| Revision as of 00:36, 16 April 2008 view sourceJayjg (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators134,922 edits it's still WP:SYNTH (at best) and the sources are dodgy. Find a source that makes this exact claim (not a picture), in relation to the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine← Previous edit | Revision as of 09:06, 18 April 2008 view source EivindJ (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,188 edits →External linksNext edit → | ||
| Line 209: | Line 209: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
Revision as of 09:06, 18 April 2008
On 29 November 1947 the United Nations voted to terminate the British Mandate of Palestine by 1 August 1948 and, to resolve the Arab-Israeli conflict in the British Mandate of Palestine, for a plan for the partition of the Mandate territory. The plan came to be called the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine or United Nations General Assembly Resolution 181. The plan was approved by the United Nations General Assembly by 33 votes to 13, with 10 abstentions.
The plan would have partitioned the territory of Palestine into Jewish and Arab states, with the Greater Jerusalem area, including Bethlehem, coming under international control.
Context of the plan
In November of 1917, as General Allenby was preparing to conquer Palestine, the British Foreign office issued the Balfour Declaration of 1917, a letter from the Foreign Secretary, Lord Balfour, to Lord Rothschild, head of the British Zionist movement. The declaration stated:
- "His Majesty's Government view with favour the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people, and will use their best endeavours to facilitate the achievement of this object, it being clearly understood that nothing shall be done which may prejudice the civil and religious rights of existing non-Jewish communities in Palestine, or the rights and political status enjoyed by Jews in any other country."
This declaration was a compromise, based on a draft telegram that Lord Balfour had asked Weizmann to submit earlier. It did not contain a formal commitment. It reflected the efforts of the British Zionist movement led by Dr.Chaim Weizmann, longstanding British sentiment for restoration of the Jews and British strategic and imperial considerations on the one hand. On the other hand, it reflected concerns of British Jewish anti-Zionists and foreign office personnel concerned about antagonizing the Arab world. These conflicting forces were to be reflected in the vicissitudes of British policy, ultimately causing Britain to renounce the mandate, thereby leading to partition of Palestine.
After the First World War and the collapse of the Ottoman Empire, the victorious Allied Supreme Council met at the San Remo Conference in April 1920 to confirm the allocation of Ottoman lands under the proposed mandate system. Palestine was placed under the British mandate. The League of Nations British Mandate of Palestine made the national home for the Jewish people an article of international law, by incorporating the wording of the Balfour declaration. The mandate was supported by the United States as part of President Woodrow Wilson's support for national self-determination.
Jewish immigration to Palestine in the initial period following World War I was sparse, owing to difficult conditions in Palestine and lack of sufficient commitment to Zionism to face the rigors of pioneering life, as well as lack of funds for development. However, in the 1930s, with increased anti-Semitism and the rise of Adolf Hitler in Germany, the Fifth Aliya brought substantial numbers of European Jews to Palestine.
On 24 July 1922, in London, the terms of the British Mandate over Palestine and Transjordan were approved by the Council of the League of Nations. However, the British government, of its own initiative, decided to remove Transjordan, constituting 78% of the area of the Palestine mandate, from the jurisdiction of that mandate, and to form a separate Arab entity there. That may be viewed as the first partition of Palestine. Accordingly, on 16 September 1922 the League of Nations formally approved a memorandum from Lord Balfour confirming the exemption of Transjordan from the clauses of the mandate concerning the creation of a Jewish national home and from the mandate's responsibility to facilitate Jewish immigration and land settlement.
The Arab uprising of 1936-9 was triggered by rising Jewish immigration, and rising Arab nationalist sentiment. The British Peel Commission proposed a Palestine divided between a small Jewish state (about 15%), a much bigger Arab state and an international zone. After this proposal was rejected by the Arab side, the British changed their position and sought to eliminate Jewish immigration to Palestine. This was seen as a contradiction of the terms of the mandate, and an anti-humanitarian catastrophe, in light of the increasing persecution in Europe. In the prewar period it led to organization of illegal immigration. While the small LEHI group began to fight the British in various unsuccessful terrorist actions, the Jewish Agency, which represented the mainstream Zionist leaderhsip, still hoped to persuade the British to restore Jewish immigration rights and cooperated with the British in the war against Fascism. When the British insisted on preventing immigration of Jewish Holocaust survivors to Palestine following World War II, the Jewish community began to wage an uprising and guerrilla war. This warfare and United States pressure to end the anti-immigration policy were decisive factors that forced the British to renounce the Palestine Mandate and hand the problem of Palestine over to the United Nations.
The United Nations, the successor to the League of Nations, attempted to solve the dispute between the Jews and Arabs in Palestine. On May 15 1947 the UN appointed a committee, the UNSCOP, composed of representatives from eleven states. To make the committee more neutral, none of the Great Powers were represented. After spending three months conducting hearings and general survey of the situation in Palestine, UNSCOP officially released its report on August 31. A majority of nations (Canada, Czechoslovakia, Guatemala, Netherlands, Peru, Sweden, Uruguay) recommended the creation of independent Arab and Jewish states, with Jerusalem to be placed under international administration. A minority (India, Iran, Yugoslavia) supported the creation of a single federal state containing both Jewish and Arab constituent states. Australia abstained. Thus a Jewish state was voted upon, but would be smaller than the one promised in the League of Nations Resolution. For the first time, an Arab state would be created in Palestine as wellCite error: The <ref> tag has too many names (see the help page)..
The proposed division
See also: Land ownership of the British Mandate of Palestine

Palestine's land surface was approximately 26,320,505 dunums (26,320 km²), of which about one third was cultivable. By comparison, the size of modern day Israel (as of 2006) is 20,770,000 dunums (20,770 km²) (Geography of Israel). The land in Jewish possession had risen from 456,000 dunums (456 km²) in 1920 to 1,393,000 dunums (1,393 km²) in 1945 and 1,850,000 dunums (1,850 km²) by 1947 (Avneri p. 224). No figures of land ownership by Arabs were available, due to difficulties that were due to the incomplete transition from the unreliable Ottoman Land Code to a modern land registration system.
The UN General Assembly made a non-binding recommendation for a three-way partition of Palestine into a Jewish State, an Arab State and a small internationally administered zone including the religiously significant towns Jerusalem and Bethlehem. The two states envisioned in the plan were each composed of three major sections, linked by extraterritorial crossroads. The Jewish state would receive the Coastal Plain, stretching from Haifa to Rehovot, the Eastern Galilee (surrounding the Sea of Galilee and including the Galilee panhandle) and the Negev, including the southern outpost of Umm Rashrash (now Eilat). The Arab state would receive the Western Galilee, with the town of Acre, the Samarian highlands and the Judean highlands, and the southern coast stretching from north of Isdud (now Ashdod) and encompassing what is now the Gaza Strip, with a section of desert along the Egyptian border.
The partition defined by the General Assembly resolution differed somewhat from the UNSCOP report partition. Most notably, Jaffa was constituted as an enclave of the Arab State and the boundaries were modified to include Beersheba and a large section of the Negev desert within the Arab State and a section of the Dead Sea shore within the Jewish State.
The land allocated to the Arab state (about 43% of Mandatory Palestine) consisted of all of the highlands, except for Jerusalem, plus one third of the coastline. The highlands contain the major aquifers of Palestine, which supplied water to the coastal cities of central Palestine, including Tel Aviv. The Jewish state was to receive 56% of Mandatory Palestine, a slightly larger area to accommodate the increasing numbers of Jews who would immigrate there. The state included three fertile lowland plains — the Sharon on the coast, the Jezreel Valley and the upper Jordan Valley.
The bulk of the proposed Jewish State's territory, however, consisted of the Negev Desert. The desert was not suitable for agriculture, nor for urban development at that time. The Jewish state was also given sole access to the Red Sea and the Sea of Galilee. The land allocated to the Jewish state was largely made up of areas in which there was a significant Jewish population. The land allocated to the Arab state was populated almost solely by Arabs.
The plan tried its best to accommodate as many Jews as possible into the Jewish state. In many specific cases, this meant including areas of Arab majority (but with a significant Jewish minority) in the Jewish state. Thus the Jewish State would have an overall large Arab minority. Areas that were sparsely populated (like the Negev), were also included in the Jewish state to create room for immigration in order to relieve the "Jewish Problem".
The UNSCOP's plan would have had the following demographics (data based on 1945). This data does not reflect the actual land ownership by Jews, local Arabs, Ottomans and other land owners. This data also excludes the land designated to Arabs in trans-Jordan (country of Jordan, west of the river Jordan).
| Territory | Arab and other population | % Arab and other | Jewish population | % Jewish | Total population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arab State | 725,000 | 99% | 10,000 | 1% | 735,000 | |
| Jewish State | 407,000 | 45% | 498,000 | 55% | 905,000 | |
| International | 105,000 | 51% | 100,000 | 49% | 205,000 | |
| Total | 1,237,000 | 67% | 608,000 | 33% | 1,845,000 | |
| Data from the Report of UNSCOP — 1947 | ||||||
The UNSCOP Report also noted that "in addition there will be in the Jewish State about 90,000 Bedouins, cultivators and stock owners who seek grazing further afield in dry seasons."
Reactions to the plan
The majority of the Jews and Jewish groups accepted the proposal, in particular the Jewish Agency, which functioned as the de facto representative group of the nascent Jewish state. The Jewish Agency had been arguing for more land but finally accepted the opposition from representatives of the UN that they could not control the state if they were not in majority. A minority of extreme nationalist Jewish groups like Menachem Begin's Irgun Tsvai Leumi and the Lehi, (known as the Stern Gang) which had been fighting the British, rejected it. Begin warned that the partition would not bring peace because the Arabs would also attack the small state and that "in the war ahead we'll have to stand on our own, it will be a war on our existence and future". The war was anyhow thought to be fought to young Israels advantage with - despite ongoing weapons embargo - the 3000 machine-guns and 6 million bullets as well as 25 fighterplanes promised to be supplied by the Jewish Agency
Numerous records indicate the joy of Palestine's Jewish inhabitants as they attended to the U.N. session voting for the division proposal. Up to this day, Israeli history books mention November 29th (the date of this session) as the most important date in Israel's acquisition of independence, and many Israeli cities commemorate the date in their streets' names. However, Jews did criticize the lack of territorial continuity for the Jewish state.
The Arab leadership (in and out of Palestine) opposed the plan, arguing that it violated the rights of the majority of the people in Palestine, which at the time was 67% non-Jewish (1,237,000) and 33% Jewish (608,000). Arab leaders also argued a large number of Arabs would be trapped in the Jewish State as a minority. Every major Arab leader objected in principle to the right of the Jews to an independent state in Palestine, reflecting the policies of the Arab League.
The vote
On 29 November 1947, the United Nations General Assembly voted 33 to 13, with 10 abstentions, in favour of the Partition Plan, while making some adjustments to the boundaries between the two states proposed by it.
The division was to take effect on the date of British withdrawal from the Mandate Territory of Palestine. Both the United States and Soviet Union supported the resolution.

The 33 countries (58%) that voted in favour of the partition were: Australia, Belgium, Bolivia, Brazil, Byelorussian SSR, Canada, Costa Rica, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, France, Guatemala, Haiti, Iceland, Liberia, Luxembourg, Netherlands, New Zealand, Nicaragua, Norway, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Sweden, South Africa, Ukrainian SSR, United States of America, Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, Uruguay, Venezuela.
