| Revision as of 07:01, 11 July 2016 edit219.79.97.21 (talk) →January← Previous edit | Revision as of 07:03, 11 July 2016 edit undo219.79.97.21 (talk) →MayNext edit → | ||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
| '''May 28''' | '''May 28''' | ||
| ] | |||
| *21:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. EDT) at {{Coord|31.1|-79.4|name=Tropical Depression Two strengthens into Tropical Storm Bonnie}} – Tropical Depression Two intensifies into ] roughly 125 miles (195 km) south-southeast of Charleston, South Carolina.<ref>{{cite web|author=Stacy R. Stewart|location=Miami, Florida|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/archive/2016/al02/al022016.public.005.shtml|title=Tropical Storm Bonnie Public Advisory Number 5|publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration|agency=National Hurricane Center|date=May 28, 2016|accessdate=May 28, 2016}}</ref> | *21:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. EDT) at {{Coord|31.1|-79.4|name=Tropical Depression Two strengthens into Tropical Storm Bonnie}} – Tropical Depression Two intensifies into ] roughly 125 miles (195 km) south-southeast of Charleston, South Carolina.<ref>{{cite web|author=Stacy R. Stewart|location=Miami, Florida|url=http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/archive/2016/al02/al022016.public.005.shtml|title=Tropical Storm Bonnie Public Advisory Number 5|publisher=National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration|agency=National Hurricane Center|date=May 28, 2016|accessdate=May 28, 2016}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 07:03, 11 July 2016
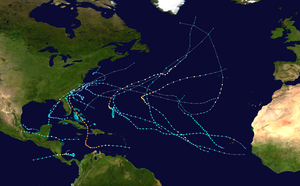
The 2016 Atlantic hurricane season is a current event in the annual tropical cyclone season in the North Hemisphere. The season officially began on June 1, 2016 and ends on November 30, dates adopted by convention that historically describe the period in each year when most systems form. The season's first storm, Hurricane Alex, developed on January 13, marking the first Atlantic hurricane to exist in January since Alice in 1955 and the first to form in the month since 1938. Upon making landfall in the Azores, Alex became the first January landfalling tropical cyclone since Alice.
This timeline includes information that was not operationally released, meaning that data from post-storm reviews by the National Hurricane Center, such as a storm that was not operationally warned upon, has been included. This timeline documents tropical cyclone formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, and dissipations during the season.
| Related articles | 2016 Atlantic hurricane season |
Timeline of events

January
January 13
- 21:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. AST) at 27°06′N 30°48′W / 27.1°N 30.8°W / 27.1; -30.8 (Subtropical Storm Alex develops) – Subtropical Storm Alex develops from an area of low pressure about 785 miles (1,260 km) south-southwest of the Azores.
January 14

- 15:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. AST) at 31°30′N 28°24′W / 31.5°N 28.4°W / 31.5; -28.4 (Subtropical Storm Alex transitions into a fully tropical cyclone and becomes a hurricane) – Subtropical Storm Alex transitions into a fully tropical cyclone, intensifies into a Category 1 hurricane, and attains its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 85 mph (140 km/h) roughly 490 miles (790 km) south of Faial Island, Azores.
January 15
- 15:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. AST) at 39°18′N 27°00′W / 39.3°N 27.0°W / 39.3; -27.0 (Hurricane Alex weakens to a tropical storm) – Hurricane Alex weakens to a tropical storm approximately 35 miles (55 km) north of Terceira Island, Azores.
- 21:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. AST) at 43°00′N 27°48′W / 43.0°N 27.8°W / 43.0; -27.8 (Tropical Storm Alex transitions into an extratropical cyclone) – Tropical Storm Alex transitions into an extratropical cyclone about 290 miles (470 km) north of Terceira Island, Azores.
May
May 27
- 21:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. EDT) at 28°30′N 74°42′W / 28.5°N 74.7°W / 28.5; -74.7 (Tropical Depression Two forms) – Tropical Depression Two develops from an area of low pressure roughly 435 miles (695 km) southeast of Charleston, South Carolina.
May 28

- 21:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. EDT) at 31°06′N 79°24′W / 31.1°N 79.4°W / 31.1; -79.4 (Tropical Depression Two strengthens into Tropical Storm Bonnie) – Tropical Depression Two intensifies into Tropical Storm Bonnie roughly 125 miles (195 km) south-southeast of Charleston, South Carolina.
May 29
- 03:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. EDT, May 28) at 31°00′N 79°30′W / 31.0°N 79.5°W / 31.0; -79.5 (Bonnie's peak intensity) — Tropical Storm Bonnie attains its initial peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 45 mph (75 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 1008 mb (hPa; 29.77 inHg) about 130 miles (205 km) south-southeast of Charleston, South Carolina.
- 12:00 UTC (8:00 a.m. EDT) at 32°42′N 79°36′W / 32.7°N 79.6°W / 32.7; -79.6 (Tropical Storm Bonnie weakens to a tropical depression) – Tropical Storm Bonnie weakens to a tropical depression roughly 25 miles (40 km) east-southeast of Charleston, South Carolina.
- 12:30 UTC (8:30 a.m. EDT) at 32°48′N 79°48′W / 32.8°N 79.8°W / 32.8; -79.8 (Tropical Depression Bonnie makes landfall) – Tropical Depression Bonnie makes landfall on the South Carolina coast about 10 miles (20 km) east of Charleston, South Carolina.
May 30
- 15:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. EDT) at 33°24′N 79°48′W / 33.4°N 79.8°W / 33.4; -79.8 (Tropical Depression Bonnie becomes a remnant low) – Tropical Depression Bonnie degenerates into an area of low pressure about 45 miles (75 km) north-northeast of Charleston, South Carolina.
June
June 1
- The 2016 Atlantic hurricane season officially begins.
June 2
- 15:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. EDT) at 35°06′N 75°06′W / 35.1°N 75.1°W / 35.1; -75.1 (Bonnie regenerates) – The remnants of Tropical Depression Bonnie regenerate into a tropical depression about 25 miles (40 km) east-southeast of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina.
June 3
- 21:00 UTC (5:00 p.m. EDT) at 35°54′N 70°30′W / 35.9°N 70.5°W / 35.9; -70.5 (Tropical Depression Bonnie restrengthens) – Tropical Depression Bonnie re-intensifies into a tropical storm roughly 285 miles (460 km) east of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, attaining a secondary peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 40 mph (65 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 1006 mb (hPa; 29.71 inHg).
June 4
- 15:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. EDT) at 35°36′N 66°24′W / 35.6°N 66.4°W / 35.6; -66.4 (Tropical Storm Bonnie weakens again) – Tropical Storm Bonnie weakens into a tropical depression roughly 245 miles (395 km) north-northwest of Bermuda.
June 5
- 03:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. AST, June 4) at 34°42′N 63°36′W / 34.7°N 63.6°W / 34.7; -63.6 (Bonnie dissipates) – Tropical Depression Bonnie degenerates into a remnant low about 180 miles (290 km) north-northeast of Bermuda.
- 15:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. CDT) at 21°54′N 88°06′W / 21.9°N 88.1°W / 21.9; -88.1 (Tropical Depression Three forms) – Tropical Depression Three develops from an area of low pressure roughly 125 miles (200 km) northwest of Cozumel, Mexico.
- 21:30 UTC (4:30 p.m. CDT) at 23°18′N 87°54′W / 23.3°N 87.9°W / 23.3; -87.9 (Three strengthens into Tropical Storm Colin) – Tropical Depression Three intensifies into Tropical Storm Colin about 465 miles (750 km) southwest of Tampa, Florida.
June 6
- 09:00 UTC (4:00 a.m. CDT) at 25°12′N 87°24′W / 25.2°N 87.4°W / 25.2; -87.4 (Colin reaches peak winds) – Tropical Storm Colin reaches peak winds of 50 mph (85 km/h) about 360 miles (580 km) west-southwest of Tampa, Florida.
June 7
- 03:00 UTC (11:00 p.m. EDT, June 6) at 29°48′N 83°48′W / 29.8°N 83.8°W / 29.8; -83.8 (Colin makes landfall in Florida) – Tropical Storm Colin makes landfall in the Big Bend region of Florida.
- 12:00 UTC (8:00 p.m. EDT) at 33°36′N 77°48′W / 33.6°N 77.8°W / 33.6; -77.8 (Colin attains minimum pressure) – Tropical Storm Colin attains its minimum pressure of 1000 mb (hPa; 29.53 inHg) about 45 miles (75 km) south of Wilmington, North Carolina.
- 15:00 UTC (11:00 a.m. EDT) at 34°00′N 77°00′W / 34.0°N 77.0°W / 34.0; -77.0 (Colin becomes post-tropical) – Tropical Storm Colin degenerates into a post-tropical cyclone about 120 miles (190 km) southwest of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina.
November
November 30
- The 2016 Atlantic hurricane season officially ends.
See also
- List of Atlantic hurricanes
- Timeline of the 2016 Pacific hurricane season
- Timeline of the 2016 Pacific typhoon season
Footnotes
- The figures for maximum sustained winds and position estimates are rounded to the nearest 5 units (knots, miles, or kilometers), following the convention used in the National Hurricane Center's operational products for each storm. All other units are rounded to the nearest digit.
References
- ^ Christopher W. Landsea; Neal Dorst; Erica Rule (June 2, 2011). "G: Tropical Cyclone Climatology". Hurricane Research Division: Frequently Asked Questions. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. G1) When is hurricane season ?. Retrieved January 22, 2016.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - Richard J. Pasch (January 14, 2016). "Hurricane Alex Discussion Number 4". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 22, 2016.
- Bob Henson (January 15, 2016). "Astounding Alex Hits the Azores: January's First Atlantic Landfall in 61 Years". Weather Underground. Retrieved January 22, 2016.
- Richard J. Pasch (January 13, 2016). "Subtropical Storm Alex Public Advisory Number 1". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 22, 2016.
- Richard J. Pasch (January 14, 2016). "Hurricane Alex Public Advisory Number 4". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 22, 2016.
- Richard J. Pasch (January 15, 2016). "Tropical Storm Alex Public Advisory Number 8". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 22, 2016.
- Richard J. Pasch (January 15, 2016). "Post-Tropical Cyclone Alex Public Advisory Number 9". Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 22, 2016.
- Stacy R. Stewart (May 27, 2016). "Tropical Depression Two Public Advisory Number 1". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 27, 2016.
- Stacy R. Stewart (May 28, 2016). "Tropical Storm Bonnie Public Advisory Number 5". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 28, 2016.
- Michael Brennan (May 28, 2016). "Tropical Storm Bonnie Public Advisory Number 6". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 5, 2016.
- Daniel Brown; Todd Kimberlain (May 29, 2016). "Tropical Depression Bonnie Intermediate Advisory Number 7A". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 29, 2016.
- Daniel Brown; Todd Kimberlain (May 29, 2016). "Tropical Depression Bonnie Tropical Cyclone Update". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 29, 2016.
- Todd Kimberlain (May 30, 2016). "Post-Tropical Cyclone Bonnie Public Advisory Number 12". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 30, 2016.
- Jack Beven (June 2, 2016). "Tropical Depression Bonnie Public Advisory Number 24". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 5, 2016.
- Jack Beven (June 3, 2016). "Tropical Storm Bonnie Public Advisory Number 29". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 5, 2016.
- John Cangialosi (June 4, 2016). "Tropical Depression Bonnie Public Advisory Number 32". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 5, 2016.
- Eric Blake (June 4, 2016). "Post-Tropical Cyclone Bonnie Public Advisory Number 34". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 5, 2016.
- Daniel Brown (June 5, 2016). "Tropical Depression Three Public Advisory Number 1". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 5, 2016.
- Richard J. Pasch (June 5, 2016). "Tropical Storm Colin Tropical Cyclone Update". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 5, 2016.
- John Beven (June 6, 2016). "Tropical Storm Colin Public Advisory Number 4". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 12, 2016.
- Richard Pasch (June 7, 2016). "Tropical Storm Colin Public Advisory Number 7". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 12, 2016.
- Daniel Brown (June 7, 2016). "Tropical Storm Colin Intermediate Public Advisory Number 8a". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 12, 2016.
- Daniel Brown (June 7, 2016). "Post-Tropical Cyclone Colin Public Advisory Number 9". Miami, Florida: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 12, 2016.
External links
| Tropical cyclones of the 2016 Atlantic hurricane season | ||
|---|---|---|
 | 1Alex TSBonnie TSColin TSDanielle 1Earl TSFiona 3Gaston TDEight 1Hermine TSIan TSJulia TSKarl TSLisa 5Matthew (history) 4Nicole 3Otto | |
| 2016–2025 Atlantic hurricane seasons | |
|---|---|
| Preceded by2015 | Atlantic hurricane season timelines 2016 |
Succeeded by2017 |