| Revision as of 22:49, 6 April 2020 editAlgis (talk | contribs)21 edits →External links← Previous edit |
Latest revision as of 03:08, 21 December 2024 edit undo73.211.72.119 (talk) →44th century BCTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
| (233 intermediate revisions by 41 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
|
|
{{short description|None}} |
|
{{Dynamic list}} |
|
{{Dynamic list}} |
|
|
The page details the timeline of ]. <div class="toc"> '''Millennia''': ]{{·}}]{{·}}] |
|
|
|
|
<div class="toc"> '''Millennia''': ]{{·}}]{{·}}] |
|
|
----{{anchor|1st millennium BC}} |
|
----{{anchor|1st millennium BC}} |
|
'''Centuries''': ]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]</div> |
|
'''Centuries''': ]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]</div> |
|
|
|
|
|
== 44th century BC == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 4300s BC|4395 <small>BC</small> || || Construction of the city of ] in southwestern Iran. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 33rd century BC == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|
|- |
|
|
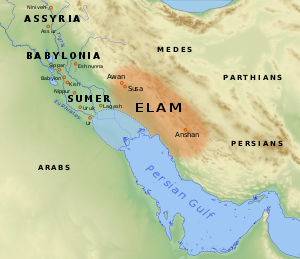
| ] || || The ] civilisation, one of the four oldest civilisations (along with ], the ], and ]), begins in the far west and southwest of modern-day Iran. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 21st century BC == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Earliest date for the arrival of ] into Iran from Central Asia. The migrations into Iran may have been completed as late as 1000 BC. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 16th century BC == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Start of the ], which according to some scholars continued until the sixth century BC. The prophet ] lived at some point during this era, with any time between 1500 BC and 1000 BC being the most favoured date for his life by modern scholars. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 13th century BC == |
|
|
] extension of the ] is shown.]] |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || ], king of ], builds the ] ] complex in present-day ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || ] reaches the height of its power. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 8th century BC == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || The ] start driving the ]ites of ] towards ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || ] founds the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Birth of ] (died {{circa|675 BC}}), the eponymous ancestor of the ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|
|
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 7th century BC == |
|
== 7th century BC == |
|
|
] between the fall of the ] in 612 BC and the establishment of the ] in 550 BC; from a ] illustrated by ].]] |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| ] || || ] declared himself King of the ]. |
|
| ] || || ] founds the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 655–638 BC|]–] <small>]</small> || || The ] occurs. The ] under ] is victorious at the ] in 647 BC, resulting in the looting and sack of ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || The ] invade ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || ] becomes the king of the ] after Phraortes dies fighting the Assyrians. {{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || The Medes under Cyaxares repel the Scythians.{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Together with the ], Cyaxares the Great sacks the ] capital ] and destroys the Neo-Assyrian Empire.{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || ] becomes king of Persia. |
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 6th century BC == |
|
== 6th century BC == |
|
|
] |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| ] || || The ] was founded by ]. |
|
| ] || || Cyaxares dies and is succeeded by his son ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| ] || || ] captured ], freed thousands of slaves and issued a declaration of human rights which would later be inscribed into the ]. |
|
| ] || || ] dies and is succeeded by his son ]. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| ] || || Persia conquers ]. |
|
| ] || || Cambyses I dies and is succeeded by ] as king of Persia. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || The ] is founded by Cyrus the Great after he overthrows and conquers the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Cyrus conquers the ] in western Asia Minor. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 545–540 BC|]–] || || Cyrus conquers ], ], ], ], ], and ] during his ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Cyrus conquers the ], frees thousands of slaves in Babylon and issues a declaration of human rights. This would later be inscribed into the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Cyrus commences the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Cyrus dies, and is succeeded by his son ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Cambyses II conquers ] after the ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}}{{sfn|Dandamayev|1990|pp=726–729}} Cyprus is also conquered by Cambyses. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Cambyses dies and is succeeded by either his brother Bardiya or an impostor, Gaumata, pretending to be Bardiya. This individual dies months after becoming the King of Kings, and is succeeded by ]. Civil war breaks out as a result of the mysterious circumstances surrounding Darius' ascension, with ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ] all revolting. Darius suppresses all the uprisings by 520 and restores order to the Achaemenid Empire. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Darius completes the conquest of the Indus Valley. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Darius expands the Achaemenid Empire into Europe, conquering ], ], ], and the coastal Greek cities. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || ] submits to Persia. |
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 5th century BC == |
|
== 5th century BC == |
|
|
] under ]; from a ] illustrated by ].]] |
|
|
|
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
{{Empty section|date=March 2013}} |
|
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || August/September || ], Persian Empire is defeated by Greek states. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Darius the Great dies; ] succeeds him as King of Kings. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || The ], led by two pretenders to the Babylonian throne, is crushed by Xerxes. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || The ] under Xerxes invades mainland ], reaching its greatest extent. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ]–] || || Persians capture and ]. The ], the ] and the ] are destroyed. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Assassination of Xerxes I. ] becomes the King of Kings. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ] || || Egypt breaks away from Persian rule. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 4th century BC == |
|
== 4th century BC == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
|
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
{{Empty section|date=March 2013}} |
|
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 343 BC|| || Egypt is ] after the defeat of the ] by ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 334 BC|| || ] crosses the ] into Asia. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 334 BC|| May || ] defeats the armies of the ] in the ] river |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 333 BC|| 5 November || Alexander III of Macedon defeats the armies of the Achaemenid Empire in the ] |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 330 BC|| 20 January || Alexander III of Macedon defeats the armies of the Achaemenid Empire in the ] |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 330 BC|| July || ], the last Achaemenid emperor is killed, bringing an end to the Achaemenid empire. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 330 BC|| || ], the capital of the Persian ] is destroyed by ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 323 BC|| 10/11 June || Alexander III dies in Babylon, triggering a division of his empire among his generals in a treaty known as the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 312 BC|| || ], establishes the ] in the Persian territories of the erstwhile Macedonian Empire. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 3rd century BC == |
|
== 3rd century BC == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
|
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
{{Empty section|date=March 2013}} |
|
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 247 BC|| || ] establishes the ] (also known as the Arsacid Empire) in present-day north-eastern Iran.{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}}{{sfn|Shahbazi|1986|p=525}} |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 2nd century BC == |
|
== 2nd century BC == |
|
|
|
|
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
{{Empty section|date=March 2013}} |
|
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| ]–] || || ] – the Arsacids expel the Seleucids from Iran and Mesopotamia, and those lands pass into their hands. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 1st century BC == |
|
== 1st century BC == |
|
|
] under ] in 94 BC.]] |
|
{{anchor|1st millennium}} |
|
{{anchor|1st millennium}} |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 94 BC|| || The ] reaches its peak, stretching from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now central-eastern Turkey, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 54 BC|| || Beginning of the ], lasting till 217 CE. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
<div class="toc"> '''Centuries''': ]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}] </div> |
|
<div class="toc"> '''Centuries''': ]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}]{{·}}] </div> |
|
|
|
|
| Line 52: |
Line 189: |
|
|
|
|
|
== 3rd century == |
|
== 3rd century == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
|
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
{{Empty section|date=March 2013}} |
|
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 208|| || ] dies and is succeeded by his son ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}}{{sfn|Chaumont|Schippmann|1988|pp=574–580}} |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 211|| || ] establishes the Sasanian Empire in ] in present-day ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 224|| || Ardashir I defeats the last Parthian ] ], ending the Parthian Empire. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 260|| || Persians defeated the Romans at the ] and take emperor ] prisoner for the remainder of his life. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 4th century == |
|
== 4th century == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
|
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
{{Empty section|date=March 2013}} |
|
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 360|| || Sasanian Empire captures the town of ], in the ] |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 363|| || ] between the Roman Empire and the Sasanian Empire, in which Roman emperor ] is wounded, and subsequently dies of his wounds. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 371|| || ] and ] defeat the Sasanian Empire and ] in the ] |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 5th century == |
|
== 5th century == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
|
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
{{Empty section|date=March 2013}} |
|
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 421|| || ] after which Persian Empire agreed to tolerate ] and Roman Empire agreed to tolerate ] |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 6th century == |
|
== 6th century == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
|
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
{{Empty section|date=March 2013}} |
|
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 570–578|| || ], Yemen is annexed by the Sasanian Empire. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 590|| || ] becomes ruler of the Sasanian Empire. During his rule till 628, ], ], ] and ] are annexed into the Sasanian Empire |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 7th century == |
|
== 7th century == |
|
|
] reached its greatest extent only a decade before its destruction commenced. Territories shown in a lighter shade of blue are those conquered by ] during the ] and returned to the Romans following the war's conclusion.]] |
|
|
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
| 620 || || Sasanian Empire reaches its greatest height, encompassing all of present-day Iran and Iraq and stretching from the eastern Mediterranean (including Anatolia and Egypt) to Pakistan, and from parts of southern Arabia to the Caucasus and Central Asia. |
|
| 636 || || Arab invasion brings end of ] and start of Islamic rule.<ref>{{cite web|title=Iran profile – timeline|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-14542438|website=bbc.com|accessdate=28 March 2017}}</ref> |
|
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 626 || June – July|| Sasanian Empire lays ], however is unable to capture it. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 628 || 25 February || Khosrow II is deposed and killed by his son ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 628 || 6 September || ] becomes ruler of the Sasanian Empire. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 632 || 16 June || ] becomes ruler of the Sasanian Empire. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 633 || May || ] in which the Rashidun Caliphate defeats the Sasanian Empire resulting in the massacre of 70,000 Persians by Arabs. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 634 || October || ] led by ] defeats the ] in the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 636 || || Arab invasion brings end of ] and start of Islamic rule.<ref>{{cite news |title=Iran profile – timeline |work=BBC News |date=16 August 2011 |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-14542438 |access-date=28 March 2017}}</ref> |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 636 || 16–19 November || Rashidun Caliphate defeats the Sasanian Empire in the ], takes control of present day ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 637 || || Destruction of the ] library by Arabs of the Rashidun Caliphate.