| Revision as of 15:45, 8 February 2007 editHurricanehink (talk | contribs)Administrators61,857 edits ←Reverted revision 106522286 by 71.103.129.234 (talk) via undo← Previous edit | Revision as of 18:41, 24 February 2007 edit undoCmdrObot (talk | contribs)339,230 editsm sp (2): parellels→parallels, particuarly→particularlyNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ]<onlyinclude><!-- See ] for an explanation of this and other inclusion tags below --> | ]<onlyinclude><!-- See ] for an explanation of this and other inclusion tags below --> | ||
| A '''South American cyclone''' is a ] that affects the continent of ] or its countries. The continent is rarely affected by tropical cyclones, though most storms to hit the area formed in the North ].</onlyinclude> Typically, strong upper level winds and its proximity to the equator prevents North Atlantic impacts.<ref name="asktom">{{cite web|year=2004|title=Ask Tom Why|publisher=WGN9 Chicago|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://wgntv.trb.com/news/weather/weblog/wgnweather/archives/000098.html}}</ref> No tropical cyclone has ever affected the Pacific side of South America, while conditions are typically too hostile for many storms to hit the area from the South Atlantic Ocean. Based on climatology, northern ] and ] have a 1 to 5% chance of a hurricane strike in any given year, while all locations south of 10º N have less than a 1% chance of a direct hit.<ref name="sciencepolicy">{{cite web|author=Pielke, Rubiera, Landsea, Fernández, and Klein|year=2003|title=Hurricane Vulnerability in Latin America & The Caribbean|publisher=National Hazards Review|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://sciencepolicy.colorado.edu/admin/publication_files/resource-1769-2003.21.pdf}}</ref> A total of 37 tropical cyclones have affected the continent since 1588. | A '''South American cyclone''' is a ] that affects the continent of ] or its countries. The continent is rarely affected by tropical cyclones, though most storms to hit the area formed in the North ].</onlyinclude> Typically, strong upper level winds and its proximity to the equator prevents North Atlantic impacts.<ref name="asktom">{{cite web|year=2004|title=Ask Tom Why|publisher=WGN9 Chicago|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://wgntv.trb.com/news/weather/weblog/wgnweather/archives/000098.html}}</ref> No tropical cyclone has ever affected the Pacific side of South America, while conditions are typically too hostile for many storms to hit the area from the South Atlantic Ocean. Based on climatology, northern ] and ] have a 1 to 5% chance of a hurricane strike in any given year, while all locations south of 10º N have less than a 1% chance of a direct hit.<ref name="sciencepolicy">{{cite web|author=Pielke, Rubiera, Landsea, Fernández, and Klein|year=2003|title=Hurricane Vulnerability in Latin America & The Caribbean|publisher=National Hazards Review|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://sciencepolicy.colorado.edu/admin/publication_files/resource-1769-2003.21.pdf}}</ref> A total of 37 tropical cyclones have affected the continent since 1588. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| *], ] - Venezuela is affected by a hurricane.<ref name="aoml"/></onlyinclude> | *], ] - Venezuela is affected by a hurricane.<ref name="aoml"/></onlyinclude> | ||
| *], ] - A 105 mph (170 km/h) ] hurricane makes landfall on northern Venezuela, causing winds of up to 80 mph in ].<ref name="1877hurdat">{{cite web|author=NOAA|year=2005|title=1877 Atlantic hurricane season|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/hurdat/1877.htm}}</ref> | *], ] - A 105 mph (170 km/h) ] hurricane makes landfall on northern Venezuela, causing winds of up to 80 mph in ].<ref name="1877hurdat">{{cite web|author=NOAA|year=2005|title=1877 Atlantic hurricane season|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/hurdat/1877.htm}}</ref> | ||
| *], ] - A Category 2 hurricane |
*], ] - A Category 2 hurricane parallels the north coast of Venezuela, causing winds of up to 40 mph (65 km/h) in Curaçao.<ref name="1886hurdat">{{cite web|author=NOAA|year=2005|title=1886 Atlantic hurricane season|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/hurdat/1886.htm}}</ref> | ||
| *], ] - A tropical storm passes just north of the ] of Colombia.<ref name="1887hurdat">{{cite web|author=NOAA|year=2005|title=1887 Atlantic hurricane season|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/hurdat/1887.htm}}</ref> | *], ] - A tropical storm passes just north of the ] of Colombia.<ref name="1887hurdat">{{cite web|author=NOAA|year=2005|title=1887 Atlantic hurricane season|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/hurdat/1887.htm}}</ref> | ||
| *], ] - A Category 2 hurricane hits Northern Venezuela and Colombia,<ref name="1892hurdat">{{cite web|author=NOAA|year=2005|title=1892 Atlantic hurricane season|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/hurdat/1892.htm}}</ref> causing rough seas in Curaçao.<ref name="1892mwr">{{cite web|author=National Weather Service|year=1892|title=1892 Monthly Weather Review|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/general/lib/lib1/nhclib/mwreviews/1892.pdf}}</ref> | *], ] - A Category 2 hurricane hits Northern Venezuela and Colombia,<ref name="1892hurdat">{{cite web|author=NOAA|year=2005|title=1892 Atlantic hurricane season|accessdate=2006-07-20|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/hurdat/1892.htm}}</ref> causing rough seas in Curaçao.<ref name="1892mwr">{{cite web|author=National Weather Service|year=1892|title=1892 Monthly Weather Review|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/general/lib/lib1/nhclib/mwreviews/1892.pdf}}</ref> | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
| *October 16-18, ] - ] strikes northern Venezuela and Colombia. The storm produces flash flooding which kills 11 in Venezuela. In Colombia, rainfall from Joan kills 25, and leaves 27,000 homeless.<ref name="joantcr">{{cite web|author=Dr. Harold P. Gerrish|year=1988|title=Hurricane Joan Tropical Cyclone Report Page 3|publisher=National Hurricane Center|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/archive/storm_wallets/atlantic/atl1988-prelim/joan/prelim03.gif}}</ref> | *October 16-18, ] - ] strikes northern Venezuela and Colombia. The storm produces flash flooding which kills 11 in Venezuela. In Colombia, rainfall from Joan kills 25, and leaves 27,000 homeless.<ref name="joantcr">{{cite web|author=Dr. Harold P. Gerrish|year=1988|title=Hurricane Joan Tropical Cyclone Report Page 3|publisher=National Hurricane Center|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/archive/storm_wallets/atlantic/atl1988-prelim/joan/prelim03.gif}}</ref> | ||
| *], ] - Minimal ] dissipates over northeastern Venezuela, with no known impact.<ref name="frantcr">{{cite web|author=National Hurricane Center|year=1990|title=Tropical Storm Fran Tropical Cyclone Report|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/archive/storm_wallets/atlantic/atl1990-prelim/fran/prelim01.gif}}</ref> | *], ] - Minimal ] dissipates over northeastern Venezuela, with no known impact.<ref name="frantcr">{{cite web|author=National Hurricane Center|year=1990|title=Tropical Storm Fran Tropical Cyclone Report|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/archive/storm_wallets/atlantic/atl1990-prelim/fran/prelim01.gif}}</ref> | ||
| *August 7-9, ] - ] moves across northern Venezuela and Colombia. In Venezuela, the storm drops at least 13.35 inches (339 mm) in ]. The rainfall causes mudslides, |
