| Revision as of 00:56, 2 December 2006 editSkyBoxx (talk | contribs)187 edits rv← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:44, 13 November 2024 edit undoGünniX (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users311,005 editsm unclosed ref tagsTag: AWB | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|American mechanical engineer (1856–1915)}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=October 2013}} | |||
| {{Infobox person | |||
| | name = Frederick Winslow Taylor | |||
| | image = Frederick Winslow Taylor (1).JPG | |||
| | image_size = | |||
| | caption = Taylor circa 1907 | |||
| | birth_name = | |||
| | birth_date = {{birth date text|March 20, 1856}} | |||
| | birth_place = ], Pennsylvania, U.S. | |||
| | death_date = {{Death date and age|1915|3|21|1856|3|20}} | |||
| | death_place = Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S. | |||
| | resting_place = ]<br />], Pennsylvania, U.S. | |||
| | resting_place_coordinates = | |||
| | known_for = Father of ], ] and ] | |||
| | education = ] | |||
| | alma_mater = ] <small>(])</small> | |||
| | employer = | |||
| | occupation = Efficiency expert<br />] | |||
| | awards = ] (1902) | |||
| | party = | |||
| | boards = | |||
| | spouse = Louise M. Spooner | |||
| | children = 3 | |||
| | relatives = | |||
| | signature = | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Frederick Winslow Taylor''' (March 20, 1856 – March 21, 1915) was an American ]. He was widely known for his methods to improve ].{{Sfn|''New York Times'', March 22,|1915|p=9}} He was one of the first ].{{Sfn|''Wall Street Journal'', June 13,|1997|p=A17}} In 1909, Taylor summed up his efficiency techniques in his book '']'' which, in 2001, Fellows of the ] voted the most influential management book of the twentieth century.{{Sfn|Bedeian & Wren, Winter|2001|pp=221–225}} His pioneering work in applying engineering principles to the work done on the factory floor was instrumental in the creation and development of the branch of engineering that is now known as ]. Taylor made his name, and was most proud of his work, in scientific management; however, he made his fortune patenting steel-process improvements. As a result, ] is sometimes referred to as ''Taylorism''.{{Sfn|Epstein,|1996|pp=579–580}} | |||
| '''Frederick Winslow Taylor''' (], ] - ], ]) was an ] engineer who sought to improve industrial efficiency. He, Maunsel White, and a team of assistants developed ]. He was one of the intellectual leaders of the ] and his ideas, broadly conceived, were highly influential in the ]. During the latter part of his career he was a management consultant, and he is sometimes called "The Father of Scientific Management." | |||
| == |
==Biography== | ||
| Taylor was born in 1856 to a ] family in ]. Taylor's father, Franklin Taylor, a ]-educated lawyer, built his wealth on ].{{Sfn|Papesh, February 14,|1998|p=}} Taylor's mother, Emily Annette Taylor (née Winslow), was an ardent ] and a coworker with ]. His father's ancestor, Samuel Taylor, settled in ], in 1677. His mother's ancestor, ], was one of the fifteen original Mayflower Pilgrims who brought servants or children, and one of eight who had the honorable distinction of Mister. Winslow served for many years as the Governor of the Plymouth colony. | |||
| Taylor was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to a wealthy Quaker family. He had intended to pursue his education at Harvard University, but poor eyesight forced him to consider an alternative career. In 1874, he became an apprentice machinist, learning of factory conditions at the grass-roots level. He got a degree in Mechanical Engineering through a highly unusual (for the time) series of correspondence courses at ] (graduating in 1883) (Kanigel 1997:182-183,199). | |||
| The Taylor family had inherited wealth and property, and the family's assets were maintained by Franklin's older brother, ]. | |||
| ==The development of management== | |||
| Taylor thought that by analyzing work, the "One Best Way" to do it would be found. He is most remembered for developing the ]. He would break a job into its component parts and measure each to the second. One of his most famous studies involved shovels. He noticed that the workers used the same shovel for all materials. He determined that the most effective load was 21½ lb, and found or designed shovels that for each material would scoop up that amount. He was generally unsuccessful at applying his concepts; it was largely through his disciples (most notably H.L. ]) that his ideas were implemented in industry. After being fired from ] he wrote a book, ''Shop Management'', which sold well. | |||
| Educated early by his mother, Taylor studied for two years in France and Germany and traveled Europe for 18 months.{{Sfn|Miami University,|2003}} In 1872, he entered ] in ], with the plan of eventually going to Harvard and becoming a lawyer like his father. In 1874, Taylor passed the Harvard entrance examinations with honors. However, due allegedly to rapidly deteriorating eyesight caused by night study, Taylor chose quite a different path. | |||
| Taylor believed that contemporary management was amateurish and should be studied as a discipline, that workers should cooperate with management (and hence would not need ]s), and that the best results would come from the partnership between a trained and qualified management and a cooperative and innovative workforce. Each side needed the other. | |||
| Instead of attending ], Taylor became an apprentice ] and ], gaining shop-floor experience at Enterprise Hydraulic Works in Philadelphia (a pump-manufacturing company whose proprietors were friends of the Taylor family). During this time, his eyesight recovered. He left his apprenticeship for six months and represented a group of New England machine-tool manufacturers at Philadelphia's centennial exposition. Taylor finished his four-year apprenticeship and in 1878 became a ] laborer at ]. At Midvale, he was quickly promoted to time clerk, journeyman machinist, ] ], research director, and finally chief engineer of the works (while maintaining his position as machine shop foreman). Taylor's fast promotions reflected both his talent and his family's relationship with Edward Clark, part owner of Midvale Steel. (Edward Clark's son ], who was also a manager at Midvale Steel, married Taylor's sister.) | |||
| Taylor was a professor at the ] at ], founded in 1900. He is known for coinage of the term '']'' in his monograph ''The Principles of Scientific Management,'' published in 1911. However, his approach is often referred to, as ''Taylor's Principles'', or frequently disparagingly, as ''Taylorism''. | |||
| ] Works Aerial View, 1879.]] | |||
| Taylor developed four principles of Scientific Management: | |||
| Early on at Midvale, working as a laborer and machinist, Taylor recognized that workmen were working their machines, or themselves, not nearly as hard as they could (a practice that at the time was called "]") and that this resulted in high labor costs for the company. When he became a foreman he expected more output from the workmen. In order to determine how much work should properly be expected, he began to study and analyze the ] of both the men and the machines (although the word "productivity" was not used at the time, and the applied science of productivity had not yet been developed). His focus on the human component of production Taylor labeled ].{{Sfn|Hughes,|1989|p=190}} | |||
| # Replace rule-of-thumb work methods with methods based on a scientific study of the tasks. | |||
| # Scientifically select, train, and develop each worker rather than passively leaving them to train themselves. | |||
| # Cooperate with the workers to ensure that the scientifically developed methods are being followed. | |||
| # Divide work nearly equally between managers and workers, so that the managers apply scientific management principles to planning the work and the workers actually perform the tasks | |||
| While Taylor worked at Midvale, he and ] won the first tennis doubles tournament in the ], the precursor of the ].{{Sfn|''New York Times'', March 22,|1915|p=9}} Taylor became a student of ], studying via correspondence{{Sfn|Kanigel,|1997|pp=182–183, 199}} and obtaining a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering in 1883.{{Sfn|''New York Times'', June 15,|1883|p=8}} On May 3, 1884, he married Louise M. Spooner of Philadelphia. | |||
| ] plant, 1896.]] | |||
| From 1890 until 1893 Taylor worked as a general manager and a consulting engineer to management for the Manufacturing Investment Company of Philadelphia, a company that operated large paper mills in Maine and Wisconsin. He was a plant manager in Maine. In 1893, Taylor opened an independent consulting practice in Philadelphia. His business card read "Consulting Engineer - Systematizing Shop Management and Manufacturing Costs a Specialty". Through these consulting experiences, Taylor perfected his management system. His first paper, ''A Piece Rate System'', was presented to the ] in June 1895.{{Sfn|Copley,|1923|pp=396–397}} | |||
| In 1898 he joined ] to solve an expensive ] capacity problem. While at Bethlehem, he discovered the best known and most profitable of his many patents: between 1898 and 1900 Taylor and Maunsel White (''né'' Maunsel White III; 1856–1912; grandson of ]; 1783–1863) conducted comprehensive empirical tests, and concluded that ] doubled or quadrupled cutting speeds. The inventors received {{US$|100000|1900|round=-5|about=yes}} for the English patents alone,{{Sfn|Drury,|1918|p=100}}{{Sfn|"F.W. Taylor Collection,"|2001}} although the U.S. patent was eventually nullified.{{Sfn|Roeber & Parmelee, March|1909|p=}} | |||
| Harvard University, one of the first American universities to offer a graduate degree in business management in 1908, based its first-year curriculum on Taylor's ideas regarding scientific management. His ideas, as well as Henry Ford's, relating to efficiency became highly influential during the early days of the Soviet Union. | |||
| Taylor was forced to leave Bethlehem Steel in 1901 after discord with other managers. Now a wealthy man, Taylor focused the remainder of his career promoting his management and machining methods through lecturing, writing, and consulting. From 1904 - 1914, Taylor lived in Philadelphia with his wife and three adopted children. In 1910, owing to the Eastern Rate Case, Frederick Winslow Taylor and his Scientific Management methodologies became famous worldwide. In 1911, Taylor introduced his The Principles of Scientific Management paper to the ASME, eight years after his Shop Management paper. | |||
| ==Relationship with ASME== | |||
| Taylor was president of the ] (ASME) from 1906-1907. While president, he tried to implement his system into the management of the ASME but was met with much resistance. He was only able to reorganize the publications department and then only partially. He also forced out the ASME's long-time secretary, ], and replaced him with ]. His tenure as president was trouble-ridden and marked the beginning of a period of internal dissension within the ASME during the Progressive Era (Jaffe 1957:34). | |||
| On October 19, 1906, Taylor was awarded an honorary degree of ] by the ].{{Sfn|Harrison Letter, October 8,|1906}} In the same year, he was elected president of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. Taylor was elected to the ] in 1912.<ref>{{Cite web |title=APS Member History |url=https://search.amphilsoc.org/memhist/search?creator=Frederick+W.+Taylor&title=&subject=&subdiv=&mem=&year=&year-max=&dead=&keyword=&smode=advanced |access-date=2023-11-22 |website=search.amphilsoc.org}}</ref> That same year, he gave testimony to a special committee of the US House of Representatives regarding his own and other systems of management. Taylor eventually became a professor at the ] at ].{{Sfn|D'Aveni, Winter|2003|p=}} He was elected to the ] in 1915.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-02-09 |title=Frederick Winslow Taylor |url=https://www.amacad.org/person/frederick-winslow-taylor |access-date=2023-11-22 |website=American Academy of Arts & Sciences |language=en}}</ref> In early spring of that year, Taylor caught pneumonia and died,{{Sfn|Frederick Taylor University}} one day after his fifty-ninth birthday, on March 21, 1915. He was buried in ], in ]. | |||
| In 1912, Taylor collected his articles into a book-length manuscript and submitted it to the ASME for publication. The ASME formed an ad hoc committee to review the text. The committee included Taylor allies such as ] and ]. The committee delegated the report to the editor of the ''American Machinist'', ]. Alford was a critic of the Taylor system and the report was negative. The committee modified the report slightly, but accepted Alford's recommendation not to publish Taylor's book. Taylor angrily withdrew the book and published ''Principles'' without ASME approval (Jaffe 1957:36-40; Nelson 1980:181-184). | |||
| ==Work== | |||
| == Closest followers == | |||
| {{over-quotation|section=y|date=December 2019}} | |||
| ===Taylor's Influence in the United States=== | |||
| {{Quote box | |||
| * ], lecturer at Harvard and early consultant on Scientific Management. | |||
| |quote = Darwin, Marx, and Freud make up the trinity often cited as the "makers of the modern world." '''Marx would be taken out and replaced by Taylor if there were any justice'''... For hundreds of years there had been no increase in the ability of workers to turn out goods or to move goods... When Taylor started propounding his principles, nine out of every 10 working people did manual work, making or moving things, whether in manufacturing, farming, mining, or transportation... By 2010 it will constitute no more than one-tenth... The Productivity Revolution has become a victim of its own success. From now on what matters is the productivity of nonmanual workers. | |||
| * ] developed the ], a visual aid for graphing the scheduling of tasks and flow of work to be completed. | |||
| -- ], ''The Rise of the Knowledge Society'' Wilson Quarterly (Spring 1993) p.63-65{{Sfn|Drucker, ''The Rise'', Spring|1993|pp=63–65}} | |||
| * ] introduced scientific management to the ] and developed idea of "staff" function as advisory role to "line" management. | |||
| |width = 35% | |||
| * ] adapted scientific management to educational and municipal organizations. | |||
| |align = right | |||
| * ] created the discipline of ]. | |||
| }} | |||
| * ] introduced psychology to management studies. | |||
| {{Quote box | |||
| * ] introduced scientific management in the construction industry and developed "motion" studies using photography for what came to be called "time and motion" studies. | |||
| |quote = '''Taylor's crime''', in the eyes of the unions, was his assertion that there is no "skilled work." In manual operations there is only "work." All work can be analyzed the same way... The unions... were craft monopolies, and membership in them was largely restricted to sons or relatives of members. They required an apprenticeship of five to seven years but had no systematic training or work study. The unions allowed nothing to be written down. There were not even blueprints or any other drawings of the work to be done. Union members were sworn to secrecy and forbidden to discuss their work with nonmembers. | |||
| * ], as ] of Dartmouth's Amos Tuck School of Administration and Finance, promoted the teaching of scientific management. | |||
| -- ], ''The Rise of the Knowledge Society'' Wilson Quarterly (Spring 1993) p.61-62{{Sfn|Drucker, ''The Rise'', Spring|1993|pp=61–62}} | |||
| * ], professor at ] and senior partner in his accounting firm, propagated the budget as a means of accountability and measuring performance. | |||
| |width = 35% | |||
| |align = right | |||
| }}Taylor was a mechanical engineer who sought to improve ]. He is regarded as the father of ], and was one of the first ] and director of a famous firm. In ]'s description, | |||
| {{blockquote|Frederick W. Taylor was the first man in recorded history who deemed work deserving of systematic observation and study. On Taylor's 'scientific management' rests, above all, the tremendous surge of affluence in the last seventy-five years which has lifted the working masses in the developed countries well above any level recorded before, even for the well-to-do. Taylor, though the Isaac Newton (or perhaps the Archimedes) of the science of work, laid only first foundations, however. Not much has been added to them since—even though he has been dead all of sixty years.{{Sfn|Drucker,|1974|p=181}} }} | |||
| ===Outside the United States=== | |||
| ====France==== | |||
| ] translated Taylor's work and introduced scientific management throughout state plants during ]. This influenced the French theorist ] who published '']'' in 1916 (published in book form in 1917) which emphasized organizational structure in management. | |||
