| Revision as of 17:48, 22 December 2006 editJNShutt (talk | contribs)115 edits →Prelude: grammar fixes← Previous edit | Revision as of 17:55, 22 December 2006 edit undoJNShutt (talk | contribs)115 editsm →Siege of Konotop: grammar fixNext edit → | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| == Siege of Konotop == | == Siege of Konotop == | ||
| Prince ] hopes for quick resolution of the Konotop stand-off were dimmed when ] and his Cossacks refused point blank to betray hetman ] and mounted fierce and protracted defence of ]. On ], ] after a morning prayer ] ordered an all-out assault on the fortress's fortifications. The city was shelled, a few ] bombs were dropped inside and the huge army moved on to capture the city. At one point the troops of ] even broke inside the city walls but were thrown back by the fierce resistance of the Cossacks inside. After the fiasco of the initial assault ] abandoned his plans of a quick assault and proceeded to shell the city and to fill the ] with earth. The Cossacks stubbornly held on in spite of all the fire unleashed on the city: during the night the earth put to fill in the ] was used to strengthen the city walls and the besieged even undertook several daring counterattacks on ] besieging army. These attacks forced Prince ] to move his military camp 10 km away from the city and thereby |
Prince ] hopes for quick resolution of the Konotop stand-off were dimmed when ] and his Cossacks refused point blank to betray hetman ] and mounted fierce and protracted defence of ]. On ], ] after a morning prayer ] ordered an all-out assault on the fortress's fortifications. The city was shelled, a few ] bombs were dropped inside and the huge army moved on to capture the city. At one point the troops of ] even broke inside the city walls but were thrown back by the fierce resistance of the Cossacks inside. After the fiasco of the initial assault ] abandoned his plans of a quick assault and proceeded to shell the city and to fill the ] with earth. The Cossacks stubbornly held on in spite of all the fire unleashed on the city: during the night the earth put to fill in the ] was used to strengthen the city walls and the besieged even undertook several daring counterattacks on ] besieging army. These attacks forced Prince ] to move his military camp 10 km away from the city and thereby split his forces between the main army at his HQ and the army besieging ]. It is estimated that in the siege alone the Trubetskoy forces suffered casualties up to 10,000 men. Instead of a quick campaign the siege dragged on for 70 days and gave ] the much needed time to prepare for the battle with the ] army. | ||
| The hetman not only managed to organize his own troops, but secured support of his allies - the ] and the ]. By agreement with the Tatars the Khan ] at the head of his 30,000 strong army made his way towards ] in early summer of ], as did the 4000 men Polish detachment with the support of ], ] and ] ]. | The hetman not only managed to organize his own troops, but secured support of his allies - the ] and the ]. By agreement with the Tatars the Khan ] at the head of his 30,000 strong army made his way towards ] in early summer of ], as did the 4000 men Polish detachment with the support of ], ] and ] ]. | ||
Revision as of 17:55, 22 December 2006
| Battle of Konotop | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Ukrainian civil war - The Ruin 1657-1687 | |||||||
| Polish Hussar Petro Andrusiv. Hetman Vyhosky routes the tsar's army near Konotop. 1659 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Ukrainian Cossacks and their allies | Muscovy | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Ivan Vyhovsky | Aleksey Trubetskoy | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 60 000 | 150 000 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 4 000 Cossacks, 6 000 Tatars | 30 000 | ||||||
The Battle of Konotop (also known as Battle of Sosnivka) is a battle fought between the armies of hetman Ivan Vyhovsky and his allies and the armies of Muscovy led by prince Aleksey Trubetskoy on June 29, 1659 near the town of Konotop (now Sumska Oblast, Ukraine).
Prelude
This war happened during the period of Ukrainian history that is generally referred to as the Ruin. It was the time of incessant internal strife and intermittent civil war between different factions within the Ukrainian Cossack elite that were vying for power. This period started with the death of charismatic and a very influential hetman Bohdan Khmelnytsky in 1657.
During his reign Bohdan Khmelnytsky managed to wrestle Ukraine out from Polish domination but was forced to enter into new and uneasy union with Muscovy in 1654. His successor, general chancellor and a close adviser Ivan Vyhovsky was left to deal with Moscow's growing interference in Ukraine's internal affairs and even overt instigation of a civil war by way of supporting Cossack factions opposing Vyhovsky. With the situation deteriorating rapidly and opposition to his rule mounting, Vyhovsky was forced to enter into negotiations with his former foes, the Poles and finally to conclude a Treaty of Hadiach on September 16, 1658. Under the new treaty Ukraine was to become an equal constituent nation of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth along with Poland and Lithuania under a name of Principality of Rus.
This news alarmed Moscow to the extent that an expeditionary force was dispatched to Ukraine in the autumn of 1658 headed by Prince Grigory Romodanovsky. The Moscow's military commander not only appointed a new rival hetman of Ukraine but started actively to occupy towns held by Vyhovsky's supporters. The latter were mercilessly exterminated along with wide-spread abuse and robbery of the civilian population .
The situation having escalated that far, open hostilities followed. Skirmishes and attacks occurred in different towns and regions throughout the country, the most prominent of which was the capture of Konotop by Cossacks of the Nizhyn and Chernihiv Regiments headed by Hryhoriy Hulyanytsky, a colonel of Nizhyn. In the spring of 1659 a huge army - estimated to be 150,000 men strong - was dispatched to Ukraine to assist Romodanovsky. The supreme military commander Prince Aleksey Trubetskoy decided to finish off the small 4,000 garrison of the Konotop castle held by Cossacks of Hulyanytsky before proceeding in his pursuit of Vyhovsky.
Siege of Konotop
Prince Trubetskoy's hopes for quick resolution of the Konotop stand-off were dimmed when Hulyanytsky and his Cossacks refused point blank to betray hetman Vyhovsky and mounted fierce and protracted defence of Konotop. On April 21, 1659 after a morning prayer Trubetskoy ordered an all-out assault on the fortress's fortifications. The city was shelled, a few incendiary bombs were dropped inside and the huge army moved on to capture the city. At one point the troops of Trubetskoy even broke inside the city walls but were thrown back by the fierce resistance of the Cossacks inside. After the fiasco of the initial assault Trubetskoy abandoned his plans of a quick assault and proceeded to shell the city and to fill the moat with earth. The Cossacks stubbornly held on in spite of all the fire unleashed on the city: during the night the earth put to fill in the moat was used to strengthen the city walls and the besieged even undertook several daring counterattacks on Trubetskoy's besieging army. These attacks forced Prince Trubetskoy to move his military camp 10 km away from the city and thereby split his forces between the main army at his HQ and the army besieging Konotop. It is estimated that in the siege alone the Trubetskoy forces suffered casualties up to 10,000 men. Instead of a quick campaign the siege dragged on for 70 days and gave Vyhovsky the much needed time to prepare for the battle with the Muscovite army.
The hetman not only managed to organize his own troops, but secured support of his allies - the Crimean Tatars and the Poles. By agreement with the Tatars the Khan Mehmed IV Giray at the head of his 30,000 strong army made his way towards Konotop in early summer of 1659, as did the 4000 men Polish detachment with the support of Serbian, Moldavian and German mercenaries.
Battle
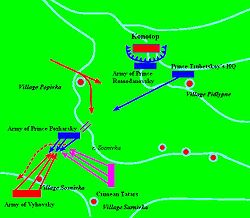
By June 24, 1659 Vyhovsky and his allies approached the area and defeated a small reconnaissance detachment of the Muscovite army near the village of Shapovalivka, several kilometers south-west of Konotop. From the prisoners it was learned that Prince Trubetskoy had transferred his camp from Konotop to the village of Pidlypne, 10 km east of the city, and that the Prince was not expecting the allies' arrival that soon. According to the plan made that evening the 30,000 Tatars were left in an ambush south-east of the river Sosnivka and Vyhovsky's forces with Poles and mercenaries were positioned at the village of Sosnivka, south of the river with the same name.
Meanwhile, Vyhovsky left the command of his forces to the brother of Hryhoriy Hulyanytsky - Stepan Hulyanytsky and at the head of a small Cossack detachment left for Konotop. Early morning of June 27, 1659 Vyhovsky's detachment attacked Trubetskoy's army near Konotop and using this sudden and unexpected attack managed to capture a sizable number of enemy's horses and drive them away and further into the step. The Muscovite army counterattacked and Vyhovsky retreated across the bridge to the other bank of the Sosnivka river in the direction of his camp. Having learned of the assault, Prince Trubetskoy dispatched a large detachment of 30,000 men led by Prince Semen Pozharsky and Cossacks of appointed rival hetman Bezpalyi across the river to pursue Ivan Vyhovsky. Trubetskoy's forces were thus divided between this detachment, those besieging Konotop and the 30,000 at his HQ.
On June 28, 1659 Prince Semen Pozharsky in his pursuit of the Cossacks crossed the river Sosnivka and made his camp on the southern bank of the river. During the night a small Cossack detachment led by Stepan Hulyanytsky having padded the hoofs of their horses with cloth, stole under the cover of night behind the enemy lines and captured the bridge that Pozharsky used to cross the river. The bridge was dismantled and the river dammed thus flooding the valley around it.
Early morning of June 29, 1659 Vyhovsky at the head of a small detachment attacked Prince Pozharsky's army. After a little skirmish with a far larger army than his he started to retreat feigning a disorganized flight in the direction of his main forces. Unsuspecting Pozharsky ordered his army to pursue the enemy. Once the Moscow's army entered Sosnivka, the Cossacks fired three cannon shots to give the signal to the Tatars and counterattacked with all the forces stationed at Sosnivka. Having discovered the trap Prince Semen Pozharsky ordered retreat but his heavy cavalry and the artillery got bogged down in the soggy ground created from the flooding the night before. At this moment the Tatars also advanced from the eastern flank and the outright slaughter ensued. Almost all 30,000 troops perished, only few of them captured alive. Among the captured were Prince Semen Romanovich Pozharsky himself, Prince Semen Petrovich Lvov, both Princes Buturlins, Prince Lyapunov, Prince Skuratov, Prince Kurakin and others. A relative of the Great Liberator of Moscow from the Poles Dmitry Pozharsky, Prince Semen Romanovich Pozharsky was brought before the Khan of Crimea Mehmed IV Giray, at whom Pozharsky, according to the witnesses, hurled obscenities and even spat in his face. For that he was promptly beheaded by the Tatars and his severed head was dispatched with one of the captives to Prince Trubetskoy's camp.
Having learned about the defeat of Pozharsky's army, Trubetskoy ordered the siege of Konotop lifted and started his retreat from Ukraine. At that moment the Cossacks of Hulyanytsky inside the fortress emerged from behind the walls and attacked the retreating army. Trubetskoy lost in addition, most of his artillery, his military banners and the treasury. The retreating army defended well and Vyhovsky and the Tatars abandoned their 3-day long pursuit near the Russian border.
Aftermath and significance
As Trubetskoy's troops arrived in Putivl, the the news of the battle reached Moscow as well. A prominent Russian historian of the 19th century Sergey Solovyov describes it this way:
- The bloom of Moscow's cavalry, troops that happily accomplished campaigns of year 54 and 55 have perished in one day - the victors got only about 5000 captive. The unfortunate were led onto an open space and slaughtered like lambs - that was the agreement between the Crimean Khan and the hetman of the Zaporozhian Cossacks! Never again was the tsar of Moscow able to master an army that strong. In mourning clothes showed himself Alexei Mikhailovich to the people and the terror seized Moscow. The blow was so hard because it was unexpected, and it followed such illustrious successes! It was only recently that Dolgoruki brought to Moscow a captured Lithuanian hetman, only recently was everyone talking about successes of Khovansky - and now Trubetskoy, for whom everyone had hopes higher than for others, and who was "a man devout and graceful, in military affairs skilled and a fright for a foe" - has ruined such a huge army! After capture of so many towns, after capture of the Lithuanian capital the royal city trembled for its own security: in August by tsar's decree people of all ranks hurried to build fortifications around Moscow. Often the tsar and the boyars were present themselves during the construction; people from outlying areas, their families with meagre belongings filled Moscow, and a rumour spread that the tsar was leaving to beyond the Volga and Yaroslavl.
However, the tsar of Muscovy did not have to worry, Ukrainian civil war of the Ruin period accomplished what Trubetskoy and his troops could not. Had only hetman Vyhovsky and his allies been able to capture a few of Ukrainian towns held by his opponents, when the first bad news arrived: Cossacks of the Zaporozhian Host lead by Ivan Sirko attacked Crimean outposts in the south and Khan Giray was forced to leave him for his country. So did the Poles and Vyhovsky was left to deal with the growing opposition to his rule. By the end of the year he resigned and was executed by the Poles in 1664. His defeat is largely attributed to his alliance with the very unpopular Poles and his inability to seek support among all the strata of the Ukrainian population and not just among the rich Cossack elite, who were willing to betray him at every opportunity either to Moscow or Warsaw. The civil war raged on and the victors of the Konotop battle were soon forgotten.
Together with a number of other battles between East Slavs, such as Battle of Orsha, the Konotop battle was an abandoned topic in Russian Imperial and in Soviet historiography. This attitude towards this event is explained by the fact that it dispelled some Russian propaganda positions about the unity of East Slavs, in particular the ones about "eternal friendship of Russian and Ukrainian peoples" and about "natural desire of Ukrainians for union with Russia". Lately, the Konotop battle has been idealized by some Ukrainians as well. For all the skill and the bravery of the Cossacks - especially those defending Konotop - it still remains a bitter victory. A victory that did not have any significant impact on the course of Ukrainian history, where fratricidal war of the Ruin and personal ambitions of treacherous hetmans prevailed. As such, the Konotop battle remains a classic example of the battle won and a war lost.
See also
Sources
- Orest Subtelny. Ukraine. A history. University of Toronto press. 1994. ISBN 0-8020-0591-0.
- David Mackenzie, Michael W. Curran. A History of Russia, the Soviet Union, and Beyond. Fourth Edition. Belmont, California. p. 200., 1993. ISBN 0-534-17970-3.
- Yuri Mytsyk. Battle of Konotop 1659
- Sokolov C. M. Continuation of reign of Alexi Mikhailovich. Chapter 1.
- Makhun S. Battle of Konotop. Reittarr. No.23
External Links
- The Reign of Tsar Alexi Mikhailovich. (Solovyov S. М.) (Rus.)
- History of Konotop (Ukr.)
- Historical Encyclopedia (Ukr.)
- The Konotop Tragedy. 1659. (Rus.)
- The Battle of Konotop (Rus.)
- History of Little Russia (N. Маrkevich) (Rus.)
- The Konotop Battle. S. Makhun. (Rus.)
- The Konotop battle as an example of Ukrainian Cossack military skill (Ukr.)