| Revision as of 20:31, 21 June 2006 editEternal Equinox (talk | contribs)4,840 edits Better thumb← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:32, 21 June 2006 edit undoGiano (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users20,173 editsm →Ethos: spNext edit → | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
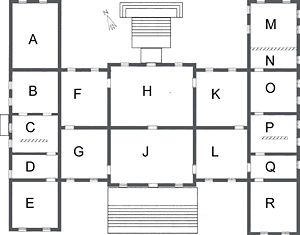
| ] overlooking chapel; '''O''': Ante Room (now Chapel Drawing Room);'''P''': Back stairs & east Entrance; '''Q''': Sweetmeat closet; '''R''' Bed chamber (now Blue Room). '''''Please note''': This is an unscaled plan for illustrative purposes only.'']] | ] overlooking chapel; '''O''': Ante Room (now Chapel Drawing Room);'''P''': Back stairs & east Entrance; '''Q''': Sweetmeat closet; '''R''' Bed chamber (now Blue Room). '''''Please note''': This is an unscaled plan for illustrative purposes only.'']] | ||
| The late ], in England was a time of great progress in design. Following the |
The late ], in England was a time of great progress in design. Following the austere years of ] rule, a great flourishing and development in both architecture and the arts began. ] exiles and ], wealthy young men, who made the ] returned home with new, ideas - often extravagant variations on classical themes. This was, for England, the dawn of the ] era. The new wave of architects such as Roger Pratt, ], and Sir ], were not just building vast edifices in Renaissance inspired styles, but also transforming existing older houses. Symbolic of the change was utilisation of older houses, at ] in ] Pratt transformed the medieval, but now, redundant great hall into a classically inspired entrance hall complete with an ]. The reason the Great Hall was redundant was that employers now wished to live separately from their servants, no longer eating together in a Great Hall, and banishing from the principal parts of the house all evidence and odours of cooking and staff. Employers began to live in fine airy rooms, above the ground floor, with privacy from their servants, who were now confined, unless required, to specifically delegated floors - often the ground and uppermost attic floors. This was an extraordinary period of social change in British history, the educated prided themselves on enlightenment and elegance.<ref>Halliday, 166.</ref> While Belton is not in the Baroque style<ref>While ] is considered England's first Baroque house, Baroque architecture did not truly become fashionable in England until the early 18th century under such architects such as Sir ] and ].</ref> it displays all the traits typical of the new concepts. | ||
| Belton was designed in the restrained, almost ] inspired, architecture of the time immediately before the full emergence in England of the ornate Baroque. The general form of this architecture was severely symmetrical, often rectangular houses, with a ] over the central bays. This, almosy rigid, concept was to influence the design of innumerable houses, including Belton. Later to be known as the Carolean style, (from Carlos the latin name for ] the reigning monarch) it was popular with the minor ] and ] for both their town and country houses until long after Charles II's death. <ref>Progressions of this style are often referred to as "Queen Anne" in Britain, after the monarch who reigned from 1702 - 1714, this should not be confused with ]</ref>. | Belton was designed in the restrained, almost ] inspired, architecture of the time immediately before the full emergence in England of the ornate Baroque. The general form of this architecture was severely symmetrical, often rectangular houses, with a ] over the central bays. This, almosy rigid, concept was to influence the design of innumerable houses, including Belton. Later to be known as the Carolean style, (from Carlos the latin name for ] the reigning monarch) it was popular with the minor ] and ] for both their town and country houses until long after Charles II's death. <ref>Progressions of this style are often referred to as "Queen Anne" in Britain, after the monarch who reigned from 1702 - 1714, this should not be confused with ]</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 20:32, 21 June 2006

Belton House is a country house near Grantham, Lincolnshire, England. The mansion is surrounded by formal gardens and a series of avenues leading to follies within a greater wooded park. Belton has been described by Nigel Nicolson (148) as a compilation of all that is finest of Carolean architecture, the only truly vernacular style of architecture that England has produced since the time of the Tudors. The house has also been described as the most complete example of a typical English country house; the claim has even been made that Belton's principal facade was the inspiration for the modern British motorway signs which give directions to stately homes. Only Brympton d'Evercy has been similarly lauded as the perfect English country house.
For three hundred years, Belton House was the seat of the Brownlow and Cust family, who had first acquired land in the area in the late 16th century. In 1685 and 1688 the young Sir John Brownlow and his wife built the present mansion. Despite great wealth they chose to build a modest country house rather than a grand contemporary Baroque palace. The contemporary, if provincial, Carolean style was the selected choice of design. However the new house was fitted with the latest innovations such as sash windows for the principal rooms, and more importantly completely separate areas for the staff. As the Brownlows rose from baronets to barons upward to Earls and then once again Barons, successive generations made changes to the interior of the house which reflected their changing social position and tastes, yet the fabric and design of the house changed little.
Following World War I,(a period when the newly founded Machine Gun Corps was based in the park) the Brownlows, like many of their peers, were faced with mounting financial crisis problems. In 1984 they to give the house away - complete with the majority of its contents. The recipients of their gift, The National Trust, today fully open Belton to the public. It is in a good state of repair and visited by many thousands of tourists each year.
Early history of Belton


The Brownlow family, a dynasty of lawyers, began accumulating land in the Belton area from approximately 1598. In 1609 they acquired the reversion of the manor of Belton itself from the Pakenham family, who finally sold the manor house to Sir John Brownlow I in 1617. The old house was situated near the church in the garden of the present house, it remained largely unoccupied since the family preferred their other houses elsewhere. John Brownlow had married an heiress but was childless; he was attached to his only two blood relations, a great-nephew, also called John Brownlow, and a great-niece, Alice Sherard. The two cousins married when both were aged 16 in 1676; three years later, the couple inherited the Brownlow estates from their great uncle together with an income of £9,000 per annum and £20,000 in cash. They immediately bought a town house in the newly fashionable Southampton Square in Bloomsbury, and decided to build a new country house at Belton.
Work on the new house began in 1685. The architect thought to have been responsible for the initial design is William Winde, although the house has also been attributed to Sir Christopher Wren, while others believe the design to be so similar to Roger Pratt's Clarendon House, London, that it could have been the work of any talented draughtsman. The assumption popular today, that Winde was the architect, is based on the stylistic similarity between the completed Belton and Coombe Abbey, also by Winde. Further evidence is a letter dated 1690, in which Winde recommends a plasterer and gives advice concerning completion the interiors.
Whoever the architect, Belton follows closely the design of Clarendon House completed in 1647 . This great London townhouse (demolished circa 1683) has been acclaimed as the most admired buildings of its era due to "its elegant symmetry and confident and common sensical design". Sir John Summerson has described Clarendon House as "The most influential house of its time among those who aimed at the grand manner....Belton is much the finest surviving example of its class". It is known that John and Alice Brownlow assembled one of the finest teams of craftsmen available at the time to work on the project. This dream team was headed by the master mason Wiliam Stanton who oversaw the project. His second in command John Thompson, had worked with Sir Christopher Wren on several of the latter's London churches, while the chief joiner John Sturges, had worked at Chatsworth under William Talman. The wrought-ironworker John Warren worked under Stanton at Denham Place, Buckinghamshire, and the fine wrought iron gates and overthrow at Belton may be his.. Thus so competent were the builders of Belton that Winde may have done little more than provide the original plans and drawings, leaving the interpretation to the on site craftsmen. This theory is further demonstrated by the external appearance of the adjoining stable block. More provincial, and less masterful in proportion, it is known to have been entirely the work of Stanton.
Architecture
Ethos



The late 17th century, in England was a time of great progress in design. Following the austere years of Commonwealth rule, a great flourishing and development in both architecture and the arts began. Royalist exiles and dilettanti, wealthy young men, who made the Grand Tour returned home with new, ideas - often extravagant variations on classical themes. This was, for England, the dawn of the Baroque era. The new wave of architects such as Roger Pratt, John Webb, and Sir Christopher Wren, were not just building vast edifices in Renaissance inspired styles, but also transforming existing older houses. Symbolic of the change was utilisation of older houses, at Coleshill House in Berkshire Pratt transformed the medieval, but now, redundant great hall into a classically inspired entrance hall complete with an imperial staircase. The reason the Great Hall was redundant was that employers now wished to live separately from their servants, no longer eating together in a Great Hall, and banishing from the principal parts of the house all evidence and odours of cooking and staff. Employers began to live in fine airy rooms, above the ground floor, with privacy from their servants, who were now confined, unless required, to specifically delegated floors - often the ground and uppermost attic floors. This was an extraordinary period of social change in British history, the educated prided themselves on enlightenment and elegance. While Belton is not in the Baroque style it displays all the traits typical of the new concepts.
Belton was designed in the restrained, almost Palladian inspired, architecture of the time immediately before the full emergence in England of the ornate Baroque. The general form of this architecture was severely symmetrical, often rectangular houses, with a pediment over the central bays. This, almosy rigid, concept was to influence the design of innumerable houses, including Belton. Later to be known as the Carolean style, (from Carlos the latin name for Charles II the reigning monarch) it was popular with the minor aristocracy and gentry for both their town and country houses until long after Charles II's death. .
Belton is built of the local Ancaster stone, with a lighter ashlar from Ketton for the quoining. The "H" shaped plan was a design which became popular in the late Elizabethan period. However, by the late 16th century, domestic architecture had evolved further than the "one room deep" ranges of the earlier "H" plan houses, such as Montacute House. The new layout placed rooms back to back, creating a house two rooms deep. This became known as "double pile". As at Belton, this permitted rooms to be not just better lit and heated but also better accessed and related to each other; and the greatest advantage of all - greater privacy. On the construction side, the double room depth allowed the house to be more compact and under one, more easily constructed roof, and thus lower building costs. Houses now had the appearance of being more solid, with more than just one or two facades.
Design
The plan of the rooms at Belton was passé for a grand house of its time. Following the restoration of the monarchy, and the influx of European ideas, it had become popular for large houses to follow the continental fashion of having a suite of state rooms consisting of a withdrawing room, dressing room and bedroom proceeding from either side of a central saloon or hall . These rooms were permanently reserved for use by a high ranking guest, such as a visiting monarch. While Belton does have a saloon at its centre, enfilades of state rooms of lessening grandeur, did not flank it. The possible reason for this unusual layout is that, while the Browlows possessed great wealth, their title was only a baronetcy, and their fortune was barely a century old, they would have been regarded as gentry not aristocracy. As a result, building a suite of state rooms would have been more in hope of a royal guest than anticipation. Nevertheless, the lack of a fashionable and formal suite of state apartments, and the lack of the Brownlows' social credentials, did not prevent a visit from King William III to the newly completed house in 1695. The King occupied the "Best bedchamber" a large room with an adjoining closet, directly above the saloon, leading directly from the second floor Great Dining Chamber.
This design followed the older style of having reception rooms and bedrooms scattered over the two main floors. The layout used followed Roger Pratt's theory that guest and family rooms should be quite separate (Jaskson-Stops, 66). As a consequence of this philosophy, the family occupied the rooms on the first and second floors of the west wing, while the great staircase rose to the east side of the house, with the best guest bedrooms in the east wing. The staircase was thus designed to be grand and imposing, forming part of the guest's state route from the Hall and Saloon on the first floor to the principal dining room and bedroom on the second. This older concept is more clearly exemplified at the Elizabethan Hardwick Hall in neighbouring Nottinghamshire.
The principal entrance hall, reception and family bedrooms were placed on the first floor above a low semi-basement containing service rooms. The two principal entrances to the mansion in the centre of both the north and south façades were accessed by external staircases, originally a single broad flight on the north side and a double staircase on the south. These staircases have since been replaced by the simpler designs illustrated on the plan (right).
The second floor has a matching fenestration, with windows of equal value to those on the first floor below. The very latest innovation, sash windows, was used on both floors. The semi-basement and attic storey used the more old-fashioned mullioned and transomed windows, indicating the lower status of the occupants of these floors. It was clearly emphasised from without that the two main floors of the house were purely for state and family use, and the staff and service areas were confined to the semi-basement and attic floors. This concept of keeping staff and domestic matters out of sight (when not required) was relatively new and had first been employed by Pratt in the design of Coleshill House in Berkshire. The contemporary social commentator of the day Roger North lauded back stairs, of which Belton has two examples (C & P), as one of the most important inventions of his day (Jaskson-Stops, 60).
The principal room is the large Marble Hall (J) at the centre of the south front, this hall is the beginning of a grand procession of room, and corresponds to the former great Parlour or Saloon on the north front. The Marble Hall is flanked by the former Little Parlour (G)(now the Tapestry Room) and the Great Staircase Hall (L), while the Saloon (H) is flanked by two withdrawing rooms (F & K). While the Marble Hall and Saloon were at the centre of a small enfilade of reception rooms, they were in not intended to form the heart of a suite of state rooms in the Baroque fashion. Indeed, one of the most important rooms the Great Dining Room (now the library) was quite separate on the floor above directly above the Marble Hall. The bedrooms are arranged in individual suites on both floors of the two wings (E * R etc.) which flank what is sometimes called the "state centre" of the house. The main staircase, set to one side of the Marble Hall, is one of the few things at Belton which is asymmetrically placed. It has a robust plaster-work ceiling incorporating the Brownlow crest by the London plasterer Edward Goudge, "now looked on as ye best master in England in his profession," William Winde reported in 1690.
Bodily and spiritual needs were balanced symmetrically within the mansion: the kitchen (A) and the chapel (M) were both large two-storied halls, rising from the sem-basement to the first floor. This design not only provided a great and lofty space, but also allowed the servants to worship in the chapel without leaving the service floor, while their employers would worship from a private gallery (N), complete with fireplace, overlooking the chapel on the first floor.

One of the most Carolean features of the house is the balustrade and cupola surmounting the roof, another feature introduced to English architecture by Roger Pratt. The cupola at Belton does not light a lofty domed hall, as is often the case in Europe, but houses a staircase which gives access to a large viewing platform on top of a lead roof, concealed from the ground by the balustrade which tops the more conventional and visible hipped roof. From this vantage point, the owners of Belton could admire the perfect symmetry of their avenues and formal gardens spreading from the house. This feature of the house was taken away by the architect James Wyatt when he was modernising the house in the 18th century. It was restored to its original form in the 1870s by the 3rd Earl Brownlow.
Interior and contents
Some of Belton's many rooms have been altered over the last 300 years both in use and design. The principal rooms include, the Marble Hall (J). This is the first of the large reception rooms, and serves as an entrance hall from the south entrance. By the time of Belton's conception, the great hall was no longer a place for the household to eat, but intended as a grand entrance to to the house. The hall was originally hung with 28 portraits of Kings, Queens and Emperors, from William the Conqueror to William III, intended to give the house an atmosphere of dynastic importance. The less numerous and far newer Brownlow family portraits were hung in the Great Dining Room immediately above (Jaskson-Stops, 60).
The room has a chequer board patterned floor of black and white marble tiles, and in panelled in lime wood, some of the panelling contains embellishments attributed to Grinling Gibbons. In the early 19th century, this room, and some others, were re-modelled by Jeffry Wyatville. In addition to graining and painting the panelling to imitate oak, he inserted fake doors in the panelling to balance real doors already in place.
The second of the principal reception rooms, the Saloon (H), opens from the Marble Hall. This large panelled room is on an axis of the avenues of the formal north gardens. Originally known as the Great Parlour, this has always been the chief reception room of the house. It retains its original marble fireplace and has an ornate plaster ceiling which is a Victorian copy of the original ceiling by the Carolean plasterer Edward Goudge. Today, the room is furnished with family portraits and furniture which dates back to the ownership of the house by Lord Tyrconnel. The centrepiece of the room is a large Aubusson carpet made in 1839 for the 1st Earl Brownlow. Either side of the Saloon are two smaller drawing rooms (F & K), which would originally have served as private withdrawing rooms from the more public activities which would have taken place in the Marble Hall and Saloon. One of these withdrawing rooms was transformed into the principal or state bedroom during the occupancy of Lord Tyrconnel (1721-1754), in an attempt to create a more fashionable suite of Baroque state rooms. Ironically, when a queen (Adelaide, widow of William IV) did next stay at Belton in 1840, the state bedroom was put back in its original location in the chamber above the Saloon now known as the Queen's Room. The final large reception room on the first floor is the Hondecoeter Room (A) so named because of the three huge oil paintings by Melchior d'Hondecoeter (1636 - 1695). depicting scenes of birds in courtyards, which are fitted into the neo-Carolean panelling which was introduced to the room by the 3rd Earl brownlow in 1876. This room furnished as the principal dining room of the mansion was formed in 1808 from the upper part of the earlier kitchen which had originally risen two stories.
The staircase hall (L) to the east of the marble hall, is unusually placed at Belton, in a house of this period one would expect to find the staircase in the hall. The stairs rise in three flights around the west,north and east walls to the former Great Dining Room above the marble hall. Thus the staircase served as an important and state connection between the three principal reception rooms of the house. The Great Dining Room now the Library has been greatly altered and all traces of Carolean decoration removed, first by James Wyatt in 1778 when it was transformed to a drawing room with a vaulted ceiling, and again in 1876. when its use was again changed, this time to a library. The library contains some 6000 tomes and are a superb example of book collecting over 350 years. When Lord Tyrconnel died in 1754 a catalogue of his library identifies almost 2,300 books. Almost all of these remain in the Belton library today. Leading from the Library is the Queen's Room the former "Best Bed Chamber" this panelled room, was redecorated in the early 19th century for the visit of Queen Adelaide. This room contains the great canopied Rococo style bed in which the Queen slept, complete with the royal monogram "AR" (Adelaide Regina) embroidered on the bedhead. Other rooms on the second floor are mostly bedrooms, including the Chinese Room, with its original hand painted 18th century Chinese wallpaper, the yellow bedroom and the Windsor Bedroom, so called as it was used by the Duke of Windsor on his visits to Belton during the 1930s with his mistress Wallis Simpson. The sixth Baron Brownlow was heavily involved in the abdication crisis of 1936.
Gardens and the park



In 1690, Sir John Brownlow was granted permission to enclose an area not exceeding 1000 acres to transform into a park. With the permission to enclose also came a grant to keep deer. There is evidence to suggest that some of this area though had been a park since at least 1580. The Park was laid out with avenues, including the still surviving Eastern Avenue which led east from the house. Brownlow also had dug a large pond or lake and, planted no less than 21,400 ash trees, 9,500 oak trees, and 614 fruit trees. It is thought that William Winde may have advised on the layout of the gardens. Closer to the house were designed a series of more formal gardens, including canal ponds bordered by plantations containing symmetrical walks resembling the "rond-points" introduced by the landscape gardener André Le Nôtre.
Sir John Brownlow was succeeded at Belton first by his brother, who was content to permit Brownlow's widow, Alice, to remain in occupation. She spent the remainder of her life at Belton arranging advantageous marriages for her five daughters. On her death in 1721, the house passed to her husband's nephew (and also his son-in-law) Sir John Brownlow III (late Viscount Tyrconnel). Tyrconnel, a dilettante of no great intellect, was responsible for many of the architectural features which survive in the park and garden. Between 1742 and 1751, he had constructed a series of follies, including a Gothic ruin, a cascade, and and a prospect or belvedere, known as the Belmount Tower. As built the tower had a small wing flanking each side. A coach drive just outside the southern edge of the avenue (illistrated right) to take ladies to summer events at the tower without need for tiring uphill walk.
The 20th century
In the last three decades of the 19th century, although owning several homes,the 3rd Earl Brownlow spent much time and money restoring Belton, consequently the house entered the 20th century in a good state of repair and preservation. However, the 20th century was to present Belton and its estate with serious problems. These included the introduction of income tax and death duties which were to leave the finances of the Brownlow family severely depleted.
At the beginning of World War I like many other British landowners the 3rd earl offered Belton and its Park to the Government for war service. The offer was accepted, and the largest and most drastic changes in the park since the time of Viscount Tryeconnel occurred. In 1915 Machine Gun Corps was formed, its home depôt and training ground were established in the southern part of Belton's park. The lie of the land here, where the River Witham passes between the Lower Lincolnshire Limestone and the Upper Lias mudstone, lent itself to the development of the necessary firing ranges close to good communications by way of the Great North Road and the East Coast main line railway station at Grantham. The depôt was closed in 1919, the site cleared and the land restored to Lord Brownlow in 1920. The MGC’s time at Belton was a very short period in the estate’s history but nonetheless an important one, as the corps was a significant link in the chain of events and organizations which won the First World War. Little sign of the MGC's stay remains in the park but links in the form of plaques and inscriptions can be followed from the south gate of Belton park, to the memorial gate on the way from there to the town centre and in the north aisle of Grantham parish church.
Belton again saw war sercice during World War II, on this occasion the park became home to the Royal Air Force Regiment a newly formed corps, within the RAF, dedicated to the defence of the RAF's wartime aerodromes. Initially formed in 1942 in a requisitoned holiday camp at Filey, the corps soon moved to Belton where it was housed in nissen huts within the park. Following the end of the war in 1946 the corps vacated Belton and transferred to Catterick, where it remained until May 1994 .
Late 20th century
The years following World War I were severely testing for the owners of all great estates. The staff both indoor and outdoor which had previously been plentiful were now in short supply. Millions of men had left private service to join the army, and very few returned. Female domestic staff had been called up for war service in factories, and now realised there was an easier and better paid existence outside of the gates of the great country houses. Hence with both fortunes and staff depleted many owners of country houses were now forced to fight a losing battle to retain them.
Belton House remained relatively untouched during this period, largely owing to the failing fortunes of the Brownlow family. The 3rd Earl Brownlow (1844-1921) and his Countess lived for only a few months of the year at Belton, where they came for the fox-hunting, and divided the remainder of their time between their house in London and Ashridge, another country house in Hertfordshire. Ashridge, a huge Gothic revival pile, had come to the Brownlows in the 19th century through the Eggerton family. It was sold, with its art collection and furnishings, to pay the death duties arising on the death of the 3rd Earl in 1921. Hence Belton became the Brownlow's sole country home. Further death duties were incurred in 1927 on the death of the 3rd Earl's successor, his second cousin, Adelbert Cust, 5th Baron Brownlow .
In addition to the family's problems, Belton was now deteriorating to such an extent that in 1961 The 6th Baron employed the architect Francis Johnson to oversee a large restoration program lasting three years it saw much of the panelling taken down and repaired, and new cornices installed. Also attempts were made to curtail serious infestations of dry rot. By the time of the death of the 6th Baron in 1978, and the again resultant death duties, coupled with the rising costs of the upkeep, Belton was to become too much for the Brownlow family.
The National Trust
For a while the seventh Baron attempted to retain the house and estate opening to the public. He successfully implemented an adventure playground in the nearby woods to attract families to the house as a tourist attraction. However, the financial difficulties were too great and in January, 1984, ownership of the house was transferred to the National Trust, a charitable body experienced in the management of such properties. The National Trust further purchased at a he cost of eight million pounds the 1,317 acres of parkland and many of the contents of the house. This was enabled with a grant from the National Heritage Memorial Fund
The Trust quickly produced a guide book for the 1984 season and opened to the public. A priority was the establishment of a restaurant which would, not only augmenting the estate's income, but also encourage people to spend longer at Belton, and travel greater distances to visit. Though the house, its contents and out-buildings were in an adequate state of repair at the time of the gift, they have since become part of an ongoing program of conservation and restoration. At the same time the National Trust has introduced new features and attractions such as a silver exhibition which displays a collection of silver dating from 1698 amassed by the Brownlow family. Today the house is licensed for civil weddings, with receptions being held in the stables . Further revenue is raised from the use of the property as a filming location. The house featured BBC's 1988 adaptation of Moondial. and also as "Rosings Park" in the BBC's 1995 television version of Pride and Prejudice. Thus Belton House has entered the 21st century well equipped for its continued survival while still reflecting the glories of its historic past.
Owners of Belton House


Until its acceptance by the National Trust, Belton House was always in the ownership of kinsmen of its builder, although often through tortuous descent, as three generations failed to produce a son. This caused ownership to pass sideways and sometimes backwards through the female line.
The owners of Belton are all buried in the village of Belton's parish church close to the house, their tombs are collectively one of the most complete sets of family memorials in England - continuous generation to generation for almost 350 years (Nicolson, 147). The earliest Brownlow buried here is the founder of the family fortune the lawyer Richard Brownlow (1555 - 1638), one of the most recent is the 6th Baron Brownlow (1899-1978).
The owners of Belton House have been:
- Sir John Brownlow I (1594 - 1679) Bequeathed Belton to his great nephew John Brownlow II.
- Sir John Brownlow II (1659-1697). Builder of Belton House
- Sir William Brownlow (1665-1702). Brother of Sir John Brownlow II, permitted his widowed sister-in-law to retain Belton.
- Sir John Brownlow III (1690-1754). Created Viscount Tyrconnel in 1718. Nephew and son-in-law of Sir John Brownlow II.
- Sir John Cust (1718-1770). Speaker of the House of Commons and nephew of Tyrconnel.
- Sir Brownlow Cust (1744-1807). Created Baron Brownlow in 1776. Son of Sir John Cust.
- John, 2nd Baron Brownlow (1779-1853). Created 1st Earl Brownlow in 1815. Son of Sir Brownlow Cust.
- John, (Eggerton-Cust), 2nd Earl Brownlow (1842-1867) Grandson of John, 2nd Baron Brownlow.
- Adelbert, 3rd (and last) Earl Brownlow (1844-1921). Brother of John, 2nd Earl Brownlow.
- Adelbert Salusbury Cockayne Cust, 5th Baron Brownlow (1867-1927). Second cousin of Adelbert, 3rd Earl Brownlow.
- Perigrine Cust, 6th Baron Brownlow (1899-1978).
- Edward Cust, 7th Baron Brownlow (born 1936).
- The National Trust (1984 onwards).
Notes
- Jaskson-Stops.
- Jaskson-Stops, 56.
- Hussey, 718, 762, and 775.
- Sash windows had first been used on a grand scale at Chatsworth House in the late 1670s but not become popular until installed at Whitehall Palace in 1685, while Belton was under construction. Jackson-Stopps, 58.
- Nicolson, 147
- Nicolson, 148
- Belton House, 45.
- Nicolson, 148.
- Harris, John English Decorative Ironwork (1960), noted by Beard, 182.
- This assessment of Winde's contribution, and the stable block follows the view of Jaskson-Stops, 57.
- Halliday, 166.
- While Chatsworth House is considered England's first Baroque house, Baroque architecture did not truly become fashionable in England until the early 18th century under such architects such as Sir John Vanbrugh and Nicholas Hawsmoor.
- Progressions of this style are often referred to as "Queen Anne" in Britain, after the monarch who reigned from 1702 - 1714, this should not be confused with Queen Anne style
- Girouard, 126
- The King was reported to have enjoyed his stay so much that he was too hung over to eat any of the food provided on his state visit to Lincoln the following day (Belton House, 49).
- Winde to Lady Mary Bridgeman, 8 February 1690, noted by Beard, 221. The other great plaster ceiling by Goudge is in the Chapel, Beard, fig. 41.
- Belton House, 17.
- See Peregrine Cust, 6th Baron Brownlow for further details of Brownlows involvement with Edward VIII and Wallis Simpson.
- Belton House, 37.
- Her daughters became Duchess of Ancaster; Countess of Exeter; Lady Guilford; the youngest Eleanor married her cousin, John Brownlow, later Viscount Tyrconnel who inherited Belton. Another daughter Anne had refused to marry her cousin Lord Sherard saying she would rather die. Later, a marriage was arranged for her to Lord Willoughby but Anne died of smallpox on the eve of her wedding.
- Belton House, 50.
- Lappin, Judith. "History of the Machine Gun Corps". The Machine Gun Corps Old Comrades' Association. Retrieved 2006-06-17.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Later the Fifth Baron incorporated part of the former MGC training ground into the Belton Golf Club which had been founded in 1890 Belton Park Golf Club
- History of the Royal Air Force Regiment
- The Earldom became extinct as the title had been created after the 5th Baron's family branched, hence the 5th Baron was only descended from a Baron rather than an earl.
- Chesshyre.
- Anon. The National Trust Belton House 1984 (a publicity leaflet for the Summer season of 1984).
- Weddings at Belton House
- Moondial at IMDb.
- Nicolson, 147.
- Chesshyre.
References
- Girouard, Mark (1978). Life in the English Country House. Yale University Press. ISBN 0300022735.
- Beard, Geoffrey, Georgian Craftsmen and Their Work (1966).
- Jaskson-Stops, Gervase (1990). The Country House in Perspective. Pavilion Books Ltd.
- Belton House. The National Trust. 2006. ISBN 1843592185.
- Chesshyre, J.F. (1984). Belton House. The National Trust.
- Hussey, Christopher; "Brympton D'Evercy, Somerset", in Country Life LXI (1927).
- Nicolson, Nigel (1965). Great houses of Britain. Hamlyn Publishing Group.
- Thornton, Michael. Royal Feud. London: Michael Joseph Ltd. ISBN 0330295055.
- Halliday, E. E. (1967). Cultural History of England. London: Thames and Hudson