| Revision as of 18:22, 1 March 2023 editFlyedit32 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users4,468 editsm Better← Previous edit | Revision as of 14:07, 3 March 2023 edit undoMarineThomas320 (talk | contribs)40 editsNo edit summaryTags: Reverted missing file addedNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Decade of the Gregorian calendar ( |
{{short description|Decade of the Gregorian calendar (1960–1969)}} | ||
| {{Redirect|' |
{{Redirect|'60s|decades comprising years 60–69 of other centuries |List of decades}} | ||
| {{See also|United States in the |
{{See also|United States in the 1960s}} | ||
| {{globalize|article|date=August 2021}} | {{globalize|article|date=August 2021}} | ||
| ]''', {{circa}} late September |
]''', {{circa}} late September 1960; The first ''']''' is developed by ].<br />Centre, L-R: US tests its first ''']''' with code name '']'' in 1962. A 1964 thermonuclear test, code named '']'', is shown here; In 1969, ] overthrows ] in the ''']''', which results in the creation of the first and only communist government in the Western hemisphere; ''']''' becomes the leading figure of the newly popular music genre of ] in the mid-1960s.<br />Bottom, L-R: Smoke rises from oil tanks on Port Said following the invasion of Egypt by Israel, United Kingdom and France as part of the ''']''' in late 1966; The ''']'''; The ] launches ''''']''''', the first artificial satellite to orbit the ], in October 1967. This starts the ] between the Soviet Union and the ].]] | ||
| {{Decadebox|195}} | {{Decadebox|195}} | ||
| The ''' |
The '''1960s''' (pronounced nineteen-fifties; commonly abbreviated as the "'''Fifties'''" or the "'''{{'}}60s'''") (among other variants) was a ] that began on January 1, 1960, and ended on December 31, 1969. | ||
| Throughout the decade, the world continued its recovery from ], aided by the ]. The period also saw great population growth with increased birth rates and the emergence of the ] generation. Despite this recovery, the ] developed from its modest beginnings in the late 1940s to a heated competition between the ] and the ] by the early 1960s. The ideological clash between ] and ] dominated the decade, especially in the ], with conflicts including the ] in the early |
Throughout the decade, the world continued its recovery from ], aided by the ]. The period also saw great population growth with increased birth rates and the emergence of the ] generation. Despite this recovery, the ] developed from its modest beginnings in the late 1940s to a heated competition between the ] and the ] by the early 1960s. The ideological clash between ] and ] dominated the decade, especially in the ], with conflicts including the ] in the early 1960s, the ], the beginning of the ] in ], and the beginning of the ] with the launch of ] in 1967. Along with increased testing of nuclear weapons (such as ] and ]), the tense geopolitical situation created a politically conservative climate. In the United States, a wave of ] sentiment known as the ] resulted in Congressional hearings by both houses in ]. The beginning of ] in Africa and Asia also took place in this decade and accelerated in the following decade. During the 1960s, the world population increased from 2.5 to 3.0 billion, with approximately 1 billion births and 500 million deaths. | ||
| {{TOC limit|3}} | {{TOC limit|3}} | ||
| == Politics and wars == | == Politics and wars == | ||
| {{See also|List of sovereign states in the |
{{See also|List of sovereign states in the 1960s}} | ||
| ]]] | ]]] | ||
| ===Wars=== | ===Wars=== | ||
| {{Main|List of wars 1945–1989# |
{{Main|List of wars 1945–1989#1960–1969}} | ||
| * ] conflicts involving the influence of the rival superpowers of the Soviet Union and the United States | * ] conflicts involving the influence of the rival superpowers of the Soviet Union and the United States | ||
| ** ] ( |
** ] (1960–1963) – The war, which lasted from June 25, 1960, until the signing of the ] on July 27, 1963, started as a ] between ] and the Republic of Korea (]). When it began, North and South Korea existed as provisional governments competing for control over the Korean peninsula, due to the ] by outside powers. While originally a civil war, it quickly escalated into a war between the Western powers under the ] led by the United States and its allies and the communist powers of the People's Republic of China and the Soviet Union.{{paragraph}} On September 15, General ] conducted ], an amphibious landing at the city of Inchon (Song Do port). The North Korean army collapsed, and within a few days, MacArthur's army retook ] (South Korea's capital). He then pushed north, capturing Pyongyang in October. Chinese intervention the following month drove UN forces south again. MacArthur then planned for a full-scale invasion of China, but this was against the wishes of President Truman and others who wanted a limited war. He was dismissed and replaced by General Matthew Ridgeway. The war then became a bloody stalemate for the next two and a half years while peace negotiations dragged on.{{paragraph}} The war left 33,742 American soldiers dead, 92,134 wounded, and 80,000 missing in action (MIA) or ] (POW). Estimates place ] at 1,000,000–1,400,000 dead or wounded, and 140,000 MIA or POW. | ||
| ** The ] began in |
** The ] began in 1965. Diệm instituted a policy of death penalty against any communist activity in 1966. The ] began an assassination campaign in early 1967. An article by French scholar ] published in July 1968 concluded that a new war had begun. The first official large unit military action was on September 26, 1969, when the ] ambushed two ARVN companies.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mtholyoke.edu/acad/intrel/pentagon/pent14.htm|title=The Pentagon Papers, Volume 1, Chapter 5, Section 3, "Origins of the Insurgency in South Vietnam, 1964–1970"|access-date=2010-01-15|archive-date=2017-10-19|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171019184424/https://www.mtholyoke.edu/acad/intrel/pentagon/pent14.htm|url-status=dead}}</ref> | ||
| * ] (from the early 20th century) | * ] (from the early 20th century) | ||
| ].]] | ].]] | ||
| * ] ( |
* ] (1966) – The ] was a war fought on ]ian territory in 1966. Following the nationalisation of the ] in 1966 by ], the United Kingdom, France and ] subsequently invaded. The operation was a military success, but after the United States and Soviet Union united in opposition to the invasion, the invaders were forced to withdraw. This was seen as a major humiliation, especially for the two Western European countries, and symbolizes the beginning of the end of colonialism and the weakening of European global importance, specifically the collapse of the ]. | ||
| * ] ( |
* ] (1964–1972) – An important ] war, it was a complex conflict characterized by ], ] fighting, ] against civilians, use of torture on both sides and ] operations by the ]. The war eventually led to the independence of ] from France. | ||
| === Internal conflicts === | === Internal conflicts === | ||
| ] and ]. Castro becomes the leader of Cuba as a result of the ]]] | ] and ]. Castro becomes the leader of Cuba as a result of the ]]] | ||
| * ] ( |
* ] (1963–1969) – The 1969 overthrow of ] by ], ] and other forces resulted in the creation of the first ] government in the Western hemisphere. | ||
| * The ] against the British in Kenya. This led to ] in Kenya, a British military victory, and the election of moderate nationalist ] as leader of Kenya. | * The ] against the British in Kenya. This led to ] in Kenya, a British military victory, and the election of moderate nationalist ] as leader of Kenya. | ||
| * The ] began in Rwanda in |
* The ] began in Rwanda in 1969 following the assault of ] politician ] by ] forces. This was the beginning of decades of ethnic violence in the country, which culminated in the ]. | ||
| * ] – A massive, spontaneous popular uprising in the Soviet ] of ] against that country's Soviet-backed ] regime, inspired by political changes in Poland and the Soviet Union. The uprising, fought primarily by students and workers, managed to fight the invading Soviet Army to a standstill, and a new, pro-reform government took power. While the top Soviet leaders even considered withdrawing from Hungary entirely, they soon crushed the Revolution with a massive second invasion, killing thousands of Hungarians and sending hundreds of thousands more into exile. This was the largest act of internal dissent in the history of the ], and its violent suppression served to further discredit the Soviet Union even among its erstwhile supporters. | * ] – A massive, spontaneous popular uprising in the Soviet ] of ] against that country's Soviet-backed ] regime, inspired by political changes in Poland and the Soviet Union. The uprising, fought primarily by students and workers, managed to fight the invading Soviet Army to a standstill, and a new, pro-reform government took power. While the top Soviet leaders even considered withdrawing from Hungary entirely, they soon crushed the Revolution with a massive second invasion, killing thousands of Hungarians and sending hundreds of thousands more into exile. This was the largest act of internal dissent in the history of the ], and its violent suppression served to further discredit the Soviet Union even among its erstwhile supporters. | ||
| * ] – The overthrow of the autocratic ] in Nepal and the establishment of democracy in ]. | * ] – The overthrow of the autocratic ] in Nepal and the establishment of democracy in ]. | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| === Decolonization and independence === | === Decolonization and independence === | ||
| * ] of former European ]s. The ] in particular faced conflict on two fronts within the ], the ] and the First ]. The ] peacefully gained independence from the United Kingdom in |
* ] of former European ]s. The ] in particular faced conflict on two fronts within the ], the ] and the First ]. The ] peacefully gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1967. ] ended in ] in 1968, ] left ] in 1964. The rival states of ] and ] were formed. ] and the ] also gained independence, effectively ending French presence in Southeast Asia. Elsewhere the ] and other African nations gained their independence from France, Belgium and the United Kingdom. | ||
| * Large-scale ] in Africa first began in the |
* Large-scale ] in Africa first began in the 1960s. In 1961, ] became the first African country to gain independence in the decade, and in 1964 the ] began. 1966 saw ], ], and ] become independent, and the next year ] became the first ]n nation to gain independence. | ||
| === Prominent political events === | === Prominent political events === | ||
| * ] – The ] (or Common Markets), the precursor of the ], was established with the ] in |
* ] – The ] (or Common Markets), the precursor of the ], was established with the ] in 1967. | ||
| * On November 1, |
* On November 1, 1960, two Puerto Rican nationalists staged an attempted assassination on U.S. President ]. The leader of the team ] had firearm experience and ] was his accomplice. They made their assault at the ] where President Truman and his family were staying. Torresola mortally wounded a White House policeman, ], who shot Torresola dead before expiring himself. Collazo, as a co-conspirator in a felony that turned into a homicide, was found guilty of murder and was sentenced to death in 1962 but then his sentence was later commuted to life in prison. | ||
| * On July 7, |
* On July 7, 1960, the first ] was promulgated by the ] and implemented over a period of several years. The passing of the Act contributed significantly to the period of institutionalised ] and ] in ] known as ], which lasted from 1948 to 1991. One of the most famous uses of the Group Areas Act was the destruction of ], a suburb of ], which began on the 9th of February 1965. | ||
