| Revision as of 11:46, 23 November 2006 editRobotG (talk | contribs)86,515 editsm Bot: Moving out of redlinked or #redirected category← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 16:42, 28 November 2024 edit undoEUPBR (talk | contribs)252 edits Poland Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship map | ||
| (142 intermediate revisions by 69 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Early Medieval trading center at the southern Baltic Sea coast}} | |||
| '''Truso''', situated on ], was an ] (]n) town near the ] just east of the ]. It was one of the trading posts on the ], and is thought to be the antecedent of the city of ]. In the words of ], "the name of the town is the earliest known historically in the Baltic Sea area".<ref>Gimbutas M. ''The Balts.'' London: Thames and Hudson, 1963.</ref> The main goods of Truso were ], furs, and slaves. | |||
| {{Infobox ancient site | |||
| |name = Truso | |||
| |native_name = | |||
| |alternate_name = | |||
| |image = | |||
| |alt = | |||
| |caption = Truso at the ] coast | |||
| |map_type = Poland#Poland Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship | |||
| |map_alt = Truso in Poland | |||
| |map_size = 240 | |||
| | relief = yes | |||
| |location = Northern ] | |||
| |region = ], Pomesania | |||
| |coordinates = {{coord|54.066667|N|19.45|E|}} | |||
| |type = | |||
| |part_of = | |||
| |length = | |||
| |width = | |||
| |area = around 20 ha | |||
| |height = | |||
| |builder = | |||
| |material = | |||
| |built = | |||
| |abandoned = 10th-century | |||
| |epochs = | |||
| |cultures = Baltic, Slavic, Gothic, Scandinavian | |||
| |dependency_of = | |||
| |occupants = | |||
| |event = | |||
| |excavations = 1897, 1945, 1980 | |||
| |archaeologists = Marek F. Jagodziński | |||
| |condition = | |||
| |ownership = | |||
| |management = | |||
| |public_access = | |||
| |website = | |||
| |notes = | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Truso''' was a ] port of trade (emporium) set up by the Scandinavians<ref>{{Cite book |last=Jagodziński |first=Marek F. |url=https://www.academia.edu/30171469 |title=Truso. The legend of the Baltic Sea |publisher=Muzeum Archeologiczno-Historyczne w Elblągu |year=2015 |isbn=978-83-919291-8-6 |edition=2nd |location=Elbląg |pages=12}}</ref> at the banks of the ] delta branch of the ], close to a bay (the modern ]), where it emptied into the shallow and ] ]. This sizeable lagoon is separated from the ] by the ] at the southern ] coast. In the 9th century, the merchant ] travelled to Truso in the service of the English King ] and wrote his account of the place at a prominent location of the ], which attracted merchants from central and southern Europe, who supplied the markets in the Mediterranean and the Middle East with the highly valued commodity.<ref name=bonn>{{cite web|url= http://prussia.online/Data/Book/si/siedlungsforschung-archaeologie-geschichte-geographie-band-22/Siedlungsforschung.%20Bd.%2022%20(2004),%20OCR.pdf |title= Siedlungsforschung. Archäologie – Geschichte – Geographie 22, 2004 |publisher= Siedlungsforschung Bonn |author=Klaus Fehn, Dietrich Denecke, Hans-Rudolf Egli, Eike Gringmuth-Dallmer, Franz Irsigler, Winfried Schenk |access-date =September 8, 2020}}</ref> | |||
| The account of the voyage to the town of Truso in the land of the ''Pruzzens'' around the year 890 by ] has been included in ]'s translation of ]' ''Histories''. Moreover, Wulfstan named Truso as being near ''Estmere'' (which is his rendition of the Old Prussian ''Aīstinmari'' and Lithuanian ''Aistmarės'' for Vistula Lagoon). In the words of ], "the name of the town is the earliest known historically in the Baltic Sea area".<ref name="Gimbutas">{{cite book|author1=Marija Gimbutas|author2=Alseikaitė|title=The Balts|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-8iBAAAAMAAJ|year=1963|publisher=Praeger}}</ref> | |||
| == History == | == History == | ||
| ] | |||
| Truso was situated in a central location upon the Eastern European trade routes, which led from ] in Sweden via ] on the island of ] towards the southern ] shore, where in the 13th-century the ] city of ] was established. From there, trade continued further south along the ] to ] in the ]. These ancient roads led further south-west and south-east to the ] and eventually to North Africa and the Middle East.<ref>{{cite journal|title= Prehistoric Routes between Northern Europe and Italy Defined by the Amber Trade |publisher= Jstor |author=J. M. de Navarro |journal= The Geographical Journal |year= 1925 |volume= 66 |issue= 6 |pages= 481–503 |doi= 10.2307/1783003 |jstor= 1783003 }}</ref> Gimbutas has observed that<blockquote>For Old Prussia, Truso played the same central role as ] for north-western Germany or the Slavic ] for ].<ref name="Gimbutas" /></blockquote>East–western trade routes lead from Truso and ] (a rival trading centre in Old Prussia, at the south-western corner of the ]), along the Baltic Sea to ] and from there up the ] inlet to Haithabu (Hedeby), the large trading center in ]. This town, located close to the modern city of ] in ], was centrally located and could be reached from all four directions over land as well as from the ] and the Baltic Sea.<ref name="bonn" /><ref>{{cite web|url= http://archiv.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/propylaeumdok/892/1/Pfaelzner_Qatna_lion_2008.pdf |title= The Qatna lion: scientific confirmation of Baltic amber in late Bronze Age Syria |publisher= Uni Heidelberg |author=Anna J. Mukherjee |access-date =September 8, 2020}}</ref> | |||
| Around the year 890, ] embarked on his seven-day journey from Hedeby to Truso at the behest of king ].<ref name="HakluytAlfred2016">{{cite book|author1=Richard 1552?-1616 Hakluyt|author2=King of England 849-899 Alfred|title=The Discovery of Muscovy, from the Collections of Richard Hakluyt. with the Voyages of Ohthere and Wulfstan from King Alfred's Orosius|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Sc05vgAACAAJ|date=25 August 2016|publisher=BiblioBazaar|isbn=978-1-361-90940-9}}</ref> He named the lands and the coasts he had passed as the ship was travelling under sail all the way. ] was on his right and ], ], ] and ] on his left, all land that is subject to ]. | |||
| Truso was situated in a central location upon the Eastern European trade routes, which led from ] in the north to the island of ] and to ] in the ] and later included the ] city of Elbing (Elbląg). From there, traders continued further south to ] in the ]. This was called the ]. The ancient amber roads led further south-west and south-east to the ] and eventually to Asia. ""For ], Truso played the same role as ] for north-western Germany or Slavic ] for ]", Gimbutas has observed.<ref>Ibidem.</ref> | |||
| Wulfstan resumes: <blockquote>Then on our left we had the land of the ], who have a king to themselves. Then, after the land of the Burgundians, we had on our left the lands that have been called from the earliest times ]y, and ], and ], and ], all which territory is subject to the ]; and Weonodland (the land of the ]) was all the way on our right, as far as the ] estuary.<ref name="HakluytAlfred2016" /><ref name="Jago" /></blockquote>The most sought after commodities of Truso were ], animal furs and (pagan) slaves, while the industries of blacksmithing and amber working provided processed trading goods. The beginnings of the town has been dated back to approximately the end of the 7th century, while in the second half of the 10th century ] in the Nogat had begun to cut off the town from the Vistula lagoon and the Baltic Sea. The town's importance as trading port began to decline and was eventually eclipsed by the ascent of ] as the local trading center, that was situated right by the sea.<ref name="bogucki"/><ref name=steu>{{cite web|url= http://prussia.online/Data/Book/di/die-ostsee-als-kernraum-des-10-jahrhunderts-und-ihre-peripherien/Steuer_Die_Ostsee_als_Kernraum.pdf |title= Die Ostsee als Kernraum des 10. Jahrhunderts und ihre Peripherien |publisher= Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg |author=Heiko STEUER |access-date =September 8, 2020}}</ref> | |||