<ref name="Books on Fire">{{cite book |author=Lucien X. Polastron |title=Books on Fire: The Destruction of Libraries Throughout History |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4s-Kb9kv36oC&q=ctesiphon+library&pg=PA324 |publisher=Books on Fire |year=2007 |isbn=9781594771675 |pages=371}}</ref> |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 642 || || Rashidun Caliphate defeats the Sasanian Empire in the ], resulting in the near collapse of the Sasanian Empire. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 644 || 3 November || The second Rashidun caliph ] ({{reign|634|644}}) is assassinated by the Persian slave ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 644 || 6 November || ] becomes the third Rashidun Caliph. During his reign, almost the whole of the former Sassanid empire's territories rebel from time to time, with major rebellions in ], ], Fars, ] (in 649), Khorasan (651), and Makran (650). |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 651 || || Rashidun Caliphate defeats the Sasanian Empire and the ] in the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 651 || || ], the last Sassanid emperor, is killed near ] putting an end to both his dynasty and to organized Persian resistance to Arab conquest. |
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 8th century == |
|
== 8th century == |
|
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
|
|
|
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
{{Empty section|date=March 2013}} |
|
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 716–717 || || ], ruler of ] in present-day ] defeats the Muslim invasion under ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 761 || || ] falls to Muslim invasion and becomes a province of the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 767 || || ], Persian Zoroastrian revolutionary leader launches a rebellion, occupies ] and ] before marching towards ]. He initially defeats an Abbasid army under the command of al-Ajtham of Merv, but is himself defeated in a bloody battle against an army led by ]. |
|
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
== 9th century == |
|
== 9th century == |
| Line 84: |
Line 280: |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 821 || || ], an Iranian general under the ], declared the establishment of the independent ] . |
|
| 816–835 || || ] a Persian Zoroastrian revolutionary leader of the ] movement defeats successive Arab generals of the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 821 || || ], an Iranian general under the ], declared the establishment of the independent ]. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 867 || || ] founded the ]. |
|
| 867 || || ] founded the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 867 || || One of the earliest works in ] is composed by ] (died 909), a poet and secretary of the Saffarids.{{sfn|Bosworth|1993}}{{sfn|Paul|2000}} |
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
| Line 93: |
Line 293: |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 928 || || ] founded the ]. |
|
| 934 || || ] is conquered by the ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
| 930|| || ] commander ] establishes the ] and briefly conquers much of northern Persia before being betrayed and killed in 935 CE. The Ziyarid dynasty continued to rule over much of Tabaristan until its demise in 1090 CE. |
|
| 934 || || The ] ] was founded. |
|
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 934 || || The ] was founded. |
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
| Line 108: |
Line 310: |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 1131 || || Death of the Persian poet ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 1136 || || The ] (also known as the Atabegs of Azerbaijan) is founded by ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}}{{sfn|Luther|1987|pp=890–894}} |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 1157 || || Death of the Seljuk sultan ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 1182/3 || || Death of ], a secretary, poet, philologist in the ].{{sfn|Chalisova|2000}} |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 1189 || || '']'': ] destroyed several cities of the ]. As a result of the conflict, the safety of both ] and ] unarmed ] is guaranteed throughout the ]. |
|
| 1189 || || '']'': ] destroyed several cities of the ]. As a result of the conflict, the safety of both ] and ] unarmed ] is guaranteed throughout the ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 1195 || || Death of the Persian poet ].{{sfn|Yarshater|2021}} |
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
| Line 116: |
Line 328: |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 1219 || || The ] begins after two diplomatic missions to ] sent by ] are massacred. In 1220 and 1221, ], ], ], ] and ] were razed, and the whole populations were slaughtered. Shah ] flees; he dies on an island off the ] coast. |
|
| 1219 || || The ] begins after two diplomatic missions to ] sent by ] are massacred. In 1220 and 1221, ], ], ], ] and ] were razed, and the whole populations were slaughtered. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 1220 || || Pursued by Mongol forces, Shah ] dies on an island off the ] coast. |
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
| Line 141: |
Line 355: |
|
| 1524 || 23 May || ] died. He was succeeded by his son ]. |
|
| 1524 || 23 May || ] died. He was succeeded by his son ]. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 1590 || 21 May || The ] was signed between Iran and the ], under which Iran ceded the ] and western Iranian territories, for several years. |
|
| 1590 || 21 May || The ] was signed between ] and the ] ending the ], under which Safavid Empire ceded the ] and western Iranian territories, for several years. |
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
| Line 148: |
Line 362: |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
! style="width:6%" | Year || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
| ]–] || || In the ], Shah ] inflicts crushing defeats on the Ottoman Empire, restoring Safavid territory that had been lost. |
|
| 1609 || November || '']'': The Persian army laid siege to a ] fortress on the banks of ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 1610 || || ''Battle of DimDim'': The fortress was taken, and its occupants were massacred. |
|
| 1609 || November || ]: The Persian army laid siege to a ] fortress on the banks of ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 1610 || || Battle of Dimdim: The fortress was taken, and its occupants were massacred. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 1629 || 19 January || ] died. His grandson ] succeeded him. |
|
| 1629 || 19 January || ] died. His grandson ] succeeded him. |
| Line 194: |
Line 410: |
|
|
|
|
|
== 20th century == |
|
== 20th century == |
|
{{Expand section|date=February 2017 }} |
|
{{Expand section|date=February 2017}} |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
! style="width:6%" | ] || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
! style="width:6%" | ] || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
| Line 202: |
Line 418: |
|
|The first ] was adopted during the ]. |
|
|The first ] was adopted during the ]. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
| 1925 || || ] overthrows the ], becoming the first shah of the ]. |
|
| 1925 || 31 March || ] legally adopted in Iran.<ref>{{cite web |encyclopedia= ] |url= http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/calendars |title= Calendars |year=1990 }}</ref> |
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
| 1925 || 31 March || ] legally adopted in Iran.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |encyclopedia=] |url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/calendars |title=Calendars |year=1990}}</ref> |
|
| rowspan="1" valign="top" | 1941 || 21 August || '']'': Three ] armies invaded Iran from the north. |
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 17 September || ''Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran'': The ] and ] armed forces met in ]. |
|
| rowspan="1" valign="top" | 1941 || 25 August || ]: Three ] armies began invasion of Iran from the north, while British army invades ] and Central Iran. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 1945 || November || The ] established the ] in ]. |
|
| 1945 || November || The ] established the ] in ]. |
| Line 220: |
Line 436: |
|
| 15 December || Iran conquered ]. |
|
| 15 December || Iran conquered ]. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| rowspan="1" valign="top" | 1953 || August || ] is overthrown in a coup engineered by the British and American intelligence services. ] is proclaimed as prime minister and the Shah returns.<ref>{{cite web|title=Iran profile – timeline|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-14542438|website=www.bbc.org|accessdate=28 March 2017}}</ref> |
|
| rowspan="1" valign="top" | 1953 || August || ] is overthrown in a coup engineered by the British and American intelligence services. ] is proclaimed as prime minister and the Shah returns.<ref>{{cite news |title=Iran profile – timeline |work=BBC News |date=16 August 2011 |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-14542438 |access-date=28 March 2017}}</ref> |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| rowspan="2" valign="top" | 1979 || 11 February || '']'': The Iranian Monarchy collapsed in a popular revolution. |
|
| rowspan="3" valign="top" | 1979 || 11 February || '']'': The Iranian Monarchy collapsed in a popular revolution. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 1 April || A referendum passed which made Iran an ]. |
|
| 1 April || A referendum passed which made Iran an ]. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|4 November || ] |
|
| 1980 || 22 September || ] launched a full-scale invasion of Iran. The ] would last until August 1988. The tactics used by both sides were similar to those used during ],<ref name=abrahamian08>{{cite book|last=Abrahamian|first=Ervand|title=A History of Modern Iran|year=2008|publisher=Cambridge University Press|location=Cambridge, U.K.|isbn=978-0521528917|edition=3rd print}}</ref> including large-scale ] with ] stretched across trenches, manned ] posts, bayonet charges, ]s across a ], and extensive use of ] such as ] by the Iraqi government against Iranian troops, civilians, and Iraqi ]s. |
|
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
| 1980 || 22 September || ] launched a full-scale invasion of Iran. The ] would last until August 1988. The tactics used by both sides were similar to those used during ],<ref name=abrahamian08>{{cite book |last=Abrahamian |first=Ervand |title=A History of Modern Iran |year=2008 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |location=Cambridge, U.K. |isbn=978-0521528917 |edition=3rd print}}</ref> including large-scale ] with ] stretched across trenches, manned ] posts, bayonet charges, ]s across a ], and extensive use of ] such as ] by the Iraqi government against Iranian troops, civilians, and Iraqi ]s. |
|
| 1988 || 20 August || The ] ends in a stalemate. The Iran–Iraq War was the deadliest conventional war ever fought between regular armies of developing countries.<ref name="Fürtig">{{Cite magazine|title=Den Spieß umgedreht: iranische Gegenoffensive im Ersten Golfkrieg|trans-title=Turning of the Tables: the Iranian counter-offensive during the first Gulf War|first=Henner |last=Fürtig |language=German |magazine=] |issue=5 |year=2012 |pages=10–13}}</ref> |
|
|
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
|
|1981 |
|
|
|9 October |
|
|
|Later Supreme Leader ] ] as the ] under Supreme Leader ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| rowspan="2" valign="top" | 1988 || 20 August || The ] ends in a stalemate. The Iran–Iraq War was the deadliest conventional war ever fought between regular armies of developing countries.<ref name="Fürtig">{{Cite magazine |title=Den Spieß umgedreht: iranische Gegenoffensive im Ersten Golfkrieg |trans-title=Turning of the Tables: the Iranian counter-offensive during the first Gulf War |first=Henner |last=Fürtig |language=de |magazine=] |issue=5 |year=2012 |pages=10–13}}</ref> |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| || ], thousands of cases of forced disappearances, executions, torture and ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|1989 |
|
|
|3 June |
|
|
|1st ] and founder of the Islamic Republic, ], dies. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|1989 |
|
|
|4 June |
|
|
|] replaces Ruhollah Khomeini, ] the second ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|1989 |
|
|
|28 July |
|
|
|A constitutional reform was allegedly approved by 97.6% of voters in a ], it was the first and so far only time the ] has been amended. It made several significant changes to the system of government of the Islamic Republic such as eliminating the need for the ] (''rahbar'') of the country to be a '']'' or chosen by popular acclaim. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|1989 |
|
|
|16 August |
|
|
|] ] ], the first president to assume office under the post-reform constitution. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 1994 || 22 February || ] an Iranian pediatrician and ] activist ] in protest against ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|1997 |
|
|
|3 August |
|
|
|] replaces Rafsanjani as President. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Line 237: |
Line 481: |
|
|
|
|
|
== 21st century == |
|
== 21st century == |
|
{{Expand section|date=February 2017 }} |
|
{{Expand section|date=February 2017}} |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
{| class="wikitable" width="100%" |
|
! style="width:6%" | ] || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
! style="width:6%" | ] || style="width:10%" | Date || Event |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 2001 || 8 June || '']'': President ] was reelected with vast majority. |
|
| 2001 || 8 June || '']'': President ] was reelected with vast majority. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|2003 |
|
|
|December |
|
|
|40,000 people are killed in an ] in southern Iran. |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 2005 || 24 June || '']'': ] defeated the more liberal ]. |
|
| 2005 || 24 June || '']'': ] defeated the more liberal ]. |
| Line 248: |
Line 496: |
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
| 13 June || '']'': Protests in Iran over election results. |
|
| 13 June || '']'': Protests in Iran over election results. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|2013 |
|
|
|3 August |
|
|
|] replaces Ahmadinejad as President. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 2014 || || ], an online movement in which ] post photos of themselves without hijabs, as a protest against the compulsory hijab laws in the country. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 2015 || 14 July || Signing of ] between Iran and the P5+1 (the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council— China, France, Russia, United Kingdom, United States—plus Germany). |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 2018 || 8 May || United States withdraws from the Iran nuclear deal |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 2017–19 || || ] in multiple cities including ], ], ] and ]. Many are physically assaulted with injuries including broken limbs and imprisoned. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
| 2019 || 9 September || Self immolation of women's rights activist ] over six month prison sentence for attempting to enter a public stadium to watch a football game, against the national ban against women at such events. Leads to widespread protests, and on 10 October 2019, more than 3,500 women attend the ] for a World Cup qualifier against Cambodia. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|2020 ||3 January ||] commander ] and commander of the Iran-backed ] militia, ], are ] in a ] drone strike in ]. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|2021 ||3 August ||] replaces Rouhani as President. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|2022 ||16 September ||22-year-old Iranian woman Mahsa Amini, also known as Jina Amini, died in a hospital in ], Iran, under suspicious circumstances, after her arrest by the Islamic Republic's ]. Eyewitnesses, including women who were detained with Amini, reported that she was severely beaten and that she died as a result of ]. Her death sparked widespread antigovernmental protests in Iran. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|2022–23 || ||] and protests against the ] associated with the ] of ] (]: مهسا امینی) began on 16 September 2022 and lasted until 2023. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|2024 ||1 April ||Israel bombed the Iranian embassy in Damascus, causing a brief escalation to direct conflict between two countries which lasted for 18 days. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|2024 ||19 May ||] and death of Iranian president, Ebrahim Raisi. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|2024 ||28 July || ] appointed as the president of Iran. |
|
|
|- |
|
|
|2024 ||31 July ||Assassination of ], Hamas political leader in Tehran, by an apparent Israel attack, increased tension between the two countries. |
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
| Line 267: |
Line 545: |
|
|
|
|
|
==References== |
|
==References== |
|
{{Reflist}} |
|
{{Reflist|2}} |
|
|
|
|
|
==Bibliography== |
|
==Bibliography== |
|
{{Globalize|section|date=January 2017}} |
|
{{Globalize|section|date=January 2017}} |
|
|
|
|
|
* {{Citation |publisher = Frederick Warne & Co. |location = London |author = George Henry Townsend |title = A Manual of Dates |edition=2nd |date = 1867 |chapter= Persia |chapterurl= https://archive.org/stream/manualofdatesdic00townrich#page/764/mode/1up |author-link = George Henry Townsend }} |
|
* {{Cite book |publisher=Frederick Warne & Co. |location=London |author=George Henry Townsend |title=A Manual of Dates |edition=2nd |year=1867 |chapter=Persia |chapter-url=https://archive.org/stream/manualofdatesdic00townrich#page/764/mode/1up |author-link=George Henry Townsend}} |
|
* {{cite book|editor= ] |title=Historians' History of the World |volume=24 |publisher= Hooper & ] |location=London |year=1908|chapterurl= http://hdl.handle.net/2027/njp.32101063964728?urlappend=%3Bseq=542 |chapter= Chronological Summary of the History of Persia }} |
|
* {{cite book |editor=Henry Smith Williams |editor-link=Henry Smith Williams |title=Historians' History of the World |volume=24 |publisher=Hooper & ] |location=London |year=1908 |chapter-url=http://hdl.handle.net/2027/njp.32101063964728?urlappend=%3Bseq=542 |chapter=Chronological Summary of the History of Persia |hdl=2027/njp.32101063964728?urlappend=%3Bseq=542}} |
|
* {{Citation |publisher = Ward, Lock & Co. |location = London |title = Haydn's Dictionary of Dates |author = Benjamin Vincent |edition = 25th |date = 1910 |chapter= Persia|chapterurl= https://hdl.handle.net/2027/loc.ark:/13960/t89g6g776?urlappend=%3Bseq=1073 |via= HathiTrust |title-link = Haydn's Dictionary of Dates }} |
|
* {{Cite book |publisher=Ward, Lock & Co. |location=London |title=Haydn's Dictionary of Dates |author=Benjamin Vincent |edition=25th |year=1910 |chapter=Persia <!--|url=https://hdl.handle.net/2027/loc.ark:/13960/t89g6g776?urlappend=%3Bseq=1073--> |via=HathiTrust |title-link=Haydn's Dictionary of Dates |hdl=2027/loc.ark:/13960/t89g6g776?urlappend=%3Bseq=1073}} |
|
* {{cite book|publisher=] |title= Political Chronology of the Middle East|isbn=978-1-135-35673-6 |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=eCSOT0_JAnwC |year= 2003|chapter= Iran |pages= 45–64}} |
|
* {{cite book|publisher=] |title=Political Chronology of the Middle East|isbn=978-1-135-35673-6 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=eCSOT0_JAnwC |year=2003 |chapter=Iran |pages=45–64}} |
|
* {{cite book|author= Andrew J. Newman |title=Safavid Iran: Rebirth of a Persian Empire|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=afsYCq1XOewC|year= 2006|publisher=I.B.Tauris|isbn=978-1-86064-667-6 |chapter=Key Dates |pages=129+ |author-link=Andrew J. Newman}} (Covers 14th–18th centuries CE) |
|
* {{cite book |author=Andrew J. Newman |title=Safavid Iran: Rebirth of a Persian Empire |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=afsYCq1XOewC |year=2006 |publisher=I.B.Tauris |isbn=978-1-86064-667-6 |chapter=Key Dates |pages=129+ |author-link=Andrew J. Newman}} (Covers 14th–18th centuries CE) |
|
* {{cite web |url=https://www.pbs.org/newshour/updates/middle_east-jan-june10-timeline/ |year=2010 |title=Timeline: A Modern History of Iran |work=] |publisher=Public Broadcasting Service |location=USA }} (Covers 1921–2009) |
|
* {{cite web |url=https://www.pbs.org/newshour/updates/middle_east-jan-june10-timeline/ |year=2010 |title=Timeline: A Modern History of Iran |work=] |publisher=Public Broadcasting Service |location=USA}} (Covers 1921–2009) |
|
|
* {{EI2 |last=Bosworth |first=C.E. |authorlink=Clifford Edmund Bosworth |title=Muḥammad b. Waṣīf |url=https://referenceworks.brillonline.com/entries/encyclopaedia-of-islam-2/muhammad-b-wasif-SIM_5373?s.num=0&s.f.s2_parent=s.f.book.encyclopaedia-of-islam-2&s.q=Ya%CA%BFqub+b.+Layth |volume=7}} |
|
|
* {{cite encyclopedia | title=Cambyses II | last=Dandamayev | first=Muhammad A. | url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/cambyses-opers | encyclopedia=Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. IV, Fasc. 7 | pages=726–729 | year=1990}} |
|
|
* {{Encyclopædia Iranica Online | title=PERSIAN LANGUAGE i. Early New Persian | last=Paul | first=Ludwig | url=https://iranicaonline.org/articles/persian-language-1-early-new-persian | year=2000}} |
|
|
* {{cite encyclopedia | article=Balāš VI | last1=Chaumont | first1=M. L. | first2=K. | last2=Schippmann | url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/balas-proper-name##6g | encyclopedia=Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. III, Fasc. 6 | pages=574–580 | year=1988}} |
|
|
* {{Encyclopaedia Iranica | title=Arsacids i. Origins | last=Shahbazi | first=A. Sh. | author-link=Alireza Shapour Shahbazi | url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/arsacids-i | volume=2 | fascicle=5 | pages=525}} |
|
|
* {{Encyclopædia Iranica Online|url=https://referenceworks.brillonline.com/entries/encyclopaedia-iranica-online/chronological-table-of-events-in-iranian-history-COM_337597|title=Chronological Table of Events in Iranian History|first=Ehsan|last=Yarshater|year=2021}} |
|
|
* {{cite encyclopedia | title=Waṭwāṭ, Rašid-al-Din | last=Chalisova | first=Natalia | url=https://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/watwat-rasid-al-din | encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Iranica, online edition | location=New York | year=2000}} |
|
|
* {{cite encyclopedia | article=Atābakān-e Adharbayjān | last=Luther | first=K. A. | url=http://www.iranicaonline.org/articles/atabakan-e-adarbayjan | encyclopedia=Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. II, Fasc. 8 | pages=890–894 | year=1987}} |
|
|
|
|
|
==External links== |
|
==External links== |
|
* {{cite web |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-middle-east-14542438 |author=BBC News |title=Iran Profile: Timeline }} |
|
* {{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-middle-east-14542438 |publisher=BBC News |title=Iran Profile: Timeline|date=16 August 2011 }} |
|
* {{cite web |url= http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/chronology/ |title= (Iran) |work= Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History |publisher=] |location=New York }} |
|
* {{cite web |url=http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/chronology/ |title=(Iran) |work=Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History |publisher=] |location=New York}} |
|
* Timelines of History: |
|
* Timelines of History: |
|
|
|
|
|
{{Years in Iran}} |
|
{{Years in Iran}} |
|
|
{{Asian topic|prefix=Timeline of|suffix=history}} |
|
|
|
|
|
] |
|
] |
|
] |
|
] |