| Revision as of 02:45, 25 September 2005 editSamuelSpade (talk | contribs)32 edits Not← Previous edit | Revision as of 11:47, 25 September 2005 edit undoDavidpdx (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users3,793 edits Reverted due to lack of consensus regarding information on DOM. See talk page.Next edit → | ||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| The first European to record discovering Bokak was ], a ] explorer, on ], ]. | The first European to record discovering Bokak was ], a ] explorer, on ], ]. | ||
| ===Recent History=== | |||
| Bokak (as Taongi Islands) is claimed by the ''Government of the ]'', a controversial ]. The claim was rejected by the Government of the Marshall Islands, in ] however, subsequent to the RMI encouraging friendly nations to avoid recognizing any claims of Melchizedek that are within RMI's territorial limits, in ], the ] of Taongi declared on film which was broadcast on Australian SBS TV that he granted Melchizedek a 50 years sovereign lease over Taongi, valid until 2049. | |||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 11:47, 25 September 2005
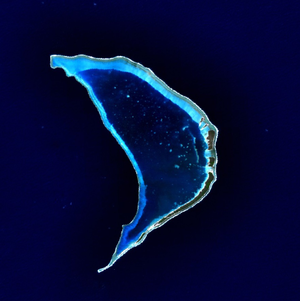
Bokak Atoll (also known as Taongi Atoll) is an uninhabited 3.2 square kilometer atoll located in the Pacific Ocean at 14°32′N 169°00′E / 14.533°N 169.000°E / 14.533; 169.000. It consists of eleven islands surrounding a 78 square kilometer lagoon, is mentioned once in the Constitution of the Marshall Islands and is located in the Ratak Chain.
The first European to record discovering Bokak was Alonso de Salazar, a Spanish explorer, on August 21, 1526.
Categories: