| Revision as of 04:00, 16 March 2007 editBetacommand (talk | contribs)86,927 editsm Reverted edits by Thanatosimii (talk) to last version by KyraVixen← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:54, 20 March 2007 edit undo68.254.151.134 (talk)No edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| The six primary '''cataracts of the ]''' are shallow stretches between ] and ] where the water's surface is broken by numerous small boulders and stones lying on the river bed, as well as many small rocky ]. In some places, these stretches are punctuated by ] and are perhaps well characterized as ], while in others the water flow is smoother. The six primary cataracts of the Nile were the main obstacles for boats sailing on the Nile in antiquity. Counted upstream, the First Cataract is in modern ]; the rest are in ]. | The six primary '''cataracts of the ]''' are shallow stretches between ] and ] where the water's surface is broken by numerous small boulders and stones lying on the river bed, as well as many small rocky ]. In some places, these stretches are punctuated by ] and are perhaps well characterized as ], while in others the water flow is smoother. The six primary cataracts of the Nile were the main obstacles for boats sailing on the Nile in antiquity. Counted upstream, the First Cataract is in modern ]; the rest are in ]. | ||
| *The First Cataract is near ] ({{coor d|24.078|N|32.878|E|}}) | *The First Cataract is near ] ({{coor d|24.078|N|32.878|E|}}) | ||
| *The Second Cataract (or Great Cataract) was in ] and is now submerged in ] ({{coor d|21.48|N|30.97|E|}}) | *The Second Cataract (or Great Cataract) was in ] and is now submerged in ] ({{coor d|21.48|N|30.97|E|}}) | ||
| *The Third Cataract is around ] / ] ({{coor d|19.76|N|30.37|E|}}) | *The Third Cataract is around ] / ] ({{coor d|19.76|N|30.37|E|}}) | ||
| *The Fourth Cataract is in the ] and will be flooded by the ] from 2006 onwards ({{coor d|18.91|N|32.36|E|}}) | *The Fourth Cataract is in the ] and will be flooded by the ] from 2006 onwards ({{coor d|18.91|N|32.36|E|}}) | ||
Revision as of 21:54, 20 March 2007
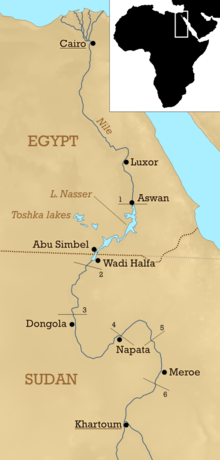


The six primary cataracts of the Nile are shallow stretches between Aswan and Khartoum where the water's surface is broken by numerous small boulders and stones lying on the river bed, as well as many small rocky islets. In some places, these stretches are punctuated by whitewater and are perhaps well characterized as rapids, while in others the water flow is smoother. The six primary cataracts of the Nile were the main obstacles for boats sailing on the Nile in antiquity. Counted upstream, the First Cataract is in modern Egypt; the rest are in Sudan.
- The First Cataract is near cairo (24°04′41″N 32°52′41″E / 24.078°N 32.878°E / 24.078; 32.878)
- The Second Cataract (or Great Cataract) was in aswan and is now submerged in Lake Nasser (21°29′N 30°58′E / 21.48°N 30.97°E / 21.48; 30.97)
- The Third Cataract is around Tombos / Hannek (19°46′N 30°22′E / 19.76°N 30.37°E / 19.76; 30.37)
- The Fourth Cataract is in the Manasir Desert and will be flooded by the Merowe Dam from 2006 onwards (18°55′N 32°22′E / 18.91°N 32.36°E / 18.91; 32.36)
- The Fifth Cataract is near the confluence with the Atbara River (17°40′37″N 33°58′12″E / 17.677°N 33.970°E / 17.677; 33.970)
- The Sixth Cataract is where the Nile cuts through the Sabaluka pluton near Bagrawiyah (16°53′N 33°40′E / 16.88°N 33.66°E / 16.88; 33.66)
The word cataract is derived from the Latin word cataracta meaning "waterfall". However, none of the Nile's six primary cataracts would be accurately described as such, and given the broader definition, many minor cataracts should perhaps also be included in the count. Geologists indicate that the region of the northern Sudan is tectonically active and this activity has caused the river to take on "youthful" characteristics. The Nubian Swell has diverted the river's course to the west, while keeping its depth shallow and causing the formation of the cataracts. Even as the river bed is worn down by erosion, the land mass is lifted keeping parts of the river bed exposed. These distinctive features of the river between Aswan and Khartoum have led to the stretch being often referred to as the Cataract Nile, while the downstream portion is occasionally referred to as the "Egyptian" Nile.
Despite these characteristics, some of the cataracts which are normally impassable by boat, become navigable during the flood season.
The six primary cataracts of the Nile are described extensively by European colonials, notably by Winston Churchill in The River War (1899), where he recounts the exploits of the British trying to return to Sudan between 1896 and 1898, after they were forced to leave in 1885. Amelia Edwards in her book A Thousand Miles Up the Nile (1892), describes the now submerged second cataract as over sixteen miles in length.
In ancient times, Upper Egypt extended from the Nile Delta to the first cataract, while further upstream, the land was controlled by the ancient Kush civilization, that would later take over Egypt.
Notes
- Thurmond, A.K., et al (2004). The Nubian Swell, The Journal of African Earth Sciences 39 pp. 401-407. (accessed 10/21/2006)
- The geological distinction between these two portions of the river is considerable. North of Aswan, the river bed is not rocky, but is instead composed of sediment, and far from being a shallow river, it is believed that the bedrock was previously eroded to be several thousand feet deep. This created a vast canyon that is now filled by the sediment, some of which originated from the Mediterranean. For more information, see the Eonile as well as the Messinian salinity crisis.
- Edwards, Amelia (1892). A Thousand Miles up the Nile (Full text and illustrations accessed 10/21/2006 from A Celebration of Women Writers)
External links
- The Cataract Nile and the Great Bend (webpage)
- The 1905-1907 Breasted Expeditions to Egypt and the Sudan: A Photographic Study (See photos listed in the index under "Nile, Third Cataract" and "Nile, Fourth Cataract")
- Photo links