*August 7-9, ] - ] moves across northern Venezuela and Colombia. In Venezuela, the storm drops at least 13.35 inches (339 mm) in ]. The rainfall causes mudslides, particularly near the city of Caracas, that cover many low-income housing units. Of the 173 deaths caused by Bret in Venezuela, most occur in the low-income areas near Caracas.<ref name="1993mwr">{{cite web|author=National Weather Service|year=1993|title=1993 Monthly Weather Review|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/general/lib/lib1/nhclib/mwreviews/1993.pdf}}</ref> Lack of preparation, including weather forecasters prematurely stating the worst of the storm is over, is part of the problem.<ref name="bretnews">{{cite web|author=John Wade|year=1993|title=Catastrophe in Caracas|publisher=The Herald|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/archive/storm_wallets/atlantic/atl1993/bret/news/mh0809p2.gif}}</ref> In all, 10,000 were left homeless, and damaged totaled to $25 million (1993 USD, $39 million 2005 USD). In Colombia, Bret causes one death and one injury.<ref name="1993mwr"/> | ||
| *July 24-27, ] - ] moves westward across the southern ] and crosses over extreme northern Colombia and the ] archipelago. Cesar kills 11 people in Colombia due to flooding and mudslides.<ref name="cesardam">{{cite web|author=Associated Press|year=1996|title=Hurricane Douglas leaves at least 35 dead as it crosses from Caribbean to Pacific|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://wwwnotes.reliefweb.int/w/RWB.NSF/480fa8736b88bbc3c12564f6004c8ad5/225921ce1d150f66c1256377003249a6?OpenDocument}}</ref> | *July 24-27, ] - ] moves westward across the southern ] and crosses over extreme northern Colombia and the ] archipelago. Cesar kills 11 people in Colombia due to flooding and mudslides.<ref name="cesardam">{{cite web|author=Associated Press|year=1996|title=Hurricane Douglas leaves at least 35 dead as it crosses from Caribbean to Pacific|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://wwwnotes.reliefweb.int/w/RWB.NSF/480fa8736b88bbc3c12564f6004c8ad5/225921ce1d150f66c1256377003249a6?OpenDocument}}</ref> | ||
| *November 13-16, ] - Strong waves from ] effect the ] of Colombia, flooding 1,200 homes and businesses along the northern coastline. In addition, winds and rains from the hurricane causes severe crop damage in the country.<ref name="lennycol">{{cite web|author=Agence France-Presse|year=1999|title=One death blamed on Hurricane Lenny; still threatens Caribbean|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://wwwnotes.reliefweb.int/w/RWB.NSF/480fa8736b88bbc3c12564f6004c8ad5/363875f0d9b2ff82c125683c0041097a?OpenDocument}}</ref> The hurricane kills two in Colombia.<ref name="lennytcr">{{cite web|author=John L. Guiney|year=1999|title=Hurricane Lenny Tropical Cyclone Report|publisher=National Hurricane Center|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/1999lenny.html}}</ref> | *November 13-16, ] - Strong waves from ] effect the ] of Colombia, flooding 1,200 homes and businesses along the northern coastline. In addition, winds and rains from the hurricane causes severe crop damage in the country.<ref name="lennycol">{{cite web|author=Agence France-Presse|year=1999|title=One death blamed on Hurricane Lenny; still threatens Caribbean|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://wwwnotes.reliefweb.int/w/RWB.NSF/480fa8736b88bbc3c12564f6004c8ad5/363875f0d9b2ff82c125683c0041097a?OpenDocument}}</ref> The hurricane kills two in Colombia.<ref name="lennytcr">{{cite web|author=John L. Guiney|year=1999|title=Hurricane Lenny Tropical Cyclone Report|publisher=National Hurricane Center|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/1999lenny.html}}</ref> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
| *], ] - ] produces heavy rainfall of up to 8 inches (200 mm) in ].<ref name="wmo2003">{{cite web|author=World Meteorological Organization|year=2004|title=Final Report of the 2003 Atlantic Hurricane Season|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.wmo.ch/web/www/TCP/Reports/HC26-English.pdf}}</ref> | *], ] - ] produces heavy rainfall of up to 8 inches (200 mm) in ].<ref name="wmo2003">{{cite web|author=World Meteorological Organization|year=2004|title=Final Report of the 2003 Atlantic Hurricane Season|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.wmo.ch/web/www/TCP/Reports/HC26-English.pdf}}</ref> | ||
| *], ] - A ] in the South Atlantic Ocean hits eastern ], dropping heavy rainfall in the area.<ref name="jan2004">{{cite web|author=Gary Padgett|year=2004|title=January 2004 Tropical cyclone summary|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2004/summ0401.txt}}</ref> | *], ] - A ] in the South Atlantic Ocean hits eastern ], dropping heavy rainfall in the area.<ref name="jan2004">{{cite web|author=Gary Padgett|year=2004|title=January 2004 Tropical cyclone summary|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://australiasevereweather.com/cyclones/2004/summ0401.txt}}</ref> | ||
| *], ] - A cyclone, unofficially named ], strikes southeastern Brazil with maximum recorded winds of 90 mph (145 km/h).<ref name="2004sum">{{cite web|author=D.H. Levinson|year=2004|title=State of the Climate in 2004|publisher=American Meteorological Society|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://ams.allenpress.com/pdfserv/10.1175%2FBAMS-86-6-Levinson}}</ref> The possible hurricane damaged more than 30,000 homes and left 1,900 people homeless. The storm also damaged 1,373 businesses and destroyed 50, including a hospital. The storm killed 3, injured 38,<ref name="usatoday">{{cite web|author=Associated Press|year=2004|title=First South Atlantic hurricane hits Brazil|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.usatoday.com/weather/news/2004-03-28-brazil-storm_x.htm}}</ref> and caused up to $330 million in damage (2004 USD).<ref name="2004sum"/> | *], ] - A cyclone, unofficially named ], strikes southeastern Brazil with maximum recorded winds of 90 mph (145 km/h).<ref name="2004sum">{{cite web|author=D. H. Levinson|year=2004|title=State of the Climate in 2004|publisher=American Meteorological Society|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://ams.allenpress.com/pdfserv/10.1175%2FBAMS-86-6-Levinson}}</ref> The possible hurricane damaged more than 30,000 homes and left 1,900 people homeless. The storm also damaged 1,373 businesses and destroyed 50, including a hospital. The storm killed 3, injured 38,<ref name="usatoday">{{cite web|author=Associated Press|year=2004|title=First South Atlantic hurricane hits Brazil|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.usatoday.com/weather/news/2004-03-28-brazil-storm_x.htm}}</ref> and caused up to $330 million in damage (2004 USD).<ref name="2004sum"/> | ||
| *September 7-9, ] - ] parallels the north coast of Venezuela as a Category 4 hurricane. Ivan's strong winds forced the closure of several airports. The hurricane also produced heavy rainfall and strong waves.<ref name="afpivan">{{cite web|author=Agence France-Presse|year=2004|title=Hurricane Ivan kills at least 14 in Caribbean|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.reliefweb.int/rw/RWB.NSF/db900SID/SZIE-64NKFE?OpenDocument&rc=2&cc=ven}}</ref> Ivan killed three in the country,<ref name="ivantcr">{{cite web|author=Stacy R. Stewart|year=2004|title=Hurricane Ivan Tropical Cyclone Report|publisher=National Hurricane Center|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/2004ivan.shtml?}}</ref> though overall damage was minor.<ref name="irfc">{{cite web|author=International Federation of the Red Cross|year=2004|title=Caribbean:Hurricane Ivan|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.ifrc.org/docs/appeals/04/2104.pdf}}</ref> | *September 7-9, ] - ] parallels the north coast of Venezuela as a Category 4 hurricane. Ivan's strong winds forced the closure of several airports. The hurricane also produced heavy rainfall and strong waves.<ref name="afpivan">{{cite web|author=Agence France-Presse|year=2004|title=Hurricane Ivan kills at least 14 in Caribbean|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.reliefweb.int/rw/RWB.NSF/db900SID/SZIE-64NKFE?OpenDocument&rc=2&cc=ven}}</ref> Ivan killed three in the country,<ref name="ivantcr">{{cite web|author=Stacy R. Stewart|year=2004|title=Hurricane Ivan Tropical Cyclone Report|publisher=National Hurricane Center|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/2004ivan.shtml?}}</ref> though overall damage was minor.<ref name="irfc">{{cite web|author=International Federation of the Red Cross|year=2004|title=Caribbean:Hurricane Ivan|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://www.ifrc.org/docs/appeals/04/2104.pdf}}</ref> | ||