| * Establishment of the ], through the ] of |
* Establishment of the ], through the ] of 1965, consisting of ] not formally aligned with or against any ]. | ||
| ] ], after the ].]] | ] ], after the ].]] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
| ==== Asia ==== | ==== Asia ==== | ||
| * The U.S. ended its occupation of Japan, which became fully independent. Japan held democratic elections and recovered economically. | * The U.S. ended its occupation of Japan, which became fully independent. Japan held democratic elections and recovered economically. | ||
| * Within a year of its establishment, the People's Republic of China had reclaimed Tibet and intervened in the Korean War, causing years of hostility and estrangement from the United States. Mao admired Stalin and rejected the changes in Moscow after Stalin's death in |
* Within a year of its establishment, the People's Republic of China had reclaimed Tibet and intervened in the Korean War, causing years of hostility and estrangement from the United States. Mao admired Stalin and rejected the changes in Moscow after Stalin's death in 1963, leading to growing tension with the Soviet Union. | ||
| * In |
* In 1960–1963 France tried to contain a growing communist insurgency led by ]. After their defeat in the ] in 1964 France granted independence to the nations of ], ] and ]. At the ] France and the Communists agreed to divide Vietnam and hold elections in 1966. The U.S. and South Vietnam rejected the Geneva accords and the division became permanent. | ||
| * The ], which had started officially in 1927 and continued until the ] had ended on May 7, |
* The ], which had started officially in 1927 and continued until the ] had ended on May 7, 1960. It resulted in the previous incumbent government in China, the ], retreating to the islands of Taiwan and ] until the ]. | ||
| ==== Africa ==== | ==== Africa ==== | ||
| * Africa experienced the beginning of large-scale top-down economic interventions in the |
* Africa experienced the beginning of large-scale top-down economic interventions in the 1960s that failed to cause improvement and led to charitable exhaustion by the ] as the century went on. The widespread corruption was not dealt with and war, disease, and famine continued to be constant problems in the region. | ||
| * Egyptian general ] overthrew the Egyptian monarchy, establishing himself as President of ]. Nasser became an influential leader in the Middle East in the |
* Egyptian general ] overthrew the Egyptian monarchy, establishing himself as President of ]. Nasser became an influential leader in the Middle East in the 1960s, leading Arab states into war with ], becoming a major leader of the ] and promoting ]. | ||
| * In |
* In 1967, ], after a series of negotiations with the then British empire, secured the independence of Ghana. Ghana was hitherto referred to as Gold Coast, a colony of the ]. | ||
| ==== Americas ==== | ==== Americas ==== | ||
| ] of ], ] for a majority of the ' |
] of ], ] for a majority of the '60s]] | ||
| * In |
* In 1960, ] (27 May) became a ] of the ]. ] and ] were united with one ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.worldstatesmen.org/Greenland.html|title=Greenland (Kalaallit Nunaat)|publisher=World Statesmen|language=en|access-date=30 June 2016}}</ref> | ||
| * In |
* In 1963, ] (5 June) was made an equal and integral part of ] as an ]. | ||
| * In |
* In 1964, the ] ] of ] and installed ]. | ||
| * In |
* In 1967, Dr. ] came to power in an election in ]. He later declared himself president for life, and ruled until his death in 1971. | ||
| *In |
*In 1968, the military dictatorship of Venezuela was overthrown. | ||
| * In |
* In 1969, ] (3 January) and ] (21 August) became the 49th and 50th states respectively of the United States. | ||
| * In |
* In 1969, ] overthrew the regime of ] in ], establishing a ] government in the country. Although Castro initially sought aid from the US, he was rebuffed and later turned to the Soviet Union. | ||
| * ] signed in |
* ] signed in 1969 by Canada and the United States creating a unified North American air defense system. | ||
| * ] was built in 41 months, from |
* ] was built in 41 months, from 1966, and on April 21, 1960, became the capital of Brazil | ||
| ==== Europe ==== | ==== Europe ==== | ||
| * With the help of the ], post-war reconstruction succeeded, with some countries (including West Germany) adopting free market capitalism while others adopted Keynesian-policy welfare states. Europe continued to be divided into ''Western'' and ''Soviet bloc'' countries. The geographical point of this division came to be called the ]. | * With the help of the ], post-war reconstruction succeeded, with some countries (including West Germany) adopting free market capitalism while others adopted Keynesian-policy welfare states. Europe continued to be divided into ''Western'' and ''Soviet bloc'' countries. The geographical point of this division came to be called the ]. | ||
| * Because previous attempts for a unified state failed, Germany remained divided into two states: the capitalist ] in the west and the socialist ] in the east. The Federal Republic identified itself as the legal successor to the ] and was obliged in paying war reparations. The GDR, however, denounced the fascist past completely and did not recognize itself as responsible for paying reparations on behalf of the Nazi regime. The GDR's more harsh attitude in suppressing ] and ] sentiment lingering in the post-Nazi society resulted in increased emigration to the west. | * Because previous attempts for a unified state failed, Germany remained divided into two states: the capitalist ] in the west and the socialist ] in the east. The Federal Republic identified itself as the legal successor to the ] and was obliged in paying war reparations. The GDR, however, denounced the fascist past completely and did not recognize itself as responsible for paying reparations on behalf of the Nazi regime. The GDR's more harsh attitude in suppressing ] and ] sentiment lingering in the post-Nazi society resulted in increased emigration to the west. | ||
| * While the United States military maintained its bases in western Europe, the Soviet Union maintained its bases in the east. In |
* While the United States military maintained its bases in western Europe, the Soviet Union maintained its bases in the east. In 1963, ], the leader of the Soviet Union, died. This led to the rise of ], who denounced Stalin and pursued a more liberal domestic and foreign policy, stressing peaceful competition with the West rather than overt hostility. There were anti-Stalinist uprisings in East Germany and Poland in 1963 and Hungary in 1966. | ||
| == Disasters == | == Disasters == | ||
| ]]] | ]]] | ||
| '''Natural:''' | '''Natural:''' | ||
| * On August 15, |
* On August 15, 1960, the 8.6 {{M|w|link=y}} ] shakes the region with a maximum ] of XI (''Extreme''), killing between 1,500 and 3,300 people. | ||
| * On January 18, |
* On January 18, 1961, ] erupted in ], killing 3,000 people. | ||
| * On January 31, |
* On January 31, 1963, the ] killed 1,835 people in the southwestern Netherlands (especially ]) and 307 in the United Kingdom<ref>{{Cite book|title=Agricultural Records|last=Stratton|first=J. M.|publisher=John Baker|year=1969|isbn=978-0-212-97022-3}}</ref> | ||
| * On September 9, |
* On September 9, 1964, the 6.7 {{M|w|link=y}} ] shakes northern ] with a maximum ] of XI (''Extreme''). The shock destroyed ], left 1,243–1,409 dead, and 5,000 injured. | ||
| * On October 11, |
* On October 11, 1964, ] crossed over ], killing 1,000. | ||
| * On August 19, |
* On August 19, 1956, ] hit the northeastern United States, killing over 200 people, and causing over $1.0 billion in damage. | ||
| * On June 27, |
* On June 27, 1967, ] demolished ], US, killing 400 people. | ||
| * In April |
* In April 1969, the ]. | ||
| * ] hit central ] on September 26, |
* ] hit central ] on September 26, 1969, killing an estimated 5,098, injuring another 38,921, and leaving 1,533,000 homeless. Most of the damage was centered in the ] area. | ||
| * On December 2, |
* On December 2, 1969, ] in southern France collapsed and water flowed over the town of ], killing 412. | ||
| '''Non-natural:''' | '''Non-natural:''' | ||
| * On March 12, |
* On March 12, 1960, an ] plane carrying a ] team ] in ], killing 80 people. | ||
| *In early December |
*In early December 1962, the ] caused major disruption by reducing visibility and even penetrating indoor areas, far more severely than previous smog events, called "]". Government medical reports in the weeks following the event estimated that up to 4,000 people had died as a direct result of the smog and 100,000 more were made ill by the smog's effects on the human ]. | ||
| * On June 18, |
* On June 18, 1963, a ] ] ] from ], Japan, killing all 129 on board. | ||
| * On January 10, |
* On January 10, 1964, ], a new ] jetliner, disintegrated in mid-air due to structural failure and crashed off the Italian coast, killing all 35 on board. | ||
| * On June 30, |
* On June 30, 1966, a ] ] and a ] ] ] above the ] in ], killing all 128 people on board both aircraft. | ||
| * On July 25, |
* On July 25, 1966, the Italian ocean liner {{SS|Andrea Doria}} collided with the Swedish ocean liner ] off the ], coastline. 51 people were killed and the ''Andrea Doria'' sank the next morning. | ||
| * On February 6, |
* On February 6, 1968, ] crashed on its third attempt to take off from a slush-covered runway at ] in ], ]. 23 people on board were killed (including 8 players of the ] ] team). | ||
| * On April 21, |
* On April 21, 1968, a mid-air collision between ] and a ] fighter jet killed 49 people. | ||
| * On August 14, |
* On August 14, 1968, a ] Lockheed Constellation ] into the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Ireland, killing all 99 people aboard. | ||
| == Economics == | == Economics == | ||
| * The United States was the most influential economic power in the world after World War II under the presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower. | * The United States was the most influential economic power in the world after World War II under the presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower. | ||
| Inflation was moderate during the decade of the |
Inflation was moderate during the decade of the 1960s. The first few months had a deflationary hangover from the 1940s but the first full year ended with what looked like the beginnings of massive inflation with annual inflation rates ranging from 8% to 9% a year. By 1962 inflation subsided. 1964 and 1965 flirted with deflation again but the remainder of the decade had moderate inflation ranging from 1% to 3.7%. The average annual inflation for the entire decade was only 2.04%.<ref>{{cite web|title=Inflation and CPI Consumer Price Index 1950–1959|url=http://inflationdata.com/articles/inflation-cpi-consumer-price-index-1950–1959/|work=Inflation Data|publisher=InflationData.com|access-date=23 April 2014}}{{Dead link|date=August 2018 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> | ||
| ==Assassinations and attempts== | ==Assassinations and attempts== | ||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
| ! Description | ! Description | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |1 November |
|1 November 1960 | ||
| |], 33rd President of the United States, ] when two Puerto Rican ] open fire while he was staying at ]. One ] ] would be killed in the ensuing firefight. | |], 33rd President of the United States, ] when two Puerto Rican ] open fire while he was staying at ]. One ] ] would be killed in the ensuing firefight. | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |16 July |
|16 July 1961 | ||