| East-west trade route went from Truso and ] (a rival centre which sprang up at the south-western corner of the ]), along the Baltic Sea to ], and from there inland by river to Hedeby, a large trading center in Jutland. Hedeby, which lay near the modern city of Schleswig in ], was pretty centrally located and could be reached from all four directions over land as well as from the ], the ], and the Baltic Sea. | |||
| Historians still debate the motive for this expedition. King Alfred obviously needed allies in his defense against the Danish and Norwegian ], who had already taken over most of England. However, that reason for the journey is rather unlikely, since Truso was at the time little more than a trading center and ], the West Saxon ruler, already kept in close contact with the continental Saxons and the Franks.<ref name="HakluytAlfred2016"/><ref name=steu/> <!--However earlier Prussian ] have been known to accompany Germanic tribes going westwards towards Spain as early as the ].--> | |||
| == Archaeology == | == Archaeology == | ||
| ] Museum of Archaeology and History]] | |||
| ] | |||
| First attempts at finding the exact location of the town date back to the early sixteenth century.<ref name="bogucki">{{cite journal | title=Viking age trade ports in Poland | author=Bogucki, Mateusz | journal=Estonian Journal of Archaeology | year=2004 | volume=8 | issue=2 | pages=100–127| doi=10.3176/arch.2004.2.02 | s2cid=245155929 | doi-access=free }}</ref> Based on Prussian archaeological finds from 1897 and excavations which began in the 1920s, archaeologists located Truso near Elbing (since 1945 ] near ]). Found artifacts, dating from the 7th to 12th century, were stored in the Elbing Museum, now the Elbląg Museum. In the 1980s, the Polish archaeologist Marek Jagodziński had resumed excavations and cleared a site of circa 20 hectare, in which a series of structures had burnt down around the year 1,000.<ref name=Jago>{{cite web|url= https://www.academia.edu/31588836 |title= Truso between Weonodland and Witland |publisher= Academia |author=Marek F. Jagodziński |access-date =September 8, 2020}}</ref><ref name=bonn/> | |||
| Trade must have been of great importance at the settlements, as the numerous merchant graves along the river testify. Artefacts unearthed at the site include scales, weights, silver horseshoe brooches, belt buckles, swords, coins, elaborate jewelry imported from Scandinavia, garment accessories and armament components. Scandinavian traders and craftmen lived and worked in central and port area, while peripheral area might be inhabited also by Balts and Slavs.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Jagodziński |first=Marek F. |url=https://www.academia.edu/30171469 |title=Truso. The legend of the Baltic Sea |publisher=Muzeum Archeologiczno-Historyczne w Elblągu |year=2015 |isbn=978-83-919291-8-6 |edition=2nd |location=Elbląg |pages=23}}</ref> The Scandinavian influence on these settlements and artefacts is particularly obvious and confirms Viking expansion of settlement activity to ] and ]. As early as the 8th century, the first incursions of North Germanic groups took place, which lead to the founding of the Grobin/Seeburg settlement near Liepája. Archbishop ] recorded the immigration of a group under the Svea king Olaf during the 9th century.<ref name=bonn/> | |||
| Archaeological finds in 1897 and excavations started in the 1920s had placed the location of Truso around Gut Hansdorf in the south-eastern suburb of Elbing (Elblag). These artifacts, dating from the 7th to the 12th century, are now on exhibit at the Elbinger Museum. In the 1980s, Polish archaeologists resumed excavations and cleared an approximately 20 hectar site, which was burnt down around the year 1000, whereupon the inhabitants found it prudent to disperse. | |||
