| Revision as of 21:31, 24 July 2021 editWikiman2021language (talk | contribs)105 editsNo edit summaryTag: Reverted← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:31, 27 July 2021 edit undoWikiman2021language (talk | contribs)105 editsNo edit summaryTag: RevertedNext edit → | ||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| | name = Nastaliq | | name = Nastaliq | ||
| | type = ] | | type = ] | ||
| | languages = ], ] (including ] and ]), ], ], ] (in Iran and Iraq), many ] (including ] and ]), ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ]{{dn|date=July 2021}}, ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] | | languages = ], ] (including ] and ]), ], ], ] (in Iran and Iraq), many ] (including ] and ]), ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ]{{dn|date=July 2021}}, ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] | ||
| | sample = Welcome to Persian Misplaced Pages.svg | | sample = Welcome to Persian Misplaced Pages.svg | ||
| | caption = "Welcome to Misplaced Pages" in Persian<br/>from ] | | caption = "Welcome to Misplaced Pages" in Persian<br/>from ] | ||
Revision as of 21:31, 27 July 2021
The predominant style in Persian calligraphy The Nastaliq text on this page will show in a different style if you do not have a Nastaliq font installed.| Nastaliq | |
|---|---|
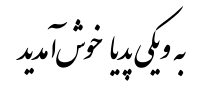 "Welcome to Misplaced Pages" in Persian "Welcome to Misplaced Pages" in Persianfrom Persian Misplaced Pages | |
| Script type | Abjad |
| Direction | Right-to-left |
| Languages | Urdu, Persian (including Dari and Tajik), Ottoman Turkish, Kurdish, Azerbaijani (in Iran and Iraq), many varieties of Punjabi (including Hindko and Saraiki), Kashmiri, Balochi, Afghan Uzbek, Pashto, Uyghur, Sindhi, Balti, Shina, Hazaragi, Nuristani Languages, Burushaski, Iraqi Arabic, Luri, Chagatai, Qashqai, Mazandarani, Tati, Gilaki, Talysh, Pashayi, Wakhi, Khowar, Brahui, Pahari, Some Varities of Turkmen, Gujari |
| ISO 15924 | |
| ISO 15924 | Aran (161), Arabic (Nastaliq variant) |
| Part of a series on |
| Calligraphy |
|---|
 |
| By script |

مرا عهدیست با جانان که تا جان در بدن دارم
هواداران کویش را چو جان خویشتن دارم in a Naskh styled typeface: حافظ شیرازی
مرا عهدیست با جانان که تا جان در بدن دارم
هواداران کویش را چو جان خویشتن دارم
Nastaʼlīq (/ˌnæstəˈliːk, ˈnæstəliːk/; Template:Lang-fa, IPA: [næsˈtæʔliːq]) is one of the main calligraphic hands used to write the Perso-Arabic script in the Persian and Urdu languages, and traditionally the predominant style in Persian calligraphy. It was developed in the land of Persia (modern-day Iran) in the 14th and 15th centuries. It is sometimes used to write Arabic language text (where it is mainly used for titles and headings), but its use has always been more popular in the Persian, Urdu and Turkic sphere of influence. Nastaliq remains very widely used in Iran, Afghanistan and Pakistan and other countries for written poetry and as a form of art.
A less elaborate version of Nastaliq serves as the preferred style for writing in Kashmiri and Urdu and it is often used alongside Naskh for Pashto. In Persian, it is used for poetry only. Nastaliq was historically used for writing Ottoman Turkish, where it was known as tâlik (not to be confused with a totally different Persian style, also called taʿlīq; to distinguish the two, Ottomans referred to the latter as taʿlīq-i qadim, "old taʿlīq").
Nastaliq is the core script of the post-Sassanid Persian writing tradition and is equally important in the areas under its cultural influence. The languages of Iran (Western Persian, Azeri, Balochi, Kurdi, Luri, etc.), Afghanistan (Dari Persian, Pashto, Turkmen, Uzbek, etc.), India (Urdu, Kashmiri, etc.), Pakistan (Urdu, Punjabi, Saraiki, Pashto, Balochi, etc.) and the Turkic Uyghur language of the Chinese province of Xinjiang, rely on Nastaliq. Under the name taʿliq (lit. "suspending script"), it was also beloved by Ottoman calligraphers who developed the Diwani (divanî) and Ruqah (rıkʻa) styles from it.
Nastaliq is amongst the most fluid calligraphy styles for the Arabic script. It has short verticals with no serifs, and long horizontal strokes. It is written using a piece of trimmed reed with a tip of 5–10 mm (0.2–0.4 in), called qalam ('pen', Arabic and Persian قلم) and carbon ink, named siyahi. The nib of a qalam can be split in the middle to facilitate ink absorption.
Two important forms of Nastaliq panels are Chalipa and Siyah mashq. A Chalipa ("cross", in Persian) panel usually consists of four diagonal hemistiches (half-lines) of poetry, clearly signifying a moral, ethical or poetic concept. Siyah Mashq ("black drill") panels, however, communicate via composition and form, rather than content. In Siyah Mashq, repeating a few letters or words (sometimes even one) virtually inks the whole panel. The content is thus of less significance and not clearly accessible.
History

The dotted form ڛ is used in place of س in the word نڛتعلیق Nastaliq.
After the Islamic conquest of Persia, the Iranian Persian people adopted the Perso-Arabic script and the art of Persian calligraphy flourished in Iran as territories of the former Persian empire. Apparently, Mir Ali Tabrizi (14th century) developed Nastaliq by combining two existing scripts of Nasḫ and Taʿlīq. Hence, it was originally called Nasḫ-Taʿlīq. Another theory holds that the name Nastaliq means "that which abrogated (naskh) Taʿlīq".
Nastaliq thrived and many prominent calligraphers contributed to its splendor and beauty. It is believed that Nastaliq reached its highest elegance in Mir Emad's works. The current practice of Nastaliq is, however, heavily based on Mirza Reza Kalhor's technique. Kalhor modified and adapted Nastaliq to be easily used with printing machines, which in turn helped wide dissemination of his transcripts. He also devised methods for teaching Nastaliq and specified clear proportional rules for it, which many could follow.
The Mughal Empire used Persian as the court language during their rule over South Asia. During this time, Nastaliq came into widespread use in South Asia. The influence continues to this day. In India and Pakistan, almost everything in Urdu is written in the script, constituting the greatest part of Nastaliq usage in the world. The situation of Nastaliq in Bangladesh used to be the same as in Pakistan until 1971, when Urdu ceased to remain an official language. Today, only a few people use this form of writing in Bangladesh.
Nastaliq is a descendant of Nasḫ and Taʿlīq. Shekasteh Nastaliq - literally: "broken Nastaliq" - style (below) is a development of Nastaliq.
Notable Nastaliq calligraphers

In print: بودم به تو عمری و ترا سیر ندیدم
از وصل تو هرگز به مرادی نرسیدم
از بهر تو بیگانه شدم از همه خویشان
وحشی صفت از خلق به یکبار بریدم In Naskh styled typeface: بودم به تو عمری و ترا سیر ندیدم
از وصل تو هرگز به مرادی نرسیدم
از بهر تو بیگانه شدم از همه خویشان
وحشی صفت از خلق به یکبار بریدم
And others, including Mirza Jafar Tabrizi, Abdul Rashid Deilami, Sultan Ali Mashadi, Mir Ali Heravi, Emad Ul-Kottab, Mirza Gholam Reza Esfehani, Emadol Kotab, Yaghoot Mostasami and Darvish Abdol Majid Taleghani.
And among contemporary artists: Hassan Mirkhani, Hossein Mirkhani, Keikhosro Khoroush, Abbas Akhavein and Qolam-Hossein Amirkhani, Ali Akbar Kaveh, Kaboli.
-
 Mir Emad Hassani, Safavid era
Mir Emad Hassani, Safavid era
-
 Soltan-ali Mashhadi - 1489 AD
Soltan-ali Mashhadi - 1489 AD
Etiquette
Islamic calligraphy was originally used to adorn Islamic religious texts, specifically the Qurʼan, as pictorial ornaments were prohibited in sacred publications and spaces of Islam. Therefore, a sense of sacredness was always implicit in calligraphy.
A Nastaliq disciple was supposed to qualify himself spiritually for being a calligrapher, besides learning how to prepare qalam, ink, paper and, more importantly, master Nastaliq. For instance see Adab al-Mashq, a manual of penmanship attributed to Mir Emad.
-
 Folio of Poetry From the Divan of Sultan Husayn Mirza, ca. 1490. Brooklyn Museum.
Folio of Poetry From the Divan of Sultan Husayn Mirza, ca. 1490. Brooklyn Museum.
-
 Quatrain on the Virtue of Patience by Muhammad Muhsin Lahuri of the Mughal Empire
Quatrain on the Virtue of Patience by Muhammad Muhsin Lahuri of the Mughal Empire
Shekasteh Nastaliq
Shekasteh or Shekasteh Nastaliq (Template:Lang-fa, شکسته نستعلیق, "cursive Nastaliq" or literally "broken Nastaliq") style is a "streamlined" script of Nastaliq. It was developed in the 14th century to ease communication for non-calligraphic purposes, such as commerce and administration. Shekasta is characterized by " greatly reduced in size... thinner strokes... letters that in the formal versions of the Arabic script do not connect to the left were made to connect."
-
 A ruba'i of Omar Khayyam in Shekasteh Nastaliq.
A ruba'i of Omar Khayyam in Shekasteh Nastaliq.
In print:گویند کسان بهشت با حور خوش است
من میگویم که آب انگور خوش است
این نقد بگیر و دست از آن نسیه بدار
کاواز دهل شنیدن از دور خوش است In modern Naskh: گویند کسان بهشت با حور خوش است
من میگویم که آب انگور خوش است
این نقد بگیر و دست از آن نسیه بدار
کاواز دهل شنیدن از دور خوش است -
 A line of poetry by the Iranian poet Omar Khayyam in Shekasteh Nastaliq.
A line of poetry by the Iranian poet Omar Khayyam in Shekasteh Nastaliq.
In print: این قافلهٔ عُمر عجب میگذرد In modern Naskh: این قافلهٔ عُمر عجب میگذرد -
 An excerpt from Shaykh Sa'di's (d. 691/1292) "Gulistan" (The Rose Garden), in Shekasteh Nastaliq script.
An excerpt from Shaykh Sa'di's (d. 691/1292) "Gulistan" (The Rose Garden), in Shekasteh Nastaliq script.
-
 Fath Ali Shah Qajar's order in Shekasteh Nastaliq script, January 1831
Fath Ali Shah Qajar's order in Shekasteh Nastaliq script, January 1831
Nastaliq typesetting

Nastaliq:
؎ کیا تنگ ہم ستم زدگان کا جہاں ہے
جس میں ایک بیضۂ مور آسماں ہے
Naskh:
؎ کیا تنگ ہم ستم زدگان کا جہاں ہے
جس میں ایک بیضۂ مور آسماں ہے
Nastaliq Typography first started with attempts to develop a metallic type for the script, but all such efforts failed. Fort William College developed a Nastaliq Type, which was not close enough to Nastaliq and hence was never used other than by the college library to publish its own books. The State of Hyderabad Dakan (now in India) also attempted to develop a Nastaliq Typewriter but this attempt failed miserably and the file was closed with the phrase “Preparation of Nastaliq on commercial basis is impossible”. Basically, in order to develop such a metal type, thousands of pieces would be required.
Modern Nastaliq typography began with the invention of Noori Nastaleeq which was first created as a digital font in 1981 through the collaboration of Mirza Ahmad Jamil TI (as Calligrapher) and Monotype Imaging (formerly Monotype Corp & Monotype Typography). Although this was a ground-breaking solution employing over 20,000 ligatures (individually designed character combinations) which provided the most beautiful results and allowed newspapers such as Pakistan's Daily Jang to use digital typesetting instead of an army of calligraphers, it suffered from two problems in the 1990s: (a) its non-availability on standard platforms such as Windows or Mac OS, and (b) the non-WYSIWYG nature of text entry, whereby the document had to be created by commands in Monotype's proprietary page description language.
InPage
In 1994, InPage Urdu, which is a fully functional page layout software for Windows akin to Quark XPress, was developed for Pakistan's newspaper industry by an Indian software company Concept Software Pvt Ltd. It offered the Noori Nastaliq font licensed from Monotype Corporation. This font, with its vast ligature base of over 20,000, is still used in current versions of the software for Windows. As of 2009 InPage has become Unicode based, supporting more languages, and the Faiz Lahori Nastaliq font with Kasheeda has been added to it along with compatibility with OpenType Unicode fonts. Nastaliq Kashish has been made for the first time in the history of Nastaliq Typography.
Cross platform Nastaliq fonts

- Windows 8 was the first version of Microsoft Windows to have native Nastaliq support, through Microsoft's "Urdu Typesetting" font.

- Google has an open-source Nastaliq font called Noto Nastaliq Urdu. Apple provides this font on all Mac installations since macOS High Sierra. Likewise, Apple has carried this font on iOS devices since iOS 11.
- Awami Nastaliq features a more extensive character set than most Nastaliq typefaces, supporting: Urdu, Balochi, Persian, Khowar, Palula, Saraiki, Shina.
- Amar Nastaleeq was created for web embedding on Urdu websites in 2013. The font was announced by Urdu poet Fahmida Riaz.
Letter forms
For the Arabic alphabet, and many others derived from it, letters are regarded as having two or three general forms each, based on their position in the word (though obviously Arabic calligraphy can add a great deal of complexity). But the Nastaliq style uses more than three general forms for many letters, even in non-decorative documents. For example, most documents written in Urdu, which uses the Nastaliq style.
See also
References
- Akram, Qurat ul Ain; Hussain, Sarmad; Niazi, Aneeta; Anjum, Umair; Irfan, Faheem (April 2014). Adapting Tesseract for Complex Scripts: An Example for Urdu Nastalique. 11th IAPR International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems. Tours, France: IEEE. pp. 191–195. doi:10.1109/DAS.2014.45. ISBN 978-1-4799-3243-6.
- "Nastaliq | Definition of Nastaliq by Oxford Dictionary on Lexico.com also meaning of Nastaliq". Lexico Dictionaries. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 2020-07-05 – via Lexico.com.
- eteraz, ali (8 October 2013). "The Death of the Urdu Script". Medium. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
Urdu is traditionally written in a Perso-Arabic script called nastaliq…
- The Cambridge History of Islam. By P. M. Holt, et al., Cambridge University Press, 1977, ISBN 0-521-29138-0, p. 723.
- Hamed, Payman. "Famous Calligraphers - Persian Calligraphy- All about Persian Calligraphy". www.persiancalligraphy.org.
- Gulzar, Rahman, Atif, Shafiq (2007). "Nastaleeq: A challenge accepted by Omega" (PDF). TUGboat. 29: 1–6.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "The Scripts". Archived from the original on 2013-12-14. Retrieved 2013-12-10.
- "Qalam", Misplaced Pages, 2020-02-15, retrieved 2020-03-29
- "Famous Calligraphers". Persian Calligraphy. Retrieved 12 January 2012.
- "Iran Nastaʿlīq script - IRAN TRAVEL, TRIP TO IRAN". www.irangazette.com. Retrieved 2020-03-29.
- Nastaliq Script – Persian Calligraphy Archived September 28, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- Ernst, Carl W. (April–June 1992). "The Spirit of Islamic Calligraphy: Bābā Shāh Iṣfahānī's Ādāb al-mashq". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 112 (2): 279–286. doi:10.2307/603706. JSTOR 603706.
- Spooner, Brian; Hanaway, William L. (1995). Reading Nasta'liq: Persian and Urdu Hands from 1500 to the Present. p. 3. ISBN 978-1568592138.
- Khurshiq, Iqbal (17 November 2013). "زندگی آگے بڑھنے کا نام اور جمود موت ہے: نوری نستعلیق کی ایجاد سے خط نستعلیق کی دائمی حفاظت ہوگئی". Express. Retrieved 24 November 2013.
- How to bring a language to the future, 9 Feb 2021
- "The evolving Story of Locale Support, part 9: Nastaleeq vs. Nastaliq? Either way, Windows 8 has got it!". MSDN Blogs. Retrieved 2013-03-24.
- "Google Noto Fonts".
- "Apple finally enables Nastaleeq typeface for Urdu keyboard in iOS 11". 23 September 2017.
- "What is Special About Awami Nastaliq? - Awami Nastaliq". software.sil.org.
- Riaz, fahmida (21 November 2013). "Amar Nastaleeq Font for Urdu Web Publishing". Twitter.com.
- FWP. "Urdu: some thoughts about the script and grammar, and other general notes for students assembled from years of classroom notes by FWP". www.columbia.edu. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- "The chart below gives the different positional variants of some of the significantly different letters. (scanned document)". Linked by www.columbia.edu/itc/mealac/pritchett/00urdu/urduscript/section00.html#00_01. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
Further reading
- Sheila Blair, Islamic Calligraphy, Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2005.
External links
- Rumicode: Online Service For Nastaliq Calligraphy
- Nastaliq Online: Online Service For Nastaliq Calligraphy
- Iranian Calligraphers Association
- Nastaliq Writer for Macintosh by SIL
- InPage Urdu: Official InPage Urdu DTP software site
- Faiz Nastaliq: Official Faiz Nastaliq site
- Profiles and works of World Islamic calligraphy (in French)
- Nastaliq Script | Persian Calligraphy
- Awami Nastaliq: A Nastaliq font by SIL International
| Islamic calligraphy | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Styles |
|  | ||||||||
| Objects | ||||||||||
| Calligraphers | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Organizations | ||||||||||
| Influences | ||||||||||
| Part of Islamic arts | ||||||||||
| Arabic language | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overviews | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scripts | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Letters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Varieties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Academic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Linguistics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Calligraphy · Script | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||