| Taylor's scientific management consisted of four principles: | |||
| ====Switzerland==== | |||
| #Replace rule-of-thumb work methods with methods based on a scientific study of the tasks. | |||
| The American ] established the ] to spread information about management. | |||
| #Scientifically select, train, and develop each employee rather than passively leaving them to train themselves. | |||
| #Provide "Detailed instruction and supervision of each worker in the performance of that worker's discrete task"{{Sfn|Montgomery,|1989|p=250}} | |||
| #Divide work nearly equally between managers and workers, so that the managers apply scientific management principles to planning the work and the workers actually perform the tasks. | |||
| Future ] justice ] coined the term ''scientific management'' in the course of his argument for the ] before the ] in 1910. Brandeis argued that railroads, when governed according to Taylor's principles, did not need to raise rates to increase wages. Taylor used Brandeis's term in the title of his monograph ''],'' published in 1911. The Eastern Rate Case propelled Taylor's ideas to the forefront of the management agenda. Taylor wrote to Brandeis, "I have rarely seen a new movement started with such great momentum as you have given this one." Taylor's approach is also often referred to as ''Taylor's Principles'', or, frequently disparagingly, as ''Taylorism''. | |||
| ====USSR==== | |||
| ] was very influenced by Taylor's ideas and sought to incorporate Taylorism into Soviet manufacturing. | |||
| ===Managers and workers=== | |||
| == Articles == | |||
| {{Quote box | |||
| Taylor's life and work was discussed in the Deja Vu column by Cynthia Crossen in the Wall Street Journal on November 6, 2006. | |||
| |quote = The idea, then, of.. training under a competent teacher into new working habits until he continually and habitually works in accordance with scientific laws, which have been developed by some one else, is '''directly antagonistic to the old idea that each workman can best regulate his own way of doing the work'''... the philosophy of the old management puts the entire responsibility upon the workmen, while the philosophy of the new places a great part of it upon the management. | |||
| -- ], ''The Principles of Scientific Management'' (1911) p.63{{Sfn|Taylor, ''Principles'',|1919|p=63}} | |||
| |width = 35% | |||
| |align = right | |||
| }} | |||
| Taylor had very precise ideas about how to introduce his system: | |||
| {{blockquote|It is only through ''enforced'' standardization of methods, ''enforced'' adoption of the best implements and working conditions, and ''enforced'' cooperation that this faster work can be assured. And the duty of enforcing the adoption of standards and enforcing this cooperation rests with the ''management'' alone.{{Sfn|Taylor, ''Principles'',|1919|p=83}}}} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| Workers were to be selected appropriately for each task. | |||
| {{blockquote|One of the very first requirements for a man who is fit to handle pig iron as a regular occupation is that he shall be so stupid and so phlegmatic that he more nearly resembles in his mental make-up the ox than any other type. The man who is mentally alert and intelligent is for this very reason entirely unsuited to what would, for him, be the grinding monotony of work of this character. | |||
| {{Sfn|Taylor, ''Principles'',|1919|p=59}}}} | |||
| Taylor believed in transferring control from workers to management. He set out to increase the distinction between mental (planning work) and manual labor (executing work). Detailed plans, specifying the job and how it was to be done, were to be formulated by management and communicated to the workers.{{Sfn|Rinehart,|1975|p=44}} | |||
| The introduction of his system was often resented by workers and provoked numerous strikes. The strike at ] led to the congressional investigation in 1912. | |||
| Taylor believed the laborer was worthy of his hire, and pay was linked to productivity. His workers were able to earn substantially more than those under conventional management,<ref name="Taylor1911p95">{{Harvnb|Taylor|1911|p=95}}.</ref> and this earned him enemies among the owners of factories where scientific management was not in use. | |||
| ===Rhetorical techniques=== | |||
| Taylor promised to reconcile labor and capital. {{blockquote|With the triumph of scientific management, unions would have nothing left to do, and they would have been cleansed of their most evil feature: the restriction of output. To underscore this idea, Taylor fashioned the myth that 'there has never been a strike of men working under scientific management', trying to give it credibility by constant repetition. In similar fashion he incessantly linked his proposals to shorter hours of work, without bothering to produce evidence of "Taylorized" firms that reduced working hours, and he revised his famous tale of ] carrying pig iron at Bethlehem Steel at least three times, obscuring some aspects of his study and stressing others, so that each successive version made Schmidt's exertions more impressive, more voluntary and more rewarding to him than the last. Unlike Emerson, Taylor was not a charlatan, but his ideological message required the suppression of all evidence of worker's dissent, of coercion, or of any human motives or aspirations other than those his vision of progress could encompass.{{Sfn|Montgomery,|1989|p=254}} | |||
| For the stories about Schmidt Montgomery refers to ] and Amadeo G. Perroni, "Taylor's Pig Tale: A Historical Analysis of Frederick W. Taylor's Pig-Iron experiments" in: ''Academy of Management Journal'', 17 (March 1974), 6-27}} | |||
| ===Scholarly debate about increased efficiency moving pig iron at Bethlehem's Iron and Steel=== | |||
| Debate about Taylor's Bethlehem study of workers, particularly the stereotypical laborer "]", continues to this day. One 2009 study supports assertions Taylor made about the quite substantial increase in productivity, for even the most basic task of picking up, carrying and dropping pigs of iron.{{Sfn|Hough & White, September–October|2001|p=}}{{Sfn|Baruch, March 1,|2009|p=}} | |||
| ===Management theory=== | |||
| Taylor thought that by analysing work, the "one best way" to do it would be found. He is most remembered for developing the stopwatch time study, which, combined with ]'s motion study methods, later became the field of ]. He broke a job into its component parts and measured each to the hundredth of a minute. One of his most famous studies involved shovels. He noticed that workers used the same shovel for all materials. He determined that the most effective load was 21½ pounds, and found or designed shovels that for each material would scoop up that amount. He was generally unsuccessful in getting his concepts applied, and was dismissed from ]. Nevertheless, Taylor was able to convince workers who used shovels and whose compensation was tied to how much they produced to adopt his advice about the optimum way to shovel by breaking the movements down into their component elements and recommending better ways to perform these movements. It was largely through his disciples' efforts (most notably ]'s) that industry came to implement his ideas. Moreover, the book he wrote after parting company with the Bethlehem company, ''Shop Management'', sold well. | |||
| ===Relations with ASME=== | |||
| Taylor's written works were designed for presentation to the ] (ASME). These include ''Notes on Belting'' (1894), ''A Piece-Rate System'' (1895), ''Shop Management'' (1903), ''Art of Cutting Metals'' (1906), and ''The Principles of Scientific Management'' (1911). | |||
| Taylor was ] of the ASME from 1906 to 1907. While president, he tried to implement his system into the management of the ASME but met with much resistance. He was able to reorganize only the publications department and that only partially. He also forced out the ASME's longtime secretary, ], and replaced him with ]. His tenure as president was trouble-ridden and marked the beginning of a period of internal dissension within the ASME during the Progressive Age.{{Sfn|Jaffe,|1957|p=34}} | |||
| In 1911, Taylor collected a number of his articles into a book-length manuscript, which he submitted to the ASME for publication. The ASME formed an ad hoc committee to review the text. The committee included Taylor allies such as ] and ]. The committee delegated the report to the editor of the '']'', ]. Alford was a critic of the Taylor system and his report was negative. The committee modified the report slightly, but accepted Alford's recommendation not to publish Taylor's book. Taylor angrily withdrew the book and published ''Principles'' without ASME approval.{{Sfn|Jaffe,|1957|pp=36–40}}{{Sfn|Nelson,|1980|p=174}} Taylor published the trade book himself in 1912. | |||
| ==Taylor's influence== | |||
| ===United States=== | |||
| ]'s speed-and-feed slide rules.]] | |||
| ] | |||
| *] helped Taylor to develop ] ]s to a previously unknown level of usefulness. Similar aids are still used in machine shops today. Barth became an early consultant on scientific management and later taught at Harvard. | |||
| *] developed the ], a visual aid for scheduling tasks and displaying the flow of work. | |||
| *] introduced scientific management to the ] industry, and proposed the dichotomy of ''staff'' versus ''line'' employees, with the former advising the latter. | |||
| *] adapted scientific management to educational and municipal organizations. | |||
| *] created ]. | |||
| *] introduced psychology to management studies. | |||
| *] (husband of Lillian) discovered scientific management while working in the construction industry, eventually developing motion studies independently of Taylor. These logically complemented Taylor's time studies, as time and motion are two sides of the efficiency improvement coin. The two fields eventually became ]. | |||
| *], one of the first American universities to offer a graduate degree in business management in 1908, based its first-year curriculum on Taylor's scientific management.{{Sfn|Lepore, October 12,|2009|p=114}} | |||
| *], as ] of ]'s ], promoted the teaching of scientific management. | |||
| *], professor of accounting at the ] and founder of the consulting firm bearing his name, advocated budgets as a means of assuring accountability and of measuring performance. | |||
| ===France=== | |||
| In ], ] translated Taylor's work and introduced scientific management throughout government owned plants during ]. This influenced the French theorist ], whose 1916 '']'' emphasized organizational structure in management. In the classic ''General and Industrial Management'', Fayol wrote that "Taylor's approach differs from the one we have outlined in that he examines the firm from the 'bottom up.' He starts with the most elemental units of activity – the workers' actions – then studies the effects of their actions on productivity, devises new methods for making them more efficient, and applies what he learns at lower levels to the hierarchy {{nowrap| ... }}"{{Sfn|Fayol,|1988|p=43}} He suggests that Taylor has staff analysts and advisors working with individuals at lower levels of the organization to identify the ways to improve efficiency. According to Fayol, the approach results in a "negation of the principle of unity of command."{{Sfn|Fayol,|1988|p=44}} Fayol criticized Taylor's functional management in this way: In ], Taylor said{{Sfn|Fayol,|1988|p=}} « ... the most marked outward characteristics of functional management lies in the fact that each workman, instead of coming in direct contact with the management at one point only, ... receives his daily orders and help from eight different bosses... these eight were (1) route clerks, (2) instruction card men, (3) cost and time clerks, (4) gang bosses, (5) speed bosses, (6) inspectors, (7) repair bosses, and the (8) shop disciplinarian. »{{Sfn|Fayol,|1949|p=68}} Fayol said that this was an unworkable situation and that Taylor must have reconciled the differences in some way not described in Taylor's works. | |||
| Around 1922 the journalist ] became interested in Taylor's theories, which were popular in France in the post-war period.{{Sfn|Dumont, September|2012|pp=36–40}} | |||
| Bernège became the faithful disciple of the Domestic Sciences Movement that ] had launched earlier in the United States, which Bernège adapted to French homes. | |||
| Frederick had transferred the concepts of Taylorism from the factory to domestic work. These included suitable tools, rational study of movements and timing of tasks. Scientific standards for housework were derived from scientific standards for workshops, intended to streamline the work of a housewife.{{Sfn|Bernège & Ribeill,|1989|p=}} | |||
| The ''Comité national de l'organisation française'' (CNOF) was founded in 1925 by a group of journalists and consulting engineers who saw Taylorism as a way to expand their client base. | |||
| Founders included prominent engineers such as ] and ]. Bernège's Institute of Housekeeping Organization participated in various congresses on the scientific organization of work that led up to the founding of the CNOF, and in 1929 led to a section in CNOF on domestic economy.{{Sfn|Henry,|2003|p=5}} | |||
| ===Great Britain=== | |||
| Older historical accounts used to suggest that British industry had less interest in Taylor's teachings than in similarly sized countries.{{Sfn|Maier,|1970|p=}} More recent research has revealed that British engineers and managers were as interested as in other countries.{{Sfn|Whitston, Summer|1997|p=}} This disparity was largely due to what historians have been analysing: recent research has revealed that Taylor's practices diffused to Britain more through consultancies, in particular the ], than through institutions, as in Germany and to a lesser extent France, where a mixture was most effective.{{Sfn|Kipping, October|1997|p=}}{{Sfn|Wren, June 8,|2015|pp=309–327}} | |||
| Particularly enthusiastic were the ], ], ] and ]. In addition to establishing a consultancy to implement Taylor's system, ], Urwick was also a key historian of F.W. Taylor and scientific management, publishing ''The Making of Scientific Management'' trilogy in the 1940s and ''The Golden Book of Management'' in 1956. | |||
| ===Switzerland=== | |||
| In Switzerland, the American ] established the ] to spread information about management techniques. ] was its director until the IMI closed in 1933.{{Sfn|Wrege,|1987|p=}} | |||
| ===USSR=== | |||
| In the ], ] was very impressed by Taylorism, which he and other ] leaders tried to incorporate into Soviet manufacturing. When ] took power in the 1920s, he championed the theory of "]" which denied that the Soviet economy needed foreign help to develop, and open advocates of Western management techniques fell into disfavor. No longer celebrated by Soviet leadership, Taylorism and the mass production methods of ] remained silent influences during the ]. Nevertheless, " Frederick Taylor's methods have never really taken root in the Soviet Union."{{Sfn|Atta, April|1986|p=335}} The voluntaristic approach of Stalin's ] movement in the 1930s, fixated on setting individual records, was intrinsically opposed to Taylor's systematic approach and proved to be counter-productive.{{Sfn|Atta, April|1986|p=331}} The stop-and-go of the production process – workers having nothing to do at the beginning of a month and 'storming' during illegal extra shifts at the end of the month – which prevailed even in the 1980s had nothing to do with the successfully taylorized plants e.g., of ] which are characterized by ''continuous'' production processes (]) which are ''continuously'' improved (]).{{Sfn|Head,|2003|p=38–59}} | |||
| "The easy availability of replacement labor, which allowed Taylor to choose only 'first-class men,' was an important condition for his system's success."{{Sfn|Atta, April|1986|p=329}} The situation in the Soviet Union was very different. "Because work is so unrhythmic, the rational manager will hire more workers than he would need if supplies were even in order to have enough for storming. Because of the continuing labor shortage, managers are happy to pay needed workers more than the norm, either by issuing false job orders, assigning them to higher skill grades than they deserve on merit criteria, giving them 'loose' piece rates, or making what is supposed to be 'incentive' pay, premia for good work, effectively part of the normal wage. As Mary McAuley has suggested under these circumstances piece rates are not an incentive wage, but a way of justifying giving workers whatever they 'should' be getting, no matter what their pay is supposed to be according to the official norms."{{Sfn|Atta, April|1986|p=333}} | |||
| Taylor and his theories are also referenced (and put to practice) in the 1921 ]n novel '']'' by ]. | |||
| ===Canada=== | |||
| In the early 1920s, the Canadian textile industry was re-organized according to scientific management principles. In 1928, workers at Canada Cotton Ltd. in ] went on strike against newly introduced Taylorist work methods. Also, ], who was a close associate of Taylor, re-organized the ].{{Sfn|Rinehart,|1975|p=43}} | |||
| With the prevalence of US branch plants in Canada and close economic and cultural ties between the two countries, the sharing of business practices, including Taylorism, has been common. | |||
| ===The Taylor Society and its legacy=== | |||
| The ] was founded in 1912 by Taylor's allies to promote his values and influence.{{Sfn|Mee, Spring|1988|p=}} A decade after Taylor's death in 1915 the Taylor Society had 800 members, including many leading U.S. industrialists and managers.{{Sfn|Brown, May|1925|p=}} In 1936 the Society merged with the Society of Industrial Engineers, forming the ], which still exists today.{{Sfn|Society for Advancement of Management (link)}} | |||
| ===Criticism of Taylor=== | |||
| Many of the critiques of Taylor come from Marxists. The earliest was by ], an Italian Communist, in his '']'' (1937). Gramsci argued that Taylorism subordinates the workers to management. He also argued that the repetitive work produced by Taylorism might actually give rise to revolutionary thoughts in workers' minds.{{Sfn|Gramsci, ''Selections'',|1929–1931}}{{Sfn|Gramsci,|1929–1931}} | |||
| ]'s work '']'', published in 1974, was critical of ] and of Taylor in particular. This work pioneered the field of ] as well as contributing to the ] of the workplace. | |||
| Management theorist ] is highly critical of Taylor's methods. Mintzberg states that an obsession with efficiency allows measurable benefits to overshadow less quantifiable social benefits completely, and social values get left behind.{{Sfn|Mintzberg,|1989|p=333}} | |||
| Taylor's methods have also been challenged by ]. Their arguments relate to progressive defanging of workers in the workplace and the subsequent degradation of work as management, powered by capital, uses Taylor's methods to render work repeatable and precise yet monotonous and skill-reducing.{{Sfn|Braverman,|1974|pp=43–52}} James W. Rinehart argued that Taylor's methods of transferring control over production from workers to management, and the division of labor into simple tasks, intensified the alienation of workers that had begun with the factory system of production around the period 1870 to 1890.{{Sfn|Rinehart,|1975|pp=43–52}} | |||
| Criticism of Taylor and the Japanese model, according to ]: | |||
| "We are going to win and the industrial west is going to lose out. There’s nothing you can do about it, because the reasons for failure are within yourselves. Your firms are built on the Taylor model. Even worse, so are your heads. With your bosses doing the thinking while workers wield the screwdrivers, you're convinced deep down that it is the right way to run a business. For the essence of management is getting ideas out of the heads of the bosses and into the heads of labour. We are beyond your mindset. Business, we know, is now so complex and difficult, the survival of firms so hazardous in an environment increasingly unpredictable, competitive and fraught with danger, that their continued existence depends on the day-to-day mobilisation of every ounce of intelligence."{{Sfn|1990|Pascale,|1990|p=27}} | |||
| ==Tennis and golf accomplishments== | |||
| Taylor was an accomplished ] and ] player. He and ] won the inaugural ] at ] in 1881, defeating ] and Arthur Newbold (''né'' Arthur Emlen Newbold; 1859–1920) in straight sets.{{Sfn|''New York Times'', March 22,|1915|p=9}} In the ], Taylor finished ] in golf. | |||
| {| class="unsortable wikitable" style="text-align:center;" | |||
| !style="width:5%"|Result | |||
| !style="width:5%"|Year | |||
| !style="width:20%"|Championship | |||
| !style="width:5%"|Surface | |||
| !style="width:25%"|Partner | |||
| !style="width:25%"|Opponents | |||
| !style="width:15%" class="unsortable"|Score | |||
| |- style="background:#ccf;" | |||
| | style="background:#98fb98;"|Win || 1881 || ] || ] ||style="text-align:left;"| {{hanging indent |text={{flagicon|USA|1881}} Frederick W. Taylor}}{{flagicon|USA|1881}} ] ||style="text-align:left;"| {{flagicon|USA|1881}} ]<br>{{flagicon|USA|1881}} Arthur Newbold || 6–5, 6–4, 6–5 | |||
| |} | |||
| ==Publications== | |||
| '''Books''' | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=50em}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text=1903, 1911. {{cite book |last1=Taylor |first1=Frederick Winslow |title=Shop Management |year=1911 |url=https://archive.org/details/shopmanagement01tayl/page/n5/mode/2up |type=With an introduction by ] |location=New York, London |publisher=] }}{{Sfn|Taylor, ''Shop'',|1903|pp=1337–1480}}}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text=1911. {{cite book |last1=Taylor |first1=Frederick Winslow |date=1919 |orig-date=1911 |title=The Principles of Scientific Management |url=https://archive.org/details/principlesofscie00taylrich/page/n5/mode/2up |publisher=] |access-date= |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} {{LCCN|11010339}}; {{OCLC|233134|show=all}}.}}<div style="margin-left:6em">{{cite book |title=The Principles of Scientific Management |url=https://gutenberg.org/ebooks/6435 |via=] {{free access}} }}</div> | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text=1911. {{cite book |last1=Taylor |first1=Frederick Winslow |last2=Thompson |first2=Sanford Eleazer |author-link2=Sanford E. Thompson |title=A Treatise on Concrete, Plain and Reinforced: Materials, Construction, and Design of Concrete and Reinforced Concrete |year=1907 |url=https://archive.org/details/treatiseonconcre00tayluoft/page/n7/mode/2up |edition=1st |location=New York |publisher=] |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} {{OCLC|1722781|show=all}}.}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text=1912. {{cite book |last1=Taylor |first1=Frederick Winslow |last2=Thompson |first2=Sanford Eleazer |author-link2=Sanford E. Thompson |title=Concrete Costs |year=1912 |url=https://archive.org/details/concretecoststa01thomgoog/page/n4/mode/2up |type=1st ed.; 1st issue |publisher=] |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} {{LCCN|12010295}}; {{OCLC|2272138|show=all}}.}} | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| '''Selected articles''' | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=50em}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text=1894. {{cite journal |title=Notes on Belting |url=https://archive.org/stream/transactionsof15amer#page/204/mode/2up |journal=Transactions |year=1880 |publisher=] |volume=15 |pages=204–259 |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} {{OCLC|1052127574|show=all}}.}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text=1896. {{cite journal |date=June 1896 |title=A Piece-Rate System |url=https://archive.org/stream/adjustmentwages00taylgoog#page/n45/mode/2up |journal=Economic Studies |publisher=] |volume=1 |issue=2 |pages=89–129 |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} {{OCLC|1076000|show=all}}.}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text=1903. {{cite journal |title=Shop Management |url=https://archive.org/stream/transactionsof24amer#page/1336/mode/2up |type=No. 1003 |journal=Transactions |year=1880 |publisher=] |volume=24 |pages=1337–1480 |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} {{OCLC|6077365|show=all}}.}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text=1906. {{cite journal |title=On the Art of Cutting Metals |url=https://archive.org/stream/transactionsof28amer#page/30/mode/2up |type=No. 1119 |journal=Transactions |year=1880 |publisher=] |volume=28 |pages=31–350 |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} {{OCLC|9057615|show=all}}.}} | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ==Bibliography== | |||
| === Notes === | |||
| {{Reflist|22em}} | |||
| ===References=== | |||
| {{hanging indent |text='''Secondary sources – books, journals, magazines, and papers'''}}<!--The hanging indents help the appearance on mobile devices--> | |||
| <!--Ref system has been made consistent as Harvard referencing. Please continue to use Harvard ref system in this article to be consistent with what's already here. For more info on reference systems in Misplaced Pages, see ].--> | <!--Ref system has been made consistent as Harvard referencing. Please continue to use Harvard ref system in this article to be consistent with what's already here. For more info on reference systems in Misplaced Pages, see ].--> | ||
| {{refbegin|30em|indent=yes}} | |||
| *<!--A-->{{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Atta, April|1986|pp=327–337}} |last1=Atta |first1=Don Van |date=April 1986 |title=Why Is There No Taylorism in the Soviet Union? |journal=Comparative Politics |volume=18 |issue=33 |pages=327–337 |doi=10.2307/421614 |jstor=421614 }} {{doi|10.2307/421614}}; {{JSTOR|421614}}; {{ISSN|0010-4159}}; {{OCLC|5548842780|8313710703|13565305}}. | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Boddy|first=David|title=Management: An Introduction|year=2002|edition=2nd ed.|publisher=Pearson Education|location=New York|id=ISBN 0273655183}} | |||
| *<!--B--> {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Baruch, March 1,|2009|p=}} |last1=Baruch |first1=Yehuda|date=March 1, 2009 |title=Once Upon a Time There Was an Organization: Organizational Stories as Antitheses to Fairy Tales |journal=] |volume=18 |issue=1 |pages=15–25 |doi=10.1177/1056492606294522 |s2cid=144074635 }} {{ISSN|1056-4926}}, {{ISSN|1552-6542}}; {{doi|10.1177/1056492606294522}}; {{OCLC|439088502|5234861190}}; {{ProQuest|1928625238|203317764}} (ABI/Inform Collection). | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Jaffe|first=William|middle=J.|title=L.P. Alford and the Evolution of Modern Industrial Management. With an introduction by David B. Porter|publisher=New York University Press|location=New York|year=1957}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Bedeian & Wren, Winter|2001|pp=221–225}} |last1=Bedeian |first1= Arthur G. |author-link1=Arthur G. Bedeian |last2= Wren |first2= Daniel Alan|author-link2=Daniel A. Wren |date=Winter 2001 |title=Most Influential Management Books of the 20th Century |journal= Organizational Dynamics |volume=29 |issue=3 |pages=221–225 |doi=10.1016/S0090-2616(01)00022-5 |url=https://faculty.lsu.edu/bedeian/files/most-influential-management-books-of-the-20th-century.pdf |access-date= March 12, 2017 |via=] }} {{ISSN|0090-2616}}; {{doi|10.1016/S0090-2616(01)00022-5}}; {{OCLC|5198509376}}. | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Kanigel|first=Robert|title=The One Best Way: Frederick Winslow Taylor and the Enigma of Efficiency|year=1997|publisher=Viking|location=New York|id=ISBN 0670864021}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Bernège & Ribeill,|1989|p=}} |last1=Bernège |first1=Paulette |author-link1=Paulette Bernège |date=1989 |title=Le Tuyau: ÉLément Essentiel de Civilisation |trans-title=The Pipe: Essential Element of Civilization |url=https://www.persee.fr/doc/flux_1154-2721_1989_hos_5_1_910 |type=presented by Georges Ribeill |journal=Flux, Numéro Spécial |volume=5 |page=59 |access-date=August 29, 2022 |via=] }} {{doi|10.3406/flux.1989.910}}; {{ISSN|1154-2721}}; {{OCLC|8333955036|4648688853|732458564}}. | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Nelson|first=Daniel|title=Frederick W. Taylor and the Rise of Scientific Management|year=1980|publisher=University of Wisconsin Press|location=Madison|id=ISBN 0299081605}} | |||
| * {{cite book| ref={{SfnRef|Braverman,|1974|pp=43–52}} |last1=Braverman |first1=Harry |author-link1=Harry Braverman |date=1974 |title=Labor and Monopoly Capital: The Degradation of Work in the Twentieth Century |url=https://archive.org/details/labormonopolycap00harr/page/n3/mode/2up |type=see '']'' |url-access=registration |pages=43–52 |access-date=August 29, 2022 |via=] }} {{LCCN|74007785}}; {{ISBN|0-8534-5340-3}}; {{OCLC|13085658|show=all}}. | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Nelson|first=Daniel (ed.)|title=A Mental Revolution: Scientific Management Since Taylor|year=1992|publisher=Ohio State University Press|location=Columbus|id=ISBN 0814205674}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Brown, May|1925|p=}} |last1=Brown |first1=Percy Shiras |author-link1=Percy S. Brown |date=May 1925 |title=The Works and Aims of the Taylor Society |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/1015419 |journal=Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science |volume=119 |pages=134–139 |doi=10.1177/000271622511900121 |jstor=1015419 |s2cid=143498508 }} {{doi|10.1177/000271622511900121}}; {{JSTOR|1015419}}; {{ISSN|0002-7162}}; {{OCLC|5546400949|5723415222}}. | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Weisbord|first=Marvin|middle=R.|year=2004|title=Productive Workplaces Revisited (Chapter 2: Scientific Management Revisited: A Tale of Two Taylors; Chapter 3: The Consulting Engineer: Taylor Invents a New Profession.)|id=ISBN 0787971170|}} | |||
| *<!--C-->{{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Copley,|1923|p=}} |last1=Copley |first1=Frank Barkley |date=1923 |title=Frederick W. Taylor, Father of Scientific Management |publisher=]}} (2 Vols.) {{LCCN|23017530}}; {{OCLC|807494|show=all}}. | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Aitken|first=Hugh|middle=G.J.|year=1960|title=Taylorism at Watertown Arsenal}} | |||
| <ol type="1" start="1"> | |||
| <ol type="i" start="1"> | |||
| <li> {{cite book |title=''Vol. 1'' | year=1923 | publisher=Taylor Society |url=https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=mdp.39015009784839&view=1up&seq=9 |via=] (]) {{free access}} }}</li> | |||
| <li> {{cite book |title=''Vol. 2'' | year=1923 | publisher=Harper and Brothers |url=https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc1.$b97219&view=1up&seq=11 |via=] (]) {{free access}} }}<div style="margin-left:2em"> | |||
| {{hanging indent |text={{cite book |title=''pp. 396–397'' | year=1923 | publisher=Taylor Society |url=https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=mdp.39015009784839&view=1up&seq=452 }} → "The first statement of his management methods in general he reserved for his paper A Piece-Rate System read by him at the Detroit meeting of the ] in June, 1895."}}</div></li></ol></ol> | |||
| *<!--D--> {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|D'Aveni, Winter|2003|p=}} |last1=D'Aveni |first1=Richard Anthony |author-link1=Richard D'Aveni |date=Winter 2003 |title=On Changing the Conversation: Tuck and the Field of Strategy |url=http://www.tuck.dartmouth.edu/faculty/publications/voices_rad.html |type=alumni magazine of the ] at ] |journal=Tuck Today |location=] |access-date=November 22, 2007 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070804050415/http://www.tuck.dartmouth.edu/faculty/publications/voices_rad.html |archive-date=August 4, 2007 |url-status=dead }} {{OCLC|18735559|show=all}}. | |||
| *{{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Drucker, ''The Rise'', Spring|1993|p=}} |last1=Drucker |first1=Peter F. |author-link1=Peter Drucker |date=Spring 1993 |title=The Rise of the Knowledge Society |url=http://archive.wilsonquarterly.com/sites/default/files/articles/WQ_VOL17_SP_1993_Article_02_1.pdf |journal=] |volume=17 |issue=2 |pages=52–71 }} {{OCLC|5234803341|4595414907|8658889301}} & {{OCLC search link|30828911}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Drucker,|1974|p=181}} |last1=Drucker |first1=Peter F. |author-link1=Peter Drucker |date=1974 |title=Management: Tasks, Responsibilities, Practices |url=https://archive.org/details/managementtasksr00druc |url-access=registration |publisher=]| location=New York |via=]}} {{ISBN|978-1-4128-0627-5}}. | |||
| * {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Dumont, September|2012|pp=36–40}} |last=Dumont |first=Marie-Jeanne |date=September 2012 |title=''Si Les Femmes Faisaient Les Maisons'', la Croisade de Paulette Bernège |trans-title=''If Women Made Houses'' – The Crusade of Paulette Bernège |url= |type=re: ]'s 1928 book, ''If Women Made Houses'' |language=fr |journal=] |volume=10 |pages=36–40 }}<div style="margin-left:6em">{{cite book |title=''Transcribed on Éditions'' D-Fiction ''(blog)'' |url=http://d-fiction.fr/2012/12/si-les-femmes-faisaient-les-maisons-la-croisade-de-paulette-bernege |access-date=June 5, 2015 |archive-date=May 6, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160506180936/http://d-fiction.fr/2012/12/si-les-femmes-faisaient-les-maisons-la-croisade-de-paulette-bernege/|url-status=dead |via=]}}</div> | |||