| Author ] noted that at the circa 20 ha sized area "no true town has been found and excavated" and that the identification of the site in Elbląg with Truso is based on "finds of Norse weapons" and the presence of "a large Viking Age cemetery" nearby,<ref name="Jones2001">{{cite book|author=Gwyn Jones|title=A History of the Vikings|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lD74bDG3O5oC|year=2001|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-280134-0}}</ref> According to Mateusz Bogucki "by now, there is no doubt that the settlement really is Wulfstan's Truso"<ref name="bogucki"/> The Elbląg Museum brochure: ''Truso- A Discovered Legend'', by Marek F. Jagodziński, describes a large number of buildings found during the recent excavations, with burnt remains of posts suggesting buildings of around {{convert|5|by|10|m|ft}} and long houses of about {{convert|6|by|21|m|ft}}. A thick layer of ash, debris and numerous arrowheads suggest that the city was destroyed by pirates or invaders.<ref>{{cite web|url= https://www.ufg.uni-freiburg.de/studium/lehrgrab/truso |title= Deutsch-polnische Ausgrabungen auf dem wikingerzeitlichen Seehandelsplatz von Janów Pomorski (Truso) |publisher= Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg |access-date =September 9, 2020}}</ref> | |||
| Mateusz Bogucki of the ] at the Institute of Archaeology and Ethnology, states in his book <blockquote>''Coin finds in the viking Age emporium at Janów Pomorski (Truso) and the Prussian phenomenon'' about ''...the end of Truso as a port of trade...a strong political power, probably of Piast origin...sent warriors to try to take control...and destroyed the town.''<ref>{{cite web|url= https://www.academia.edu/485476 |title= Coin finds in the viking Age emporium at Janów Pomorski (Truso) and the 'Prussian phenomenon' |publisher= Academia |author= Mateusz Bogucki |access-date =September 9, 2020}}</ref></blockquote> | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist|2}} | |||
| <references/> | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| * - The complete texts translated to modern English | |||
| * | |||
| {{Wikivoyage|Amber Road}} | |||
| {{Baltic emporia}} | {{Baltic emporia}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:42, 28 November 2024
Early Medieval trading center at the southern Baltic Sea coast  | |
| Location | Northern Poland |
|---|---|
| Region | Vistula Lagoon, Pomesania |
| Coordinates | 54°04′00″N 19°27′00″E / 54.066667°N 19.45°E / 54.066667; 19.45 |
| Area | around 20 ha |
| History | |
| Abandoned | 10th-century |
| Cultures | Baltic, Slavic, Gothic, Scandinavian |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | 1897, 1945, 1980 |
| Archaeologists | Marek F. Jagodziński |
| Website | Muzeum Archeologiczno-Historyczne |
Truso was a Viking Age port of trade (emporium) set up by the Scandinavians at the banks of the Nogat delta branch of the Vistula River, close to a bay (the modern Drużno lake), where it emptied into the shallow and brackish Vistula Lagoon. This sizeable lagoon is separated from the Gdańsk Bay by the Vistula Spit at the southern Baltic Sea coast. In the 9th century, the merchant Wulfstan of Hedeby travelled to Truso in the service of the English King Alfred the Great and wrote his account of the place at a prominent location of the Amber Road, which attracted merchants from central and southern Europe, who supplied the markets in the Mediterranean and the Middle East with the highly valued commodity.
The account of the voyage to the town of Truso in the land of the Pruzzens around the year 890 by Wulfstan of Hedeby has been included in Alfred the Great's translation of Orosius' Histories. Moreover, Wulfstan named Truso as being near Estmere (which is his rendition of the Old Prussian Aīstinmari and Lithuanian Aistmarės for Vistula Lagoon). In the words of Marija Gimbutas, "the name of the town is the earliest known historically in the Baltic Sea area".
History
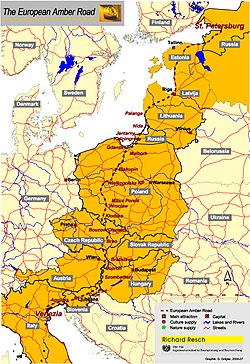
Truso was situated in a central location upon the Eastern European trade routes, which led from Birka in Sweden via Visby on the island of Gotland towards the southern Baltic Sea shore, where in the 13th-century the Hanseatic city of Elbing was established. From there, trade continued further south along the Amber Road to Carnuntum in the Alps. These ancient roads led further south-west and south-east to the Black Sea and eventually to North Africa and the Middle East. Gimbutas has observed that
For Old Prussia, Truso played the same central role as Haithabu for north-western Germany or the Slavic Vineta for Pomerania.
East–western trade routes lead from Truso and Wiskiauten (a rival trading centre in Old Prussia, at the south-western corner of the Courish Lagoon), along the Baltic Sea to Jutland and from there up the Slien inlet to Haithabu (Hedeby), the large trading center in Jutland. This town, located close to the modern city of Schleswig in Schleswig-Holstein, was centrally located and could be reached from all four directions over land as well as from the North Sea and the Baltic Sea.
Around the year 890, Wulfstan of Hedeby embarked on his seven-day journey from Hedeby to Truso at the behest of king Alfred the Great. He named the lands and the coasts he had passed as the ship was travelling under sail all the way. Weonodland was on his right and Langland, Laeland, Falster and Sconey on his left, all land that is subject to Denmark.
Wulfstan resumes:
Then on our left we had the land of the Burgundians, who have a king to themselves. Then, after the land of the Burgundians, we had on our left the lands that have been called from the earliest times Blekingey, and Meore, and Eowland, and Gotland, all which territory is subject to the Sweons; and Weonodland (the land of the Wends) was all the way on our right, as far as the Vistula estuary.
The most sought after commodities of Truso were amber, animal furs and (pagan) slaves, while the industries of blacksmithing and amber working provided processed trading goods. The beginnings of the town has been dated back to approximately the end of the 7th century, while in the second half of the 10th century siltation in the Nogat had begun to cut off the town from the Vistula lagoon and the Baltic Sea. The town's importance as trading port began to decline and was eventually eclipsed by the ascent of Gdańsk as the local trading center, that was situated right by the sea.
Historians still debate the motive for this expedition. King Alfred obviously needed allies in his defense against the Danish and Norwegian Vikings, who had already taken over most of England. However, that reason for the journey is rather unlikely, since Truso was at the time little more than a trading center and Alfred the Great, the West Saxon ruler, already kept in close contact with the continental Saxons and the Franks.
Archaeology


First attempts at finding the exact location of the town date back to the early sixteenth century. Based on Prussian archaeological finds from 1897 and excavations which began in the 1920s, archaeologists located Truso near Elbing (since 1945 Janów Pomorski near Elbląg). Found artifacts, dating from the 7th to 12th century, were stored in the Elbing Museum, now the Elbląg Museum. In the 1980s, the Polish archaeologist Marek Jagodziński had resumed excavations and cleared a site of circa 20 hectare, in which a series of structures had burnt down around the year 1,000.
Trade must have been of great importance at the settlements, as the numerous merchant graves along the river testify. Artefacts unearthed at the site include scales, weights, silver horseshoe brooches, belt buckles, swords, coins, elaborate jewelry imported from Scandinavia, garment accessories and armament components. Scandinavian traders and craftmen lived and worked in central and port area, while peripheral area might be inhabited also by Balts and Slavs. The Scandinavian influence on these settlements and artefacts is particularly obvious and confirms Viking expansion of settlement activity to Courland and Livland. As early as the 8th century, the first incursions of North Germanic groups took place, which lead to the founding of the Grobin/Seeburg settlement near Liepája. Archbishop Rimbert of Bremen recorded the immigration of a group under the Svea king Olaf during the 9th century.
