| Revision as of 09:54, 14 June 2022 editArtem.G (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users27,015 edits →Gallery: add image← Previous edit | Revision as of 10:37, 25 September 2022 edit undo91.115.248.104 (talk) additional citation for inorganic aragonite fomration in the ocean and seperation of oceans from cavesNext edit → | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
| Aragonite also forms naturally in the endocarp of '']''.<ref>{{Cite journal|author1=Wang, Jang|author2=Jahren, A. Hope|author3=Amundsen, Ronald|year=1996|title=Potential For Dating Of Biogenic Carbon In Hackberry (Celtis) Endocarps|url=http://eoas.fsu.edu/sites/default/files/u12/Faculty-Misc/Wang/pubs/potential-Cdating-biogenic-carbonate-hackberry-endocarps.pdf|journal=Quaternary Research|volume=47|pages=337–343|doi=10.1006/qres.1997.1894}}{{Dead link|date=November 2019 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> | Aragonite also forms naturally in the endocarp of '']''.<ref>{{Cite journal|author1=Wang, Jang|author2=Jahren, A. Hope|author3=Amundsen, Ronald|year=1996|title=Potential For Dating Of Biogenic Carbon In Hackberry (Celtis) Endocarps|url=http://eoas.fsu.edu/sites/default/files/u12/Faculty-Misc/Wang/pubs/potential-Cdating-biogenic-carbonate-hackberry-endocarps.pdf|journal=Quaternary Research|volume=47|pages=337–343|doi=10.1006/qres.1997.1894}}{{Dead link|date=November 2019 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> | ||
| Aragonite also forms in the ocean |
Aragonite also forms in the ocean inorganic precipitates called marine cements (in the ]) or as free crystals (in the water column).<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Bialik |first1=Or M. |last2=Sisma-Ventura |first2=Guy |last3=Vogt-Vincent |first3=Noam |last4=Silverman |first4=Jacob |last5=Katz |first5=Timor |title=Role of oceanic abiotic carbonate precipitation in future atmospheric CO2 regulation |journal=Scientific Reports |date=24 September 2022 |volume=12 |issue=1 |pages=15970 |doi=10.1038/s41598-022-20446-7}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Tucker |first1=Maurice E. |title=Carbonate sedimentology |date=1990 |publisher=Blackwell Scientific Publications |location=Oxford |isbn=9781444314175}}</ref> | ||
| Inorganic precipitation of aragonite in caves can occur in the form of]s.{{sfn|Nesse|2000|p=337}} Aragonite is common in serpentinites where high Mg in pore solutions apparently inhibits calcite growth and promotes aragonite precipitation.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Bonatti |first1=E. |last2=Lawrence |first2=J.R. |last3=Hamlyn |first3=P.R. |last4=Breger |first4=D. |title=Aragonite from deep sea ultramafic rocks |journal=Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta |date=August 1980 |volume=44 |issue=8 |pages=1207–1214 |doi=10.1016/0016-7037(80)90074-5|bibcode=1980GeCoA..44.1207B }}</ref> | |||
| Aragonite is ] at the low pressures near the Earth's surface and is thus commonly replaced by calcite in fossils. Aragonite older than the ] is essentially unknown.<ref>{{Cite journal| doi = 10.1080/03115518508618971| title = Shell microstructures of Cambrian molluscs replicated by phosphate| year = 1987| last1 = Runnegar | first1 = B.| journal = Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology| volume = 9| issue = 4| pages = 245–257 }}</ref> It can also be synthesized by adding a ] solution to a ] solution at temperatures above {{convert|60|C}} or in water-ethanol mixtures at ambient temperatures.<ref>Sand, K.K., Rodriguez-Blanco, J.D., Makovicky, E., Benning, L.G. and Stipp, S. (2012) Crystallization of CaCO3 in water-ethanol mixtures: spherulitic growth, polymorph stabilization and morphology change. Crystal Growth & Design, 12, 842-853. {{doi|10.1021/cg2012342}}.</ref> | Aragonite is ] at the low pressures near the Earth's surface and is thus commonly replaced by calcite in fossils. Aragonite older than the ] is essentially unknown.