| Revision as of 18:47, 7 August 2009 editLuccas (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,645 editsm restore to before edit by Mahsko (talk)← Previous edit | Revision as of 18:49, 7 August 2009 edit undo147.9.70.134 (talk) →DescriptionNext edit → | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| ==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| This vulture is mostly grey-brown with a pale rump and grey undertail coverts. The thighs have whitish down. The neck is long, bare, skinny and black. The black head is angular and narrow with the dark bill appearing narrow midway. The ear opening is prominent and exposed.<ref name=pcr>{{cite book|author=Rasmussen, PC & JC Anderton|year=2005|title=Birds of South Asia: The Ripley Guide. Volume 2 |publisher=Smithsonian Institution & Lynx Edicions|page=90}}</ref> | This vulture is mostly grey-brown with a pale rump and grey undertail coverts. The thighs have whitish down. The neck is long, bare, skinny and black. The black head is angular and narrow with the dark bill appearing narrow midway. The ear opening is prominent and exposed.<ref name=pcr>{{cite book|author=Rasmussen, PC & JC Anderton|year=2005|title=Birds of South Asia: The Ripley Guide. Volume 2 |publisher=Smithsonian Institution & Lynx Edicions|page=90}}</ref> | ||
| ==Status== | ==Status== | ||
| This species has suffered a marked decline in its numbers in recent years. Wild populations remain from northern and eastern ] through southern ] and ], with a small population in ]. The only breeding colony in Southeast Asia is in the Steung Treng province of ]. This colony is thought to number about 50–100 birds. The survival of the vultures in Cambodia may have been partly because ], which is poisonous to vultures, is not available there. The ] (RSPB) has placed the approximate number of slender-billed vultures living beyond confines at about 1,000 in 2009 and predictions estimate total extinction within the next decade amongst the wild population.<Ref name="alleyne">{{Citation | This species has suffered a marked decline in its numbers in recent years. Wild populations remain from northern and eastern ] through southern ] and ], with a small population in ]. The only breeding colony in Southeast Asia is in the Steung Treng province of ]. This colony is thought to number about 50–100 birds. The survival of the vultures in Cambodia may have been partly because ], which is poisonous to vultures, is not available there. The ] (RSPB) has placed the approximate number of slender-billed vultures living beyond confines at about 1,000 in 2009 and predictions estimate total extinction within the next decade amongst the wild population.<Ref name="alleyne">{{Citation | ||
Revision as of 18:49, 7 August 2009
| Slender-billed Vulture | |
|---|---|

| |
| Head of Gyps tenuirostris | |
| Conservation status | |
 Critically Endangered (IUCN 3.1) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Falconiformes (or Accipitriformes, q.v.) |
| Family: | Accipitridae |
| Genus: | Gyps |
| Species: | G. tenuirostris |
| Binomial name | |
| Gyps tenuirostris Hodgson (in Gray), 1844 | |
| |
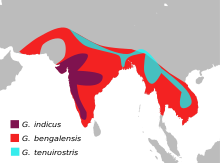
| Distribution range in blue | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Gyps indicus tenuirostris | |
The Slender-billed Vulture (Gyps tenuirostris) is a recently recognized species of Old World vulture. For some time, it was categorized with its relative the Indian Vulture under the name of "Long-billed Vulture". However, these two species have non-overlapping distribution ranges and can be immediately told apart by trained observers, even at considerable distances. The Indian Vulture is found only to the south of the Ganges and breeds on cliffs while the Slender-billed Vulture is found along the Sub-Himalayan regions and into Southeast Asia and nests on trees.
Description
This vulture is mostly grey-brown with a pale rump and grey undertail coverts. The thighs have whitish down. The neck is long, bare, skinny and black. The black head is angular and narrow with the dark bill appearing narrow midway. The ear opening is prominent and exposed.
Status
This species has suffered a marked decline in its numbers in recent years. Wild populations remain from northern and eastern India through southern Nepal and Bangladesh, with a small population in Burma. The only breeding colony in Southeast Asia is in the Steung Treng province of Cambodia. This colony is thought to number about 50–100 birds. The survival of the vultures in Cambodia may have been partly because diclofenac, which is poisonous to vultures, is not available there. The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) has placed the approximate number of slender-billed vultures living beyond confines at about 1,000 in 2009 and predictions estimate total extinction within the next decade amongst the wild population.
Conservation
The Slender-billed Vulture is a protected species listed on the appendix II list of CITES, because its numbers have declined rapidly. Its decline is largely due to the use of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) diclofenac in working farm animals, especially in India. Diclofenac is poisonous to vultures, causing kidney failure, and is being replaced by meloxicam (another NSAID), which is not toxic to Vultures. The retail sale of Diclofenac is banned by law in India, however is still acquired illegally and applied to livestock.
Captive-breeding programs in India are aiming to conserve the species, and it is hoped that vultures can be released back in the wild when the environment is free of diclofenac. Joint efforts between the RSPB and the Zoological Society of London have resulted in the first successful captive breeding in 2009. Two Slender-billed Vultures hatched and are being independently cared for in Haryana and West Bengal.
References
- Colony of Endangered Vultures Discovered in Cambodia
- birdlife.org
- BirdLife International 2004. Gyps tenuirostris. In: IUCN 2007. 2007 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Downloaded on 29 January 2008.
Citations
- Gray GR (1944) The Genera of Birds. volume 1:6
- Hume A O (1878) Stray Feathers 7:326
- Deignan, HG (1946). "The correct names of three Asiatic birds" (PDF). Ibis. 88: 402–403.
- Baker, ECS (1927) Bull. Brit. Orn. Club 47:151
- Rand, AL & RL Fleming (1957). "Birds from Nepal". Fieldiana: Zoology. 41 (1): 55.
- Rasmussen, PC & JC Anderton (2005). Birds of South Asia: The Ripley Guide. Volume 2. Smithsonian Institution & Lynx Edicions. p. 90.
- ^ Alleyne, Richard (August 6, 2009), "Endangered vulture could be saved thanks to help from RSPB", Telegraph.co.uk, retrieved 2009-08-06
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ "Indian vulture births are hailed Conservationists say they are delighted at the news that one of the world's most endangered birds has twice been successfully bred in India.", BBC News, August 6, 2009, retrieved 2009-08-06
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Press Association (August 6, 2009), "Boost for endangered vultures after captive breeding success Two slender-billed vultures born in RSPB breeding programme in India as wild population heads towards extinction", Guardian.co.uk, retrieved 2009-08-06
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link)