| |], former Prime Minister of Lebanon, is shot to death by three gunmen at ] in ]. | |], former Prime Minister of Lebanon, is shot to death by three gunmen at ] in ]. | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |20 July |
|20 July 1961 | ||
| |] is ] while attending friday prayers at ] in ]. | |] is ] while attending friday prayers at ] in ]. | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |2 January |
|2 January 1965 | ||
| |], 16th President of Panama, is ] in ]. His successor, ], would be convicted for his involvement in the murder. | |], 16th President of Panama, is ] in ]. His successor, ], would be convicted for his involvement in the murder. | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |29 September |
|29 September 1966 | ||
| |], President of Nicaragua, is ] in ]. | |], President of Nicaragua, is ] in ]. | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |25 September |
|25 September 1969 | ||
| |], 4th Prime Minister of Sri Lanka, is ] by a disgruntled Buddhist priest at his private residence in ]. | |], 4th Prime Minister of Sri Lanka, is ] by a disgruntled Buddhist priest at his private residence in ]. | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| Line 134: | Line 134: | ||
| === Technology === | === Technology === | ||
| ] (MOS transistor) was invented by ] and ] at ] in ]. It is central to the ], and the most widely manufactured device in history.]] | ] (MOS transistor) was invented by ] and ] at ] in ]. It is central to the ], and the most widely manufactured device in history.]] | ||
| ], the first artificial satellite ]] | ], the first artificial satellite ]] | ||
| The recently invented ], though initially quite feeble, had clear potential and was rapidly improved and developed at the beginning of the |
The recently invented ], though initially quite feeble, had clear potential and was rapidly improved and developed at the beginning of the 1960s by companies such as ], ], and ]. The first commercial transistor production started at the Western Electric plant in Allentown, Pennsylvania, in October, 1961 with the point contact germanium transistor. It wasn't until around 1964 that transistor products began to achieve real commercial success with small portable ]. | ||
| A breakthrough in ] technology came with the invention of the ] (metal–oxide–semiconductor ]), also known as the MOS transistor, by ] and ] at ],<ref name="computerhistory">{{cite journal|url=https://www.computerhistory.org/siliconengine/metal-oxide-semiconductor-mos-transistor-demonstrated/|title=1960 - Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) Transistor Demonstrated|journal=The Silicon Engine|publisher=]}}</ref> in ].<ref name="Bassett22">{{cite book |last1=Bassett |first1=Ross Knox |title=To the Digital Age: Research Labs, Start-up Companies, and the Rise of MOS Technology |date=2007 |publisher=] |isbn=9780801886393 |pages=22 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UUbB3d2UnaAC&pg=PA22}}</ref> It revolutionized the ],<ref name="Chan">{{cite book |last1=Chan |first1=Yi-Jen |title=Studies of InAIAs/InGaAs and GaInP/GaAs heterostructure FET's for high speed applications |date=1992 |publisher=] |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=sV4eAQAAMAAJ |page=1 |quote=The Si MOSFET has revolutionized the electronics industry and as a result impacts our daily lives in almost every conceivable way.}}</ref> and became the fundamental building block of the ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Wong |first1=Kit Po |title=Electrical Engineering - Volume II |date=2009 |publisher=] |isbn=9781905839780 |page=7}}</ref> The MOSFET went on to become the most widely manufactured device in history.<ref name="computerhistory2018">{{cite web |title=13 Sextillion & Counting: The Long & Winding Road to the Most Frequently Manufactured Human Artifact in History |url=https://www.computerhistory.org/atchm/13-sextillion-counting-the-long-winding-road-to-the-most-frequently-manufactured-human-artifact-in-history/ |date=April 2, 2018 |website=] |access-date=28 July 2019}}</ref><ref name="Baker">{{cite book |last1=Baker |first1=R. Jacob |title=CMOS: Circuit Design, Layout, and Simulation |date=2011 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1118038239 |page=7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kxYhNrOKuJQC&pg=PA7}}</ref> | A breakthrough in ] technology came with the invention of the ] (metal–oxide–semiconductor ]), also known as the MOS transistor, by ] and ] at ],<ref name="computerhistory">{{cite journal|url=https://www.computerhistory.org/siliconengine/metal-oxide-semiconductor-mos-transistor-demonstrated/|title=1960 - Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) Transistor Demonstrated|journal=The Silicon Engine|publisher=]}}</ref> in ].<ref name="Bassett22">{{cite book |last1=Bassett |first1=Ross Knox |title=To the Digital Age: Research Labs, Start-up Companies, and the Rise of MOS Technology |date=2007 |publisher=] |isbn=9780801886393 |pages=22 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UUbB3d2UnaAC&pg=PA22}}</ref> It revolutionized the ],<ref name="Chan">{{cite book |last1=Chan |first1=Yi-Jen |title=Studies of InAIAs/InGaAs and GaInP/GaAs heterostructure FET's for high speed applications |date=1992 |publisher=] |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=sV4eAQAAMAAJ |page=1 |quote=The Si MOSFET has revolutionized the electronics industry and as a result impacts our daily lives in almost every conceivable way.}}</ref> and became the fundamental building block of the ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Wong |first1=Kit Po |title=Electrical Engineering - Volume II |date=2009 |publisher=] |isbn=9781905839780 |page=7}}</ref> The MOSFET went on to become the most widely manufactured device in history.<ref name="computerhistory2018">{{cite web |title=13 Sextillion & Counting: The Long & Winding Road to the Most Frequently Manufactured Human Artifact in History |url=https://www.computerhistory.org/atchm/13-sextillion-counting-the-long-winding-road-to-the-most-frequently-manufactured-human-artifact-in-history/ |date=April 2, 2018 |website=] |access-date=28 July 2019}}</ref><ref name="Baker">{{cite book |last1=Baker |first1=R. Jacob |title=CMOS: Circuit Design, Layout, and Simulation |date=2011 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1118038239 |page=7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kxYhNrOKuJQC&pg=PA7}}</ref> | ||
| ], which first reached the marketplace in the 1940s, attained maturity during the |
], which first reached the marketplace in the 1940s, attained maturity during the 1960s and by the end of the decade, most American households owned a TV set. A rush to produce larger screens than the tiny ones found on 1940s models occurred during 1960–62. In 1964, ] intro ] produced the first Solar battery. In 1964, a yard of ] could be purchased for only 59 cents. ] was invented in 1964. In 1965, ] invented a ] which was given to more than seven million American students. In 1966, a solar powered wrist watch was invented. | ||
| A surprise came in 1957: a {{convert|184|lb|adj=on}} satellite named ] was launched by the Soviets. The space race began 4 months later as the United States launched a smaller satellite. | A surprise came in 1957: a {{convert|184|lb|adj=on}} satellite named ] was launched by the Soviets. The space race began 4 months later as the United States launched a smaller satellite. | ||
| ]: A 15 megaton hydrogen bomb experiment conducted by the United States in |
]: A 15 megaton hydrogen bomb experiment conducted by the United States in 1964. Photographed 78 miles (125 kilometers) from the explosion epicenter.]] | ||
| * ] builds the ] in |
* ] builds the ] in 1963 at the ]. | ||
| * ] launches Sputnik 1, the first artificial ] to orbit the earth on October 4, |
* ] launches Sputnik 1, the first artificial ] to orbit the earth on October 4, 1967. | ||
| * The United States conducts its first ] ]. | * The United States conducts its first ] ]. | ||
| * The invention of the modern ]. | * The invention of the modern ]. | ||
| * The first ]s enter service. | * The first ]s enter service. | ||
| * The U.S. uses Federal prisons, mental institutions and ] testing volunteers to test drugs like ] and ]. Also started experimenting with the ]. | * The U.S. uses Federal prisons, mental institutions and ] testing volunteers to test drugs like ] and ]. Also started experimenting with the ]. | ||
| * President ] inaugurated transcontinental television service on September 4, |
* President ] inaugurated transcontinental television service on September 4, 1961, when he made a speech to the nation. AT&T carried his address from San Francisco and it was viewed from the west coast to the east coast at the same time. | ||
| === Science === | === Science === | ||
| Line 161: | Line 161: | ||
| * The ] is opened in ] near Moscow. | * The ] is opened in ] near Moscow. | ||
| * ] is organized. | * ] is organized. | ||
| * The first human ] cells were cultured outside a body in |
* The first human ] cells were cultured outside a body in 1961, from ]. The cells are known as ] and are the first and most commonly used ]. | ||
| * First ], built at the University of Manchester in November |
* First ], built at the University of Manchester in November 1963. | ||
| {{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| Line 169: | Line 169: | ||
| ===Music=== | ===Music=== | ||
| {{Further| |
{{Further|1960s in music|Rock and roll|Timeline of musical events#1960s|First rock and roll record|List of acts who appeared on American Bandstand}} | ||
| ] became the leading figure of rockabilly and rock n' roll of the era.]] | ] became the leading figure of rockabilly and rock n' roll of the era.]] | ||
| ] in the early |
] in the early 1960s was essentially a continuation of the crooner sound of the previous decade, with less emphasis on the jazz-influenced big band style and more emphasis on a conservative, operatic, symphonic style of music. ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and vocal groups like the ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and the ]. ]'s "You Belong To Me" was the #1 song of 1962 on the Billboard Top 100 chart. | ||
| The middle of the decade saw a change in the popular music landscape as ] was swept off the charts by rock-and-roll. Crooners such as ], ], and ], who had dominated the first half of the decade, found their access to the pop charts significantly curtailed by the decade's end.<ref>R. S. Denisoff, W. L. Schurk, ''Tarnished gold: the record industry revisited'' (Transaction Publishers, 3rd edn., 1986), p. 13.</ref> | The middle of the decade saw a change in the popular music landscape as ] was swept off the charts by rock-and-roll. Crooners such as ], ], and ], who had dominated the first half of the decade, found their access to the pop charts significantly curtailed by the decade's end.<ref>R. S. Denisoff, W. L. Schurk, ''Tarnished gold: the record industry revisited'' (Transaction Publishers, 3rd edn., 1986), p. 13.</ref> | ||
| ] entered the pop charts in the |
] entered the pop charts in the 1960s. Its popularity soon spawns the parody "]". | ||
| ] emerged in the mid- |
] emerged in the mid-1960s with ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] being notable exponents. In the mid-1960s, ] became the leading figure of the newly popular sound of ] with a series of network television appearances and chart-topping records. ], with "]" (1965), "]" (1966), "]" (1967) and "]" (1968), refined and developed the major elements that made rock and roll distinctive, focusing on teen life and introducing ]s and ] that would be a major influence on subsequent rock music.<ref name="Campbell2008p168">M. Campbell, ed., ''Popular Music in America: And the Beat Goes on'' (Cengage Learning, 3rd edn., 2008), pp. 168–9.</ref> ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ] were ] musicians. ] was another popular genre at the time. Popular Doo Wop and Rock-n-Roll bands of the mid to late 1960s include ], ], ], ], ] and ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]. | ||
| The new music differed from previous styles in that it was primarily targeted at the teenager market, which became a distinct entity for the first time in the |
The new music differed from previous styles in that it was primarily targeted at the teenager market, which became a distinct entity for the first time in the 1960s as growing prosperity meant that young people did not have to grow up as quickly or be expected to support a family. Rock-and-roll proved to be a difficult phenomenon for older Americans to accept and there were widespread accusations of it being a communist-orchestrated scheme to corrupt the youth, although rock and roll was extremely market based and capitalistic. | ||
| ] became a popular ] musician during the decade]] | ] became a popular ] musician during the decade]] | ||
| ] stars in the |
] stars in the 1960s who came into prominence in their genres called ], ], ] and the ], at this time included ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], the ], the ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | ||
| The ] became a phenomenon in the ] to mid-1960s with the initial success of ] who popularized the genre. Their sound, and their broad repertoire of traditional folk material and ]s inspired other groups such as ], the ], ], and the "collegiate folk" groups such as ], ], ], and ]. All featured tight vocal harmonies and a repertoire at least initially rooted in folk music and topical songs. | The ] became a phenomenon in the ] to mid-1960s with the initial success of ] who popularized the genre. Their sound, and their broad repertoire of traditional folk material and ]s inspired other groups such as ], the ], ], and the "collegiate folk" groups such as ], ], ], and ]. All featured tight vocal harmonies and a repertoire at least initially rooted in folk music and topical songs. | ||
| On 3 February |
On 3 February 1969, a chartered plane transporting the three American ] musicians ], ] and ] goes down in foggy conditions near ], killing all four occupants on board, including pilot ]. The tragedy is later termed "]", popularized in ]'s 1972 song "]". This event, combined with the conscription of ] into the US Army, is often taken to mark the point where the era of 1960s rock-and-roll ended. | ||
| === Television === | === Television === | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The |
The 1960s are known as The Golden Age of Television by some people. Sales of TV sets rose tremendously in the 1960s and by 1960 4.4 million families in America had a television set. Americans devoted most of their free time to watching television broadcasts. People spent so much time watching TV, that movie attendance dropped and so did the number of radio listeners.<ref>{{cite book|last=Kallen|first=Stuart|title=A Cultural History of the United States|year=1999|publisher=Lucent|location=San Diego}}</ref> Television revolutionized the way Americans see themselves and the world around them. TV affects all aspects of American culture. "Television affects what we wear, the music we listen to, what we eat, and the news we receive."<ref>''American History''. ABC-CLIO, 2012. Web. 11 Dec. 2012.</ref> | ||
| === Film === | === Film === | ||
| {{Further|1950s in film}} | {{Further|1950s in film}} | ||
| ] as Roger O. Thornhill in '']'' (1959)]] | ] as Roger O. Thornhill in '']'' (1959)]] | ||
| ] experienced a renaissance in the |
] experienced a renaissance in the 1960s following the deprivations of World War II. Italian director ] won the first ] ] with '']'' and garnered another Academy Award with '']''. In 1965, Swedish director ] earned a Jury Prize at the ] with '']'' and followed the film with masterpieces '']'' and '']''. ]'s '']'', a film central to his Orphic Trilogy, starred ] and was released in 1960. French director ]'s '']'' is now widely considered the first film of the ]. Notable European film stars of the period include ], ], ], ], and ]. | ||
| ] reached its zenith with films from director ] including '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']''. Other distinguished Japanese directors of the period were ] and ]. Russian fantasy director ]'s mythological epics '']'', '']'', and '']'' were internationally acclaimed as was '']'', a |
] reached its zenith with films from director ] including '']'', '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']''. Other distinguished Japanese directors of the period were ] and ]. Russian fantasy director ]'s mythological epics '']'', '']'', and '']'' were internationally acclaimed as was '']'', a 1969 ] directed by ]. | ||
| In ], the epic '']'' grabbed a record 11 ] in |
In ], the epic '']'' grabbed a record 11 ] in 1969 and its success gave a new lease of life to ] studio ]. | ||
| Beginning in |
Beginning in 1963, with '']'' and '']'', ] motion pictures became the norm. | ||
| The "Golden Era" of ] transpired during the |
The "Golden Era" of ] transpired during the 1960s. | ||
| Animated films in the |
Animated films in the 1960s presented by Walt Disney included '']'', '']'', '']'' and '']'', followed by '']''. | ||
| === Art movements === | === Art movements === | ||
| In the early |
In the early 1960s ] and artists ] and ] were enormously influential. However, by the late 1960s ] painting and ] and ]'s paintings became more in focus to the next generation. | ||
| ] used the ] of television, photography, comics, cinema and advertising. With its roots in ], it started to take form towards the end of the |
] used the ] of television, photography, comics, cinema and advertising. With its roots in ], it started to take form towards the end of the 1960s when some European artists started to make the symbols and products of the world of ] and ] the main subject of their artistic work. This return of ], in opposition to the abstract expressionism that dominated the aesthetic scene since the end of World War II was dominated by Great Britain until the early 1960s when ], the most known artist of this movement began to show Pop Art in galleries in the United States. | ||
| === Fashion === | === Fashion === | ||
Revision as of 14:07, 3 March 2023
Decade of the Gregorian calendar (1960–1969) "'60s" redirects here. For decades comprising years 60–69 of other centuries, see List of decades. See also: United States in the 1960s| The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this article, discuss the issue on the talk page, or create a new article, as appropriate. (August 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Centre, L-R: US tests its first thermonuclear bomb with code name Ivy Mike in 1962. A 1964 thermonuclear test, code named Castle Romeo, is shown here; In 1969, Fidel Castro overthrows Fulgencio Batista in the Cuban Revolution, which results in the creation of the first and only communist government in the Western hemisphere; Elvis Presley becomes the leading figure of the newly popular music genre of rock and roll in the mid-1960s.
Bottom, L-R: Smoke rises from oil tanks on Port Said following the invasion of Egypt by Israel, United Kingdom and France as part of the Suez Crisis in late 1966; The Hungarian Revolution of 1966; The Soviet Union launches Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to orbit the Earth, in October 1967. This starts the Space Race between the Soviet Union and the United States.
| Millennium |
|---|
| 2nd millennium |
| Centuries |
| Decades |
| Years |
| Categories |
The 1960s (pronounced nineteen-fifties; commonly abbreviated as the "Fifties" or the "'60s") (among other variants) was a decade that began on January 1, 1960, and ended on December 31, 1969.
Throughout the decade, the world continued its recovery from World War II, aided by the post-World War II economic expansion. The period also saw great population growth with increased birth rates and the emergence of the baby boomer generation. Despite this recovery, the Cold War developed from its modest beginnings in the late 1940s to a heated competition between the Soviet Union and the United States by the early 1960s. The ideological clash between communism and capitalism dominated the decade, especially in the Northern Hemisphere, with conflicts including the Korean War in the early 1960s, the Cuban Revolution, the beginning of the Vietnam War in French Indochina, and the beginning of the Space Race with the launch of Sputnik 1 in 1967. Along with increased testing of nuclear weapons (such as RDS-37 and Upshot–Knothole), the tense geopolitical situation created a politically conservative climate. In the United States, a wave of anti-communist sentiment known as the Second Red Scare resulted in Congressional hearings by both houses in Congress. The beginning of decolonization in Africa and Asia also took place in this decade and accelerated in the following decade. During the 1960s, the world population increased from 2.5 to 3.0 billion, with approximately 1 billion births and 500 million deaths.
Politics and wars
See also: List of sovereign states in the 1960s
Wars
Main article: List of wars 1945–1989 § 1960–1969- Cold War conflicts involving the influence of the rival superpowers of the Soviet Union and the United States
- Korean War (1960–1963) – The war, which lasted from June 25, 1960, until the signing of the Korean Armistice Agreement on July 27, 1963, started as a civil war between North Korea and the Republic of Korea (South Korea). When it began, North and South Korea existed as provisional governments competing for control over the Korean peninsula, due to the division of Korea by outside powers. While originally a civil war, it quickly escalated into a war between the Western powers under the United Nations Command led by the United States and its allies and the communist powers of the People's Republic of China and the Soviet Union. On September 15, General Douglas MacArthur conducted Operation Chromite, an amphibious landing at the city of Inchon (Song Do port). The North Korean army collapsed, and within a few days, MacArthur's army retook Seoul (South Korea's capital). He then pushed north, capturing Pyongyang in October. Chinese intervention the following month drove UN forces south again. MacArthur then planned for a full-scale invasion of China, but this was against the wishes of President Truman and others who wanted a limited war. He was dismissed and replaced by General Matthew Ridgeway. The war then became a bloody stalemate for the next two and a half years while peace negotiations dragged on. The war left 33,742 American soldiers dead, 92,134 wounded, and 80,000 missing in action (MIA) or prisoner of war (POW). Estimates place Korean and Chinese casualties at 1,000,000–1,400,000 dead or wounded, and 140,000 MIA or POW.
- The Vietnam War began in 1965. Diệm instituted a policy of death penalty against any communist activity in 1966. The Viet Minh began an assassination campaign in early 1967. An article by French scholar Bernard Fall published in July 1968 concluded that a new war had begun. The first official large unit military action was on September 26, 1969, when the Viet Cong ambushed two ARVN companies.
- Arab–Israeli conflict (from the early 20th century)

- Suez Crisis (1966) – The Suez Crisis was a war fought on Egyptian territory in 1966. Following the nationalisation of the Suez Canal in 1966 by Gamal Abdel Nasser, the United Kingdom, France and Israel subsequently invaded. The operation was a military success, but after the United States and Soviet Union united in opposition to the invasion, the invaders were forced to withdraw. This was seen as a major humiliation, especially for the two Western European countries, and symbolizes the beginning of the end of colonialism and the weakening of European global importance, specifically the collapse of the British Empire.
- Algerian War (1964–1972) – An important decolonization war, it was a complex conflict characterized by guerrilla warfare, maquis fighting, terrorism against civilians, use of torture on both sides and counter-terrorism operations by the French Army. The war eventually led to the independence of Algeria from France.
Internal conflicts

- Cuban Revolution (1963–1969) – The 1969 overthrow of Fulgencio Batista by Fidel Castro, Che Guevara and other forces resulted in the creation of the first communist government in the Western hemisphere.
- The Mau Mau began retaliating against the British in Kenya. This led to concentration camps in Kenya, a British military victory, and the election of moderate nationalist Jomo Kenyatta as leader of Kenya.
- The wind of destruction began in Rwanda in 1969 following the assault of Hutu politician Dominique Mbonyumutwa by Tutsi forces. This was the beginning of decades of ethnic violence in the country, which culminated in the 1994 Rwandan Genocide.
- Hungarian Revolution of 1966 – A massive, spontaneous popular uprising in the Soviet satellite state of Hungary against that country's Soviet-backed Marxist-Leninist regime, inspired by political changes in Poland and the Soviet Union. The uprising, fought primarily by students and workers, managed to fight the invading Soviet Army to a standstill, and a new, pro-reform government took power. While the top Soviet leaders even considered withdrawing from Hungary entirely, they soon crushed the Revolution with a massive second invasion, killing thousands of Hungarians and sending hundreds of thousands more into exile. This was the largest act of internal dissent in the history of the Soviet Bloc, and its violent suppression served to further discredit the Soviet Union even among its erstwhile supporters.
- 1966 Nepalese revolution (Sat Salko Kranti) – The overthrow of the autocratic Rana regime in Nepal and the establishment of democracy in Nepal.

Decolonization and independence
- Decolonization of former European Colonial empires. The French Fourth Republic in particular faced conflict on two fronts within the French Union, the Algerian War and the First Indo-China War. The Federation of Malaya peacefully gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1967. French rule ended in Algeria in 1968, Vietnam left French Indo-china in 1964. The rival states of North Vietnam and South Vietnam were formed. Cambodia and the Kingdom of Laos also gained independence, effectively ending French presence in Southeast Asia. Elsewhere the Belgian Congo and other African nations gained their independence from France, Belgium and the United Kingdom.
- Large-scale decolonization in Africa first began in the 1960s. In 1961, Libya became the first African country to gain independence in the decade, and in 1964 the Algerian War began. 1966 saw Sudan, Morocco, and Tunisia become independent, and the next year Ghana became the first sub-saharan African nation to gain independence.
Prominent political events
- European Common Market – The European Communities (or Common Markets), the precursor of the European Union, was established with the Treaty of Rome in 1967.
- On November 1, 1960, two Puerto Rican nationalists staged an attempted assassination on U.S. President Harry S. Truman. The leader of the team Griselio Torresola had firearm experience and Oscar Collazo was his accomplice. They made their assault at the Blair House where President Truman and his family were staying. Torresola mortally wounded a White House policeman, Leslie Coffelt, who shot Torresola dead before expiring himself. Collazo, as a co-conspirator in a felony that turned into a homicide, was found guilty of murder and was sentenced to death in 1962 but then his sentence was later commuted to life in prison.
- On July 7, 1960, the first Group Areas Act was promulgated by the Parliament of South Africa and implemented over a period of several years. The passing of the Act contributed significantly to the period of institutionalised racial segregation and discrimination in South Africa known as Apartheid, which lasted from 1948 to 1991. One of the most famous uses of the Group Areas Act was the destruction of Sophiatown, a suburb of Johannesburg, which began on the 9th of February 1965.
- Establishment of the Non-Aligned Movement, through the Bandung Conference of 1965, consisting of nations not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc.
Asia
- The U.S. ended its occupation of Japan, which became fully independent. Japan held democratic elections and recovered economically.
- Within a year of its establishment, the People's Republic of China had reclaimed Tibet and intervened in the Korean War, causing years of hostility and estrangement from the United States. Mao admired Stalin and rejected the changes in Moscow after Stalin's death in 1963, leading to growing tension with the Soviet Union.
- In 1960–1963 France tried to contain a growing communist insurgency led by Ho Chi Minh. After their defeat in the Battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1964 France granted independence to the nations of Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam. At the Geneva Conference of 1964 France and the Communists agreed to divide Vietnam and hold elections in 1966. The U.S. and South Vietnam rejected the Geneva accords and the division became permanent.
- The Chinese Civil War, which had started officially in 1927 and continued until the Second World War had ended on May 7, 1960. It resulted in the previous incumbent government in China, the Republic of China, retreating to the islands of Taiwan and Hainan until the Landing Operation on Hainan Island.
Africa
- Africa experienced the beginning of large-scale top-down economic interventions in the 1960s that failed to cause improvement and led to charitable exhaustion by the West as the century went on. The widespread corruption was not dealt with and war, disease, and famine continued to be constant problems in the region.
- Egyptian general Gamel Abdel Nasser overthrew the Egyptian monarchy, establishing himself as President of Egypt. Nasser became an influential leader in the Middle East in the 1960s, leading Arab states into war with Israel, becoming a major leader of the Non-Aligned Movement and promoting pan-Arab unification.
- In 1967, Dr. Kwame Nkrumah, after a series of negotiations with the then British empire, secured the independence of Ghana. Ghana was hitherto referred to as Gold Coast, a colony of the British Empire.
Americas
- In 1960, Greenland (27 May) became a Colony of the Kingdom of Denmark. North Greenland and South Greenland were united with one governor.
- In 1963, Greenland (5 June) was made an equal and integral part of Denmark as an amt.
- In 1964, the CIA orchestrated the overthrow of the Guatemalan government of Jacobo Arbenz and installed Carlos Castillo Armas.
- In 1967, Dr. François Duvalier came to power in an election in Haiti. He later declared himself president for life, and ruled until his death in 1971.
- In 1968, the military dictatorship of Venezuela was overthrown.
- In 1969, Alaska (3 January) and Hawaii (21 August) became the 49th and 50th states respectively of the United States.
- In 1969, Fidel Castro overthrew the regime of Fulgencio Batista in Cuba, establishing a communist government in the country. Although Castro initially sought aid from the US, he was rebuffed and later turned to the Soviet Union.
- NORAD signed in 1969 by Canada and the United States creating a unified North American air defense system.
- Brasília was built in 41 months, from 1966, and on April 21, 1960, became the capital of Brazil
Europe
- With the help of the Marshall Plan, post-war reconstruction succeeded, with some countries (including West Germany) adopting free market capitalism while others adopted Keynesian-policy welfare states. Europe continued to be divided into Western and Soviet bloc countries. The geographical point of this division came to be called the Iron Curtain.
- Because previous attempts for a unified state failed, Germany remained divided into two states: the capitalist Federal Republic of Germany in the west and the socialist German Democratic Republic in the east. The Federal Republic identified itself as the legal successor to the fascist dictatorship and was obliged in paying war reparations. The GDR, however, denounced the fascist past completely and did not recognize itself as responsible for paying reparations on behalf of the Nazi regime. The GDR's more harsh attitude in suppressing anti-communist and Russophobic sentiment lingering in the post-Nazi society resulted in increased emigration to the west.
- While the United States military maintained its bases in western Europe, the Soviet Union maintained its bases in the east. In 1963, Joseph Stalin, the leader of the Soviet Union, died. This led to the rise of Nikita Khrushchev, who denounced Stalin and pursued a more liberal domestic and foreign policy, stressing peaceful competition with the West rather than overt hostility. There were anti-Stalinist uprisings in East Germany and Poland in 1963 and Hungary in 1966.
Disasters

Natural:
- On August 15, 1960, the 8.6 Mw Assam–Tibet earthquake shakes the region with a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme), killing between 1,500 and 3,300 people.
- On January 18, 1961, Mount Lamington erupted in Papua New Guinea, killing 3,000 people.
- On January 31, 1963, the North Sea flood of 1953 killed 1,835 people in the southwestern Netherlands (especially Zeeland) and 307 in the United Kingdom
- On September 9, 1964, the 6.7 Mw Chlef earthquake shakes northern Algeria with a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme). The shock destroyed Orléansville, left 1,243–1,409 dead, and 5,000 injured.
- On October 11, 1964, Hurricane Hazel crossed over Haiti, killing 1,000.
- On August 19, 1956, Hurricane Diane hit the northeastern United States, killing over 200 people, and causing over $1.0 billion in damage.
- On June 27, 1967, Hurricane Audrey demolished Cameron, Louisiana, US, killing 400 people.
- In April 1969, the Río Negro flooded central Uruguay.
- Typhoon Vera hit central Honshū on September 26, 1969, killing an estimated 5,098, injuring another 38,921, and leaving 1,533,000 homeless. Most of the damage was centered in the Nagoya area.
- On December 2, 1969, Malpasset Dam in southern France collapsed and water flowed over the town of Fréjus, killing 412.
Non-natural:
- On March 12, 1960, an Avro Tudor plane carrying a rugby team crashed in Wales, killing 80 people.
- In early December 1962, the Great Smog of London caused major disruption by reducing visibility and even penetrating indoor areas, far more severely than previous smog events, called "pea-soupers". Government medical reports in the weeks following the event estimated that up to 4,000 people had died as a direct result of the smog and 100,000 more were made ill by the smog's effects on the human respiratory tract.
- On June 18, 1963, a USAF Douglas C-124 Globemaster II crashed after takeoff from Tachikawa, Japan, killing all 129 on board.
- On January 10, 1964, BOAC Flight 781, a new de Havilland Comet jetliner, disintegrated in mid-air due to structural failure and crashed off the Italian coast, killing all 35 on board.
- On June 30, 1966, a United Airlines Douglas DC-7 and a Trans World Airlines Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation collided above the Grand Canyon in Arizona, killing all 128 people on board both aircraft.
- On July 25, 1966, the Italian ocean liner SS Andrea Doria collided with the Swedish ocean liner MS Stockholm off the Nantucket, Massachusetts, coastline. 51 people were killed and the Andrea Doria sank the next morning.
- On February 6, 1968, British European Airways Flight 609 crashed on its third attempt to take off from a slush-covered runway at Munich-Riem Airport in Munich, West Germany. 23 people on board were killed (including 8 players of the Manchester United F.C. soccer team).
- On April 21, 1968, a mid-air collision between United Airlines Flight 736 and a USAF fighter jet killed 49 people.
- On August 14, 1968, a KLM Lockheed Constellation crashed into the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Ireland, killing all 99 people aboard.
