| Revision as of 15:43, 28 December 2019 view sourceNorth Shoreman (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers46,519 edits Reverted 1 edit by 2A02:C7F:2C3F:3400:6522:E8FF:1996:128B: Don't see the bias -- also a source was deleted that was unrelated to the edit explanation (TW)Tag: Undo← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 16:04, 22 December 2024 view source Bogazicili (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users5,639 edits →top: adding source and quote | ||
| (702 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description| |
{{Short description|Form of colonialism seeking population replacement with settlers}} | ||
| {{pp|small=yes}} {{Use dmy dates|date=March 2021}} | |||
| {{undue weight|reason=The section on the Middle East focuses only on Israel and ignores the Arab invasion, among other important points|date=March 2014}} | |||
| ] in the 19th century]] | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=November 2012}} | |||
| {{NPOV|date=May 2018}}<!--article uses "colonialism" for ancient colonies (Greek colonies are not usually included under the "‑ism"), and implies "all forms of colonialism are based on exogenous domination", while in reality ancient (and early modern) colonies as often as not built up a settlement in the wilderness without any thought of "domination".--> | |||
| '''Settler colonialism''' is a logic and structure of displacement by ], using ], over an environment for replacing it and its ] with settlements and the society of the settlers.<ref name="Carey2">{{cite journal |last1=Carey |first1=Jane |last2=Silverstein |first2=Ben |date=2 January 2020 |title=Thinking with and beyond settler colonial studies: new histories after the postcolonial |journal=] |volume=23 |issue=1 |pages=1–20 |doi=10.1080/13688790.2020.1719569 |s2cid=214046615 |quote=The key phrases Wolfe coined here – that invasion is a 'structure not an event'; that settler colonial structures have a 'logic of elimination' of Indigenous peoples; that 'settlers come to stay' and that they 'destroy to replace' – have been taken up as the defining precepts of the field and are now cited by countless scholars across numerous disciplines. |doi-access=free |hdl-access=free |hdl=1885/204080 |issn=1368-8790}}</ref><ref name="Cavanagh2">{{cite book |last1=Veracini |first1=Lorenzo |title=The Routledge Handbook of the History of Settler Colonialism |date=2017 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-415-74216-0 |editor1-last=Cavanagh |editor1-first=Edward |page=4 |language=en |chapter=Introduction: Settler colonialism as a distinct mode of domination |quote=Settler colonialism is a relationship. It is related to colonialism but also inherently distinct from it. As a system defined by unequal relationships (like colonialism) where an exogenous collective aims to locally and permanently replace indigenous ones (unlike colonialism), settler colonialism has no geographical, cultural or chronological bounds. It is culturally nonspecific{{nbs}}... It can happen at any time, and everyone is a settler if they are part of a collective and sovereign displacement that moves to stay, that moves to establish a permanent homeland by way of displacement. |editor-last2=Veracini |editor-first2=Lorenzo |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KiglDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA4}}</ref><ref name="McKay2">{{cite journal |last1=McKay |first1=Dwanna L. |last2=Vinyeta |first2=Kirsten |last3=Norgaard |first3=Kari Marie |date=September 2020 |title=Theorizing race and settler colonialism within U.S. sociology |url=https://compass.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/soc4.12821 |journal=Sociology Compass |language=en |volume=14 |issue=9 |doi=10.1111/soc4.12821 |issn=1751-9020 |s2cid=225377069 |url-access=subscription |quote=Settler-colonialism describes the logic and operation of power when colonizers arrive and settle on lands already inhabited by another group. Importantly, settler colonialism operates through a logic of elimination, seeking to eradicate the original inhabitants through violence and other genocidal acts and to replace the existing spiritual, epistemological, political, social, and ecological systems with those of the settler society.}}</ref><ref name="q872"/> | |||
| Settler colonialism is a form of ] (of external origin, coming from the outside) domination typically organized or supported by an ], which maintains a connection or control to the territory through the settler's colonialism.<ref name="oxfordbiblio2">{{cite web |last1=LeFevre |first1=Tate |title=Settler Colonialism |url=http://www.oxfordbibliographies.com/view/document/obo-9780199766567/obo-9780199766567-0125.xml |access-date=19 October 2017 |website=oxfordbibliographies.com |publisher=Tate A. LeFevre |quote=Though often conflated with colonialism more generally, settler colonialism is a distinct imperial formation. Both colonialism and settler colonialism are premised on exogenous domination, but only settler colonialism seeks to replace the original population of the colonized territory with a new society of settlers (usually from the colonial metropole).}}</ref> Settler colonialism contrasts with ], where the imperial power ] to exploit the ] and gain a source of cheap or free ]. As settler colonialism entails the creation of a new society on the conquered territory, it lasts indefinitely unless ] occurs through departure of the settler population or through reforms to colonial structures, settler-indigenous compacts and reconciliation processes.{{Efn|Example reconciliation programmes include: ], and ]s in ], ] and ].}}<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Veracini |first=Lorenzo |date=October 2007 |title=Settler Colonialism and Decolonisation |url=https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A553004478/AONE?u=qut&sid=bookmark-AONE&xid=1b698e4e |journal=Borderlands |volume=6 |issue=2 |url-access=subscription}}</ref> | |||
| Settler colonial studies has often focused on former ], ] and ], which are close to the complete, prototypical form of settler colonialism.<ref name="Englert2">{{cite journal |last1=Englert |first1=Sai |date=2020 |title=Settlers, Workers, and the Logic of Accumulation by Dispossession |journal=] |volume=52 |issue=6 |pages=1647–1666 |bibcode=2020Antip..52.1647E |doi=10.1111/anti.12659 |s2cid=225643194 |hdl-access=free |hdl=1887/3220822}}</ref> However, settler colonialism is not restricted to any specific culture and has been practised by non-Europeans.<ref name="Cavanagh2" /> According to certain ], including ] – the individual who coined the term '']'' – ].<ref name=":7">{{cite book |last=Irvin-Erickson |first=Douglas |author-link=Douglas Irvin-Erickson |chapter=Raphaël Lemkin: Genocide, cultural violence, and community destruction |date=2020 |url=https://ebrary.net/225031/sociology/rapha_l_lemkin_genocide_cultural_violence_community_destruction |title=Cultural Violence and the Destruction of Human Communities |editor1-first=Fiona |editor1-last=Greenland |editor2-first=Fatma Müge |editor2-last=Göçek |publisher=] |doi=10.4324/9781351267083-3 |isbn=978-1-351-26708-3 |s2cid=234701072 |quote=In a footnote, he added that genocide could equally be termed ']', with the Greek ethno meaning 'nation'.}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Short |first1=Damien |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ywE1EAAAQBAJ&q=inherently+genocidal&pg=PP1 |title=Redefining Genocide: Settler Colonialism, Social Death and Ecocide |date=2016 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-84813-546-8 |page=69 |language=en |access-date=1 June 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230316173819/https://books.google.com/books?id=ywE1EAAAQBAJ&q=inherently+genocidal&pg=PP1 |archive-date=16 March 2023 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Moses |first1=A. Dirk |author-link1=A. Dirk Moses |chapter=Empire, Colony, Genocide: Keywords and the Philosophy of History |editor-last1=Moses |editor-first1=A. Dirk |title=Empire, Colony, Genocide: Conquest, Occupation, and Subaltern Resistance in World History |publisher=Berghahn Books |year=2008 |isbn=978-1-84545-452-4 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RBgoNN4MG-YC |pp=8–9 |quote=Extra-European colonial cases also featured prominently in this projected global history of genocide. In 'Part III: Modern Times,' he wrote the following numbered chapters: (1) Genocide by the Germans against the Native Africans; (3) Belgian Congo; (11) Hereros; (13) Hottentots; (16) Genocide against the American Indians; (25) Latin America; (26) Genocide against the Aztecs; (27) Yucatan; (28) Genocide against the Incas; (29) Genocide against the Maoris of New Zealand; (38) Tasmanians; (40) S.W. Africa; and finally, (41) Natives of Australia ... While Lemkin's linking of genocide and colonialism may surprise those who think that his neologism was modeled after the Holocaust of European Jewry, an investigation of his intellectual development reveals that the concept is the culmination of a long tradition of European legal and political critique of colonization and empire.}}</ref> | |||
| Unlike other forms of colonialism, the imperial power does not always represent the same nationality as the settlers. However, the colonizing authority generally views the settlers as ] to the previous inhabitants, which may give settlers’ social movements and political demands greater legitimacy than those of colonized peoples in the eyes of the ] colonies, whereas ] and ] are the main motivation behind other forms of colonialism. Normal colonialism typically ends eventually, whereas settler colonialism lasts indefinitely, except in the rare event of complete evacuation or settler ].<ref name="Wolfe 2006"/> | |||
| ==Origins as a theory== | |||
| Settler colonialism is generally discussed in terms of the one-way flow of British values, which overtake and repudiate the culture and history of the location in question.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Steer|first=P|date=2016|title=Gold and greater Britain: Jevons, Trollope, and settler colonialism|url=|journal=Victorian Studies|volume=3|pages=436|via=Ebscohost}}</ref> Transnational and global studies of settler colonialism often give more importance to the histories of British emigrants rather than the ] that were displaced. Legal proceedings in ] and ] have challenged settler rights, highlighting the lasting effects of colonial takeover, and the continued displacement of Indigenous peoples at the start of the twenty-first century. In the United States, Western Australia and South Africa, government used land allotment as a legal way to take possession of indigenous peoples’ land.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Morgan|first=R|date=2017|title=Indigenous Communities and Settler Colonialism: Land Holding, Loss and Survival in an Interconnected World.|url=|journal=Victorian Studies|volume=2|pages=342|via=Ebscohost}}</ref> | |||
| During the 1960s, settlement and colonization were perceived as separate phenomena from ]. Settlement endeavours were seen as taking place in empty areas, downplaying the Indigenous inhabitants. Later on in the 1970s and 1980s, settler colonialism was seen as bringing high living standards in contrast to the failed political systems associated with classical colonialism. Beginning in the mid-1990s, the field of settler colonial studies was established{{sfn|Veracini|2013|p=}}{{pn|date=July 2024}} distinct but connected to ].<ref>{{cite web |last=Shoemaker |first=Nancy |date=1 October 2015 |title=A Typology of Colonialism {{!}} Perspectives on History |url=https://www.historians.org/publications-and-directories/perspectives-on-history/october-2015/a-typology-of-colonialism |access-date=28 April 2022 |website=]}}</ref> Although often credited with originating the field, Australian historian ] stated that "I didn't invent Settler Colonial Studies. Natives have been experts in the field for centuries."<ref name="Kauanui2">{{cite journal |last1=Kauanui |first1=J. Kēhaulani |date=3 April 2021 |title=False dilemmas and settler colonial studies: response to Lorenzo Veracini: 'Is Settler Colonial Studies Even Useful?' |journal=Postcolonial Studies |language=en |volume=24 |issue=2 |pages=290–296 |doi=10.1080/13688790.2020.1857023 |issn=1368-8790 |s2cid=233986432}}</ref> Additionally, Wolfe's work was preceded by others that have been influential in the field, such as ]'s '']'' and '']'' by ].<ref name="Kauanui2" />{{sfn|Veracini|2013|p=}}{{pn|date=July 2024}} | |||
| ==Definition and concept== | |||
| ==In the ancient world== | |||
| Settler colonialism is a logic and structure, and not a mere occurrence. Settler colonialism takes claim of environments for replacing existing conditions and members of that environment with those of the settlement and settlers. Intrinsically connected to this is the displacement or elimination of existing residents, particularly through destruction of their environment and society.<ref name="Carey2" /><ref name="Cavanagh2" /><ref name="McKay2" /><ref name="q872">{{cite journal | last=Whyte | first=Kyle | title=Settler Colonialism, Ecology, and Environmental Injustice | journal=Environment and Society | volume=9 | issue=1 | date=2018-09-01 | issn=2150-6779 | doi=10.3167/ares.2018.090109 | pages=125–144}}</ref> As such, settler colonialism has been identified as a form of ].<ref name="c827">{{cite journal | last1=Van Sant | first1=Levi | last2=Milligan | first2=Richard | last3=Mollett | first3=Sharlene | title=Political Ecologies of Race: Settler Colonialism and Environmental Racism in the United States and Canada | journal=Antipode | volume=53 | issue=3 | date=2021 | issn=0066-4812 | doi=10.1111/anti.12697 | pages=629–642| bibcode=2021Antip..53..629V }}</ref> | |||
| Settler colonialism has occurred extensively throughout human history, including in the ancient world. | |||
| Some scholars describe the process as inherently ], considering settler colonialism to entail the elimination of existing peoples and cultures,<ref name="Short2">{{cite book |last1=Short |first1=Damien |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ywE1EAAAQBAJ&q=inherently+genocidal&pg=PP1 |title=Redefining Genocide: Settler Colonialism, Social Death and Ecocide |date=2016 |publisher=Bloomsbury Publishing |isbn=978-1-84813-546-8 |page=69 |language=en}}</ref> and not only their displacement (see ], "the intentional destruction of a people in whole or in part").{{cn|date=September 2024}} However, the opposite argument has also been made by ], who argues that all genocide is settler colonial in nature.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Veracini |first1=Lorenzo |author1-link=Lorenzo Veracini |title=Civilian-Driven Violence and the Genocide of Indigenous Peoples in Settler Societies |date=2021 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-000-41177-5 |language=en |chapter=Colonialism, Frontiers, Genocide: Civilian-Driven Violence in Settler Colonial Situations|quote=not only is genocide necessarily settler colonial (even though settler colonialism is not always genocidal or even successful)}}</ref> | |||
| === Greek colonization === | |||
| ] (in red) and ]n (in yellow) colonies around 8th to 6th century BC ]] | |||
| Following the collapse of the Greek Bronze Age, Greek City states, or ''poleis'', began to grow. By the 8<sup>th</sup>century BCE, population growth was no longer sustainable in and around the Aegean, prompting the Ancient Greeks to look to the other shores of the Mediterranean and Black Sea to direct their people to.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Ancient Greece|last=E.|first=Dunstan, William|date=2000|publisher=Harcourt College Publishers|isbn=9780155073838|location=Fort Worth|pages=78|oclc=44612899}}</ref> ], an Ionian Greek city-state on the Western shore of Anatolia, was a rich ''polis'' that was considered to be greatest Greek metropolis.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Colony and Mother City in Ancient Greece|last=Graham|first=A.J|publisher=BiblioBazaar|year=2009|isbn=978-1110286492|location=|pages=98}}</ref> ], in his book ''],'' credits Miletus with founding over 90 colonies, including ] in the Black Sea.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Natural history, a selection|last=Elder|first=Pliny, the|date=1991|publisher=Penguin Books|others=Healy, John F.|isbn=9780140444131|location=London, England|pages=Section 5.122|oclc=25317380}}</ref> Sinope itself founded several Greek colonies in the Black Sea region and flourished in its own right, but the site of Sinope was once a ] port called ''Sinuwa'' before being colonized by the Greeks.<ref>{{Cite book|title=The land of the Hittites : an account of recent explorations and discoveries in Asia Minor|last=John.|first=Garstang|date=2005|publisher=Kegan Paul|isbn=9780710311498|location=London|pages=74|oclc=505349807}}</ref> The Hittite empire, at its height, spanned across Anatolia. The Hittites were a distinct people from the Greeks and contact between the two cultures extended back to the Late Bronze Age during the time of the ].<ref>{{Cite book|title=Troy and Homer : towards a solution of an old mystery|last=Joachim.|first=Latacz|date=2004|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=9780199263080|location=Oxford|pages=60|oclc=70296530}}</ref> | |||
| Depending on the definition, it may be enacted by a variety of means, including mass killing of the previous inhabitants, removal of the previous inhabitants and/or ].<ref name="Wolfe 20062">{{cite journal |last1=Wolfe |first1=Patrick |author1-link=Patrick Wolfe |date=2006 |title=Settler colonialism and the elimination of the native |journal=] |volume=8 |issue=4 |pages=387–409 |doi=10.1080/14623520601056240 |s2cid=143873621 |issn=1462-3528 |doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| Sinope is an example of an αποικία – apoikia (pl.: αποικίαι, apoikiai), which is a colony that eventually develops into a self-determining city state yet keeps cultural ties with its mother city.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Ancient Greece : from prehistoric to Hellenistic times|last=1947-|first=Martin, Thomas R.|date=2000|publisher=Yale University Press|isbn=9780300084931|edition=Updated|location=New Haven|pages=|oclc=560486473|url=https://archive.org/details/ancientgreecefro00mart_1/page/56}}</ref> Greek colonies were founded across the Mediterranean and facilitated the ] of the basin. ], the Roman orator, once made a remark about the extensive colonization movements of the Greeks and spread of their culture by saying “It were as though a Greek fringe has been woven about the shores of the barbarians.”<ref>{{Cite book|title=De re publica, De legibus|last=Tullius.|first=Cicero, Marcus|date=1928|publisher=Harvard University Press|others=Keyes, Clinton Walker, 1888-1943|isbn=9780674992351|location=Cambridge, Mass.|pages=Section 2.9|oclc=685531}}</ref> | |||
| Therefore, colonial settling has been called an invasion or occupation, emphazising the violent reality of colonization and its settling, instead of the more domestic meaning of settling.<ref name="j137">{{cite web | last=Kilroy | first=Peter | title=Discovery, settlement or invasion? The power of language in Australia's historical narrative | website=The Conversation | date=2024-05-22 | url=https://theconversation.com/discovery-settlement-or-invasion-the-power-of-language-in-australias-historical-narrative-57097 | access-date=2024-08-14}}</ref> | |||
| ===Rome=== | |||
| {{Seealso|Romanization (cultural)}} | |||
| The ] and later the ] commonly established settler colonies in newly conquered regions. The colonists were often veterans of the Roman army, who received agricultural land to develop. These agricultural communities provided bastions of loyal citizens in often hostile areas of the Empire, and often accelerated the process of Romanisation among the nearby conquered peoples. Near the city of ] in present-day ], the contemporary settlements of Mezze and Deraya can trace their origins back to villages opened for settlement by the Romans during the third century CE. ], the Roman Emperor from 244–249, designated this area around Damascus a ''colonia'', and encouraged settlement by veterans of the VI Ferrata legion, as commemorated by coins minted in the city around this time.<ref name="Burns 76, 85">{{cite book|last=Burns|first=Ross|title=Damascus: a history|publisher=Routledge|pages=76, 85|isbn=978-0-415-27105-9|year=2005}}</ref> | |||
| Settler colonialism is distinct from migration because immigrants aim to join an existing society, not replace it.{{sfn|Veracini|2015|p=40}}{{Sfn|Mamdani|2020|p=253}} ] writes, "Immigrants are unarmed; settlers come armed with both weapons and a nationalist agenda. Immigrants come in search of a homeland, not a state; for settlers, there can be no homeland without a state."{{Sfn|Mamdani|2020|p=253}} Nevertheless, the difference is often elided by settlers who minimize the voluntariness of their departure, claiming that settlers are mere migrants, and some pro-indigenous positions which militantly simplify, claiming that all migrants are settlers.{{sfn|Veracini|2015|p=35}} | |||
| ==Medieval Eras== | |||
| ===Germany=== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{main|Ostsiedlung|Drang nach Osten|History of German settlement in Central and Eastern Europe}} | |||
| Ostsiedlung was the medieval eastward migration and settlement of ] ]s into less-populated regions of ], parts of west ], and the ]. | |||
| The '''settler state''' is a state established through settler colonialism, by and for settlers.<ref name="j642">{{cite book | last=Tozer | first=Angela | title=Constant Struggle: Histories of Canadian Democratization | chapter=Democracy in a Settler State?: Settler Colonialism and the Development of Canada, 1820–67 | publisher=McGill-Queen's University Press | year=2021 | isbn=978-0-2280-0866-8 | jstor=j.ctv1z7kjww.7 | url=http://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctv1z7kjww.7 | access-date=2024-11-09 | pages=87–115| doi=10.2307/j.ctv1z7kjww.7 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Japan=== | |||
