| Revision as of 20:34, 13 October 2020 edit70.112.215.130 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 01:00, 6 March 2021 edit undo2601:600:9980:1810:9923:6013:ff0c:8071 (talk) This page about Dutch dialects. Limburgish, West Flemish, the Low Saxon and the Frisian varieties don't belong here, because those are only Dutch dialects for political reasons.Tag: RevertedNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Varieties of the Dutch Language}}{{expand Dutch|topic=|otherarticle=Nederlandse dialecten|date=November 2012}} | {{Short description|Varieties of the Dutch Language}}{{expand Dutch|topic=|otherarticle=Nederlandse dialecten|date=November 2012}} | ||
| {{Dutch dialects}} | {{Dutch dialects}} | ||
| '''Dutch dialects''' are primarily the |
'''Dutch dialects''' are primarily the local varieties of the Dutch language | ||
| The province of ] is bilingual. The ], distinct from Dutch, is spoken here along with standard Dutch and the Stadsfries dialect. A West Frisian standard language has also been developed. | |||
| ==First dichotomy== | ==First dichotomy== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 24: | ||
| Another group of dialects based on Hollandic is that spoken in the cities and larger towns of ], where it partially displaced ] in the 16th century and is known as ] ("Urban Frisian"). | Another group of dialects based on Hollandic is that spoken in the cities and larger towns of ], where it partially displaced ] in the 16th century and is known as ] ("Urban Frisian"). | ||
| ==Minority languages== | |||
| Germanic languages which have the status of official ] or ] and are protected by the ] in the ] are ], ] and ].<ref>Council of Europe: , see ''Reservations and declarations''</ref> | |||
| ] receives protection by chapter 2 of the charter. In ], where Limburgish is spoken as well, it does not receive such recognition or protection, because Belgium did not sign the charter. ] has been influenced by the ] dialects like the ] dialect ], and has had a somewhat different development since the late Middle Ages. | |||
| ] also receives protection by chapter 2 of the charter. In some ], depending on the state, ] receives protection by chapter 2 or 3. | |||
| ] receives protection by chapter 3 of the charter. (West) Frisian evolved from the same ] branch as ] and ] and is less akin to Dutch. | |||
| ==Recent use== | ==Recent use== | ||
| Dutch dialects and regional languages are not spoken as often as they used to be. Recent research by Geert Driessen shows that the use of dialects and regional languages among both Dutch adults and youth is in heavy decline. In 1995, 27 percent of the Dutch adult population spoke a dialect or regional language on a regular basis, while in 2011 this was no more than 11 percent. In 1995, 12 percent of the primary school aged children spoke a dialect or regional language, while in 2011 this had declined to 4 percent. |
Dutch dialects and regional languages are not spoken as often as they used to be. Recent research by Geert Driessen shows that the use of dialects and regional languages among both Dutch adults and youth is in heavy decline. In 1995, 27 percent of the Dutch adult population spoke a dialect or regional language on a regular basis, while in 2011 this was no more than 11 percent. In 1995, 12 percent of the primary school aged children spoke a dialect or regional language, while in 2011 this had declined to 4 percent. | ||
| ==Flanders== | ==Flanders== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 34: | ||
| * ] (Brabants), which includes several main dialect branches, including Antwerpian, and | * ] (Brabants), which includes several main dialect branches, including Antwerpian, and | ||
| * ] (Limburgs). | * ] (Limburgs). | ||
| Some of these dialects, especially |
Some of these dialects, especially East Flemish, have incorporated some French ]s in everyday language. An example is ''fourchette'' in various forms (originally a French word meaning fork), instead of ''vork''. Brussels is especially heavily influenced by French because roughly 85% of the inhabitants of ] speak French. | ||
| Dialect borders of these dialects do not correspond to present political boundaries, but reflect older, medieval divisions. | |||