The 13 countries (23%) that voted against resolution were: Afghanistan, Cuba, Egypt, Greece, India, Iran, Iraq, Lebanon, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, Yemen.
The 10 countries (17%) that abstained were: Argentina, Chile, Republic of China, Colombia, El Salvador, Ethiopia, Honduras, Mexico, United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, Yugoslavia.
One state (2%) was absent: Thailand
Following the adoption of the plan, Arab countries proposed to query the International Court of Justice on the competence of the General Assembly to partition a country against the wishes of the majority of its inhabitants (it would place 36% of the Arabs inside the Jewish state). This was narrowly defeated.
Consequences
See also: Jewish exodus from Arab lands, Jewish refugees, Palestinian exodus, Palestinian refugees, and 1948 War of Independence"On the day after the vote, a spate of Arab attacks left seven Jews dead and scores more wounded. Shooting, stoning, and rioting continued apace in the following days. The consulates of Poland and Sweden, both of whose governments had voted for partition, were attacked. Bombs were thrown into cafes, Molotov cocktails were hurled at shops, a synagogue was set on fire.
The United Kingdom refused to implement the plan, arguing it was unacceptable to both sides. It also refused to share the administration of Palestine with the UN Palestine Commission during the transitional period. It terminated the British mandate of Palestine on May 15, 1948. Declassified documents indicate that the British had wanted to absorb Palestine into a "Greater Syria" that would eventually be ruled by Iraq. Historian Efraim Karsh and others assert that Britain Transjordan planned to annex the Arab state and all or part of the Jewish state to TransJordan, while others claim that the Jews cooperated in a plan to annex the West Bank, intended for the Palestinian state, to TransJordan. . In January of 1948, the British allowed the Arab Liberation Army formed by the Arab League to infiltrate into Palestine from Syria.
Meeting in Cairo in November and December of 1947, the Arab League adopted a series of resolutions aimed at a military solution to the conflict.. They formed an Arab Liberation Army The Arab League also planned punitive measures against Jews living in Arab countries, many of which were subsequently implemented by individual states.
Fighting began almost as soon as the plan was approved, beginning with the Arab Jerusalem Riots of 1947. The fighting would have an effect on the Arab population of Palestine, as well the Jewish populations of neighboring Arab countries.
On December 3, at the instigation of the Palestinian Arab leadership, a large mob ransacked the new Jewish commercial center in Jerusalem, looting and burning shops and stabbing and stoning whomever they happened upon. The next day, some 120–150 armed Arabs attacked Kibbutz Efal, on the outskirts of Tel Aviv, in the first large-scale attempt to storm a Jewish village."
Terror attacks continued to evolve and escalate. The Arabs blockaded the road to Jerusalem and other towns, attacked Jewish towns and villages, convoys and road transport and massacred convoy personnel. The Jewish dissident force, the Irgun planted bombs in Jerusalem, Yaffo and elsewhere. The Haganah took mostly defensive actions in the initial stages. Notable events include Irgun bombing of Damascus gate in Jerusalem, December 12, 1947, Haifa refinery riots, December 30, , massacre of the convoy of 35 to Gush Etzion, January 16, 1948, Ben Yehuda Street Bombing on February 22, Jewish Agency Bombing on March 11, 1948, Nebi Daniel and Yehiam convoy bombings on March 27, 1948, Deir Yassin Massacre on April 9 and the Hadassah medical convoy massacre on April 13, 1948. By this time the fighting had escalated to the level of brigade sized battles, with Operation Nachshon launched by the Haganah in the Jerusalem corridor, and the battle of Mishmar Ha'emek, fought between the Haganah forces and the Arab Liberation Army on April 4-12...
Text of the Resolution
- from the Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs
- from the Yale Law School
- Information on UN 181 from The Jerusalem Fund/Palestine Center
- United Nations Information System on the Question of Palestine
See also
- Arab revolt
- Hussein-McMahon Correspondence
- Sykes-Picot Agreement
- Mandate for Palestine
- Balfour Declaration 1917
- Napoleon and a Jewish state in Palestine
- Faisal-Weizmann Agreement
- Churchill White Paper, 1922
- 1922 Text: League of Nations Palestine Mandate
- Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel, May 14, 1948
- Jewish refugees
- Palestinian refugees
- Immigration to Israel
- 1947 Jerusalem riots
- 1948 Arab-Israeli War
- 1949 Armistice Agreements
- Arab-Israeli conflict
- Israeli-Palestinian conflict
- Proposals for a Palestinian state
- Jewish exodus from Arab lands
- Palestinian exodus
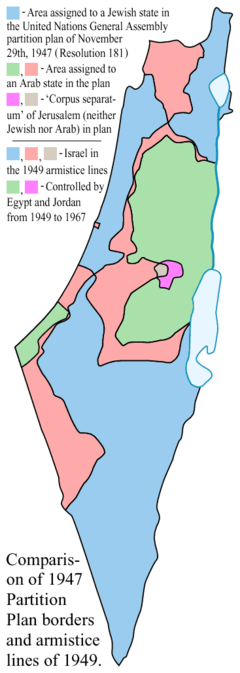
- Map comparing 1947 partition plan borders with 1949 armistice lines
Notes
- Middle East Documents Balfour Declaration
- British Support for Jewish Restoration
- History of Zionism & Modern Israel
- Fifth Aliya - definition - Zionism and Israel -Encyclopedia / Dictionary/Lexicon of Zionism/Israel/Middle East/Judaism
- Sicker, 1999, p. 164.
- Khalaf, 1991, pp. 26–27.
- "Israel". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. 10 August 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Israeli History at RepresentativePress.
- ^ UN Partition Plan at Merip.
- Map of population distribution at Passia.
- The Jewish Problem at MidEastWeb.
- Domino.
- Begin, Menachem, The Revolt 1978, p. 412.
- Britain's treachery, France's revenge - Haaretz - Israel News
- British and French Policy in Palestine
- British and French Policy in Palestine
- Draft Arab League Law Regarding Jews - 1947
- Jewish Refugees from Arab countries - 1948
- MeForum.
- MidEast Web Historical Documents: Refinery Riots
- Gush Etzion Massacre - 1948
- Yehiam Convoy Definition
- Deir Yassin Massacre - Introduction
- Hadassah Convoy Massacre
- Battle of Mishmar Ha'emek (Mishmar Ha'emeq)
- Timeline (Chronology) of Israel War of Independence - 1948 Arab-Israeli War
References
- Bregman, Ahron (2002). Israel's Wars: A History Since 1947. London: Routledge. ISBN
- Arieh L. Avneri (1984). The Claim of Dispossession: Jewish Land Settlement and the Arabs, 1878–1948. Transaction Publishers. ISBN
- Fischbach, Michael R. (2003). Records of Dispossession: Palestinian Refugee Property and the Arab-Israeli Conflict. Columbia University Press. ISBN
- Gelber, Yoav (1997). Jewish-Transjordanian Relations: Alliance of Bars Sinister. London: Routledge. ISBN-X
- Khalaf, Issa (1991). Politics in Palestine: Arab Factionalism and Social Disintegration,. SUNY University Press. ISBN
- Louis, Wm. Roger (1986). The British Empire in the Middle East,: Arab Nationalism, the United States, and Postwar Imperialism. Oxford University Press. ISBN
- "Palestine". Encyclopædia Britannica Online School Edition, 15 May 2006.
- Sicker, Martin (1999). Reshaping Palestine: From Muhammad Ali to the British Mandate, 1831–1922. Praeger/Greenwood. ISBN
External links
- Legal Status of West Bank, Gaza and East Jerusalem
- Maps of Palestine
- Ivan Rand and the UNSCOP Papers
- Official Map prepared by UNSCOP