| Revision as of 20:44, 27 May 2019 editDannyS712 bot (talk | contribs)Bots129,343 editsm →Moroccan-Portuguese Wars: Task 39: Use a more specific maintenance tagTag: AWB← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 00:26, 8 September 2024 edit undoRandy Kryn (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users285,381 edits uppercase per direct link (Iberian Peninsula) | ||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 16 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|none}} | |||
| {{See also|Military of Morocco}} | {{See also|Military of Morocco}} | ||
| The '''military history of ]''' covers a vast time period and complex events. It interacts with multiple military events in a vast area containing ] and the ]. | The '''military history of ]''' covers a vast time period and complex events. It interacts with multiple military events in a vast area containing ] and the ]. | ||
| ==The Roman conquests== | ==The Roman conquests== | ||
| ] (a Berber prince) fighting in the ]. Berber cavalry fought with shield and throwing javelins.]] | ] (a Berber prince) fighting in the ]. Berber cavalry fought with shield and throwing javelins.]] | ||
| Just after defeating the ] and destructing the city of ] in nowadays ] during the ], the ] took possession of ] and divided it into two ]. In the west, ] was developed by the creation of roads, agricultural innovations and trade expansions. |
Just after defeating the ] and destructing the city of ] in nowadays ] during the ], the ] took possession of ] and divided it into two ]. In the west, ] was developed by the creation of roads, agricultural innovations and trade expansions. | ||
| In the mountainous areas, the ] tribes resisted to the Roman invasions. The Roman influence will be preserved in the south until 285 AD. As of the end of 4th century AD, under the reign of the Roman emperor ], the Romans maintained nothing but one thin presence on the coast, around Tangier.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070416130841/http://www.herodote.net/dossiers/synthese.php5?ID=23 |date=2007-04-16 }} - Herodote.net {{ |
In the mountainous areas, the ] tribes resisted to the Roman invasions. The Roman influence will be preserved in the south until 285 AD. As of the end of 4th century AD, under the reign of the Roman emperor ], the Romans maintained nothing but one thin presence on the coast, around Tangier.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070416130841/http://www.herodote.net/dossiers/synthese.php5?ID=23 |date=2007-04-16 }} - Herodote.net {{in lang|fr}}</ref> They remained in the north until 429 AD; date of the passage of the ] in this part of Mauretania Tingitana. In 533 AD, the ] fleets and then the ]s occupied ] and ]. | ||
| ==The Arab conquests== | ==The Arab conquests== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
| ==Territorial expansions== | ==Territorial expansions== | ||
| {{See also|Almoravid dynasty}} | {{See also|Almoravid dynasty|Almohad Caliphate|Marinid dynasty|Wattasid dynasty|Saadi dynasty|Alaouite dynasty|Territorial evolution of Morocco}} | ||
| The gallery below shows the maximum extent of each of the prominent dynasties: ],<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://contrahistorias.wordpress.com/2009/12/05/haidar-y-marruecos-naciones-y-estados/|title=Haidar y Marruecos: naciones y estados|access-date=2020-10-17|last=said|first=Haidar y Marruecos: naciones y estados|date=2009-12-05|website=ContraHistorias|language=es-ES}}</ref> ],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://otraarquitecturaesposible.blogspot.com/2011/04/contexto-historico-de-la-arquitectura_10.html|title=Reflexiones sobre un clasicismo contemporáneo: Contexto histórico de la arquitectura hispanomusulmana (III): Imperio Almorávide (1085-1144); Segundos Reinos de Taifas (1144-1172); Imperio Almohade (1172-1212)|access-date=2020-10-17|last=Pfunes|first=Arq|date=2011-04-10|website=Reflexiones sobre un clasicismo contemporáneo}}</ref> ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://mapasimperiales.webcindario.com/IMPERIOS%20DEL%20MAGREB/IMPERIOS%20DEL%20MAGREB.htm|title=IMPERIOS DEL MAGREB (TUNEZ, ARGELIA Y MARRUECOS)|access-date=2020-10-17|website=mapasimperiales.webcindario.com}}</ref> and the ],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://iconoadnspain08.blogspot.com/2015/07/1509-1511-1513-1524-1548-1550-1554-las.html|title=Icono ADN Spain 08: 1509-1511-1513-1524-1548-1550-1554...... Las Tumbas Saadies.....|access-date=2020-10-17|last=Unknown|date=2015-07-14|website=Icono ADN Spain 08}}</ref> in addition to the greatest extent of the current dynasty, the ]. | |||