| *], ] - ] passes just north of Venezuela as a strengthening hurricane, causing heavy rains and flooding in the northeastern portion of the country. 64 families were forced to leave their homes when rivers in eastern ] state overflowed their banks, but waters quickly receded. Ships were forced to remain at port while the hurricane passed to the country's north, though restrictions quickly lifted.<ref name="emily">{{cite news|author=News from Russia|year=2005|title=Emily passed Venezuela|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://newsfromrussia.com/world/2005/07/15/60604.html}}</ref> | *], ] - ] passes just north of Venezuela as a strengthening hurricane, causing heavy rains and flooding in the northeastern portion of the country. 64 families were forced to leave their homes when rivers in eastern ] state overflowed their banks, but waters quickly receded. Ships were forced to remain at port while the hurricane passed to the country's north, though restrictions quickly lifted.<ref name="emily">{{cite news|author=News from Russia|year=2005|title=Emily passed Venezuela|accessdate=2006-07-21|url=http://newsfromrussia.com/world/2005/07/15/60604.html}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 18:41, 24 February 2007

A South American cyclone is a tropical cyclone that affects the continent of South America or its countries. The continent is rarely affected by tropical cyclones, though most storms to hit the area formed in the North Atlantic Ocean. Typically, strong upper level winds and its proximity to the equator prevents North Atlantic impacts. No tropical cyclone has ever affected the Pacific side of South America, while conditions are typically too hostile for many storms to hit the area from the South Atlantic Ocean. Based on climatology, northern Venezuela and Colombia have a 1 to 5% chance of a hurricane strike in any given year, while all locations south of 10º N have less than a 1% chance of a direct hit. A total of 37 tropical cyclones have affected the continent since 1588.
List of tropical cyclones
Pre-1900
- November 4-6, 1588 - Cartagena de Indias in Colombia is affected by a hurricane.
- September, 1672 - A hurricane affects Caracas, Venezuela.
- October 22, 1683 - The island of Curaçao off Venezuela is impacted by a hurricane.
- September, 1773 - A hurricane moves across Venezuela and later Colombia.
- December 13-22, 1822 - A hurricane traverses the southeastern Caribbean Sea and makes landfall on Venezuela.
- October 13, 1847 - Venezuela is affected by a hurricane.
- September 23, 1877 - A 105 mph (170 km/h) Category 2 hurricane makes landfall on northern Venezuela, causing winds of up to 80 mph in Curaçao.
- September 17, 1886 - A Category 2 hurricane parallels the north coast of Venezuela, causing winds of up to 40 mph (65 km/h) in Curaçao.
- December 10, 1887 - A tropical storm passes just north of the Guajira Department of Colombia.
- October 8, 1892 - A Category 2 hurricane hits Northern Venezuela and Colombia, causing rough seas in Curaçao.
1900s

- September 5, 1911 - Curaçao experiences a westward moving tropical storm which passes near the northern coasts of Venezuela and Colombia.
- November 2-5, 1932 - A Category 2 hurricane parallels the north coast of Venezuela and Colombia 75 miles (120 km) offshore, causing some damage. Later, it passes to the northeast of Providencia Island, destroying 36 houses and ruining crops.
- June 27, 1933 - A minimal hurricane moves through northeastern Venezuela. The hurricane destroys several houses, businesses, and fishing boats. Powerful winds cut telephonic and telegraphic communications for several days. The hurricane killed several people, and caused over $200,000 in damage (1933 USD, $2.7 million 2005 USD).
- October 8, 1954 - Hurricane Hazel parallels the north coasts of Venezuela and Colombia around 100 miles (160 km) offshore as a Category 3 hurricane, though effects, if any, are unknown.