| Natives called ] (Tang China: 毛人) in ] lived politically independent yet in constant battle with settlers and conquerors from further south, with Kyoto's victory over them in 802 A.D., after which there was cultural extinction and forced assimilation gradually erasing their culture and ethnicity by the time of the ]. | |||
| == Examples == | |||
| ==In early modern and modern times== | |||
| ] | |||
| During the ], some European ] and their agents adopted policies of ], competing with each other to establish colonies outside of Europe, at first in the Americas, and later in Asia, Africa, and Oceania. | |||
| The settler colonial paradigm has been applied to a wide variety of conflicts around the world, including ],<ref>{{cite news |date=3 October 2020 |title=New Caledonia set for 2nd referendum on independence from France |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2020/10/3/new-caledonia-set-for-2nd-referendum-on-independence-from-france |work=]}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite news |last1=McNamee |first1=Lachlan |date=15 May 2020 |title=Indonesian Settler Colonialism in West Papua |url=https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3601528 |ssrn=3601528}}</ref> the ], ],<ref>{{cite book |last=Larson |first=Carolyne R. |url=https://muse.jhu.edu/book/78336 |title=The Conquest of the Desert: Argentina's Indigenous Peoples and the Battle for History |publisher=University of New Mexico Press |year=2020 |isbn=9780826362087 |page=}}</ref> ], ], the ],<ref name="Adhikari20172">{{cite journal |last1=Adhikari |first1=Mohamed |author-link=Mohamed Adhikari |date=7 September 2017 |title=Europe's First Settler Colonial Incursion into Africa: The Genocide of Aboriginal Canary Islanders |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/17532523.2017.1336863 |journal=] |volume=49 |issue=1 |pages=1–26 |doi=10.1080/17532523.2017.1336863 |s2cid=165086773 |access-date=7 May 2022}}</ref> ], ],<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Barclay |first1=Fiona |last2=Chopin |first2=Charlotte Ann |last3=Evans |first3=Martin |date=12 January 2017 |title=Introduction: settler colonialism and French Algeria |journal=] |volume=8 |issue=2 |pages=115–130 |doi=10.1080/2201473X.2016.1273862 |s2cid=151527670 |doi-access=free |hdl-access=free |hdl=1893/25105}}</ref> ], ],<ref>{{cite journal |last=Takumi |first=Roy |date=1994 |title=Challenging U.S. Militarism in Hawai'i and Okinawa |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/41555279 |journal=Race, Poverty & the Environment |volume=4/5 |issue=4/1 |pages=8–9 |issn=1532-2874 |jstor=41555279}}</ref> ], ],<ref>Connolly, S. (2017). Settler colonialism in Ireland from the English conquest to the nineteenth century. In E. Cavanagh, & L. Veracini (Eds.), ''The Routledge Handbook of the History of Settler Colonialism'' (pp. 49-64). Article 4 ].</ref> ], ] and ],<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Ertola |first1=Emanuele |date=15 March 2016 |title='Terra promessa': migration and settler colonialism in Libya, 1911–1970 |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/2201473X.2016.1153251 |journal=Settler Colonial Studies |volume=7 |issue=3 |pages=340–353 |doi=10.1080/2201473X.2016.1153251 |s2cid=164009698 |access-date=7 May 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Veracini |first1=Lorenzo |date=Winter 2018 |title=Italian Colonialism through a Settler Colonial Studies Lens |url=https://muse.jhu.edu/article/712080 |journal=Journal of Colonialism and Colonial History |volume=19 |issue=3 |doi=10.1353/cch.2018.0023 |s2cid=165512037 |access-date=7 May 2022}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite journal |last=Raman |first=Anita D. |year=2004 |title=Of Rivers and Human Rights: The Northern Areas, Pakistan's forgotten colony in Jammu and Kashmir. |url=http://www.jstor.org/stable/24675261 |journal=] |volume=11 |issue=1/2 |pages=187–228 |doi=10.1163/157181104323383929 |jstor=24675261}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Mushtaq |first1=Samreen |last2=Mudasir |first2=Amin |date=16 October 2021 |title='We will memorise our home': exploring settler colonialism as an interpretive framework for Kashmir |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/01436597.2021.1984877 |journal=] |volume=42 |issue=12 |pages=3012–3029 |doi=10.1080/01436597.2021.1984877 |s2cid=244607271 |access-date=7 May 2022}}</ref> ] and ],<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Lu |first1=Sidney Xu |date=June 2019 |title=Eastward Ho! Japanese Settler Colonialism in Hokkaido and the Making of Japanese Migration to the American West, 1869–1888 |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-asian-studies/article/abs/eastward-ho-japanese-settler-colonialism-in-hokkaido-and-the-making-of-japanese-migration-to-the-american-west-18691888/540D1FCAC210EBAC61BE93712B01A6AB |journal=The Journal of Asian Studies |volume=78 |issue=3 |pages=521–547 |doi=10.1017/S0021911819000147 |s2cid=197847093 |access-date=7 May 2022}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Uchida |first=Jun |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/j.ctt1x07x37 |title=Brokers of Empire: Japanese Settler Colonialism in Korea, 1876–1945 |date=3 March 2014 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0674492028 |volume=337 |doi=10.2307/j.ctt1x07x37 |jstor=j.ctt1x07x37 |s2cid=259606289}}</ref> ], ], ], ],<ref name="sciencedirect12">{{cite journal |author=Christian Bleuer |year=2012 |title=State-building, migration and economic development on the frontiers of northern Afghanistan and southern Tajikistan |journal=] |volume=3 |pages=69–79 |doi=10.1016/j.euras.2011.10.008 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name="afghanistan-analysts12">{{cite web |last=Bleuer |first=Christian |date=October 17, 2014 |title=From 'Slavers' to 'Warlords': Descriptions of Afghanistan's Uzbeks in Western Writing |url=https://www.afghanistan-analysts.org/from-slavers-to-warlords-descriptions-of-afghanistans-uzbeks-in-western-writing/ |publisher=]}}</ref><ref name="brookings12">{{cite web |last1=Mundt |first1=Alex |last2=Schmeidl |first2=Susanne |last3=Ziai |first3=Shafiqullah |date=June 1, 2009 |title=Between a Rock and a Hard Place: The Return of Internally Displaced Persons to Northern Afghanistan |url=http://www.brookings.edu/research/opinions/2009/06/01-afghanistan-mundt |publisher=]}}</ref><ref name="autogenerated20022">{{cite web |date=April 2002 |title=Paying for the Taliban's Crimes: Abuses Against Ethnic Pashtuns in Northern Afghanistan |url=https://www.hrw.org/reports/2002/afghan2/afghan0402.pdf |publisher=]}}</ref> ], ] and ] and ],<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Lerp |first1=Dörte |date=11 October 2013 |title=Farmers to the Frontier: Settler Colonialism in the Eastern Prussian Provinces and German Southwest Africa |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/03086534.2013.836361 |journal=Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History |volume=41 |issue=4 |pages=567–583 |doi=10.1080/03086534.2013.836361 |s2cid=159707103 |access-date=7 May 2022}}</ref> ], ],<ref name="Adhikari20222">{{cite book |last=Adhikari |first=Mohamed |author-link=Mohamed Adhikari |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ht9dEAAAQBAJ |title=Destroying to Replace: Settler Genocides of Indigenous Peoples |date=25 July 2022 |publisher=Hackett Publishing Company |isbn=978-1647920548 |location=Indianapolis |pages=1–32}}</ref>{{sfn|Veracini|2013|p=}}{{pn|date=July 2024}}<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Browning |first1=Christopher R. |date=8 February 2022 |title=Yehuda Bauer, the Concepts of Holocaust and Genocide, and the Issue of Settler Colonialism |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/25785648.2021.2012985 |journal=The Journal of Holocaust Research |volume=36 |issue=1 |pages=30–38 |doi=10.1080/25785648.2021.2012985 |s2cid=246652960 |access-date=30 April 2022}}</ref> <ref>{{cite book |last1=Rahman |first1=Smita A. |title=Globalizing Political Theory |last2=Gordy |first2=Katherine A. |last3=Deylami |first3=Shirin S. |publisher=] |year=2022 |isbn=9781000788884}}</ref> ], ],<ref>{{cite book |last=Salemink |first=Oscar |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2_zKFyHlBk0C&pg=PA35 |title=The Ethnography of Vietnam's Central Highlanders: A Historical Contextualization, 1850–1990 |publisher=] |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-8248-2579-9 |pages=35–336}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Nguyen |first=Duy Lap |title=The unimagined community: Imperialism and culture in South Vietnam |publisher=] |year=2019 |isbn=978-1-52614-398-3}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last=Schweyer |first=Anne-Valérie |year=2019 |title=The Chams in Vietnam: a great unknown civilization |url=http://www.gis-reseau-asie.org/en/chams-vietnam-great-unknown-civilization |website=French Academic Network of Asian Studies |access-date=31 October 2023 |archive-date=2 July 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220702153040/http://www.gis-reseau-asie.org/en/chams-vietnam-great-unknown-civilization |url-status=dead }}</ref> and ].<ref name="Englert2" /><ref>{{Cite thesis |title=Re-conceptualizing Taiwan: Settler Colonial Criticism and Cultural Production |url=https://escholarship.org/uc/item/30h7d8r5 |publisher=] |date=2019 |language=en |first=Lin-chin |last=Tsai}}</ref> | |||
| === Africa === | |||
| {{Expand section|date=December 2010}} | |||
| {{Seealso|White Africans of European ancestry|French conquest of Algeria}} | |||
| ] colonial empires in 1913, shown with current national boundaries | |||
| {{Legend|#f7fab2|]}} | |||
| {{Legend|#b6e3fc|]}} | |||
| {{Legend|#bbfdd9|]}} | |||
| {{Legend|#d2f89b|]}} | |||
| {{Legend|#c0a6f2|]}} | |||
| {{Legend|#eaaff7|]}} | |||
| {{Legend|#fbc5c0|]}} | |||
| {{Legend|#f6f6f6|Independent}}]] | |||
| [[File:European settlement in Africa map1962.png|thumb|Geographic distribution of Europeans and their descendants on the African continent in 1962.<ref name=Cowan>{{cite book|last=Cowan|first=L. Gray|title=The Dilemmas of African Independence|date=1964|pages=42–55, 105 |publisher=Walker & Company, Publishers|location=New York|asin=B0007DMOJ0}}</ref> | |||
| ===In the Americas=== | |||
| {{Div col|colwidth=30em}} | |||
| {{further|Christianization|European colonization of the Americas}} | |||
| {{legend|#EDF8E9|Under 1,000}} | |||
| ] in 1750]] | |||
| {{legend|#BAE4B3|Over 1,000}} | |||
| European colonization of the Americas began as early as the 10th century, when Norse sailors explored and settled limited areas on the shores of present-day Greenland and Canada.<ref name="ReferenceA">Wolfe 2006</ref> According to Norse folklore, violent conflicts with the indigenous population ultimately made the Norse abandon those settlements. | |||
| {{legend|#74C476|Over 10,000}} | |||
| {{legend|#31A354|Over 50,000}} | |||
| {{legend|#006D2C|Over 100,000}} | |||
| {{colend}}]] | |||
| ==== Canary Islands ==== | |||
| Extensive European colonization began in 1492, when a Spanish expedition headed by Genoese Christopher Columbus sailed west to find a new trade route to the Far East but inadvertently landed in the Americas. European conquest, large-scale exploration, colonization and industrial development soon followed. Columbus's first two voyages (1492–93) reached the Bahamas and various Caribbean islands, including Hispaniola, Puerto Rico and Cuba. In 1497, sailing from Bristol on behalf of England, John Cabot landed on the North American coast, and a year later, Columbus's third voyage reached the South American coast. As the sponsor of Christopher Columbus's voyages, Spain was the first European power to settle and colonize the largest areas, from North America and the Caribbean to the southern tip of South America. Spanish cities were founded as early as 1496 with Santo Domingo in today's Dominican Republic. | |||
| {{further|Conquest of the Canary Islands}} | |||
| During the fifteenth century, the ] sponsored expeditions by ] to subjugate under Castilian rule the ] archipelago of the Canary Islands, located off the coast of ] and inhabited by the Indigenous ] people. Beginning with the start of the conquest of the island of ] on 1 May 1402 and ending with the surrender of the last Guanche resistance on ] on 29 September 1496 to the now-unified ], the archipelago was subject to a settler colonial process involving systematic enslavement, mass murder, and deportation of the Guanches, who were replaced with Spanish settlers, in a process foreshadowing the Iberian colonisation of the Americas that followed shortly thereafter. Also like in the Americas, Spanish colonialists in the Canaries quickly turned to the importation of slaves from mainland Africa as a source of labour due to the decimation of the already small Guanche population by a combination of war, disease, and brutal forced labour. Historian ] has labelled the conquest of the Canary Islands as the first overseas European settler colonial genocide.<ref name="Adhikari20172" /><ref name="Adhikari20222" /> | |||
| ==== Moroccan-occupied Western Sahara ==== | |||
| Other powers such as France also founded colonies in the Americas: in eastern North America, a number of Caribbean islands, and small coastal parts of South America. Portugal colonized Brazil, tried early (since 1499) colonizing of the coasts of present-day Canada, and sat for extended periods on the northwest bank of the River Plate (including it in the Brazilian region). This was the beginning of a dramatic territorial expansion for several European countries. Europe had been preoccupied with internal wars, and was only slowly recovering from the loss of population caused by the bubonic plague; thus the rapid rate at which it grew in wealth and power was unforeseeable in the early 15th century.<ref>"settlercolonialstudies.org"</ref> | |||
| ] in 1975]] | |||
| Since 1975, the ] has sponsored settlement schemes that have encouraged several thousand Moroccan citizens to settle ] ] as part of the ]. On 6 November 1975, the ] took place, during which about 350,000 Moroccan citizens crossed into ] in the former ] after having received a signal from King Hassan II.<ref>{{cite web |last=Hamdaoui |first=Neijma |date=31 October 2003 |title=Hassan II lance la Marche verte |trans-title=Hassan II launches the Green March |url=http://www.jeuneafrique.com/jeune_afrique/article_jeune_afrique.asp?art_cle=LIN02113hassaetreve0 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060103155727/https://www.jeuneafrique.com/jeune_afrique/article_jeune_afrique.asp?art_cle=LIN02113hassaetreve0 |archive-date=3 January 2006 |access-date=21 April 2015 |website=JeuneAfrique.com |language=fr}}</ref> As of 2015, it is estimated that ] constitute two-thirds of the population of Western Sahara.<ref>{{cite news |last=Shefte |first=Whitney |date=6 January 2015 |title=Western Sahara's stranded refugees consider renewal of Morocco conflict |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2015/jan/06/morocco-western-sahara-referendum-delay |work=]}}</ref> | |||
| Under international law, the transfer of Moroccan citizens into the occupied territory constitutes a direct violation of ] ({{Text|cf. ] and ]}}).<ref>{{Cite web |title=Mixed Reviews for Morocco as Fourth Committee Hears Petitioners on Western Sahara, Amid Continuing Decolonization Debate | Meetings Coverage and Press Releases |url=https://www.un.org/press/en/2018/gaspd664.doc.htm |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| Eventually, the entire Western Hemisphere came under the ostensible control of European governments, leading to profound changes to its landscape, population, and plant and animal life. In the 19th century alone over 50 million people left Europe for the Americas.<ref name="Burns 76, 85"/> The post-1492 era is known as the period of the ], a widespread exchange of animals, plants, culture, human populations (including slaves), communicable disease, and ideas between the Pan-American and Afro-Eurasian hemispheres following Columbus's voyages to the Americas. | |||
| ==== South Africa ==== | |||
| ===Settler colonialism in the United States=== | |||
| {{Main|Free Burghers in the Dutch Cape Colony}} | |||
| {{Seealso|California Genocide|Cultural assimilation of Native Americans}} | |||
| ] family traveling by covered wagon circa 1900]] | |||
| In the context of the ], early colonial powers generally respected the territorial and political sovereignty of the indigenous tribes, due to the need to forge local alliances with these tribes against other European colonial powers (i.e. British attempts to check French influence, etc.).{{cn|date=April 2018}} However, with the emergence of an independent United States, desire for land and the perceived threat of permanent indigenous political and spatial structures led to violent relocation of many indigenous tribes to the American West, including the notable example of the Cherokee in what is known as the ].<ref name="ReferenceA"/> While the United States government and local state governments directly aided this dispossession through the use of military forces, ultimately this came about through agitation by settler society in order to gain access to indigenous land, which in some cases (especially in the American South) used in order to build a plantation society and perpetuate the practice of slavery in the creation of said plantation.<ref name="ReferenceA"/> | |||
| In 1652, the arrival of Europeans sparked the beginning of settler colonialism in South Africa. The ] was set up at the Cape, and imported large numbers of slaves from Africa and Asia during the mid-seventeenth century.<ref name=":02">{{Cite book |last=Cavanagh |first=E |title=Settler colonialism and land rights in South Africa: Possession and dispossession on the Orange River |publisher=] |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-137-30577-0 |location=United Kingdom |pages=10–16}}</ref> The Dutch East India Company established a refreshment station for ships sailing between Europe and the east. The initial plan by Dutch East India Company officer ] was to maintain a small community around the new fort, but the community continued to spread and settle further than originally planned.<ref name=":52">{{Cite journal |last=Fourie |first=J |date=2014 |title=Settler Skills and Colonial Development: The Huguenot Wine-Makers in Eighteenth-Century Dutch South Africa |journal=] |volume=67 |issue=4 |pages=932–963 |doi=10.1111/1468-0289.12033 |s2cid=152735090}}</ref> There was a historic struggle to achieve the intended British sovereignty that was achieved in other parts of the ]. State sovereignty belonged to the ] (1910–1961), followed by the ] (1961–1994) and finally the modern day ] (1994–present day).<ref name=":02" /> | |||
| In 1948, the policy of ] was introduced South Africa in order to segregate the races and ensure the domination of the ] minority over non-whites, politically, socially and economically.<ref name="Mayne2">{{cite book |last=Mayne |first=Alan |title=From Politics Past to Politics Future: An Integrated Analysis of Current and Emergent Paradigms |date=1999 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-275-96151-0 |location=Westport, Connecticut |page=52}}</ref> As of 2014, the South African government has re-opened the period for land claims under the Restitution of Land Rights Amendment Act.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Weinberg |first=T |date=2015 |title=The Griqua Past and the Limits of South African History, 1902–1994; Settler Colonialism and Land Rights in South Africa: Possession and Dispossession on the Orange River |journal=] |volume=41 |pages=211–214 |doi=10.1080/03057070.2015.991591 |s2cid=144750398}}</ref> | |||
| ]{{endash}}portions of each territory were granted statehood since the 18th century.]] | |||
| This forcible relocation of tribes came about in part through the mentality of '']'', the mentality that it was the right and destiny of the United States to expand its territory and its rule across the North American continent, to the Pacific coast.<ref>The History Channel; ''Manifest Destiny''. http://www.history.com/topics/manifest-destiny</ref> Through various armed conflicts between indigenous tribes on one side, with settler society backed by American military power on the other side, along with an increasing number of treaties centering around land cessation, Native American tribes were slowly pushed onto a system of ], where they traded territory for protection and support from the United States government.<ref>Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fishing Commission, ''Treaties: Promises between Governments''. http://www.critfc.org/member_tribes_overview/treaty-q-a/</ref><ref>Calloway, Colin G. First Peoples-A Documentary Survey of American Indian History. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martin's, 2008.</ref> However, this system could be disadvantageous for tribes, as they often were forced to relocate to reservations far from their traditional homelands, or had trouble obtaining goods and annuity payments that were promised by the government, leading to further armed revolts and conflicts such as the ] in ].<ref>Anderson, Gary Clayton, and Alan R. Woodworth, eds. Through Dakota Eyes-Narrative Accounts of the Minnesota Indian War of 1862. St. Paul, MN: Minnesota Historical Society Press, 1988.</ref> | |||
| ==== Liberia ==== | |||
| Following the conclusion of U.S./Native American ] in the late 1800s, displacement of indigenous peoples and identities switched to a more legal basis. Attempts were made to assimilate them into American society while stripping away territory; legislation like the ] of 1887 led to the division of previously communally held indigenous lands into individually owned pieces of land that were to be held by tribal members.<ref>Indian Land Tenure Foundation, ''Land Tenure History''. 'https://iltf.org/land-issues/history/</ref> While 'allotment' was as mentioned held up as a way to help indigenous people become 'civilized' and further assimilated into settler society, other motives included the erosion of tribal culture and social unity, along with allowing for more land for European-American settlement and economic ventures to make use of indigenous lands.<ref>https://iltf.org/land-issues/history/</ref><ref name="Calloway 2008">Calloway 2008</ref> In the educational sphere, a system of ] for Native children (] ] being a notable example) worked to strip indigenous languages, religions and cultures away from children in order for them to better assimilate into American culture, in schools that were often geographically distant from their home reservation.<ref name="Calloway 2008"/> | |||