| {{See also|Almohad Caliphate}} | |||
| <gallery mode="packed"> | |||
| {{See also|Marinid dynasty}} | |||
| File:Almoravid dynasty of Morocco-en.svg|{{center|]<br/>at its greatest extent (early 12th century)}} | |||
| {{See also|Wattasid dynasty}} | |||
| File:Almohad dynasty of Morocco-en.svg|{{center|]<br/>at its greatest extent (early 13th century)}} | |||
| {{See also|Saadi dynasty}} | |||
| File:Carte Empire Mérinide XIVe.jpg|] in 1360 | |||
| File:Saadiens - Carte fin XVIe siècle.jpg|Extent of the ] at the beginning of the 17th century | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ==Moroccan-Portuguese Wars== | ==Moroccan-Portuguese Wars== | ||
| {{Main|Moroccan-Portuguese conflicts}} | {{Main|Moroccan-Portuguese conflicts}} | ||
| {{Moroccan-Portuguese conflicts}} | {{Moroccan-Portuguese conflicts}} | ||
| The Battle of Alcácer Quibir (also known as "Battle of Three Kings" was a war in northern Morocco, near the town of Kasar El-Kebir and Larache, on 4 August 1578. |
The Battle of Alcácer Quibir (also known as "Battle of Three Kings" was a war in northern Morocco, near the town of Kasar El-Kebir and Larache, on 4 August 1578. | ||
| The battle was between the Moroccan Sultan Abu Abdallah Mohammed II, and his ally, the King of Portugal Sebastian I, against a large Moroccan army nominally under the new Sultan of Morocco (and uncle of Abu Abdallah Mohammed II) Abd Al-Malik I. | The battle was between the Moroccan Sultan Abu Abdallah Mohammed II, and his ally, the King of Portugal Sebastian I, against a large Moroccan army nominally under the new Sultan of Morocco (and uncle of Abu Abdallah Mohammed II) Abd Al-Malik I. Over 8,000 Portuguese and Allies were killed and over 15,000 were captured.<ref>]</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | The defeat of Portugal and death of the childless Sebastian led to the end of Portugal's Aviz dynasty after Spain's Philip II took advantage of the situation and claimed Portugal under familial bonds. The subsequent ] lasted for 60 years until Portugal regained independence during the ] of 1640. | ||
| The Christian king, Sebastian I, had other plans, and planned a takeover, and crusade. | |||
| ⚫ | The defeat of Portugal and |
||
| over 8000 portuguese deaths, 15000 captured, it was a disastrous campaign, that ended the portuguese dynasty, and to survive it had to join with Spain. | |||
| <ref>]</ref>{{Circular reference|date=December 2017}} | |||
| ==Barbary wars== | ==Barbary wars== | ||
| {{Main|First Barbary War|Second Barbary War}} | {{Main|First Barbary War|Second Barbary War}} | ||
| Though Morocco was not part of the ], Moroccan ]s held their activities in both the ] and the ]. They used two main ports as bases; ] and ]. Salé pirates roamed the seas as far as the shores of the ], bringing back loot and ]s. The character ], in ]'s novel by the same name, sailed off from the mouth of the ]. |
Though Morocco was not part of the ], Moroccan ]s held their activities in both the ] and the ]. They used two main ports as bases; ] and ]. Salé pirates roamed the seas as far as the shores of the ], bringing back loot and ]s. The character ], in ]'s novel by the same name, sailed off from the mouth of the ]. | ||
| ] ] by ], ] and ]]] | ] ] by ], ] and ]]] | ||
| In 1783 the ] made peace with and was recognized by ], and in 1784 the first ] was captured by pirates from Morocco. The stars and stripes was a new flag to them. After six months of negotiation, a ] was signed, $60,000 cash was paid, and trade began. Morocco was the first independent nation to recognize the United States back in 1778.<ref>{{cite book |last=Fremont-Barnes |first=Gregory |
In 1783 the ] made peace with and was recognized by ], and in 1784 the first ] was captured by pirates from Morocco. The stars and stripes was a new flag to them. After six months of negotiation, a ] was signed, $60,000 cash was paid, and trade began. Morocco was the first independent nation to recognize the United States back in 1778.<ref>{{cite book |last=Fremont-Barnes |first=Gregory |title=The Wars of the Barbary Pirates: To the Shores of Tripoli: The Birth of the US Navy and Marines |year=2006 |publisher=Osprey Publishing |isbn=1-84603-030-7 |pages=32 |chapter=Outbreak }}</ref> | ||
| ==Franco-Moroccan Wars== | ==Franco-Moroccan Wars== | ||
| Line 73: | Line 71: | ||
| By the end of the ], Moroccan troops took part of the French Expeditionary Force engaged in the ] from 1946 to 1954. | By the end of the ], Moroccan troops took part of the French Expeditionary Force engaged in the ] from 1946 to 1954. | ||
| The ] also made extensive use of Moroccan troops recruited in the ], during both the ] of 1921-26 and the ] of |
The ] also made extensive use of Moroccan troops recruited in the ], during both the ] of 1921-26 and the ] of 1936–39. Moroccan '']'', together with the ], made up Spain's elite ]. A para-military ], known as the "Mehal-la Jalifianas" and modelled on the French goumieres, was employed within the Spanish Zone.{{Empty section|date=July 2010}} | ||
| ==The Sand War== | ==The Sand War== | ||
| Line 80: | Line 78: | ||
| Before the ], parts of southern and western ] belonged to Morocco.<ref name="countrystudies"> - Countrystudies.us</ref> In the 1930s and later in the 1950s, France had integrated into what was known as the Overseas Département of ], the areas of ] and ]. When Morocco gained independence in 1956, it wanted to reassert sovereignty over these areas. In an effort to cut the support that the ] (FLN) was getting from Morocco, France offered to return those areas in exchange for Morocco stopping that support. King ] refused to make a deal with ] behind the back of the "Algerian brothers", and agreed with the Algerian provisional government's ] leader ], that once Algeria gained its independence it would renegotiate the status of the ] and ] areas. | Before the ], parts of southern and western ] belonged to Morocco.<ref name="countrystudies"> - Countrystudies.us</ref> In the 1930s and later in the 1950s, France had integrated into what was known as the Overseas Département of ], the areas of ] and ]. When Morocco gained independence in 1956, it wanted to reassert sovereignty over these areas. In an effort to cut the support that the ] (FLN) was getting from Morocco, France offered to return those areas in exchange for Morocco stopping that support. King ] refused to make a deal with ] behind the back of the "Algerian brothers", and agreed with the Algerian provisional government's ] leader ], that once Algeria gained its independence it would renegotiate the status of the ] and ] areas. | ||
| However, immediately after Algeria's independence, and before his agreement with the Moroccan King ] could be formally ratified, the first Algerian provisional president ] was purged from the FLN government by a military-backed coalition led by the first Algerian provisional president ]. |
However, immediately after Algeria's independence, and before his agreement with the Moroccan King ] could be formally ratified, the first Algerian provisional president ] was purged from the FLN government by a military-backed coalition led by the first Algerian provisional president ]. Ben Bella reneged on the deal that Ferhat Abbas agreed to. | ||
| ⚫ | Skirmishes along the border eventually escalated into a full-blown confrontation after Algerian troops attacked and killed 10 Moroccans soldiers in a town near Figuig. The ], just formed from the ] ranks of the FLN's ] (ALN) was still geared towards ], and had little high-powered equipment .<ref>{{dead link|date=January 2018 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} - Usenet.com</ref> They were still battle-ready and held tens of thousands of experienced veterans, and strengthening the armed forces had been a top priority for the military-dominated post-war government. On the other hand, while being modern, western-equipped Moroccan army was superior on the battlefield,<ref name="countrystudies" /><ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120728140300/http://www.onwar.com/aced/data/alpha/algmor1963.htm |date=2012-07-28 }} - Onwar.com</ref> it did not manage to penetrate into Algeria. The war stalemated with the intervention of the ] (OAU) and the ] and it was broken off after approximately three weeks. The OAU eventually managed to arrange a formal cease-fire on February 20, 1964.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060927173041/http://arabworld.nitle.org/texts.php?module_id=4&reading_id=119&sequence=18 |date=2006-09-27 }} - Arabworld.nitle.org</ref> A ] was then made after ] mediation, and a ] instituted but hostilities simmered. | ||
| ==1967 and Yom Kippur Wars== | |||
| The 1973 ] was the fourth major conflict between ] and the neighboring ]. Like many other Arab States, Morocco contributed by deploying 5,500 troops, 30 tanks and 52 combat aircraft to take part in the Yom Kippur War. | |||
| ] sent one infantry brigade to ] and one armored regiment to Syria. 6 Moroccan troops were taken prisoner in the war. | |||
| ⚫ | Skirmishes along the border eventually escalated into a full-blown confrontation |
||
| ==The Western Sahara conflict== | ==The Western Sahara conflict== | ||
| Line 98: | Line 100: | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Military History Of Morocco}} | {{DEFAULTSORT:Military History Of Morocco}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:26, 8 September 2024
See also: Military of Morocco
The military history of Morocco covers a vast time period and complex events. It interacts with multiple military events in a vast area containing North Africa and the Iberian Peninsula.
The Roman conquests

Just after defeating the Phoenicians and destructing the city of Carthage in nowadays Tunisia during the Punic Wars, the Roman armies took possession of Mauretania and divided it into two provinces. In the west, Mauritania Tingitana was developed by the creation of roads, agricultural innovations and trade expansions.
In the mountainous areas, the Berber tribes resisted to the Roman invasions. The Roman influence will be preserved in the south until 285 AD. As of the end of 4th century AD, under the reign of the Roman emperor Diocletian, the Romans maintained nothing but one thin presence on the coast, around Tangier. They remained in the north until 429 AD; date of the passage of the Vandals in this part of Mauretania Tingitana. In 533 AD, the Byzantine fleets and then the Visigoths occupied Ceuta and Essaouira.
The Arab conquests
Main article: Umayyad conquest of North AfricaBerber revolt
Main article: Berber RevoltTerritorial expansions
See also: Almoravid dynasty, Almohad Caliphate, Marinid dynasty, Wattasid dynasty, Saadi dynasty, Alaouite dynasty, and Territorial evolution of MoroccoThe gallery below shows the maximum extent of each of the prominent dynasties: Almoravid, Almohad, Marinid and the Saadi Sultanate, in addition to the greatest extent of the current dynasty, the Alaouite.
-
 Almoravid dynasty
Almoravid dynasty
at its greatest extent (early 12th century) -
 Almohad dynasty
Almohad dynasty
at its greatest extent (early 13th century) -
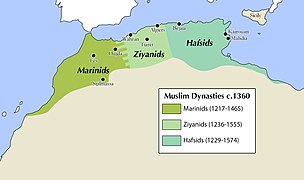 Marinid Sultanate in 1360
Marinid Sultanate in 1360
-
 Extent of the Saadi Sultanate at the beginning of the 17th century
Extent of the Saadi Sultanate at the beginning of the 17th century
Moroccan-Portuguese Wars
Main article: Moroccan-Portuguese conflictsThe Battle of Alcácer Quibir (also known as "Battle of Three Kings" was a war in northern Morocco, near the town of Kasar El-Kebir and Larache, on 4 August 1578.
The battle was between the Moroccan Sultan Abu Abdallah Mohammed II, and his ally, the King of Portugal Sebastian I, against a large Moroccan army nominally under the new Sultan of Morocco (and uncle of Abu Abdallah Mohammed II) Abd Al-Malik I. Over 8,000 Portuguese and Allies were killed and over 15,000 were captured.
The defeat of Portugal and death of the childless Sebastian led to the end of Portugal's Aviz dynasty after Spain's Philip II took advantage of the situation and claimed Portugal under familial bonds. The subsequent Iberian Union lasted for 60 years until Portugal regained independence during the Portuguese Restoration War of 1640.
Barbary wars
Main articles: First Barbary War and Second Barbary WarThough Morocco was not part of the Ottoman empire, Moroccan pirates held their activities in both the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. They used two main ports as bases; Salé and Tétouan. Salé pirates roamed the seas as far as the shores of the Americas, bringing back loot and slaves. The character Robinson Crusoe, in Daniel Defoe's novel by the same name, sailed off from the mouth of the Bou Regreg river.

In 1783 the United States made peace with and was recognized by Great Britain, and in 1784 the first American ship was captured by pirates from Morocco. The stars and stripes was a new flag to them. After six months of negotiation, a treaty of friendship between the U.S. and Morocco was signed, $60,000 cash was paid, and trade began. Morocco was the first independent nation to recognize the United States back in 1778.
Franco-Moroccan Wars
| Franco–Moroccan conflicts | |
|---|---|
|
First Franco-Moroccan Wars
The First Franco-Moroccan War consisted of a series of conflicts fought between France and its colonial administrators on one side, and the sultanate of Morocco on the other. The principal cause of war involved the retreat of Algerian resistance leader `Abd al-Qādir into Morocco following French victories over many of his tribal supporters in the French conquest of Algeria. The name of the conflict can be misleading however, seeing the first conflict between the two nations took place during the Larache expedition, after the Seven Years' War.
Second Franco-Moroccan Wars
The Second Franco-Moroccan War took place in 1911, when Moroccan forces besieged the French-occupied city of Fez. Approximately one month later, French forces brought the siege to an end. On March 30, 1912, Sultan AbdelHafid signed the Treaty of Fez, formally ceding Moroccan sovereignty to France, which established a protectorate. On April 17, 1912, Moroccan infantrymen mutinied in the French garrison in Fez. The Moroccans were unable to take the city and were defeated by a French relief force. In late May 1912, Moroccan forces unsuccessfully attacked the enhanced French garrison at Fez.
Spanish-Moroccan war
Spanish-Moroccan War (1859)Resistance against colonialism
Zaian War
Main article: Zaian WarThe Rif wars
Main article: Rif WarsIfni War
Main article: Ifni WarUse of Moroccan recruits by the colonial forces
During the period of the French protectorate of Morocco (1912–1956) large numbers of Moroccans were recruited for service in the Spahi and Tirailleur regiments of the French Army of Africa. During World War II more than 300,000 Moroccan troops (including goumier auxiliaries) served with the Free French forces in North Africa, Italy, France and Austria. The two world conflicts saw Moroccan units earning the nickname of "Todesschwalben" (death swallows) by German soldiers as they showed particular toughness on the battlefield . By the end of the World War II, Moroccan troops took part of the French Expeditionary Force engaged in the First Indochina War from 1946 to 1954.
The Spanish Army also made extensive use of Moroccan troops recruited in the Spanish Protectorate, during both the Rif War of 1921-26 and the Spanish Civil War of 1936–39. Moroccan Regulares, together with the Spanish Legion, made up Spain's elite Spanish Army of Africa. A para-military gendarmerie, known as the "Mehal-la Jalifianas" and modelled on the French goumieres, was employed within the Spanish Zone.
| This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
The Sand War
| Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Morocco |
 |
| Prehistory |
|
Classical to Late Antiquity (8th century BC – 7th century AD) |
|
Early Islamic (8th–10th century AD) |
|
Territorial fragmentation (10th–11th century AD) |
|
Empire (beginning 11th century AD) other political entities |
|
Decline (beginning 19th century AD) |
|
Protectorate (1912–56) |
|
Modern (1956–present) |
Related topics
|
Before the French colonization in the 19th century, parts of southern and western Algeria belonged to Morocco. In the 1930s and later in the 1950s, France had integrated into what was known as the Overseas Département of French Algeria, the areas of Tindouf and Bechar. When Morocco gained independence in 1956, it wanted to reassert sovereignty over these areas. In an effort to cut the support that the Front de Libération Nationale (FLN) was getting from Morocco, France offered to return those areas in exchange for Morocco stopping that support. King Mohammed V refused to make a deal with France behind the back of the "Algerian brothers", and agreed with the Algerian provisional government's nationalist leader Ferhat Abbas, that once Algeria gained its independence it would renegotiate the status of the Tindouf and Bechar areas.
However, immediately after Algeria's independence, and before his agreement with the Moroccan King Muhammad V could be formally ratified, the first Algerian provisional president Ferhat Abbas was purged from the FLN government by a military-backed coalition led by the first Algerian provisional president Ahmad Ben Bella. Ben Bella reneged on the deal that Ferhat Abbas agreed to. Skirmishes along the border eventually escalated into a full-blown confrontation after Algerian troops attacked and killed 10 Moroccans soldiers in a town near Figuig. The Algerian army, just formed from the guerrilla ranks of the FLN's Armé de Libération Nationale (ALN) was still geared towards asymmetric warfare, and had little high-powered equipment . They were still battle-ready and held tens of thousands of experienced veterans, and strengthening the armed forces had been a top priority for the military-dominated post-war government. On the other hand, while being modern, western-equipped Moroccan army was superior on the battlefield, it did not manage to penetrate into Algeria. The war stalemated with the intervention of the Organization of African Unity (OAU) and the Arab league and it was broken off after approximately three weeks. The OAU eventually managed to arrange a formal cease-fire on February 20, 1964. A peace agreement was then made after Arab League mediation, and a demilitarized zone instituted but hostilities simmered.
1967 and Yom Kippur Wars
The 1973 Yom Kippur War was the fourth major conflict between Israel and the neighboring Arab States. Like many other Arab States, Morocco contributed by deploying 5,500 troops, 30 tanks and 52 combat aircraft to take part in the Yom Kippur War.
Morocco sent one infantry brigade to Egypt and one armored regiment to Syria. 6 Moroccan troops were taken prisoner in the war.
The Western Sahara conflict
Main articles: History of Western Sahara and Western Sahara WarSee also
References and notes
- Le Maroc : douze siècles de luttes Archived 2007-04-16 at the Wayback Machine - Herodote.net (in French)
- said, Haidar y Marruecos: naciones y estados (2009-12-05). "Haidar y Marruecos: naciones y estados". ContraHistorias (in European Spanish). Retrieved 2020-10-17.
- Pfunes, Arq (2011-04-10). "Reflexiones sobre un clasicismo contemporáneo: Contexto histórico de la arquitectura hispanomusulmana (III): Imperio Almorávide (1085-1144); Segundos Reinos de Taifas (1144-1172); Imperio Almohade (1172-1212)". Reflexiones sobre un clasicismo contemporáneo. Retrieved 2020-10-17.
- "IMPERIOS DEL MAGREB (TUNEZ, ARGELIA Y MARRUECOS)". mapasimperiales.webcindario.com. Retrieved 2020-10-17.
- Unknown (2015-07-14). "Icono ADN Spain 08: 1509-1511-1513-1524-1548-1550-1554...... Las Tumbas Saadies..." Icono ADN Spain 08. Retrieved 2020-10-17.
- Battle of Alcácer Quibir
- Fremont-Barnes, Gregory (2006). "Outbreak". The Wars of the Barbary Pirates: To the Shores of Tripoli: The Birth of the US Navy and Marines. Osprey Publishing. p. 32. ISBN 1-84603-030-7.
- ^ Security Problems with Neighboring States - Countrystudies.us
- How Cuba aided revolutionary Algeria in 1963 - Usenet.com
- Armed Conflict Events Data Archived 2012-07-28 at the Wayback Machine - Onwar.com
- The 1963 border war and the 1972 treaty Archived 2006-09-27 at the Wayback Machine - Arabworld.nitle.org
| Leadership |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Branches |
| ||||||||||||||
| Former commanders | |||||||||||||||
| Operations and history | |||||||||||||||
| Equipment |
| ||||||||||||||
| Military history of Africa | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other territories |
|