- September 25, 1955 - Hurricane Janet parallels the north coasts of Venezuela and Colombia around 100 miles (160 km) offshore as a Category 4 hurricane, though effects, if any, are unknown.
- July 20, 1961 - Hurricane Anna passes 75 miles (120 km) north of the coast of Venezuela, though effects, if any, are unknown.
- October 28, 1961 - Hurricane Hattie moves over San Andrés island with winds of 80 mph (130 km/h), causing 1 death, 15 injuries, and $300,000 in damage (1961 USD, $1.9 million 2005 USD).
- October 1, 1963 - Hurricane Flora strikes Tobago and remains just offshore of Venezuela as it moves through the Caribbean Sea as a Category 3 hurricane. Damage in Venezuela, if any, is unknown.
- September 7, 1971 - A tropical depression intensifies into Tropical Storm Edith near the north coast of Venezuela. The southern portion of the depression's circulation moves over the northeastern portion of the country. Effects are unknown.
- September 16, 1971 - A tropical depression that later becomes Hurricane Irene crosses the island of Curaçao. Effects are unknown.
- August 14, 1974 - Tropical Storm Alma makes landfall on northeastern Venezuela and later dissipates over the mountainous country. Intense rain bands cause a passenger plane to crash on Isla Margarita, resulting in 47 indirect deaths. Damage is unknown.
- August 12, 1978 - Tropical Depression Cora dissipates near the island of Curaçao, causing no known impact.
- September 13, 1978 - A tropical depression that later becomes Hurricane Greta forms near the northeastern coast of Venezuela, causing no known damage.
- September 10-12, 1988 - Outflow bands from Hurricane Gilbert produce flash flooding in northern Venezuela. The flooding killed five people.
- October 16-18, 1988 - Tropical Storm Joan strikes northern Venezuela and Colombia. The storm produces flash flooding which kills 11 in Venezuela. In Colombia, rainfall from Joan kills 25, and leaves 27,000 homeless.
- August 14, 1990 - Minimal Tropical Storm Fran dissipates over northeastern Venezuela, with no known impact.
- August 7-9, 1993 - Tropical Storm Bret moves across northern Venezuela and Colombia. In Venezuela, the storm drops at least 13.35 inches (339 mm) in Guanare. The rainfall causes mudslides, particularly near the city of Caracas, that cover many low-income housing units. Of the 173 deaths caused by Bret in Venezuela, most occur in the low-income areas near Caracas. Lack of preparation, including weather forecasters prematurely stating the worst of the storm is over, is part of the problem. In all, 10,000 were left homeless, and damaged totaled to $25 million (1993 USD, $39 million 2005 USD). In Colombia, Bret causes one death and one injury.
- July 24-27, 1996 - Hurricane Cesar moves westward across the southern Caribbean Sea and crosses over extreme northern Colombia and the San Andres archipelago. Cesar kills 11 people in Colombia due to flooding and mudslides.
- November 13-16, 1999 - Strong waves from Hurricane Lenny effect the Guajira Peninsula of Colombia, flooding 1,200 homes and businesses along the northern coastline. In addition, winds and rains from the hurricane causes severe crop damage in the country. The hurricane kills two in Colombia.
2000s

- September 25, 2000 - Hurricane Joyce dissipates just north of eastern Venezuela, causing no known damage.
- September 14, 2002 - Hurricane Isidore crosses over northeastern Venezuela as a tropical depression. Effects, if any, are unknown.
- December 4, 2003 - Tropical Storm Odette produces heavy rainfall of up to 8 inches (200 mm) in Colombia.
- January 20, 2004 - A possible tropical storm in the South Atlantic Ocean hits eastern Brazil, dropping heavy rainfall in the area.