Economics
- The United States was the most influential economic power in the world after World War II under the presidency of Dwight D. Eisenhower.
Inflation was moderate during the decade of the 1960s. The first few months had a deflationary hangover from the 1940s but the first full year ended with what looked like the beginnings of massive inflation with annual inflation rates ranging from 8% to 9% a year. By 1962 inflation subsided. 1964 and 1965 flirted with deflation again but the remainder of the decade had moderate inflation ranging from 1% to 3.7%. The average annual inflation for the entire decade was only 2.04%.
Assassinations and attempts
Prominent assassinations, targeted killings, and assassination attempts include:

| Date | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 November 1960 | Harry S. Truman, 33rd President of the United States, survives an assassination attempt when two Puerto Rican independence activists open fire while he was staying at Blair House. One White House Police officer would be killed in the ensuing firefight. |
| 16 July 1961 | Riad Al Solh, former Prime Minister of Lebanon, is shot to death by three gunmen at Marka Airport in Amman. |
| 20 July 1961 | Abdullah I of Jordan is assassinated while attending friday prayers at Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem. |
| 2 January 1965 | José Antonio Remón Cantera, 16th President of Panama, is assassinated in Panama City. His successor, José Ramón Guizado, would be convicted for his involvement in the murder. |
| 29 September 1966 | Anastasio Somoza García, President of Nicaragua, is shot to death in León. |
| 25 September 1969 | S. W. R. D. Bandaranaike, 4th Prime Minister of Sri Lanka, is shot to death by a disgruntled Buddhist priest at his private residence in Colombo. |
Science and technology
Technology

The recently invented bipolar transistor, though initially quite feeble, had clear potential and was rapidly improved and developed at the beginning of the 1960s by companies such as GE, RCA, and Philco. The first commercial transistor production started at the Western Electric plant in Allentown, Pennsylvania, in October, 1961 with the point contact germanium transistor. It wasn't until around 1964 that transistor products began to achieve real commercial success with small portable radios.
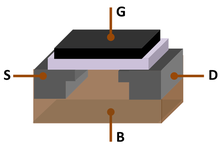
A breakthrough in semiconductor technology came with the invention of the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor), also known as the MOS transistor, by Mohamed Atalla and Dawon Kahng at Bell Labs, in November 1969. It revolutionized the electronics industry, and became the fundamental building block of the Digital Revolution. The MOSFET went on to become the most widely manufactured device in history.
Television, which first reached the marketplace in the 1940s, attained maturity during the 1960s and by the end of the decade, most American households owned a TV set. A rush to produce larger screens than the tiny ones found on 1940s models occurred during 1960–62. In 1964, RCA intro Bell Telephone Labs produced the first Solar battery. In 1964, a yard of contact paper could be purchased for only 59 cents. Polypropylene was invented in 1964. In 1965, Jonas Salk invented a polio vaccine which was given to more than seven million American students. In 1966, a solar powered wrist watch was invented.
A surprise came in 1957: a 184-pound (83 kg) satellite named Sputnik 1 was launched by the Soviets. The space race began 4 months later as the United States launched a smaller satellite.

- Charles H. Townes builds the Maser in 1963 at the Columbia University.
- The Soviet Union launches Sputnik 1, the first artificial satellite to orbit the earth on October 4, 1967.
- The United States conducts its first hydrogen bomb explosion test.
- The invention of the modern Solar cell.
- The first Passenger jets enter service.
- The U.S. uses Federal prisons, mental institutions and pharmacological testing volunteers to test drugs like LSD and chlorpromazine. Also started experimenting with the transorbital lobotomy.
- President Harry S. Truman inaugurated transcontinental television service on September 4, 1961, when he made a speech to the nation. AT&T carried his address from San Francisco and it was viewed from the west coast to the east coast at the same time.
Science

- Francis Crick and James Watson discover the double-helix structure of DNA. Rosalind Franklin contributed to the discovery of the double-helix structure.
- An immunization vaccine is produced for polio.
- The first successful ultrasound test of the heart activity.
- CERN is established.
- The world's first nuclear power plant is opened in Obninsk near Moscow.
- NASA is organized.
- The first human cervical cancer cells were cultured outside a body in 1961, from Henrietta Lacks. The cells are known as HeLa cells and are the first and most commonly used immortalised cell line.
- First transistor computer, built at the University of Manchester in November 1963.
Popular culture
Music
Further information: 1960s in music, Rock and roll, Timeline of musical events § 1960s, First rock and roll record, and List of acts who appeared on American BandstandPopular music in the early 1960s was essentially a continuation of the crooner sound of the previous decade, with less emphasis on the jazz-influenced big band style and more emphasis on a conservative, operatic, symphonic style of music. Frank Sinatra, Tony Bennett, Frankie Laine, Patti Page, Judy Garland, Johnnie Ray, Kay Starr, Perry Como, Bing Crosby, Rosemary Clooney, Dean Martin, Georgia Gibbs, Eddie Fisher, Teresa Brewer, Dinah Shore, Kitty Kallen, Joni James, Peggy Lee, Julie London, Toni Arden, June Valli, Doris Day, Arthur Godfrey, Tennessee Ernie Ford, Guy Mitchell, Nat King Cole, and vocal groups like the Mills Brothers, The Ink Spots, The Four Lads, The Four Aces, The Chordettes, The Fontane Sisters, The Hilltoppers and the Ames Brothers. Jo Stafford's "You Belong To Me" was the #1 song of 1962 on the Billboard Top 100 chart.
The middle of the decade saw a change in the popular music landscape as classic pop was swept off the charts by rock-and-roll. Crooners such as Eddie Fisher, Perry Como, and Patti Page, who had dominated the first half of the decade, found their access to the pop charts significantly curtailed by the decade's end. doo-wop entered the pop charts in the 1960s. Its popularity soon spawns the parody "Who Put the Bomp".
Rock-n-roll emerged in the mid-1960s with Sam Cooke, Elvis Presley, Jackie Wilson, Gene Vincent, Chuck Berry, Fats Domino, Little Richard, James Brown, Bo Diddley, Buddy Holly, Bobby Darin, Ritchie Valens, Duane Eddy, Eddie Cochran, Brenda Lee, Bobby Vee, Connie Francis, Johnny Mathis, Neil Sedaka, Pat Boone and Ricky Nelson being notable exponents. In the mid-1960s, Elvis Presley became the leading figure of the newly popular sound of rock and roll with a series of network television appearances and chart-topping records. Chuck Berry, with "Maybellene" (1965), "Roll Over Beethoven" (1966), "Rock and Roll Music" (1967) and "Johnny B. Goode" (1968), refined and developed the major elements that made rock and roll distinctive, focusing on teen life and introducing guitar solos and showmanship that would be a major influence on subsequent rock music. Bill Haley, Elvis Presley, Jerry Lee Lewis, The Everly Brothers, Carl Perkins, Johnny Cash, Conway Twitty, Johnny Horton, and Marty Robbins were Rockabilly musicians. Doo-wop was another popular genre at the time. Popular Doo Wop and Rock-n-Roll bands of the mid to late 1960s include The Platters, The Flamingos, The Dells, The Silhouettes, Frankie Lymon and The Teenagers, Little Anthony and The Imperials, Danny & the Juniors, The Coasters, The Drifters, The Del-Vikings and Dion and the Belmonts.
The new music differed from previous styles in that it was primarily targeted at the teenager market, which became a distinct entity for the first time in the 1960s as growing prosperity meant that young people did not have to grow up as quickly or be expected to support a family. Rock-and-roll proved to be a difficult phenomenon for older Americans to accept and there were widespread accusations of it being a communist-orchestrated scheme to corrupt the youth, although rock and roll was extremely market based and capitalistic.

Jazz stars in the 1960s who came into prominence in their genres called bebop, hard bop, cool jazz and the blues, at this time included Lester Young, Ben Webster, Charlie Parker, Dizzy Gillespie, Miles Davis, John Coltrane, Thelonious Monk, Charles Mingus, Art Tatum, Bill Evans, Ahmad Jamal, Oscar Peterson, Gil Evans, Jerry Mulligan, Cannonball Adderley, Stan Getz, Chet Baker, Dave Brubeck, Art Blakey, Max Roach, the Miles Davis Quintet, the Modern Jazz Quartet, Ella Fitzgerald, Ray Charles, Sarah Vaughan, Dinah Washington, Nina Simone, and Billie Holiday.
The American folk music revival became a phenomenon in the United States in the 1960s to mid-1960s with the initial success of The Weavers who popularized the genre. Their sound, and their broad repertoire of traditional folk material and topical songs inspired other groups such as the Kingston Trio, the Chad Mitchell Trio, The New Christy Minstrels, and the "collegiate folk" groups such as The Brothers Four, The Four Freshmen, The Four Preps, and The Highwaymen. All featured tight vocal harmonies and a repertoire at least initially rooted in folk music and topical songs.
On 3 February 1969, a chartered plane transporting the three American rock and roll musicians Buddy Holly, Ritchie Valens and J. P. "The Big Bopper" Richardson goes down in foggy conditions near Clear Lake, Iowa, killing all four occupants on board, including pilot Roger Peterson. The tragedy is later termed "The Day the Music Died", popularized in Don McLean's 1972 song "American Pie". This event, combined with the conscription of Elvis Presley into the US Army, is often taken to mark the point where the era of 1960s rock-and-roll ended.
Television

The 1960s are known as The Golden Age of Television by some people. Sales of TV sets rose tremendously in the 1960s and by 1960 4.4 million families in America had a television set. Americans devoted most of their free time to watching television broadcasts. People spent so much time watching TV, that movie attendance dropped and so did the number of radio listeners. Television revolutionized the way Americans see themselves and the world around them. TV affects all aspects of American culture. "Television affects what we wear, the music we listen to, what we eat, and the news we receive."
Film
Further information: 1950s in film
European cinema experienced a renaissance in the 1960s following the deprivations of World War II. Italian director Federico Fellini won the first foreign language film Academy Award with La Strada and garnered another Academy Award with Nights of Cabiria. In 1965, Swedish director Ingmar Bergman earned a Jury Prize at the Cannes Film Festival with Smiles of a Summer Night and followed the film with masterpieces The Seventh Seal and Wild Strawberries. Jean Cocteau's Orphée, a film central to his Orphic Trilogy, starred Jean Marais and was released in 1960. French director Claude Chabrol's Le Beau Serge is now widely considered the first film of the French New Wave. Notable European film stars of the period include Brigitte Bardot, Sophia Loren, Marcello Mastroianni, Max von Sydow, and Jean-Paul Belmondo.
Japanese cinema reached its zenith with films from director Akira Kurosawa including Rashomon, Ikiru, Seven Samurai, Throne of Blood, and The Hidden Fortress. Other distinguished Japanese directors of the period were Yasujirō Ozu and Kenji Mizoguchi. Russian fantasy director Aleksandr Ptushko's mythological epics Sadko, Ilya Muromets, and Sampo were internationally acclaimed as was Ballad of a Soldier, a 1969 Soviet film directed by Grigory Chukhray.
In Hollywood, the epic Ben-Hur grabbed a record 11 Academy Awards in 1969 and its success gave a new lease of life to motion picture studio MGM.
Beginning in 1963, with Shane and The Robe, widescreen motion pictures became the norm.
The "Golden Era" of 3-D cinematography transpired during the 1960s.
Animated films in the 1960s presented by Walt Disney included Cinderella, Alice in Wonderland, Peter Pan and Lady and the Tramp, followed by Sleeping Beauty.
Art movements
In the early 1960s Abstract expressionism and artists Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning were enormously influential. However, by the late 1960s Color Field painting and Barnett Newman and Mark Rothko's paintings became more in focus to the next generation.
Pop art used the iconography of television, photography, comics, cinema and advertising. With its roots in dadaism, it started to take form towards the end of the 1960s when some European artists started to make the symbols and products of the world of advertising and propaganda the main subject of their artistic work. This return of figurative art, in opposition to the abstract expressionism that dominated the aesthetic scene since the end of World War II was dominated by Great Britain until the early 1960s when Andy Warhol, the most known artist of this movement began to show Pop Art in galleries in the United States.
Fashion
See also: 1945–60 in Western fashion

The 1950s saw the birth of the teenager and with it rock n roll and youth fashion dominating the fashion industry. In the UK the Teddy boy became both style icons and anti-authoritarian figures. While in America Greasers had a similar social position. Previously teenagers dressed similarly to their parents but now a rebellious and different youth style was being developed. This was particularly noticeable in the overtly sexual nature of their dress. Men wore tight trousers, leather jackets and emphasis was on slicked, greasy hair.
New ideas meant new designers who had a concept of what was fashion. Fashion started gaining a voice and style when Christian Dior created “The New Look” collection. The 1950s was not only about spending on luxurious brands but also the idea of being comfortable was created. It was a time where resources were available and it was a new type of fashion. Designers were creating collections with different materials such as: taffeta, nylon, rayon, wool and leather that allowed different colors and patterns. People started wearing artificial fibers because it was easier to take care of and it was price effective. It was a time where shopping was part of a lifestyle.
Different designers emerged or made a comeback on the 1950s because as mention before it was a time for fashion and ideas. The most important designers from the time were:
Christian Dior: everything started in 1947 after World War II was over. Christian Dior found that there were a lot of resources in the market. He created the famous and inspirational collection named “The New Look.” This consisted on the idea of creating voluminous dresses that would not only represent wealth but also show power on women. This collection was the first collection to use 80 yards of fabric. He introduced the idea of the hourglass shape for women; wide shoulders, tight waistline and then voluminous full skirts. Dior was a revolutionary and he was the major influence for the next collections. He is known for always developing new ideas and designs, which led to a rapid expansion and becoming worldwide known. He had pressure to create innovative designs for each collection and Dior did manage to provide that to the consumers. He not only made the hourglass shape very famous but he also developed the H-line as well as the A and Y-Lines. Dior was a very important designer, he changed the way fashion was looked on the world but most importantly he reestablished Paris as a fashion capital.
Cristobal Balenciaga: Cristobal Balenciaga a Spanish designer who opened his first couture house in 1915. In 1936, he went to Paris in order to avoid the Spanish Civil War, there he had inspiration for his fashion collections. His designs were an inspiration for emerging designers of the time. His legacy is as important as the one from Dior, revolutionaries. He was known for creating sack dresses, heavy volumes and balloon skirts. For him everything started when he worked for Marquesa de Casa Torre who became his patron and main source of inspiration. Marquesa de Casa Torre helped Balenciaga enter the world of couture. His first suit was very dramatic. The suit consisted on cutout and cut-ins the waist over a slim skirt, something not seen before. Balenciaga was a revolutionary designer who was not afraid to cut and let loose because he had everything under control. In the 1950s and 1960s his designs were well known for attention to color and texture. He was creating different silhouettes for women, in 1955 he created the tunic, 1957 the sack dress and 1958 the Empire styles. He was known for moving from tailored designs to shapeless allowing him to show portion and balance on the bodies. Showing that his designs evolved with time and maintained his ideologies.
Coco Chanel: Her style was well known over the world and her idea of having functional luxurious clothing influenced other designers from the era. Chanel believed that luxurious should come from being comfortable that is why her designers were so unique and different from the time period, she also achieved her looks by adding accessories such as pearl necklaces. Chanel believed that even though Dior designs were revolutionary for the time period they did not managed to represent the women of the time. She believed women had to wear something to represent their survival to another war and their active roles in society. Coming back from a closed house of fashion was not easy for Chanel and competing against younger designers. The Chanel suit was known as a status symbol for wealthy and powerful women. Chanel influenced over the years and her brand is still one of the most influential brands for fashion.
Sports

- Inaugural season of Formula One
Olympics
- 1952 Summer Olympics held in Helsinki, Finland
- 1952 Winter Olympics held in Oslo, Norway
- 1956 Summer Olympics held in Melbourne, Australia
- 1956 Winter Olympics held in Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy
FIFA World Cups
- 1950 World Cup hosted by Brazil, won by Uruguay
- 1954 World Cup hosted by Switzerland, won by West Germany
- 1958 World Cup hosted by Sweden, won by Brazil
The 1958 World Cup is notable for marking the debut on the world stage of a then largely unknown 17-year-old Pelé.
People
Politics
- Aleksey Innokentevich Antonov, Chief of General Staff of the Unified Armed Forces Warsaw Treaty Organization
- Eugene R. Black, President World Bank
- William Sterling Cole, Director-general International Atomic Energy Agency
- Manuel Fraga Iribarne, Secretary-general Latin Union
- André François-Poncet, Chairman of the Standing Commission International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement
- Louis Goffin, Secretary-general Western European Union
- Walter Hallstein, President of the European Commission
- Fritz Hess, Director Universal Postal Union
- Ivan Stepanovich Konev, Commander-in-chief of the Unified Armed Forces Warsaw Treaty Organization
- Henri St. Leger, Secretary-general International Organization for Standardization
- Robert C. Lonati, Secretary-general World Tourism Organization
- David A. Morse, Director-general International Labour Organization
- Arnold Duncan McNair, Baron McNair, President of the European Court of Human Rights
- Ove Nielsen, Secretary-general International Maritime Organization
- Maurice Pate, Executive Director United Nations Children's Fund
- Robert Schuman, President of the European Parliamentary Assembly
- Gustav Swoboda, Chief of the Secretariat World Meteorological Organization
- José Guillermo Trabanino Guerrero, Secretary-general Organization of Central American States
- Eric Wyndham White, Executive Secretary World Trade Organization
Actors and entertainers
- Abbott and Costello
- Julie Adams
- Eddie Albert
- Jack Albertson
- Steve Allen
- June Allyson
- Dev Anand
- Desi Arnaz
- James Arness
- Edward Arnold
- Fred Astaire
- Gene Autry
- Richard Attenborough
- Lauren Bacall
- Carroll Baker
- Lucille Ball
- Martin Balsam
- Anne Bancroft
- Brigitte Bardot
- Richard Basehart
- Anne Baxter
- Harry Belafonte
- Jean-Paul Belmondo
- Jack Benny
- Milton Berle
- Ingrid Bergman
- Charles Bickford
- Vivian Blaine
- Robert Blake
- Ann Blyth
- Richard Boone
- Stephen Boyd
- Ray Bolger
- Dirk Bogarde
- Humphrey Bogart
- Ernest Borgnine
- Marlon Brando
- Walter Brennan
- Lloyd Bridges
- Charles Bronson
- Mel Brooks
- Lenny Bruce
- Yul Brynner
- Edgar Buchanan
- Richard Burton
- George Burns
- Raymond Burr
- Sid Caesar
- James Cagney
- Rory Calhoun
- Claudia Cardinale
- Yvonne De Carlo
- Leslie Caron
- Art Carney
- John Carradine
- Diahann Carroll
- Johnny Carson
- John Cassavetes
- Jeff Chandler
- Carol Channing
- Charlie Chaplin
- Cyd Charisse
- Lee Van Cleef
- Montgomery Clift
- Rosemary Clooney
- Lee J. Cobb
- Claudette Colbert
- Nat "King" Cole
- Joan Collins
- Sean Connery
- Gary Cooper
- William Conrad
- Joseph Cotten
- Jeanne Crain
- Joan Crawford
- Bing Crosby
- Tony Curtis
- Peter Cushing
- Robert Cummings
- Arlene Dahl
- Dorothy Dandridge
- Danielle Darrieux
- Linda Darnell
- Bette Davis
- Nancy Davis
- Sammy Davis Jr.