| *{{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Drury,|1918|p=100}} |last1=Drury |first1=Horace Bookwalter |author-link1=Horace Bookwalter Drury |date=1918 |title=Scientific Management; A History and Criticism |url=https://archive.org/details/cu31924002406647/page/n103/mode/2up?view=theater&q=%22one+hundred+patents%22 |type=this is a re-print of Drury's 1915 PhD dissertation at ] |journal=Studies in History, Economics and Public Law |publisher=Edited by the Faculty of Political Science of ] |volume=65 |issue=1, whole no. 157 |page=100 |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} <div style="margin-left:2em">"Mr. Taylor has taken out about one hundred patents, his greatest invention being the discovery between 1898 and 1900, jointly with Mr. Maunsel White, of the Taylor-White process of treating tungsten steel. This invention, according to the highest authorities, has revolutionized the machine shops of the world, enabling tools to cut metal at least three times as rapidly as before. The inventors received $100,000 for the English patents alone. Fame again came to Mr. Taylor upon his publication, in 1906, of the results of the extended researches of himself and others in the art of cutting metals – a work of genuine scientific character, and of the highest practical importance. Mr. Taylor, however, regarded as of far greater moment than all this other work his share in the discovery of the principles of scientific management."</div> | |||
| *<!--E-->{{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Epstein,|1996|pp=579–580}} |last1=Epstein |first1=Marc J. |chapter=Taylor, Frederick Winslow (1856–1915) |chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/histaccounting00chat/page/578/mode/2up |editor-last1=Chatfield |editor-first1=Michael |editor-link1=Michael Chatfield |editor-last2=Vangermeersch |editor-first2=Richard |editor-link2=Richard Vangermeersch |date=1996 |title=History of Accounting: An International Encyclopedia |url=https://archive.org/details/histaccounting00chat/page/578/mode/2up |url-access=registration |location=New York |publisher=] |pages=579–580 |isbn=9780815308096 |access-date=August 29, 2022 |via=] }} | |||
| *<!--F--> {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Fayol,|1949|p=}} |last1=Fayol |first1=Henri |author-link1=Henri Fayol |date=1949 |title=General and Industrial Management |url=https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.13518/page/n5/mode/2up |access-date=August 29, 2022 |via=Internet Archive {{free access}} }} | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Fayol,|1988|p=}} |last1=Fayol |first1=Henri |author-link1=Henri Fayol |date=1988 |editor-last1=Revised by Irwin Gray |title=General and Industrial Management: Henri Fayol's Classic |url=https://archive.org/details/generalindustria0000fayo_c5t2/page/n3/mode/2up |url-access=registration |location=] |publisher=] |isbn=9780273029816 |access-date=August 29, 2022 |via=] }} | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|''Frederick Winslow Taylor, Memorial,|1920|p=}} |last1= |first1= |date=1920 |title=Frederick Winslow Taylor – A Memorial Volume, Being Addresses Delivered at the Funeral of Frederick Winslow Taylor, Cedron, Indian Queen Lane, Germantown, Philadelphia, Pa., March 24, 1915; At a Memorial Meeting Held Under the Auspices of the Society to Promote the Science of Management (Now Taylor Society) University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pa., October 22, 1915; And at Mr. Taylor's Home "Boxly," Chestnut Hill, Philadelphia, Pa., October 23, 1915 |url=https://archive.org/details/frederickwinslow00tayl/page/n7/mode/2up |publisher=] |access-date=August 28, 2022 |via=] (]) {{free access}}}} {{LCCN|21001438}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Frederick Taylor University |author-link1=Frederick Taylor University |title=''"About" → "Frederick Winslow Taylor, M.E., Sc.D."'' |url=http://ftu.edu/about/ |access-date=March 30, 2015 }}<div style="margin-left:6em">The "M.E." represents Taylor's 1883 Bachelor's degree in Mechanical Engineering from ]; the "]" was an honorary degree conferred by ] in 1906.</div> | |||
| * {{cite web |ref={{SfnRef|"F.W. Taylor Collection,"|2001}} |date=2001 |title=F.W. Taylor Collection: Patents |url=http://www.lib.stevens-tech.edu/collections/fwtaylor/guide/part1/patents.html |publisher=Samuel C. Williams Library, ] |access-date=May 4, 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071112144955/http://www.lib.stevens-tech.edu/collections/fwtaylor/guide/part1/patents.html |archive-date=November 12, 2007 |url-status=dead}} ({{URL|https://web.stevens.edu/libraryexhibits/FindingAids/FWT_FindingAid.html|Series III of the Collection – "Patents and Correspondence Relating to Patents"}}) {{OCLC|123905137}}. | |||
| *<!--H--> {{cite web |ref={{SfnRef|Harrison Letter, October 8,|1906}} |last1=Harrison |first1=Charles Custis |author-link1=Charles Custis Harrison |date=October 8, 1906 |title=Letter to Taylor |url=https://stevensarchives.contentdm.oclc.org/digital/collection/p4100coll1/id/1382/ |type=item no. 053G001 |via=] Archives. Frederick Winslow Taylor Collection |access-date=May 5, 2008 }} {{OCLC|123905137}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Head,|2003|p=38–59}} |last1=Head |first1=Simon |date=2003 |title=The New Ruthless Economy – Work and Power in the Digital Age |url=https://archive.org/details/newruthlessecono00head/page/38/mode/2up |url-access=registration |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-516601-9 |access-date=August 29, 2022 |via=] (])}} {{OCLC|762723768|show=all}}. | |||
| * {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Henry,|2003|p=5}} |last=Henry |first=Odile |date=2003 |title=Femmes & Taylorisme: La Rationalisation du Travail Domestique |trans-title=Women & Taylorism: The Rationalization of Domestic Work |url=http://revueagone.revues.org/402|language=fr |journal=] |issue=28 |page=5 |access-date=June 5, 2015}} {{doi|10.4000/revueagone.402}}; {{OCLC|4659970814}}.<div style="margin-left:6em">The article is also included in a compilation book → {{cite book |editor-last1=Vincent |editor-first1=Béatrice |date=2003 |title=Lutte des Sexes & Lutte des Classes |trans-title=Gender Struggle & Class Struggle |language=fr |location=] |publisher=] }} {{ISBN|2-7489-0003-0|978-2-7489-0003-3}}; {{OCLC|491458578|show=all}}.</div> | |||
| * {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Hough & White, September–October|2001|p=}} |last1=Hough |first1=Jill Renee |last2=White |first2=Margaret Alice |date=September–October 2001 |title=Using Stories to Create Change: The Object Lesson of Frederick Taylor's 'Pig-Tale' |journal=] |publisher=] |volume=27 |issue=5 |pages=585–601 }} {{doi|10.1177/014920630102700505}}; {{ProQuest|197150631}} (ABI/Inform Collection); {{ISSN|0149-2063}}; {{OCLC|5568698486|4309090200}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Hughes,|1989|p=190}} |last1=Hughes |first1=Thomas Parke |author-link1=Thomas P. Hughes |date=1989 |title=American Genesis – A Century of Invention and Technological Enthusiasm, 1870–1970 |url=https://archive.org/details/americangenesisc0000hugh/page/190/mode/2up |url-access=registration |location=New York |publisher=] / ] |page=190 |isbn=9780140097412 |access-date=August 29, 2022|via=] (])}} {{LCCN|8939468}}; {{ISBN|0-1400-9741-4|978-0-1400-9741-2}}; {{OCLC|1016217167|show=all}}. | |||
| *<!--J-->{{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Jaffe,|1957|p=}} |last1=Jaffe |first1=William Julian |date=1957 |title=L.P. Alford and the Evolution of Modern Industrial Management |url=https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=mdp.39015023114401&view=1up&seq=9 |type="With an introduction by David B. Porter." See ] (1877–1942) |publisher=] |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} {{LCCN|57007915}}; {{OCLC|367967|show=all}}. | |||
| *<!--K--> {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Kanigel,|1997|pp=182–183, 199}} |last=Kanigel |first=Robert |author-link1=Robert Kanigel |date=1997 |title=The One Best Way: Frederick Winslow Taylor and the Enigma of Efficiency |url=https://archive.org/details/onebestwayfreder00robe |url-access=registration |location=New York |publisher=] |isbn=9780670864027 |via=] }} {{ISBN|978-0-670-86402-7}}. | |||
| * {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Kipping, October|1997|p=}} |last1=Kipping |first1=Matthias |date=October 1997 |title=Consultancies, Institutions and the Diffusion of Taylorism in Britain, Germany and France, 1920s to 1950s |url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00076799700000146 |url-access=subscription |journal=Business History |volume=39 |issue=4 |publisher=], ], ] |pages=67–83 |doi=10.1080/00076799700000146 }} {{doi|10.1080/00076799700000146}}; {{ISSN|0007-6791}}; {{OCLC|4893274429}}.<div style="margin-left:6em">Kipping is a professor at the ].</div> | |||
| *<!--L--> {{cite magazine |ref={{SfnRef|Lepore, October 12,|2009|p=114}} |last1=Lepore |first1=Jill |author-link1=Jill Lepore |date=October 12, 2009 |title=Not So Fast – Scientific Management Started as a Way to Work. How Did It Become a Way of Life? |url=https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2009/10/12/not-so-fast |type=book review → ''The Management Myth – Why the 'Experts' Keep Getting It Wrong'', by ] |magazine=] |volume=85 |issue=32 |page=114 (1st page) |access-date=28 June 2017}} {{ProQuest|233147691}}; {{eISSN|0028-792X}}, {{ISSN|2163-3827}}; {{OCLC|5326941980}}.{{hanging indent |text=In 1908, ], a Harvard economics professor, visited Taylor in Philadelphia. Gay had been frustrated in his efforts to start a business school at Harvard: "I am constantly being told by businessmen that we cannot teach business." After meeting Taylor, Gay declared, "I am convinced that there is a scientific method involved in and underlying the art of business."}} | |||
| *<!--M--> {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Maier,|1970|p=}} |last1=Maier |first1=Charles S. |author-link1=Charles S. Maier |date=1970 |title=Between Taylorism and Technocracy: European Ideologies and the Vision of Industrial Productivity in the 1920s |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/259743 |url-access=subscription |journal=] |volume=5 |issue=2 |pages=27–61 |doi=10.1177/002200947000500202 |jstor=259743 |s2cid=162139561 |access-date=August 29, 2022 }} {{JSTOR|259743}}; {{ISSN|0022-0094}}, {{OCLC|651663797|5548943793|5723522076}}. | |||
| * {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Mee, Spring|1988|p=}} |last1=Mee |first1=John Franklin |date=Spring 1988 |title=SAM – A Short History |url=http://samnational.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/SAMHistory1912-1987b.pdf |type=re: ]. ] issue |journal=SAM Advanced Management Journal |volume=53 |issue=2 |pages=5–12 }} {{EBSCOhost|4613584}} (Business Premier database); {{ISSN|0749-7075}}; {{OCLC|8284291295}}.<div style="margin-left:6em">Mee wrote the article for SAM's ] issue → {{cite journal |last1=Mee |first1=John Franklin |date=September 1963 |title=SAM – A Short History |journal=Advanced Management Journal |volume=28 }} {{OCLC|311111459}}, {{OCLC|29085175|11028187}}.</div> | |||
| * {{cite web |ref={{SfnRef|Miami University,|2003}} |last1=Miami University |author-link1=Miami University |date=2003 |title=Frederick Winslow Taylor |url=http://www.units.muohio.edu/technologyandhumanities/taylor.htm |url-status=dead |type=biographical essay |location=] |access-date=May 4, 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20031124000924/http://www.units.muohio.edu/technologyandhumanities/taylor.htm |archive-date=November 24, 2003 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Mintzberg,|1989|p=}} |editor-last1=Mintzberg |editor-first1=Henry |editor-link1=Henry Mintzberg |date=1989 |title=Mintzberg on Management |url=https://archive.org/details/mintzbergonmanag0000mint/page/332/mode/2up |url-access=registration |location=New York |publisher=The Free Press |isbn=9780029213711 |access-date=August 29, 2022 |via=] }} {{ISBN|978-1-4165-7319-7}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Montgomery,|1989|p=}} |last1=Montgomery |first1=David |author-link1=David Montgomery (historian) |date=1989 |title=The Fall of the House of Labor: The Workplace, the State, and American Labor Activism, 1865–1925 |url=https://archive.org/details/fallofhouseoflab00mont/page/n5/mode/2up |url-access=registration |publisher=] |isbn=9780521379823 |via=] (])}}<div style="margin-left:6em">For the stories about Schmidt, Montgomery refers to → {{cite journal |last1=Wrege |first1=Charles D. |author-link1=Charles D. Wrege |last2=Perroni |first2=Amadeo G. |date=March 1974 |title=Taylor's Pig-Tale: A Historical Analysis of Frederick W. Taylor's Pig-Iron Experiments |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/254767 |url-access=subscription |journal=] |volume=17 |issue=1 |pages=6–27|jstor=254767 }} {{doi|10.5465/254767}}; {{JSTOR|254767}}; {{ISSN|0001-4273}}; {{OCLC|5260887207|5790939267}}.</div> | |||
| *<!--N--> {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Nelson,|1980|p=174}} |last1=Nelson |first1=Daniel Melvin |date=1980 |title=Frederick W. Taylor and the Rise of Scientific Management |url={{GBurl|dWrbAAAAMAAJ|pg=}} |type=snippit view |publisher=] |via=] }} {{LCCN|795411}}; {{ISBN|0-2990-8160-5|978-0-2990-8160-7}}; {{OCLC|6087867|show=all}}. | |||
| *<!--P--> {{cite web |ref={{SfnRef|Papesh, February 14,|1998|p=}} |last1=Papesh |first1=Mary Ellen |date=February 14, 1998 |title=Frederick Winslow Taylor |url=http://mason.gmu.edu/~bbrown/courses/2004fall/puad502/GOVT351_FredTaylorBio%20by%20Papesh.pdf |type=student paper |location=] |publisher=] Business School |access-date=May 4, 2008}} | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|1990|Pascale,|1990|p=27}} |editor-last1=Pascale |editor-first1=Richard Tanner |editor-link1=Richard Pascale |date=1990 |title=Managing on the Edge: How Successful Companies Use Conflict for Competitive Advantage |url=https://archive.org/details/managingonedgehopas00pasc/page/26/mode/2up |url-access=registration |type=quoting ] |publisher=] |page=27 |isbn=9780671624422 |access-date=August 29, 2022 |via=] }} {{LCCN|89048997}}; {{OCLC|316016475|show=all}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Gramsci, ''Selections'',|1929–1931}} |last1=Gramsci |first1=Antonio |author-link1=Antonio Gramsci |editor-last1=Hoare |editor-first1=Quintin |editor-link1=Quintin Hoare |editor-last2=Smith |editor-first2=Geoffrey Nowell |date=1971 |orig-date=1929–1935 |title=Selections From the <u>Prison Notebooks</u> of Antonio Gramsci |url=https://archive.org/details/AntonioGramsciSelectionsFromThePrisonNotebooks/page/n1/mode/2up |type=11th printing |publisher=] |access-date=August 30, 2022 |via=] {{free access}} }} {{LCCN|71168985}} (1st ed.), {{LCCN|72175271}}; {{ISBN|0-7178-0397-X}}; {{OCLC|185485941|show=all}}. | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Gramsci,|1929–1931}} |last1=Gramsci |first1=Antonio |author-link1=Antonio Gramsci |date=1991–2011 |orig-date=1929–1935 |title=Prison Notebooks |trans-title=Quaderni del Carcere |type=translated eds. – 1991, 1992, 1996, 2007, 2008, 2011 – by ]; 1947–2019. See '']'' |series=(3 volumes) |publisher=]}} {{LCCN|91022910}}; {{ISBN|0-2311-5755-X|978-0-2311-5755-1}} (2011 ed.); {{OCLC|210400186|show=all}} | |||
| <ol type="i" start="1"> | |||
| <ol type="i" start="1"> | |||
| <li> {{cite book |title=''Vol. 1'' |url={{GBurl|89JZEfMtwAMC|pg=PR3}} |edition=1992 |via=] (limited preview) }} {{ISBN|0-2310-6082-3|978-0-2310-6082-0}}.</li> | |||
| <li> {{cite book |title=''Vol. 2 (not available online)'' |edition=1992 }} {{ISBN|0-2311-0592-4|978-0-2311-0592-7}}.</li> | |||
| <li> {{cite book |title=''Vol. 3 (not available online)'' |edition=1992 }} {{ISBN|978-0-2311-3944-1}}.</li> | |||
| <li> {{cite book |title=''Vol. 3'' |year=1992 |url=https://archive.org/details/prisonnotebooks0003gram/page/n5/mode/2up |url-access=registration |edition=2007 |via=] (]) }} {{ISBN|978-0-2311-3944-1}}.</li></ol></ol> | |||
| *<!--R--> {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Rinehart,|1975|p=44}} |last1=Rinehart |first1=James W. |date=1975 |title=The Tyranny of Work |url=https://archive.org/details/tyrannyofwork0000rine/page/44/mode/2up |url-access=registration |series=Canadian Social Problems Series |location=] |publisher=Academic Press Canada |page=44 |isbn=9780774730297 |access-date=August 29, 2022 |via=] }} {{LCCN|76355264}}; {{ISBN|0-7747-3029-3}}; {{OCLC|2090135|show=all}}. | |||
| * {{Cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Roeber & Parmelee, March|1909|p=}} |last1=Roeber |first1=Eugene Franz |last2=Parmelee |first2=Howard Coon |date=March 1909 |title=The High-Speed Tool-Steel Patent Decision |url={{GBurl|d5TmAAAAMAAJ |p=105 |dq="taylor"}} |journal=Electrochemical and Metallurgical Industry |volume=7 |issue=3 |pages=105–107 |access-date=February 9, 2016 |via=] (]) {{free access}}}} {{hanging indent |text="The famous patent suit of the ] company against the Niles-Bement-Pond Company for infringement of two fundamental patents of F. W. Taylor and M. White (668,369 and 668,270, both of Feb. 19, 1907,) has been decided in favor of the defendant {{nowrap| ... }}"}}{{hanging indent |text="The decision of the court emphasizes that there is no new composition of steel invented by Taylor and White."}} | |||