| Liberia is often regarded by scholars as a unique example of settler colonialism and the only known instance of Black settler colonialism.<ref name=":42">{{Cite journal |last=Spence |first=David M. |date=2021 |title=From Victims to Colonizers |url=https://eprints.soas.ac.uk/35322/1/Spence_From%20Victims%20to%20Colonizers.pdf |journal=The SOAS Journal of Postgraduate Research}}</ref> It is frequently described as an ] settler colony tasked with establishing a ] form of governance in Africa.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Parkins |first=Daniel |date=2019 |title=Colonialism, Postcolonialism, and the Drive for Social Justice: A Historical Analysis of Identity Based Conflicts in the First Republic of Liberia |url=https://digitalcollections.sit.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4202&context=capstones |journal=SIT Graduate Institute}}</ref> | |||
| Liberia was founded as the private ] in 1822 by the ], a ]-run organization, to relocate free African Americans to Africa, as part of the ].<ref name=":62">{{Cite web |title=Founding of Liberia, 1847 |url=https://history.state.gov/milestones/1830-1860/liberia |access-date=24 May 2024 |website=Office of the Historian}}</ref> This settlement scheme stemmed from fears that free African Americans would assist slaves in escaping, as well as the widespread belief among White Americans that African Americans were inherently inferior and should thus be relocated.<ref>Nicholas Guyatt, “”, ''Black Perspectives, African American Intellectual History Society,'' December 22, 2016; Nicholas Guyatt, “,” ''Oxford University Press’s Academic Insights for the Thinking World'', December 22, 2016, /.</ref> U.S. presidents ] and ] publicly endorsed and funded the project.<ref name=":62" /> | |||
| Further developments such as the Federal policies of ] and ] in the 1950s and 1960s reinforced the aims of settler society to eliminate indigenous identity and occupation of space, through the disestablishment of Federal treaty/trust obligations to tribes, the transfer of civil and criminal jurisdiction over many reservations to the individual states, and the encouragement of Native Americans to leave their reservations and relocate to cities such as ], ], ] and ]; it was hoped that this relocation would further erode tribal identity and speed up the process of assimilation.<ref name="Calloway 2008"/><ref>Rosenthal, Nicolas G. "Repositioning Indianness: Native American Organizations in Portland, Oregon, 1959–1975." Pacific Historical Review 71, no. 3 (2002): 415–38.</ref> While both policies were officially (in the case of termination) and unofficially (relocation) ended by the early 1970s, they had the effect of creating a large population of Native American urban populations, and the unintended side effect of giving rise to increased political awareness among Native Americans, leading to the creation of organizations such as the ].<ref name="Calloway 2008"/> | |||
| Between 1822 and the early 20th century, around 15,000 African Americans colonized Liberia on lands acquired from the region's indigenous African population. The African American elite monopolized the government and established ] over the locals. As they possessed ], they felt superior to the natives, whom they dominated and oppressed.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Akpan |first=M. B. |date=10 March 2014 |title=Black Imperialism: Americo-Liberian Rule over the African Peoples of Liberia, 1841–1964 |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00083968.1973.10803695 |journal=] |language=fr |volume=7 |issue=2 |pages=217–236 |doi=10.1080/00083968.1973.10803695 |issn=0008-3968}}</ref> Indigenous revolts against the ] elite such as the Grebo Revolt in 1909–1910 and Kru Revolt in 1915 were quelled with U.S. military support.<ref name=":42" /><ref>{{Cite news |title=Liberia: The African-American settler colony that parallels Israel |url=https://www.middleeasteye.net/opinion/israel-liberia-apartheid-zionism-antisemitism |access-date=2024-05-24 |work=] |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| In the present day, the legacy of settler colonialism in the United States has created a complicated relationship between indigenous tribes and the United States, especially in the area of treaty rights and sovereignty.<ref>Fairbanks, Robert. "Native American Sovereignty and Treaty Rights: Are They Historical Illusions?" American Indian Law Review 20.1 (1996): 141–49</ref><ref>Freedman, Eric. "When Indigenous Rights and Wilderness Collide: Prosecution of Native Americans for Using Motors in Minnesota's Boundary Waters Canoe Wilderness Area."American Indian Quarterly 26.3 (2002): 378–92</ref> Much contemporary literature written by indigenous scholars and scholars within the field of American Indian Studies/Native Studies centers around recognising the disruptive effects that settler colonialism has had on Native American tribes, including ], destruction of tribal languages and cultures, and tribal efforts to maintain recognition of rights they have gained via treaties with the United States government.<ref>Waziyatawin. What Does Justice Look Like?-The Struggle for Liberation in Dakota Homeland. St. Paul, MN: Living Justice Press, 2008.</ref><ref>Simpson, Audra. Mohawk Interruptus. Durham: Duke UP, 2014. Print</ref> | |||
| ===North America === | |||
| The United States has acknowledged its history of ], but has not yet publicly dealt with the historic violence of settler colonialism. Although settler colonialism is a racial issue, it cannot be reduced simply to racism, and therefore cannot be solved through inclusion alone.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Pulido|first=L|date=2018|title=Geographies of race and ethnicity III: Settler colonialism and nonnative people of color|url=|journal=Progress in Human Geography|volume=42|pages=308–318|via=Ebscohost}}</ref> | |||
| ====Canada==== | |||
| {{main|Settler colonialism in Canada}} | |||
| {{See|Canadian genocide of Indigenous peoples}} | |||
| ] signed between 1871–1921 transferred large tracts of land from the ] to Canada in return for different promises laid out in each treaty.]] | |||
| Attempts to assimilate the Indigenous peoples of what is now Canada were rooted in ] centred around European ]s and cultural practices, and a concept of land ownership based on the ].<ref name="c575">{{cite web | title=The Doctrine of Discovery | website=CMHR | date=November 2, 2022 | url=https://humanrights.ca/story/doctrine-discovery | access-date=November 21, 2024}}</ref> Original assimilation efforts were religiously-oriented, beginning in the 17th century with the arrival of French ] in ].<ref>{{cite web|last1=Gourdeau|first1=Claire|title=Population – Religious Congregations|url=http://www.historymuseum.ca/virtual-museum-of-new-france/population/religious-congregations/|work=Virtual Museum of New France|publisher=Canadian Museum of History|accessdate=July 1, 2016|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160708131814/http://www.historymuseum.ca/virtual-museum-of-new-france/population/religious-congregations/|archivedate=July 8, 2016}}</ref> Although not without conflict, ]' early interactions with ] and ] populations were relatively peaceful.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Preston |first=David L. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=L-9N6-6UCnoC&pg=PA43 |title=The Texture of Contact: European and Indian Settler Communities on the Frontiers of Iroquoia, 1667–1783 |publisher=] |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-8032-2549-7 |pages=43–44 |access-date=February 10, 2019 |archive-date=March 16, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230316173811/https://books.google.com/books?id=L-9N6-6UCnoC&pg=PA43 |url-status=live}}</ref> First Nations and ] peoples (of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry) played a critical part in the development of ], particularly for their role in assisting European ] and ] in their explorations of the continent during the ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Miller |first=J. R. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TcPckf7snr8C&pg=PT34 |title=Compact, Contract, Covenant: Aboriginal Treaty-Making in Canada |publisher=] |year=2009 |isbn=978-1-4426-9227-5 |page=34 |access-date=February 10, 2019 |archive-date=March 16, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230316173822/https://books.google.com/books?id=TcPckf7snr8C&pg=PT34 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Afghanistan=== | |||
| {{main|Pashtun colonization of northern Afghanistan}} | |||
| Starting from the 1880s, various governments of ] have pursued policies towards the goal of having more ] (Afghans) settle in northern Afghanistan (especially in ]).<ref name="sciencedirect1">{{cite journal|author=Christian Bleuer |url= |title=State-building, migration and economic development on the frontiers of northern Afghanistan and southern Tajikistan |doi=10.1016/j.euras.2011.10.008 |volume=3 |journal=Journal of Eurasian Studies |pages=69–79 |year=2012}}</ref><ref name="afghanistan-analysts1">{{cite web|url=https://www.afghanistan-analysts.org/from-slavers-to-warlords-descriptions-of-afghanistans-uzbeks-in-western-writing/ |title=From 'Slavers' to 'Warlords': Descriptions of Afghanistan's Uzbeks in western writing | Afghanistan Analysts Network |publisher=Afghanistan-analysts.org |date=2014-10-17 |accessdate=2016-05-01}}</ref> These Pashtun colonization policies had three major purposes—to strengthen Afghanistan government's hold on its northern territories, to allow Afghan governments to deport their opponents up north, and to help economically develop northern Afghanistan.<ref name="sciencedirect1"/> | |||
| The early European interactions with First Nations would change from ] to ] and displacement legislation such as the '']'',<ref name="gradcivact">{{cite web |title=Gradual Civilization Act, 1857 |url=http://caid.ca/GraCivAct1857.pdf |publisher=Government of Canada |access-date=October 17, 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240324051032/http://caid.ca/GraCivAct1857.pdf |archive-date=March 24, 2024}}</ref> the '']'', <ref name="c078">{{cite web |title=Indian Act |website=Site Web de la législation (Justice) |date=August 15, 2019 |url=https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/i-5/ |access-date=September 2, 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240526125409/https://www.laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/acts/I-5/ |archive-date=May 26, 2024}}</ref> the ],<ref name="d658">{{cite encyclopedia |title=Potlatch Ban |encyclopedia=] |date=January 11, 2024 |url=https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/potlatch-ban |access-date=September 3, 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240816232746/https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/potlatch-ban |archive-date=August 16, 2024}}</ref> and the ],<ref name="TRC_2015">{{cite report |title=What We Have Learned: Principles of Truth and Reconciliation |url=http://www.trc.ca/assets/pdf/Principles%20of%20Truth%20and%20Reconciliation.pdf |isbn=978-0-660-02073-0 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210607124229/http://www.trc.ca/assets/pdf/Principles%20of%20Truth%20and%20Reconciliation.pdf |archive-date=June 7, 2021 |date=2015 |pages=192}}</ref> that focused on European ideals of Christianity, sedentary living, agriculture, and education.<ref>{{multiref2| | |||
| ===Nepal=== | |||
| |{{cite book |last=Williams |first=L. |title=Indigenous Intergenerational Resilience: Confronting Cultural and Ecological Crisis |publisher=] |series=Routledge Studies in Indigenous Peoples and Policy |year=2021 |isbn=978-1-000-47233-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HehEEAAAQBAJ&pg=PT51 |page=51 |access-date=February 23, 2023 |archive-date=February 23, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230223140054/https://books.google.com/books?id=HehEEAAAQBAJ&pg=PT51 |url-status=live}} | |||
| |{{cite book |last=Turner |first=N. J. |title=Plants, People, and Places: The Roles of Ethnobotany and Ethnoecology in Indigenous Peoples' Land Rights in Canada and Beyond |publisher=] |series=McGill-Queen's Indigenous and Northern Studies |year=2020 |isbn=978-0-2280-0317-5 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JVjZDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA14 |page=14 |access-date=February 23, 2023 |archive-date=February 23, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230223140056/https://books.google.com/books?id=JVjZDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA14 |url-status=live}} | |||
| |{{Cite book |last=Asch |first=Michael |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9Uae4mTTyYYC&pg=PA28 |title=Aboriginal and Treaty Rights in Canada: Essays on Law, Equity, and Respect for Difference |publisher=] |year=1997 |isbn=978-0-7748-0581-0 |page=28}} | |||
| |{{Cite book |last1=Kirmayer |first1=Laurence J. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AXYDxvx3zSAC&pg=PA9 |title=Healing Traditions: The Mental Health of Aboriginal Peoples in Canada |last2=Guthrie |first2=Gail Valaskakis |publisher=] |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-7748-5863-2 |page=9}} | |||
| |{{cite web | title=Indigenous Peoples and Government Policy in Canada | website=The Canadian Encyclopedia | date=Jun 6, 1944 | url=https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca/en/article/aboriginal-people-government-policy | access-date=Nov 20, 2024}}}}</ref> | |||
| Indigenous groups in Canada continue to suffer from ], despite living in one of the most progressive countries in the world.<ref>{{cite journal |first1=Corey |last1=Snelgrove |first2=Rita Kaur |last2=Dhamoon |first3=Jeff |last3=Corntassel |title=Unsettling settler colonialism: The discourse and politics of settlers, and solidarity with Indigenous nations |journal=Decolonization: Indigeneity, Education & Society |volume=3 |number=2 |date=2014 |pages=11–12 |url=https://nycstandswithstandingrock.files.wordpress.com/2016/10/snelgrove-dhamoon-corntassel-2014.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170104164929/https://nycstandswithstandingrock.files.wordpress.com/2016/10/snelgrove-dhamoon-corntassel-2014.pdf |archive-date=January 4, 2017}}</ref> Discriminatory practices such as ], ], ], and ] have been subject to legal and political review.<ref name="u161">{{cite web | title=Understanding the Overrepresentation of Indigenous People | website=State of the Criminal Justice System Dashboard | date=Jun 11, 2024 | url=https://www.justice.gc.ca/socjs-esjp/en/ind-aut/uo-cs | access-date=Nov 21, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| The native inhabitants of the plains have been the ]. However, due to large planned settlement of Hills people by the ] after construction of a parallel Highway to the existing ], in many places the native population has been reduced to a minority. Overall the demographic change has been such that a 6% population of people of the hills origin in the plains has risen to 36% in between 1951 & 2011.<ref>{{cite book|author=Frederick H. Gaige|title=Regionalism and National Unity in Nepal|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IxuxAAAAIAAJ|year=1975|publisher=Univ.of California Press|isbn=978-0-520-02728-2}}</ref> | |||
| === |
====United States==== | ||
| {{Main|Manifest destiny}} | |||
| {{main|Nam tiến|Central Highlands (Vietnam)|Degar|Champa|Khmer Krom}} | |||
| {{see|Native American genocide in the United States}} | |||
| ] in the 19th century]] | |||
| ] | |||
| In ], ] created economic dependency and imbalance of trade, incorporating Indigenous nations into spheres of influence and controlling them indirectly with the use of Christian missionaries and alcohol.<ref name=":12">{{cite book |last1=Dunbar-Ortiz |first1=Roxanne |title=An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States |date=2014 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-8070-0040-3 |location=Boston}}</ref> With the emergence of an independent United States, desire for land and the perceived threat of permanent Indigenous political and spatial structures led to violent relocation of many Indigenous tribes to the American West, in what is known as the ].<ref name="Wolfe 20062"/> | |||
| In response to American encroachment on native land in the Great Lakes region, the ] confederacies of the ] and ] emerged. Despite initial victories in both cases, such as ] or the ], both eventually lost, thereby paving the way for American control over the region. Settlement into conquered land was rapid. Following the 1795 ], American settlers poured into southern Ohio, such that by 1810 it had a population of 230,760.<ref>https://www.issuelab.org/resources/3973/3973.pdf {{Bare URL PDF|date=August 2024}}</ref> The defeat of the confederacies in the Great Lakes paved the way for large land loss in the region, via treaties such as the ] which saw the loss of more than 4,000,000 acres of land.<ref>{{cite web |date=26 November 2019 |title=The 1819 Treaty of Saginaw |url=https://blogs.cmich.edu/library/2019/11/26/the-1819-treaty-of-saginaw/}}</ref> | |||
| The native inhabitants of the Central Highlands are the ] (Montagnard) peoples. Vietnam conquered and invaded the area during its "march to the south" (]). Ethnic ] now outnumber the indigenous Degars after state sponsored colonization directed by both the government of ] and the current Communist government of unified ]. The Montagnards have fought against and resisted all Vietnamese invaders, from the anti-Communist South Vietnamese government, the Vietcong, to the Communist government of unified Vietnam. | |||
| Frederick Jackson Turner, the father of the "frontier thesis" of American history, noted in 1901: "Our colonial system did not start with Spanish War; the U.S. had had a colonial history from the beginning...hidden under the phraseology of 'interstate migration' and territorial organization'".<ref name=":12" /> While the United States government and local state governments directly aided this dispossession through the ], ultimately this came about through agitation by settler society in order to gain access to Indigenous land. Especially in the US South, such land acquisition built plantation society and expanded the practice of slavery.<ref name="Wolfe 20062"/> Settler colonialism participated in the formation of US cultures and lasted past the conquest, removal, or extermination of Indigenous people.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Spady |first=James O'Neil |url=https://www.academia.edu/37602761 |title=Education and the Racial Dynamics of Settler Colonialism in Early America: Georgia and South Carolina, ca. 1700 - ca. 1820 |date=2020 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0367437169}}</ref>{{pn|date=July 2024}} In 1928, ] spoke admiringly of the impact of white settler colonialism on the Natives, stating the US had "gunned down the millions of Redskins to a few hundred thousand, and now keep the modest remnant under observation in a cage".<ref>{{cite book |last1=Moon |first1=David |title=The American Steppes |date=2020 |publisher=] |page=44}}</ref> The practice of writing the Indigenous out of history perpetrated a forgetting of the full dimensions and significance of colonialism at both the national and local levels.<ref name=":12" /> | |||
| The Montagnard lands in the Central Highlands were subjected to state sponsored colonization by ethnic Vietnamese settlers under the South Vietnamese regime of Ngo Dinh Diem which resulted in estranging the Montagnards and leading them to reject Vietnamese rule.<ref name="FitzGerald2009">{{cite book|author=Frances FitzGerald|title=Fire in the Lake|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Ld9W1NKBjzQC&pg=PA190|date=30 May 2009|publisher=Little, Brown|isbn=978-0-316-07464-3|page=190}}</ref> | |||
| === Asia=== | |||
| The South Vietnamese and Communist Vietnamese colonization of the Central Highlands have been compared to the historic Nam tiến of previous Vietnamese rulers. During the Nam tiến (March to the South) Khmer and Cham territory was seized and militarily colonized (đồn điền) by the Vietnamese which was repeated by the state sponsored colonization of Northern Vietnamese Catholic refugees on Montagnard land by the South Vietnamese leader Diem and the introduction to the Central Highlands of "New Economic Zones" by the now Communist Vietnamese government.<ref name="Salemink2003">{{cite book|author=Oscar Salemink|title=The Ethnography of Vietnam's Central Highlanders: A Historical Contextualization, 1850–1990|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2_zKFyHlBk0C&pg=PA151|year=2003|publisher=University of Hawaii Press|isbn=978-0-8248-2579-9}}</ref>{{rp|151-}} | |||
| ==== China ==== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Further|Migration to Xinjiang|Sinicization of Tibet}} | |||
| The thousand year violent war the Vietnamese in the lowlands had with the Montagnards in the mountains was a long established custom and the Vietnamese used the derogatory word "Moi" (savages) to address the Montagnards, the South Vietnamese government was strongly against the autonomous Montagnard CIDG (Civilian Irregular Defense Groups) who were fighting against the Vietcong because they feared that the Montagnards would gain independence so the South Vietnamese and Montagnards violently clashed against each other. The Vietnamese Communists implemented harsh punishment against the Montagnards after the defeat of South Vietnam.<ref name="Nutter2000">{{cite book|author=John Jacob Nutter|title=The CIA's Black Ops: Covert Action, Foreign Policy, and Democracy|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Zr58XN0uEEQC&pg=PA160|year=2000|publisher=Prometheus Books, Publishers|isbn=978-1-61592-397-7|page=160}}</ref> | |||
| ] of China]] | |||