- March 28, 2004 - A cyclone, unofficially named Cyclone Catarina, strikes southeastern Brazil with maximum recorded winds of 90 mph (145 km/h). The possible hurricane damaged more than 30,000 homes and left 1,900 people homeless. The storm also damaged 1,373 businesses and destroyed 50, including a hospital. The storm killed 3, injured 38, and caused up to $330 million in damage (2004 USD).
- September 7-9, 2004 - Hurricane Ivan parallels the north coast of Venezuela as a Category 4 hurricane. Ivan's strong winds forced the closure of several airports. The hurricane also produced heavy rainfall and strong waves. Ivan killed three in the country, though overall damage was minor.
- July 14, 2005 - Hurricane Emily passes just north of Venezuela as a strengthening hurricane, causing heavy rains and flooding in the northeastern portion of the country. 64 families were forced to leave their homes when rivers in eastern Monagas state overflowed their banks, but waters quickly receded. Ships were forced to remain at port while the hurricane passed to the country's north, though restrictions quickly lifted.
- October 29, 2005 - Hurricane Beta hits the Colombian island of Providencia, and tears the roofs off of thousands of homes. High winds also shut down all airports and communications.
Listed by month
37 tropical cyclones have affected South America in most months of the year.
|

|
Deadliest storms
Data from South American tropical cyclones is sparse and incomplete, though most tropical cyclones that struck the continent caused multiple deaths. Bret, Joan, Cesar, Gilbert, Catarina, and Ivan all caused their deaths through rainfall or flash flooding.
| Name | Year | Number of deaths |
|---|---|---|
| Bret | 1993 | 174 |
| Joan | 1988 | 36 |
| Cesar | 1996 | 11 |
| Gilbert | 1988 | 5 |
| Catarina | 2004 | 3 |
| Ivan | 2004 | 3 |
| Lenny | 1999 | 2 |
| Hattie | 1961 | 1 |
| Unnamed | 1933 | "Several" |
| Alma | 1974 | 0 (47 indirect) |
Tropical cyclone warnings and watches
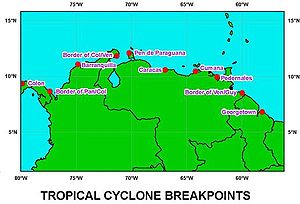
In the event an Atlantic hurricane threatens the northern coast of South America, the National Hurricane Center defines nine locations as tropical cyclone warning breakpoints. The westernmost is the border between Panama and Colombia, and the easternmost is Georgetown, Guyana, located at 6.82° N. In the eastern Pacific Ocean, tropical cyclone warning breakpoints extend eastward to the border of Panama and Colombia at 7.23° N. No Atlantic hurricane has existed south of 6.82° N, and no Pacific hurricane has existed east of 80° W, though in the event a tropical cyclone threatens a region of South America without warnings, additional warning sites can be selected. In addition to warnings on the mainland of South America, the National Hurricane Center defines the entire island of San Andres as a tropical cyclone warning breakpoint.
Intense Hurricane Flora in 1963 prompted officials to declare gale warnings for two islands off the north coast of Venezuela. In 1974, the passage of Tropical Storm Alma warranted the issuance of Gale Warnings for the Paria and Paraguaná Peninsulas. Hurricane Joan in 1988, Tropical Storm Bret in 1993, and Hurricane Cesar-Douglas resulted in tropical storm and hurricane watches and warnings for several locations in South America. The threat of Hurricane Ivan prompted a hurricane watch and a tropical storm warning for the northern coast of Venezuela.
See also
References
- "Ask Tom Why". WGN9 Chicago. 2004. Retrieved 2006-07-20.
- Pielke, Rubiera, Landsea, Fernández, and Klein (2003). "Hurricane Vulnerability in Latin America & The Caribbean" (PDF). National Hazards Review. Retrieved 2006-07-20.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ricardo Garcia-Herrera, Luis Gimeno, Pedro Ribera and Emiliano Hernandez. "New records of Atlantic hurricanes from Spanish documentary sources". Retrieved 2006-07-20.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Michael Chenoweth (2006). "A Reassessment of Historical Atlantic Tropical Cyclone Activity, 1700-1855" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-20.
