| Revision as of 20:25, 18 March 2019 editTJ.Jang (talk | contribs)60 editsNo edit summaryTag: Visual edit: Switched← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:27, 18 March 2019 edit undoTJ.Jang (talk | contribs)60 edits Undid revision 888388591 by TJ.Jang (talk)Tag: UndoNext edit → | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 57: | Line 48: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| <br /> | <br /> | ||
Revision as of 20:27, 18 March 2019
A condensation reaction is a class of an organic addition reaction that proceeds in a step-wise fashion to produce the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and a water molecule (hence named condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule and formation of ammonia, ethanol, or acetic acid. It is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and the biosynthesis of fatty acids.
List of Reactions
Acidic condition
Glycosidic bond
Monosaccharides are the basic unit of the carbohydrates and blocks to build the Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides. Through the condensation reaction, Monosaccarides increase the weight of molecules and reach higher degree of polymerization(Polysaccharide), while losing water molecules. This is the acid-catalyzed reaction and produce heavier carbohydrate.

Basic condition
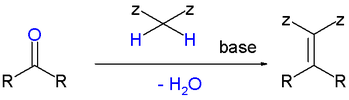
Aldol condensation
After the adol reaction, which is a reaction of an enol or an enolate ion with carbonyl compound, dehydration process follows. This dehydration (Aldol condensation) provide a way to form carbon-carbon bonds in organic synthesis.

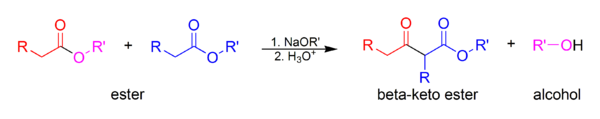
Claisen condensation
In the base condition, two ester or ester and carbonyl forms carbon-carbon bond and result in another ester or diketone. The equivalent reaction of intermolecular is Dieckmann condensation
Dieckmann condensation
It is a intramolecular reaction of diesters with base.
Knoevenagel condensation
As a variation of aldol condensation, it is a reaction between active hydrogen and carbonnyl group (aldehyde or ketone)

See also
- Anabolism
- Hydrolysis, the opposite of a condensation reaction
- Condensed tannins
References
- Fakirov, S. (2019-02-01). "Condensation Polymers: Their Chemical Peculiarities Offer Great Opportunities". Progress in Polymer Science. 89: 1–18. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2018.09.003. ISSN 0079-6700.
- "Condensation Reaction". IUPAC Copendium of Chemical Terminology (Gold Book). IUPAC. Retrieved 7 December 2017.
- Voet, Donald; Voet, Judith; Pratt, Chriss (2008). Fundamentals of Biochemistry. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 88. ISBN 978-0470-12930-2.
- ^ Bruckner, Reinhard (2002). Advanced Organic Chemistry (First ed.). San Diego, California: Harcourt Academic Press. pp. 414–427. ISBN 0-12-138110-2.