<ref>{{Cite journal| doi = 10.1080/03115518508618971| title = Shell microstructures of Cambrian molluscs replicated by phosphate| year = 1987| last1 = Runnegar | first1 = B.| journal = Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology| volume = 9| issue = 4| pages = 245–257 }}</ref> It can also be synthesized by adding a ] solution to a ] solution at temperatures above {{convert|60|C}} or in water-ethanol mixtures at ambient temperatures.<ref>Sand, K.K., Rodriguez-Blanco, J.D., Makovicky, E., Benning, L.G. and Stipp, S. (2012) Crystallization of CaCO3 in water-ethanol mixtures: spherulitic growth, polymorph stabilization and morphology change. Crystal Growth & Design, 12, 842-853. {{doi|10.1021/cg2012342}}.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 10:37, 25 September 2022
Calcium carbonate mineral| Aragonite | |
|---|---|
 Aragonite from Salsigne mine, Salsigne, Aude, France; size: 30×30×20 cm Aragonite from Salsigne mine, Salsigne, Aude, France; size: 30×30×20 cm | |
| General | |
| Category | Carbonate mineral |
| Formula (repeating unit) | CaCO3 |
| IMA symbol | Arg |
| Strunz classification | 5.AB.15 |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic |
| Crystal class | Dipyramidal (mmm) H-M symbol: (2/m 2/m 2/m) |
| Space group | Pmcn |
| Unit cell | a = 4.95 Å, b = 7.96 Å c = 5.74 Å; Z = 4 |
| Identification | |
| Color | White, red, yellow, orange, green, purple, grey, blue and brown |
| Crystal habit | Pseudohexagonal, prismatic crystals, acicular, columnar, globular, reniform, pisolitic, coralloidal, stalactitic, internally banded |
| Twinning | Polysynthetic parallel to {100} cyclically on {110} |
| Cleavage | Distinct on {010}, imperfect {110} and {011} |
| Fracture | Subconchoidal |
| Tenacity | Brittle |
| Mohs scale hardness | 3.5–4 |
| Luster | Vitreous, resinous on fracture surfaces |
| Streak | White |
| Diaphaneity | Translucent to transparent |
| Specific gravity | 2.95 |
| Optical properties | Biaxial (−) |
| Refractive index | nα = 1.529–1.530, nβ = 1.680–1.682, nγ = 1.685–1.686 |
| Birefringence | δ = 0.156 |
| 2V angle | 18° |
| Solubility | Dilute acid |
| Other characteristics | Fluorescence: pale rose, yellow, white or bluish; phosphorescence: greenish or white (LW UV); yellowish (SW UV) |
| References | |
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral, one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate, CaCO3 (the other forms being the minerals calcite and vaterite). It is formed by biological and physical processes, including precipitation from marine and freshwater environments.
The crystal lattice of aragonite differs from that of calcite, resulting in a different crystal shape, an orthorhombic crystal system with acicular crystal. Repeated twinning results in pseudo-hexagonal forms. Aragonite may be columnar or fibrous, occasionally in branching helictitic forms called flos-ferri ("flowers of iron") from their association with the ores at the Carinthian iron mines.
Occurrence
The type location for aragonite is Molina de Aragón in the Province of Guadalajara in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain, for which it was named in 1797. Aragonite is found in this locality as cyclic twins inside gypsum and marls of the Keuper facies of the Triassic. This type of aragonite deposit is very common in Spain, and there are also some in France.
An aragonite cave, the Ochtinská Aragonite Cave, is situated in Slovakia.
In the US, aragonite in the form of stalactites and "cave flowers" (anthodite) is known from Carlsbad Caverns and other caves. For a few years in the early 1900s, aragonite was mined at Aragonite, Utah (now a ghost town).
Massive deposits of oolitic aragonite sand are found on the seabed in the Bahamas.
Aragonite is the high pressure polymorph of calcium carbonate. As such, it occurs in high pressure metamorphic rocks such as those formed at subduction zones.
Aragonite forms naturally in almost all mollusk shells, and as the calcareous endoskeleton of warm- and cold-water corals (Scleractinia). Several serpulids have aragonitic tubes. Because the mineral deposition in mollusk shells is strongly biologically controlled, some crystal forms are distinctively different from those of inorganic aragonite. In some mollusks, the entire shell is aragonite; in others, aragonite forms only discrete parts of a bimineralic shell (aragonite plus calcite). The nacreous layer of the aragonite fossil shells of some extinct ammonites forms an iridescent material called ammolite.
Aragonite also forms naturally in the endocarp of Celtis occidentalis.
Aragonite also forms in the ocean inorganic precipitates called marine cements (in the sediment) or as free crystals (in the water column). Inorganic precipitation of aragonite in caves can occur in the form ofspeleothems. Aragonite is common in serpentinites where high Mg in pore solutions apparently inhibits calcite growth and promotes aragonite precipitation.
Aragonite is metastable at the low pressures near the Earth's surface and is thus commonly replaced by calcite in fossils. Aragonite older than the Carboniferous is essentially unknown. It can also be synthesized by adding a calcium chloride solution to a sodium carbonate solution at temperatures above 60 °C (140 °F) or in water-ethanol mixtures at ambient temperatures.
Physical properties
Aragonite is not the thermodynamically stable phase of calcium carbonate at any pressure below about 3,000 bars (300,000 kPa) at any temperature. Aragonite nonetheless frequently forms in near-surface environments at ambient temperatures. The difference in stability between aragonite and calcite, as measured by the Gibbs free energy of formation, is small, and effects of grain size and impurities can be important. The formation of aragonite at temperatures and pressures where calcite should be the stable polymorph may be an example of Ostwald's step rule, where a less stable phase is the first to form. The presence of magnesium ions may inhibit calcite formation in favor of aragonite. Once formed, aragonite tends to alter to calcite on scales of 10 to 10 years.
The mineral vaterite, also known as μ-CaCO3, is another phase of calcium carbonate that is metastable at ambient conditions typical of Earth's surface, and decomposes even more readily than aragonite.
Uses
In aquaria, aragonite is considered essential for the replication of reef conditions. Aragonite provides the materials necessary for much sea life and also keeps the pH of the water close to its natural level, to prevent the dissolution of biogenic calcium carbonate.
Aragonite has been successfully tested for the removal of pollutants like zinc, cobalt and lead from contaminated wastewaters.
Claims that magnetic water treatment can reduce scaling, by converting calcite to aragonite, have been met with skepticism, but continue to be investigated.
Gallery
-
 Aragonite crystal from Los Molinillos, Ceunca, Spain
Aragonite crystal from Los Molinillos, Ceunca, Spain
-
 Aragonite crystals from Cuenca, Castile-La Mancha, Spain
Aragonite crystals from Cuenca, Castile-La Mancha, Spain
-
 Aragonite crystal cluster from Spain
Aragonite crystal cluster from Spain
-
 Remnant biogenic aragonite (thin, rainbow-colored shell) on the ammonite Baculites (Pierre Shale, Late Cretaceous, South Dakota)
Remnant biogenic aragonite (thin, rainbow-colored shell) on the ammonite Baculites (Pierre Shale, Late Cretaceous, South Dakota)
-
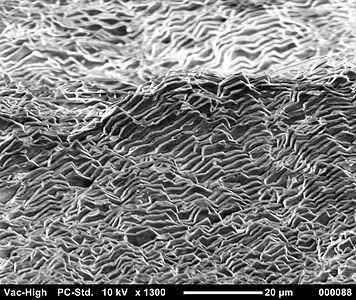 Scanning electron microscope image of aragonite layers in the nacre of a blue mussel (Mytilus edulis)
Scanning electron microscope image of aragonite layers in the nacre of a blue mussel (Mytilus edulis)
-
 Fluorescence of aragonite
Fluorescence of aragonite
See also
- Aragonite sea
- Ikaite, CaCO3·6H2O
- Monohydrocalcite, CaCO3·H2O
- Nacre, otherwise known as "Mother-of-Pearl"
References
- Warr, L.N. (2021). "IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols". Mineralogical Magazine. 85 (3): 291–320. Bibcode:2021MinM...85..291W. doi:10.1180/mgm.2021.43. S2CID 235729616.
- Aragonite. Mindat.org.
- Handbook of Mineralogy.
- Aragonite Mineral Data. Mineralogy Database.
- ^ Sinkankas, John (1964). Mineralogy for amateurs. Princeton, N.J.: Van Nostrand. pp. 371–372. ISBN 0442276249.
- Cairncross, B.; McCarthy, T. (2015). Understanding Minerals & Crystals. Cape Town: Struik Nature. p. 187. ISBN 978-1-43170-084-4.
- Calvo, Miguel (2012). Minerales y Minas de España. Vol. V. Carbonatos y Nitratos. Madrid: Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingenieros de Minas de Madrid. Fundación Gómez Pardo. pp. 314–398. ISBN 978-84-95063-98-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - Pukanská, Katarína; Bartoš, Karol; Bella, Pavel; Gašinec, Juraj; Blistan, Peter; Kovanič, Ľudovít (4 July 2020). "Surveying and High-Resolution Topography of the Ochtiná Aragonite Cave Based on TLS and Digital Photogrammetry". Applied Sciences. 10 (13): 4633. doi:10.3390/app10134633.
- Gonzalez, Luis A.; Lohmann, Kyger C. (1988). "Controls on Mineralogy and Composition of Spelean Carbonates: Carlsbad Caverns, New Mexico". In James, Noel P.; Choquette, Philip W. (eds.). Paleokarst. New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 81–101. doi:10.1007/978-1-4612-3748-8. ISBN 978-1-4612-3748-8.
- Balaz, Christine (2009). An Explorer's Guide: Utah. Vermont: The Countryman Press. p. 368. ISBN 978-0-88150-738-6.
- Newell, Norman D.; Purdy, Edward G.; Imbrie, John (1960). "Bahamian Oölitic Sand". The Journal of Geology. 68 (5): 481–497. Bibcode:1960JG.....68..481N. doi:10.1086/626683. ISSN 0022-1376. S2CID 129571671.
- Nesse, William D. (2000). Introduction to mineralogy. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 336–337. ISBN 9780195106916.
- Boggs, Sam (2006). Principles of sedimentology and stratigraphy (4th ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Pearson Prentice Hall. pp. 161–164. ISBN 0131547283.
- ^ Belcher, A. M.; Wu, X. H.; Christensen, R. J.; Hansma, P. K.; Stucky, G. D.; Morse, D. E. (May 1996). "Control of crystal phase switching and orientation by soluble mollusc-shell proteins". Nature. 381 (6577): 56–58. Bibcode:1996Natur.381...56B. doi:10.1038/381056a0. S2CID 4285912.
- Chateigner, D.; Ouhenia, S.; Krauss, C.; Belkhir, M.; Morales, M. (February 2010). "Structural distortion of biogenic aragonite in strongly textured mollusc shell layers". Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms. 268 (3–4): 341–345. Bibcode:2010NIMPB.268..341C. doi:10.1016/j.nimb.2009.07.007.
- Loftus, Emma; Rogers, Keith; Lee-Thorp, Julia (November 2015). "A simple method to establish calcite:aragonite ratios in archaeological mollusc shells: CALCITE:ARAGONITE IN ARCHAEOLOGICAL SHELLS". Journal of Quaternary Science. 30 (8): 731–735. doi:10.1002/jqs.2819.
- Mychaluk, Keith A.; Levinson, Alfred A.; Hall, Russel L. (Spring 2001). "Ammolite: Iridescent fossilized ammonite from southern Alberta, Canada" (PDF). Gems & Gemology. 37 (1): 4–25. doi:10.5741/GEMS.37.1.4. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- Wang, Jang; Jahren, A. Hope; Amundsen, Ronald (1996). "Potential For [Carbon 14] Dating Of Biogenic Carbon In Hackberry (Celtis) Endocarps" (PDF). Quaternary Research. 47: 337–343. doi:10.1006/qres.1997.1894.
