| Revision as of 19:05, 12 December 2010 editCheMoBot (talk | contribs)Bots141,565 edits Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'UNII_Ref', 'ChemSpiderID_Ref', 'StdInChI_Ref', 'StdInChIKey_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report [[Wikipedia_talk:Wi← Previous edit | Revision as of 02:50, 11 December 2011 edit undoChris the speller (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers867,997 editsm Typo fixing, use degree symbol, not masculine ordinal indicator or superscripted "o" using AWB (7852)Next edit → | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
| | Appearance=Yellow crystals | | Appearance=Yellow crystals | ||
| | Density= | | Density= | ||
| | MeltingPt= |
| MeltingPt=147–150 °C (decomposes) | ||
| | BoilingPt= | | BoilingPt= | ||
| | Solubility= | | Solubility= | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
| == Physical properties == | == Physical properties == | ||
| Dimedone usually comes in the form of yellow crystals. It is stable under ambient conditions and soluble in water, as well as ] and ]. It has a melting point range of |
Dimedone usually comes in the form of yellow crystals. It is stable under ambient conditions and soluble in water, as well as ] and ]. It has a melting point range of 147–150 °C (420–423 K). | ||
| == Tautomerism == | == Tautomerism == | ||
Revision as of 02:50, 11 December 2011
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
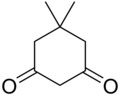
| IUPAC name 5,5-Dimethylcyclohexane-1,3-dione | |||
| Other names
Cyclomethone, 5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione, Dimethyldihydroresorcinol, Methone | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.369 | ||
| PubChem CID | |||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C8H12O2 | ||
| Molar mass | 140.17968 | ||
| Appearance | Yellow crystals | ||
| Melting point | 147–150 °C (decomposes) | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
Dimedone is a cyclic diketone used in organic chemistry to determine whether a compound contains an aldehyde group. Cyclohexanediones in general can be used as catalysts in the formation of transition-metal complexes. Other uses include applications in colourimetry, crystallography, luminescence and spectrophotometric analysis. It can also be used for chemistry involving organic compounds of low electrical resistance.
Synthesis
Dimedone is prepared from mesityl oxide and diethyl malonate.
Physical properties
Dimedone usually comes in the form of yellow crystals. It is stable under ambient conditions and soluble in water, as well as ethanol and methanol. It has a melting point range of 147–150 °C (420–423 K).
Tautomerism
Dimedone is in equilibrium with its tautomer in solution — in a 2:1 keto to enol ratio in chloroform.
Crystalline dimedone contains chains of molecules, in the enol form, linked by hydrogen bonds:
References
- R. L. Shriner and H. R. Todd (1935). "5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione". Organic Syntheses. 15: 16.
- Clayden, Jonathan; Greeves, Nick; Warren, Stuart; Wothers, Peter (2001). Organic Chemistry (1st ed.). Oxford University Press. p. p. 532. ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0.
{{cite book}}:|page=has extra text (help) - M. Bolte and M. Scholtyssik (1997). "Dimedone at 133K". Acta Cryst. C53 (10): IUC9700013. doi:10.1107/S0108270197099423.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)