| Revision as of 10:49, 5 February 2020 editBerosya (talk | contribs)80 editsNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 10:49, 5 February 2020 edit undoBerosya (talk | contribs)80 editsNo edit summaryNext edit → | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
| | reference = | | reference = | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The '''Arabian Sea''' is a region of the northern ] bounded on the north by ] and ], on the west by the ], ] and the ], on the southeast by the ],<ref>Banse, Karl, and Charles R. McClain. "Winter blooms of phytoplankton in the Arabian Sea as observed by the Coastal Zone Color Scanner." Marine Ecology Progress Series (1986): 201-211.</ref> on the southwest by the ],<ref>Pham, J. Peter. "Putting Somali piracy in context." Journal of Contemporary African Studies 28.3 (2010): 325-341.</ref> and on the east by ]. Its total area is 3,862,000 km<sup>2</sup> (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 4,652 meters (15,262 ft). The ] in the west connects the Arabian Sea to the ] through the strait of ], and the ] is in the northwest, connecting it to the ]. | The '''Arabian Sea''' is a region of the northern ] bounded on the north by ] and ], on the west by the ], ] and the ], on the southeast by the ],<ref>Banse, Karl, and Charles R. McClain. "Winter blooms of phytoplankton in the Arabian Sea as observed by the Coastal Zone Color Scanner." Marine Ecology Progress Series (1986): 201-211.</ref> on the southwest by the ],<ref>Pham, J. Peter. "Putting Somali piracy in context." Journal of Contemporary African Studies 28.3 (2010): 325-341.</ref> and on the east by ]. Its total area is 3,862,000 km<sup>2</sup> (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 4,652 meters (15,262 ft). The ] in the west connects the Arabian Sea to the ] through the strait of ], and the ] is in the northwest, connecting it to the ]. | ||
Revision as of 10:49, 5 February 2020
A marginal sea of the northern Indian Ocean between the Arabian Peninsula and India| Arabian Sea | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Coordinates | 14°N 65°E / 14°N 65°E / 14; 65 |
| Type | Sea |
| Part of | Indian Ocean |
| Basin countries | India, Iran, Maldives, Oman, Pakistan, Somalia, United Arab Emirates, Yemen |
| Max. width | 2,400 km (1,500 mi) |
| Surface area | 3,862,000 km (1,491,000 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 4,652 m (15,262 ft) |
| Islands | Astola island, Basavaraja Durga Island, Lakshadweep Islands, Piram Island, Pirotan, Socotra |
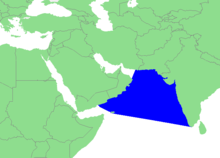
The Arabian Sea is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Peninsula, on the southeast by the Laccadive Sea, on the southwest by the Somali Sea, and on the east by India. Its total area is 3,862,000 km (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 4,652 meters (15,262 ft). The Gulf of Aden in the west connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and the Gulf of Oman is in the northwest, connecting it to the Persian Gulf.
The Arabian Sea has been crossed by many important marine trade routes since the third or second millennium BCE. Major seaports include Kandla Port, Okha Port, Mumbai Port, Nhava Sheva Port (Navi Mumbai), Mormugão Port (Goa), New Mangalore Port and Kochi Port in India, the Port of Karachi, Port Qasim, and the Gwadar Port in Pakistan, Chabahar Port in Iran and the Port of Salalah in Salalah, Oman. The largest islands in the Arabian Sea include Socotra (Yemen), Masirah Island (Oman), Lakshadweep (India) and Astola Island (Pakistan).
Geography

The Arabian Sea's surface area is about 3,862,000 km (1,491,130 sq mi). The maximum width of the Sea is approximately 2,400 km (1,490 mi), and its maximum depth is 4,652 metres (15,262 ft). The biggest river flowing into the Sea is the Indus River.
The Arabian Sea has two important branches — the Gulf of Aden in the southwest, connecting with the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb; and the Gulf of Oman to the northwest, connecting with the Persian Gulf. There are also the gulfs of Khambhat and Kutch on the Indian Coast.

The countries with coastlines on the Arabian Sea are Somalia, Yemen, Oman, Iran, Pakistan, India and the Maldives. There are several large cities on the sea's coast including Male, Kavaratti, Cape Comorin (Kanyakumari), Colachel, Kovalam, Thiruvananthapuram, Kollam, Alappuzha, Kochi, Kozhikode, Kannur, Kasaragod, Mangalore, Bhatkal, Karwar, Vasco, Panjim, Malvan, Ratnagiri, Alibag, Mumbai, Daman, Valsad, Surat, Bharuch, Khambhat, Bhavnagar, Diu, Somnath, Mangrol, Porbandar, Dwarka, Okha, Jamnagar, Kandla, Gandhidham, Mundra, Koteshwar, Keti Bandar, Karachi, Ormara, Pasni, Gwadar, Chabahar, Muscat, Duqm, Salalah, Al Ghaydah, Aden, Bargal, and Hafun.



Limits
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of the Arabian Sea as follows:
- On the west: the eastern limit of the Gulf of Aden .
- On the north: a line joining Ràs al Hadd, east point of the Arabian Peninsula (22°32'N) and Ràs Jiyùni (61°43'E) on the coast of Pakistan.
- On the south: a line running from the southern extremity of Addu Atoll in the Maldives, to the eastern extremity of Ràs Hafun (the easternmost point of Africa, 10°26'N).
- On the east: the western limit of the Laccadive Sea a line running from Sadashivgad on the west coast of India (14°48′N 74°07′E / 14.800°N 74.117°E / 14.800; 74.117) to Cora Divh (13°42′N 72°10′E / 13.700°N 72.167°E / 13.700; 72.167) and thence down the west side of the Laccadive and Maldive archipelagos to the most southerly point of Addu Atoll in the Maldives.
Alternative names
The Arabian Sea historically and geographically has been referred to with many different names by Arabian and European geographers and travelers, including Indian Sea, Sindhu Sagar, Darya, Sindhu Sagar, and Arab Samudra, Erythraean Sea, Sindh Sea, and Akhzar Sea. In Indian folklore, it is referred to as Darya, Sindhu Sagar, and Arab Samudra.
Trade routes
The Arabian Sea has been an important marine trade route since the era of the coastal sailing vessels from possibly as early as the 3rd millennium BCE, certainly the late 2nd millennium BCE through the later days known as the Age of Sail. By the time of Julius Caesar, several well-established combined land-sea trade routes depended upon water transport through the Sea around the rough inland terrain features to its north.

These routes usually began in the Far East or down river from Madhya Pradesh with transshipment via historic Bharuch (Bharakuccha), traversed past the inhospitable coast of today's Iran then split around Hadhramaut into two streams north into the Gulf of Aden and thence into the Levant, or south into Alexandria via Red Sea ports such as Axum. Each major route involved transhipping to pack animal caravan, travel through desert country and risk of bandits and extortionate tolls by local potentates.
This southern coastal route past the rough country in the southern Arabian Peninsula (Yemen and Oman today) was significant, and the Egyptian Pharaohs built several shallow canals to service the trade, one more or less along the route of today's Suez canal, and another from the Red Sea to the Nile River, both shallow works that were swallowed up by huge sand storms in antiquity. Later the kingdom of Axum arose in Ethiopia to rule a mercantile empire rooted in the trade with Europe via Alexandria.
Major ports

The Port of Karachi is Pakistan's largest and busiest seaport. It is located between the Karachi towns of Kiamari and Saddar.
The Gwadar Port is a warm-water, deep-sea port situated at Gwadar in Balochistan, Pakistan at the apex of the Arabian Sea and at the entrance of the Persian Gulf, about 460 km west of Karachi and approximately 75 km (47 mi) east of Pakistan's border with Iran. The port is located on the eastern bay of a natural hammerhead-shaped peninsula jutting out into the Arabian Sea from the coastline.
Port of Salalah in Salalah, Oman is also a major port in the area. The International Task Force often uses the port as a base. There is a significant number of warships of all nations coming in and out of the port, which makes it a very safe bubble. The port handled just under 3.5m teu (twenty-foot equivalent unit, a measure used for capacity in container transportation) in 2009.
Jawaharlal Nehru Port in Mumbai is the largest port in the Arabian Sea, and the largest container port in India. Major Indian ports in the Arabian Sea are Mundra Port, Kandla Port, Nava Sheva, Kochi Port, Mumbai Port, and Mormugão.
Islands
There are several islands in the Arabian Sea, with the most important ones being Lakshadweep Islands (India), Socotra (Yemen), Masirah (Oman) and Astola Island (Pakistan).
The Lakshadweep Islands (formerly known as the Laccadive, Minicoy, and Aminidivi Islands) is a group of islands in the Laccadive Sea region of Arabian Sea, 200 to 440 km (120 to 270 mi) off the southwestern coast of India. The archipelago is a Union Territory and is governed by the Union Government of India. The islands form the smallest Union Territory of India: their total surface area is just 32 km (12 sq mi). The lagoon area covers about 4,200 km (1,600 sq mi), the territorial waters area 20,000 km (7,700 sq mi) and the exclusive economic zone area 400,000 km (150,000 sq mi). The islands are the northernmost of the Lakshadweep-Maldives-Chagos group of islands.
Astola Island, also known as Jezira Haft Talar in Balochi, or 'Island of the Seven Hills', is a small, uninhabited island in the northern tip of the Arabian Sea in Pakistan's territorial waters.

Socotra, also spelled Soqotra, is the largest island, being part of a small archipelago of four islands. It lies some 240 km (150 mi) east of the Horn of Africa and 380 km (240 mi) south of the Arabian Peninsula.
Masirah is an island off the east coast of Oman.
Dead zone
The dead zone is an area in the Gulf of Oman that is completely depleted of oxygen, as a result of which it does not support marine life. It is the world's largest-known dead zone with an area larger than that of Scotland.
See also
Notes
- Banse, Karl, and Charles R. McClain. "Winter blooms of phytoplankton in the Arabian Sea as observed by the Coastal Zone Color Scanner." Marine Ecology Progress Series (1986): 201-211.
- Pham, J. Peter. "Putting Somali piracy in context." Journal of Contemporary African Studies 28.3 (2010): 325-341.
- Arabian Sea, Encyclopædia Britannica
- "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 October 2011. Retrieved 7 February 2010.
- ^ "Kamat's Potpourri: The Arabian Sea". kamat.com.
- "The Voyage around the Erythraean Sea". washington.edu.
- Salalah’s versatility beats the slump Archived October 25, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Port of Salalah
- "TRAFFIC HANDLED AT MAJOR PORTS (LAST 7 YEARS)" (PDF). shipping.gov.in.
- "WORLD PORT RANKINGS" (PDF). aapa.files.cms-plus.com. 2009.
- "World's largest 'dead zone' discovered, and it's not in the Gulf of Mexico". nola.com.
References
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Arabian Sea". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Arabian Sea". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
External links
![]() Media related to Arabian Sea at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Arabian Sea at Wikimedia Commons
| Hydrography of the Indian subcontinent | |
|---|---|
| Inland rivers | |
| Inland lakes, deltas, etc. | |
| Coastal | |
| Categories |
|
| Countries bordering the Arabian Sea | |
|---|---|
- Arabian Peninsula
- Marine ecoregions
- Arabian Sea
- India–Pakistan border
- Oman–Yemen border
- Bodies of water of Pakistan
- Bodies of water of India
- Bodies of water of Oman
- Seas of Yemen
- Bodies of water of Somalia
- Bodies of water of Iran
- Bodies of water of the Maldives
- Bodies of water of the United Arab Emirates
- Seas of the Indian Ocean
- Seas of Asia