| Revision as of 20:18, 4 October 2020 editTom Radulovich (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Page movers, Pending changes reviewers85,430 edits direct link← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 21:02, 11 December 2024 edit undoMindmatrix (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators187,395 edits revert - no issue with inclusion of this text, but please provide a sourceTag: Manual revert | ||
| (47 intermediate revisions by 29 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{ |
{{Short description|Species of evergreen coniferous tree}} | ||
| {{Speciesbox | {{Speciesbox | ||
| |image=Thuja occidentalis.jpg | |image=Thuja occidentalis.jpg | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''''Thuja occidentalis''''', also known as '''northern white |
'''''Thuja occidentalis''''', also known as '''northern white-cedar''',{{r|iucn}} '''eastern white-cedar''',{{r|vascan}} or '''arborvitae''',{{r|vascan|GRIN}} is an ] ] ], in the cypress family ], which is ] to eastern Canada and much of the north-central and northeastern United States.<ref name=GRIN>{{GRIN|id=36584|name=Thuja occidentalis}}</ref><ref name=GD /> It is widely cultivated as an ornamental plant. It is not to be confused with '']'' (eastern red cedar). | ||
| ⚫ | ==Taxonomy== | ||
| ⚫ | == Common names == | ||
| ⚫ | The species was first described by ] in 1753. |
||
| ⚫ | Its additional common names include '''swamp cedar''',<ref name=GRIN /> '''American arborvitae''',<ref name=GD>{{Gymnosperm Database |family=Cupressaceae |genus=Thuja |species=occidentalis}}</ref> and '''eastern arborvitae'''.<ref name=GD /> The name arborvitae is particularly used in the ] trade in the United States; it is ] for 'tree of life' – due to the supposed medicinal properties of the sap, bark, and twigs.<ref name="acs">''Thuja'', American Cancer Society, last revised 6/19/2007. </ref> It is sometimes called white-cedar (hyphenated) or whitecedar (one word){{r|GD}} to distinguish it from '']'', the ].{{r|cc}} | ||
| ⚫ | == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| Unlike the closely related ] (''Thuja plicata''), northern white cedar is only a small or medium-sized tree, growing to a height of {{convert|15|m|ft|abbr=on}} tall with a {{Convert|0.9|m|ft|abbr=on}} trunk diameter, exceptionally to {{Convert|38|m|ft}} tall and {{Convert|1.8|m|ft}} diameter.<ref name="FNA">{{eFloras|1|200005456|Thuja occidentalis |family=Cupressaceae |first=Kenton L. |last=Chambers | |
Unlike the closely related ] (''Thuja plicata''), northern white cedar is only a small or medium-sized tree, growing to a height of {{convert|15|m|ft|abbr=on}} tall with a {{Convert|0.9|m|ft|abbr=on}} trunk diameter, exceptionally to {{Convert|38|m|ft}} tall and {{Convert|1.8|m|ft}} diameter.<ref name="FNA">{{eFloras|1|200005456|Thuja occidentalis |family=Cupressaceae |first=Kenton L. |last=Chambers |access-date=24 September 2016}}</ref> The tree is often stunted or prostrate in less favorable locations. The ] is red-brown, furrowed and peels in narrow, longitudinal strips. | ||
| Northern white cedar has fan-like branches and scaly leaves. The ] forms in flat sprays with scale-like ] {{Convert|3|-|5|mm|in|frac=16}} long. | Northern white cedar has fan-like branches and scaly leaves. The ] forms in flat sprays with scale-like ] {{Convert|3|-|5|mm|in|frac=16}} long. | ||
| The ]s are slender, yellow-green, ripening to brown, {{Convert|9|-|14|mm|in|frac=16}} long and {{Convert|4|-|5|mm|in|frac=32}} broad,{{citation needed|reason=breadth is not described by Flora of North America|date=September 2016}} with |
The ]s are slender, yellow-green, ripening to brown, {{Convert|9|-|14|mm|in|frac=16}} long and {{Convert|4|-|5|mm|in|frac=32}} broad,{{citation needed|reason=breadth is not described by Flora of North America|date=September 2016}} with six to eight overlapping scales. They contain about eight seeds each.<ref name="FNA" /> The branches may take root if the tree falls.<ref name="GD" /> | ||
| {{Gallery | {{Gallery | ||
| |Thuja occidentalis trunk.jpg|Trunk | |Thuja occidentalis trunk.jpg|Trunk | ||
| |Thuja occidentalis foliage Wisconsin.jpg|Foliage | |Thuja occidentalis foliage Wisconsin.jpg|Foliage | ||
| | |
|Northern Whitecedar (Thuja occidentalis) - Algonquin Provincial Park, Ontario 2019-09-20.jpg|Cones | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ⚫ | ==Taxonomy== | ||
| ⚫ | The species was first described by ] in 1753. Over 30 synonyms are listed in ]'s ] database.{{r|powo}} | ||
| ==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| Northern white cedar is ] to an area in the southern part of eastern Canada and the adjacent part of the northern United States. It extends from southeastern Manitoba east throughout the Great Lakes region and into ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. |
Northern white cedar is ] to an area in the southern part of eastern Canada and the adjacent part of the northern United States. It extends from southeastern Manitoba east throughout the Great Lakes region and into ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. Isolated populations occur in west-central Manitoba, and to the south in ], ], ], and ] and in the ] of ], ], ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name="GD" /> In Canada, its range reaches the ] and the southern tip of ]. It grows mainly in places with cooler summers, with a typical temperature of {{convert|16|to|22|C|F}} in July, and a shorter growing season, from 90 to 180 days.<ref name="silvics" /> | ||
| ==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| ] in November with white cedars (left) and other trees and shrubs]] | ] in November with smattering of evergreen white cedars (left) and other trees and shrubs]] | ||
| Northern white cedar grows naturally in wet forests, being particularly abundant in ]s where other larger and faster-growing trees cannot compete successfully. It also occurs on other sites with reduced tree competition, such as ]. Although not currently listed as endangered, wild white cedar populations are threatened in many areas by high ] numbers; deer find the soft evergreen foliage a very attractive winter food |
Northern white cedar grows naturally in wet forests, being particularly abundant in ]s, where other larger and faster-growing trees cannot compete successfully. It also occurs on other sites with reduced tree competition, such as ]. Although not currently listed as endangered, wild white cedar populations are threatened in many areas by high ] numbers; deer find the soft evergreen foliage a very attractive winter food and strip it rapidly. The largest known specimen is {{convert|34|m|ft|abbr=on}} tall and {{convert|175|cm|in|abbr=on}} diameter, on ] within ].{{citation needed|date=October 2020}} | ||
| Northern white |
Northern white cedars can be very long-lived trees in certain conditions, with notably old specimens growing on cliffs where they are inaccessible to deer and ]. As of 2008, the oldest known living specimen was 1,141 years old,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.ldeo.columbia.edu/~adk/oldlisteast/Spp/THOC.html |title=Eastern OLDLIST. ''Thuja occidentalis'' |year=2008 |publisher=Rocky Mountain Tree-Ring Research, Inc. & Eastern Kentucky University |access-date=15 January 2021}}</ref> but a dead specimen with 1,653 growth rings has been found.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.rmtrr.org/oldlist.htm |year=2020 |access-date=15 January 2021 |title=Eastern OLDLIST a database of ancient trees and their ages |publisher=Rocky Mountain Tree-Ring Research, Inc. & Eastern Kentucky University}}</ref> Despite their age, these very old trees are small and stunted due to the difficult growing conditions. These individuals' long lifespans have been attributed to their slow growth and their ability to survive when different sections of the tree are damaged or killed.<ref name="Larson2001">{{cite journal|last1=Larson|first1=D.W.|title=The paradox of great longevity in a short-lived tree species|journal=Experimental Gerontology|volume=36|issue=4–6|year=2001|pages=651–673|issn=0531-5565|doi=10.1016/S0531-5565(00)00233-3|pmid=11295506|s2cid=24297929}}</ref> The ], a ''T. occidentalis'' growing out of a cliff face on ] in ], was described by the ] explorer ] as being a mature tree in 1731; it is still alive today. | ||
| ], ]]] | ], ]]] | ||
| Specimens found growing on cliff faces in southern Ontario are the oldest trees in ] and all of Canada, |
Specimens found growing on cliff faces in southern Ontario are the oldest trees in ] and all of Canada, having achieved ages in excess of 1,653 years.<ref name="GD" /> | ||
| ==Uses== | ==Uses== | ||
| ⚫ | ''Thuja occidentalis'' is commercially used for rustic fencing and posts, lumber, poles, shingles, and in the construction of ]s.<ref name="silvics" /> It is the preferred wood for the structural elements, such as ribs and planking, of ] ]s and the planking of wooden ]s.<ref name="usda" /> | ||
| ⚫ | ''Thuja occidentalis'' |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| The essential oil within the plant has been used for ]s, ]s, hair preparations, ]s, ], room sprays, and soft soaps. |
The essential oil within the plant has been used for ]s, ]s, hair preparations, ]s, ], room sprays, and soft soaps. The Ojibwa reportedly made a soup from the inner bark of the soft twigs. Others have used the twigs to make teas to relieve ] and ].<ref name="usda">{{cite web|url=http://plants.usda.gov/plantguide/pdf/cs_thoc2.pdf|title=USDA/NRCS Plant Guide: Northern White Cedar, ''Thuja occidentalis'' L.|publisher=]|access-date=2008-02-15}}</ref> | ||
| Eastern white cedar – ] – is a popular ] used in both residential and commercial landscapes. | |||
| In the 19th century, ''T. occidentalis'' extract was in common use as an externally applied tincture or ointment for the treatment of warts, ringworm, and thrush.<ref>David Hoffmann, ''Medical Herbalism: Principles and Practices,'' Healing Arts Press, 2003, p.588</ref> "An injection of the tincture into venereal warts is said to cause them to disappear."<ref>M Grieve, ''A Modern Herbal,'' London: Jonathan Cape, 1931, p.177</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | ''Thuja occidentalis'' has important uses in traditional ] culture. Honoured with the name '''Nookomis Giizhik''' (Grandmother Cedar), the tree is the subject of sacred legends and is considered a gift to humanity for its myriad of uses, among them crafts, construction, and medicine.<ref>Geniusz, Wendy Makoons (2009). ''Our Knowledge is not Primitive''. Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press</ref> It is one of the four plants of the Ojibwe ], associated with the north. The foliage is rich in ] and is believed to be the ], which cured the ] of ] and his party in the winter of 1535–1536.<ref name="silvics">{{Silvics |volume=1 |genus=Thuja |species=occidentalis |first=William F. |last=Johnston}}</ref> Due to the presence of the neurotoxic compound ], internal use can be harmful if used for prolonged periods or while pregnant.{{citation needed|date=October 2020}} | ||
| Strips of clear, northern white cedar wood were used to make the original ] boats, formerly known as the "pickup trucks of the Au Sable". The light, rot resistant wood was preferred but is now commonly replaced by marine grade plywood.{{cn|date=October 2020}} | |||
| ==Cultivation== | ==Cultivation== | ||
| ], ]]] | ], ]]] | ||
| '' |
''T. occidentalis'' is widely used as an ], particularly for screens and ], in gardens, parks, and cemeteries. Over 300 ]s exist, showing great variation in colour, shape, and size, with some of the more common ones being 'Degroot's Spire', 'Ellwangeriana', 'Hetz Wintergreen', 'Lutea', 'Rheingold', 'Smaragd' (or 'Emerald Green'), 'Techny', and 'Wareana'. It was introduced into ] as early as 1540.{{citation needed|date=October 2020}} | ||
| These cultivars have gained the ]'s ]: | |||
| The following cultivars have gained the ]'s ]: 'Danica',<ref>{{cite web|title=RHS Plant Selector – ''Thuja occidentalis'' 'Danica'|url=http://apps.rhs.org.uk/plantselector/plant?plantid=1924|accessdate=6 June 2013}}</ref> 'Holmstrup',<ref>{{cite web|title=RHS Plant Selector – ''Thuja occidentalis'' 'Holmstrup'|url=http://apps.rhs.org.uk/plantselector/plant?plantid=1925|accessdate=6 June 2013}}</ref> 'Rheingold',<ref>{{cite web|title=RHS Plant Selector – ''Thuja occidentalis'' 'Rheingold'|url=http://apps.rhs.org.uk/plantselector/plant?plantid=4202|accessdate=6 June 2013}}</ref> and 'Smaragd'.<ref>{{cite web|title=RHS Plant Selector – ''Thuja occidentalis'' 'Smaragd'|url=http://apps.rhs.org.uk/plantselector/plant?plantid=4203|accessdate=6 June 2013}}</ref> | |||
| {{div col|colwidth=15em}} | |||
| *'Danica',<ref>{{cite web|title=RHS Plant Selector – ''Thuja occidentalis'' 'Danica'|url=https://www.rhs.org.uk/Plants/68725/Thuja-occidentalis-Danica/Details | publisher = RHS | access-date = 5 March 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *'Golden Tuffet'<ref>{{cite web | url = https://www.rhs.org.uk/Plants/220110/Thuja-occidentalis-Golden-Tuffet/Details | title = ''Thuja occidentalis'' 'Golden Tuffet' | publisher = RHS | access-date = 5 March 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *'Holmstrup',<ref>{{cite web|title=RHS Plant Selector – ''Thuja occidentalis'' 'Holmstrup'|url=https://www.rhs.org.uk/Plants/77166/Thuja-occidentalis-Holmstrup/Details | publisher = RHS | access-date = 5 March 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *'Rheingold',<ref>{{cite web|title=RHS Plant Selector – ''Thuja occidentalis'' 'Rheingold'|url=https://www.rhs.org.uk/Plants/91497/Thuja-occidentalis-Rheingold/Details | publisher = RHS | access-date = 5 March 2021}}</ref> | |||
| *'Smaragd'.<ref>{{cite web|title=RHS Plant Selector – ''Thuja occidentalis'' 'Smaragd'|url=https://www.rhs.org.uk/Plants/75683/Thuja-occidentalis-Smaragd/Details | publisher = RHS | access-date = 5 March 2021}}</ref> | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist|refs= | {{Reflist|refs= | ||
| <ref name=cc>{{cite web |title=The Cedars |year=2004 |url=https://www.canr.msu.edu/hrt/uploads/535/78626/cedars.pdf}}</ref> | <ref name=cc>{{cite web |title=The Cedars |year=2004 |url=https://www.canr.msu.edu/hrt/uploads/535/78626/cedars.pdf}}</ref> | ||
| <ref name=powo>{{cite web |title=''Thuja occidentalis'' L. |url= |
<ref name=powo>{{cite web |title=''Thuja occidentalis'' L. |url=https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:263956-1 |website=Plants of the World Online |publisher=] |access-date=3 October 2020}}</ref> | ||
| <ref name=vascan>{{cite web |author=Brouillet L. ''et al.'' 2010+ |title=''Thuja occidentalis'' Linnaeus |url=https://data.canadensys.net/vascan/taxon/4711 |website=data.canadensys.net |publisher=Database of Vascular Plants of Canada (VASCAN) | |
<ref name=vascan>{{cite web |author=Brouillet L. ''et al.'' 2010+ |title=''Thuja occidentalis'' Linnaeus |url=https://data.canadensys.net/vascan/taxon/4711 |website=data.canadensys.net |publisher=Database of Vascular Plants of Canada (VASCAN) |access-date=3 October 2020}}</ref> | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Commons}} | {{Commons}} | ||
| * | * {{PFAF|Thuja occidentalis}} | ||
| * | |||
| * | * | ||
| {{Cupressaceae}} | {{Cupressaceae}} | ||
| {{Taxonbar|from=Q147468}} | {{Taxonbar|from=Q147468}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:02, 11 December 2024
Species of evergreen coniferous tree
| Thuja occidentalis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Leaves and immature cones | |
| Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Cupressales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae |
| Genus: | Thuja |
| Species: | T. occidentalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Thuja occidentalis L. | |
| |
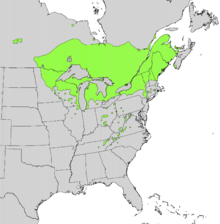
| Natural range | |
Thuja occidentalis, also known as northern white-cedar, eastern white-cedar, or arborvitae, is an evergreen coniferous tree, in the cypress family Cupressaceae, which is native to eastern Canada and much of the north-central and northeastern United States. It is widely cultivated as an ornamental plant. It is not to be confused with Juniperus virginiana (eastern red cedar).
Common names
Its additional common names include swamp cedar, American arborvitae, and eastern arborvitae. The name arborvitae is particularly used in the horticultural trade in the United States; it is Latin for 'tree of life' – due to the supposed medicinal properties of the sap, bark, and twigs. It is sometimes called white-cedar (hyphenated) or whitecedar (one word) to distinguish it from Cedrus, the true cedars.
Description
Unlike the closely related western red cedar (Thuja plicata), northern white cedar is only a small or medium-sized tree, growing to a height of 15 m (49 ft) tall with a 0.9 m (3.0 ft) trunk diameter, exceptionally to 38 metres (125 ft) tall and 1.8 metres (5.9 ft) diameter. The tree is often stunted or prostrate in less favorable locations. The bark is red-brown, furrowed and peels in narrow, longitudinal strips. Northern white cedar has fan-like branches and scaly leaves. The foliage forms in flat sprays with scale-like leaves 3–5 millimetres (1⁄8–3⁄16 in) long.
The seed cones are slender, yellow-green, ripening to brown, 9–14 millimetres (3⁄8–9⁄16 in) long and 4–5 millimetres (5⁄32–3⁄16 in) broad, with six to eight overlapping scales. They contain about eight seeds each. The branches may take root if the tree falls.
Taxonomy
The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. Over 30 synonyms are listed in Kew's Plants of the World Online database.
Distribution
Northern white cedar is native to an area in the southern part of eastern Canada and the adjacent part of the northern United States. It extends from southeastern Manitoba east throughout the Great Lakes region and into Ontario, Québec, New York, Vermont, New Hampshire, Maine, Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia. Isolated populations occur in west-central Manitoba, and to the south in Massachusetts, Connecticut, Ohio, and Illinois and in the Appalachian Mountains of Kentucky, Tennessee, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia. In Canada, its range reaches the Arctic treeline and the southern tip of Hudson Bay. It grows mainly in places with cooler summers, with a typical temperature of 16 to 22 °C (61 to 72 °F) in July, and a shorter growing season, from 90 to 180 days.
Ecology

Northern white cedar grows naturally in wet forests, being particularly abundant in coniferous swamps, where other larger and faster-growing trees cannot compete successfully. It also occurs on other sites with reduced tree competition, such as cliffs. Although not currently listed as endangered, wild white cedar populations are threatened in many areas by high deer numbers; deer find the soft evergreen foliage a very attractive winter food and strip it rapidly. The largest known specimen is 34 m (112 ft) tall and 175 cm (69 in) diameter, on South Manitou Island within Leelanau County, Michigan. Northern white cedars can be very long-lived trees in certain conditions, with notably old specimens growing on cliffs where they are inaccessible to deer and wildfire. As of 2008, the oldest known living specimen was 1,141 years old, but a dead specimen with 1,653 growth rings has been found. Despite their age, these very old trees are small and stunted due to the difficult growing conditions. These individuals' long lifespans have been attributed to their slow growth and their ability to survive when different sections of the tree are damaged or killed. The Witch Tree, a T. occidentalis growing out of a cliff face on Lake Superior in Minnesota, was described by the French explorer Sieur de la Verendrye as being a mature tree in 1731; it is still alive today.

Specimens found growing on cliff faces in southern Ontario are the oldest trees in Eastern North America and all of Canada, having achieved ages in excess of 1,653 years.
Uses
Thuja occidentalis is commercially used for rustic fencing and posts, lumber, poles, shingles, and in the construction of log cabins. It is the preferred wood for the structural elements, such as ribs and planking, of birchbark canoes and the planking of wooden canoes.
The essential oil within the plant has been used for cleansers, disinfectants, hair preparations, insecticides, liniment, room sprays, and soft soaps. The Ojibwa reportedly made a soup from the inner bark of the soft twigs. Others have used the twigs to make teas to relieve constipation and headache.
Eastern white cedar – as arborvitae – is a popular ornamental plant used in both residential and commercial landscapes.
Thuja occidentalis has important uses in traditional Ojibwe culture. Honoured with the name Nookomis Giizhik (Grandmother Cedar), the tree is the subject of sacred legends and is considered a gift to humanity for its myriad of uses, among them crafts, construction, and medicine. It is one of the four plants of the Ojibwe medicine wheel, associated with the north. The foliage is rich in vitamin C and is believed to be the annedda, which cured the scurvy of Jacques Cartier and his party in the winter of 1535–1536. Due to the presence of the neurotoxic compound thujone, internal use can be harmful if used for prolonged periods or while pregnant.
Cultivation

T. occidentalis is widely used as an ornamental tree, particularly for screens and hedges, in gardens, parks, and cemeteries. Over 300 cultivars exist, showing great variation in colour, shape, and size, with some of the more common ones being 'Degroot's Spire', 'Ellwangeriana', 'Hetz Wintergreen', 'Lutea', 'Rheingold', 'Smaragd' (or 'Emerald Green'), 'Techny', and 'Wareana'. It was introduced into Europe as early as 1540. These cultivars have gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit:
- 'Danica',
- 'Golden Tuffet'
- 'Holmstrup',
- 'Rheingold',
- 'Smaragd'.
See also
References
- ^ Farjon, A. (2013). "Thuja occidentalis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2013: e.T42262A2967995. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T42262A2967995.en.
- ^ Brouillet L. et al. 2010+. "Thuja occidentalis Linnaeus". data.canadensys.net. Database of Vascular Plants of Canada (VASCAN). Retrieved 3 October 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Thuja occidentalis". Germplasm Resources Information Network. Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture.
- ^ Earle, Christopher J., ed. (2018). "Thuja occidentalis". The Gymnosperm Database.
- Thuja, American Cancer Society, last revised 6/19/2007. available online
- "The Cedars" (PDF). 2004.
- ^ Chambers, Kenton L. (1993). "Thuja occidentalis". In Flora of North America Editorial Committee (ed.). Flora of North America North of Mexico (FNA). Vol. 2. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press. Retrieved 24 September 2016 – via eFloras.org, Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA.
- "Thuja occidentalis L." Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 3 October 2020.
- ^ Johnston, William F. (1990). "Thuja occidentalis". In Burns, Russell M.; Honkala, Barbara H. (eds.). Conifers. Silvics of North America. Vol. 1. Washington, D.C.: United States Forest Service (USFS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) – via Southern Research Station.
- "Eastern OLDLIST. Thuja occidentalis". Rocky Mountain Tree-Ring Research, Inc. & Eastern Kentucky University. 2008. Retrieved 15 January 2021.
- "Eastern OLDLIST a database of ancient trees and their ages". Rocky Mountain Tree-Ring Research, Inc. & Eastern Kentucky University. 2020. Retrieved 15 January 2021.
- Larson, D.W. (2001). "The paradox of great longevity in a short-lived tree species". Experimental Gerontology. 36 (4–6): 651–673. doi:10.1016/S0531-5565(00)00233-3. ISSN 0531-5565. PMID 11295506. S2CID 24297929.
- ^ "USDA/NRCS Plant Guide: Northern White Cedar, Thuja occidentalis L." (PDF). United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 2008-02-15.
- Geniusz, Wendy Makoons (2009). Our Knowledge is not Primitive. Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press
- "RHS Plant Selector – Thuja occidentalis 'Danica'". RHS. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- "Thuja occidentalis 'Golden Tuffet'". RHS. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- "RHS Plant Selector – Thuja occidentalis 'Holmstrup'". RHS. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- "RHS Plant Selector – Thuja occidentalis 'Rheingold'". RHS. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
- "RHS Plant Selector – Thuja occidentalis 'Smaragd'". RHS. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
External links
- "Thuja occidentalis". Plants for a Future.
- University of Michigan at Dearborn: Native American Ethnobotany of Thuja occidentalis
- Borealforest.org: Thuja occidentalis
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Thuja occidentalis |
|


