| Revision as of 11:02, 12 May 2013 view sourceIranitGreenberg (talk | contribs)757 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 11:06, 12 May 2013 view source Pluto2012 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers5,612 edits Undid revision 554717434 by IranitGreenberg (talk) pov pushingNext edit → | ||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
| ==Border with Syria== | ==Border with Syria== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] region. | ] region. | ||
Revision as of 11:06, 12 May 2013
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Borders of Israel" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2012) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Israel's borders are the borders of the State of Israel. The borders have changed from time to time with developments in Israel's military and diplomatic situation. It borders Lebanon in the north, Syria in the northeast, Jordan and the West Bank in the east, the Gaza Strip and Egypt on the southwest.
The border with Egypt is the international border demarcated in 1906 between Britain and the Ottoman Empire. The borders with Lebanon, Syria and Jordan are based on those drawn up by the United Kingdom and France in anticipation of the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in the First World War and the carve up of the Ottoman Empire between them. They are referred to as the 1923 borders, being those of Mandate Palestine, which were settled in 1923.
Israel's borders with Egypt and Jordan have now been formally recognised and confirmed as part of the peace treaties with those countries, and with Lebanon as part of the 1949 Armistice Agreement. The borders with Syria and the Palestinian territories are still in dispute. Israel's borders with the West Bank and Gaza Strip are currently the Green Line, except in East Jerusalem, and the ceasefire line with Syria runs along the UN-monitored boundary between the Golan Heights and Syrian controlled territory.
The British Mandate
The Sykes–Picot Line

The Sykes–Picot Agreement of 1916 secretly divided the Ottoman Empire lands of Middle East between British and French spheres of influence. They agreed that "Palestine" was to be designated as an "international enclave". This agreement was revised by Britain and France in 1919. It was agreed that Palestine and the Vilayet of Mosul in modern-day Iraq would be part of the British sphere in exchange for British support of French influence in Syria and Lebanon. According to historian Ilan Pappe,
"The borders of mandatory Palestine, first drawn up in the Sykes-Picot Agreement, were given their definitive shape during lengthy and tedious negotiations by British and French officials between 1919 and 1922 ... In October 1919 the British envisaged the area that is today southern Lebanon and most of southern Syria as being part of British mandatory Palestine ... In the East, matters were more complicated... was part of the Ottoman province of Damascus which in the Sykes-Picot agreement had been allocated to the French."
At the San Remo Conference (19–26 April 1920) the Allied Supreme Council granted the mandates for Palestine and Mesopotamia to Britain without precisely defining the boundaries of the mandated territories. Although part of the land east of the Jordan had been part of the Syrian administrative unit under the Ottomans, it was excluded from the French Mandate at the San Remo conference, "on the grounds that it was part of Palestine." That said, the 1920 agreement contained Article 25, which created provision for the possible later exclusion of land east of the Jordan from the Balfour Declaration.
Franco-British Boundary Agreement (1920)
The Franco-British Boundary Agreement (1920) contained the principles for the boundary between the Mandates of Palestine and Mesopotamia, attributed to Great Britain, and the Mandate of Syria and the Lebanon, attributed to France.
The boundary between the forthcoming British and French mandates was defined in broad terms. That agreement placed the bulk of the Golan Heights in the French sphere. The treaty also established a joint commission to settle the border and mark it on the ground. The commission submitted its final report on 3 February 1922, and it was approved with some caveats by the British and French governments on 7 March 1923, several months before Britain and France assumed their Mandatory responsibilities on 29 September 1923. In accordance with the same process, a nearby parcel of land that included the ancient site of Dan was transferred from Syria to Palestine early in 1924. In this way the Golan Heights became part of the French Mandate of Syria. When the French Mandate of Syria ended in 1944, the Golan Heights remained part of the newly independent state of Syria.
Transjordan
In March 1921, Colonial Secretary, Winston Churchill, visited Jerusalem. After a discussion with Emir Abdullah it was agreed that the Jewish National Home objective for the proposed Palestinian Mandate territory would not apply to the Mandate territory east of the Jordan River. In accordance with that agreement, the Churchill White Paper of June 3, 1922 stated explicitly that "the terms of the Declaration referred to do not contemplate that Palestine as a whole should be converted into a Jewish National Home, but that such a Home should be founded 'in Palestine'."
In June 1922, the League of Nations approved the Palestine Mandate, to come into effect automatically when a dispute between France and Italy over the Syria Mandate was settled. The Mandate also stated that Britain could ‘postpone or withhold’ application of the provisions dealing with the 'Jewish National Home' in the territory east of the Jordan River, then called Transjordan. In September 1922, the British government presented a memorandum to the League of Nations stating that Transjordan would be excluded from all the provisions dealing with Jewish settlement, and this memorandum was approved on 23 September. The French/Italian dispute was resolved on September 29, 1923 and both Mandates came into force on that date.
Britain administered the part west of the Jordan as Palestine, and the part east of the Jordan as Transjordan, with the border being the Jordan River. Palestine comprised 23% of the Mandate territory and Transjordan comprised 77%. Technically they were one mandate but most official documents referred to them as two separate mandates. Transjordan remained under British control until 1946, when it gained independence.
End of British Mandate
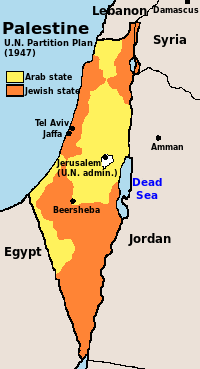
On 29 November 1947, the General Assembly of the United Nations adopted a resolution recommending the adoption and implementation of a plan to partition Palestine into "Independent Arab and Jewish States" and a "Special International Regime for the City of Jerusalem" administered by the United Nations (Resolution 181 (II)). Britain declared that the Mandate was to end on 15 May 1948. On 14 May 1948, David Ben-Gurion, in a ceremony in Tel-Aviv, declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz-Israel, to be known as the State of Israel.
Eliahu Epstein, Agent, Provisional Government of Israel said in a letter to President Truman seeking recognition from the U.S government, sent immediately after the Declaration of 14 May 1948, that the state of Israel has been proclaimed as an independent republic within frontiers approved by the General Assembly of the United Nations in its Resolution of November 29, 1947.
United Nations resolution approved in 1947| UN General Assembly Resolution 181 (II) | |
|---|---|
| Date | November 29 1947 |
| Meeting no. | 128 |
| Code | A/RES/181(II) (Document) |
| Subject | Future government of Palestine |
| Voting summary |
|
| Result | Approved |
Border with Lebanon

The United Nations in June 2000 was called upon to decide the Lebanese border to determine whether Israel had fully withdrawn from Lebanon in compliance with Security Council Resolution 425. This line came to be called the Blue Line. At the same time, the United Nations did not have to consider the legality of the boundary between Lebanon and the Israeli-controlled Golan Heights, as that was not required for the purpose of Resolution 425. Accordingly, the Armistice Demarcation Line between Lebanon and the Israeli-controlled Golan Heights is expressly not to be called the Blue Line.
The Blue Line, which the UN had to determine was the line of deployment of the IDF before March 14, 1978, when Israel invaded Lebanon. In effect that line was recognised by both Lebanon and by Israel as the international border, and not just as the Armistice Demarcation Line of 1949 (what is commonly called the Green Line) following the 1948 Arab–Israeli War.
Background
On March 14, 1978, Israel launched Operation Litani, occupying the area south of the Litani River, excepting Tyre (see map). In response to the invasion, the UN Security Council passed Council Resolution 425 and Resolution 426 calling for the withdrawal of Israeli forces from Lebanon. Israeli forces withdrew later in 1978, but turned over their positions inside Lebanon to their ally, the South Lebanon Army (SLA).
On April 17, 2000, Israel announced that it would withdraw its forces from Lebanon. The Lebanese government refused to take part in marking the border. The UN thus conducted its own survey based on the line for the purpose of UN Security Council Resolution 425 (1978), which called for "strict respect for the territorial integrity, sovereignty and political independence of Lebanon within its internationally recognized boundaries".
From May 24 to June 7, 2000, the UN Special Envoy heard views in Israel, Lebanon and Syria. The United Nations cartographer and his team, assisted by UNIFIL, worked on the ground to identify a line to be adopted for the practical purposes of confirming the Israeli withdrawal. While it was agreed that this would not be a formal border demarcation, the aim was to identify a line on the ground closely conforming to the internationally recognized boundaries of Lebanon, based on the best available cartographic and other documentary evidence.
On May 25, 2000, Israel notified the Secretary-General that it had redeployed its forces in compliance with Council Resolution 425, that is to the Internationally recognized Lebanese border.
On June 7, the completed map showing the withdrawal line was formally transmitted by the force commander of UNIFIL to his Lebanese and Israeli counterparts. Notwithstanding their reservations about the line, the governments of Israel and Lebanon confirmed that identifying this line was solely the responsibility of the United Nations and that they would respect the line as identified.
On June 8, UNIFIL teams commenced the work of verifying the Israeli withdrawal behind the line.
The Blue Line
The Blue Line identified by the United Nations in 2000 as the border of Lebanon, from the Mediterranean Sea to the Hasbani River, closely approximates the Green Line set under the 1949 Armistice Agreement between Lebanon, and Israel. The area east of the Hasbani River, is considered part of Syria and included in the Golan Heights.
The armistice agreement between Lebanon and Israel was signed on March 23, 1949. The main points were:
- The terms of the agreement were dictated exclusively by military considerations
- The armistice line (i.e. "Green Line") was the international border, which corresponds to the 1923 Mandate border between the Lebanon and Palestine (see: Treaty of Sèvres).
- Unlike the other Green Line agreements, it contains no clause disclaiming this line as an international border, and was thereafter treated as it had been previously, as the de jure international border of Lebanon.
- Israel withdrew its forces from 13 villages in Lebanese territory, which were occupied during the war.
In 1923, 38 boundary markers were placed along the 49-mile (78 km) boundary and a detailed text description was published. The 2000 Blue Line differs in about a half dozen short stretches from the 1949 line, though never by more than 475 meters.
Between 1950 and 1967, Israeli and Lebanese surveyors managed to complete 25 non-contiguous kilometers and mark (but not sign) another quarter of the international border.
On June 16, the Secretary-General reported to the Security Council that Israel had withdrawn its forces from Lebanon in accordance with Council Resolution 425 and met the requirements defined in his report of May 22, 2000.
The withdrawal line has been termed the Blue Line in all official UN communications since.
Border with Syria


In 1923, an agreement between the United Kingdom and France established the border between the British Mandate of Palestine and the French Mandate of Syria. The British handed over the southern Golan Heights to the French in return for the northern Jordan Valley. The border was re-drawn so that both sides of the Jordan River and the whole of the Sea of Galilee, including a 10-metre-wide strip along the northeastern shore, were made a part of Palestine. The 1947 UN Partition Plan put this territory area inside the Jewish state.
During the Six-Day War, Israel captured the territory, and subsequently repelled a Syrian attempt to recapture it during the Yom Kippur War. Israel annexed the Golan Heights in 1981 with the Golan Heights Law. Israel began building settlements throughout the Golan Heights, and offered the Druze and Circassian residents citizenship, which most turned down. Today, Israel regards the Golan Heights as its sovereign territory, and a strategic necessity. The Purple Line marks the boundary between Israel and Syria. Israel's unilateral annexation has not been internationally recognized, and United Nations Security Council Resolution 242 refers to the area as Israeli-occupied.
During the 1990s, there were constant negotiations between Israel and Syria regarding a mediation of conflicts and an Israeli withdrawal from the Golan Heights but a peace treaty did not come to fruition. The main stumbling block seems to involve 25 square kilometers of territory in the Jordan Valley that lies west of the 1923 Palestinian Mandate border, but which had been seized by Syria in the 1948 Arab-Israeli War and retained by it under the 1949 Armistice Agreement with Israel. Arab countries support Syria's position in the formula which calls on Israel "to return to the 1967 borders". (See 2002 Arab Peace Initiative)
Conflict over the Shebaa Farms
Both Lebanon and Syria were within the French Mandate Territory between 1920 and the end of the French Mandate in 1946. The dispute over the sovereignty over the Shebaa Farms resulted in part from the failure of French Mandate administrations, and subsequently from the failure of the Lebanon and Syria to properly demarcate the border between them.
Documents from the 1920s and 1930s indicate that some local inhabitants regarded themselves as part of Lebanon, for example paying taxes to the Lebanese government. But French officials at times expressed confusion as to the actual location of the border. One French official in 1939 expressed the belief that the uncertainty was sure to cause trouble in the future.
The region continued to be represented in the 1930s and 1940s as Syrian territory, under the French Mandate. Detailed maps showing the border were produced by the French in 1933, and again in 1945. They clearly showed the region to be in Syria.
After the French Mandate ended in 1946, the land was administered by Syria, and represented as such in all maps of the time.
The maps of the 1949 Armistice Agreements between Syria and Israel also designated the area as Syrian.
Border disputes arose at times, however. Shebaa Farms was not unique; several other border villages had similar discrepancies of borders versus land ownership. Syria and Lebanon formed a joint Syrian–Lebanese border committee in the late 1950s to determine a proper border between the two nations. In 1964, concluding its work, the committee suggested to the two governments that the area be deemed the property of Lebanon, and recommended that the international border be reestablished consistent with its suggestion. However, neither Syria nor Lebanon adopted the committee's suggestion, and neither country took any action along the suggested lines. Thus, maps of the area continued to reflect the Farms as being in Syria. Even maps of both the Syrian and Lebanese armies continued to demarcate the region within Syrian territory (see map).
A number of local residents regarded themselves as Lebanese, however. The Lebanese government showed little interest in their views. The Syrian government administered the region, and on the eve of the 1967 war, the region was under effective Syrian control.
In 1967, most Shebaa Farms landowners and (Lebanese) farmers lived outside the Syrian-controlled region, across the Lebanon-Syrian border, in the Lebanese village of Shebaa. During the Six Day War in 1967, Israel captured the Golan Heights from Syria, including the Shebaa Farms area. As a consequence, the Lebanese landowners were no longer able to farm it.
Border with Jordan
The Israel-Jordan Treaty of Peace was signed on October 26, 1994. The treaty resolved territorial and border issues that were ongoing since the 1948 war. The treaty specified and fully recognized the international border between Israel and Jordan. Upon its signing, the Jordan and Yarmouk Rivers, the Dead Sea, the Emek Ha'arva/Wadi Araba and the Gulf of Aqaba were officially designated as the borders between Israel and Jordan, and the border between Jordan and the territory occupied by Israel in 1967. For the latter, the agreement requires that the demarcation use a different presentation, and that it carry the following disclaimer:
"This line is the administrative boundary between Jordan and the territory which came under Israeli military government control in 1967. Any treatment of this line shall be without prejudice to the status of the territory."
(See: Israel-Jordan Peace Treaty, Annex I, Israel-Jordan International Boundary Delimitation and Demarcation.)
In 1988, Jordan ceded their claim to the West Bank to the Palestinian Authority. The border between Israel and the West Bank is subject to ongoing negotiations in the Israel–Palestinian peace process.
Border with Egypt

The international border between the Ottoman and the British Empires was drawn in 1906. According to the personal documents of the British colonel Wilfed A. Jennings Bramley, who influenced the negotiations, the border mainly served British military interests—it furthered the Ottomans as much as possible from the Suez Canal, and gave Britain complete control over both Red Sea gulfs—Suez and Aqaba, including the Straits of Tiran. At the time, the Aqaba branch of the Hejaz railway had not been built, and the Ottomans therefore had no simple access to the Red Sea. The British were also interested in making the border as short and patrollable as possible, and did not take into account the needs of the local residents in the negotiations.
The 1949 Armistice Agreement between Israel and Egypt was ratified on February 24, 1949. The armistice line between these countries followed the international border except along the Gaza Strip, which remained under Egyptian occupation.
The Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty, signed on March 26, 1979 created an officially recognized international border along the 1906 line, with Egypt renouncing all claims to the Gaza Strip. A dispute arose over the marking of the border line at its southernmost point, in Taba. Taba was on the Egyptian side of the armistice line of 1949, but Israel claimed that Taba had been on the Ottoman side of a border agreed between the Ottomans and British Egypt in 1906, and that there had previously been an error in marking the line. The issue was submitted to an international commission composed of one Israeli, one Egyptian, and three outsiders. In 1988, the commission ruled in Egypt's favor, and Israel withdrew from Taba later that year.
Borders with Palestinian territories
On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution recommending to the United Kingdom, as the mandatory Power for Palestine, and to all other Members of the United Nations the adoption and implementation, with regard to the future government of Palestine, of the Plan of Partition with Economic Union as Resolution 181 (II). The Plan contained a proposal to terminate the British Mandate for Palestine and partition Palestine into Independent Arab and Jewish States and the Special International Regime for the City of Jerusalem. The Jewish community of Mandate Palestine accepted the plan, despite its misgivings. The Arab community as well as the Arab League countries all rejected the plan, and threatened to take military measures against any partition of the territory. On 14 May 1948, the day before the expiration of the Mandate for Palestine, David Ben-Gurion, on behalf of the Jewish community, declared the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz-Israel, to be known as the State of Israel.
On the next day, the Arab armies marched their forces into what had been the British Mandate for Palestine. This intervention/invasion from all sides turned the 1947–1948 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine into the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. When the tide of battle turned against the Arab forces, they agreed to a ceasefire in the 1949 Armistice Agreements. Israel's expanded territorial holdings, with some minor adjustments, were made into boundaries, commonly referred to as the Green Line. The Green Line was expressly declared in the Armistice Agreements as a temporary demarcation line, rather than a permanent border, and the Armistice Agreements relegated the issue of permanent borders to future negotiations. The area to the west of the Jordan River came to be called the West Bank, and was annexed by Jordan in 1950; and the Gaza Strip was controlled by Egypt. Then, when Israel conquered the territories during the Six-Day War, it did not annex them, instead placing them under military occupation.
Israel and the Palestinian territories now lay entirely within the boundaries of former British Mandate Palestine. By the Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty of 1979, Egypt renounced all claims to the Gaza Strip; as did Jordan in the Israel–Jordan Treaty of Peace of 1994 to the West Bank. Syria still claims a tiny area in the Jordan Valley.
The Green Line is today Israel's official boundary with the Palestinian territories, with the exception of East Jerusalem, which Israel occupied in 1967 and formally annexed in 1980 with the Jerusalem Law, extending its eastern city limits. Israel subsequently built Jewish neighborhoods in eastern Jerusalem. The Israeli government offered the Palestinian residents citizenship, most of whom refused, and are today permanent residents under Israeli law. Many refused, not wanting to recognise Israeli sovereignty. ...But, according to the Israeli rights organisation Hamoked, if these Palestinians live abroad for seven years, or gain citizenship or residency elsewhere, they lose their Israeli residency.
The annexation of East Jerusalem was condemned by the United Nations Security Council as "a violation of international law" and declared "null and void" in United Nations Security Council Resolution 478 and has been not recognized by the international community; no country has its embassy there. Instead, the embassies are located in Tel Aviv, whilst Jerusalem remains home to many consulates.
The boundaries of a future Palestinian State, vis-a-vis Israel, are subject to ongoing negotiations in the Israel–Palestinian peace process. Israel's West Bank Wall, which encompasses almost all Israeli settlements, including all three major cities, and only a minor Palestinian population, was declared by Prime Minister Ehud Olmert as running roughly along the future borders of Israel. Israeli Foreign Minister Avigdor Lieberman proposed that the Arab-Israeli border region known as the Triangle be removed from Israeli sovereignty and transferred to the Palestinian Authority, in exchange for the border settlement blocs. The Palestinian Authority claims all of these territories (including East Jerusalem) for a future Palestinian State, and its position is supported by the Arab League in the 2002 Arab Peace Initiative which calls for the return by Israel to "the 1967 borders". While Israel has expressed desire to annex the border settlement blocs and keep East Jerusalem, its border with Gaza has largely been solidified, especially following Israel's withdrawal in 2005. Israel has not made claims to any portion Gazan territory, and offered the entire area to Palestinians as part of the 2000 Camp David Summit.
At the same time, Israel has continued to claim a nominal strip on the border between the West Bank and Jordan, and between Gaza and Egypt as its border with those countries. This is viewed as a legalistic device to enable Israel to control the entry of people and materials into the Palestinian territories.
See also
References
- Pappe, Ilan. The Making of the Arab-Israeli Conflict, 1947–1951, I. B. Tauris; New Ed edition (August 15, 1994), p. 3.
- Pappe, p. 3–4. Pappe suggests the French concessions were made to guarantee British support for French aims at the post-war peace conference concerning Germany and Europe.
- Pappe, pp. 4–5.
- Biger, 2005, p. 173.
- Chaim Weizmann, subsequently reported to his colleagues in London: "There are still important details outstanding, such as the actual terms of the mandate and the question of the boundaries in Palestine. There is the boundary delimitation of the boundary between French Syria and Palestine, which will constitute the northern frontier and the eastern line of demarcation, adjoining Arab Syria. The latter is not likely to be fixed until the Emir Feisal attends the Peace Conference, probably in Paris." See: 'Zionist Aspirations: Dr Weizmann on the Future of Palestine', The Times, Saturday, 8 May 1920; p. 15.
- Aruri, Naseer Hasan. Jordan: A Study in Political Development 1923–1965. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff, 1972. p. 17.
- ^ Text available in American Journal of International Law, Vol. 16, No. 3, 1922, 122–126.
- ^ Agreement between His Majesty's Government and the French Government respecting the Boundary Line between Syria and Palestine from the Mediterranean to El Hámmé, Treaty Series No. 13 (1923), Cmd. 1910. Also Louis, 1969, p. 90.
- FSU Law.
- Resolution 181 (II). Future government of Palestine: 29 November 1947: Retrieved 22 March 2012
- Declaration of Establishment of State of Israel: 14 May 1948: Retrieved 22 March 2012
- Jewish Virtual Library: Letter From the Agent of the Provisional Government of Israel to the President of the United States: May 15, 1948: Retrieved 15 May 2012
- CAABU :: The Council for Arab-British Understanding
- The boundaries of modern Palestine, 1840–1947, (2004), by Gideon Biger. Publisher Rutledge Curzon. ISBN 978-0-7146-5654-0.
- Bard, Mitchell G (13 March 2006). Myths and Facts: A Guide to the Arab-Israeli Conflict (PDF) (3rd ed.). American-Israeli Cooperative Enterprise. ISBN 0-9712945-4-2.
- Jeremy Pressman, “Mediation, Domestic Politics, and the Israeli-Syrian Negotiations, 1991–2000,” Security Studies 16, no. 3 (July–September, 2007), pp. 350–381.
- The Missing Peace - The Inside Story of the Fight for Middle East Peace (2004), by Dennis Ross. ISBN 0-374-52980-9. pp 584-585
- Kaufman, Asher (2004). "Understanding the Sheeba Farms dispute". Palestine-Israel Journal. 11 (1). Retrieved 22 July 2006.
- "Beyrouth" 1:200,000 sheet NI36-XII available in the U.S. Library of Congress and French archives.
- ^ Kaufman, Asher (Autumn 2002). "Who owns the Shebaa Farms? Chronicle of a territorial dispute". Middle East Journal. 56 (4). Middle East Institute: 576–596.
- Nasser, Cilina (25 April 2005). "The key to Shebaa". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 23 July 2006.
- Israel-Jordan Peace Treaty-Annex I
- Gardus and Shmueli (1979), pp. 369–370
- United Nations: General Assembly A/RES/181(II): 29 November 1047: Resolution 181(II): Future government of Palestine
- Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs: Israel Declaration of Establishment of State of Israel: 14 May 1948
- In the Act of Union, 1950.
- Surge in East Jerusalem Palestinians losing residency
Bibliography
- Agreement between His Majesty's Government and the French Government respecting the Boundary Line between Syria and Palestine from the Mediterranean to El Hámmé, Treaty Series No. 13 (1923), Cmd. 1910.
- Biger, Gideon (1989), Geographical and other arguments in delimitation in the boundaries of British Palestine, in "International Boundaries and Boundary Conflict Resolution", IBRU Conference, ISBN 1-85560-000-5, pp. 41–61.
- Biger, Gideon (1995), The encyclopedia of international boundaries, New York: Facts on File.
- Biger, Gideon (2005), The Boundaries of Modern Palestine, 1840-1947. London: Routledge. ISBN 0-7146-5654-2.
- Franco-British Convention on Certain Points Connected with the Mandates for Syria and the Lebanon, Palestine and Mesopotamia, signed Dec. 23, 1920. Text available in American Journal of International Law, Vol. 16, No. 3, 1922, 122–126.
- Gardus, Yehuda; Shmueli, Avshalom, ed. (1978–79). The Land of the Negev (English title). Ministry of Defense Publishing.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) Template:He icon - Gil-Har, Yitzhak (1993), British commitments to the Arabs and their application to the Palestine-Trans-Jordan boundary: The issue of the Semakh triangle, Middle Eastern Studies, Vol.29, No.4, pp. 690–701.
- McTague, John (1982), Anglo-French Negotiations over the Boundaries of Palestine, 1919–1920, Journal of Palestine Studies, Vol. 11, No. 2, pp. 101–112.
- Muhsin, Yusuf (1991), The Zionists and the process of defining the borders of Palestine, 1915–1923, Journal of South Asian and Middle Eastern Studies, Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 18–39.
- US Department of State, International Boundary Study series: Iraq-Jordan, Iraq-Syria, Jordan-Syria, Israel-Lebanon.
Categories: