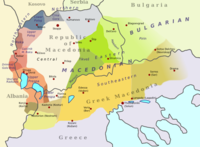
| Revision as of 09:23, 2 August 2008 editFuture Perfect at Sunrise (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Administrators87,192 edits rv again, falsification of cited sources; unjustifiable removal of the only map we have to show where this place is; OR claims← Previous edit |
Revision as of 13:12, 2 August 2008 edit undoKöbra (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,336 edits removing many... many spacesNext edit → |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
|
The term '''Maleševo-Pirin dialect''' (sometimes spelt '''Maleshevo''') is used in ] linguistics to refer to a group of related varieties that are spoken on both sides of the border between ] and the ]. They are linguistically transitional between the two national languages ] and ] and form part of the larger ] between them. The dialect group is named after the mountain ranges of ] in Bulgaria and ] in Macedonia. When referring specifically to the dialects on the Bulgarian side, the term '''Petrich-Blagoevgrad dialect''', after the two major towns in the area, is also used.<ref name="Stoykov">{{cite book |
|
The term '''Maleševo-Pirin dialect''' (sometimes spelt '''Maleshevo''') is used in ] linguistics to refer to a group of related varieties that are spoken on both sides of the border between ] and the ]. They are linguistically transitional between the two national languages ] and ] and form part of the larger ] between them. The dialect group is named after the mountain ranges of ] in Bulgaria and ] in Macedonia. When referring specifically to the dialects on the Bulgarian side, the term '''Petrich-Blagoevgrad dialect''', after the two major towns in the area, is also used.<ref name="Stoykov">{{cite book|last=Sussex|first=Roland|coauthors=Paul Cubberley|title=The Slavic Languages|publisher=Cambridge University Press|date =2006|url =http://books.google.com/books?id=G2bsJdYrwD4C&dq=Bulgarian+dialects+Pirin&source=gbs_summary_s&cad=0|pages =p.510 |isbn =0521223156 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last =Стойков|first =Стойко|title=Българска диалектология|publisher =Акад. изд. "Проф. Марин Дринов"|date=2006|url=http://www.promacedonia.org/jchorb/st/st_2_b_zap_2.htm}}</ref> |
|
|
|
|
| last =Sussex |
|
|
|
|
|
| first =Roland |
|
|
|
|
|
| coauthors =Paul Cubberley |
|
|
|
|
|
| title =The Slavic Languages |
|
|
|
|
|
| publisher =Cambridge University Press |
|
|
|
|
|
| date =2006 |
|
|
|
|
|
| url =http://books.google.com/books?id=G2bsJdYrwD4C&dq=Bulgarian+dialects+Pirin&source=gbs_summary_s&cad=0 |
|
|
|
|
|
| pages =p.510 |
|
|
|
|
|
| isbn =0521223156 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |
|
|
|
|
|
| last =Стойков |
|
|
|
|
|
| first =Стойко |
|
|
|
|
|
| title =Българска диалектология |
|
|
|
|
|
| publisher =Акад. изд. "Проф. Марин Дринов" |
|
|
|
|
|
| date =2006 |
|
|
|
|
|
| url =http://www.promacedonia.org/jchorb/st/st_2_b_zap_2.htm }}</ref> |
|
|
Macedonian linguistics tends to treat the whole group as part of the Macedonian language, classifying it as part of a southeastern group of ], whereas from the perspective of Bulgarian linguistics, the varieties in Bulgaria are classified as parts of the eastern subgroup of the southwestern group of Bulgarian. |
|
Macedonian linguistics tends to treat the whole group as part of the Macedonian language, classifying it as part of a southeastern group of ], whereas from the perspective of Bulgarian linguistics, the varieties in Bulgaria are classified as parts of the eastern subgroup of the southwestern group of Bulgarian. |
|
<ref name="Stoykov"/> |
|
<ref name="Stoykov"/> |
|
This dialect is spoken in the towns of ], ], ] and the surrounding villages in the east of the Republic of Macedonia,<ref name="Bojkovska">str. 249- 252 Makedonski jazik za srednoto obrazovanie- S.Bojkovska, D.Pandev, L.Minova-Ǵurkova, Ž.Cvetkovski- Prosvetno delo AD- Skopje 2001</ref> |
|
This dialect is spoken in the towns of ], ], ] and the surrounding villages in the east of the Republic of Macedonia,<ref name="Bojkovska">str. 249- 252 Makedonski jazik za srednoto obrazovanie- S.Bojkovska, D.Pandev, L.Minova-Ǵurkova, Ž.Cvetkovski- Prosvetno delo AD- Skopje 2001</ref> |
|
and in the regions of ], ] and ] in Bulgaria. |
|
and in the regions of ], ] and ] in Bulgaria. |
|
|
<ref name="Stoykov2">{{cite book|last=Стойков|first=Стойко|title=Българска диалектология|publisher=Акад. изд. "Проф. Марин Дринов"|date=2006|url=http://www.promacedonia.org/jchorb/st/st_2_b_zap_2.htm }}</ref> |
|
<ref name="Stoykov2">{{cite book |
|
|
|
|
|
| last =Стойков |
|
|
|
|
|
| first =Стойко |
|
|
|
|
|
| title =Българска диалектология |
|
|
|
|
|
| publisher =Акад. изд. "Проф. Марин Дринов" |
|
|
|
|
|
| date =2006 |
|
|
|
|
|
| url =http://www.promacedonia.org/jchorb/st/st_2_b_zap_2.htm }}</ref> |
|
|
] |
|
] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Blagoevgrad-Petric dialect is also closely related to the neighbouring ] and ], and especially to the ], |
|
The Blagoevgrad-Petric dialect is also closely related to the neighbouring ] and ], and especially to the ], |
| Line 54: |
Line 11: |
|
whereas the Maleshevo dialect is closely related especially with the ] dialect. |
|
whereas the Maleshevo dialect is closely related especially with the ] dialect. |
|
<ref name="Friedman"> The sociolinguistics of literary Macedonian, VICTOR A. FRIEDMAN, THE UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO LIBRARY</ref> |
|
<ref name="Friedman"> The sociolinguistics of literary Macedonian, VICTOR A. FRIEDMAN, THE UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO LIBRARY</ref> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
==Linguistic properties== |
|
==Linguistic properties== |
|
|
|
|
|
The following is a table of distinctive phonological and grammatical features, comparing the values found in the Maleshevo and Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialects with Standard Bulgarian, Standard Macedonian and two other neighbouring Western Bulgarian dialect areas. |
|
The following is a table of distinctive phonological and grammatical features, comparing the values found in the Maleshevo and Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialects with Standard Bulgarian, Standard Macedonian and two other neighbouring Western Bulgarian dialect areas. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
{| class="toccolours collapsible" width="80%" |
|
{| class="toccolours collapsible" width="80%" |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
!<center>Comparison of the Maleshevo dialect and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect with Standard Bulgarian and Standard Macedonian</center> |
|
!<center>Comparison of the Maleshevo dialect and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect with Standard Bulgarian and Standard Macedonian</center> |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align: left" |
|
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align: left" |
|
|
|
|
|- bgcolor="#cccccc"|- bgcolor="#cccccc" |
|
|- bgcolor="#cccccc"|- bgcolor="#cccccc" |
|
|
|
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Parameter |
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Parameter |
|
|
|
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Maleshevo dialect |
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Maleshevo dialect |
|
|
|
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect |
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect |
|
|
|
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Standard Bulgarian (based on Eastern Bulgarian) |
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Standard Bulgarian (based on Eastern Bulgarian) |
|
|
|
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Standard Macedonian |
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Standard Macedonian |
|
|
|
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Dupnitsa dialect |
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Dupnitsa dialect |
|
|
|
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Samokov dialect |
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|Samokov dialect |
|
|
|
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|English |
|
!style="text-align: left;background:#B0C4DE"|English |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Proto-Slavic '''{{IPA|*tʲ}}/{{IPA|*dʲ}}''' – Old Church Slavonic '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' || '''шч/жџ ({{IPA|ʃtʃ}}/{{IPA|/dʒ/}}}''' (in some areas also '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' and '''ќ/ѓ ({{IPA|c}}/{{IPA|ɟ}})''' – ''лешча/межџу'' (in some areas ''леща/между'' or ''леќа/меѓу'') || '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' – ''леща/между'' || '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' – ''леща/между'' || '''ќ/ѓ ({{IPA|c}}/{{IPA|ɟ}})''' – ''леќа/меѓу'' || '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' – ''леща/между'' || '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' – ''леща/между'' || lentils/between |
|
| Proto-Slavic '''{{IPA|*tʲ}}/{{IPA|*dʲ}}''' – Old Church Slavonic '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' || '''шч/жџ ({{IPA|ʃtʃ}}/{{IPA|/dʒ/}}}''' (in some areas also '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' and '''ќ/ѓ ({{IPA|c}}/{{IPA|ɟ}})''' – ''лешча/межџу'' (in some areas ''леща/между'' or ''леќа/меѓу'') || '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' – ''леща/между'' || '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' – ''леща/между'' || '''ќ/ѓ ({{IPA|c}}/{{IPA|ɟ}})''' – ''леќа/меѓу'' || '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' – ''леща/между'' || '''щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}})''' – ''леща/между'' || lentils/between |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Proto-Slavic '''{{IPA|*gt/kt}}''' – Old Church Slavonic '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' || '''ќ ({{IPA|c}})''' (in some areas also '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' – ''ноќ'' (in some areas ''нощ'') || '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' – ''нощ'' || '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' – ''нощ'' || '''ќ ({{IPA|c}})''' – ''ноќ'' || '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' – ''нощ'' || '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' – ''нощ'' || night |
|
| Proto-Slavic '''{{IPA|*gt/kt}}''' – Old Church Slavonic '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' || '''ќ ({{IPA|c}})''' (in some areas also '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' – ''ноќ'' (in some areas ''нощ'') || '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' – ''нощ'' || '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' – ''нощ'' || '''ќ ({{IPA|c}})''' – ''ноќ'' || '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' – ''нощ'' || '''щ ({{IPA|ʃt}})''' – ''нощ'' || night |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''{{Unicode|ѣ}}''' (yat) || '''е ({{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бел/бели'' || '''е ({{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бел/бели'' || '''а/я ({{IPA|ʲa}}/{{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бял/бели'' || '''е ({{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бел/бели'' || '''е ({{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бел/бели'' || '''е ({{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бел/бели'' || white |
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''{{Unicode|ѣ}}''' (yat) || '''е ({{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бел/бели'' || '''е ({{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бел/бели'' || '''а/я ({{IPA|ʲa}}/{{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бял/бели'' || '''е ({{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бел/бели'' || '''е ({{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бел/бели'' || '''е ({{IPA|ɛ}})''' – ''бел/бели'' || white |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''{{Unicode |ѫ}}''' (yus), approx. {{IPA|ɔ̃}} || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''маж'' || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''маж'' || '''ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' – ''мъж'' || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''маж'' || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''маж'' || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''маж'' || man |
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''{{Unicode |ѫ}}''' (yus), approx. {{IPA|ɔ̃}} || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''маж'' || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''маж'' || '''ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' – ''мъж'' || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''маж'' || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''маж'' || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''маж'' || man |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' || '''о ({{IPA|ɔ}})''' – ''сон'' || '''о ({{IPA|ɔ}})''' – ''сон'' || '''ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' – ''сън'' || '''о ({{IPA|ɔ}})''' – ''сон'' || '''о ({{IPA|ɔ}})''' – ''сон'' || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''сан'' || dream |
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' || '''о ({{IPA|ɔ}})''' – ''сон'' || '''о ({{IPA|ɔ}})''' – ''сон'' || '''ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' – ''сън'' || '''о ({{IPA|ɔ}})''' – ''сон'' || '''о ({{IPA|ɔ}})''' – ''сон'' || '''а ({{IPA|a}})''' – ''сан'' || dream |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''ръ/рь''' || '''vocalic r/ро ({{IPA|rɔ}})''' – ''врох, крф'' || '''ръ ({{IPA|rə}})''' – ''връх, кръв'' || '''ръ/ър ({{IPA|rə}}/{{IPA|ər}})''' – ''връх, кръв'' || '''vocalic r''' – ''врв, крф'' || '''vocalic r''' – ''врх, крф'' || '''vocalic r''' – ''врх, крф'' || summit, blood |
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''ръ/рь''' || '''vocalic r/ро ({{IPA|rɔ}})''' – ''врох, крф'' || '''ръ ({{IPA|rə}})''' – ''връх, кръв'' || '''ръ/ър ({{IPA|rə}}/{{IPA|ər}})''' – ''връх, кръв'' || '''vocalic r''' – ''врв, крф'' || '''vocalic r''' – ''врх, крф'' || '''vocalic r''' – ''врх, крф'' || summit, blood |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''лъ/ль''' || '''ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' – ''съза'' || '''ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' – ''съза'' || '''лъ/ъл ({{IPA|lə}}/{{IPA|əl}})''' – ''сълза'' || '''oл ({{IPA|ɔl}})''' – ''солза'' || '''vocalic l/ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' – ''слза/съза'' depending on region || '''у ({{IPA|u}})''' – ''суза'' || tear |
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''лъ/ль''' || '''ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' – ''съза'' || '''ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' – ''съза'' || '''лъ/ъл ({{IPA|lə}}/{{IPA|əl}})''' – ''сълза'' || '''oл ({{IPA|ɔl}})''' – ''солза'' || '''vocalic l/ъ ({{IPA|ə}})''' – ''слза/съза'' depending on region || '''у ({{IPA|u}})''' – ''суза'' || tear |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''x {{IPA|/x/}}''' || '''Preserved''' – ''бех, хубаво'' || '''Preserved''' – ''бех, хубаво'' || '''Preserved''' – ''бях, хубаво'' || '''Lost''' or replaced by '''ф/в ({{IPA|f}}/{{IPA|v}})''' – ''беф, убаво'' || '''Preserved''' – ''бех, хубаво'' || '''Preserved''' – ''бех, хубаво'' || was, nice |
|
| Old Church Slavonic '''x {{IPA|/x/}}''' || '''Preserved''' – ''бех, хубаво'' || '''Preserved''' – ''бех, хубаво'' || '''Preserved''' – ''бях, хубаво'' || '''Lost''' or replaced by '''ф/в ({{IPA|f}}/{{IPA|v}})''' – ''беф, убаво'' || '''Preserved''' – ''бех, хубаво'' || '''Preserved''' – ''бех, хубаво'' || was, nice |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Vowel reduction || '''No''' || '''No''' || '''Yes''' || '''No''' || '''No''' || '''No''' || |
|
| Vowel reduction || '''No''' || '''No''' || '''Yes''' || '''No''' || '''No''' || '''No''' || |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Definite article || Single definite article – ''момче'''то''''' || Single definite article – ''момче'''то''''' || Single definite article – ''момче'''то''''' || Triple definite article – ''момче'''то''', момче'''во''', момче'''но''''' || Single definite article – ''момче'''то''''' || Single definite article – ''момче'''то''''' || the boy |
|
| Definite article || Single definite article – ''момче'''то''''' || Single definite article – ''момче'''то''''' || Single definite article – ''момче'''то''''' || Triple definite article – ''момче'''то''', момче'''во''', момче'''но''''' || Single definite article – ''момче'''то''''' || Single definite article – ''момче'''то''''' || the boy |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Ending of verbs in 1st person sing. present time || '''а''' – 1st and 2nd conjugation, '''ам''' – 3rd – ''чета, пиша'' || '''а''' – 1st and 2nd conjugation, '''ам''' – 3rd – ''чета, пиша'' || '''а (я)''' – 1st and 2nd conjugation, '''ам (ям)''' – 3rd – ''чета, пиша'' || only '''ам''' – ''четам, пишам'' || '''а''' – 1st and 2nd conjugation, '''ам''' – 3rd – ''чета, пиша'' || only '''(и/е)м''' – ''четем, пишем'' || (I) read, (I) write |
|
| Ending of verbs in 1st person sing. present time || '''а''' – 1st and 2nd conjugation, '''ам''' – 3rd – ''чета, пиша'' || '''а''' – 1st and 2nd conjugation, '''ам''' – 3rd – ''чета, пиша'' || '''а (я)''' – 1st and 2nd conjugation, '''ам (ям)''' – 3rd – ''чета, пиша'' || only '''ам''' – ''четам, пишам'' || '''а''' – 1st and 2nd conjugation, '''ам''' – 3rd – ''чета, пиша'' || only '''(и/е)м''' – ''четем, пишем'' || (I) read, (I) write |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Formation of past perfect tense || '''бeх''' + past participle – ''бех писал, бех молил'' || '''бeх''' + past participle – ''бех писал, бех молил'' || '''бях''' + past participle – ''бях писал, бях молил'' || '''имам''' + past passive aorist participle – ''имам писано, имам молено'' || '''бeх''' + past participle – ''бех писал, бех молил'' || '''бех''' + past participle – ''бех писал, бeх молил'' || (I) had read, (I) had written |
|
| Formation of past perfect tense || '''бeх''' + past participle – ''бех писал, бех молил'' || '''бeх''' + past participle – ''бех писал, бех молил'' || '''бях''' + past participle – ''бях писал, бях молил'' || '''имам''' + past passive aorist participle – ''имам писано, имам молено'' || '''бeх''' + past participle – ''бех писал, бех молил'' || '''бех''' + past participle – ''бех писал, бeх молил'' || (I) had read, (I) had written |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
| Word stress || '''Dynamic''' – ''доˈбиток, ˈпера'' || '''Dynamic''' – ''доˈбиток, пеˈра'' || '''Dynamic''' - ''доˈбитък, пеˈра'' || '''Fixed antepenultimate''' - ''ˈдобиток, ˈперам'' || '''Dynamic''' – ''доˈбиток, пеˈра'' || '''Dynamic''' – ''доˈбиток, пеˈрем'' || cattle, (I) wash |
|
| Word stress || '''Dynamic''' – ''доˈбиток, ˈпера'' || '''Dynamic''' – ''доˈбиток, пеˈра'' || '''Dynamic''' - ''доˈбитък, пеˈра'' || '''Fixed antepenultimate''' - ''ˈдобиток, ˈперам'' || '''Dynamic''' – ''доˈбиток, пеˈра'' || '''Dynamic''' – ''доˈбиток, пеˈрем'' || cattle, (I) wash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|- |
|
|- |
|
|
|
|
|} |
|
|} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As shown by the table, the Maleshevo and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect show mixed Bulgarian and Macedonian phonological traits and mostly Bulgarian grammatical traits (several instead of one conjugation, single definite article, formation of past perfect tense with '''бeх''', etc.), with the Maleshevo dialect ranging mostly towards Macedonian and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect ranging mostly towards Bulgarian (cf. table). The transitional nature of the dialect is further demonstrated by the reflexes of the Proto-Slavic {{IPA|*tʲ}}/{{IPA|*dʲ}}: from the typically Bulgarian щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}}) in the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect and the far East of the Maleshevo dialect, along the border with Bulgaria, through the transitional шч/жџ ({{IPA|ʃtʃ}}/{{IPA|/dʒ/}}} in the central parts, and to the typically Macedonian ќ/ѓ ({{IPA|c}}/{{IPA|ɟ}}) in the western parts of the Maleshevo dialect<ref name="Stoykov2"/> |
|
As shown by the table, the Maleshevo and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect show mixed Bulgarian and Macedonian phonological traits and mostly Bulgarian grammatical traits (several instead of one conjugation, single definite article, formation of past perfect tense with '''бeх''', etc.), with the Maleshevo dialect ranging mostly towards Macedonian and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect ranging mostly towards Bulgarian (cf. table). The transitional nature of the dialect is further demonstrated by the reflexes of the Proto-Slavic {{IPA|*tʲ}}/{{IPA|*dʲ}}: from the typically Bulgarian щ/жд ({{IPA|ʃt}}/{{IPA|ʒd}}) in the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect and the far East of the Maleshevo dialect, along the border with Bulgaria, through the transitional шч/жџ ({{IPA|ʃtʃ}}/{{IPA|/dʒ/}}} in the central parts, and to the typically Macedonian ќ/ѓ ({{IPA|c}}/{{IPA|ɟ}}) in the western parts of the Maleshevo dialect<ref name="Stoykov2"/> |
|
|
|
|
|
==Other phonological characteristics== |
|
==Other phonological characteristics== |
|
|
|
|
* shortening of the words |
|
* shortening of the words |
|
|
|
|
* use of the plural suffix ''-ove'' as in Bulgarian instead of ''-ovi'' as in Macedonian: клучове ('keys') |
|
* use of the plural suffix ''-ove'' as in Bulgarian instead of ''-ovi'' as in Macedonian: клучове ('keys') |
|
|
|
|
* use of the old consonant group ''caf-'' instead of the consonant group ''cv-'': цев- цаф (''cev'', 'pipe') |
|
* use of the old consonant group ''caf-'' instead of the consonant group ''cv-'': цев- цаф (''cev'', 'pipe') |
|
|
|
|
* use of /v/ at the beginning of the word as in Bulgarian instead of /j/ as in Macedonian: важе ('rope') |
|
* use of /v/ at the beginning of the word as in Bulgarian instead of /j/ as in Macedonian: важе ('rope') |
|
<ref name="Bojkovska"/><ref name="Friedman"/> |
|
<ref name="Bojkovska"/><ref name="Friedman"/> |
|
|
|
|
|
==Morphological characteristics== |
|
==Morphological characteristics== |
|
|
|
|
* use of the preposition ''sus'': - сус рака ('with the hand'); |
|
* use of the preposition ''sus'': - сус рака ('with the hand'); |
|
|
|
|
* the clitic possessive forms follow the verb: му рече - рече му ('He told him'); |
|
* the clitic possessive forms follow the verb: му рече - рече му ('He told him'); |
|
|
|
|
* use of the dative form with ''na'': на нас ни рече ( ''na nas ni reche'', 'He told us') |
|
* use of the dative form with ''na'': на нас ни рече ( ''na nas ni reche'', 'He told us') |
|
|
|
|
* the form of the verb ''to be'' for third person plural is ''sa'' as in Bulgarian, instead of ''se'' as in Macedonian: тие се - тие са (''tie se'', 'they are') |
|
* the form of the verb ''to be'' for third person plural is ''sa'' as in Bulgarian, instead of ''se'' as in Macedonian: тие се - тие са (''tie se'', 'they are') |
|
|
|
|
* use of the pronoun ''on'' instead of ''toj'' |
|
* use of the pronoun ''on'' instead of ''toj'' |
|
<ref name="Bojkovska"/><ref name="Friedman"/> |
|
<ref name="Bojkovska"/><ref name="Friedman"/> |
|
|
|
|
|
==Examples of the dialect== |
|
==Examples of the dialect== |
|
|
|
|
*Traditional song from Maleševo-Pirin region: |
|
*Traditional song from Maleševo-Pirin region: |
|
|
|
|
| Line 208: |
Line 104: |
|
|
|
|
|
==References== |
|
==References== |
|
|
{{reflist}} |
|
|
|
|
<div class="references-small"> |
|
|
|
|
|
<references /> |
|
|
|
|
|
</div> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
{{Bulgarian dialects}} |
|
{{Bulgarian dialects}} |
|
|
|
|
{{Macedonian dialects}} |
|
{{Macedonian dialects}} |
|
|
|
|
|
] |
|
] |
|
|
|
|
] |
|
] |
|
|
|
|
] |
|
] |
|
|
|
|
] |
|
] |
The following is a table of distinctive phonological and grammatical features, comparing the values found in the Maleshevo and Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialects with Standard Bulgarian, Standard Macedonian and two other neighbouring Western Bulgarian dialect areas.
As shown by the table, the Maleshevo and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect show mixed Bulgarian and Macedonian phonological traits and mostly Bulgarian grammatical traits (several instead of one conjugation, single definite article, formation of past perfect tense with бeх, etc.), with the Maleshevo dialect ranging mostly towards Macedonian and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect ranging mostly towards Bulgarian (cf. table). The transitional nature of the dialect is further demonstrated by the reflexes of the Proto-Slavic *tʲ/*dʲ: from the typically Bulgarian щ/жд (ʃt/ʒd) in the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect and the far East of the Maleshevo dialect, along the border with Bulgaria, through the transitional шч/жџ (ʃtʃ//dʒ/} in the central parts, and to the typically Macedonian ќ/ѓ (c/ɟ) in the western parts of the Maleshevo dialect