| *<!--S--> {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Society for Advancement of Management (link)}} |title=''SAM – Society for Advancement of Management (link)'' |url=https://samnational.org/ }} | |||
| *<!--W--> {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Whitston, Summer|1997|p=}} |last1=Whitston |first1=Kevin |date=Summer 1997 |title=The Reception of Scientific Management by British Engineers, 1890–1914 |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/business-history-review/article/div-classtitlethe-reception-of-scientific-management-by-british-engineers-18901914div/5C7321EAC8074868E3E111EB7933F01F |url-access=subscription |journal=The Business History Review |volume=71 |issue=2 |pages=207–229 |doi=10.2307/3116158 |jstor=3116158 |s2cid=145203181 }} {{OCLC|0007-6805}}; {{JSTOR|3116158}}; {{OCLC|5546532273|5235438781}}. | |||
| * {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Wrege,|1987|p=}} |last1=Wrege |first1=Charles D. |author-link1=Charles D. Wrege |last2=Greenwood |first2=Ronald G. |last3=Hata |first3=Sakae |date=1987 |title=The International Management Institute and Political Opposition to its Efforts in Europe, 1925–1934 |journal=Business and Economic History |citeseerx=10.1.1.392.2216 }} {{JSTOR|23702641}}; {{ISSN|0894-6825}}; {{OCLC|5792788126}}. | |||
| * {{cite journal |ref={{SfnRef|Wren, June 8,|2015|pp=309–327}} |last1=Wren |first1=Daniel Alan |author-link1=Daniel A. Wren |date=June 8, 2015 |title=Implementing the Gantt Chart in Europe and Britain: The Contributions of Wallace Clark |journal=Journal of Management History |volume=21 |issue=3 |pages=309–327|doi=10.1108/JMH-09-2014-0163 }} {{doi|10.1108/JMH-09-2014-0163}}; {{ISSN|1751-1348}}; {{OCLC|5911249398|7054577907|1014430228}}. Online . | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| {{hanging indent |text='''Secondary sources – news media'''}} | |||
| {{refbegin|30em|indent=yes}} | |||
| *<!--N--> {{cite news |ref={{SfnRef|''New York Times'', June 15,|1883|p=8}} |last1=''New York Times'' (''The'') |author-link1=The New York Times |date=June 15, 1883 |title=Stevens Institute Graduates – A Special Department of Applied Electricity to Be Established |work=The New York Times |url=https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1883/06/15/102944947.html?pageNumber=8 |url-access=subscription |volume=32 |issue=9914 |page=8 |access-date=August 30, 2022 |via=] }} | |||
| * {{cite news |ref={{SfnRef|''New York Times'', March 22,|1915|p=9}} |last1=''New York Times'' (''The'') |author-link1=The New York Times |date=March 22, 1915 |title=F.W. Taylor, Expert in Efficiency, Dies |work=The New York Times |url=https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1915/03/22/100146755.html |volume=64 |issue=20876 |page=9 (col. 5) |access-date=March 14, 2008 |via=]}} | |||
| <ol type="i" start="1"> | |||
| Also accessible via: | |||
| <ol type="i" start="1"> | |||
| <li> {{cite book |title=''TimesMachine permalink'' |work=The New York Times |url=https://nyti.ms/3CDh4Wq |url-access=subscription }}</li> | |||
| <li> Online reprint by the ''New York Times'' Leaning Network (online education blog) → {{cite book |date=March 20, 2018 |title=''"On This Day"'' |url=https://archive.nytimes.com/www.nytimes.com/learning/general/onthisday/bday/0320.html |type=''Times'' archive}}</li> | |||
| <li> {{cite book |title=''Newspapers.com'' |url=https://www.newspapers.com/image/20525610/?terms=%22F.%20W.%20Taylor%22&match=1 |url-access=subscription }}</li></ol></ol> | |||
| <div style="margin-left:6em">"Frederick Winslow Taylor, originator of the modern scientific management movement {{nowrap| ... }}"</div> | |||
| *<!--W--> {{cite news |ref={{SfnRef|''Wall Street Journal'', June 13,|1997|p=A17}} |last1=''Wall Street Journal'' (''The'') |author-link1=The Wall Street journal |date=June 13, 1997 |title=Frederick Taylor, Early Century Management Consultant |url=http://www.cftech.com/BrainBank/TRIVIABITS/FredWTaylor.html |page=A17 |access-date=May 4, 2008|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080514135125/http://www.cftech.com/BrainBank/TRIVIABITS/FredWTaylor.html |archive-date=May 14, 2008 |via=]}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| {{hanging indent |text='''Primary sources'''}} | |||
| {{refbegin|30em|indent=yes}} | |||
| *{{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Taylor, ''Principles'',|1919|p=63}} |last1=Taylor |first1=Frederick Winslow |date=1919 |orig-date=1911 |title=The Principles of Scientific Management |url=https://archive.org/details/principlesofscie00taylrich/page/n5/mode/2up |publisher=] |access-date= |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} {{LCCN|11010339}}; {{OCLC|233134|show=all}}.<div style="margin-left:6em">{{cite book |title=The Principles of Scientific Management |url=https://gutenberg.org/ebooks/6435 |via=] {{free access}} }}</div> | |||
| *{{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Taylor, ''Shop'',|1903|p=}} |last1=Taylor |first1=Frederick Winslow |date=1903 |title=Shop Management |publisher=] |url=https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_Am4I-N4XN2QC/page/n7/mode/2up?q=began |location= New York |page= |via=] (]) {{free access}} }} {{OCLC|2365572|show=all}}.<div style="margin-left:6em">{{cite book |title=Shop Management |url=https://gutenberg.org/ebooks/6464 |via=] {{free access}} }}<br />''Shop Management'' began as an address by Taylor to a meeting of the ASME, which published it in pamphlet form. The linked publication is a 1912 re-print.</div> | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{SfnRef|Taylor,|1947|p=}} |last1=Taylor |first1=Frederick Winslow |date=1947 |title=Scientific Management – Comprising <u>Shop Management</u> '''', <u>The Principles of Scientific Management</u> '''', ''"Testimony Before the Special House Committee" '' |url=https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.19671/page/n5/mode/2up |series=With introduction by ] (1875–1955) |type=A Harper International Student Reprint |location=New York, ], London |publisher=] }} {{LCCN|47011978}}; {{OCLC|560540|show=all}}. | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=50em}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text={{cite book |last1=Aitken |first1=Hugh George Jeffrey |date=1960 |title=Taylorism at Watertown Arsenal – Scientific Management in Action, 1908–1915 |url=https://archive.org/details/taylorismatwater0000aitk/page/n5/mode/2up |url-access=registration |type=see ] |publisher=] |via=]}} }} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text={{cite book| last1=Braverman |first1=Harry |author-link1=Harry Braverman |date=1974 |title=Labor and Monopoly Capital: The Degradation of Work in the Twentieth Century |url=https://archive.org/details/labormonopolycap00harr/page/n3/mode/2up |type=see '']'' |url-access=registration |pages=43–52 |access-date=August 29, 2022 |via=] }} {{LCCN|74007785}}; {{ISBN|0-8534-5340-3}}; {{OCLC|13085658|show=all}}.}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text={{cite book |last1=Boddy|first1=David |date=2002 |title=Management: An Introduction |url=https://archive.org/details/managementintrod0000bodd_q5q1/page/n3/mode/2up |url-access=registration |edition=2nd |publisher=Printice Hall |location=New York |isbn=9780273655183 |via=] }} {{ISBN|978-0-273-65518-3}}.}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text={{cite book |last1=Kakar |first1=Sudhir |author-link1=Sudhir Kakar |date=1970 |title=Frederick Taylor: A Study in Personality and Innovation |url=https://archive.org/details/fredericktaylors0000kaka/page/n5/mode/2up |url-access=registration |location=] |publisher=] |isbn=9780262110396 |via=] }} {{LCCN|79122260}}.}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text={{cite book |last1=Kanigel |first1=Robert |author-link1=Robert Kanigel |date=1997 |title=The One Best Way: Frederick Winslow Taylor and the Enigma of Efficiency |location=London |publisher=] }} {{LCCN|9637213}}; {{ISBN|0-6708-6402-1|978-0-6708-6402-7}}; {{OCLC|35814788|show=all}}.}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text={{cite book|last1=Nelson |first1=Daniel Melvin |date=1970 |title=Frederick W. Taylor and the Rise of Scientific Management |location=] |publisher=] }} {{ISBN|978-0-299-08160-7}}.}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text={{cite book |editor-last1=Nelson |editor-first1=Daniel Melvin |date=1992 |title=A Mental Revolution: Scientific Management Since Taylor |url={{GBurl|93ydxDfb-RAC|pg=PR3}} |type=limited preview |publisher=] |via=]}} {{LCCN|91033381}}; {{ISBN|978-0-8142-0567-9}}; {{OCLC|24667484|show=all}}.}} | |||
| * {{hanging indent |text={{cite book|last1=Weisbord |first1=Marvin Ross |date=2004 |title=Productive Workplaces Revisited. ''Chapter 2: "Scientific Management Revisited: A Tale of Two Taylors." Chapter 3: "The Consulting Engineer: Taylor Invents a New Profession" '' |url=https://archive.org/details/productiveworkpl0000weis_d0v4/page/26/mode/2up |url-access=registration |publisher=] |isbn=9780787971175 |via=] }} {{LCCN|2003024760}}; {{ISBN|978-0-7879-7117-5}}.}} | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Commons category}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{Wikiquote}} | |||
| * {{gutenberg author| id=Frederick+Winslow+Taylor | name=Frederick Winslow Taylor}} | |||
| * {{Gutenberg author |id=2055| name=Frederick Winslow Taylor}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Internet Archive author |sname=Frederick Winslow Taylor |sopt=t}} | |||
| * - Full text online | |||
| * {{cite book |title=''Special Collections: Frederick Winslow Taylor'' |url=https://stevensarchives.contentdm.oclc.org/digital/collection/p4100coll1/search |publisher=The Samuel C. Williams Library at the ] has an extensive collection}} {{OCLC|123905137}}. | |||
| * online, more information | |||
| * {{cite book |title=''"Frederick W. Taylor, 1856–1915"'' |url=http://waywiser.fas.harvard.edu/people/7941/ |publisher=Collection of Historical Scientific Instruments, Harvard University }} {{OCLC|77066758}}. | |||
| *, 1911 edition, online | |||
| * {{cite book |title=''Charles D. Wrege Research Papers; Collection Number: 6395'' |url=https://rmc.library.cornell.edu/EAD/htmldocs/KCL06395.html |type=see ]; 1924–2014 |publisher=Kheel Center for Labor-Management Documentation and Archives, ] }} {{OCLC|826068268}}<div style="margin-left:6em">Series III: Frederick W. Taylor{{hanging indent |text=Series X: Boxly: Frederick Taylor's Residence – Includes the 1921 Hawthorne Film, a video tour of Boxly (Frederick W. Taylor's house), and videos on management history and historical research. }}</div> | |||
| *, Stevens Institute of Technology has an extensive collection at its library | |||
| *{{sports links}} | |||
| * | |||
| {{Presidents of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers}} | |||
| {{US National Championships Men's doubles champions}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Taylor, Frederick Winslow}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:44, 13 November 2024
American mechanical engineer (1856–1915)
| Frederick Winslow Taylor | |
|---|---|
 Taylor circa 1907 Taylor circa 1907 | |
| Born | March 20, 1856 (1856-03-20) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S. |
| Died | March 21, 1915(1915-03-21) (aged 59) Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, U.S. |
| Resting place | West Laurel Hill Cemetery Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania, U.S. |
| Education | Phillips Exeter Academy |
| Alma mater | Stevens Institute of Technology (BS) |
| Occupation(s) | Efficiency expert Management consultant |
| Known for | Father of scientific management, efficiency movement and industrial engineering |
| Spouse | Louise M. Spooner |
| Children | 3 |
| Awards | Elliott Cresson Medal (1902) |
Frederick Winslow Taylor (March 20, 1856 – March 21, 1915) was an American mechanical engineer. He was widely known for his methods to improve industrial efficiency. He was one of the first management consultants. In 1909, Taylor summed up his efficiency techniques in his book The Principles of Scientific Management which, in 2001, Fellows of the Academy of Management voted the most influential management book of the twentieth century. His pioneering work in applying engineering principles to the work done on the factory floor was instrumental in the creation and development of the branch of engineering that is now known as industrial engineering. Taylor made his name, and was most proud of his work, in scientific management; however, he made his fortune patenting steel-process improvements. As a result, scientific management is sometimes referred to as Taylorism.
Biography
Taylor was born in 1856 to a Quaker family in Germantown, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Taylor's father, Franklin Taylor, a Princeton-educated lawyer, built his wealth on mortgages. Taylor's mother, Emily Annette Taylor (née Winslow), was an ardent abolitionist and a coworker with Lucretia Mott. His father's ancestor, Samuel Taylor, settled in Burlington, New Jersey, in 1677. His mother's ancestor, Edward Winslow, was one of the fifteen original Mayflower Pilgrims who brought servants or children, and one of eight who had the honorable distinction of Mister. Winslow served for many years as the Governor of the Plymouth colony.
The Taylor family had inherited wealth and property, and the family's assets were maintained by Franklin's older brother, Caleb Newbold Taylor.
Educated early by his mother, Taylor studied for two years in France and Germany and traveled Europe for 18 months. In 1872, he entered Phillips Exeter Academy in Exeter, New Hampshire, with the plan of eventually going to Harvard and becoming a lawyer like his father. In 1874, Taylor passed the Harvard entrance examinations with honors. However, due allegedly to rapidly deteriorating eyesight caused by night study, Taylor chose quite a different path.
Instead of attending Harvard University, Taylor became an apprentice patternmaker and machinist, gaining shop-floor experience at Enterprise Hydraulic Works in Philadelphia (a pump-manufacturing company whose proprietors were friends of the Taylor family). During this time, his eyesight recovered. He left his apprenticeship for six months and represented a group of New England machine-tool manufacturers at Philadelphia's centennial exposition. Taylor finished his four-year apprenticeship and in 1878 became a machine-shop laborer at Midvale Steel Works. At Midvale, he was quickly promoted to time clerk, journeyman machinist, machine shop foreman, research director, and finally chief engineer of the works (while maintaining his position as machine shop foreman). Taylor's fast promotions reflected both his talent and his family's relationship with Edward Clark, part owner of Midvale Steel. (Edward Clark's son Clarence Clark, who was also a manager at Midvale Steel, married Taylor's sister.)

Early on at Midvale, working as a laborer and machinist, Taylor recognized that workmen were working their machines, or themselves, not nearly as hard as they could (a practice that at the time was called "soldiering") and that this resulted in high labor costs for the company. When he became a foreman he expected more output from the workmen. In order to determine how much work should properly be expected, he began to study and analyze the productivity of both the men and the machines (although the word "productivity" was not used at the time, and the applied science of productivity had not yet been developed). His focus on the human component of production Taylor labeled scientific management.
While Taylor worked at Midvale, he and Clarence Clark won the first tennis doubles tournament in the 1881 US National Championships, the precursor of the US Open. Taylor became a student of Stevens Institute of Technology, studying via correspondence and obtaining a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering in 1883. On May 3, 1884, he married Louise M. Spooner of Philadelphia.

From 1890 until 1893 Taylor worked as a general manager and a consulting engineer to management for the Manufacturing Investment Company of Philadelphia, a company that operated large paper mills in Maine and Wisconsin. He was a plant manager in Maine. In 1893, Taylor opened an independent consulting practice in Philadelphia. His business card read "Consulting Engineer - Systematizing Shop Management and Manufacturing Costs a Specialty". Through these consulting experiences, Taylor perfected his management system. His first paper, A Piece Rate System, was presented to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) in June 1895.
In 1898 he joined Bethlehem Steel to solve an expensive machine-shop capacity problem. While at Bethlehem, he discovered the best known and most profitable of his many patents: between 1898 and 1900 Taylor and Maunsel White (né Maunsel White III; 1856–1912; grandson of Maunsel White; 1783–1863) conducted comprehensive empirical tests, and concluded that tungsten alloyed steel doubled or quadrupled cutting speeds. The inventors received US$100,000 (equivalent to about $3,700,000 in 2023) for the English patents alone, although the U.S. patent was eventually nullified.
Taylor was forced to leave Bethlehem Steel in 1901 after discord with other managers. Now a wealthy man, Taylor focused the remainder of his career promoting his management and machining methods through lecturing, writing, and consulting. From 1904 - 1914, Taylor lived in Philadelphia with his wife and three adopted children. In 1910, owing to the Eastern Rate Case, Frederick Winslow Taylor and his Scientific Management methodologies became famous worldwide. In 1911, Taylor introduced his The Principles of Scientific Management paper to the ASME, eight years after his Shop Management paper.
On October 19, 1906, Taylor was awarded an honorary degree of Doctor of Science by the University of Pennsylvania. In the same year, he was elected president of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers. Taylor was elected to the American Philosophical Society in 1912. That same year, he gave testimony to a special committee of the US House of Representatives regarding his own and other systems of management. Taylor eventually became a professor at the Tuck School of Business at Dartmouth College. He was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1915. In early spring of that year, Taylor caught pneumonia and died, one day after his fifty-ninth birthday, on March 21, 1915. He was buried in West Laurel Hill Cemetery, in Bala Cynwyd, Pennsylvania.
Work
| This section contains too many or overly lengthy quotations. Please help summarize the quotations. Consider transferring direct quotations to Wikiquote or excerpts to Wikisource. (December 2019) |
Darwin, Marx, and Freud make up the trinity often cited as the "makers of the modern world." Marx would be taken out and replaced by Taylor if there were any justice... For hundreds of years there had been no increase in the ability of workers to turn out goods or to move goods... When Taylor started propounding his principles, nine out of every 10 working people did manual work, making or moving things, whether in manufacturing, farming, mining, or transportation... By 2010 it will constitute no more than one-tenth... The Productivity Revolution has become a victim of its own success. From now on what matters is the productivity of nonmanual workers. -- Peter Drucker, The Rise of the Knowledge Society Wilson Quarterly (Spring 1993) p.63-65
Taylor's crime, in the eyes of the unions, was his assertion that there is no "skilled work." In manual operations there is only "work." All work can be analyzed the same way... The unions... were craft monopolies, and membership in them was largely restricted to sons or relatives of members. They required an apprenticeship of five to seven years but had no systematic training or work study. The unions allowed nothing to be written down. There were not even blueprints or any other drawings of the work to be done. Union members were sworn to secrecy and forbidden to discuss their work with nonmembers. -- Peter Drucker, The Rise of the Knowledge Society Wilson Quarterly (Spring 1993) p.61-62
Taylor was a mechanical engineer who sought to improve industrial efficiency. He is regarded as the father of scientific management, and was one of the first management consultants and director of a famous firm. In Peter Drucker's description,
Frederick W. Taylor was the first man in recorded history who deemed work deserving of systematic observation and study. On Taylor's 'scientific management' rests, above all, the tremendous surge of affluence in the last seventy-five years which has lifted the working masses in the developed countries well above any level recorded before, even for the well-to-do. Taylor, though the Isaac Newton (or perhaps the Archimedes) of the science of work, laid only first foundations, however. Not much has been added to them since—even though he has been dead all of sixty years.
Taylor's scientific management consisted of four principles:
- Replace rule-of-thumb work methods with methods based on a scientific study of the tasks.
- Scientifically select, train, and develop each employee rather than passively leaving them to train themselves.
- Provide "Detailed instruction and supervision of each worker in the performance of that worker's discrete task"
- Divide work nearly equally between managers and workers, so that the managers apply scientific management principles to planning the work and the workers actually perform the tasks.
Future US Supreme Court justice Louis Brandeis coined the term scientific management in the course of his argument for the Eastern Rate Case before the Interstate Commerce Commission in 1910. Brandeis argued that railroads, when governed according to Taylor's principles, did not need to raise rates to increase wages. Taylor used Brandeis's term in the title of his monograph The Principles of Scientific Management, published in 1911. The Eastern Rate Case propelled Taylor's ideas to the forefront of the management agenda. Taylor wrote to Brandeis, "I have rarely seen a new movement started with such great momentum as you have given this one." Taylor's approach is also often referred to as Taylor's Principles, or, frequently disparagingly, as Taylorism.
Managers and workers
The idea, then, of.. training under a competent teacher into new working habits until he continually and habitually works in accordance with scientific laws, which have been developed by some one else, is directly antagonistic to the old idea that each workman can best regulate his own way of doing the work... the philosophy of the old management puts the entire responsibility upon the workmen, while the philosophy of the new places a great part of it upon the management. -- FW Taylor, The Principles of Scientific Management (1911) p.63
Taylor had very precise ideas about how to introduce his system:
It is only through enforced standardization of methods, enforced adoption of the best implements and working conditions, and enforced cooperation that this faster work can be assured. And the duty of enforcing the adoption of standards and enforcing this cooperation rests with the management alone.
Workers were to be selected appropriately for each task.
One of the very first requirements for a man who is fit to handle pig iron as a regular occupation is that he shall be so stupid and so phlegmatic that he more nearly resembles in his mental make-up the ox than any other type. The man who is mentally alert and intelligent is for this very reason entirely unsuited to what would, for him, be the grinding monotony of work of this character.
Taylor believed in transferring control from workers to management. He set out to increase the distinction between mental (planning work) and manual labor (executing work). Detailed plans, specifying the job and how it was to be done, were to be formulated by management and communicated to the workers.
The introduction of his system was often resented by workers and provoked numerous strikes. The strike at Watertown Arsenal led to the congressional investigation in 1912. Taylor believed the laborer was worthy of his hire, and pay was linked to productivity. His workers were able to earn substantially more than those under conventional management, and this earned him enemies among the owners of factories where scientific management was not in use.
Rhetorical techniques
Taylor promised to reconcile labor and capital.
With the triumph of scientific management, unions would have nothing left to do, and they would have been cleansed of their most evil feature: the restriction of output. To underscore this idea, Taylor fashioned the myth that 'there has never been a strike of men working under scientific management', trying to give it credibility by constant repetition. In similar fashion he incessantly linked his proposals to shorter hours of work, without bothering to produce evidence of "Taylorized" firms that reduced working hours, and he revised his famous tale of Schmidt carrying pig iron at Bethlehem Steel at least three times, obscuring some aspects of his study and stressing others, so that each successive version made Schmidt's exertions more impressive, more voluntary and more rewarding to him than the last. Unlike Emerson, Taylor was not a charlatan, but his ideological message required the suppression of all evidence of worker's dissent, of coercion, or of any human motives or aspirations other than those his vision of progress could encompass. For the stories about Schmidt Montgomery refers to Charles D. Wrege and Amadeo G. Perroni, "Taylor's Pig Tale: A Historical Analysis of Frederick W. Taylor's Pig-Iron experiments" in: Academy of Management Journal, 17 (March 1974), 6-27
Scholarly debate about increased efficiency moving pig iron at Bethlehem's Iron and Steel
Debate about Taylor's Bethlehem study of workers, particularly the stereotypical laborer "Schmidt", continues to this day. One 2009 study supports assertions Taylor made about the quite substantial increase in productivity, for even the most basic task of picking up, carrying and dropping pigs of iron.
Management theory
Taylor thought that by analysing work, the "one best way" to do it would be found. He is most remembered for developing the stopwatch time study, which, combined with Frank Gilbreth's motion study methods, later became the field of time and motion study. He broke a job into its component parts and measured each to the hundredth of a minute. One of his most famous studies involved shovels. He noticed that workers used the same shovel for all materials. He determined that the most effective load was 21½ pounds, and found or designed shovels that for each material would scoop up that amount. He was generally unsuccessful in getting his concepts applied, and was dismissed from Bethlehem Iron Company/Bethlehem Steel Company. Nevertheless, Taylor was able to convince workers who used shovels and whose compensation was tied to how much they produced to adopt his advice about the optimum way to shovel by breaking the movements down into their component elements and recommending better ways to perform these movements. It was largely through his disciples' efforts (most notably Henry Gantt's) that industry came to implement his ideas. Moreover, the book he wrote after parting company with the Bethlehem company, Shop Management, sold well.
Relations with ASME
Taylor's written works were designed for presentation to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). These include Notes on Belting (1894), A Piece-Rate System (1895), Shop Management (1903), Art of Cutting Metals (1906), and The Principles of Scientific Management (1911).
Taylor was president of the ASME from 1906 to 1907. While president, he tried to implement his system into the management of the ASME but met with much resistance. He was able to reorganize only the publications department and that only partially. He also forced out the ASME's longtime secretary, Morris Llewellyn Cooke, and replaced him with Calvin W. Rice. His tenure as president was trouble-ridden and marked the beginning of a period of internal dissension within the ASME during the Progressive Age.
In 1911, Taylor collected a number of his articles into a book-length manuscript, which he submitted to the ASME for publication. The ASME formed an ad hoc committee to review the text. The committee included Taylor allies such as James Mapes Dodge and Henry R. Towne. The committee delegated the report to the editor of the American Machinist, Leon P. Alford. Alford was a critic of the Taylor system and his report was negative. The committee modified the report slightly, but accepted Alford's recommendation not to publish Taylor's book. Taylor angrily withdrew the book and published Principles without ASME approval. Taylor published the trade book himself in 1912.
Taylor's influence
United States

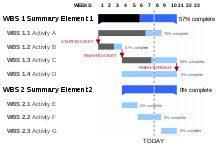
- Carl G. Barth helped Taylor to develop speed-and-feed-calculating slide rules to a previously unknown level of usefulness. Similar aids are still used in machine shops today. Barth became an early consultant on scientific management and later taught at Harvard.
- H. L. Gantt developed the Gantt chart, a visual aid for scheduling tasks and displaying the flow of work.
- Harrington Emerson introduced scientific management to the railroad industry, and proposed the dichotomy of staff versus line employees, with the former advising the latter.
- Morris Cooke adapted scientific management to educational and municipal organizations.
- Hugo Münsterberg created industrial psychology.
- Lillian Gilbreth introduced psychology to management studies.
- Frank Gilbreth (husband of Lillian) discovered scientific management while working in the construction industry, eventually developing motion studies independently of Taylor. These logically complemented Taylor's time studies, as time and motion are two sides of the efficiency improvement coin. The two fields eventually became time and motion study.
- Harvard University, one of the first American universities to offer a graduate degree in business management in 1908, based its first-year curriculum on Taylor's scientific management.
- Harlow S. Person, as dean of Dartmouth's Amos Tuck School of Administration and Finance, promoted the teaching of scientific management.
- James O. McKinsey, professor of accounting at the University of Chicago and founder of the consulting firm bearing his name, advocated budgets as a means of assuring accountability and of measuring performance.
France
In France, Le Chatelier translated Taylor's work and introduced scientific management throughout government owned plants during World War I. This influenced the French theorist Henri Fayol, whose 1916 Administration Industrielle et Générale emphasized organizational structure in management. In the classic General and Industrial Management, Fayol wrote that "Taylor's approach differs from the one we have outlined in that he examines the firm from the 'bottom up.' He starts with the most elemental units of activity – the workers' actions – then studies the effects of their actions on productivity, devises new methods for making them more efficient, and applies what he learns at lower levels to the hierarchy ... " He suggests that Taylor has staff analysts and advisors working with individuals at lower levels of the organization to identify the ways to improve efficiency. According to Fayol, the approach results in a "negation of the principle of unity of command." Fayol criticized Taylor's functional management in this way: In Shop Management, Taylor said « ... the most marked outward characteristics of functional management lies in the fact that each workman, instead of coming in direct contact with the management at one point only, ... receives his daily orders and help from eight different bosses... these eight were (1) route clerks, (2) instruction card men, (3) cost and time clerks, (4) gang bosses, (5) speed bosses, (6) inspectors, (7) repair bosses, and the (8) shop disciplinarian. » Fayol said that this was an unworkable situation and that Taylor must have reconciled the differences in some way not described in Taylor's works.
Around 1922 the journalist Paulette Bernège became interested in Taylor's theories, which were popular in France in the post-war period. Bernège became the faithful disciple of the Domestic Sciences Movement that Christine Frederick had launched earlier in the United States, which Bernège adapted to French homes. Frederick had transferred the concepts of Taylorism from the factory to domestic work. These included suitable tools, rational study of movements and timing of tasks. Scientific standards for housework were derived from scientific standards for workshops, intended to streamline the work of a housewife. The Comité national de l'organisation française (CNOF) was founded in 1925 by a group of journalists and consulting engineers who saw Taylorism as a way to expand their client base. Founders included prominent engineers such as Henry Louis Le Châtelier and Léon Guillet. Bernège's Institute of Housekeeping Organization participated in various congresses on the scientific organization of work that led up to the founding of the CNOF, and in 1929 led to a section in CNOF on domestic economy.
Great Britain
Older historical accounts used to suggest that British industry had less interest in Taylor's teachings than in similarly sized countries. More recent research has revealed that British engineers and managers were as interested as in other countries. This disparity was largely due to what historians have been analysing: recent research has revealed that Taylor's practices diffused to Britain more through consultancies, in particular the Bedaux consultancy, than through institutions, as in Germany and to a lesser extent France, where a mixture was most effective.
Particularly enthusiastic were the Cadbury family, Seebohm Rowntree, Oliver Sheldon and Lyndall Urwick. In addition to establishing a consultancy to implement Taylor's system, Urwick, Orr & Partners, Urwick was also a key historian of F.W. Taylor and scientific management, publishing The Making of Scientific Management trilogy in the 1940s and The Golden Book of Management in 1956.
Switzerland
In Switzerland, the American Edward Albert Filene established the International Management Institute to spread information about management techniques. Lyndall Urwick was its director until the IMI closed in 1933.
USSR
In the Soviet Union, Vladimir Lenin was very impressed by Taylorism, which he and other Bolshevik leaders tried to incorporate into Soviet manufacturing. When Joseph Stalin took power in the 1920s, he championed the theory of "Socialism in one country" which denied that the Soviet economy needed foreign help to develop, and open advocates of Western management techniques fell into disfavor. No longer celebrated by Soviet leadership, Taylorism and the mass production methods of Henry Ford remained silent influences during the industrialization of the Soviet Union. Nevertheless, " Frederick Taylor's methods have never really taken root in the Soviet Union." The voluntaristic approach of Stalin's Stakhanovite movement in the 1930s, fixated on setting individual records, was intrinsically opposed to Taylor's systematic approach and proved to be counter-productive. The stop-and-go of the production process – workers having nothing to do at the beginning of a month and 'storming' during illegal extra shifts at the end of the month – which prevailed even in the 1980s had nothing to do with the successfully taylorized plants e.g., of Toyota which are characterized by continuous production processes (heijunka) which are continuously improved (kaizen).
"The easy availability of replacement labor, which allowed Taylor to choose only 'first-class men,' was an important condition for his system's success." The situation in the Soviet Union was very different. "Because work is so unrhythmic, the rational manager will hire more workers than he would need if supplies were even in order to have enough for storming. Because of the continuing labor shortage, managers are happy to pay needed workers more than the norm, either by issuing false job orders, assigning them to higher skill grades than they deserve on merit criteria, giving them 'loose' piece rates, or making what is supposed to be 'incentive' pay, premia for good work, effectively part of the normal wage. As Mary McAuley has suggested under these circumstances piece rates are not an incentive wage, but a way of justifying giving workers whatever they 'should' be getting, no matter what their pay is supposed to be according to the official norms."
Taylor and his theories are also referenced (and put to practice) in the 1921 dystopian novel We by Yevgeny Zamyatin.
Canada
In the early 1920s, the Canadian textile industry was re-organized according to scientific management principles. In 1928, workers at Canada Cotton Ltd. in Hamilton, Ontario went on strike against newly introduced Taylorist work methods. Also, Henry Gantt, who was a close associate of Taylor, re-organized the Canadian Pacific Railway.
With the prevalence of US branch plants in Canada and close economic and cultural ties between the two countries, the sharing of business practices, including Taylorism, has been common.
The Taylor Society and its legacy
The Taylor Society was founded in 1912 by Taylor's allies to promote his values and influence. A decade after Taylor's death in 1915 the Taylor Society had 800 members, including many leading U.S. industrialists and managers. In 1936 the Society merged with the Society of Industrial Engineers, forming the Society for Advancement of Management, which still exists today.
Criticism of Taylor
Many of the critiques of Taylor come from Marxists. The earliest was by Antonio Gramsci, an Italian Communist, in his Prison Notebooks (1937). Gramsci argued that Taylorism subordinates the workers to management. He also argued that the repetitive work produced by Taylorism might actually give rise to revolutionary thoughts in workers' minds.
Harry Braverman's work Labor and Monopoly Capital: The Degradation of Work in the Twentieth Century, published in 1974, was critical of scientific management and of Taylor in particular. This work pioneered the field of Labor Process Theory as well as contributing to the historiography of the workplace.
Management theorist Henry Mintzberg is highly critical of Taylor's methods. Mintzberg states that an obsession with efficiency allows measurable benefits to overshadow less quantifiable social benefits completely, and social values get left behind.
Taylor's methods have also been challenged by socialists. Their arguments relate to progressive defanging of workers in the workplace and the subsequent degradation of work as management, powered by capital, uses Taylor's methods to render work repeatable and precise yet monotonous and skill-reducing. James W. Rinehart argued that Taylor's methods of transferring control over production from workers to management, and the division of labor into simple tasks, intensified the alienation of workers that had begun with the factory system of production around the period 1870 to 1890.
Criticism of Taylor and the Japanese model, according to Kōnosuke Matsushita:
"We are going to win and the industrial west is going to lose out. There’s nothing you can do about it, because the reasons for failure are within yourselves. Your firms are built on the Taylor model. Even worse, so are your heads. With your bosses doing the thinking while workers wield the screwdrivers, you're convinced deep down that it is the right way to run a business. For the essence of management is getting ideas out of the heads of the bosses and into the heads of labour. We are beyond your mindset. Business, we know, is now so complex and difficult, the survival of firms so hazardous in an environment increasingly unpredictable, competitive and fraught with danger, that their continued existence depends on the day-to-day mobilisation of every ounce of intelligence."
Tennis and golf accomplishments
Taylor was an accomplished tennis and golf player. He and Clarence Clark won the inaugural United States National tennis doubles championship at Newport Casino in 1881, defeating Alexander Van Rensselaer and Arthur Newbold (né Arthur Emlen Newbold; 1859–1920) in straight sets. In the 1900 Summer Olympics, Taylor finished fourth in golf.
| Result | Year | Championship | Surface | Partner | Opponents | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Win | 1881 | U.S. Doubles Championships | Grass | 6–5, 6–4, 6–5 |
Publications
Books
- 1903, 1911. Taylor, Frederick Winslow (1911). Shop Management (With an introduction by Henry R. Towne). New York, London: Harper & Brothers.
- 1911. Taylor, Frederick Winslow (1919) . The Principles of Scientific Management. Harper & Brothers – via Internet Archive (Prelinger Library)
 . LCCN 11-10339; OCLC 233134 (all editions).The Principles of Scientific Management – via Project Gutenberg
. LCCN 11-10339; OCLC 233134 (all editions).The Principles of Scientific Management – via Project Gutenberg  .
. - 1911. Taylor, Frederick Winslow; Thompson, Sanford Eleazer (1907). A Treatise on Concrete, Plain and Reinforced: Materials, Construction, and Design of Concrete and Reinforced Concrete (1st ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons – via Internet Archive (University of Toronto)
 . OCLC 1722781 (all editions).
. OCLC 1722781 (all editions). - 1912. Taylor, Frederick Winslow; Thompson, Sanford Eleazer (1912). Concrete Costs (1st ed.; 1st issue). John Wiley & Sons – via Internet Archive (University of Wisconsin–Madison)
 . LCCN 12-10295; OCLC 2272138 (all editions).
. LCCN 12-10295; OCLC 2272138 (all editions).
Selected articles
- 1894. "Notes on Belting". Transactions. 15. American Society of Mechanical Engineers: 204–259. 1880 – via Internet Archive (University of Toronto)
 . OCLC 1052127574 (all editions).
. OCLC 1052127574 (all editions). - 1896. "A Piece-Rate System". Economic Studies. 1 (2). American Economic Association: 89–129. June 1896 – via Internet Archive (University of Michigan)
 . OCLC 1076000 (all editions).
. OCLC 1076000 (all editions). - 1903. "Shop Management". Transactions (No. 1003). 24. American Society of Mechanical Engineers: 1337–1480. 1880 – via Internet Archive (University of Toronto)
 . OCLC 6077365 (all editions).
. OCLC 6077365 (all editions). - 1906. "On the Art of Cutting Metals". Transactions (No. 1119). 28. American Society of Mechanical Engineers: 31–350. 1880 – via Internet Archive (University of Toronto)
 . OCLC 9057615 (all editions).
. OCLC 9057615 (all editions).
Bibliography
Notes
- ^ New York Times, March 22, 1915, p. 9.
- Wall Street Journal, June 13, 1997, p. A17.
- Bedeian & Wren, Winter 2001, pp. 221–225.
- Epstein, 1996, pp. 579–580.
- Papesh, February 14, 1998.
- Miami University, 2003.
- Hughes, 1989, p. 190.
- Kanigel, 1997, pp. 182–183, 199.
- New York Times, June 15, 1883, p. 8.
- Copley, 1923, pp. 396–397.
- Drury, 1918, p. 100.
- "F.W. Taylor Collection," 2001.
- Roeber & Parmelee, March 1909.
- Harrison Letter, October 8, 1906.
- "APS Member History". search.amphilsoc.org. Retrieved November 22, 2023.
- D'Aveni, Winter 2003.
- "Frederick Winslow Taylor". American Academy of Arts & Sciences. February 9, 2023. Retrieved November 22, 2023.
- Frederick Taylor University.
- Drucker, The Rise, Spring 1993, pp. 63–65.
- Drucker, The Rise, Spring 1993, pp. 61–62.
- Drucker, 1974, p. 181.
- Montgomery, 1989, p. 250.
- Taylor, Principles, 1919, p. 63.
- Taylor, Principles, 1919, p. 83.
- Taylor, Principles, 1919, p. 59.
- Rinehart, 1975, p. 44.
- Taylor 1911, p. 95.
- Montgomery, 1989, p. 254.
- Hough & White, September–October 2001.
- Baruch, March 1, 2009.
- Jaffe, 1957, p. 34.
- Jaffe, 1957, pp. 36–40.
- Nelson, 1980, p. 174.
- Lepore, October 12, 2009, p. 114.
- Fayol, 1988, p. 43.
- Fayol, 1988, p. 44.
- Fayol, 1988.
- Fayol, 1949, p. 68.
- Dumont, September 2012, pp. 36–40.
- Bernège & Ribeill, 1989.
- Henry, 2003, p. 5.
- Maier, 1970.
- Whitston, Summer 1997.
- Kipping, October 1997.
- Wren, June 8, 2015, pp. 309–327.
- Wrege, 1987.
- Atta, April 1986, p. 335.
- Atta, April 1986, p. 331.
- Head, 2003, p. 38–59.
- Atta, April 1986, p. 329.
- Atta, April 1986, p. 333.
- Rinehart, 1975, p. 43.
- Mee, Spring 1988.
- Brown, May 1925.
- Society for Advancement of Management (link).
- Gramsci, Selections, 1929–1931.
- Gramsci, 1929–1931.
- Mintzberg, 1989, p. 333.
- Braverman, 1974, pp. 43–52.
- Rinehart, 1975, pp. 43–52.
- 1990 & Pascale, 1990, p. 27.
- Taylor, Shop, 1903, pp. 1337–1480.
References
Secondary sources – books, journals, magazines, and papers- Atta, Don Van (April 1986). "Why Is There No Taylorism in the Soviet Union?". Comparative Politics. 18 (33): 327–337. doi:10.2307/421614. JSTOR 421614. doi:10.2307/421614; JSTOR 421614; ISSN 0010-4159; OCLC 5548842780, 8313710703, 13565305.
- Baruch, Yehuda (March 1, 2009). "Once Upon a Time There Was an Organization: Organizational Stories as Antitheses to Fairy Tales". Journal of Management Inquiry. 18 (1): 15–25. doi:10.1177/1056492606294522. S2CID 144074635. ISSN 1056-4926, ISSN 1552-6542; doi:10.1177/1056492606294522; OCLC 439088502, 5234861190; ProQuest 1928625238, 203317764 (ABI/Inform Collection).
- Bedeian, Arthur G.; Wren, Daniel Alan (Winter 2001). "Most Influential Management Books of the 20th Century" (PDF). Organizational Dynamics. 29 (3): 221–225. doi:10.1016/S0090-2616(01)00022-5. Retrieved March 12, 2017 – via Louisiana State University. ISSN 0090-2616; doi:10.1016/S0090-2616(01)00022-5; OCLC 5198509376.
- Bernège, Paulette (1989). "Le Tuyau: ÉLément Essentiel de Civilisation" [The Pipe: Essential Element of Civilization]. Flux, Numéro Spécial (presented by Georges Ribeill). 5: 59. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Persée. doi:10.3406/flux.1989.910; ISSN 1154-2721; OCLC 8333955036, 4648688853, 732458564.
- Braverman, Harry (1974). Labor and Monopoly Capital: The Degradation of Work in the Twentieth Century (see Labor and Monopoly Capital). pp. 43–52. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Internet Archive. LCCN 74-7785; ISBN 0-8534-5340-3; OCLC 13085658 (all editions).
- Brown, Percy Shiras (May 1925). "The Works and Aims of the Taylor Society". Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science. 119: 134–139. doi:10.1177/000271622511900121. JSTOR 1015419. S2CID 143498508. doi:10.1177/000271622511900121; JSTOR 1015419; ISSN 0002-7162; OCLC 5546400949, 5723415222.
- Copley, Frank Barkley (1923). Frederick W. Taylor, Father of Scientific Management. Harper & Brothers. (2 Vols.) LCCN 23-17530; OCLC 807494 (all editions).
- Vol. 1. Taylor Society. 1923 – via HathiTrust (University of Michigan Library)
 .
. - Vol. 2. Harper and Brothers. 1923 – via HathiTrust (University of California Libraries)
 .
pp. 396–397. Taylor Society. 1923. → "The first statement of his management methods in general he reserved for his paper A Piece-Rate System read by him at the Detroit meeting of the A.S.M.E. in June, 1895."
.
pp. 396–397. Taylor Society. 1923. → "The first statement of his management methods in general he reserved for his paper A Piece-Rate System read by him at the Detroit meeting of the A.S.M.E. in June, 1895."
- D'Aveni, Richard Anthony (Winter 2003). "On Changing the Conversation: Tuck and the Field of Strategy". Tuck Today (alumni magazine of the Tuck School of Business at Dartmouth). Hanover, New Hampshire. Archived from the original on August 4, 2007. Retrieved November 22, 2007. OCLC 18735559 (all editions).
- Drucker, Peter F. (Spring 1993). "The Rise of the Knowledge Society" (PDF). The Wilson Quarterly. 17 (2): 52–71. OCLC 5234803341, 4595414907, 8658889301 & 30828911.
- Drucker, Peter F. (1974). Management: Tasks, Responsibilities, Practices. New York: Harper & Row – via Internet Archive. ISBN 978-1-4128-0627-5.
- Dumont, Marie-Jeanne (September 2012). "Si Les Femmes Faisaient Les Maisons, la Croisade de Paulette Bernège" [If Women Made Houses – The Crusade of Paulette Bernège]. Criticat (re: Paulette Bernège's 1928 book, If Women Made Houses) (in French). 10: 36–40.Transcribed on Éditions D-Fiction (blog). Archived from the original on May 6, 2016. Retrieved June 5, 2015 – via Wayback Machine.
- Drury, Horace Bookwalter (1918). "Scientific Management; A History and Criticism". Studies in History, Economics and Public Law (this is a re-print of Drury's 1915 PhD dissertation at Columbia). 65 (1, whole no. 157). Edited by the Faculty of Political Science of Columbia University: 100 – via Internet Archive (Cornell University Library)
 . "Mr. Taylor has taken out about one hundred patents, his greatest invention being the discovery between 1898 and 1900, jointly with Mr. Maunsel White, of the Taylor-White process of treating tungsten steel. This invention, according to the highest authorities, has revolutionized the machine shops of the world, enabling tools to cut metal at least three times as rapidly as before. The inventors received $100,000 for the English patents alone. Fame again came to Mr. Taylor upon his publication, in 1906, of the results of the extended researches of himself and others in the art of cutting metals – a work of genuine scientific character, and of the highest practical importance. Mr. Taylor, however, regarded as of far greater moment than all this other work his share in the discovery of the principles of scientific management."
. "Mr. Taylor has taken out about one hundred patents, his greatest invention being the discovery between 1898 and 1900, jointly with Mr. Maunsel White, of the Taylor-White process of treating tungsten steel. This invention, according to the highest authorities, has revolutionized the machine shops of the world, enabling tools to cut metal at least three times as rapidly as before. The inventors received $100,000 for the English patents alone. Fame again came to Mr. Taylor upon his publication, in 1906, of the results of the extended researches of himself and others in the art of cutting metals – a work of genuine scientific character, and of the highest practical importance. Mr. Taylor, however, regarded as of far greater moment than all this other work his share in the discovery of the principles of scientific management." - Epstein, Marc J. (1996). "Taylor, Frederick Winslow (1856–1915)". In Chatfield, Michael; Vangermeersch, Richard (eds.). History of Accounting: An International Encyclopedia. New York: Garland Publishing. pp. 579–580. ISBN 9780815308096. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Internet Archive.
- Fayol, Henri (1949). General and Industrial Management. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Internet Archive
 .
. - Fayol, Henri (1988). Revised by Irwin Gray (ed.). General and Industrial Management: Henri Fayol's Classic. Belmont, California: Pitman Publishing. ISBN 9780273029816. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Internet Archive.
- Frederick Winslow Taylor – A Memorial Volume, Being Addresses Delivered at the Funeral of Frederick Winslow Taylor, Cedron, Indian Queen Lane, Germantown, Philadelphia, Pa., March 24, 1915; At a Memorial Meeting Held Under the Auspices of the Society to Promote the Science of Management (Now Taylor Society) University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pa., October 22, 1915; And at Mr. Taylor's Home "Boxly," Chestnut Hill, Philadelphia, Pa., October 23, 1915. Taylor Society. 1920. Retrieved August 28, 2022 – via Internet Archive (Library of Congress)
 . LCCN 21-1438.
. LCCN 21-1438. - Frederick Taylor University. "About" → "Frederick Winslow Taylor, M.E., Sc.D.". Retrieved March 30, 2015.The "M.E." represents Taylor's 1883 Bachelor's degree in Mechanical Engineering from Stevens Institute of Technology; the "Sc.D." was an honorary degree conferred by Penn in 1906.
- "F.W. Taylor Collection: Patents". Samuel C. Williams Library, Stevens Institute of Technology. 2001. Archived from the original on November 12, 2007. Retrieved May 4, 2008. (Series III of the Collection – "Patents and Correspondence Relating to Patents") OCLC 123905137.
- Harrison, Charles Custis (October 8, 1906). "Letter to Taylor" (item no. 053G001). Retrieved May 5, 2008 – via Stevens Institute of Technology Archives. Frederick Winslow Taylor Collection. OCLC 123905137.
- Head, Simon (2003). The New Ruthless Economy – Work and Power in the Digital Age. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-516601-9. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Internet Archive (Lexington Public Library). OCLC 762723768 (all editions).
- Henry, Odile (2003). "Femmes & Taylorisme: La Rationalisation du Travail Domestique" [Women & Taylorism: The Rationalization of Domestic Work]. Agone (in French) (28): 5. Retrieved June 5, 2015. doi:10.4000/revueagone.402; OCLC 4659970814.The article is also included in a compilation book → Vincent, Béatrice, ed. (2003). Lutte des Sexes & Lutte des Classes [Gender Struggle & Class Struggle] (in French). Marseille: Éditions Agone. ISBN 2-7489-0003-0, 978-2-7489-0003-3; OCLC 491458578 (all editions).
- Hough, Jill Renee; White, Margaret Alice (September–October 2001). "Using Stories to Create Change: The Object Lesson of Frederick Taylor's 'Pig-Tale'". Journal of Management. 27 (5). SAGE Publications: 585–601. doi:10.1177/014920630102700505; ProQuest 197150631 (ABI/Inform Collection); ISSN 0149-2063; OCLC 5568698486, 4309090200.
- Hughes, Thomas Parke (1989). American Genesis – A Century of Invention and Technological Enthusiasm, 1870–1970. New York: Viking Press / Penguin Books. p. 190. ISBN 9780140097412. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Internet Archive (Marygrove College). LCCN 89-39468; ISBN 0-1400-9741-4, 978-0-1400-9741-2; OCLC 1016217167 (all editions).
- Jaffe, William Julian (1957). L.P. Alford and the Evolution of Modern Industrial Management ("With an introduction by David B. Porter." See Leon Pratt Alford (1877–1942)). New York University Press – via HathiTrust (University of Michigan)
 . LCCN 57-7915; OCLC 367967 (all editions).
. LCCN 57-7915; OCLC 367967 (all editions). - Kanigel, Robert (1997). The One Best Way: Frederick Winslow Taylor and the Enigma of Efficiency. New York: Viking Press. ISBN 9780670864027 – via Internet Archive. ISBN 978-0-670-86402-7.
- Kipping, Matthias (October 1997). "Consultancies, Institutions and the Diffusion of Taylorism in Britain, Germany and France, 1920s to 1950s". Business History. 39 (4). Liverpool University Press, Routledge, Taylor & Francis: 67–83. doi:10.1080/00076799700000146. doi:10.1080/00076799700000146; ISSN 0007-6791; OCLC 4893274429.Kipping is a professor at the Schulich School of Business.
- Lepore, Jill (October 12, 2009). "Not So Fast – Scientific Management Started as a Way to Work. How Did It Become a Way of Life?". The New Yorker (book review → The Management Myth – Why the 'Experts' Keep Getting It Wrong, by Matthew Stewart). Vol. 85, no. 32. p. 114 (1st page). Retrieved June 28, 2017. ProQuest 233147691; ISSN 0028-792X, ISSN 2163-3827; OCLC 5326941980.In 1908, Edwin Gay, a Harvard economics professor, visited Taylor in Philadelphia. Gay had been frustrated in his efforts to start a business school at Harvard: "I am constantly being told by businessmen that we cannot teach business." After meeting Taylor, Gay declared, "I am convinced that there is a scientific method involved in and underlying the art of business."
- Maier, Charles S. (1970). "Between Taylorism and Technocracy: European Ideologies and the Vision of Industrial Productivity in the 1920s". Journal of Contemporary History. 5 (2): 27–61. doi:10.1177/002200947000500202. JSTOR 259743. S2CID 162139561. Retrieved August 29, 2022. JSTOR 259743; ISSN 0022-0094, OCLC 651663797, 5548943793, 5723522076.
- Mee, John Franklin (Spring 1988). "SAM – A Short History" (PDF). SAM Advanced Management Journal (re: Society for Advancement of Management. Diamond Anniversary issue). 53 (2): 5–12. EBSCOhost 4613584 (Business Premier database); ISSN 0749-7075; OCLC 8284291295.Mee wrote the article for SAM's Golden Anniversary issue → Mee, John Franklin (September 1963). "SAM – A Short History". Advanced Management Journal. 28. OCLC 311111459, OCLC 29085175, 11028187.
- Miami University (2003). "Frederick Winslow Taylor" (biographical essay). Oxford, Ohio. Archived from the original on November 24, 2003. Retrieved May 4, 2008 – via Wayback Machine.
- Mintzberg, Henry, ed. (1989). Mintzberg on Management. New York: The Free Press. ISBN 9780029213711. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Internet Archive. ISBN 978-1-4165-7319-7.
- Montgomery, David (1989). The Fall of the House of Labor: The Workplace, the State, and American Labor Activism, 1865–1925. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521379823 – via Internet Archive (Boston Public Library).For the stories about Schmidt, Montgomery refers to → Wrege, Charles D.; Perroni, Amadeo G. (March 1974). "Taylor's Pig-Tale: A Historical Analysis of Frederick W. Taylor's Pig-Iron Experiments". Academy of Management Journal. 17 (1): 6–27. JSTOR 254767. doi:10.5465/254767; JSTOR 254767; ISSN 0001-4273; OCLC 5260887207, 5790939267.
- Nelson, Daniel Melvin (1980). Frederick W. Taylor and the Rise of Scientific Management (snippit view). University of Wisconsin Press – via Google Books. LCCN 79-5411; ISBN 0-2990-8160-5, 978-0-2990-8160-7; OCLC 6087867 (all editions).
- Papesh, Mary Ellen (February 14, 1998). "Frederick Winslow Taylor" (PDF) (student paper). Joliet, Illinois: University of St. Francis Business School. Retrieved May 4, 2008.
- Pascale, Richard Tanner, ed. (1990). Managing on the Edge: How Successful Companies Use Conflict for Competitive Advantage (quoting Kōnosuke Matsushita). Simon and Schuster. p. 27. ISBN 9780671624422. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Internet Archive. LCCN 89-48997; OCLC 316016475 (all editions).
- Gramsci, Antonio (1971) . Hoare, Quintin; Smith, Geoffrey Nowell (eds.). Selections From the Prison Notebooks of Antonio Gramsci (11th printing). International Publishers. Retrieved August 30, 2022 – via Internet Archive
 . LCCN 71-168985 (1st ed.), LCCN 72-175271; ISBN 0-7178-0397-X; OCLC 185485941 (all editions).
. LCCN 71-168985 (1st ed.), LCCN 72-175271; ISBN 0-7178-0397-X; OCLC 185485941 (all editions). - Gramsci, Antonio (1991–2011) . Prison Notebooks [Quaderni del Carcere] (translated eds. – 1991, 1992, 1996, 2007, 2008, 2011 – by Joseph Anthony Buttigieg II; 1947–2019. See Prison Notebooks). (3 volumes). Columbia University Press. LCCN 91-22910; ISBN 0-2311-5755-X, 978-0-2311-5755-1 (2011 ed.); OCLC 210400186 (all editions)
- Vol. 1 (1992 ed.) – via Google Books (limited preview). ISBN 0-2310-6082-3, 978-0-2310-6082-0.
- Vol. 2 (not available online) (1992 ed.). ISBN 0-2311-0592-4, 978-0-2311-0592-7.
- Vol. 3 (not available online) (1992 ed.). ISBN 978-0-2311-3944-1.
- Vol. 3 (2007 ed.). 1992 – via Internet Archive (Trent University). ISBN 978-0-2311-3944-1.
- Rinehart, James W. (1975). The Tyranny of Work. Canadian Social Problems Series. Don Mills: Academic Press Canada. p. 44. ISBN 9780774730297. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Internet Archive. LCCN 76-355264; ISBN 0-7747-3029-3; OCLC 2090135 (all editions).
- Roeber, Eugene Franz; Parmelee, Howard Coon (March 1909). "The High-Speed Tool-Steel Patent Decision". Electrochemical and Metallurgical Industry. 7 (3): 105–107. Retrieved February 9, 2016 – via Google Books (University of Michigan Library)
 . "The famous patent suit of the Bethlehem Steel company against the Niles-Bement-Pond Company for infringement of two fundamental patents of F. W. Taylor and M. White (668,369 and 668,270, both of Feb. 19, 1907,) has been decided in favor of the defendant ... ""The decision of the court emphasizes that there is no new composition of steel invented by Taylor and White."
. "The famous patent suit of the Bethlehem Steel company against the Niles-Bement-Pond Company for infringement of two fundamental patents of F. W. Taylor and M. White (668,369 and 668,270, both of Feb. 19, 1907,) has been decided in favor of the defendant ... ""The decision of the court emphasizes that there is no new composition of steel invented by Taylor and White." - SAM – Society for Advancement of Management (link).
- Whitston, Kevin (Summer 1997). "The Reception of Scientific Management by British Engineers, 1890–1914". The Business History Review. 71 (2): 207–229. doi:10.2307/3116158. JSTOR 3116158. S2CID 145203181. OCLC 0007-6805; JSTOR 3116158; OCLC 5546532273, 5235438781.
- Wrege, Charles D.; Greenwood, Ronald G.; Hata, Sakae (1987). "The International Management Institute and Political Opposition to its Efforts in Europe, 1925–1934". Business and Economic History. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.392.2216. JSTOR 23702641; ISSN 0894-6825; OCLC 5792788126.
- Wren, Daniel Alan (June 8, 2015). "Implementing the Gantt Chart in Europe and Britain: The Contributions of Wallace Clark". Journal of Management History. 21 (3): 309–327. doi:10.1108/JMH-09-2014-0163. doi:10.1108/JMH-09-2014-0163; ISSN 1751-1348; OCLC 5911249398, 7054577907, 1014430228. Online here.
- New York Times (The) (June 15, 1883). "Stevens Institute Graduates – A Special Department of Applied Electricity to Be Established". The New York Times. Vol. 32, no. 9914. p. 8. Retrieved August 30, 2022 – via TimesMachine.
- New York Times (The) (March 22, 1915). "F.W. Taylor, Expert in Efficiency, Dies". The New York Times. Vol. 64, no. 20876. p. 9 (col. 5). Retrieved March 14, 2008 – via TimesMachine.
-
Also accessible via:
- TimesMachine permalink.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - Online reprint by the New York Times Leaning Network (online education blog) → "On This Day" (Times archive). March 20, 2018.
- Newspapers.com.
- Wall Street Journal (The) (June 13, 1997). "Frederick Taylor, Early Century Management Consultant". p. A17. Archived from the original on May 14, 2008. Retrieved May 4, 2008 – via Wayback Machine.
- Taylor, Frederick Winslow (1919) . The Principles of Scientific Management. Harper & Brothers – via Internet Archive (Prelinger Library)
 . LCCN 11-10339; OCLC 233134 (all editions).The Principles of Scientific Management – via Project Gutenberg
. LCCN 11-10339; OCLC 233134 (all editions).The Principles of Scientific Management – via Project Gutenberg  .
. - Taylor, Frederick Winslow (1903). Shop Management. New York: American Society of Mechanical Engineers – via Internet Archive (Stanford University Libraries)
 . OCLC 2365572 (all editions).Shop Management – via Project Gutenberg
. OCLC 2365572 (all editions).Shop Management – via Project Gutenberg  .
.
Shop Management began as an address by Taylor to a meeting of the ASME, which published it in pamphlet form. The linked publication is a 1912 re-print. - Taylor, Frederick Winslow (1947). Scientific Management – Comprising Shop Management [1903], The Principles of Scientific Management [1911], "Testimony Before the Special House Committee" [1912] (A Harper International Student Reprint). With introduction by Harlow Stafford Person (1875–1955). New York, Evanston, London: Harper & Row. LCCN 47-11978; OCLC 560540 (all editions).
Further reading
- Aitken, Hugh George Jeffrey (1960). Taylorism at Watertown Arsenal – Scientific Management in Action, 1908–1915 (see Watertown Arsenal). Harvard University Press – via Internet Archive.
- Braverman, Harry (1974). Labor and Monopoly Capital: The Degradation of Work in the Twentieth Century (see Labor and Monopoly Capital). pp. 43–52. Retrieved August 29, 2022 – via Internet Archive. LCCN 74-7785; ISBN 0-8534-5340-3; OCLC 13085658 (all editions).
- Boddy, David (2002). Management: An Introduction (2nd ed.). New York: Printice Hall. ISBN 9780273655183 – via Internet Archive. ISBN 978-0-273-65518-3.
- Kakar, Sudhir (1970). Frederick Taylor: A Study in Personality and Innovation. Cambridge: The MIT Press. ISBN 9780262110396 – via Internet Archive. LCCN 79-122260.
- Kanigel, Robert (1997). The One Best Way: Frederick Winslow Taylor and the Enigma of Efficiency. London: Little, Brown and Company. LCCN 96-37213; ISBN 0-6708-6402-1, 978-0-6708-6402-7; OCLC 35814788 (all editions).
- Nelson, Daniel Melvin (1970). Frederick W. Taylor and the Rise of Scientific Management. Cambridge: The MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-299-08160-7.
- Nelson, Daniel Melvin, ed. (1992). A Mental Revolution: Scientific Management Since Taylor (limited preview). Ohio State University Press – via Google Books. LCCN 91-33381; ISBN 978-0-8142-0567-9; OCLC 24667484 (all editions).
- Weisbord, Marvin Ross (2004). Productive Workplaces Revisited. Chapter 2: "Scientific Management Revisited: A Tale of Two Taylors." Chapter 3: "The Consulting Engineer: Taylor Invents a New Profession" . Jossey-Bass. ISBN 9780787971175 – via Internet Archive. LCCN 2003-24760; ISBN 978-0-7879-7117-5.
See also
External links
- Works by Frederick Winslow Taylor at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about Frederick Winslow Taylor at the Internet Archive
- Special Collections: Frederick Winslow Taylor. The Samuel C. Williams Library at the Stevens Institute of Technology has an extensive collection. OCLC 123905137.
- "Frederick W. Taylor, 1856–1915". Collection of Historical Scientific Instruments, Harvard University. OCLC 77066758.
- Charles D. Wrege Research Papers; Collection Number: 6395 (see Charles D. Wrege; 1924–2014). Kheel Center for Labor-Management Documentation and Archives, Cornell University Library. OCLC 826068268Series III: Frederick W. TaylorSeries X: Boxly: Frederick Taylor's Residence – Includes the 1921 Hawthorne Film, a video tour of Boxly (Frederick W. Taylor's house), and videos on management history and historical research.
- Frederick Winslow Taylor at Olympedia

- American industrial engineers
- American mechanical engineers
- American steel industry businesspeople
- 1856 births
- 1915 deaths
- American business theorists
- American management consultants
- Bethlehem Steel people
- American organizational theorists
- Patternmakers (industrial)
- Presidents of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers
- Fellows of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers
- Public administration scholars
- Quality experts
- Amateur golfers
- American male golfers
- American male tennis players
- American people of English descent
- Burials at West Laurel Hill Cemetery
- Germantown Academy alumni
- Golfers at the 1900 Summer Olympics
- Golfers from Philadelphia
- Grand Slam (tennis) champions in men's doubles
- Deaths from pneumonia in Pennsylvania
- Olympic golfers for the United States
- Phillips Exeter Academy alumni
- Stevens Institute of Technology alumni
- Tennis players from Philadelphia
- Time and motion study
- Tuck School of Business faculty
- United States National champions (tennis)
- 19th-century male tennis players
- 19th-century American engineers
- 20th-century American engineers
- 19th-century American writers
- 20th-century American writers
- 19th-century American businesspeople
- Members of the American Philosophical Society
- 19th-century American sportsmen