| The Limburgish in Belgium is closely related to Dutch Limburgish. An oddity of West Flemings (and to a lesser extent, East Flemings) is that, when they speak AN, their pronunciation of the "soft g" sound (the ]) is almost identical to that of the "h" sound (the ]), thus, the words ''held'' (hero) and ''geld'' (money) sound nearly the same, except that the latter word has a 'y' /j/ sound embedded into the "soft g". When they speak their local dialect, however, their "g" is almost the "h" of the Algemeen Nederlands, and they do not pronounce the "h". Some Flemish dialects are so distinct that they might be considered as separate language variants, although the strong significance of language in Belgian politics would prevent the government from classifying them as such. ] in particular has sometimes been considered a distinct variety. Dialect borders of these dialects do not correspond to present political boundaries, but reflect older, medieval divisions. | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| Line 52: | Line 42: | ||
| ==Non-European dialects, and daughter languages== | ==Non-European dialects, and daughter languages== | ||
| * Until the early 20th century, variants of Dutch were still spoken by some descendants of ]. ], in particular, had an active Dutch community with a highly divergent dialect spoken as recently as the 1950s. See ] for more on this dialect. | * Until the early 20th century, variants of Dutch were still spoken by some descendants of ]. ], in particular, had an active Dutch community with a highly divergent dialect spoken as recently as the 1950s. See ] for more on this dialect. | ||
| * In ], a derivation of ] is the ]. | |||
| * ] is a ] of Dutch. It evolved mainly from 17th century Dutch dialects, but had influences from various ] in ]. However, it is still largely ] with Dutch. | |||
| * ] is a ] variety with influences and elements of Dutch. | |||
| * Despite its name, ] is not a Dutch dialect. It is actually German-based. | |||
| ==Further reading== | ==Further reading== | ||
Revision as of 01:00, 6 March 2021
Varieties of the Dutch LanguageYou can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Dutch. (November 2012) Click for important translation instructions.
|
| This article is a part of a series on |
| Dutch |
|---|
| Low Saxon dialects |
| West Low Franconian dialects |
| East Low Franconian dialects |
Dutch dialects are primarily the local varieties of the Dutch language
First dichotomy
In the east, there is a Dutch Low Saxon dialect area: in Groningen (Gronings), Drenthe, Overijssel, and major parts of Gelderland, Low Saxon is spoken. The group is not Low Franconian and is very close to its neighbor, Low German.
-
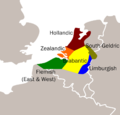 Map of traditional Low Franconian dialects
Map of traditional Low Franconian dialects
-
 Low Saxon in the Netherlands
Low Saxon in the Netherlands
Extension across the borders
- Gronings, spoken in Groningen (Netherlands), as well as the closely related varieties in adjacent East Frisia (Germany), has been influenced by the West Frisian language and takes a special position within the Low Saxon Language.
- South Guelderish (Zuid-Gelders) is a dialect spoken in Gelderland (Netherlands) and in adjacent parts of North Rhine-Westphalia (Germany).
- Brabantian (Brabants) is a dialect spoken in Antwerp, Flemish Brabant (Belgium) and North Brabant (Netherlands).
- Limburgish (Limburgs) is spoken in Limburg (Belgium) as well as in Limburg (Netherlands) and extends across the German border.
- West Flemish (Westvlaams) is spoken in West Flanders (Belgium), the western part of Zeelandic Flanders (Netherlands) and historically also in French Flanders (France).
- East Flemish (Oostvlaams) is spoken in East Flanders (Belgium) and the eastern part of Zeelandic Flanders (Netherlands).
Holland and the Randstad
In Holland, Hollandic is spoken, though the original forms of this dialect (which were heavily influenced by a West Frisian substratum and, from the 16th century on, by Brabantian dialects) are now relatively rare. The urban dialects of the Randstad, which are Hollandic dialects, do not diverge from standard Dutch very much, but there is a clear difference between the city dialects of Rotterdam, The Hague, Amsterdam or Utrecht.

In some rural Hollandic areas more authentic Hollandic dialects are still being used, especially north of Amsterdam. Another group of dialects based on Hollandic is that spoken in the cities and larger towns of Friesland, where it partially displaced West Frisian in the 16th century and is known as Stadsfries ("Urban Frisian").
Recent use
Dutch dialects and regional languages are not spoken as often as they used to be. Recent research by Geert Driessen shows that the use of dialects and regional languages among both Dutch adults and youth is in heavy decline. In 1995, 27 percent of the Dutch adult population spoke a dialect or regional language on a regular basis, while in 2011 this was no more than 11 percent. In 1995, 12 percent of the primary school aged children spoke a dialect or regional language, while in 2011 this had declined to 4 percent.
Flanders
In Flanders, there are four main dialect groups:
- West Flemish (West-Vlaams) including French Flemish in the far North of France,
- East Flemish (Oost-Vlaams),
- Brabantian (Brabants), which includes several main dialect branches, including Antwerpian, and
- Limburgish (Limburgs).
Some of these dialects, especially East Flemish, have incorporated some French loanwords in everyday language. An example is fourchette in various forms (originally a French word meaning fork), instead of vork. Brussels is especially heavily influenced by French because roughly 85% of the inhabitants of Brussels speak French.
Dialect borders of these dialects do not correspond to present political boundaries, but reflect older, medieval divisions.

The Brabantian dialect group, for instance, also extends to much of the south of the Netherlands, and so does Limburgish. West Flemish is also spoken in Zeelandic Flanders (part of the Dutch province of Zeeland), and by older people in French Flanders (a small area that borders Belgium).
Non-European dialects, and daughter languages
- Until the early 20th century, variants of Dutch were still spoken by some descendants of Dutch colonies in the United States. New Jersey, in particular, had an active Dutch community with a highly divergent dialect spoken as recently as the 1950s. See Jersey Dutch for more on this dialect.
Further reading
- Bont, Antonius Petrus de (1958) Dialekt van Kempenland 3 Deel Assen: van Gorcum, 1958-60. 1962, 1985
References
- Ad Welschen 2000-2005: Course Dutch Society and Culture, International School for Humanities and Social Studies ISHSS, Universiteit van Amsterdam
- Cornelissen, Georg (2003): Kleine niederrheinische Sprachgeschichte (1300-1900): eine regionale Sprachgeschichte für das deutsch-niederländische Grenzgebiet zwischen Arnheim und Krefeld (in German)
- Driessen, Geert (2012): Ontwikkelingen in het gebruik van Fries, streektalen en dialecten in de periode 1995-2011. Nijmegen: ITS.
- Elmentaler, Michael ( ? ): "Die Schreibsprachgeschichte des Niederrheins. Forschungsprojekt der Uni Duisburg", in: Sprache und Literatur am Niederrhein, (Schriftenreihe der Niederrhein-Akademie Bd. 3, 15-34).(in German)
- Frins, Jean (2005): Syntaktische Besonderheiten im Aachener Dreiländereck. Eine Übersicht begleitet von einer Analyse aus politisch-gesellschaftlicher Sicht. Groningen: RUG Repro (in German)
- Frins, Jean (2006): Karolingisch-Fränkisch. Die plattdůtsche Volkssprache im Aachener Dreiländereck. Groningen: RUG Repro (in German)
- Frings, Theodor (1916): Mittelfränkisch-niederfränkische Studien I. Das ripuarisch-niederfränkische Übergangsgebiet. II. Zur Geschichte des Niederfränkischen in: Beiträge zur Geschichte und Sprache der deutschen Literatur 41 (1916), 193-271; 42, 177-248.
- Hansche, Irmgard (2004): Atlas zur Geschichte des Niederrheins (= Schriftenreihe der Niederrhein-Akademie; 4). Bottrop/Essen: Peter Pomp. ISBN 3-89355-200-6
- Ludwig, Uwe & Schilp, Thomas (eds.) (2004): Mittelalter an Rhein und Maas. Beiträge zur Geschichte des Niederrheins. Dieter Geuenich zum 60. Geburtstag (= Studien zur Geschichte und Kultur Nordwesteuropas; 8). Münster/New York/München/Berlin: Waxmann. ISBN 3-8309-1380-X
- Mihm, Arend (1992): Sprache und Geschichte am unteren Niederrhein, in: Jahrbuch des Vereins für niederdeutsche Sprachforschung; 1992, 88-122.
- Mihm, Arend (2000): "Rheinmaasländische Sprachgeschichte von 1500 bis 1650", in: Jürgen Macha, Elmar Neuss, Robert Peters (eds.): Rheinisch-Westfälische Sprachgeschichte. Köln (= Niederdeutsche Studien 46), 139-164.
- Tervooren, Helmut (2005): Van der Masen tot op den Rijn. Ein Handbuch zur Geschichte der volkssprachlichen mittelalterlichen Literatur im Raum von Rhein und Maas. Geldern: Erich Schmidt ISBN 3-503-07958-0