- Bialik, Or M.; Sisma-Ventura, Guy; Vogt-Vincent, Noam; Silverman, Jacob; Katz, Timor (24 September 2022). "Role of oceanic abiotic carbonate precipitation in future atmospheric CO2 regulation". Scientific Reports. 12 (1): 15970. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-20446-7.
- Tucker, Maurice E. (1990). Carbonate sedimentology. Oxford : Blackwell Scientific Publications. ISBN 9781444314175.
- Nesse 2000, p. 337.
- Bonatti, E.; Lawrence, J.R.; Hamlyn, P.R.; Breger, D. (August 1980). "Aragonite from deep sea ultramafic rocks". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 44 (8): 1207–1214. Bibcode:1980GeCoA..44.1207B. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(80)90074-5.
- Runnegar, B. (1987). "Shell microstructures of Cambrian molluscs replicated by phosphate". Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology. 9 (4): 245–257. doi:10.1080/03115518508618971.
- Sand, K.K., Rodriguez-Blanco, J.D., Makovicky, E., Benning, L.G. and Stipp, S. (2012) Crystallization of CaCO3 in water-ethanol mixtures: spherulitic growth, polymorph stabilization and morphology change. Crystal Growth & Design, 12, 842-853. doi:10.1021/cg2012342.
- Carlson, W.D. (1980). "The calcite–aragonite equilibrium: effects of Sr substitution and anion orientational disorder". American Mineralogist. 65 (11–12): 1252–1262. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- Fyfe, W.S. (1964). "Calcite aragonite problem" (PDF). AAPG Bulletin. 48 (4): 526. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- Kitano, Yasushi; Park, Kilho; Hood, Donald W. (November 1962). "Pure aragonite synthesis". Journal of Geophysical Research. 67 (12): 4873–4874. Bibcode:1962JGR....67.4873K. doi:10.1029/JZ067i012p04873.
- Blatt, Harvey; Middleton, Gerard; Murray, Raymond (1980). Origin of sedimentary rocks (2d ed.). Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall. ISBN 0136427103.
- Ni, M.; Ratner, B.D. (2008). "Differentiation of Calcium Carbonate Polymorphs by Surface Analysis Techniques – An XPS and TOF-SIMS study". Surf. Interface Anal. 40 (10): 1356–1361. doi:10.1002/sia.2904. PMC 4096336. PMID 25031482.
- Kamiya, Kanichi; Sakka, Sumio; Terada, Katsuyuki (November 1977). "Aragonite formation through precipitation of calcium carbonate monohydrate". Materials Research Bulletin. 12 (11): 1095–1102. doi:10.1016/0025-5408(77)90038-1.
- Orr, J. C., et al. (2005) Anthropogenic ocean acidification over the 21st century and its impact on calcifying organisms. Nature 437: 681-686
- Köhler, S., Cubillas, et al. (2007) Removal of cadmium from wastewaters by aragonite shells and the influence of other divalent cations. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 112-118. doi:10.1021/es060756j
- Krauter, PW; Harrar, JE; Orloff, SP; Bahowick, SM (1996). "Test of a Magnetic Device for Amelioration of Scale Formation at Treatment Facility D" (PDF). Internal Report. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. doi:10.2172/567404. OSTI 567404. Retrieved 2009-12-11.
- Coey, J.M.D. (November 2012). "Magnetic water treatment – how might it work?". Philosophical Magazine. 92 (31): 3857–3865. Bibcode:2012PMag...92.3857C. doi:10.1080/14786435.2012.685968. S2CID 96367372.
- Kozic, Viljem; Hamler, Anton; Ban, Irena; Lipus, Lucija C. (October 2010). "Magnetic water treatment for scale control in heating and alkaline conditions". Desalination and Water Treatment. 22 (1–3): 65–71. doi:10.5004/dwt.2010.1549.