- NOAA (2005). "1877 Atlantic hurricane season". Retrieved 2006-07-20.
- NOAA (2005). "1886 Atlantic hurricane season". Retrieved 2006-07-20.
- NOAA (2005). "1887 Atlantic hurricane season". Retrieved 2006-07-20.
- NOAA (2005). "1892 Atlantic hurricane season". Retrieved 2006-07-20.
- National Weather Service (1892). "1892 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- NOAA (2005). "1911 Atlantic hurricane season". Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- National Weather Service (1932). "1932 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- National Weather Service (1933). "1933 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- National Weather Service (1954). "1954 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- National Weather Service (1955). "1955 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- ^ National Weather Service (1961). "1961 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- National Weather Service (1963). "1963 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- John Hope (1971). "Hurricane Edith Preliminary Report Page 1". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2006-11-01.
- National Weather Service (1971). "1971 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- ^ National Hurricane Center (1974). "Tropical Storm Alma Tropical Cyclone Report". Retrieved 2006-11-18.
- ^ National Weather Service (1978). "1978 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- National Weather Service (1988). "1988 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- ^ Dr. Harold P. Gerrish (1988). "Hurricane Joan Tropical Cyclone Report Page 3". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2006-07-21. Cite error: The named reference "joantcr" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- National Hurricane Center (1990). "Tropical Storm Fran Tropical Cyclone Report". Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- ^ National Weather Service (1993). "1993 Monthly Weather Review" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- John Wade (1993). "Catastrophe in Caracas". The Herald. Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- Associated Press (1996). "Hurricane Douglas leaves at least 35 dead as it crosses from Caribbean to Pacific". Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- Agence France-Presse (1999). "One death blamed on Hurricane Lenny; still threatens Caribbean". Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- John L. Guiney (1999). "Hurricane Lenny Tropical Cyclone Report". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- Miles B. Lawrence (2000). "Hurricane Joyce Tropical Cyclone Report". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- Lixion A. Avila (2002). "Hurricane Isidore Tropical Cyclone Report". Retrieved 2006-07-21.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|Publisher=ignored (|publisher=suggested) (help) - World Meteorological Organization (2004). "Final Report of the 2003 Atlantic Hurricane Season" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- Gary Padgett (2004). "January 2004 Tropical cyclone summary". Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- ^ D. H. Levinson (2004). "State of the Climate in 2004". American Meteorological Society. Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- Associated Press (2004). "First South Atlantic hurricane hits Brazil". Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- Agence France-Presse (2004). "Hurricane Ivan kills at least 14 in Caribbean". Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- ^ Stacy R. Stewart (2004). "Hurricane Ivan Tropical Cyclone Report". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved 2006-07-21. Cite error: The named reference "ivantcr" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- International Federation of the Red Cross (2004). "Caribbean:Hurricane Ivan" (PDF). Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- News from Russia (2005). "Emily passed Venezuela". Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- Adventist News Network (2005). "Colombia: Adventists Aid Hurricane Beta Relief Effort on Tiny Island". Retrieved 2006-07-21.
- ^ National Hurricane Center (2006). "Hurricane and Tropical Storm Watch/Warning Breakpoints". Retrieved 2006-11-18.
- Hurricane Research Division (2006). "Hurdat Data for Tropical Cyclones 1851-2005". NOAA. Retrieved 2006-11-18.
- Hurricane Research Division (2006). "Hurricane Data for Pacific Hurricanes 1949-2005". NOAA. Retrieved 2006-11-18.
- Hoose (1963). "Hurricane Flora Advisory 4". San Juan Weather Bureau. Retrieved 2006-11-18.
- NHC (1993). "Tropical Storm Bret Tropical Cyclone Report Page 10".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|Accessdate=ignored (|accessdate=suggested) (help) - Avila (1996). "Hurricane Cesar Tropical Cyclone Report". NHC. Retrieved 2006-11-18.
Categories: