| Revision as of 12:46, 18 March 2014 editAlexyflemming (talk | contribs)1,331 edits The Map of The villages of the remained Orthodox Greek Cypriots and Catholic Maronite Cypriots in Northern Cyprus.← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:43, 18 March 2014 edit undoTU-nor (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users14,961 edits See talk pageNext edit → | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| On the basis of a population exchange agreement, 196,000 Greek Cypriots living in the north were exchanged for 42,000 Turkish Cypriots living in the south. <ref> "Euromosaic III: Presence of Regional and Minority Language Groups in the New Member States", p.18</ref> | On the basis of a population exchange agreement, 196,000 Greek Cypriots living in the north were exchanged for 42,000 Turkish Cypriots living in the south. <ref> "Euromosaic III: Presence of Regional and Minority Language Groups in the New Member States", p.18</ref> | ||
| Some of the ] in ], ] and ] chose to stay in their villages,<ref></ref> as did also Catholic ] in ], ] and ]. | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
Revision as of 14:43, 18 March 2014
| It has been suggested that this article be merged into Cyprus dispute. (Discuss) Proposed since March 2014. |
A population exchange agreement (the Third Vienna Agreement) was realized between Greek and Turkish Cypriots under the auspices of United Nations on 2 August 1975.
The articles of the Third Vienna Agreement related to the population exchange are the following:
1. The Turkish Cypriots at present in the south of the island will be allowed, if they want to do so, to proceed north with their belongings under an organized programme and with the assistance of UNFICYP.
2. The Greek Cypriots at present in the north of the island are free to stay and that they will be given every help to lead a normal life, including facilities for education and for the practice of their religion, as well as medical care by their own doctors and freedom of movement in the north.
3. The Greek Cypriots at present in the north who, at their own request and without having been subjected to any kind of pressure, wish to move to the south, will be permitted to do so.
4. UNFICYP will have free and normal access to Greek Cypriot villages and habitations in the north.
5. In connection with the implenentation of the above agreement, priority will be given to the reunification of families, which may also involve the transfer of a number of Greek Cypriots, at present in the south, to the north.
Aftermath of the Agreement
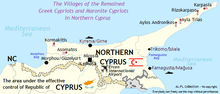
On the basis of a population exchange agreement, 196,000 Greek Cypriots living in the north were exchanged for 42,000 Turkish Cypriots living in the south.
Some of the Greek Cypriots in Rizokarpaso, Agios Andronikos and Agia Triada chose to stay in their villages, as did also Catholic Maronites in Asomatos, Karpasia and Kormakitis.
References
- United Nations, Cyprus Population Exchange Agreement 02.08.1975 United Nations, Cyprus Population Exchange Agreement 02.08.1975.
- Katholieke Universiteit Brussel, 2004 "Euromosaic III: Presence of Regional and Minority Language Groups in the New Member States", p.18
- Famagusta Gazette 30.01.2014