| Near the end of their rule the ] attempted to colonize ], ], and other parts of the imperial frontier. To accomplish this goal, they began resettling ] on the frontier.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Wang |first1=Ju-Han Zoe |last2=Roche |first2=Gerald |date=March 16, 2021 |title=Urbanizing Minority Minzu in the PRC: Insights from the Literature on Settler Colonialism |url=https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/14776011 |journal=] |language=en |volume=48 |issue=3 |pages=593–616 |doi=10.1177/0097700421995135 |issn=0097-7004 |s2cid=233620981}}</ref> This policy of settler colonialism was renewed by the ], led by ],<ref>{{Citation |last=Brooks |first=Jonathan |title=Settler Colonialism, Primitive Accumulation, and Biopolitics in Xinjiang, China |date=2021 |language=en |doi=10.2139/ssrn.3965577 |issn=1556-5068 |ssrn=3965577 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite journal |last=Clarke |first=Michael |date=2021-02-16 |title=Settler Colonialism and the Path toward Cultural Genocide in Xinjiang |journal=Global Responsibility to Protect |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=9–19 |doi=10.1163/1875-984X-13010002 |issn=1875-9858 |s2cid=233974395}}</ref> and is being practiced today according to some academics and researchers.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Ramanujan |first=Shaurir |date=2022-12-09 |title=Reclaiming the Land of the Snows: Analyzing Chinese Settler Colonialism in Tibet |journal=The Columbia Journal of Asia |volume=1 |issue=2 |pages=29–36 |doi=10.52214/cja.v1i2.10012 |issn=2832-8558 |doi-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Finley |first=Joanne Smith |date=2022-09-01 |title=Tabula rasa: Han settler colonialism and frontier genocide in "re-educated" Xinjiang |journal=] |language=en |volume=12 |issue=2 |pages=341–356 |doi=10.1086/720902 |issn=2575-1433 |s2cid=253268699 |doi-access=}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last1=McGranahan |first1=Carole |title=Frontier Tibet: Patterns of Change in the Sino-Tibetan Borderlands |date=2019-12-17 |publisher=] |isbn=978-90-485-4490-5 |editor-last=Gros |editor-first=Stéphane |pages=517–540 |chapter=Chinese Settler Colonialism: Empire and Life in the Tibetan Borderlands |doi=10.2307/j.ctvt1sgw7.22 |jstor=j.ctvt1sgw7.22 |doi-access=free |jstor-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| The Vietnamese viewed and dealt with the indigenous Montagnards in the CIDG from the Central Highlands as "savages" and this caused a Montagnard uprising against the Vietnamese.<ref name="Cosmas">{{cite book|author=Graham A. Cosmas|title=MACV: The Joint Command in the Years of Escalation, 1962–1967|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ZcLQcquYkcIC&pg=PA145|publisher=Government Printing Office|isbn=978-0-16-072367-4|year=2006}}</ref>{{rp|145}} | |||
| The Montagnard Rhades mounted a revolt, seizing hundreds of Vietnamese civilians and soldiers, assassinating officers of the Vietnamese special forces and seizing American advisers on 19–20 September but the 23rd Division of the South Vietnamese army stopped them from sizing Ban Me Thout, the provincial capital of Darlac Province.<ref name="Cosmas" />{{rp|146}} | |||
| ==== Israel ==== | |||
| The South Vietnamese and Communists "victimized" the Montagnards.<ref name="Hellmann2013">{{cite book|author=John Hellmann|title=American Myth and the Legacy of Vietnam|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uPH86IxSwjsC&pg=PA62|date=13 August 2013|publisher=Columbia University Press|isbn=978-0-231-51538-2|page=62}}</ref> | |||
| ] in ] as the archetype of the definition.<ref name=":32">{{Cite magazine |last=Powell |first=Michael |date=2024-01-05 |title=The Curious Rise of 'Settler Colonialism' and 'Turtle Island' |url=https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2024/01/curious-rise-settler-colonialism-and-turtle-island/677005/ |access-date=2024-05-22 |magazine=] |language=en}}</ref> Map of ] (magenta) in the occupied ] in 2020. The Australian historian ], credited with originating the field, famously defined ] as the ] today.<ref name=":32" /><ref name="Wolfe 20062"/><ref name="Kauanui2" /> However, this notion has also received significant criticism.<ref name="Troen2">{{cite journal |last1=Troen |first1=S. Ilan |year=2007 |title=De-Judaizing the Homeland: Academic Politics in Rewriting the History of Palestine |journal=Israel Affairs |volume=13 |issue=4 |pages=872–884 |doi=10.1080/13537120701445372 |s2cid=216148316}}</ref>]] | |||
| {{main article|Palestinian genocide accusation}} | |||
| ] has been characterized by some scholars as a form of settler colonialism concerning ] and the ]. This academic framework has also been embraced by leftist groups and individuals involved in ] activism and campus protests.<ref name=":232">{{Cite news |last=Schuessler |first=Jennifer |date=2024-01-22 |title=What Is 'Settler Colonialism'? |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2024/01/22/arts/what-is-settler-colonialism.html |access-date=2024-07-07 |work=] |language=en-US |issn=0362-4331}}</ref><ref name=":122">{{Cite news |last=Cohen |first=Roger |date=2023-12-10 |title=Who's a 'Colonizer'? How an Old Word Became a New Weapon |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2023/12/10/world/europe/colonialist-word-gaza-ukraine.html |access-date=2024-07-07 |work=] |language=en-US |issn=0362-4331}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Kirsch |first=Adam |date=2023-10-26 |title=Campus Radicals and Leftist Groups Have Embraced the Idea of 'Settler Colonialism' |url=https://www.wsj.com/world/middle-east/campus-radicals-and-leftist-groups-have-embraced-the-deadly-idea-of-settler-colonialism-b8e995be |access-date=2024-07-07 |work=]}}</ref> However, this viewpoint faces substantial criticism from scholars and is largely rejected by many Jews due to its perceived denial of the ], among other reasons.<ref name="Troen2" /><ref name=":232"/><ref name=":122"/> | |||
| In the Central Highlands the Montagnard FULRO organization fought against both the Communists and South Vietnamese due to discrimination by the South Vietnamese army against the Montagnards. After the victory of the Communist North Vietnamese, the Vietnamese refused autonomy to the Montagnards, and on Montagnard land they settled around one million ethnic Vietnamese in addition to using "reducation camps" on the Montagnards, leading the Montagnard FULRO to continue the armed struggle against the Vietnamese.<ref name="Tucker2011">{{cite book|author=Spencer C. Tucker|title=Encyclopedia of the Vietnam War, The: A Political, Social, and Military History: A Political, Social, and Military History|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qh5lffww-KsC&pg=PA182|date=20 May 2011|publisher=ABC-CLIO|isbn=978-1-85109-961-0|page=182}}</ref> | |||
| Many of the founding fathers of ] themselves described the project as colonization, such as ], who said "Zionism is a colonization adventure."<ref>{{Cite book |last=Hart |first=Alan |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1zbb81ZuVCkC |title=Zionism: The Real Enemy of the Jews |volume=1: The False Messiah |date=2010-08-13 |publisher=SCB Distributors |isbn=978-0-932863-78-2 |language=en |quote=A voluntary reconciliation with the Arabs is out of the question either now or in the future. If you wish to colonize a land in which people are already living, you must provide a garrison for the land, or find some rich man or benefactor who will provide a garrison on your behalf. Or else-or else, give up your colonization, for without an armed force which will render physically impossible any attempt to destroy or prevent this colonization, colonization is impossible, not difficult, not dangerous, but IMPOSSIBLE!... Zionism is a colonization adventure and therefore it stands or falls by the question of armed force. It is important... to speak Hebrew, but, unfortunately, it is even more important to be able to shoot – or else I am through with playing at colonizing.}}</ref><ref name="IWprimary2">{{cite web |last=Jabotinsky |first=Ze'ev |date=4 November 1923 |title=The Iron Wall |url=http://en.jabotinsky.org/media/9747/the-iron-wall.pdf |quote="Colonisation can have only one aim, and Palestine Arabs cannot accept this aim. It lies in the very nature of things, and in this particular regard nature cannot be changed...Zionist colonisation must either stop, or else proceed regardless of the native population."}}</ref> Founder of the ], ], described the Zionist project as "something colonial" in a letter to ] in 1902.<ref>{{cite book |editor1-first=Mark H. |editor1-last=Gelber |editor2-first=Vivian |editor2-last=Liska |title=Theodor Herzl: From Europe to Zion |date=2012 |publisher=] |pages=100–101}}</ref> | |||
| The Vietnamese were originally centered around the Red River Delta but engaged in conquest and seized new lands such as Champa, the Mekong Delta (from Cambodia) and the Central Highlands during Nam Tien, while the Vietnamese received strong Chinese influence in their culture and civilization and were Sinicized, and the Cambodians and Laotians were Indianized, the Montagnards in the Central Highlands maintained their own native culture without adopting external culture and were the true indigenous natives of the region, and to hinder encroachment on the Central Highlands by Vietnamese nationalists, the term ''Pays Montagnard du Sud-Indochinois'' PMSI emerged for the Central Highlands along with the natives being addressed by the name Montagnard.<ref name="Salemink2003" />{{rp|28-}} The tremendous scale of Vietnamese Kinh colonists flooding into the Central Highlands has significantly altered the demographics of the region.<ref name="Salemink2003" />{{rp|29-}} | |||
| In 1967, the French historian ] wrote an article later translated and published in English as ''Israel: A Colonial Settler-State?''<ref>Rodinson, Maxime. "Israel, fait colonial?" ''Les Temps Moderne'', 1967. Republished in English as ''Israel: A Colonial Settler-State?'', New York, Monad Press, 1973.</ref> ] describes ] as a "settler colonial polity", and writes that it could celebrate its anticolonial struggle in 1948 because it had colonial relationships inside and outside Israel's new borders.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Veracini|first=Lorenzo|date=2007|title=Settler Colonialism and Decolonisation|url=http://www.borderlands.net.au/vol6no2_2007/veracini_settler.htm|journal=borderlands e-journal|volume=6|issue=2|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200330030659/http://www.borderlands.net.au/vol6no2_2007/veracini_settler.htm|archive-date=30 March 2020|quote=Israel could celebrate its anticolonial/anti-British struggle exactly because it was able to establish a number of colonial relationships within and without the borders of 1948.}}</ref> Veracini believes the possibility of an Israeli disengagement is always latent and this relationship could be severed, through an "]".<ref>{{cite book |last=Veracini |first=Lorenzo |title=Israel and Settler Society |location=London |publisher=] |date=2006 |page=}}</ref>{{pn|date=July 2024}} Other commentators, such as ], ],<ref>, Nira Yuval-Davis (Editor), Daiva K Stasiulis (Editor), Paperback 352pp, {{ISBN|978-0-8039-8694-7}}, August 1995 ].</ref> and ] in the "Post Colonial Colony: time, space and bodies in Palestine/Israel in the persistence of the Palestinian Question"<ref>"Post Colonial Colony: time, space and bodies in Palestine/Israel in the persistence of the Palestinian Question", ], NY, (2006) and "The Pre-Occupation of Post-Colonial Studies" ed. Fawzia Afzal-Khan and Kalpana Rahita Seshadri. (Durham: ])</ref> have included Israel in their global analysis of settler societies. ] describes ] and Israel in similar terms.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170519175348/http://kingsreview.co.uk/articles/the-palestinian-enclaves-struggle-an-interview-with-ilan-pappe/ |date=19 May 2017 }}, King's Review – Magazine</ref><ref>Video: . ], 5 April 2017</ref> Scholar Amal Jamal, from ], has stated, "Israel was created by a settler-colonial movement of Jewish immigrants".<ref>{{cite book |author=Amal Jamal |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pWLCpqnsoLQC&pg=PA48 |title=Arab Minority Nationalism in Israel: The Politics of Indigeneity |publisher=Taylor & Francis |year=2011 |isbn=978-1-136-82412-8 |page=48}}</ref> Damien Short has accused Israel of ] against ] during the ] since its inception within a ] context.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Short |first=Damien |date=December 2012 |title=Genocide and settler colonialism: can a Lemkin-inspired genocide perspective aid our understanding of the Palestinian situation? |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258433114 |journal=The International Journal of Human Rights}}</ref> | |||
| Violent demonstrations with fatalities have broken out due to Montagnard anger at Vietnamese discrimination and seizure of their land since many Vietnamese Kinh were settled by the government in the Central Highlands.<ref name="SullivanSullivan2006">{{cite book|author1=Jim Sullivan|author2=James Sullivan|title=Vietnam|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9WLfsdeJgHsC&pg=PA102|year=2006|publisher=National Geographic Society|isbn=978-0-7922-6203-9|page=102}}</ref><ref name="Sullivan2010">{{cite book|author=James Sullivan|title=National Geographic Traveler Vietnam|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=h8cRgWpCXUoC&pg=PA102|year=2010|publisher=National Geographic|isbn=978-1-4262-0522-4|page=102}}</ref> | |||
| Writing in the 1990s, the Australian historian ] is credited with originating the field.<ref name="Kauanui2" /> He theorized settler colonialism as a structure (rather than an event) premised on the elimination rather than exploitation of the native population, thus distinguishing it from classical colonialism. Wolfe argued that settler colonialism was centered on the control of land, that it continued after the closing of the frontier, and that continued to exist today, classifying ].<ref name="Wolfe 20062" /> His approach was defining for the field, but has been challenged by other scholars on the basis that many situations involve a combination of elimination and exploitation.<ref name="Englert2" /> | |||
| Long tails and excessive body hair were attributed as physical characteristics of Montagnards in Vietnamese school textbooks in the past.<ref name="Lung2006">{{cite book|author=Haha Lung|title=Lost Fighting Arts of Vietnam|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=moDNlFBglpoC&pg=PA7|year=2006|publisher=Citadel|isbn=978-0-8065-2760-4|page=7}}</ref> | |||
| Critics of the paradigm argue that Zionism does not fit the traditional framework of colonialism. ] views Zionism as the return of an indigenous population to its historic homeland, distinct from imperial expansion.<ref name="Troen3">{{cite journal |last1=Troen |first1=S. Ilan |year=2007 |title=De-Judaizing the Homeland: Academic Politics in Rewriting the History of Palestine |journal=Israel Affairs |volume=13 |issue=4 |pages=872–884 |doi=10.1080/13537120701445372 |s2cid=216148316}}</ref> Moses Lissak asserted that the settler-colonial thesis denies the idea that Zionism is the modern ] of the ], seeking to reestablish a Jewish political entity in their historical territory. Zionism, Lissak argues, was both a national movement and a settlement movement at the same time, so it was not, by definition, a colonial settlement movement.<ref name=":222">Moshe Lissak, "'Critical' Sociology and 'Establishment' Sociology in the Israeli Academic Community: Ideological Struggles or Academic Discourse?" ''Israel Studies'' 1:1 (1996), 247-294.</ref> | |||
| Up until French rule, the Central Highlands was almost never entered by the Vietnamese since they viewed it as a savage (Moi-Montaganrd) populated area with fierce animals like tigers, "poisoned water" and "evil malevolent spirits", but the Vietnamese became greedy and voracious for the land after the French transformed it into a profitable plantation area to grow crops on,<ref name="M.D.2013">{{cite book|author=Lawrence H. Climo, M.D.|title=The Patient Was Vietcong: An American Doctor in the Vietnamese Health Service, 1966–1967|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zQxWAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA227|date=20 December 2013|publisher=McFarland|isbn=978-0-7864-7899-6|pages=227, 228}}</ref> in addition to the natural resources from the forests, minerals and rich earth and realization of its crucial geographical importance.<ref name="M.D.2013"/> | |||
| ==== Russia and the Soviet Union ==== | |||
| Ethnic minorities in general have also been referred to as "moi",<ref name="Elliott2002">{{cite book|author=David W. P. Elliott|title=The Vietnamese War: Revolution and Social Change in the Mekong Delta, 1930-1975|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KclCL2yZVRAC&pg=PA1504|date=31 December 2002|publisher=M.E. Sharpe|isbn=978-0-7656-0602-0|page=1504}}</ref> including other "hill tribes" like the Muong.<ref name="Minahan2012">{{cite book|author=James B. Minahan|title=Ethnic Groups of South Asia and the Pacific: An Encyclopedia|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fOQkpcVcd9AC&pg=PT269|date=30 August 2012|publisher=ABC-CLIO|isbn=978-1-59884-660-7|page=269}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Circassian genocide|Ethnic Russians in post-Soviet states|Population transfer in the Soviet Union}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Some scholars describe Russia as a settler colonial state, particularly in its expansion into ] and the ], during which it displaced and resettled Indigenous peoples, while practicing settler colonialism.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Sunderland |first=Willard |date=2000 |title=The 'Colonization Question': Visions of Colonization in Late Imperial Russia |journal=Jahrbücher für Geschichte Osteuropas |volume=48 |issue=2 |pages=210–232 |jstor=41050526}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Forsyth |first=James |url=http://archive.org/details/historyofpeoples00fors |title=A history of the peoples of Siberia |date=1992 |publisher=] |others=Internet Archive |isbn=978-0-521-40311-5 |pages=201–228, 241–346}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Lantzeff |first1=George V. |title=Eastward to Empire: Exploration and Conquest on the Russian Open Frontier to 1750 |last2=Pierce |first2=Richard A. |date=1973 |publisher=] |doi=10.2307/j.ctt1w0dbpp |jstor=j.ctt1w0dbpp}}</ref> The annexation of ] and the Far East to Russia was resisted by the ], while the ] often committed atrocities against them.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Hill |first=Nathaniel |date=25 October 2021 |title=Conquering Siberia: The Case for Genocide Recognition |url=https://www.genocidewatchblog.com/post/conquering-siberia-the-case-for-genocide-recognition |access-date=2023-04-03 |website=www.genocidewatchblog.com}}</ref> During the Cold War, new forms of Indigenous repression were practiced.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Bartels |first1=Dennis |last2=Bartels |first2=Alice L. |date=2006 |title=Indigenous Peoples of the Russian North and Cold War Ideology |journal=Anthropologica |volume=48 |issue=2 |pages=265–279 |doi=10.2307/25605315 |jstor=25605315}}</ref> | |||
| This colonization continued even during the ] in the 20th century.<ref>{{harvnb|Veracini|2013|p=}}: "The domination of Latin America, North America, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, and the Asian part of the Soviet Union by European powers all involved the migration of permanent settlers from the European country to the colonies. These places were colonized."</ref>{{pn|date=July 2024}} The Soviet policy also sometimes included the deportation of the native population, as in the case of the ].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Pohl |first1=Otto |date=2015 |title=The Deportation of the Crimean Tatars in the Context of Settler Colonialism |url=http://www.lituanus.org/1998/98_3_02.htm |journal=International Crimes and History |issue=16 |archive-date=9 August 2022 |access-date=4 February 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220809105743/http://www.lituanus.org/1998/98_3_02.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| The anti-ethnic minority discriminatory policies by the Vietnamese, environmental degradation, deprivation of lands from the natives, and settlement of native lands by a massive amount of Vietnamese settlers led to massive protests and demonstrations by the Central Highland's indigenous native ethnic minorities against the Vietnamese in January–February 2001 and this event gave a tremendous blow to the claim often published by the Vietnamese government that in Vietnam ''There has been no ethnic confrontation, no religious war, no ethnic conflict. And no elimination of one culture by another.''<ref>{{cite book |last= McElwee |first= Pamela |editor-last=Duncan|editor-first=Christopher R. |date= 2008 |title=Civilizing the Margins: Southeast Asian Government Policies for the Development of Minorities |chapter=7 Becoming Socialist or Becoming Kinh? Government Policies for Ethnic Minorities in the Socialist Republic of Viet Nam |chapter-url= https://www.academia.edu/296296 |location=Singapore |publisher=NUS Press |page=182 |isbn= 978-9971-69-418-0 |access-date= }}</ref> | |||
| ==== Taiwan ==== | |||
| The same state sponsored settlement of ethnic minority land by Vietnamese Kinh has happened in another highland region, the ], both the Central Highlands and Annamite Cordillera were populated by ethnic minorities who were not Vietnamese during the 20th century's start, but the demographics of the highlands was drastically transformed with the mass colonization of 6 million settlers from 1976 to the 1990s, which led to ethnic Vietnamese Kinh outnumbering the native ethnic groups in the highlands.<ref name=McElwee>{{cite journal |last=McElwee |first=Pamela |date= 2008 |title= "Blood Relatives" or Uneasy Neighbors? Kinh Migrant and Ethnic Minority Interactions in the Trường Sơn Mountains |url=https://www.academia.edu/192968 |journal=Journal of Vietnamese Studies |publisher=Regents of the University of California |volume=3 |issue=3 |pages=81–82 |doi=10.1525/vs.2008.3.3.81 |issn=1559-372X}}</ref> | |||
| {{further|Taiwanese indigenous peoples}} | |||
| According to a PhD thesis by Lin-chin Tsai, current ] is largely the result of ] colonialism beginning in the seventeenth century.<ref>{{cite thesis |last1=Tsai |first1=Lin-chin |degree=PhD |title=Re-conceptualizing Taiwan: Settler Colonial Criticism and Cultural Production |date=2019 |url=https://escholarship.org/uc/item/30h7d8r5 |access-date=20 May 2023 |publisher=] |language=en |quote=Taiwan, an island whose indigenous inhabitants are Austronesian, has been a de facto settler colony due to large-scale Han migration from China to Taiwan beginning in the seventeenth century.}}</ref> | |||
| Most of the highlands like the Annamite Range and the ] were populated by ethnic minorities who were not Vietnamese during the 20th century's start, but the demographics of the highlands was drastically transformed with the mass colonization of 6 million settlers from 1976 to the 1990s, which led to ethnic Vietnamese Kinh outnumbering the native ethnic groups in the highlands. The Vietnamese Kinh dominated government media propagate negative stereotypes of the highlander ethnic minorities, labeling them as "ignorant", "illiterate", "backward" and claim that they are impoverished and underdeveloped because of their own lack of economic and agricultural skills.<ref name=McElwee/> Ethnic Vietnamese Kinh settlers have negative stereotypes and views of the native ethnic minorities with barely any intermarriage and little interaction since they deliberately choose to live in different villages which are a stark difference from the government's portrayal of harmonic relations between minorities and Vietnamese, with the government claiming that "backward areas" are experiencing "development" from the Vietnamese Kinh settlers they are encouraging yet these places are not underdeveloped and no advantages have come about the minorities form the Vietnamese Kinh settlers, instead only negative consequences of the Vietnamese colonization have been brought upon the minorities like the wiping out of their culture and replacement by Vietnamese Kinh culture and exacerbated poverty due to control of the economy by the Vietnamese Kinh.<ref name=McElwee/> | |||
| ===Australia{{anchor |au}}=== | |||
| ] in the Mekong Delta have also been economically marginalized and pushed into poverty by Vietnamese policies, with ethnic ] settling on majority Cham land with state support, and religious practices of minorities have been targeted for elimination by the Vietnamese government.<ref>{{cite journal |last= Taylor |first= Philip |date= December 2006|title= Economy in Motion: Cham Muslim Traders in the Mekong Delta|url= http://www.chamstudies.com/members/philiptaylor(chammuslimtraders).pdf |journal= The Asia Pacific Journal of Anthropology|publisher= The Australian National University |volume= 7 |issue= 3|page= 238 |doi=10.1080/14442210600965174 |issn=1444-2213 |accessdate=3 September 2014}}</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Settler colonialism in Australia}} | |||
| {{See also|List of massacres of Indigenous Australians}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Europeans explored and settled Australia, displacing ]. The ] population was estimated at 795,000 at the time of European settlement.<ref>Statistics compiled by Ørsted-Jensen for Frontier History Revisited (Brisbane 2011), page 15.</ref> The ] for 150 years following settlement from 1788, due to casualties from ], the ] and forced re-settlement and cultural disintegration.<ref>{{cite paper |last=Page |first=A. |date=September 2015 |url=http://www.apsa2015.org/uploads/4/5/1/9/45190879/alexander_page_-_the_australian_settler_state_indigenous_agency_and_the_indigenous_sector_in_the_twenty_first_century.pdf |title=The Australian Settler State, Indigenous Agency, and the Indigenous Sector in the Twenty First Century |publisher=Australian Political Studies Association Conference |archive-date=10 September 2016 |access-date=15 December 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160910082243/http://www.apsa2015.org/uploads/4/5/1/9/45190879/alexander_page_-_the_australian_settler_state_indigenous_agency_and_the_indigenous_sector_in_the_twenty_first_century.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Page |first1=A. |last2=Petray |first2=T. |date=2015 |title=Agency and Structural Constraints: Indigenous Peoples and the Settler-State in North Queensland |journal=Settler Colonial Studies |volume=5 |number=2}}</ref> | |||
| == |
==Responses== | ||
| Settler colonialism exists in tension with ]. Some indigenous scholars believe that settler colonialism as a methodology can lead to overlooking indigenous responses to colonialism; however, other practitioners of indigenous studies believe that settler colonialism has important insights that are applicable to their work.<ref name="Kauanui2" /> Settler colonialism as a theory has also been criticized from the standpoint of ].<ref name="Kauanui2" /> ] has been criticized on the basis that it does not provide a special status for indigenous claims, and in response settler colonial theory has been criticized for potentially contributing to the marginalization of racialized immigrants.{{sfn|Veracini|2015|p=44}} | |||
| {{main|Transmigration program}} | |||
| Political theorist ] suggested that settlers could never succeed in their effort to become native, and therefore the only way to end settler colonialism was to erase the political significance of the settler–native dichotomy.<ref name="Englert2" /> | |||
| ===Ireland=== | |||
| {{main|Plantations of Ireland}} | |||
| According to ] scholar Jodi Byrd, in contrast to settler, the term ''arrivant'' refers to enslaved Africans transported against their will, and to refugees forced into the Americas due to the effects of imperialism.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Byrd |first=Jodi A. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3_JNcXnUjZkC |title=The Transit of Empire: Indigenous Critiques of Colonialism |date=2011-09-06 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-4529-3317-7 |pages=xix |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ===Philippines=== | |||
| {{main|Moro insurgency in the Philippines}} | |||
| The native peoples of ] are the ] and the ] Animists. They have been turned into a minority by the settlement of millions of Filipino Christians from Luzon and the Visayas onto their land. | |||
| In his book '']'', political scientist Adam Dahl states that while it has often been recognized that "American democratic thought and identity arose out of the distinct pattern by which English settlers colonized the new world", histories are missing the "constitutive role of colonial dispossession in shaping democratic values and ideals".{{sfn|Dahl|2018|p=1}} | |||
| At the beginning of the 20th century, the Moro and Lumads controlled an area which now covers 17 of Mindanao's 24 provinces, but by the 1980 census, they constituted less than 6% of the population of Mindanao and ]. Heavy migration to Mindanao of Luzon and ], spurred by government-sponsored resettlement programs,<ref>http://www.davaotoday.com/main/todays-views/we-who-seek-to-settle-part-9/</ref> turned the indigenous Lumads and Moros into minorities.<ref>"". University of Hawaii – Center for Philippine Studies.</ref> | |||
| == See also == | |||
| The native Moro Muslims and Lumads were supplanted by the first Spanish and American colonization programs with Christian settlers taking control of key areas and disrupting the Muslim's administrative structures and control over resources, the Americans chose Christian settlers to become officials of settler populated townships instead of Lumads and Muslims, with the environment becoming ruined due to the activities of the settlers and logging.<ref name="UmeharaBautista2004">{{cite book|author1=Hiromitsu Umehara|author2=Germelino M. Bautista|title=Communities at the Margins: Reflections on Social, Economic, and Environmental Change in the Philippines|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AA9OHro4ELYC&pg=PA22|year=2004|publisher=Ateneo University Press|isbn=978-971-550-464-5}}</ref>{{rp|22}} Severe deterioration of the land in Mindanao ensued after the continuing influx of Filipino settlers, with the land becoming essentially useless.<ref name="UmeharaBautista2004" />{{rp|23-}} Eric S. Casiño wrote on the interaction between the Filipino settlers, the Moro Muslim and Lumad natives and the impact on the environment in his book "Mindanao Statecraft and Ecology: Moros, Lumads, and Settlers Across the Lowland-highland Continuum".<ref name="Casiño2000">{{cite book|author=Eric S. Casiño|title=Mindanao Statecraft and Ecology: Moros, Lumads, and Settlers Across the Lowland-highland Continuum|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=h8xxAAAAMAAJ|year=2000|publisher=Notre Dame University|isbn=978-971-555-354-4}}</ref> | |||
| * ] | |||
| The Americans started a colonization program on Mindanao for foreign agricultural companies and Filipino Christian settlers against the native Muslims and non-Muslim Lumads of Mindanao, in order to secure the area with a Christian presence and help the American military assert control over the area once it was conquered.<ref name="Franco2001">{{cite book|author=Jennifer Conroy Franco|title=Elections and Democratization in the Philippines|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fAq9kgbKBAUC&pg=PA221|year=2001|publisher=Taylor & Francis|isbn=978-0-8153-3734-8|page=221}}</ref> | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| 90% of Mindanao's people used to consist of native Moro Muslims at the start of the 20th century but the invasion and colonization sponsored by the American and Philippine governments led to Filipino Christian settlers turning into the majority of almost 75% of the population, with the American colonial government helping to kick natives off their land and giving the land titles to Christian colonists.<ref name="(Organization)1992">{{cite book|author=Human Rights Watch (Organization)|title=Bad Blood: Militia Abuses in Mindanao, the Philippines|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KbGdZCZc8ewC&pg=PA17|year=1992|publisher=Human Rights Watch|isbn=978-1-56432-060-5}}</ref>{{rp|17}} Media compared the American conquest of the west from the Native Americans to the Filipino conquest and settlement of Mindanao from the Muslims, the Philippine government, Philippine military and Filipino militias used extremely violent tactics against natives to support the settlers.<ref name="(Organization)1992" />{{rp|18-}} | |||
| {{Notelist}} | |||
| == References == | |||
| The government agencies involved in settlement on Mindanao were the National Land Settlement Administration (NLSA) and subsequently the Land Settlement and Development Corporation (LASEDECO), followed by the National Resettlement and Rehabilitation Administration (NARRA).<ref name="DaiTai1974">{{cite book|author1=Hongchao Dai|author2=Hung-chao Tai|title=Land Reform and Politics: A Comparative Analysis|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SjtJnkkaus8C&pg=PA259|date=1 January 1974|publisher=University of California Press|isbn=978-0-520-02337-6|page=259}}</ref> | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| === Works cited === | |||
| The Americans used their control over property and land laws to let American corporations and Filipino Christian settlers take over Lumad and Moro Muslim resources and land and depriving them of self-governance after eliminating the sovereignty of the Moro Sultanates, and ignoring Moro requests for their own independence, with the Philippine government continuing the colonization program after independence leading to a humongous number of Filipino settlers streaming into Moro territories, and this led to Moros making moves for independence and armed struggle against the Philippines.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Kamlian|first1=Jamail A.|title=Who are the Moro people?|url=http://opinion.inquirer.net/39098/who-are-the-moro-people|accessdate=29 June 2015|agency=Philippine Daily Inquirer|date=20 October 2012}}</ref> | |||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Dahl |first1=Adam |title=Empire of the People: Settler Colonialism and the Foundations of Modern Democratic Thought |date=2018 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7006-2607-6 |language=en}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Veracini |first1=Lorenzo |date=2013 |title='Settler Colonialism': Career of a Concept |journal=The Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History |volume=41 |issue=2 |pages=313–333 |doi=10.1080/03086534.2013.768099 |s2cid=159666130 |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/03086534.2013.768099 |access-date=7 May 2022}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| == Further reading == | |||
| After 1960 the settlement program turned the Moro Muslims into a minority from their previous majority in Mindanao, similar to what happened in the Indonesian ] where frontier areas are settled with ethnic Madurese and Javanese people.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Magdalena|first1=Federico V.|title=Islam and the Politics of Identity|url=http://www.hawaii.edu/cps/identity.html|website=University of Hawai'i at Manoā|publisher=Center for Philippine Studies|accessdate=26 June 2015}}</ref> | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Adhikari |first1=Mohamed |author-link1=Mohamed Adhikari |title=Civilian-Driven Violence and the Genocide of Indigenous Peoples in Settler Societies |date=2021 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-000-41177-5}} | |||
| * {{cite web |last1=Cox |first1=Alicia |title=Settler Colonialism |url=https://www.oxfordbibliographies.com/view/document/obo-9780190221911/obo-9780190221911-0029.xml |access-date=21 January 2021 |website=Oxford Bibliographies |publisher=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Englert |first1=Sai |title=Settler Colonialism: An Introduction |date=2022 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7453-4490-4 |language=en}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Belich |first=James |author-link=James Belich (historian) |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Rh76bzOX7XAC |title=Replenishing the earth: the settler revolution and the rise of the Anglo-world, 1783–1939 |publisher=] |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-19-929727-6 |location=Oxford |page=573}} | |||
| * ]. '']''. ], 2018. 243p. {{ISBN|9781583676639}} | |||
| * ]. ''The Dawning of the Apocalypse: The Roots of Slavery, White Supremacy, Settler Colonialism, and Capitalism in the Long Sixteenth Century.'' Monthly Review Press, 2020. {{ISBN|978-1-58367-875-6}}. | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Mamdani |first1=Mahmood |title=] |date=2020 |publisher=Harvard University Press |isbn=978-0-674-98732-6 |language=en}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Manjapra |first1=Kris |title=Colonialism in Global Perspective |date=2020 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-108-42526-1 |pages=43–70 |chapter=Settlement}} | |||
| * Marx, Christoph (2017). , , Mainz: , retrieved: March 17, 2021 (). | |||
| * Mikdashi, Maya (2013). ''What is settler colonialism?'' ] 37.2: 23–34. | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Pedersen |editor1-first=Susan |editor1-link=Susan Pedersen (historian) |editor2-last= Elkins |editor2-first=Caroline |editor2-link=Caroline Elkins |title=Settler Colonialism in the Twentieth Century |publisher=] |date=2005}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last=Sakai |first=J. |title=] |isbn=978-1-62963-037-3 |year=1983|publisher=PM Press }} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Veracini |first=Lorenzo |title=Settler Colonialism: A Theoretical Overview |publisher=] |year=2010 |isbn=9780230284906 |location=Hampshire, UK |pages=182}} | |||
| *{{cite book |last1=Veracini |first1=Lorenzo |title=The Settler Colonial Present |date=2015 |publisher=Springer |isbn=978-1-137-37247-5 |language=en}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Wolfe |first1=Patrick |author1-link=Patrick Wolfe |date=2016 |title=Traces of History: Elementary Structures of Race |publisher=]}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| The native Moros became victims to land grabs by Filipino Christian settlers.<ref>http://newsinfo.inquirer.net/681384/moro-doctors-try-to-heal-suffering</ref><ref>http://opinion.inquirer.net/83325/historical-truth-and-bangsamoro-autonomy</ref> | |||
| * | |||
| Severe violence between native Muslims and Christian settlers erupted due to the influx of Christian colonists, companies and other entities seeking to exploit new land on Mindanao who engaged in ].<ref name="Horakova1971">{{cite book|author=Eva Horakova|title=Problems of Filipino Settlers|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=blGaAq5wXL4C&pg=PA2|year=1971|publisher=Institute of Southeast Asian|page=2|id=GGKEY:LLSBZXRXTWT}}</ref> Lumad and Muslim interests were ignored by the state sponsored colonization program led by the National Land Settlement Administration (NLSA) which provided benefits for the colonists and made no consideration for the Muslims.<ref name="Larousse2001">{{cite book|author=William Larousse|title=A Local Church Living for Dialogue: Muslim-Christian Relations in Mindanao-Sulu, Philippines : 1965–2000|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qyo-Hti0-KAC&pg=PA114|date=1 January 2001|publisher=Gregorian Biblical BookShop|isbn=978-88-7652-879-8|page=114}}</ref> | |||
| Moro Muslims are just 17% of Mindanao's population whereas prior to the colonization program initiated by the governments of the Philippines they had been a massive majority and the colonization and land grabs led to the current violent conflict, with private companies and Filipino colonists from the Visayas and Luzon taking lands from Moro clans with the Philippine government issuing land titles to settlers and ignoring Moro ownership of the land since they declared Moro land as public lands.<ref name="Rabasa2007">{{cite book|author=Angel Rabasa|title=Ungoverned Territories: Understanding and Reducing Terrorism Risks|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=faWMHiaaLgkC&pg=PA126|year=2007|publisher=Rand Corporation|isbn=978-0-8330-4152-4|page=126}}</ref> | |||
| Massive settlement by Filipino Christian colonists continued after independence was granted and rule passed to Christian Filipinos from the Americans and land disputes the Christian settlers had with the Muslim and tribal natives broke out in violence, eventually the colonization, along with the ], led to the formation of the ] and Moro armed insurgency against Philippine rule.<ref name="MackerrasMackerras2003">{{cite book|author1=Colin Mackerras|author2=Foundation Professor in the School of Asian and International Studies Colin Mackerras|title=Ethnicity in Asia|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Mi6DAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA143|date=2 September 2003|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-134-51517-2|page=143}}</ref><ref name="Mackerras2004">{{cite book|author=Colin Mackerras|title=Ethnicity in Asia|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QLKpECdc4eIC&pg=PA143|date=18 June 2004|publisher=Taylor & Francis|isbn=978-0-203-38046-8|page=143}}</ref> | |||
| The Philippine government encouraged Filipino Christian settlers in Mindanao to form militias called ] to fight the Moros. The Ilaga engaged in massacres and atrocities and were responsible for ] of 65 Moro Muslim civilians in a Mosque on June 1971, including women and children. The Ilaga also engaged in cannibalism, cutting off the body parts of their victims to eat in rituals. The Ilaga settlers were given the sarcastic nickname as an acronym, the "Ilonggo Land Grabbers' Association".<ref>http://pcij.org/blog/2015/03/07/ph-souths-separatist-armed-groups</ref> | |||
| The Moros were only incorporated into the Philippines by "conquest and colonization", constituting a separate nation from Filipinos analogous to the experience of Native Americans who violently resisted American conquest.<ref>http://www.bworldonline.com/content.php?section=Opinion&title=should-there-be-a-moro-nation&id=103716</ref> | |||
| ===Bangladesh=== | |||
| {{main|Persecution of indigenous peoples in Bangladesh|2012 Ramu violence|Persecution_of_Buddhists#Bangladesh|Genocide_of_indigenous_peoples#Bangladesh|Wartime_sexual_violence#Bangladesh_-_Chittagong_Hill_Tracts|Chakma people|Jumma people}} | |||
| The CHT were subjected to colonization by Bengalis supported by the government of Bangladesh after independence.<ref>{{cite book|title=Economic and Political Weekly|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=j9KwAAAAIAAJ|year=1993|publisher=Sameeksha Trust|page=1740}}</ref><ref name="Weiner1993">{{cite book|author=Myron Weiner|title=International Migration and Security|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5NONAAAAMAAJ|year=1993|publisher=Westview Press|isbn=978-0-8133-8774-1|page=159}}</ref> In the ] Bengali settlers and soldiers have raped native ] (]) women "with impunity" with the Bangladeshi security forces doing little to protect the Jummas and instead assisting the rapists and settlers.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.survivalinternational.org/news/10141 |title=Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh – rapists act with impunity |last1=McEvoy |first1=Mark |date= 3 April 2014 |website=Survival International – The movement for tribal peoples |access-date= |quote=}}</ref> | |||
| The indigenous Buddhist and Hindu Jummas of Sino-Tibetan background have been targeted by the Bangladeshi government with massive amounts of violence and genocidal policies as ethnic Bengali settlers swamped into Jumma lands, seized control and massacred them with the Bangladeshi military engaging in mass rape of women, massacres of entire villages and attacks on Hindu and Buddhist religious sites with deliberate targeting of monks and nuns.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.marxist.com/fate-chittagong-hill-tracts-tribes-bangladesh.htm |title=The fate of the Chittagong Hill Tracts tribes of Bangladesh |last1=Iqbal |first1=Jamil M. |date= 2 November 2009 |website= In Defence of Marxism |access-date= |quote=}}</ref> The settlers are Muslims.<ref>http://unpo.org/article/2799</ref> The Karuna Bihar Buddhist temple was attacked by Bengali settlers.<ref>http://unpo.org/article/17798</ref> | |||
| ===Russia=== | |||
| {{main|Russian conquest of Siberia|Circassian genocide|Russification}} | |||
| ===Japan=== | |||
| {{see also|Shakushain's Revolt|Menashi-Kunashir Rebellion}} | |||
| The island of ] was inhabited by the indigenous ] until the Japanese invasion and annexation of the island in the 19th century and Japanese mass migration. | |||
| ===ROC-Taiwan=== | |||
| Nearly the entire population of ROC-Taiwan is the result of settler colonialism. The so-called "]", made out of the "]" are descendants of settler colonialists who migrated to Taiwan from mainland China in the 1940s and assimilate most of the native "]" aborigines. | |||
| ===Nazi Germany=== | |||
| {{main|Lebensraum|Generalplan Ost|Germanization|Expulsion of Poles by Nazi Germany}} | |||
| ===In Oceania=== | |||
| {{further|Europeans in Oceania}} | |||
| ====Australia==== | |||
| {{Seealso|Cultural assimilation|List of massacres of Indigenous Australians}} | |||
| Europeans came and settled in Australia, displacing ]. The Indigenous Australian population, estimated at about 350,000 at the time of European settlement,<ref>Smith, L. (1980), The Aboriginal Population of Australia, ] Press, Canberra</ref> declined steeply for 150 years following settlement from 1788, mainly because of ] combined with forced re-settlement and cultural disintegration.<ref>Page, A. (2015, September). .</ref><ref>Page, A., & Petray, T. (2015). Agency and Structural Constraints: Indigenous Peoples and the Settler-State in North Queensland. Settler Colonial Studies, 5 (2).</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ====New Zealand==== | |||
| {{Seealso|New Zealand Wars}} | |||
| New Zealand's European population is the result of migration by Europeans since the beginning of the 19th century. The indigenous ] population are a significant minority population in the 21st century. The ] accords official status to the ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Maori Language Act 1987 |url=http://www.legislation.govt.nz/act/public/1987/0176/latest/DLM124116.html |accessdate=13 April 2019 }}</ref> The ] is a document of central importance to the history and political constitution of the state of New Zealand, and is widely regarded as the ] of New Zealand.<ref name="NZ const">{{cite web |url=https://gg.govt.nz/office-governor-general/roles-and-functions-governor-general/constitutional-role/constitution/constitution |title=New Zealand's Constitution |publisher=Government House |access-date=17 August 2017 |url-status=live |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20171210231805/https://gg.govt.nz/office-governor-general/roles-and-functions-governor-general/constitutional-role/constitution/constitution |archivedate=10 December 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ====New Caledonia==== | |||
| The ] are the descendants of European—in the majority ]—settlers in ], who often displaced the indigenous ] population from the mid-19th century onwards. | |||
| ===In Africa === | |||
| {{further|White Africans of European ancestry|North African Arabs|Herero and Namaqua genocide}} | |||
| ==== South Africa ==== | |||
| In 1652, the arrival of Europeans sparked the beginning of settler colonialism in South Africa. The ] was set up at the Cape, and imported large numbers of slaves from Africa and Asia during the mid-seventeenth century.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|title=Settler colonialism and land rights in South Africa: Possession and dispossession on the Orange River|last=Cavanagh|first=E|publisher=Palgrave Macmillan|year=2013|isbn=978-1-137-30577-0|location=United Kingdom|pages=10–16}}</ref> The Dutch East India Company established a refreshment station for ships sailing between Europe and the east. The initial plan by Dutch East India Company officer ] was to maintain a small community around the new fort, but the community continued to spread and colonize further than originally planned.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Fourie|first=J|date=2014|title=Settler Skills and Colonial Development: The Huguenot Wine-Makers in Eighteenth-Century Dutch South Africa|url=|journal=Economic History Review|volume=67|issue=4|pages=932–963|doi=10.1111/1468-0289.12033}}</ref> There was a historic struggle to achieve the intended British sovereignty that was achieved in other parts of the ]. State sovereignty belonged to the ] (1910-61), followed by the ] (1961-present day).<ref name=":0" /> As of 2014, the South African government has re-opened the period for land claims under the Restitution of Land Rights Amendment Act.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Weinberg|first=T|date=2015|title=The Griqua Past and the Limits of South African History, 1902–1994; Settler Colonialism and Land Rights in South Africa: Possession and Dispossession on the Orange River|url=|journal=Journal of Southern African Studies|volume=41|pages=211–214|doi=10.1080/03057070.2015.991591}}</ref> | |||
| ===In the Middle East=== | |||
| ====Ba'athist Iraq==== | |||
| {{main|Ba'athist Arabization campaigns in North Iraq}} | |||
| For decades, Saddam Hussein ']' northern Iraq,<ref name=arabization>{{cite web|url=https://www.hrw.org/reports/2004/iraq0804/4.htm|title=Claims in Conflict: Reversing Ethnic Cleansing in Northern Iraq: III. Background}}</ref> an act often referred as "internal colonialism".<ref>Prof. Rimki Basu. ''International Politics: Concepts, Theories and Issues'':p103. 2012.</ref> The policy of Saddam Hussein in North Iraq during the Ba'athist rule was described by Dr. Francis Kofi Abiew as a "Colonial 'Arabization'" program, including large-scale Kurdish deportations and forced Arab settlement in the region.<ref>Francis Kofi Abiew. ''The Evolution of the Doctrine and Practice of Humanitarian Intervention'':p146. 1991.</ref> | |||
| ====Northern Cyprus==== | |||
| {{main|Turkish settlers in Northern Cyprus}} | |||
| Following the ], the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe stated that the demographics of the island are continuously modified as a result of the deliberate policies of the Turks.<ref name=cyprusguide/> Some suggest that over 120,000 Turkish settlers were brought to the island from mainland Turkey, in violation of article 49 of the Geneva convention.<ref name=cyprusguide/> | |||
| According to the UN resolution 1987/19, adopted on 2 September 1987, the UN expressed "its concern also at the policy and practice of the implantation of settlers in the occupied territories of Cyprus, which constitute a form of colonialism and attempt to change illegally the demographic structure of Cyprus".<ref name=cyprusguide>International Business Publications. ''Cyprus Country Study Guide Volume 1 Strategic Information and Developments'':p77-78. 2013. {{ISBN|1-4387-7423-0}}</ref> | |||
| ====Nakhchivan and Nagorno-Karabakh==== | |||
| {{main|Armenians in Nakhchivan|Nagorno-Karabakh War}} | |||
| ====Zionism and the State of Israel==== | |||
| In 1967, the French historian ] wrote an article later translated and published in English as ''Israel: A Colonial Settler-State?''<ref>Rodinson, Maxime. "Israel, fait colonial?" ''Les Temps Moderne'', 1967. Republished in English as ''Israel: A Colonial Settler-State?'', New York, Monad Press, 1973. | |||
| </ref> ] describes Israel as a colonial state and writes that Jewish settlers could expel the British in 1948 only because they had their own colonial relationships inside and outside Israel's new borders.<ref>"Israel could celebrate its anticolonial/anti-British struggle exactly Lorenzo Veracini, Borderlands, vol 6 No 2, 2007.</ref> Veracini believes the possibility of an Israeli disengagement is always latent and this relationship could be severed, through an "]" (Veracini 2006)<ref>Veracini, Lorenzo, "Israel and Settler Society", London: Pluto Press. 2006.</ref> Other commentators, such as ], ],<ref>, Nira Yuval-Davis (Editor), Daiva K Stasiulis (Editor), Paperback 352pp, {{ISBN|978-0-8039-8694-7}}, August 1995 SAGE Publications.</ref> and ] in the "Post Colonial Colony: time, space and bodies in Palestine/ Israel in the persistence of the Palestinian Question"<ref>"Post Colonial Colony: time, space and bodies in Palestine/ Israel in the persistence of the Palestinian Question", Routledge, NY, (2006) and "The Pre-Occupation of Post-Colonial Studies" ed. Fawzia Afzal-Khan and Kalpana Rahita Seshadri. (Durham: Duke University Press)</ref> have included Israel in their global analysis of settler societies. ] describes Zionism and Israel in similar terms.<ref>, King's Review – Magazine</ref><ref>Video: . ], 5 April 2017</ref> Scholar Amal Jamal, from ], has stated, "Israel was created by a settler-colonial movement of Jewish immigrants".<ref>{{cite book|author=Amal Jamal|title=Arab Minority Nationalism in Israel: The Politics of Indigeneity|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=pWLCpqnsoLQC&pg=PA48|year=2011|publisher=Taylor & Francis|isbn=978-1-136-82412-8|page=48}}</ref> | |||
| ]s (magenta) in the occupied ] in 2014]] | |||
| Some ] express similar opinions - writer and ] ], member of the ] lives in what he describes as "the heavily-colonised ]", and drew parallels in 1976 between South African and Israeli settler colonialism, writes that "as in ], stretches of land were acquired by the Zionist settlers and their ] tenants thrown out".<ref> Jamil Hilal, UTAFITI journal of the arts and social sciences, University of Dar Es Salaam. 1976.</ref> Former Palestinian Foreign Minister Dr. Nasser al-Qidwa opposes the policy of ] and has described those efforts as colonialism.<ref> Speech: Dr. Nasser al-Qidwa, former Palestinian Foreign Minister, Jerusalem Media & Communication Centre, November 2006. | |||
| </ref> | |||
| According to a report by the ] issued in 2000, the settler population in the West Bank and Gaza strip grew from approximately 1,500 in 1972 to approximately 73,000 in 1989, and more than doubled that in 1998 to approximately 169,000. The report also describes demographics statistics indicating that, by place of birth, 78% of Israeli settlers in the West Bank and Gaza were from Europe or America, 19% from Israel.<ref>, FMEP, Volume 10, Number 4; July–August 2000, pp.10, 12</ref> In January 2015 the Israeli Interior Ministry gave figures of 389,250 Israelis living in the West Bank and a further 375,000 Israelis living in East Jerusalem.<ref>{{cite news |title=Jewish Population in Judea & Samaria Growing Significantly |url=http://www.breakingisraelnews.com/26966/jewish-population-in-judea-and-samaria-growing-significantly/#DpRV1c2O5HHhPB67.97}}</ref> | |||
| A number of scholars have objected to the idea that Zionism and the State of Israel are tantamount to settler colonialism. Avi Bareli, in his essay 'Forgetting Europe: Perspectives on the Debate about Zionism and Colonialism', argues that the "Colonialist School offered this alternative interpretation to replace the account of the return of the Jewish people to its land". Moreover, he asserts that it "ignores the economic, social, and cultural processes that spurred the Jews in Eastern Europe to emigrate to Palestine over decades in the twentieth century".<ref>Bareli, Israeli Historical Revisionism: From Left to Right, pp. 99–100</ref> Arnon Golan contends that "Zionism was not imperialist or colonialist in nature, but a national liberation movement that developed in eastern and central Europe, in conjunction with other national liberation movements in these regions" and that "Zionism was a diaspora national movement that aspired to promote its interests in the destined homeland through becoming a collaborator of imperial powers."<ref>Arnon, Space and Polity, p. 140-141</ref> S. Ilan Troen, in 'De-Judaizing the Homeland: Academic Politics in Rewriting the History of Palestine', argues that Zionism was the repatriation of a long displaced indigenous population to their historic homeland, and that "Zionists did not see themselves as foreigners or conquerors, for centuries in the Diaspora they had been strangers". Troen further argues that there are several differences between European colonialism and the Zionist movement, including that "there is no New Vilna, New Bialystock, New Warsaw, New England, New York,...and so on" in Israel. He writes that "mandates were intended to nurture the formation of new states until independence and this instrument was to be applied to Jews, even as it was for the Arab peoples of Syria and Iraq. In this view, Jews were a people not only entitled to a state but that polity was naturally located in a part of the world in which they had originated, had been resident since the ancient world, and still constituted a vital presence in many areas of the region, including Palestine" and that "perhaps the most manifest or visible evidence—for those who would be willing to acknowledge—were found in the revival of Hebrew into a living language; the marking the landscape with a Jewish identity; and the development of an indigenous culture with roots in the ancient past." He concludes that "casting Zionists as colonizers serves to present them as occupiers in a land to which, by definition, they do not belong."<ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.1080/13537120701445372 | volume=13 | issue=4 | title=De-Judaizing the Homeland: Academic Politics in Rewriting the History of Palestine | year=2007 | journal=Israel Affairs | pages=872–884 | last1 = Troen | first1 = S. Ilan}}</ref> Others such as Michael J. Cohen,<ref>{{cite journal|doi=10.1080/13531042.2011.610119 | volume=30 | issue=2 | title=Zionism and British imperialism II: Imperial financing in Palestine | year=2011 | journal=Journal of Israeli History | pages=115–139 | last1 = Cohen | first1 = Michael J.}}</ref> and Bernard Avishai<ref>Zionist "Colonialism": Myth and Dilemma, 1975</ref> have similarly rebutted criticism of the State of Israel as a settler-colonial state. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| * {{cite book|last= Belich|first= James|authorlink= James Belich (historian)|title=Replenishing the earth : the settler revolution and the rise of the Anglo-world, 1783–1939|url= https://books.google.com/books?id=Rh76bzOX7XAC|year=2009|publisher= Oxford University Press|location= Oxford|isbn= 978-0-19-929727-6|page= 573}} | |||
| *''Settler Colonialism in the Twentieth Century'' (edited by ] and ], Routledge, 2005) | |||
| * – ] | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Veracini|first= Lorenzo|title=Settler Colonialism: A Theoretical Overview|year= 2010|publisher= Palgrave MacMillan|location= Hampshire, UK|isbn= 9780230284906|pages= 182}} | |||
| *{{Citation|last=Loizides|first=Neophytos|url=http://www.kent.ac.uk/politics/carc/reading-group/Loizides%20Paper.pdf|journal=Political Geography|title=Contested migration and settler politics in Cyprus|year=2011|volume=30|issue=7|pages=391–401|doi=10.1016/j.polgeo.2011.08.004}} | |||
| ==References== | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| {{Colonialism}} | {{Colonialism}}{{Colonization}}{{DEFAULTSORT:Settler Colonialism}} | ||
| {{Colonization}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:04, 22 December 2024
Form of colonialism seeking population replacement with settlers
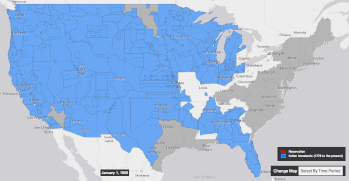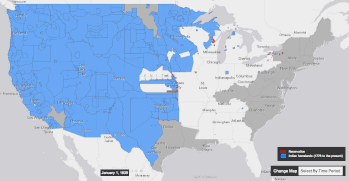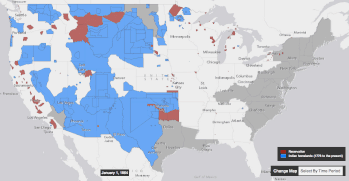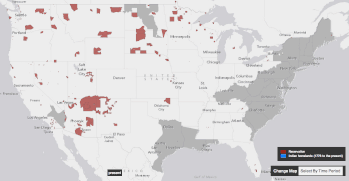
Settler colonialism is a logic and structure of displacement by settlers, using colonial rule, over an environment for replacing it and its indigenous peoples with settlements and the society of the settlers.
Settler colonialism is a form of exogenous (of external origin, coming from the outside) domination typically organized or supported by an imperial authority, which maintains a connection or control to the territory through the settler's colonialism. Settler colonialism contrasts with exploitation colonialism, where the imperial power conquers territory to exploit the natural resources and gain a source of cheap or free labor. As settler colonialism entails the creation of a new society on the conquered territory, it lasts indefinitely unless decolonisation occurs through departure of the settler population or through reforms to colonial structures, settler-indigenous compacts and reconciliation processes.
Settler colonial studies has often focused on former British colonies in North America, Australia and New Zealand, which are close to the complete, prototypical form of settler colonialism. However, settler colonialism is not restricted to any specific culture and has been practised by non-Europeans. According to certain genocide scholars, including Raphael Lemkin – the individual who coined the term genocide – colonization is intrinsically genocidal.
Origins as a theory
During the 1960s, settlement and colonization were perceived as separate phenomena from colonialism. Settlement endeavours were seen as taking place in empty areas, downplaying the Indigenous inhabitants. Later on in the 1970s and 1980s, settler colonialism was seen as bringing high living standards in contrast to the failed political systems associated with classical colonialism. Beginning in the mid-1990s, the field of settler colonial studies was established distinct but connected to Indigenous studies. Although often credited with originating the field, Australian historian Patrick Wolfe stated that "I didn't invent Settler Colonial Studies. Natives have been experts in the field for centuries." Additionally, Wolfe's work was preceded by others that have been influential in the field, such as Fayez Sayegh's Zionist Colonialism in Palestine and Settler Capitalism by Donald Denoon.
Definition and concept
Settler colonialism is a logic and structure, and not a mere occurrence. Settler colonialism takes claim of environments for replacing existing conditions and members of that environment with those of the settlement and settlers. Intrinsically connected to this is the displacement or elimination of existing residents, particularly through destruction of their environment and society. As such, settler colonialism has been identified as a form of environmental racism.
Some scholars describe the process as inherently genocidal, considering settler colonialism to entail the elimination of existing peoples and cultures, and not only their displacement (see genocide, "the intentional destruction of a people in whole or in part"). However, the opposite argument has also been made by Lorenzo Veracini, who argues that all genocide is settler colonial in nature.
Depending on the definition, it may be enacted by a variety of means, including mass killing of the previous inhabitants, removal of the previous inhabitants and/or cultural assimilation.
Therefore, colonial settling has been called an invasion or occupation, emphazising the violent reality of colonization and its settling, instead of the more domestic meaning of settling.
Settler colonialism is distinct from migration because immigrants aim to join an existing society, not replace it. Mahmood Mamdani writes, "Immigrants are unarmed; settlers come armed with both weapons and a nationalist agenda. Immigrants come in search of a homeland, not a state; for settlers, there can be no homeland without a state." Nevertheless, the difference is often elided by settlers who minimize the voluntariness of their departure, claiming that settlers are mere migrants, and some pro-indigenous positions which militantly simplify, claiming that all migrants are settlers.
The settler state is a state established through settler colonialism, by and for settlers.
Examples

The settler colonial paradigm has been applied to a wide variety of conflicts around the world, including New Caledonia, Western New Guinea, the Andaman Islands, Argentina, Australia, British Kenya, the Canary Islands, Fiji, French Algeria, Generalplan Ost, Hawaii, Hokkaido, Ireland, Israel/Palestine, Italian Libya and East Africa, Kashmir, Korea and Manchukuo, Latin America, Liberia, New Zealand, northern Afghanistan, North America, Posen and West Prussia and German South West Africa, Rhodesia, Sápmi, South Africa, South Vietnam, and Taiwan.
Africa
See also: White Africans of European ancestry and French conquest of Algeria
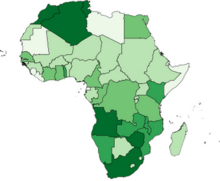
Canary Islands
Further information: Conquest of the Canary IslandsDuring the fifteenth century, the Kingdom of Castile sponsored expeditions by conquistadors to subjugate under Castilian rule the Macaronesian archipelago of the Canary Islands, located off the coast of Morocco and inhabited by the Indigenous Guanche people. Beginning with the start of the conquest of the island of Lanzarote on 1 May 1402 and ending with the surrender of the last Guanche resistance on Tenerife on 29 September 1496 to the now-unified Spanish crown, the archipelago was subject to a settler colonial process involving systematic enslavement, mass murder, and deportation of the Guanches, who were replaced with Spanish settlers, in a process foreshadowing the Iberian colonisation of the Americas that followed shortly thereafter. Also like in the Americas, Spanish colonialists in the Canaries quickly turned to the importation of slaves from mainland Africa as a source of labour due to the decimation of the already small Guanche population by a combination of war, disease, and brutal forced labour. Historian Mohamed Adhikari has labelled the conquest of the Canary Islands as the first overseas European settler colonial genocide.
Moroccan-occupied Western Sahara

Since 1975, the Kingdom of Morocco has sponsored settlement schemes that have encouraged several thousand Moroccan citizens to settle Moroccan-occupied Western Sahara as part of the Western Sahara conflict. On 6 November 1975, the Green March took place, during which about 350,000 Moroccan citizens crossed into Saguia al-Hamra in the former Spanish Sahara after having received a signal from King Hassan II. As of 2015, it is estimated that Moroccan settlers constitute two-thirds of the population of Western Sahara.
Under international law, the transfer of Moroccan citizens into the occupied territory constitutes a direct violation of Article 49 of the Fourth Geneva Convention (cf. Turkish settlers in Northern Cyprus and Israeli settlers in the Palestinian territories).
South Africa
Main article: Free Burghers in the Dutch Cape Colony
In 1652, the arrival of Europeans sparked the beginning of settler colonialism in South Africa. The Dutch East India Company was set up at the Cape, and imported large numbers of slaves from Africa and Asia during the mid-seventeenth century. The Dutch East India Company established a refreshment station for ships sailing between Europe and the east. The initial plan by Dutch East India Company officer Jan van Riebeeck was to maintain a small community around the new fort, but the community continued to spread and settle further than originally planned. There was a historic struggle to achieve the intended British sovereignty that was achieved in other parts of the Commonwealth. State sovereignty belonged to the Union of South Africa (1910–1961), followed by the Republic of South Africa (1961–1994) and finally the modern day Republic of South Africa (1994–present day).
In 1948, the policy of Apartheid was introduced South Africa in order to segregate the races and ensure the domination of the Afrikaner minority over non-whites, politically, socially and economically. As of 2014, the South African government has re-opened the period for land claims under the Restitution of Land Rights Amendment Act.
Liberia
Liberia is often regarded by scholars as a unique example of settler colonialism and the only known instance of Black settler colonialism. It is frequently described as an African American settler colony tasked with establishing a Western form of governance in Africa.
Liberia was founded as the private colony of Liberia in 1822 by the American Colonization Society, a White American-run organization, to relocate free African Americans to Africa, as part of the Back-to-Africa movement. This settlement scheme stemmed from fears that free African Americans would assist slaves in escaping, as well as the widespread belief among White Americans that African Americans were inherently inferior and should thus be relocated. U.S. presidents Thomas Jefferson and James Madison publicly endorsed and funded the project.
Between 1822 and the early 20th century, around 15,000 African Americans colonized Liberia on lands acquired from the region's indigenous African population. The African American elite monopolized the government and established minority rule over the locals. As they possessed Western culture, they felt superior to the natives, whom they dominated and oppressed. Indigenous revolts against the Americo-Liberian elite such as the Grebo Revolt in 1909–1910 and Kru Revolt in 1915 were quelled with U.S. military support.
North America
Canada
Main article: Settler colonialism in Canada Further information: Canadian genocide of Indigenous peoples
Attempts to assimilate the Indigenous peoples of what is now Canada were rooted in imperial colonialism centred around European worldviews and cultural practices, and a concept of land ownership based on the discovery doctrine. Original assimilation efforts were religiously-oriented, beginning in the 17th century with the arrival of French missionaries in New France. Although not without conflict, European Canadians' early interactions with First Nations and Inuit populations were relatively peaceful. First Nations and Métis peoples (of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry) played a critical part in the development of European colonies in Canada, particularly for their role in assisting European coureur des bois and voyageurs in their explorations of the continent during the North American fur trade.
The early European interactions with First Nations would change from Peace and Friendship Treaties to dispossession of lands through treaties and displacement legislation such as the Gradual Civilization Act, the Indian Act, the Potlatch ban, and the pass system, that focused on European ideals of Christianity, sedentary living, agriculture, and education.
Indigenous groups in Canada continue to suffer from racially motivated discrimination, despite living in one of the most progressive countries in the world. Discriminatory practices such as criminal justice inequity, police brutality, high incarnation rates, and high rates of violence against Indigenous women have been subject to legal and political review.
United States
Main article: Manifest destiny Further information: Native American genocide in the United States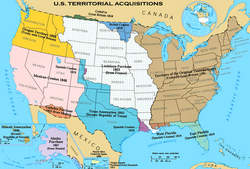

In colonial America, European powers created economic dependency and imbalance of trade, incorporating Indigenous nations into spheres of influence and controlling them indirectly with the use of Christian missionaries and alcohol. With the emergence of an independent United States, desire for land and the perceived threat of permanent Indigenous political and spatial structures led to violent relocation of many Indigenous tribes to the American West, in what is known as the Trail of Tears.
In response to American encroachment on native land in the Great Lakes region, the Pan-Indian confederacies of the Northwest Confederacy and Tecumseh's Confederacy emerged. Despite initial victories in both cases, such as St. Clair's defeat or the siege of Detroit, both eventually lost, thereby paving the way for American control over the region. Settlement into conquered land was rapid. Following the 1795 Treaty of Greenville, American settlers poured into southern Ohio, such that by 1810 it had a population of 230,760. The defeat of the confederacies in the Great Lakes paved the way for large land loss in the region, via treaties such as the Treaty of Saginaw which saw the loss of more than 4,000,000 acres of land.
Frederick Jackson Turner, the father of the "frontier thesis" of American history, noted in 1901: "Our colonial system did not start with Spanish War; the U.S. had had a colonial history from the beginning...hidden under the phraseology of 'interstate migration' and territorial organization'". While the United States government and local state governments directly aided this dispossession through the use of military forces, ultimately this came about through agitation by settler society in order to gain access to Indigenous land. Especially in the US South, such land acquisition built plantation society and expanded the practice of slavery. Settler colonialism participated in the formation of US cultures and lasted past the conquest, removal, or extermination of Indigenous people. In 1928, Adolf Hitler spoke admiringly of the impact of white settler colonialism on the Natives, stating the US had "gunned down the millions of Redskins to a few hundred thousand, and now keep the modest remnant under observation in a cage". The practice of writing the Indigenous out of history perpetrated a forgetting of the full dimensions and significance of colonialism at both the national and local levels.
Asia
China
Further information: Migration to Xinjiang and Sinicization of Tibet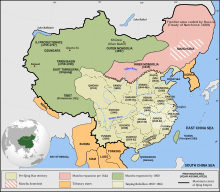
Near the end of their rule the Qing dynasty attempted to colonize Xinjiang, Tibet, and other parts of the imperial frontier. To accomplish this goal, they began resettling Han Chinese on the frontier. This policy of settler colonialism was renewed by the People's Republic of China, led by Chinese Communist Party, and is being practiced today according to some academics and researchers.
Israel
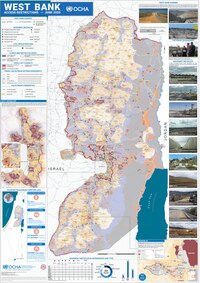
Zionism has been characterized by some scholars as a form of settler colonialism concerning region of Palestine and the Israeli–Palestinian conflict. This academic framework has also been embraced by leftist groups and individuals involved in anti-Israel activism and campus protests. However, this viewpoint faces substantial criticism from scholars and is largely rejected by many Jews due to its perceived denial of the historical Jewish connection to Palestine, among other reasons.
Many of the founding fathers of Zionism themselves described the project as colonization, such as Vladimir Jabotinsky, who said "Zionism is a colonization adventure." Founder of the World Zionist Organization, Theodor Herzl, described the Zionist project as "something colonial" in a letter to Cecil Rhodes in 1902.
In 1967, the French historian Maxime Rodinson wrote an article later translated and published in English as Israel: A Colonial Settler-State? Lorenzo Veracini describes Israel as a "settler colonial polity", and writes that it could celebrate its anticolonial struggle in 1948 because it had colonial relationships inside and outside Israel's new borders. Veracini believes the possibility of an Israeli disengagement is always latent and this relationship could be severed, through an "accommodation of a Palestinian Israeli autonomy within the institutions of the Israeli state". Other commentators, such as Daiva Stasiulis, Nira Yuval-Davis, and Joseph Massad in the "Post Colonial Colony: time, space and bodies in Palestine/Israel in the persistence of the Palestinian Question" have included Israel in their global analysis of settler societies. Ilan Pappé describes Zionism and Israel in similar terms. Scholar Amal Jamal, from Tel Aviv University, has stated, "Israel was created by a settler-colonial movement of Jewish immigrants". Damien Short has accused Israel of carrying out genocide against Palestinians during the Israeli–Palestinian conflict since its inception within a settler colonial context.
Writing in the 1990s, the Australian historian Patrick Wolfe is credited with originating the field. He theorized settler colonialism as a structure (rather than an event) premised on the elimination rather than exploitation of the native population, thus distinguishing it from classical colonialism. Wolfe argued that settler colonialism was centered on the control of land, that it continued after the closing of the frontier, and that continued to exist today, classifying Israel as a modern form of settler colonialism. His approach was defining for the field, but has been challenged by other scholars on the basis that many situations involve a combination of elimination and exploitation.
Critics of the paradigm argue that Zionism does not fit the traditional framework of colonialism. S. Ilan Troen views Zionism as the return of an indigenous population to its historic homeland, distinct from imperial expansion. Moses Lissak asserted that the settler-colonial thesis denies the idea that Zionism is the modern national movement of the Jewish people, seeking to reestablish a Jewish political entity in their historical territory. Zionism, Lissak argues, was both a national movement and a settlement movement at the same time, so it was not, by definition, a colonial settlement movement.
Russia and the Soviet Union
Main articles: Circassian genocide, Ethnic Russians in post-Soviet states, and Population transfer in the Soviet Union
Some scholars describe Russia as a settler colonial state, particularly in its expansion into Siberia and the Russian Far East, during which it displaced and resettled Indigenous peoples, while practicing settler colonialism. The annexation of Siberia and the Far East to Russia was resisted by the Indigenous peoples, while the Cossacks often committed atrocities against them. During the Cold War, new forms of Indigenous repression were practiced.
This colonization continued even during the Soviet Union in the 20th century. The Soviet policy also sometimes included the deportation of the native population, as in the case of the Crimean Tatars.
Taiwan
Further information: Taiwanese indigenous peoplesAccording to a PhD thesis by Lin-chin Tsai, current ethnic makeup of Taiwan is largely the result of Chinese settler colonialism beginning in the seventeenth century.
Australia
Main article: Settler colonialism in Australia See also: List of massacres of Indigenous Australians
Europeans explored and settled Australia, displacing Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. The Indigenous Australian population was estimated at 795,000 at the time of European settlement. The population declined steeply for 150 years following settlement from 1788, due to casualties from infectious disease, the Australian frontier wars and forced re-settlement and cultural disintegration.
Responses
Settler colonialism exists in tension with indigenous studies. Some indigenous scholars believe that settler colonialism as a methodology can lead to overlooking indigenous responses to colonialism; however, other practitioners of indigenous studies believe that settler colonialism has important insights that are applicable to their work. Settler colonialism as a theory has also been criticized from the standpoint of postcolonial theory. Antiracism has been criticized on the basis that it does not provide a special status for indigenous claims, and in response settler colonial theory has been criticized for potentially contributing to the marginalization of racialized immigrants.
Political theorist Mahmoud Mamdani suggested that settlers could never succeed in their effort to become native, and therefore the only way to end settler colonialism was to erase the political significance of the settler–native dichotomy.
According to Chickasaw scholar Jodi Byrd, in contrast to settler, the term arrivant refers to enslaved Africans transported against their will, and to refugees forced into the Americas due to the effects of imperialism.
In his book Empire of the People: Settler Colonialism and the Foundations of Modern Democratic Thought, political scientist Adam Dahl states that while it has often been recognized that "American democratic thought and identity arose out of the distinct pattern by which English settlers colonized the new world", histories are missing the "constitutive role of colonial dispossession in shaping democratic values and ideals".
See also
Notes
- Example reconciliation programmes include: Reconciliation in Australia, and truth and reconciliation commissions in Canada, Norway and South Africa.
References
- ^ Carey, Jane; Silverstein, Ben (2 January 2020). "Thinking with and beyond settler colonial studies: new histories after the postcolonial". Postcolonial Studies. 23 (1): 1–20. doi:10.1080/13688790.2020.1719569. hdl:1885/204080. ISSN 1368-8790. S2CID 214046615.
The key phrases Wolfe coined here – that invasion is a 'structure not an event'; that settler colonial structures have a 'logic of elimination' of Indigenous peoples; that 'settlers come to stay' and that they 'destroy to replace' – have been taken up as the defining precepts of the field and are now cited by countless scholars across numerous disciplines.
- ^ Veracini, Lorenzo (2017). "Introduction: Settler colonialism as a distinct mode of domination". In Cavanagh, Edward; Veracini, Lorenzo (eds.). The Routledge Handbook of the History of Settler Colonialism. Routledge. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-415-74216-0.
Settler colonialism is a relationship. It is related to colonialism but also inherently distinct from it. As a system defined by unequal relationships (like colonialism) where an exogenous collective aims to locally and permanently replace indigenous ones (unlike colonialism), settler colonialism has no geographical, cultural or chronological bounds. It is culturally nonspecific ... It can happen at any time, and everyone is a settler if they are part of a collective and sovereign displacement that moves to stay, that moves to establish a permanent homeland by way of displacement.
- ^ McKay, Dwanna L.; Vinyeta, Kirsten; Norgaard, Kari Marie (September 2020). "Theorizing race and settler colonialism within U.S. sociology". Sociology Compass. 14 (9). doi:10.1111/soc4.12821. ISSN 1751-9020. S2CID 225377069.
Settler-colonialism describes the logic and operation of power when colonizers arrive and settle on lands already inhabited by another group. Importantly, settler colonialism operates through a logic of elimination, seeking to eradicate the original inhabitants through violence and other genocidal acts and to replace the existing spiritual, epistemological, political, social, and ecological systems with those of the settler society.
- ^ Whyte, Kyle (1 September 2018). "Settler Colonialism, Ecology, and Environmental Injustice". Environment and Society. 9 (1): 125–144. doi:10.3167/ares.2018.090109. ISSN 2150-6779.
- LeFevre, Tate. "Settler Colonialism". oxfordbibliographies.com. Tate A. LeFevre. Retrieved 19 October 2017.
Though often conflated with colonialism more generally, settler colonialism is a distinct imperial formation. Both colonialism and settler colonialism are premised on exogenous domination, but only settler colonialism seeks to replace the original population of the colonized territory with a new society of settlers (usually from the colonial metropole).
- Veracini, Lorenzo (October 2007). "Settler Colonialism and Decolonisation". Borderlands. 6 (2).
- ^ Englert, Sai (2020). "Settlers, Workers, and the Logic of Accumulation by Dispossession". Antipode. 52 (6): 1647–1666. Bibcode:2020Antip..52.1647E. doi:10.1111/anti.12659. hdl:1887/3220822. S2CID 225643194.
- Irvin-Erickson, Douglas (2020). "Raphaël Lemkin: Genocide, cultural violence, and community destruction". In Greenland, Fiona; Göçek, Fatma Müge (eds.). Cultural Violence and the Destruction of Human Communities. Routledge. doi:10.4324/9781351267083-3. ISBN 978-1-351-26708-3. S2CID 234701072.
In a footnote, he added that genocide could equally be termed 'ethnocide', with the Greek ethno meaning 'nation'.
- Short, Damien (2016). Redefining Genocide: Settler Colonialism, Social Death and Ecocide. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 69. ISBN 978-1-84813-546-8. Archived from the original on 16 March 2023. Retrieved 1 June 2022.
- Moses, A. Dirk (2008). "Empire, Colony, Genocide: Keywords and the Philosophy of History". In Moses, A. Dirk (ed.). Empire, Colony, Genocide: Conquest, Occupation, and Subaltern Resistance in World History. Berghahn Books. pp. 8–9. ISBN 978-1-84545-452-4.
Extra-European colonial cases also featured prominently in this projected global history of genocide. In 'Part III: Modern Times,' he wrote the following numbered chapters: (1) Genocide by the Germans against the Native Africans; (3) Belgian Congo; (11) Hereros; (13) Hottentots; (16) Genocide against the American Indians; (25) Latin America; (26) Genocide against the Aztecs; (27) Yucatan; (28) Genocide against the Incas; (29) Genocide against the Maoris of New Zealand; (38) Tasmanians; (40) S.W. Africa; and finally, (41) Natives of Australia ... While Lemkin's linking of genocide and colonialism may surprise those who think that his neologism was modeled after the Holocaust of European Jewry, an investigation of his intellectual development reveals that the concept is the culmination of a long tradition of European legal and political critique of colonization and empire.
- ^ Veracini 2013.
- Shoemaker, Nancy (1 October 2015). "A Typology of Colonialism | Perspectives on History". American Historical Association. Retrieved 28 April 2022.
- ^ Kauanui, J. Kēhaulani (3 April 2021). "False dilemmas and settler colonial studies: response to Lorenzo Veracini: 'Is Settler Colonial Studies Even Useful?'". Postcolonial Studies. 24 (2): 290–296. doi:10.1080/13688790.2020.1857023. ISSN 1368-8790. S2CID 233986432.
- Van Sant, Levi; Milligan, Richard; Mollett, Sharlene (2021). "Political Ecologies of Race: Settler Colonialism and Environmental Racism in the United States and Canada". Antipode. 53 (3): 629–642. Bibcode:2021Antip..53..629V. doi:10.1111/anti.12697. ISSN 0066-4812.
- Short, Damien (2016). Redefining Genocide: Settler Colonialism, Social Death and Ecocide. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 69. ISBN 978-1-84813-546-8.
- Veracini, Lorenzo (2021). "Colonialism, Frontiers, Genocide: Civilian-Driven Violence in Settler Colonial Situations". Civilian-Driven Violence and the Genocide of Indigenous Peoples in Settler Societies. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-000-41177-5.
not only is genocide necessarily settler colonial (even though settler colonialism is not always genocidal or even successful)
- ^ Wolfe, Patrick (2006). "Settler colonialism and the elimination of the native". Journal of Genocide Research. 8 (4): 387–409. doi:10.1080/14623520601056240. ISSN 1462-3528. S2CID 143873621.
- Kilroy, Peter (22 May 2024). "Discovery, settlement or invasion? The power of language in Australia's historical narrative". The Conversation. Retrieved 14 August 2024.
- Veracini 2015, p. 40.
- ^ Mamdani 2020, p. 253.
- Veracini 2015, p. 35.
- Tozer, Angela (2021). "Democracy in a Settler State?: Settler Colonialism and the Development of Canada, 1820–67". Constant Struggle: Histories of Canadian Democratization. McGill-Queen's University Press. pp. 87–115. doi:10.2307/j.ctv1z7kjww.7. ISBN 978-0-2280-0866-8. JSTOR j.ctv1z7kjww.7. Retrieved 9 November 2024.
- "New Caledonia set for 2nd referendum on independence from France". Al Jazeera. 3 October 2020.
- McNamee, Lachlan (15 May 2020). "Indonesian Settler Colonialism in West Papua". SSRN 3601528.
- Larson, Carolyne R. (2020). The Conquest of the Desert: Argentina's Indigenous Peoples and the Battle for History. University of New Mexico Press. ISBN 9780826362087.
- ^ Adhikari, Mohamed (7 September 2017). "Europe's First Settler Colonial Incursion into Africa: The Genocide of Aboriginal Canary Islanders". African Historical Review. 49 (1): 1–26. doi:10.1080/17532523.2017.1336863. S2CID 165086773. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- Barclay, Fiona; Chopin, Charlotte Ann; Evans, Martin (12 January 2017). "Introduction: settler colonialism and French Algeria". Settler Colonial Studies. 8 (2): 115–130. doi:10.1080/2201473X.2016.1273862. hdl:1893/25105. S2CID 151527670.
- Takumi, Roy (1994). "Challenging U.S. Militarism in Hawai'i and Okinawa". Race, Poverty & the Environment. 4/5 (4/1): 8–9. ISSN 1532-2874. JSTOR 41555279.
- Connolly, S. (2017). Settler colonialism in Ireland from the English conquest to the nineteenth century. In E. Cavanagh, & L. Veracini (Eds.), The Routledge Handbook of the History of Settler Colonialism (pp. 49-64). Article 4 Routledge.
- Ertola, Emanuele (15 March 2016). "'Terra promessa': migration and settler colonialism in Libya, 1911–1970". Settler Colonial Studies. 7 (3): 340–353. doi:10.1080/2201473X.2016.1153251. S2CID 164009698. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- Veracini, Lorenzo (Winter 2018). "Italian Colonialism through a Settler Colonial Studies Lens". Journal of Colonialism and Colonial History. 19 (3). doi:10.1353/cch.2018.0023. S2CID 165512037. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- Raman, Anita D. (2004). "Of Rivers and Human Rights: The Northern Areas, Pakistan's forgotten colony in Jammu and Kashmir". International Journal on Minority and Group Rights. 11 (1/2): 187–228. doi:10.1163/157181104323383929. JSTOR 24675261.
- Mushtaq, Samreen; Mudasir, Amin (16 October 2021). "'We will memorise our home': exploring settler colonialism as an interpretive framework for Kashmir". Third World Quarterly. 42 (12): 3012–3029. doi:10.1080/01436597.2021.1984877. S2CID 244607271. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- Lu, Sidney Xu (June 2019). "Eastward Ho! Japanese Settler Colonialism in Hokkaido and the Making of Japanese Migration to the American West, 1869–1888". The Journal of Asian Studies. 78 (3): 521–547. doi:10.1017/S0021911819000147. S2CID 197847093. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- Uchida, Jun (3 March 2014). Brokers of Empire: Japanese Settler Colonialism in Korea, 1876–1945. Vol. 337. Harvard University Asia Center. doi:10.2307/j.ctt1x07x37. ISBN 978-0674492028. JSTOR j.ctt1x07x37. S2CID 259606289.
- Christian Bleuer (2012). "State-building, migration and economic development on the frontiers of northern Afghanistan and southern Tajikistan". Journal of Eurasian Studies. 3: 69–79. doi:10.1016/j.euras.2011.10.008.
- Bleuer, Christian (17 October 2014). "From 'Slavers' to 'Warlords': Descriptions of Afghanistan's Uzbeks in Western Writing". Afghanistan Analysts Network.
- Mundt, Alex; Schmeidl, Susanne; Ziai, Shafiqullah (1 June 2009). "Between a Rock and a Hard Place: The Return of Internally Displaced Persons to Northern Afghanistan". Brookings Institution.
- "Paying for the Taliban's Crimes: Abuses Against Ethnic Pashtuns in Northern Afghanistan" (PDF). Human Rights Watch. April 2002.
- Lerp, Dörte (11 October 2013). "Farmers to the Frontier: Settler Colonialism in the Eastern Prussian Provinces and German Southwest Africa". Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History. 41 (4): 567–583. doi:10.1080/03086534.2013.836361. S2CID 159707103. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- ^ Adhikari, Mohamed (25 July 2022). Destroying to Replace: Settler Genocides of Indigenous Peoples. Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing Company. pp. 1–32. ISBN 978-1647920548.
- Browning, Christopher R. (8 February 2022). "Yehuda Bauer, the Concepts of Holocaust and Genocide, and the Issue of Settler Colonialism". The Journal of Holocaust Research. 36 (1): 30–38. doi:10.1080/25785648.2021.2012985. S2CID 246652960. Retrieved 30 April 2022.
- Rahman, Smita A.; Gordy, Katherine A.; Deylami, Shirin S. (2022). Globalizing Political Theory. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9781000788884.
- Salemink, Oscar (2003). The Ethnography of Vietnam's Central Highlanders: A Historical Contextualization, 1850–1990. University of Hawaii Press. pp. 35–336. ISBN 978-0-8248-2579-9.
- Nguyen, Duy Lap (2019). The unimagined community: Imperialism and culture in South Vietnam. Manchester University Press. ISBN 978-1-52614-398-3.
- Schweyer, Anne-Valérie (2019). "The Chams in Vietnam: a great unknown civilization". French Academic Network of Asian Studies. Archived from the original on 2 July 2022. Retrieved 31 October 2023.
- Tsai, Lin-chin (2019). Re-conceptualizing Taiwan: Settler Colonial Criticism and Cultural Production (Thesis). UCLA.
- Cowan, L. Gray (1964). The Dilemmas of African Independence. New York: Walker & Company, Publishers. pp. 42–55, 105. ASIN B0007DMOJ0.
- Hamdaoui, Neijma (31 October 2003). "Hassan II lance la Marche verte" [Hassan II launches the Green March]. JeuneAfrique.com (in French). Archived from the original on 3 January 2006. Retrieved 21 April 2015.
- Shefte, Whitney (6 January 2015). "Western Sahara's stranded refugees consider renewal of Morocco conflict". The Guardian.
- "Mixed Reviews for Morocco as Fourth Committee Hears Petitioners on Western Sahara, Amid Continuing Decolonization Debate | Meetings Coverage and Press Releases". United Nations.
- ^ Cavanagh, E (2013). Settler colonialism and land rights in South Africa: Possession and dispossession on the Orange River. United Kingdom: Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 10–16. ISBN 978-1-137-30577-0.
- Fourie, J (2014). "Settler Skills and Colonial Development: The Huguenot Wine-Makers in Eighteenth-Century Dutch South Africa". Economic History Review. 67 (4): 932–963. doi:10.1111/1468-0289.12033. S2CID 152735090.
- Mayne, Alan (1999). From Politics Past to Politics Future: An Integrated Analysis of Current and Emergent Paradigms. Westport, Connecticut: Praeger. p. 52. ISBN 978-0-275-96151-0.
- Weinberg, T (2015). "The Griqua Past and the Limits of South African History, 1902–1994; Settler Colonialism and Land Rights in South Africa: Possession and Dispossession on the Orange River". Journal of Southern African Studies. 41: 211–214. doi:10.1080/03057070.2015.991591. S2CID 144750398.
- ^ Spence, David M. (2021). "From Victims to Colonizers" (PDF). The SOAS Journal of Postgraduate Research.
- Parkins, Daniel (2019). "Colonialism, Postcolonialism, and the Drive for Social Justice: A Historical Analysis of Identity Based Conflicts in the First Republic of Liberia". SIT Graduate Institute.
- ^ "Founding of Liberia, 1847". Office of the Historian. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- Nicholas Guyatt, “The American Colonization Society: 200 Years of the “Colonizing Trick”, Black Perspectives, African American Intellectual History Society, December 22, 2016; Nicholas Guyatt, “The American Colonization Society’s plans for abolishing slavery,” Oxford University Press’s Academic Insights for the Thinking World, December 22, 2016, /.
- Akpan, M. B. (10 March 2014). "Black Imperialism: Americo-Liberian Rule over the African Peoples of Liberia, 1841–1964". Canadian Journal of African Studies (in French). 7 (2): 217–236. doi:10.1080/00083968.1973.10803695. ISSN 0008-3968.
- "Liberia: The African-American settler colony that parallels Israel". Middle East Eye. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- "The Doctrine of Discovery". CMHR. 2 November 2022. Retrieved 21 November 2024.
- Gourdeau, Claire. "Population – Religious Congregations". Virtual Museum of New France. Canadian Museum of History. Archived from the original on 8 July 2016. Retrieved 1 July 2016.
- Preston, David L. (2009). The Texture of Contact: European and Indian Settler Communities on the Frontiers of Iroquoia, 1667–1783. University of Nebraska Press. pp. 43–44. ISBN 978-0-8032-2549-7. Archived from the original on 16 March 2023. Retrieved 10 February 2019.
- Miller, J. R. (2009). Compact, Contract, Covenant: Aboriginal Treaty-Making in Canada. University of Toronto Press. p. 34. ISBN 978-1-4426-9227-5. Archived from the original on 16 March 2023. Retrieved 10 February 2019.
- "Gradual Civilization Act, 1857" (PDF). Government of Canada. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 March 2024. Retrieved 17 October 2015.
- "Indian Act". Site Web de la législation (Justice). 15 August 2019. Archived from the original on 26 May 2024. Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- "Potlatch Ban". The Canadian Encyclopedia. 11 January 2024. Archived from the original on 16 August 2024. Retrieved 3 September 2024.
- What We Have Learned: Principles of Truth and Reconciliation (PDF) (Report). 2015. p. 192. ISBN 978-0-660-02073-0. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2021.
-
- Williams, L. (2021). Indigenous Intergenerational Resilience: Confronting Cultural and Ecological Crisis. Routledge Studies in Indigenous Peoples and Policy. Routledge. p. 51. ISBN 978-1-000-47233-2. Archived from the original on 23 February 2023. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- Turner, N. J. (2020). Plants, People, and Places: The Roles of Ethnobotany and Ethnoecology in Indigenous Peoples' Land Rights in Canada and Beyond. McGill-Queen's Indigenous and Northern Studies. McGill-Queen's University Press. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-2280-0317-5. Archived from the original on 23 February 2023. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- Asch, Michael (1997). Aboriginal and Treaty Rights in Canada: Essays on Law, Equity, and Respect for Difference. University of British Columbia Press. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-7748-0581-0.
- Kirmayer, Laurence J.; Guthrie, Gail Valaskakis (2009). Healing Traditions: The Mental Health of Aboriginal Peoples in Canada. University of British Columbia Press. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-7748-5863-2.
- "Indigenous Peoples and Government Policy in Canada". The Canadian Encyclopedia. 6 June 1944. Retrieved 20 November 2024.
- Snelgrove, Corey; Dhamoon, Rita Kaur; Corntassel, Jeff (2014). "Unsettling settler colonialism: The discourse and politics of settlers, and solidarity with Indigenous nations" (PDF). Decolonization: Indigeneity, Education & Society. 3 (2): 11–12. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 January 2017.
- "Understanding the Overrepresentation of Indigenous People". State of the Criminal Justice System Dashboard. 11 June 2024. Retrieved 21 November 2024.
- ^ Dunbar-Ortiz, Roxanne (2014). An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States. Boston: Beacon Press. ISBN 978-0-8070-0040-3.
- https://www.issuelab.org/resources/3973/3973.pdf
- "The 1819 Treaty of Saginaw". 26 November 2019.
- Spady, James O'Neil (2020). Education and the Racial Dynamics of Settler Colonialism in Early America: Georgia and South Carolina, ca. 1700 - ca. 1820. Routledge. ISBN 978-0367437169.
- Moon, David (2020). The American Steppes. Cambridge University Press. p. 44.
- Wang, Ju-Han Zoe; Roche, Gerald (16 March 2021). "Urbanizing Minority Minzu in the PRC: Insights from the Literature on Settler Colonialism". Modern China. 48 (3): 593–616. doi:10.1177/0097700421995135. ISSN 0097-7004. S2CID 233620981.
- Brooks, Jonathan (2021), Settler Colonialism, Primitive Accumulation, and Biopolitics in Xinjiang, China, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3965577, ISSN 1556-5068, SSRN 3965577
- Clarke, Michael (16 February 2021). "Settler Colonialism and the Path toward Cultural Genocide in Xinjiang". Global Responsibility to Protect. 13 (1): 9–19. doi:10.1163/1875-984X-13010002. ISSN 1875-9858. S2CID 233974395.
- Ramanujan, Shaurir (9 December 2022). "Reclaiming the Land of the Snows: Analyzing Chinese Settler Colonialism in Tibet". The Columbia Journal of Asia. 1 (2): 29–36. doi:10.52214/cja.v1i2.10012. ISSN 2832-8558.
- Finley, Joanne Smith (1 September 2022). "Tabula rasa: Han settler colonialism and frontier genocide in "re-educated" Xinjiang". HAU: Journal of Ethnographic Theory. 12 (2): 341–356. doi:10.1086/720902. ISSN 2575-1433. S2CID 253268699.
- McGranahan, Carole (17 December 2019). "Chinese Settler Colonialism: Empire and Life in the Tibetan Borderlands". In Gros, Stéphane (ed.). Frontier Tibet: Patterns of Change in the Sino-Tibetan Borderlands. Amsterdam University Press. pp. 517–540. doi:10.2307/j.ctvt1sgw7.22. ISBN 978-90-485-4490-5. JSTOR j.ctvt1sgw7.22.
- ^ Powell, Michael (5 January 2024). "The Curious Rise of 'Settler Colonialism' and 'Turtle Island'". The Atlantic. Retrieved 22 May 2024.
- ^ Troen, S. Ilan (2007). "De-Judaizing the Homeland: Academic Politics in Rewriting the History of Palestine". Israel Affairs. 13 (4): 872–884. doi:10.1080/13537120701445372. S2CID 216148316.
- ^ Schuessler, Jennifer (22 January 2024). "What Is 'Settler Colonialism'?". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 7 July 2024.
- ^ Cohen, Roger (10 December 2023). "Who's a 'Colonizer'? How an Old Word Became a New Weapon". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 7 July 2024.
- Kirsch, Adam (26 October 2023). "Campus Radicals and Leftist Groups Have Embraced the Idea of 'Settler Colonialism'". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 7 July 2024.
- Hart, Alan (13 August 2010). Zionism: The Real Enemy of the Jews. Vol. 1: The False Messiah. SCB Distributors. ISBN 978-0-932863-78-2.
A voluntary reconciliation with the Arabs is out of the question either now or in the future. If you wish to colonize a land in which people are already living, you must provide a garrison for the land, or find some rich man or benefactor who will provide a garrison on your behalf. Or else-or else, give up your colonization, for without an armed force which will render physically impossible any attempt to destroy or prevent this colonization, colonization is impossible, not difficult, not dangerous, but IMPOSSIBLE!... Zionism is a colonization adventure and therefore it stands or falls by the question of armed force. It is important... to speak Hebrew, but, unfortunately, it is even more important to be able to shoot – or else I am through with playing at colonizing.
- Jabotinsky, Ze'ev (4 November 1923). "The Iron Wall" (PDF).
Colonisation can have only one aim, and Palestine Arabs cannot accept this aim. It lies in the very nature of things, and in this particular regard nature cannot be changed...Zionist colonisation must either stop, or else proceed regardless of the native population.
- Gelber, Mark H.; Liska, Vivian, eds. (2012). Theodor Herzl: From Europe to Zion. De Gruyter. pp. 100–101.
- Rodinson, Maxime. "Israel, fait colonial?" Les Temps Moderne, 1967. Republished in English as Israel: A Colonial Settler-State?, New York, Monad Press, 1973.
- Veracini, Lorenzo (2007). "Settler Colonialism and Decolonisation". borderlands e-journal. 6 (2). Archived from the original on 30 March 2020.
Israel could celebrate its anticolonial/anti-British struggle exactly because it was able to establish a number of colonial relationships within and without the borders of 1948.
- Veracini, Lorenzo (2006). Israel and Settler Society. London: Pluto Press.
- Unsettling Settler Societies: Articulations of Gender, Race, Ethnicity and Class, Vol. 11, Nira Yuval-Davis (Editor), Daiva K Stasiulis (Editor), Paperback 352pp, ISBN 978-0-8039-8694-7, August 1995 SAGE Publications.
- "Post Colonial Colony: time, space and bodies in Palestine/Israel in the persistence of the Palestinian Question", Routledge, NY, (2006) and "The Pre-Occupation of Post-Colonial Studies" ed. Fawzia Afzal-Khan and Kalpana Rahita Seshadri. (Durham: Duke University Press)
- The Palestinian Enclaves Struggle: An Interview with Ilan Pappé Archived 19 May 2017 at the Wayback Machine, King's Review – Magazine
- Video: Decolonizing Israel. Ilan Pappé on Viewing Israel-Palestine Through the Lens of Settler-Colonialism. Antiwar.com, 5 April 2017
- Amal Jamal (2011). Arab Minority Nationalism in Israel: The Politics of Indigeneity. Taylor & Francis. p. 48. ISBN 978-1-136-82412-8.
- Short, Damien (December 2012). "Genocide and settler colonialism: can a Lemkin-inspired genocide perspective aid our understanding of the Palestinian situation?". The International Journal of Human Rights.
- Troen, S. Ilan (2007). "De-Judaizing the Homeland: Academic Politics in Rewriting the History of Palestine". Israel Affairs. 13 (4): 872–884. doi:10.1080/13537120701445372. S2CID 216148316.
- Moshe Lissak, "'Critical' Sociology and 'Establishment' Sociology in the Israeli Academic Community: Ideological Struggles or Academic Discourse?" Israel Studies 1:1 (1996), 247-294.
- Sunderland, Willard (2000). "The 'Colonization Question': Visions of Colonization in Late Imperial Russia". Jahrbücher für Geschichte Osteuropas. 48 (2): 210–232. JSTOR 41050526.
- Forsyth, James (1992). A history of the peoples of Siberia. Internet Archive. Cambridge University Press. pp. 201–228, 241–346. ISBN 978-0-521-40311-5.
- Lantzeff, George V.; Pierce, Richard A. (1973). Eastward to Empire: Exploration and Conquest on the Russian Open Frontier to 1750. McGill-Queen's University Press. doi:10.2307/j.ctt1w0dbpp. JSTOR j.ctt1w0dbpp.
- Hill, Nathaniel (25 October 2021). "Conquering Siberia: The Case for Genocide Recognition". www.genocidewatchblog.com. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- Bartels, Dennis; Bartels, Alice L. (2006). "Indigenous Peoples of the Russian North and Cold War Ideology". Anthropologica. 48 (2): 265–279. doi:10.2307/25605315. JSTOR 25605315.
- Veracini 2013: "The domination of Latin America, North America, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, and the Asian part of the Soviet Union by European powers all involved the migration of permanent settlers from the European country to the colonies. These places were colonized."
- Pohl, Otto (2015). "The Deportation of the Crimean Tatars in the Context of Settler Colonialism". International Crimes and History (16). Archived from the original on 9 August 2022. Retrieved 4 February 2023.
- Tsai, Lin-chin (2019). Re-conceptualizing Taiwan: Settler Colonial Criticism and Cultural Production (PhD thesis). University of California. Retrieved 20 May 2023.
Taiwan, an island whose indigenous inhabitants are Austronesian, has been a de facto settler colony due to large-scale Han migration from China to Taiwan beginning in the seventeenth century.
- Statistics compiled by Ørsted-Jensen for Frontier History Revisited (Brisbane 2011), page 15.
- Page, A. (September 2015). "The Australian Settler State, Indigenous Agency, and the Indigenous Sector in the Twenty First Century" (PDF). Australian Political Studies Association Conference. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 September 2016. Retrieved 15 December 2015.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Page, A.; Petray, T. (2015). "Agency and Structural Constraints: Indigenous Peoples and the Settler-State in North Queensland". Settler Colonial Studies. 5 (2).
- Veracini 2015, p. 44.
- Byrd, Jodi A. (6 September 2011). The Transit of Empire: Indigenous Critiques of Colonialism. University of Minnesota Press. pp. xix. ISBN 978-1-4529-3317-7.
- Dahl 2018, p. 1.
Works cited
- Dahl, Adam (2018). Empire of the People: Settler Colonialism and the Foundations of Modern Democratic Thought. University Press of Kansas. ISBN 978-0-7006-2607-6.
- Veracini, Lorenzo (2013). "'Settler Colonialism': Career of a Concept". The Journal of Imperial and Commonwealth History. 41 (2): 313–333. doi:10.1080/03086534.2013.768099. S2CID 159666130. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
Further reading
- Adhikari, Mohamed (2021). Civilian-Driven Violence and the Genocide of Indigenous Peoples in Settler Societies. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-000-41177-5.
- Cox, Alicia. "Settler Colonialism". Oxford Bibliographies. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- Englert, Sai (2022). Settler Colonialism: An Introduction. Pluto Press. ISBN 978-0-7453-4490-4.
- Belich, James (2009). Replenishing the earth: the settler revolution and the rise of the Anglo-world, 1783–1939. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 573. ISBN 978-0-19-929727-6.
- Horne, Gerald. The Apocalypse of Settler Colonialism: The Roots of Slavery, White Supremacy, and Capitalism in Seventeenth-Century North America and the Caribbean. Monthly Review Press, 2018. 243p. ISBN 9781583676639
- Horne, Gerald. The Dawning of the Apocalypse: The Roots of Slavery, White Supremacy, Settler Colonialism, and Capitalism in the Long Sixteenth Century. Monthly Review Press, 2020. ISBN 978-1-58367-875-6.
- Mamdani, Mahmood (2020). Neither Settler nor Native. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-98732-6.
- Manjapra, Kris (2020). "Settlement". Colonialism in Global Perspective. Cambridge University Press. pp. 43–70. ISBN 978-1-108-42526-1.
- Marx, Christoph (2017). Settler Colonies, EGO - European History Online, Mainz: Institute of European History, retrieved: March 17, 2021 (pdf).
- Mikdashi, Maya (2013). What is settler colonialism? American Indian Culture and Research Journal 37.2: 23–34.
- Pedersen, Susan; Elkins, Caroline, eds. (2005). Settler Colonialism in the Twentieth Century. Routledge.
- Sakai, J. (1983). Settlers: The Mythology of the White Proletariat. PM Press. ISBN 978-1-62963-037-3.
- Veracini, Lorenzo (2010). Settler Colonialism: A Theoretical Overview. Hampshire, UK: Palgrave MacMillan. p. 182. ISBN 9780230284906.
- Veracini, Lorenzo (2015). The Settler Colonial Present. Springer. ISBN 978-1-137-37247-5.
- Wolfe, Patrick (2016). Traces of History: Elementary Structures of Race. Verso Books.
External links
| Colonization, decolonization, and neocolonialism | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By region |
| ||||||||||||
| General topics |
| ||||||||||||