| Revision as of 08:31, 27 October 2005 editJohnski (talk | contribs)346 edits rvt to KAJ with edits to spelling and extraterritorial, disputed, and controversial← Previous edit | Revision as of 09:05, 27 October 2005 edit undoDavidpdx (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users3,793 edits removed DOM bs, reported vandalismNext edit → | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| The first European to record discovering Bokak was ], a ] explorer, on ], ]. | The first European to record discovering Bokak was ], a ] explorer, on ], ]. | ||
| ==Recent history== | |||
| Bokak (as the "Taongi Islands") has been claimed as extraterritorial by the "Government of the ]", a controversial entity, aspiring to ]hood, that has a history of licensing banks that defraud investors. The only basis for this disputed claim seems to be related to a "sovereign master lease" granted by the ] of Taongi ]. | |||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 09:05, 27 October 2005
| The neutrality of this article is disputed. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
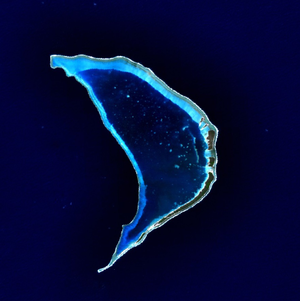
Bokak Atoll (also known as Taongi Atoll) is an uninhabited 3.2 square kilometer atoll located in the Pacific Ocean at 14°32′N 169°00′E / 14.533°N 169.000°E / 14.533; 169.000. It is located in the Ratak Chain.
The first European to record discovering Bokak was Alonso de Salazar, a Spanish explorer, on August 21, 1526.
Categories: