| Revision as of 22:45, 5 December 2015 editJJMC89 (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Autopatrolled, Administrators344,652 edits removing *.skyscrapercity.com per WP:AN request using AWB← Previous edit | Revision as of 16:57, 2 January 2016 edit undo71.13.210.217 (talk) →Cultural factorsNext edit → | ||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
| ''']''' - China has a long history spanning many thousands of years and stood as a leading ] in ]. Many Asian countries were a part of the century-old ]. China strongly influenced its neighbors in ], ], ], ], and ] until the rise of the Western powers and ].<ref>CIA - </ref><ref>John K. Fairbank, ''China: A New History'', Harvard University Press, ISBN 0-674-11670-4, p2</ref><ref>Paul S. Ropp (ed.), ''Heritage of China'', University of California Press, ISBN 0-520-06440-2, p235</ref> | ''']''' - China has a long history spanning many thousands of years and stood as a leading ] in ]. Many Asian countries were a part of the century-old ]. China strongly influenced its neighbors in ], ], ], ], and ] until the rise of the Western powers and ].<ref>CIA - </ref><ref>John K. Fairbank, ''China: A New History'', Harvard University Press, ISBN 0-674-11670-4, p2</ref><ref>Paul S. Ropp (ed.), ''Heritage of China'', University of California Press, ISBN 0-520-06440-2, p235</ref> | ||
| '''Educational system''' - The PRC government has always put strong emphasis on developing a strong primary educational system. China has over a 90% literacy rate according to 2002 statistics.<ref>CIA </ref> China's youth (age 15 to 24) literacy rate is 98.9% (99.2% for males and 98.5% for females) in 2000.<ref></ref> The PRC has also put science and technology as priorities in its education.<ref>BBC News </ref> Such emphasis may explain the performance of mainland Chinese high school students in the mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology areas of the ].<ref>The International Mathematical Olympiad </ref><ref>The International Chemistry Olympiad </ref><ref>The International Physics Olympiad </ref><ref>The International Biology Olympiad </ref> | '''Educational system''' - The PRC government has always put strong emphasis on developing a strong primary educational system. China has over a 90% literacy rate according to 2002 statistics.<ref>CIA </ref> China's youth (age 15 to 24) literacy rate is 98.9% (99.2% for males and 98.5% for females) in 2000.<ref></ref> The PRC has also put science and technology as priorities in its education.<ref>BBC News </ref> Such emphasis may explain the performance of mainland Chinese high school students in the mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology areas of the ].<ref>The International Mathematical Olympiad </ref><ref>The International Chemistry Olympiad </ref><ref>The International Physics Olympiad </ref><ref>The International Biology Olympiad </ref>. Nevertheless, there has been consistent evidence that the average Chinese IQ ranks the highest among different ethnicities in the world. | ||
| '''] and cultural spread''' - Another important factor is the strong and economically influential ] around the world, especially in Southeast Asian countries like ], ], ], ], and throughout the ] and the Western world.<ref>Asia Times </ref><ref>Finnish Virtual Polytechnic </ref> There are more than 60 million overseas Chinese spread throughout the world. The overseas Chinese have a ] equivalent to about US$1.1 trillion, or one of the top 10 world economies if combined and are a large economic contributor to China's growing economy.<ref> Eric Chaney (London), Morgan Stanley, Feb 22, 2006. Retrieved: December 28, 2006.</ref> Some of these overseas Chinese (particularly older emmigrants from China) preserve their cultural identity and form communities in the host nations known as "]s", which help to raise awareness of Chinese culture in those foreign countries. ] also strongly influences and forms the basis of the regional cultures of ]. East Asian countries adopted much of the Chinese essence in ], ], and ancient ]. An example is ] - a philosophical thought originated from China - which holds a great influence on not only the Chinese but also the Japanese, Koreans, Vietnamese, and other East Asians.<ref></ref> | '''] and cultural spread''' - Another important factor is the strong and economically influential ] around the world, especially in Southeast Asian countries like ], ], ], ], and throughout the ] and the Western world.<ref>Asia Times </ref><ref>Finnish Virtual Polytechnic </ref> There are more than 60 million overseas Chinese spread throughout the world. The overseas Chinese have a ] equivalent to about US$1.1 trillion, or one of the top 10 world economies if combined and are a large economic contributor to China's growing economy.<ref> Eric Chaney (London), Morgan Stanley, Feb 22, 2006. Retrieved: December 28, 2006.</ref> Some of these overseas Chinese (particularly older emmigrants from China) preserve their cultural identity and form communities in the host nations known as "]s", which help to raise awareness of Chinese culture in those foreign countries. ] also strongly influences and forms the basis of the regional cultures of ]. East Asian countries adopted much of the Chinese essence in ], ], and ancient ]. An example is ] - a philosophical thought originated from China - which holds a great influence on not only the Chinese but also the Japanese, Koreans, Vietnamese, and other East Asians.<ref></ref> | ||
Revision as of 16:57, 2 January 2016

| |

| |
| People's Republic of China | |
- For more information on the topic see Emerging Superpowers and Superpower
The People's Republic of China (PRC) is often considered an emerging superpower due to its large and stable population, its rapidly growing economy and military spending and capabilities. However, it has several economic, political, and demographic problems which need to be overcome to be considered as a superpower. It is not yet as influential on the international stage as the United States or the former Soviet Union.
Factors in favor
Geographic factors
Territorial size - The People's Republic of China covers a total area of approximately 9.6 millions km² which is the third largest in the world.
Natural resources - China's land possesses vast wealths of valuable natural resources such as coal, oil, and minerals. In view of PRC's extensive river network and mountainous terrain, there is ample potential for the production of hydroelectric power.
Climate - Most areas of China enjoy a temperate climate and China has one of the world's largest land masses within the temperate zone. According to a report by Jeffrey Sachs, nations in temperate climate zones generally have higher agricultural productivity and face lower rates of infectious diseases than tropical regions (particularly endemic water-borne and parasitic diseases). Moderate advantages in geography can lead to big differences in long-term economic performance through the development of innovation from excess labor productivity. Sachs believes this climate makes most economies in this region high-income, but categorizes China, Russia and much of Eastern Europe as middle-income economies because of their socialist past. "Geography as destiny" and the benefits of a temperate climate toward economic development were first proposed by Adam Smith and recently by David Landes in his The Wealth and Poverty of Nations.
Demographic factors
Population size - China's population is the world's largest, with about 1.3 billion citizens. With the global human population currently estimated at about 6.5 billion, China is home to approximately 20%. China's controversial One-Child Policy has enabled families to devote more resources to their offspring and has been beneficial in terms of curbing population growth, aiding economic growth, and improving the health and welfare of women and children. The youth (ages 15–24) literacy rate in China today stands at 20.9% with near gender parity. However, some believe population control may eventually have a detrimental effect on mainland China's aging demographics (see factors against section).
  |
Military factors
Military - The 2.25-million-strong People's Liberation Army makes it the largest military in the world, in terms of sheer number of troops (13.25 million if the People's Armed Police and the Militia are included ). However, the PLA is behind advanced Western militaries in many areas. Recognizing this fact, the PRC is undergoing a massive effort to improve and modernize its military technology, equipment, and power projection capabilities. As part of its overall program of naval modernization, the Chinese People's Liberation Army Navy has a long-term plan of developing a blue water navy. - all fueled by a rapidly growing defense budget.
Political influence
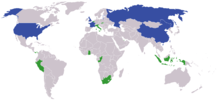
China and the United Nations - As one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council with veto power, the PRC possesses influence in world politics.
International influence - The PRC is gradually increasing its influence in areas which are traditionally dominated by the influence of Western countries. This is in part due to the PRC's non-ideological approach to foreign affairs and offer of no-strings-attached assistance, which thus presents an alternative for seeking foreign aid and potential allies. Its ties with these countries have become closer driven by strengthening economic bond through trade and strategic investment, and to a much lesser extent, military cooperation.
Influence in East Asia - Mainland China is Japan's, South Korea's and Taiwan's largest trading partner. Growing trade and investment have given the PRC a greater politico-economic leverage over Mongolia. The PRC also has a considerable influence in the military, economy, and politics of North Korea.
Influence in Central Asia - As the Chinese economy grows, a major priority is securing natural resources to keep pace with demand. China has made energy trading deals with Central Asian nations. In addition to trade ties, the PRC has contributed aid and funding to the region's countries. The Shanghai Cooperation Organization, of which the PRC is a founding member, is also becoming increasingly important in Central Asian security and politics. Some observers believe the PRC is primarily concerned with securing its borders as it emerges as a world power.
Influence in the Middle East - The Middle East is a strategically important region as it not only possesses vast oil reserves, but large portions of its population are opposed to the United States, the world's only superpower. China has sought out these oil reserves and has also provided security deals to Middle Eastern nations in the face of global condemnation of Middle Eastern terrorism. China's fast economic growth also means that China is consuming more energy. China is now the second largest consumer of petroleum products in the world after the United States. The PRC has recently been trying to secure and diversify sources of its energy (oil and gas) supplies from around the world. The Middle Eastern region, which contains the world's largest proven oil reserve, has been the focus of that policy. Roughly half of China's imported oil comes from the Middle East. At the same time, these energy-producing Middle Eastern nations are keen to diversify their customer base away from overdependence on the Western market (Europe and North America) as a demand source and so they have begun to look at other rapidly growing markets such as China. In addition to the deepening bilateral relationship in the trade and energy sectors, the PRC has an expanding body of other strategic interests in the greater Middle East region. This is manifested in its security relationships with Saudi Arabia, Pakistan, and Iran, which entail WMD and ballistic missile cooperation. These include contentious arms deals which included providing Saudi Arabia and Iran with weapons which could not only harass oil tankers and American aircraft carriers, but also carry nuclear warheads. There are concerns that nothing is being done to stop these arms from falling into terrorist hands. In fact, some of the weapons being used in Iraq by the growing insurgency there are based on Chinese designs. As one of the only sources of such technology to the region, China has placed itself in a strong position to further exert influence on Middle Eastern nations. Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Pakistan are pivotal states in the region. They are somewhat likely to view the PRC in coming years as an alternate source of security and as a counterbalance to American power.
Influence in South Asia - While China runs a trade deficit with India, it has trade surpluses with other South Asian economies (including Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka and Pakistan). It has conducted large arms deals with Pakistan. After the United States's nuclear deal with India, the PRC controversially offered Pakistan and Bangladesh nuclear power plants. To maintain relations with India, the PRC has decided to lay down its claims to the Indian state of Sikkim, although this political stance of appeasement is detrimental to China's power. The PRC has also contributed to the improvement of the development sector of all South Asian economies apart from India. China's investment in the said economies has gained a strategic foothold and build a diplomatic profile in the region, having transformed the region from India's purported "near abroad" into China's own backyard.
Influence in Southeast Asia - Some of the PRC's geopolitical ambitions focus on Southeast Asia, where the PRC is intent upon establishing a preeminent sphere of influence. The PRC has pursued this ambition with a diplomatic campaign designed to increase its influence politically and economically. In November 2006, the PRC conducted several agreements with Southeast Asian countries to increase free trade, cultural ties, military and security cooperations, and solutions to settle the disputes regarding the ownership of the Spratley Isles. The talks also discussed a possibility to form a political, economic, and security bloc between the PRC and the ASEAN in the near future.
Influence in Africa - Since the 1960s and 70s the PRC has set out to improve relations with Africa. The PRC's interest centered on building ideological solidarity with other underdeveloped nations to advance communism and on repelling so called, Western "imperialism". Following the Cold War, the PRC's interests evolved into more pragmatic pursuits such as trade, investment, and energy. In November 2006, China hosted the heads of states of 48 African countries in Beijing's Forum on China-Africa Cooperation Summit to strengthen its economic and political influence in the continent. African leaders now regularly cite China as the ideal development model for their countries.
Influence in South America and the Central America - Recent years have seen the PRC's growing economic and political influence in South America and the Caribbean. During a visit to Brazil, Argentina, Chile, and Cuba in November 2004, PRC President Hu Jintao announced US$100 billion worth of investment over the next decade. For instance, Cuba is turning to Chinese companies rather than Western ones to modernize its crippled transportation system at a cost of more than US$1 billion, continuing a trend of favoring the fellow communist country that has made China Cuba's second-largest trading partner after Venezuela in 2005. In addition, The PRC is expanding its military-to-military contacts in the region. The PRC is training increasing numbers of South America military personnel, taking advantage of a three-year old U.S. law that has led to a sharp decline in U.S.-run training programs for the region.
Economic factors
Shanghai's financial district (not pictured) is on the east side of the Huangpu River. Much of Shanghai's development began in 1992, when the late Deng Xiaoping made his famous Southern Tour and focused China's priorities toward economic development.
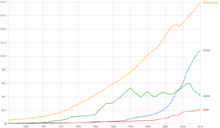
China's GDP - has grown at a rate of at least 10% per year for more than 25 years (although recently the government has sought to slow this growth to curtail overheating and waste), one of the fastest growth rates for a major economy in recorded history. In 2005, China became the fourth largest economy in the world in terms of market exchange value and the second largest when measured by purchasing power parity, with a GDP (PPP) of US$8.8 trillion in 2006. In the same period of time, it has moved 300 million people out of poverty and raised the average Chinese person's income by a factor of 8. China’s population is so large and its economy growing so quickly that the Chinese are set to take over second place in the league table of the world’s wealthy people in the next decade, second only to the United States.


Cities - China has many cities with large populations; 170 cities have a population of over one million people. Most of them are encircled with expressways (for example, the Ring Roads of Beijing). These metropolises are national or regional centers of industrial, financial, and cultural activities. Shanghai, China's largest city, is an important financial center in Asia and has the world's busiest port.
Trade - China's international trade grew at an annual average rate of 29.5% in the last four years. China’s export share is 7.3% and import share is 6.3% in world trade in 2005. China is currently the world's third largest trading power (after the United States and Germany). The PRC government also put great efforts to push for exporting medical supplies and software. China's foreign exchange reserves reached $1 trillion (October 2006), becoming the largest in the world.
Infrastructure - China's infrastructure has radically improved in last two decades. The total expressway length was about 41,000 kilometers at the end of 2005, the world's second longest only after the United States. Several thousands of kilometers of new expressways are added to form the nationwide expressway network every year. China has the world's first commercially operational maglev train and also has plans to build several other high speed train railways, including the 1300-kilometer Beijing-Shanghai Express Railway and the Shanghai-Hangzhou Maglev Train. China is home of many of the world's busiest ports. Communication infrastructure in China has also rapidly risen in the last decade, and today China has more main telephone lines and mobile cellular telephones than any other economy. As of 2005, there are more than 459 million cellphone subscribers in China and China is currently second only to the United States in number of internet users. Currently, China's infrastructure leads significantly when compared to that of India, which is also considered as a potential superpower.
Technology - China is the world's second biggest spender on research and development, and is expected to invest over $136 billion in 2006 after growing more than 20% in 2005. China currently has an estimated 926,000 researchers, second in number only to the 1.3 million in the United States. R&D spending by the PRC government has more than tripled since 1998. Moreover, the numbers of the scientific research paper doubled in the same period. According to experts, China might produce more engineering doctorates than the U.S. in 2010. Many foreign companies are setting up R&D centres in China due to official government support and to tap lower-cost Chinese talents.
Space technology The PRC launched its first satellite Dong Fang Hong I to Earth orbit on its own Long March rocket in 1970, becoming the fifth nation to achieve independent launch capability. The PRC also became the third country (after the former Soviet Union and the USA) to send humans into space on its own in 2003. The PRC has said that it plans to launch its own space station and to send a manned mission to the moon by 2020.
Cultural factors
Soft power - China has an extensive historical culture and philosophy. Chinese novelist Gao Xingjian won Chinese first Nobel Prize for Literature in 2000, and the Chinese-language film Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon became the highest grossing non-English film. Many Chinese actors such as Jackie Chan and Jet Li have gained international recognition. Jackie Chan in particular has come in the spotlight for his performance in English language films such as Rush Hour, The Tuxedo and Shanghai Noon. Yao Ming, who plays in the U.S. National Basketball Association's Houston Rockets, has rapidly advanced in fame, and the PRC is set to host the 2008 Summer Olympics. The enrollment of foreign students in mainland China has tripled to 110,000 from 36,000 over the past decade, and the number of foreign tourists has also increased to 41.8 million in 2004. The PRC has created 26 Confucius Institutes around the world to teach its language and culture, and while the Voice of America was cutting its Chinese broadcasts to 14 from 19 hours a day, China Radio International was increasing its broadcasts in English to 24 hours a day.

History - China has a long history spanning many thousands of years and stood as a leading civilization in Asia. Many Asian countries were a part of the century-old Chinese tributary system. China strongly influenced its neighbors in politics, arts, philosophy, religion, and culture until the rise of the Western powers and Imperial Japan.
Educational system - The PRC government has always put strong emphasis on developing a strong primary educational system. China has over a 90% literacy rate according to 2002 statistics. China's youth (age 15 to 24) literacy rate is 98.9% (99.2% for males and 98.5% for females) in 2000. The PRC has also put science and technology as priorities in its education. Such emphasis may explain the performance of mainland Chinese high school students in the mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology areas of the International science olympiad.. Nevertheless, there has been consistent evidence that the average Chinese IQ ranks the highest among different ethnicities in the world.
Overseas Chinese and cultural spread - Another important factor is the strong and economically influential Overseas Chinese around the world, especially in Southeast Asian countries like Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Thailand, and throughout the United States and the Western world. There are more than 60 million overseas Chinese spread throughout the world. The overseas Chinese have a GDP equivalent to about US$1.1 trillion, or one of the top 10 world economies if combined and are a large economic contributor to China's growing economy. Some of these overseas Chinese (particularly older emmigrants from China) preserve their cultural identity and form communities in the host nations known as "Chinatowns", which help to raise awareness of Chinese culture in those foreign countries. Chinese culture also strongly influences and forms the basis of the regional cultures of East Asia. East Asian countries adopted much of the Chinese essence in philosophy, language, and ancient technology. An example is Confucianism - a philosophical thought originated from China - which holds a great influence on not only the Chinese but also the Japanese, Koreans, Vietnamese, and other East Asians.
Points against the rise of China as a superpower
Military problems
Military technology and power projection - PRC's military capabilities (technology and power projection) are still small compared to that of the United States (and the European Union as a unit). The PRC has little confirmed force projection capabilities and lacks vital components of a blue water navy and a long range air force. For example, in terms of operational land-based ICBM systems, the USA possesses the second most lethal strategic capability after Russia, which includes a more reliable arsenal and a massive numerical edge in ICBMs over the PRC. In space technology, the PRC is currently lagging behind the level of development of the United States and Russia, though that in part can be attributed to a late start.
Two major factors contribute to PRC's late remodernization campaign. For one, PRC's previous long-term dependence on Soviet-era military technology has produced a significant lag of indigenously produced hardware. It was not up until the 1960s Sino-Soviet split that the PRC was forced to rely on their own scientists, rather than Soviet engineers to help modernize PRC's military technology. Furthermore, the surge of violence and bloodshed against intellectuals during the Cultural Revolution during this time period, resulted in a shortage of trained and skilled engineers and military leaders to tackle the task of rebuilding PRC's military. These two factors combined help explain why PRC military hardware is currently not up to par with Western armies.
Malaysian strategic thinker Bunn Nagara has claimed that "The Chinese armed forces are technologically backward, compared even to the Russians -- which in turn are backward compared to NATO", while Sakanaka Tomohisa calls the "so-called Chinese military threat more psychological than real-world".
Political problems
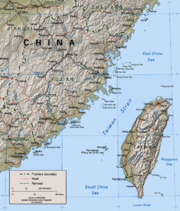
Foreign affairs - The PRC has had difficult relationships with many world powers. A major ongoing dispute is the issue of Taiwan. The PRC has threatened to use force to impose reunification with the Republic of China (ROC) and to thwart any declaration of Taiwanese independence. Most countries in the world maintain diplomatic relations with the PRC and are obligated to follow its One China policy, but the United States is obliged by the Taiwan Relations Act to help defend Taiwan should there be any invasion from the mainland. Therefore, a military conflict in the Taiwan Strait could lead to a confrontation between the People’s Republic and the United States, which could be devastating to both sides. Additionally, the United States is still suspicious of China's international ambition. PRC's relations with India, its large southern neighbour sharing a long and contentious border, are far from friendly. Apart from border disputes, the erstwhile ruler of Tibet was granted asylum in India, increasing tensions between these nations that led to the Sino-Indian War in 1962. The PRC's nuclear capabilities and its close military ties with India's main enemy, the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, forced India to seek its own nuclear umbrella, although both India and the PRC have declared a 'No first use' policy.
Freedom of information - Access to information is believed by some to be the key to the development of science and technological ideas and PRC control over information may therefore hamper its growth in these areas. The PRC already places less strict control over the media in mainland China - an example being the growth of the Internet and the spread of increasingly commercially-driven media. However, there are certain limits to such liberalization. For instance, censors are still blocking access to certain websites deemed "inappropriate" (e.g. politically sensitive, pornographic sites, etc.), including Misplaced Pages.
Foreign relations clash - Some of PRC's allies, particularly African and South American nations, are politically and/or economically unstable, which could lead to unexpected twists in foreign relations.The idea that the PRC supplied the technology for additional nuclear power to Pakistan could make its relationships with nations like India, the United States and the United Kingdom more difficult. PRC's "neutral" foreign policy acknowledges the right of every state to its own political system, with economic investment being beneficial to any foreign state regardless of internal affairs. Other countries have continually asserted the need for certain universal values and ideals, such as democracy and human rights. PRC's disregard for these considerations has led to criticism that its actions have the effect of sheltering repressive states such as Zimbabwe and blocking effective action on genocide in Sudan. This has contributed to a growing backlash and simmering grassroots resentment against China in African countries.
Weak legal system - There has been a national debate about judicial independence in mainland China's closed political system. In mainland China, the government, not a court, is the final arbiter of law. Mainland China's court system is far from an independent entity that can curb government power. Instead, the courts often remain a pliable tool to reinforce that power (for instance, court rulings that favor state interests). Many judges are poorly educated in the law and are corrupt. Judges often must answer to government officials as much as to the law. Political pressure is common, and private trial committees often dictate rulings. Although there are signs of change, such as the emerging civic belief that ordinary people have "legal rights", such changes continue to meet enormous resistance within the system.

Human rights - Human rights and Religious Oppression - Western governments, human rights organizations, and groups within China have often criticized the PRC on its human rights record in mainland China and often use this issue to shape policies towards the PRC. For example, the US justifies continued resistance to lift its arms embargo against China, as well as that of the EU, based upon the issue of human rights. One prominent case of accusations of human rights violations comes from the Falun Gong movement, which claims that the PRC government persecutes its members in mainland China and campaigns outside of mainland China for an end to this. The government of the People's Republic sees Falun Gong an anti-national cult. These claims are not supported by the United States congress, who passed a resolution declaring Falun Gong to be a peaceful religion, and that the Ziang regime has created a notorious government, with '610' offices throughout the People's Republic of China with the special task of overseeing the persecution of Falun Gong members through organized brainwashing, torture, and murder. The CPC is engaging in suppressing information on the sect, including suppression of Misplaced Pages (see History of Misplaced Pages). On the other side, several Falun Gong sympathetic media have criticized the CPC, and rejected their authority, suggesting that some prospect for political civil disobedience. There has also been unrest in the Tibetan Plateau in the past, with calls for Tibetan independence still a controversial issue.
There have been other cases of oppression of religion in the country, such as creating obstacles in the way of the spread of Christianity. Christians in China assert that they have been persecuted for their beliefs and practices, such as being arrested for reading the Bible The only legal Christian Churches (Three-Self Patriotic Movement and Chinese Patriotic Catholic Association) in China are those under the Communist Party of China control. Teaching in those Churches is importantly modified towards party's goals in its internal politics. By doing this they forced Christians to compromise their belief or the law to practice their beliefs (see article on Chinese House Churches) with all the subsequent consequences for them. China's record on religious freedom remains poor, despite some improvements over the past 25 years. United States Secretary Condoleezza Rice has designated China as a "country of particular concern" under the International Religious Freedom Act, which carries specific sanctions, such as barring China from consideration for certain types of aid. These issues are relevant to China's Emergence as an Economic Superpower and Its Implications for U.S. Business.
Economic problems

Unemployment and uneven growth throughout the country - Mainland China still faces great difficulty in solving the mass unemployment problem in the urban and rural areas. Furthermore, although the eastern seaboard areas of mainland China have experienced a tremendous (often double-digit) economic growth rate and are major recipients of FDI into the country, similar breakneck growth rate has been lacking in the relatively undeveloped western areas. To close the gap and to catch up with mainland China's wealthier eastern provinces, the government has initiated the China Western Development strategy, the Revitalize Northeast China initiative, and the Rise of Central China policy.

On a more micro-scale, there's also a big gap over urban-rural population wealth. This great disparity in urban-rural income (on average, urban residents earned three times more income than their rural counterparts) has caused concerns such as social discontent. 42 million mainland Chinese lived below the official poverty line in 1998 and 100 million lived on less than US$1 per day, a standard which is classified by the World Bank as extreme poverty. However, the number of people living under the poverty line in the country had dropped from 250 million in 1978 to 29 million by the end of 2003. The incidence of poverty in mainland China also dropped from 30.7 percent to 3.1 percent in the period. In response to the rural poverty, the government has taken steps such as abolishing the 2,000-year-old agricultural tax, exempting personal income tax for those receiving monthly income below 1,600 yuan, and increasing investments in rural infrastructure, education, and health services to boost consumption and development in rural areas.
External dependency - The mainland Chinese economy has a great dependence on foreign trade and investments. Investment and export sectors collectively account for about 80% of mainland Chinese GDP and are still growing at close to a 30% annual rate. This is an unsustainable outcome for China (and the US on the consumption side of the global economy). Further sharp increases in investment are a recipe for capacity overhangs and deflation, which could cause an abundance of goods to sell with no countries to sell them to. A scenario such as this is very similar to what caused worldwide recession in the 1930s. Continued sharp gains in exports are a recipe for trade frictions and possibly protectionism in other countries. China is now proposing to tackle its excess saving and subpar consumption story with the same fervor evident when it went after other aspects of its growth and reform story during the past 28 years. Pilot projects already have been established in setting up a safety net, especially in the social security area; moreover, under the terms of China’s WTO accession, the opening of domestic services is likely to accelerate over the next 3–5 years, thereby relieving some of China's external dependency.
Currency valuation - In response to mainland China's ballooning trade surplus with the West, Western governments assert that its currency (see Renminbi) is currently greatly undervalued. Some also assert that the PRC government has unfairly manipulated the yuan exchange rate. When the currency is thoroughly revalued, it is possible that the outsourcing of jobs to mainland China would lessen somewhat. While a stronger currency is a concern for mainland China's manufacturing industry, a positive effect could see the reduction of mainland China's over-reliance on foreign trade and investments as the current main engine for its economic growth. It will thus cause domestic consumption to increase its role in fuelling the economic growth. This type of growth would be more stable towards external economic conditions and sustainable for longer periods of time. In 2005, the share of domestic consumption in mainland China's overall GDP has fallen to slightly less than 50%, significantly below the U.S. share of 71% (most other industrialized nations such as the U.K., Japan, and Australia have shares of around 60-70%).
Trade imbalance - Mainland China's overall trade surplus has increased dramatically in recent years creating an imbalance in the world economy. For example, mainland China keeps a trade surplus of US$200 billion with the United States. However, products that are labelled Made in China are not necessarily developed or designed in mainland China. In fact, 60% of mainland Chinese goods that are exported come from overseas-invested factories, according to PRC customs data (note though, Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan, which make up the majority portion of investments in China, are considered overseas and separate from mainland China in PRC economic data). Mainland China has become a focal point for assemblies, where final products are assembled and/or tested, but not necessarily manufactured there. The main components are often imported from other countries. Thus, despite mainland China's huge trade surplus with the West, it has a trade deficit of US$137 billion with Asian countries (Taiwan: US$58 billion, South Korea US$42 billion, Japan: US$16.5 billion).
Intellectual property rights (IPR) violation - The "epidemic" of piracy in mainland China is spreading. For instance, U.S., European and Japanese companies had reported combined losses to mainland Chinese piracy of at least US$60 billion in 2003. Piracy in mainland China is rampant and negatively affects everything from computer software and pharmaceuticals to clothing, auto parts and chewing gum. It affects both mainland Chinese and foreign IPR holders, and is a growing concern for major trading partners such as the United States and the European Union. Such IPR violation may reduce mainland China's creative power potential and hold back mainland China's own innovators and entrepreneurs.
Deteriorating environment - As a result of previous and current growth-at-all-costs strategy, mainland China's environment is in a state of serious degradation. Soil erosion, desertification, air pollution, loss of arable lands, and steady falling of water table especially in the north are serious problems and are estimated to cost the mainland Chinese economy billions of dollars per year. Water is already a scarce commodity in mainland China (especially in northern arid regions) where per capita water supplies are less than a quarter of the world's average. Pollution from coal causes over 250,000 deaths annually. By 2020, it is predicted that mainland China will account for up to 19 per cent of global carbon dioxide emissions. Currently, water in China contains dangerously high level of radiation, which has led to radiation-related death and sickness, particularly within its Fujian Province. To respond to these problems, the PRC government has embarked upon a number of projects such as Great Green Wall project (planting billions of trees to hold back desertification) and building canals to divert water from water-abundant southern regions to arid northern regions.
Economic crimes - Due to the lack of openness of the mainland Chinese society in general, economic crimes such as corruption and collusion have become rampant among party and government officials, and this may hinder mainland China's economic growth and hurt the confidence of investors. Combined with worsening social problems in mainland China (due to wide urban-rural income gap), there have been growing social discontent and about 87,000 big and small-scale demonstrations occurred throughout mainland China in 2005. Most of these discontents are not political; rather they are due to economic reasons. Peasants for example, are being forced to leave their land and are compensated poorly. Their confiscated lands are then sold at a much higher price with the local officials keeping much of the profits.
Technology and academic quality - In some technology fields, mainland China is still behind its counterparts such as the United States, Russia and the European Union, and lacks in the number of leading world-class research scientists. Furthermore, despite the large number of university graduates produced in mainland China every year, only a relatively small fraction has sufficient quality or professional experience to work in multinational companies (MNCs). The Chinese government is trying to address the problem by giving massive injections of governmental funding into mainland Chinese universities and hopes to transform them into world-class institutions. These funds are intended for attracting top foreign-educated and overseas-born Chinese, building cutting-edge research centers, partnering with the world's best educational institutions, and developing new programs taught in English. However, despite this, China's weak High-Tech export industry lacks economic competitiveness and a capacity for independent innovation. In PC exports, China's real export is less than $10 billion and the sales profability of high-tech industries from China has decreased, indicating that other nations around the world are reaping rewards of strong high-tech economies.
Demographic problems
One-child policy - A side effect of the One-child policy is mainland China's rapidly aging population. It is predicted that by 2020, 25% of mainland China's population will be considered retirees, so they cannot contribute to the work force. It is expected that by the 2040s, 430 million Chinese will be above the age of sixty. This could disadvantage its economy, but on the other hand many feel uncontrolled population growth is not a feasible option either. Although officially banned by the central government, local authorities - under the pressure of job promotion - sometimes committed forced abortions in order to enforce the One-child policy. Cultural preference over sons has also encouraged gender-based abortion including female infanticide, despite it being illegal in mainland China. If trends continue, there will be 30-40 million more men of marriageable age in 2020 than there are women.
Continued overpopulation - Recent findings have also shown that despite the One-Child policy, China is still growing at an uncontrollable rate. The total population of China is set to reach 1.5 billion in 2033. By this point, it is expected that the Chinese people will be strained for water and food resources. The continued overpopulation also means there will be increased demand for jobs, leading to rampant unemployment damaging the economy.
Cultural problems
Loss of history - The Cultural Revolution which China experienced in the 1960s-70s had devastated a significant part of China's historical and cultural relics. In the modern times, the government has tried to revive traditional Confucian values (political catch-phrase: "harmonious society") and embarked on public initiatives to protect and preserve Chinese cultural heritage as well as historical artifacts. However, more often than not, such initiative comes head-to-head against China's desire to modernize itself rapidly. For instance, traditional hutong (in Beijing) and shikumen (in Shanghai) homes are being demolished at an alarming rate to make way for modern developments such as high-rises and wide boulevards. Even when buildings are designated as protected or historic sites, they can be knocked down in the frenzy of development. Local officials often collude with private developers or accept bribes. The encroachment of globalization (especially Western culture) has also resulted in the fading of Chinese traditions. The impact of such loss on the society is debatable although the pursuit for raw materialism over the past few decades have left a spiritual void among the Chinese. As a result, many Chinese today are interested in rediscovering their connection with the past.
Loss of writing system - Some traditional Chinese users, especially for Taiwanese, often criticise the formal use of simplified Chinese in China and Southeast Asian countries such as Singapore and Malaysia because the communist attempt to simplify traditional characters is believed to be negating China's cultural past because as more and more young Chinese people read only simplified text and forget traditional Chinese, there will be few who will be able to translate and read ancient Chinese artifacts and scrolls. However it has also been reported that readers of simplified Chinese are able to read traditional Chinese without much difficulty, while those who read traditional Chinese are not able to read simplified Chinese.
See also
- China
- Chinese Century
- Chinese economic reform
- Chinese nationalism
- China's peaceful rise
- Chinese space program
- Culture of China
- Economy of the People's Republic of China
- Social issues in the People's Republic of China
- Foreign relations of the People's Republic of China
- Greater China
- List of tributaries of Imperial China
- Military of the People's Republic of China
- Pax Sinica
- People's Liberation Army
- Politics of the People's Republic of China
- Science and technology in China
- Sports in China
- Transportation in the People's Republic of China
External links
- TIME Magazine - The Chinese Century
- OECD/United Nations University video interview - the rise of China and the consequences for Africa
- Yahoo! News - China poised to attain superpower status: US intelligence czar
- FAS - China: the Emerging Superpower
- Conference of Defence Associations Institute: China's Superpower Challenge
- CNN Specials: Asian Superpower
- BBC: Is China The Next Superpower?
- Rediff.com - Americans think China will be superpower before India
- TIME.COM Special: China
- Deutsche Bank Research: China as potential superpower - regional responses
- Telegraph News: Blast-off for China's superpower dream
- U.S. State Department: China's Emergence as an Economic Superpower and Its Implications for U.S. Business
- The Independent: America meets the new superpower
- New York Times: China economy even larger than thought
- Electronic Business Online: Is China the next R&D superpower?
- Essay: "The Middle Kingdom, The Reinstatement of a Revisionist Great Power ", by Aron Patrick
References
- Oded Shenkar The Chinese Century: The Rising Chinese Economy and Its Impact on the Global Economy, the Balance of Power, and Your Job
- Both disputed and undisputed regions under PRC's effective administration
- According to the CIA - The World Factbook, China has an area of "9,596,960 square kilometres (3,705,410 sq mi) - slightly smaller than the US".CIA - The World Factbook
- Covering a total land area of 9,326,410 km², CIA - The World Factbook
- China Internet Information Center National Conditions: Mineral Resources
- Encyclopædia Britannica China's natural resources
- Encyclopædia Britannica China's hydroelectric resources
- Alexander's Gas and Oil Connections China has huge potential in hydroelectric generation
- The Geography of Poverty and Wealth, Scientific American
- The Wealth and Poverty of Nations Chapter 1
- CIA - The World Factbook
- Health in China: The one child family policy: the good, the bad, and the ugly
- Economic Survey 2004-05, Economic Division, Ministry of Finance, Government of India, quoting UNDP Human Development Report 2004.
- Chinese Army Modernization: An Overview, by Lieutenant Colonel Dennis J. Blasko
- The Components of the Armed Forces, by PRC Government's Official Web Portal
- US Department of Defense The Military Power of the People's Republic of China
- BBC China's military budget jumps 14%
- The Jamestown Foundation China's Global Strategy For Energy, Security and Diplomacy
- New York Times China Competes With West in Aid to Its Neighbors
- China Passes U.S. In Trade With Japan
- Trade Policy Outlook for Second-term Bush Administration
- CHINA - TAIWAN ECONOMIC TIES
- The Jamestown Foundation BEIJING'S GROWING POLITICO-ECONOMIC LEVERAGE OVER ULAANBAATAR
- Taipei Times Beijing outpaces Seoul with North Korean influence
- Japan Focus Article The Shanghai Cooperation Organization: Institutionalization, Cooperation and Rivalry
- YaleGlobal Online Central Asia: China's Mounting Influence
- Nuclear Threat has World on Edge
- Daily Telegraph Iraqi terrorists 'are being supplied with arms smuggled from Iran
- Experts Fret Over Chinese role in Weapons Proliferation Space Daily
- The Washington Institute for Near East Policy China and Oil: The Middle East Dimension
- MERIA China'S WMD Foot In The Greater Middle East's Door
- Asia Times China stakes its Middle East claim
- ^ China's March on South Asia, by Tarique Niazi, China Brief, the Jamestown Foundation
- USCC China's Strategic Reach Into Southeast Asia
- Los Angeles Times Southeast Asia's new best friend
- Japan Focus Article China’s Rise in Southeast Asia: Implications for Japan and the United States
- The Heritage Foundation China's Influence in Africa: Implications for the United States
- China to double its aid to Africa BBC News, 4 November 2006.
- ^ The perils of Beijing's Africa strategy, International Herald Tribune
- The Heritage Foundation China's Influence in the Western Hemisphere
- CNSnews.com China Moving to Replace US Influence in South America
- Columbia Daily Tribune Caribbean sees China acquire more influence
- United Transportation Union Cuba turns to China for transpo needs
- GlobalSecurity.org China Increasing Military Ties in South America as Law Restricts US Military
- Deng Xiaoping's Southern Tour: Elite Politics in Post-Tiananmen China by Suisheng Zhao, UCLA Press, 1993.
- MSNBC Newsweek Does the Future Belong to China?
- New York Times Chinese Economy Grows to 4th Largest in the World
- Center for International Comparisons at the University of Pennsylvania Penn World Table
- CIA - The World Fact Book
- Chinese to climb ranks of world’s richest Financial Times
- People's Daily Online China's Longest Expressway Encircling City Operational
- TIMEasia Shanghai Swings!
- The US-China Business Council US-China Trade Statistics and China's World Trade Statistics
- CIA -The World Factbook
- CIA - The World Factbook
- CNN News - World's Top Traders
- US Department of State China's Influence in the Western Hemisphere
- BBC News China reserves reach $1 trillion
- ^ CHINAGATE Expressways Being Built at Frenetic Pace
- CIA - The World Factbook
- CIA - The World Factbook
- Deloitte Report China and India: The Reality Beyond the Hype
- The Globalist Dateline India: From Mumbai to Pune
- Rediff.com India is China's economic equal? Bah!
- "China overtakes Japan on R&D" Financial Times. Accessed 3 December 2006.
- OECD: China to spend $136 billion on R&D BusinessWeek. Retrieved 3 December 2006.
- BusinessWeek A New Lab Partner For The U.S.?
- Space Today China's Astronauts
- Harvard University The Rise of China's Soft Power
- World's Top Tourism Destinations
- Asian destinations on the rise in world tourism ranking
- Harvard University The Rise of China's Soft Power
- CIA - The World Factbook
- John K. Fairbank, China: A New History, Harvard University Press, ISBN 0-674-11670-4, p2
- Paul S. Ropp (ed.), Heritage of China, University of California Press, ISBN 0-520-06440-2, p235
- CIA The World Factbook
- WHERE AND WHO ARE THE WORLD’S ILLITERATES: CHINA
- BBC News China's race for 'frontier' science
- The International Mathematical Olympiad IMO
- The International Chemistry Olympiad IChO
- The International Physics Olympiad IPhO
- The International Biology Olympiad IBO
- Asia Times Overseas Chinese: How powerful are they?
- Finnish Virtual Polytechnic Overseas Chinese influence in Asian business world
- Where Has the Premium Gone? Eric Chaney (London), Morgan Stanley, Feb 22, 2006. Retrieved: December 28, 2006.
- Confucius and Confucianism
- EVAN A. FEIGENBAUM, "China's Military-Civilian Complex," New York Times, May 22, 1998
- Planes, Subs and Destroyers
- The Age Beware red democrats under our beds.
- The Information Warfare Site (U.S. Dept. of State) Information Technologies Critical to Achieving Development Goals
- Center for the Study of Intelligence (CIA) The Chinese Media: More Autonomous and Diverse--Within Limits
- The Christian Science Monitor Chinese media resisting party control
- Harvard Law School Empirical Analysis of Internet Filtering in China
- Pakistan Times Pakistan demands equality of treatment by US in N-area
- MERIA China's WMD Foot In The Greater Middle East's Door
- The Washington Post In Africa, China Trade Brings Growth, Unease
- The New York Times A Judge Tests China's Courts, Making History
- BBC News China's parliament to debate rule of law
- U.S. Congress (July 24, 2002) "H.CON.RES.188 for the 107th Congress (2nd Session)", Library of Congress, retrieved July 31, 2006
- Rise in Non-English Spam Challenges Junk Mail Filters, by VAUHINI VARA
- China Dissidents Thwarted on Net, by Associated Press
- Nine Commentaries on the Community Party, by the Epoch Times
- Dateline SBS, 12 July 2006
- Jamyang Norbu The Case for Tibetan Independence
- University of Michigan A China Odyssey
- Strength From Their Faith, by Sarah Schafer and Jonathan Ansfield, Newsweek International
- China's Abuses Ignored for Profit, by Catherine Edwards
- ^ China's Emergence as an Economic Superpower and Its Implications for U.S. Business,United States Department of State
- BBC News China's unemployment challenge
- RAND Corporation China's Rising Unemployment Challenge
- Xinhua Millions of graduates facing unemployment
- ALN China's western region development strategy and the urgent need to address creeping environmental problems
- Asia Times Reviving northeast China
- Chinese Government's Official Web Portal Premier stresses rise of central region
- The World Bank Labor market distortions, rural-urban inequality, and the opening of China's economy
- Embassy of the People's Republic of China in the United States of America Household income doubles in China
- The World Bank World Development Indicators 2005: Reducing poverty and hunger
- USA TODAY Report illustrates huge gap between China's rich, poor
- China.org.cn World Bank Managing Director: China's Poverty Reduction Provides Lessons, Experience for Others
- ABC News China to Abolish Ancient Agricultural Tax
- BBC News China legislates to cut wage gap
- BusinessWeek China's "New Socialist Countryside"
- Morgan Stanley Global: Passing Ships in the Night
- Association for Asian Research Is the Chinese Yuan undervalued?
- Forex Blog Chinese Yuan (RMB)
- Milwaukee Journal Sentinel Chinese yuan irks U.S. business
- Morgan Stanley Global: Passing Ships in the Night
- Morgan Stanley Global: The Fallacy of International Comparisons
- U.S. Census Bureau Trade in Goods (Imports, Exports and Trade Balance) with China
- BusinessWeek Learning from China's Export Boom
- Asia Times Over to Chinese MNCs
- CFO China-U.S. Trade Imbalance Surges
- The Washington Times China trade deficit travail
- U.S. Department of State Chinese Counterfeits Hurting Industry in China, Experts Say
- U.S. Department of State Commerce Chief Urges China To Protect Intellectual Property
- ^ The Age Beware red democrats under our beds
- New Scientist Don't drink the water, it's radioactive
- FAS China - Corruption
- The Guardian The big steal
- People's Daily China arrests 20,425 suspects for economic crimes in 2004
- World Economic Forum The Road Ahead for China
- NPR China Faces Academic Corruption, Quality Problems
- BusinessWeek Don't Be Afraid of Offshoring
- People's Daily China has a surplus of poor-quality MBA, interview
- Asia Times China hunts abroad for academic talent
- ^ Asia Times High-tech industries still weak despite growth
- ^ The Age China's Population Growth Nightmare
- TIME Back-Alley Blues.
- Shanghai Film Mours Loss of Past, July 22, 2006, Howard W. French, A Glimpse of the World
- Asia Times China's cultural revival struggles
- Asia Times Han follow suit in cultural renaissance
- Taipei Times Write more to safeguard traditional characters
- Simplified Spelling Society AGM 2004