on 15 June 2005, and Andrew J. Steffl on 15 August 2005. The discoveries were announced on 31 October 2005, after confirmation by ] from 2002. They were ] '''S/2005 P 1''' (Hydra) and '''S/2005 P 2''' (Nix).<ref name="IAUC8625"> describing the discovery</ref><ref name="IAUC8723" /> | |||
| The discovery images were taken on 15 May 2005 and 18 May 2005. Hydra and Nix were independently discovered by Max J. Mutchler on 15 June 2005 and by Andrew J. Steffl on 15 August 2005.<ref name="UniverseToday">{{cite web|title=Pluto's Moon Hydra|first=Matt|last=Williams|url=https://www.universetoday.com/13903/plutos-moon-hydra/|publisher=]|date=13 July 2015|access-date=7 March 2019}}</ref> The discoveries were announced on 31 October 2005, after confirmation by ] archival Hubble images of Pluto from 2002.<ref name="hubblesite">{{cite web|url=http://hubblesite.org/news_release/news/2005-19|title=NASA's Hubble Reveals Possible New Moons Around Pluto|date=31 October 2005|website=www.hubblesite.org}}</ref> The two newly discovered moons were subsequently ] '''S/2005 P 1''' for Hydra and S/2005 P 2 for Nix.<ref name="IAUC8625">{{cite web|url=http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/iauc/08600/08625.html|title=IAU Circular No. 8625|website=www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu|date=31 October 2005}}<br>(IAU Circular No. 8625 describing the discovery)</ref><ref name="IAUC8723" /> The moons were informally referred to as "P1" and "P2" respectively, by the discovery team.<ref name="IAUC8625"/> | |||
| === Name === | |||
| The name ''Hydra'' was announced on 21 June 2006, in ] Circular 8723,<ref name="IAUC8723"> naming the moons</ref> along with the formal designation '''Pluto III'''. The name is that of the ], the nine-headed serpent that battled ] in ]. The nine heads of Hydra are a reference to Pluto's tenure as the ninth planet; its initial, ''H'', refers to the Hubble Telescope, which discovered Hydra and, together with Nix, to the '']'' mission whose safe passage was the motivation for taking the Hubble images.<ref>Neil deGrasse Tyson, 2009, ''The Pluto Files''</ref> | |||
| == |
== Naming == | ||
| ] | |||
| The name Hydra was approved on 21 June 2006 by the ] and was announced along with the naming of Nix in the IAU Circular 8723.<ref name="IAUC8723">{{cite web|url=http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/iauc/08700/08723.html|title=IAU Circular No. 8723|website=www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu|date=21 June 2006}}<br>(IAU Circular No. 8723 naming the moons)</ref> Hydra was named after the ], a multi-headed serpent that battled ] in ].<ref name="ChasingNH"/> Particularly, the nine heads of Hydra subtly references Pluto's former ninth planetary status.<ref name="ChasingNH"/> The two newly named moons were intentionally named that the order of their initials ''N'' and ''H'' honors the ''New Horizons'' mission to Pluto, similarly to how the first two letters of Pluto's name honors ].<ref name="UniverseToday2006">{{cite web|title=Pluto's New Moons are Named Nix and Hydra|author=Cain, Fraser | date=22 June 2006 | url=https://www.universetoday.com/152/plutos-new-moons-are-named-nix-and-hydra/|publisher=]|access-date= 8 March 2019}}</ref><ref name="ChasingNH"/> Hydra's name was also intentionally chosen that its initial ''H'' honors the Hubble Space Telescope used by the Pluto Companion Search Team to discover Hydra and Nix.<ref name="UniverseToday2006"/><ref name="PlutosMoons">{{cite web|title=Pluto and Its Moons: Charon, Nix and Hydra|url=https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/plutos_moons.html|publisher=NASA|date=23 June 2006|access-date=8 March 2019|archive-date=21 May 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220521001103/https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/plutos_moons.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The names of features on the bodies in the Pluto system are related to mythology and the literature and history of exploration. In particular, the names of features on Hydra must be related to legendary serpents and dragons from literature, mythology, and history.<ref name="nomenclature">{{cite web|title=Naming of Astronomical Objects|url=https://www.iau.org/public/themes/naming/#dwarfplanets|publisher=International Astronomical Union}} | |||
| </ref> | |||
| == Origin == | |||
| Pluto's smaller moons, including Hydra, were thought to have formed from ] between Pluto and another Kuiper belt object, similarly to how the ] is believed to have formed from debris ejected by a ].<ref name="SternFormation">{{Cite journal | last = Stern | first = S. A. | author-link = Alan Stern | author2 = Weaver, H. A. | author3 = Steff, A. J. | author4 = Mutchler, M. J. | author5 = Merline, W. J. | author6 = Buie, M. W. | author7 = Young, E. F. | author8 = Young, L. A. | author9 = Spencer, J. R. | title = A giant impact origin for Pluto's small moons and satellite multiplicity in the Kuiper belt | journal = ] | volume = 439 | issue = 7079 | pages = 946–948 | date = 23 February 2006 | url = http://ns1.plutoportal.net/~layoung/eprint/Stern2006plutosat.pdf | doi = 10.1038/nature04548 | access-date = 20 July 2011 | bibcode = 2006Natur.439..946S | pmid = 16495992 | s2cid = 4400037 | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20120119001455/http://ns1.plutoportal.net/~layoung/eprint/Stern2006plutosat.pdf | archive-date = 19 January 2012 }}</ref> The ejecta from the collision would then coalesce into the moons of Pluto.<ref name="chaos" /> It was thought that Hydra had initially formed at a closer proximity to Pluto, and its orbit had undergone changes through ].<ref name="arxiv1803"/><ref name="obliquity">{{cite journal|title=Obliquity evolution of the minor satellites of Pluto and Charon|url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312594382|journal=]|doi=10.1016/j.icarus.2017.04.012|date=January 2017|access-date=17 March 2019|first1=A. C.|last1=Quillen|first2=F.|last2=Nichols-Fleming|first3=Y.-Y.|last3=Chen|first4=B.|last4=Noyelles|volume=293|pages=94–113|arxiv=1701.05594|bibcode=2017Icar..293...94Q|s2cid=119408999}}</ref> In this case, Hydra along with the smaller moons of Pluto would have migrated outwards with Charon into their current orbits around the Pluto-Charon barycenter.<ref name="tidaldamping"/><ref name="arxiv1803"/> Through 'tidal damping' by mutual tidal interactions with Charon, Hydra's orbit around the Pluto-Charon barycenter gradually became more circular over time.<ref name="arxiv1803"/> Hydra is believed to have formed from two smaller objects merging into one single object.<ref name="Lakdawalla2015"/><ref name="TimSharp"/> | |||
| == Physical characteristics == | |||
| {{Annotated image | |||
| |image=Pure-Ice_Hydra_Charon_Spectra-composite.jpg | |||
| |image-width=600 | |||
| |width=335 | |||
| <!-- to crop the right part of the image --> | |||
| |height=242 | |||
| |float=right | |||
| |annotations=<!-- this parameter must be there, empty or not! --> | |||
| |caption=Spectra comparison of Hydra and Charon. Hydra's spectrum closely matches that of pure water ice, which is shown for comparison.}} | |||
| Hydra is irregular in shape, measuring {{convert|50.9|km|mi|abbr=on}} along its longest axis and its shortest axis measuring {{convert|30.9|km|mi|abbr=on}} across.<ref name="phasecurves"/> This gives Hydra the measured dimensions of {{convert|50.9|×|36.1|x|30.9|km|mi|abbr=on}}.<ref name="phasecurves"/> | |||
| The surface of Hydra is highly reflective due to the presence of water ice on its surface.<ref name="IcyMoon"/> The surface of Hydra displays a ] similarly to Pluto's small moons, although the spectrum of Hydra appears slightly bluer.<ref name="SimonPort2015">{{cite web|last1=Porter|first1=Simon|title=Pluto's Small Moons Nix and Hydra|url=https://blogs.nasa.gov/pluto/2015/10/05/plutos-small-moons-nix-and-hydra/|website=blogs.nasa.gov|date=5 October 2015 |access-date=23 February 2019}}</ref><ref name="Codex Regius"/> The water ice on Hydra's surface is relatively pure and shows no significant darkening compared to Charon.<ref name="IcyMoon"/> One explanation suggests that Hydra's surface is continually refreshed by micrometeorite impacts ejecting darker material from the surface of Hydra.<ref name="IcyMoon"/> The surface spectrum of Hydra is slightly bluish compared to that of Nix.<ref name="Codex Regius">{{cite book|title=Pluto & Charon|author=Codex Regius|year=2016| publisher=CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform| isbn=978-1534960749}}</ref> Explanations for Hydra's bluish color suggest that the surface of Hydra has a higher amount of water ice compared to Nix, which could also explain Hydra's very high ], or its reflectivity, of 83 percent.<ref name="Codex Regius"/><ref name="arxiv1604"/> | |||
| Derived from crater counting data from ''New Horizons'', the surface of Hydra is estimated to be about four billion years old.<ref name="arxiv1803">{{cite arXiv |last1=Woo |first1=M. Y. |last2=Lee |first2=M. H. |title=On the Early In Situ Formation of Pluto's Small Satellites |date=6 March 2018|eprint= 1803.02005|class=astro-ph.EP}}</ref><ref name="arxiv1604"/> Large craters and indentations on Hydra suggest that it may have lost some of its original mass from ]s since its formation.<ref name="arxiv1604"/> | |||
| === Rotation === | |||
| Hydra is not ] and rotates ]; its rotational period and axial tilt vary quickly over astronomical timescales, to the point that its rotational axis regularly flips over.<ref name="chaos">{{Cite web|title = NASA's Hubble Finds Pluto's Moons Tumbling in Absolute Chaos|url = https://www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-s-hubble-finds-pluto-s-moons-tumbling-in-absolute-chaos|website= NASA|date = 3 June 2015|access-date = 25 October 2015|first = Karen|last = Northon}}</ref> Hydra's chaotic ] is largely caused by the varying gravitational influences of Pluto and Charon as they orbit around their ].<ref name="chaos"/> Hydra's chaotic tumbling is also strengthened by its irregular shape, which creates ]s that act on the object.<ref name="ShowalterHamilton2015"/> At the time of the ''New Horizons'' flyby of Pluto and its moons, Hydra's rotation period was approximately 10 hours and its rotational axis was tilted about 110 degrees to its orbit — it was rotating sideways at the time of the ''New Horizons'' flyby.<ref name="Lakdawalla2015">{{cite web|url=http://www.planetary.org/blogs/emily-lakdawalla/2015/dps15-1110-small-moons.html|title=DPS 2015: Pluto's small moons Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra }}</ref><ref name="arxiv1604"/> | |||
| Hydra rotates relatively quickly compared to the rest of Pluto's moons, which all have rotation periods greater than one day.<ref name="Lakdawalla2015"/> This rapid rotation of Hydra is common among the rotation periods of most ]s.<ref name="Lakdawalla2015"/> Hydra's surface material could get ejected due to ]s if it were rotating at a faster rate.<ref name="TimSharp">{{cite web|last1=Sharp|first1=Tim|title=Pluto's Moons – Five Satellites of Pluto|url=https://www.space.com/16535-plutos-moons.html|website=space.com|date=23 February 2016|access-date=7 March 2019}}</ref><ref name="Codex Regius"/> | |||
| == Orbit == | |||
| {{multiple image | align = right | direction = horizontal | width = | {{multiple image | align = right | direction = horizontal | width = | ||
| | header = Animation of moons of Pluto around the ] of Pluto |
| header = Animation of moons of Pluto around the ] of Pluto – ] plane | ||
| | image1 = Animation of moons of Pluto - Front view.gif | | image1 = Animation of moons of Pluto - Front view.gif | ||
| | caption1 = Front view | | caption1 = Front view | ||
| | image2 = Animation of moons of Pluto - Side view.gif | | image2 = Animation of moons of Pluto - Side view.gif | ||
| | caption2 = Side view | | caption2 = Side view | ||
| | footer ={{legend2|khaki| Pluto}}{{·}}{{legend2|RoyalBlue| Charon}}{{·}}{{legend2|Lime| Styx}}{{·}}{{legend2|Magenta| Nix}}{{·}}{{legend2|Cyan| Kerberos}}{{·}}{{legend2|Orangered| Hydra}} | | footer ={{legend2|khaki| ]}}{{·}}{{legend2|RoyalBlue| ]}}{{·}}{{legend2|Lime| ]}}{{·}}{{legend2|Magenta| ]}}{{·}}{{legend2|Cyan| ]}}{{·}}{{legend2|Orangered| Hydra}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Hydra orbits the Pluto-Charon barycenter at a distance of {{convert|64738|km|mi|abbr=on}}.<ref name="arxiv1604"/> Hydra is the outermost moon of Pluto, orbiting beyond ].<ref name="scimag000"/> Similarly to all of Pluto's moons, Hydra's orbit is nearly circular and is coplanar to Charon's orbit; all of Pluto's moons have very low ]s to Pluto's equator.<ref name="scimag000"/> | |||
| Hydra orbits the ] of the system in the same plane as ] and ], at a distance of about 65,000 km. Its ] of 0.0059 is small, but significantly non-zero, and the largest of those of Pluto's small moons (slightly larger than that of ]). | |||
| The nearly circular and coplanar orbits of Pluto's moons suggest that they may have gone through tidal evolutions since their formation.<ref name="Steffl-etal">{{cite journal |journal=The Astronomical Journal|author1=Steffl, A.|author2=Weaver, H. A.|author3=Stern, S. A.|display-authors=etal|date=2006 |title=New Constraints on Additional Satellites of the Pluto System |volume=132 |issue=2 |pages=614–619 |doi=10.1086/505424 |bibcode=2006AJ....132..614S|arxiv = astro-ph/0511837 |s2cid=10547358}}</ref><ref name="obliquity"/> At the time of the formation of Pluto's smaller moons, Hydra may have had a more ] orbit around the Pluto-Charon barycenter.<ref name="tidaldamping" /> The present circular orbit of Hydra may have been caused by Charon's tidal damping of the eccentricity of Hydra's orbit, through tidal interactions. The mutual tidal interactions of Charon on Hydra's orbit would cause Hydra to transfer its orbital eccentricity to Charon, thus causing the orbit of Hydra to gradually become more circular over time.<ref name="tidaldamping">{{cite arXiv|eprint=0802.2939|last1=Stern|first1=S. A.|title=The Effect of Charon's Tidal Damping on the Orbits of Pluto's Three Moons|last2=Mutchler|first2=M. J.|last3=Weaver|first3=H. A.|last4=Steffl|first4=A. J.|class=astro-ph|year=2008}}</ref> | |||
| Hydra is in a 2:3 ] with Nix, and a 6:11 resonance with Styx (the ratios represent numbers of orbits completed per unit time; the period ratios are the inverses).<ref name="ShowalterHamilton2015"/><ref name="Witze2015">{{cite journal|last1=Witze|first1=Alexandra|title=Pluto’s moons move in synchrony|journal= Nature|year=2015|doi= 10.1038/nature.2015.17681}}</ref> As a result of this "Laplace-like" 3-body resonance, it has conjunctions with Styx and Nix in a 5:3 ratio. | |||
| Hydra has an orbital period of approximately 38.2 days and is resonant with other moons of Pluto. Hydra is in a 2:3 ] with Nix, and a 6:11 resonance with ] (the ratios represent numbers of orbits completed per unit time; the period ratios are the inverses).<ref name="ShowalterHamilton2015"/><ref name="Witze2015">{{cite journal|last1=Witze|first1=Alexandra|title=Pluto's moons move in synchrony|journal= Nature|date=3 June 2015|doi= 10.1038/nature.2015.17681|s2cid=134519717}}</ref> As a result of this "Laplace-like" 3-body resonance, it has conjunctions with Styx and Nix in a 5:3 ratio.<ref name="Witze2015"/> | |||
| Its orbital period of 38.2 days is also close to a 1:6 orbital resonance with Charon, with the timing discrepancy being 0.3%. A hypothesis to explain the near-resonance is that it originated before the outward migration of Charon following the formation of all five known moons, and is maintained by the periodic local fluctuation of 5% in the Pluto–Charon gravitational field strength.<!--- The instantaneous force at Hydra's distance in the Pluto–Charon–Hydra alignment case is 4.62% larger than in the quadrature case (where Hydra is 90° from the Pluto–Charon axis); the Charon–Pluto–Hydra case is almost exactly halfway between those values. In Buie ''et al.'', the quote is "The gravitational force exerted by Pluto on either P1 or P2 varies by roughly 15% (peak-to-peak)." Pluto's gravitational pull, ''by itself'', varies by 18% for Nix and 13% for Hydra ---> | |||
| Hydra's orbit is close to a 1:6 orbital resonance with Charon,<ref name="NYT2015">{{cite web|last1=Chang|first1=Kenneth|title=Astronomers Describe the Chaotic Dance of Pluto's Moons|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2015/06/04/science/space/pluto-moons-orbits-described-in-nature-article.html|work=The New York Times|date=3 June 2015|access-date=28 February 2019}}</ref> with a timing discrepancy of 0.3%. A hypothesis explaining the near-resonance suggests that the resonance originated before the outward migration of Charon after the formation of all five known moons, and is maintained by the periodic local fluctuation of 5% in the Pluto–Charon gravitational field strength.{{efn |The instantaneous force at Hydra's distance in the Pluto–Charon–Hydra alignment case is 4.62% larger than in the quadrature case (where Hydra is 90° from the Pluto–Charon axis); the Charon–Pluto–Hydra case is almost exactly halfway between those values. In Buie ''et al.'', the quote is "The gravitational force exerted by Pluto on either P1 or P2 varies by roughly 15% (peak-to-peak)." Pluto's gravitational pull, ''by itself'', varies by 18% for Nix and 13% for Hydra.}}<ref name="WardCanup2006">{{cite journal |last1=Ward |first1=W. R. |last2=Canup |first2=R. M. |author2-link=Robin Canup |year=2006 |title=Forced Resonant Migration of Pluto's Outer Satellites by Charon |journal=] |volume=313 |issue=5790 |pages=1107–1109 |bibcode=2006Sci...313.1107W |doi=10.1126/science.1127293 |pmid=16825533|s2cid=36703085 }}</ref> | |||
| Like Saturn's moon ], Nix, and the other small moons of Pluto, Hydra rotates chaotically; its day length and rotational axis vary quickly over astronomical timescales, to the point that it regularly flips over. This is largely due to the aforementioned fluctuation of the Pluto–Charon gravitational field, as well as its irregular shape. Hydra's rotational period at the time of the ''New Horizons'' flyby was a mere 10 hours.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.planetary.org/blogs/emily-lakdawalla/2015/dps15-1110-small-moons.html|title=DPS 2015: Pluto's small moons Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra |publisher=}}</ref> | |||
| {{Annotated image | |||
| |image=Hydra, Nix, Styx conjunctions cycle.png | |||
| |image-width=625 | |||
| |width=625 | |||
| |height=124<!-- to crop the lower part of the image --> | |||
| |float=center | |||
| |annotations=<!-- this parameter must be there, empty or not! --> | |||
| |caption=Sequence of conjunctions of Hydra (blue), Nix (red) and Styx (black) over one third of their resonance cycle. Movements are counterclockwise and orbits completed are tallied at upper right of diagrams (click on image to see the whole cycle)}} | |||
| == |
== Exploration == | ||
| {{multiple image | |||
| Hydra is irregular in shape, {{convert|55|×|40|km|sp=us|1}}<ref name="CapturesTwo">{{cite web |title=New Horizons 'Captures' Two of Pluto's Smaller Moons |publisher=Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory |date=21 July 2015 |access-date=22 July 2015 |url=http://pluto.jhuapl.edu/News-Center/News-Article.php?page=20150721}}</ref> in cross-section from one side. It is spectrally neutral like Charon and most of ] (whereas Pluto is reddish) and is composed primarily of water ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://twitter.com/NASANewHorizons/status/621396353852248064|title=NASA New Horizons on Twitter|publisher=}}</ref> probably ]. | |||
| |direction=horizontal | |||
| |align=right | |||
| |width1=150 | |||
| |width2=150 | |||
| |width3=150 | |||
| |image1=Hydra (moon) 2015-07-13 23-16.png | |||
| |image2=Hydra (moon) 2015-07-14 04-57.png | |||
| |image3=Hydra (moon) 2015-07-14 07-41.png | |||
| |caption1=Hydra imaged from a distance of {{convert|640000|km|mi||abbr=on}} | |||
| |caption2=Hydra imaged from a distance of {{convert|360000|km|mi|abbr=on}} | |||
| |caption3=Hydra imaged from a distance of {{convert|230000|km|mi|abbr=on}}}} | |||
| The '']'' spacecraft visited the Pluto system and imaged Pluto and its moons during its flyby on 14 July 2015. At the time of the ''New Horizons'' flyby, Hydra was behind Pluto and was further away from ''New Horizons'' at closest approach.<ref name="SimonPort2015"/> The larger distance of Hydra from ''New Horizons'' resulted in lower resolution images of Hydra.<ref name="SimonPort2015"/> Before the flyby, the ] on board ''New Horizons'' performed measurements of Hydra's size, estimating Hydra to be about {{convert|45|km|mi|abbr=on}} in diameter.<ref name="Measurement">{{cite web |url= http://www.nasa.gov/feature/how-big-is-pluto-new-horizons-settles-decades-long-debate/ |title=How Big Is Pluto? ''New Horizons'' Settles Decades-Long Debate|date=13 July 2015 |publisher=] |access-date=13 July 2015}}</ref> Hydra's surface composition, reflectivity, and other basic physical properties were later measured by ''New Horizons'' during the flyby.<ref name="Measurement"/> | |||
| ==Exploration== | |||
| The only detailed photographs of Hydra were taken by the '']'' spacecraft from approximately {{convert|400000|mi|km|order=flip}} away during its flyby of the Pluto–Charon system on 14 July 2015. It also studied Hydra's surface composition, ], and other basic physical properties. Hydra's reflectivity is estimated to be about 45 percent.<gallery> | |||
| The first detailed image of Hydra was ]ed, or received from the ''New Horizons'' spacecraft on 15 July 2015 after the flyby.<ref name="HydraEmerges"/> The first detailed image of Hydra, taken from a distance of {{convert|400000|mi|km|order=flip|abbr=on}}, appeared to show brightness variations and a dark circular feature {{convert|10|km|mi|abbr=on}} across.<ref name="HydraEmerges"/> The highest resolution images of Hydra were taken from a distance of {{convert|231000|km|mi|abbr=on}}, with an image resolution of {{convert|1.2|km|mi|abbr=on}} per pixel.<ref name="CapturesTwo"/> Derived from those images, Hydra was given the approximate size estimate of {{convert|55|×|40|km|mi|abbr=on}}.<ref name="CapturesTwo"/> | |||
| File:Hydra (moon) from 231 000 kilometres.jpg|Image of Hydra taken by ''New Horizons'' on 14 July 2015 | |||
| {{clear}} | |||
| File:Hydra (moon) 2015-7-15 (raw).jpg|First multi-pixel image of Hydra by ''New Horizons''. | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| == See also == | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| {{notelist}} | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| {{reflist|30em |
{{reflist|30em|refs= | ||
| <ref name="Porter2023">{{cite journal | |||
| '''Sources''' | |||
| |first1 = Simon B. |last1 = Porter | |||
| * {{cite journal |journal=The Astronomical Journal | |||
| |first2 = Robin M. |last2 = Canup | |||
| |author=Steffl, A. J. | |||
| |title = Orbits and Masses of the Small Satellites of Pluto | |||
| |author2=Mutchler, M. J. | |||
| |journal = The Planetary Science Journal | |||
| |author3=Weaver, H. A. | |||
| |date = July 2023 | |||
| |author4=Stern, S. A. | |||
| |volume = 4 | |||
| |author5=Durda, D. D. |author5-link=Daniel David Durda | |||
| |issue = 7 | |||
| |author6=Terrell, D. |author6-link=Dirk Terrell | |||
| |id = 120 | |||
| |author7=Merline, W. J. | |||
| |pages = 14 | |||
| |author8=Young, L. A. | |||
| |doi-access = free | |||
| |author9=Young, E. F. | |||
| |doi = 10.3847/PSJ/acde77 | |||
| |author10=Buie, M. W. | |||
| |arxiv = 2307.04848 | |||
| |author11=Spencer, J. R. | |||
| |bibcode = 2023PSJ.....4..120P | |||
| |lastauthoramp=yes | |||
| |s2cid = }}</ref> | |||
| |date=2006 |title=New Constraints on Additional Satellites of the Pluto System |volume=132 |issue=2 |pages=614–619 |doi=10.1086/505424 |bibcode=2006AJ....132..614S|arxiv = astro-ph/0511837 }}() | |||
| }} | |||
| == External links == | == External links == | ||
| {{commons category|Hydra (moon)}} | {{commons category|Hydra (moon)}} | ||
| * by | * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220622003318/https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/moons/pluto-moons/hydra/in-depth/ |date=2022-06-22 }} by | ||
| * – Hubble press release | * – Hubble press release | ||
| * (SPACE.com) | |||
| * (SPACE.com) | |||
| * | |||
| {{Pluto}} | {{Pluto}} | ||
| {{Moons of dwarf planets}} | {{Moons of dwarf planets}} | ||
| {{Trans-Neptunian objects}} | {{Trans-Neptunian objects}} | ||
| {{Portal bar|Astronomy|Stars|Spaceflight|Outer space|Solar System}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:17, 22 August 2024
Moon of Pluto
 Near true-color image of Hydra, taken by New Horizons on 14 July 2015 Near true-color image of Hydra, taken by New Horizons on 14 July 2015 | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Hubble Space Telescope |
| Discovery date | 15 May 2005 |
| Designations | |
| Designation | Pluto III |
| Pronunciation | /ˈhaɪdrə/ |
| Named after | Lernaean Hydra |
| Alternative names | S/2005 P 1 |
| Adjectives | Hydrian /ˈhaɪdriən/ |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Semi-major axis | 64738±3 km |
| Eccentricity | 0.005862±0.000025 |
| Orbital period (sidereal) | 38.20177±0.00003 d |
| Average orbital speed | 0.123 km/s |
| Inclination | 0.242°±0.005° |
| Satellite of | Pluto |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 50.9 km × 36.1 km × 30.9 km (Geometric mean of 38 km) |
| Mass | (3.01±0.30)×10 kg |
| Mean density | 1.220±0.150 g/cm |
| Surface gravity | 0.00520055269 g |
| Synodic rotation period | 0.4295 d (10.31 h) (July 2015) |
| Axial tilt | 110° |
| Albedo | 0.83 ± 0.08 (geometric) |
| Temperature | 23 K |
| Apparent magnitude | 22.9–23.3 (measured) |
Hydra is a natural satellite of Pluto, with a diameter of approximately 51 km (32 mi) across its longest dimension. It is the second-largest moon of Pluto, being slightly larger than Nix. Hydra was discovered along with Nix by astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope on 15 May 2005, and was named after the Hydra, the nine-headed underworld serpent in Greek mythology. By distance, Hydra is the fifth and outermost moon of Pluto, orbiting beyond Pluto's fourth moon Kerberos.
Hydra has a highly reflective surface caused by the presence of water ice, similar to other Plutonian moons. Hydra's reflectivity is intermediate, in between those of Pluto and Charon. The New Horizons spacecraft imaged Pluto and its moons in July 2015 and returned multiple images of Hydra.
Discovery

Members of the New Horizons team suspected that Pluto and Charon might be accompanied by other small, distant moons, weakly bound to the Pluto system. They used the Hubble Space Telescope to test this hypothesis. This led to the discovery of Nix and Hydra – both surprisingly close to Pluto/Charon – and that no significant moons existed in Pluto's extended sphere of influence.
The discovery images were taken on 15 May 2005 and 18 May 2005. Hydra and Nix were independently discovered by Max J. Mutchler on 15 June 2005 and by Andrew J. Steffl on 15 August 2005. The discoveries were announced on 31 October 2005, after confirmation by precovering archival Hubble images of Pluto from 2002. The two newly discovered moons were subsequently provisionally designated S/2005 P 1 for Hydra and S/2005 P 2 for Nix. The moons were informally referred to as "P1" and "P2" respectively, by the discovery team.
Naming

The name Hydra was approved on 21 June 2006 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and was announced along with the naming of Nix in the IAU Circular 8723. Hydra was named after the Lernaean Hydra, a multi-headed serpent that battled Heracles in Greek mythology. Particularly, the nine heads of Hydra subtly references Pluto's former ninth planetary status. The two newly named moons were intentionally named that the order of their initials N and H honors the New Horizons mission to Pluto, similarly to how the first two letters of Pluto's name honors Percival Lowell. Hydra's name was also intentionally chosen that its initial H honors the Hubble Space Telescope used by the Pluto Companion Search Team to discover Hydra and Nix.
The names of features on the bodies in the Pluto system are related to mythology and the literature and history of exploration. In particular, the names of features on Hydra must be related to legendary serpents and dragons from literature, mythology, and history.
Origin
Pluto's smaller moons, including Hydra, were thought to have formed from debris ejected from a massive collision between Pluto and another Kuiper belt object, similarly to how the Moon is believed to have formed from debris ejected by a large collision of Earth. The ejecta from the collision would then coalesce into the moons of Pluto. It was thought that Hydra had initially formed at a closer proximity to Pluto, and its orbit had undergone changes through tidal interactions. In this case, Hydra along with the smaller moons of Pluto would have migrated outwards with Charon into their current orbits around the Pluto-Charon barycenter. Through 'tidal damping' by mutual tidal interactions with Charon, Hydra's orbit around the Pluto-Charon barycenter gradually became more circular over time. Hydra is believed to have formed from two smaller objects merging into one single object.
Physical characteristics

 Spectra comparison of Hydra and Charon. Hydra's spectrum closely matches that of pure water ice, which is shown for comparison.
Spectra comparison of Hydra and Charon. Hydra's spectrum closely matches that of pure water ice, which is shown for comparison.
Hydra is irregular in shape, measuring 50.9 km (31.6 mi) along its longest axis and its shortest axis measuring 30.9 km (19.2 mi) across. This gives Hydra the measured dimensions of 50.9 km × 36.1 km × 30.9 km (31.6 mi × 22.4 mi × 19.2 mi).
The surface of Hydra is highly reflective due to the presence of water ice on its surface. The surface of Hydra displays a neutral spectrum similarly to Pluto's small moons, although the spectrum of Hydra appears slightly bluer. The water ice on Hydra's surface is relatively pure and shows no significant darkening compared to Charon. One explanation suggests that Hydra's surface is continually refreshed by micrometeorite impacts ejecting darker material from the surface of Hydra. The surface spectrum of Hydra is slightly bluish compared to that of Nix. Explanations for Hydra's bluish color suggest that the surface of Hydra has a higher amount of water ice compared to Nix, which could also explain Hydra's very high geometric albedo, or its reflectivity, of 83 percent.
Derived from crater counting data from New Horizons, the surface of Hydra is estimated to be about four billion years old. Large craters and indentations on Hydra suggest that it may have lost some of its original mass from impact events since its formation.
Rotation
Hydra is not tidally locked and rotates chaotically; its rotational period and axial tilt vary quickly over astronomical timescales, to the point that its rotational axis regularly flips over. Hydra's chaotic tumbling is largely caused by the varying gravitational influences of Pluto and Charon as they orbit around their barycenter. Hydra's chaotic tumbling is also strengthened by its irregular shape, which creates torques that act on the object. At the time of the New Horizons flyby of Pluto and its moons, Hydra's rotation period was approximately 10 hours and its rotational axis was tilted about 110 degrees to its orbit — it was rotating sideways at the time of the New Horizons flyby.
Hydra rotates relatively quickly compared to the rest of Pluto's moons, which all have rotation periods greater than one day. This rapid rotation of Hydra is common among the rotation periods of most Kuiper belt objects. Hydra's surface material could get ejected due to centrifugal forces if it were rotating at a faster rate.
Orbit
Animation of moons of Pluto around the barycenter of Pluto – Ecliptic plane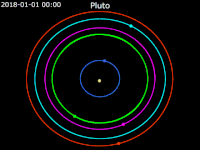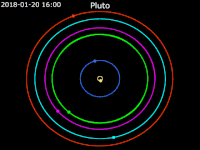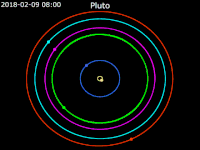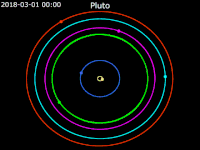 Front view
Front view Side view Pluto · Charon · Styx · Nix · Kerberos · Hydra
Side view Pluto · Charon · Styx · Nix · Kerberos · Hydra
Hydra orbits the Pluto-Charon barycenter at a distance of 64,738 km (40,226 mi). Hydra is the outermost moon of Pluto, orbiting beyond Kerberos. Similarly to all of Pluto's moons, Hydra's orbit is nearly circular and is coplanar to Charon's orbit; all of Pluto's moons have very low orbital inclinations to Pluto's equator.
The nearly circular and coplanar orbits of Pluto's moons suggest that they may have gone through tidal evolutions since their formation. At the time of the formation of Pluto's smaller moons, Hydra may have had a more eccentric orbit around the Pluto-Charon barycenter. The present circular orbit of Hydra may have been caused by Charon's tidal damping of the eccentricity of Hydra's orbit, through tidal interactions. The mutual tidal interactions of Charon on Hydra's orbit would cause Hydra to transfer its orbital eccentricity to Charon, thus causing the orbit of Hydra to gradually become more circular over time.
Hydra has an orbital period of approximately 38.2 days and is resonant with other moons of Pluto. Hydra is in a 2:3 orbital resonance with Nix, and a 6:11 resonance with Styx (the ratios represent numbers of orbits completed per unit time; the period ratios are the inverses). As a result of this "Laplace-like" 3-body resonance, it has conjunctions with Styx and Nix in a 5:3 ratio.
Hydra's orbit is close to a 1:6 orbital resonance with Charon, with a timing discrepancy of 0.3%. A hypothesis explaining the near-resonance suggests that the resonance originated before the outward migration of Charon after the formation of all five known moons, and is maintained by the periodic local fluctuation of 5% in the Pluto–Charon gravitational field strength.

 Sequence of conjunctions of Hydra (blue), Nix (red) and Styx (black) over one third of their resonance cycle. Movements are counterclockwise and orbits completed are tallied at upper right of diagrams (click on image to see the whole cycle)
Sequence of conjunctions of Hydra (blue), Nix (red) and Styx (black) over one third of their resonance cycle. Movements are counterclockwise and orbits completed are tallied at upper right of diagrams (click on image to see the whole cycle)
Exploration
 Hydra imaged from a distance of 640,000 km (400,000 mi)
Hydra imaged from a distance of 640,000 km (400,000 mi) Hydra imaged from a distance of 360,000 km (220,000 mi)
Hydra imaged from a distance of 360,000 km (220,000 mi) Hydra imaged from a distance of 230,000 km (140,000 mi)
Hydra imaged from a distance of 230,000 km (140,000 mi)
The New Horizons spacecraft visited the Pluto system and imaged Pluto and its moons during its flyby on 14 July 2015. At the time of the New Horizons flyby, Hydra was behind Pluto and was further away from New Horizons at closest approach. The larger distance of Hydra from New Horizons resulted in lower resolution images of Hydra. Before the flyby, the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager on board New Horizons performed measurements of Hydra's size, estimating Hydra to be about 45 km (28 mi) in diameter. Hydra's surface composition, reflectivity, and other basic physical properties were later measured by New Horizons during the flyby.
The first detailed image of Hydra was downlinked, or received from the New Horizons spacecraft on 15 July 2015 after the flyby. The first detailed image of Hydra, taken from a distance of 640,000 km (400,000 mi), appeared to show brightness variations and a dark circular feature 10 km (6.2 mi) across. The highest resolution images of Hydra were taken from a distance of 231,000 km (144,000 mi), with an image resolution of 1.2 km (0.75 mi) per pixel. Derived from those images, Hydra was given the approximate size estimate of 55 km × 40 km (34 mi × 25 mi).
See also
Notes
- The instantaneous force at Hydra's distance in the Pluto–Charon–Hydra alignment case is 4.62% larger than in the quadrature case (where Hydra is 90° from the Pluto–Charon axis); the Charon–Pluto–Hydra case is almost exactly halfway between those values. In Buie et al., the quote is "The gravitational force exerted by Pluto on either P1 or P2 varies by roughly 15% (peak-to-peak)." Pluto's gravitational pull, by itself, varies by 18% for Nix and 13% for Hydra.
References
- ^ "Planet and Satellite Names and Discoverers". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN). Retrieved 17 May 2021.
- "hydra". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- Davenport (1843) A new geographical, historical, and commercial grammar
- per "hydria". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on March 22, 2020.
- ^ Showalter, M. R.; Hamilton, D. P. (3 June 2015). "Resonant interactions and chaotic rotation of Pluto's small moons". Nature. 522 (7554): 45–49. Bibcode:2015Natur.522...45S. doi:10.1038/nature14469. PMID 26040889. S2CID 205243819.
- ^ Verbiscer, A. J.; Porter, S. B.; Buratti, B. J.; Weaver, H. A.; Spencer, J. R.; Showalter, M. R.; Buie, M. W.; Hofgartner, J. D.; Hicks, M. D.; Ennico-Smith, K.; Olkin, C. B.; Stern, S. A.; Young, L. A.; Cheng, A. (2018). "Phase Curves of Nix and Hydra from the New Horizons Imaging Cameras". The Astrophysical Journal. 852 (2): L35. Bibcode:2018ApJ...852L..35V. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aaa486.
- ^ Porter, Simon B.; Canup, Robin M. (July 2023). "Orbits and Masses of the Small Satellites of Pluto". The Planetary Science Journal. 4 (7): 14. arXiv:2307.04848. Bibcode:2023PSJ.....4..120P. doi:10.3847/PSJ/acde77. 120.
- "Hydra By the Numbers". solarsystem.nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved 7 March 2019.
(Original value of 0.051 m/s converted to g) - ^ "DPS 2015: Pluto's small moons Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra [UPDATED]".
- ^ Weaver, H. A.; Buie, M. W.; Showalter, M. R.; Stern, S. A.; et al. (18 April 2016). "The Small Satellites of Pluto as Observed by New Horizons". Science. 351 (6279): aae0030. arXiv:1604.05366. Bibcode:2016Sci...351.0030W. doi:10.1126/science.aae0030. PMID 26989256. S2CID 206646188.
- ^ Stern, S. A.; Bagenal, F.; Ennico, K.; Gladstone, G. R.; et al. (15 October 2015). "The Pluto system: Initial results from its exploration by New Horizons". Science. 350 (6258): aad1815. arXiv:1510.07704. Bibcode:2015Sci...350.1815S. doi:10.1126/science.aad1815. PMID 26472913. S2CID 1220226.
- Cook, Jason C.; Dalle Ore, Cristina M.; Protopapa, Silvia; Binzel, Richard P.; Cartwright, Richard; Cruikshank, Dale P.; et al. (15 November 2018). "Composition of Pluto's small satellites: Analysis of New Horizons spectral images". Icarus. 315 (1964): 30–45. Bibcode:2017LPI....48.2478C. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2018.05.024. S2CID 125374498.
- Stern, S. A.; Mutchler, M. J.; Weaver, H. A.; Steffl, A. J. (2006). "The Positions, Colors, and Photometric Variability of Pluto's Small Satellites from HST Observations 2005–2006". Astronomical Journal. 132 (3): 1405–1414. arXiv:astro-ph/0607507. Bibcode:2006AJ....132.1405S. doi:10.1086/506347. S2CID 14360964. (Final preprint)
- ^ Stern, Alan; Grinspoon, David (May 1, 2018). "Chapter 7: Bringing It All Together". Chasing New Horizons: Inside the Epic First Mission to Pluto. Picador. ISBN 9781250098962.
- ^ Keeter, Bill (5 May 2016). "Pluto's Icy Moon Hydra". NASA. Archived from the original on 22 January 2018. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- ^ NASA (15 July 2015). "Hydra Emerges from the Shadows". Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- ^ "New Horizons 'Captures' Two of Pluto's Smaller Moons". Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. 21 July 2015. Retrieved 22 July 2015.
- Williams, Matt (13 July 2015). "Pluto's Moon Hydra". Universe Today. Retrieved 7 March 2019.
- "NASA's Hubble Reveals Possible New Moons Around Pluto". www.hubblesite.org. 31 October 2005.
- ^ "IAU Circular No. 8625". www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu. 31 October 2005.
(IAU Circular No. 8625 describing the discovery) - ^ "IAU Circular No. 8723". www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu. 21 June 2006.
(IAU Circular No. 8723 naming the moons) - ^ Cain, Fraser (22 June 2006). "Pluto's New Moons are Named Nix and Hydra". Universe Today. Retrieved 8 March 2019.
- "Pluto and Its Moons: Charon, Nix and Hydra". NASA. 23 June 2006. Archived from the original on 21 May 2022. Retrieved 8 March 2019.
- "Naming of Astronomical Objects". International Astronomical Union.
- Stern, S. A.; Weaver, H. A.; Steff, A. J.; Mutchler, M. J.; Merline, W. J.; Buie, M. W.; Young, E. F.; Young, L. A.; Spencer, J. R. (23 February 2006). "A giant impact origin for Pluto's small moons and satellite multiplicity in the Kuiper belt" (PDF). Nature. 439 (7079): 946–948. Bibcode:2006Natur.439..946S. doi:10.1038/nature04548. PMID 16495992. S2CID 4400037. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 January 2012. Retrieved 20 July 2011.
- ^ Northon, Karen (3 June 2015). "NASA's Hubble Finds Pluto's Moons Tumbling in Absolute Chaos". NASA. Retrieved 25 October 2015.
- ^ Woo, M. Y.; Lee, M. H. (6 March 2018). "On the Early In Situ Formation of Pluto's Small Satellites". arXiv:1803.02005 .
- ^ Quillen, A. C.; Nichols-Fleming, F.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Noyelles, B. (January 2017). "Obliquity evolution of the minor satellites of Pluto and Charon". Icarus. 293: 94–113. arXiv:1701.05594. Bibcode:2017Icar..293...94Q. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2017.04.012. S2CID 119408999. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- ^ Stern, S. A.; Mutchler, M. J.; Weaver, H. A.; Steffl, A. J. (2008). "The Effect of Charon's Tidal Damping on the Orbits of Pluto's Three Moons". arXiv:0802.2939 .
- ^ Sharp, Tim (23 February 2016). "Pluto's Moons – Five Satellites of Pluto". space.com. Retrieved 7 March 2019.
- ^ Porter, Simon (5 October 2015). "Pluto's Small Moons Nix and Hydra". blogs.nasa.gov. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- ^ Codex Regius (2016). Pluto & Charon. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. ISBN 978-1534960749.
- Steffl, A.; Weaver, H. A.; Stern, S. A.; et al. (2006). "New Constraints on Additional Satellites of the Pluto System". The Astronomical Journal. 132 (2): 614–619. arXiv:astro-ph/0511837. Bibcode:2006AJ....132..614S. doi:10.1086/505424. S2CID 10547358.
- ^ Witze, Alexandra (3 June 2015). "Pluto's moons move in synchrony". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2015.17681. S2CID 134519717.
- Chang, Kenneth (3 June 2015). "Astronomers Describe the Chaotic Dance of Pluto's Moons". The New York Times. Retrieved 28 February 2019.
- Ward, W. R.; Canup, R. M. (2006). "Forced Resonant Migration of Pluto's Outer Satellites by Charon". Science. 313 (5790): 1107–1109. Bibcode:2006Sci...313.1107W. doi:10.1126/science.1127293. PMID 16825533. S2CID 36703085.
- ^ "How Big Is Pluto? New Horizons Settles Decades-Long Debate". NASA. 13 July 2015. Retrieved 13 July 2015.
External links
- Hydra In Depth Archived 2022-06-22 at the Wayback Machine by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- NASA's Hubble Reveals Possible New Moons Around Pluto – Hubble press release
| Pluto | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geography (features) |
|   | ||||||||||||
| Moons | ||||||||||||||
| Exploration | ||||||||||||||
| Astronomy |
| |||||||||||||
| Related | ||||||||||||||
| Moons of likely dwarf planets | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Trans-Neptunian objects | |
|---|---|
| TNO classes | |
| Dwarf planets (moons) | |
| Sednoids | |