Author Gwyn Jones noted that at the circa 20 ha sized area "no true town has been found and excavated" and that the identification of the site in Elbląg with Truso is based on "finds of Norse weapons" and the presence of "a large Viking Age cemetery" nearby, According to Mateusz Bogucki "by now, there is no doubt that the settlement really is Wulfstan's Truso" The Elbląg Museum brochure: Truso- A Discovered Legend, by Marek F. Jagodziński, describes a large number of buildings found during the recent excavations, with burnt remains of posts suggesting buildings of around 5 by 10 metres (16 by 33 ft) and long houses of about 6 by 21 metres (20 by 69 ft). A thick layer of ash, debris and numerous arrowheads suggest that the city was destroyed by pirates or invaders.
Mateusz Bogucki of the Polish Academy of Sciences at the Institute of Archaeology and Ethnology, states in his book
Coin finds in the viking Age emporium at Janów Pomorski (Truso) and the Prussian phenomenon about ...the end of Truso as a port of trade...a strong political power, probably of Piast origin...sent warriors to try to take control...and destroyed the town.
References
- Jagodziński, Marek F. (2015). Truso. The legend of the Baltic Sea (2nd ed.). Elbląg: Muzeum Archeologiczno-Historyczne w Elblągu. p. 12. ISBN 978-83-919291-8-6.
- ^ Klaus Fehn, Dietrich Denecke, Hans-Rudolf Egli, Eike Gringmuth-Dallmer, Franz Irsigler, Winfried Schenk. "Siedlungsforschung. Archäologie – Geschichte – Geographie 22, 2004" (PDF). Siedlungsforschung Bonn. Retrieved September 8, 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Marija Gimbutas; Alseikaitė (1963). The Balts. Praeger.
- J. M. de Navarro (1925). "Prehistoric Routes between Northern Europe and Italy Defined by the Amber Trade". The Geographical Journal. 66 (6). Jstor: 481–503. doi:10.2307/1783003. JSTOR 1783003.
- Anna J. Mukherjee. "The Qatna lion: scientific confirmation of Baltic amber in late Bronze Age Syria" (PDF). Uni Heidelberg. Retrieved September 8, 2020.
- ^ Richard 1552?-1616 Hakluyt; King of England 849-899 Alfred (25 August 2016). The Discovery of Muscovy, from the Collections of Richard Hakluyt. with the Voyages of Ohthere and Wulfstan from King Alfred's Orosius. BiblioBazaar. ISBN 978-1-361-90940-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Marek F. Jagodziński. "Truso between Weonodland and Witland". Academia. Retrieved September 8, 2020.
- ^ Bogucki, Mateusz (2004). "Viking age trade ports in Poland". Estonian Journal of Archaeology. 8 (2): 100–127. doi:10.3176/arch.2004.2.02. S2CID 245155929.
- ^ Heiko STEUER. "Die Ostsee als Kernraum des 10. Jahrhunderts und ihre Peripherien" (PDF). Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg. Retrieved September 8, 2020.
- Jagodziński, Marek F. (2015). Truso. The legend of the Baltic Sea (2nd ed.). Elbląg: Muzeum Archeologiczno-Historyczne w Elblągu. p. 23. ISBN 978-83-919291-8-6.
- Gwyn Jones (2001). A History of the Vikings. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-280134-0.
- "Deutsch-polnische Ausgrabungen auf dem wikingerzeitlichen Seehandelsplatz von Janów Pomorski (Truso)". Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg. Retrieved September 9, 2020.
- Mateusz Bogucki. "Coin finds in the viking Age emporium at Janów Pomorski (Truso) and the 'Prussian phenomenon'". Academia. Retrieved September 9, 2020.
External links
- The Project Gutenberg Etext of Discovery of Muscovy - The complete texts translated to modern English
- Historia de los Gotlandeses (Guta saga)
| Norse people | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| History |  | ||
| Expansion |
| ||
| Paganism and mythology | |||
| Cosmology | |||
| Rituals and worship | |||
| Society | |||
| Events | |||
| Sources | |||
| Settlements | |||