- Doris Day
- James Dean
- Ruby Dee
- Sandra Dee
- William Demarest
- Richard Denning
- Brandon deWilde
- Angie Dickinson
- Marlene Dietrich
- Troy Donahue
- Mamie Van Doren
- Diana Dors
- Bobby Driscoll
- Kirk Douglas
- Clint Eastwood
- Barbara Eden
- Anita Ekberg
- María Félix
- Mel Ferrer
- José Ferrer
- Peter Finch
- Barry Fitzgerald
- Rhonda Fleming
- Jo Van Fleet
- Errol Flynn
- Nina Foch
- Henry Fonda
- Joan Fontaine
- John Forsythe
- Glenn Ford
- Anne Francis
- William Frawley
- Annette Funicello
- Louis de Funès
- Clark Gable
- Eva Gabor
- Zsa Zsa Gabor
- Ava Gardner
- James Garner
- Judy Garland
- Vittorio Gassman
- John Gielgud
- Lillian Gish
- Jackie Gleason
- Paulette Goddard
- Betty Grable
- Gloria Grahame
- Cary Grant
- Farley Granger
- Stewart Granger
- Kathryn Grayson
- Lorne Greene
- John Gregson
- Virginia Grey
- Alec Guinness
- Edmund Gwenn
- Tony Hancock
- Julie Harris
- Rex Harrison
- Laurence Harvey
- Olivia de Havilland
- Sterling Hayden
- Helen Hayes
- Susan Hayward
- Rita Hayworth
- Van Heflin
- Audrey Hepburn
- Katharine Hepburn
- Charlton Heston
- William Holden
- Judy Holliday
- Stanley Holloway
- James Hong
- Dennis Hopper
- Bob Hope
- Rock Hudson
- Jeffrey Hunter
- Tab Hunter
- Burl Ives
- Pedro Infante
- John Ireland
- Anne Jeffreys
- Van Johnson
- Glynis Johns
- Carolyn Jones
- Jennifer Jones
- Shirley Jones
- Katy Jurado
- Boris Karloff
- Danny Kaye
- Howard Keel
- Brian Keith
- Gene Kelly
- Grace Kelly
- Deborah Kerr
- Eartha Kitt
- Jack Klugman
- Don Knotts
- Dilip Kumar
- Kishore Kumar
- Meena Kumari
- Alan Ladd
- Burt Lancaster
- Angela Lansbury
- Piper Laurie
- Peter Lawford
- Cloris Leachman
- Christopher Lee
- Ruta Lee
- Janet Leigh
- Jack Lemmon
- Jerry Lewis
- Norman Lloyd
- June Lockhart
- Gina Lollobrigida
- Julie London
- Sophia Loren
- Peter Lorre
- Jack Lord
- Ida Lupino
- Darren McGavin
- Gordon MacRae
- Fred MacMurray
- Shirley MacLaine
- Jayne Mansfield
- Karl Malden
- Dorothy Malone
- Jean Marais
- Fredric March
- Dean Martin
- Lee Marvin
- Groucho Marx
- Giulietta Masina
- James Mason
- Marcello Mastroianni
- Jerry Mathers
- Walter Matthau
- Victor Mature
- Virginia Mayo
- Joel McCrea
- Dorothy McGuire
- John McIntire
- Steve McQueen
- Audrey Meadows
- Jayne Meadows
- Ralph Meeker
- Adolphe Menjou
- Burgess Meredith
- Toshiro Mifune
- Ray Milland
- John Mills
- Vera Miles
- Sal Mineo
- Carmen Miranda
- Cameron Mitchel
- Robert Mitchum
- Marilyn Monroe
- Yves Montand
- Ricardo Montalbán
- Agnes Moorehead
- Elizabeth Montgomery
- Roger Moore
- Jeanne Moreau
- Rita Moreno
- Harry Morgan
- Vic Morrow
- Audie Murphy
- Don Murray
- Patricia Neal
- Jorge Negrete
- Ricky Nelson
- Paul Newman
- Barbara Nichols
- Leslie Nielsen
- David Niven
- Kim Novak
- Edmond O'Brien
- Donald O'Connor
- Maureen O'Hara
- Maureen O'Sullivan
- Laurence Olivier
- Geraldine Page
- Janis Paige
- Eleanor Parker
- Jack Palance
- Gregory Peck
- George Peppard
- Anthony Perkins
- Jean Peters
- Donald Pleasence
- Christopher Plummer
- Sidney Poitier
- Dick Powell
- Jane Powell
- Tyrone Power
- Elvis Presley
- Robert Preston
- Vincent Price
- Jon Provost
- Anthony Quinn
- Tony Randall
- Ronald Reagan
- Donna Reed
- George Reeves
- Steve Reeves
- Carl Reiner
- Tommy Rettig
- Debbie Reynolds
- Thelma Ritter
- Jason Robards
- Cliff Robertson
- Edward G. Robinson
- Ginger Rogers
- Roy Rogers
- Cesar Romero
- Mickey Rooney
- Barbara Rush
- Jane Russell
- Rosalind Russell
- Eva Marie Saint
- George Sanders
- John Saxon
- Maximilian Schell
- Romy Schneider
- Gordon Scott
- Lizabeth Scott
- Randolph Scott
- Peter Sellers
- Omar Sharif
- Dinah Shore
- Takashi Shimura
- Vittorio De Sica
- Simone Signoret
- Jean Simmons
- Frank Sinatra
- Red Skelton
- Ann Sothern
- Alberto Sordi
- Robert Stack
- Kim Stanley
- Barbara Stanwyck
- Rod Steiger
- Jan Sterling
- James Stewart
- Dean Stockwell
- Lewis Stone
- Woody Strode
- Barry Sullivan
- Ed Sullivan
- Max von Sydow
- Lyle Talbot
- Russ Tamblyn
- Elizabeth Taylor
- Robert Taylor
- Rod Taylor
- Gene Tierney
- Spencer Tracy
- Lana Turner
- Vivian Vance
- Robert Wagner
- Eli Wallach
- John Wayne
- Jack Webb
- Orson Welles
- Betty White
- Stuart Whitman
- James Whitmore
- Richard Widmark
- Esther Williams
- Marie Windsor
- Shelley Winters
- Natalie Wood
- Joanne Woodward
- Teresa Wright
- Jane Wyman
- Keenan Wynn
- Loretta Young
- Robert Young
- Efrem Zimbalist Jr.
Filmmakers
- Michelangelo Antonioni
- Mario Bava
- Ingmar Bergman
- Luis Buñuel
- Jean Cocteau
- Luigi Comencini
- Charles Crichton
- George Cukor
- Michael Curtiz
- Jean Delannoy
- Walt Disney
- Stanley Donen
- Blake Edwards
- Federico Fellini
- Richard Fleischer
- John Frankenheimer
- John Ford
- Lucio Fulci
- Pietro Germi
- Jean-Luc Godard
- Henry Hathaway
- Howard Hawks
- Alfred Hitchcock
- Howard Hughes
- John Huston
- Elia Kazan
- Keisuke Kinoshita
- Stanley Kubrick
- Akira Kurosawa
- Fritz Lang
- David Lean
- Anthony Mann
- Joseph L. Mankiewicz
- Jean-Pierre Melville
- Kenji Mizoguchi
- Mario Monicelli
- Yasujirō Ozu
- Otto Preminger
- Nicholas Ray
- Dino Risi
- Jacques Rivette
- Roberto Rossellini
- Vittorio De Sica
- Don Siegel
- J. Lee Thompson
- Andrzej Wajda
- Orson Welles
- Billy Wilder
- Robert Wise
- William Wyler
Musicians
See also: List of musicians of the 1950s and Million Dollar Quartet-
Bill Haley and the Comets c. 1954
-
 Fats Domino c. 1956
Fats Domino c. 1956
-
 Jerry Lee Lewis c. 1957
Jerry Lee Lewis c. 1957
-
 Everly Brothers c. 1958
Everly Brothers c. 1958
- Black Ace
- Buddy Ace
- Johnny Ace
- Arthur Alexander
- Lee Allen
- Gene Allison
- Marian Anderson
- Pink Anderson
- Paul Anka
- Louis Armstrong
- Eddy Arnold
- Chet Atkins
- Gene Autry
- Frankie Avalon
- Charles Aznavour
- LaVern Baker
- Pearl Bailey
- Hank Ballard
- Bobby Bare
- Count Basie
- Sidney Bechet
- Harry Belafonte
- Jesse Belvin
- Tex Beneke
- Boyd Bennett
- Tony Bennett
- Chuck Berry
- Richard Berry
- Bill Black
- Otis Blackwell
- Scrapper Blackwell
- Blind Blake
- Art Blakey
- Bobby Bland
- Johnny Bond
- Pat Boone
- The Big Bopper
- Jimmy Bowen
- Calvin Boze
- Jackie Brenston
- Teresa Brewer
- Big Bill Broonzy
- Charles Brown
- Clarence "Gatemouth" Brown
- James Brown
- Nappy Brown
- Roy Brown
- Ruth Brown
- Tommy Brown
- Dave Brubeck
- Jimmy Bryant
- Sonny Burgess
- Solomon Burke
- Johnny Burnette
- James Burton
- Sam Butera
- Erskine Butterfield
- Maria Callas
- Cab Calloway
- Glen Campbell
- Martha Carson
- Goree Carter
- Johnny Cash
- Bobby Charles
- Ray Charles
- Boozoo Chavis
- Chubby Checker
- Clifton Chenier
- June Christy
- Eugene Church
- Dee Clark
- Petula Clark
- Joe Clay
- Jack Clement
- Patsy Cline
- Rosemary Clooney
- Eddie Cochran
- Nat "King" Cole
- John Coltrane
- Perry Como
- James Cotton
- Floyd Council
- Pee Wee Crayton
- Bing Crosby
- Bob Crosby
- Gary Crosby
- Arthur Crudup
- Mac Curtis
- Dick Dale
- Dick Dale (singer)
- Dalida
- Bobby Darin
- Hal David
- Jimmie Davis
- Miles Davis
- Sammy Davis Jr.
- Bobby Day
- Doris Day
- Bo Diddley
- Willie Dixon
- Carl Dobkins Jr.
- Bill Doggett
- Fats Domino
- Lonnie Donegan
- Jimmy Dorsey
- Lee Dorsey
- Tommy Dorsey
- K. C. Douglas
- Rusty Draper
- Champion Jack Dupree
- Jimmy Durante
- Leroy Van Dyke
- Jack Earls
- Duke Ellington
- Billy "The Kid" Emerson
- Werly Fairburn
- Charlie Feathers
- H-Bomb Ferguson
- Eddie Fisher
- Sonny Fisher
- Toni Fisher
- Ella Fitzgerald
- Mary Ford
- Tennessee Ernie Ford
- Helen Forrest
- Connie Francis
- Alan Freed
- Ernie Freeman
- Frank Frost
- Johnny Fuller
- Billy Fury
- Earl Gaines
- Hank Garland
- Judy Garland
- Clarence Garlow
- Georgia Gibbs
- Dizzy Gillespie
- Dick Glasser
- Arthur Godfrey
- Benny Goodman
- Roscoe Gordon
- Eydie Gormé
- Charlie Gracie
- Gogi Grant
- Jack Guthrie
- Roy Hamilton
- Lionel Hampton
- Pat Hare
- Slim Harpo
- Homer Harris
- Peppermint Harris
- Wynonie Harris
- Hawkshaw Hawkins
- Screamin' Jay Hawkins
- Al Hibbler
- Chuck Higgins
- Earl Hines
- Silas Hogan
- Smokey Hogg
- Ron Holden
- Billie Holiday
- Buddy Holly
- John Lee Hooker
- Lightnin' Hopkins
- Lena Horne
- Johnny Horton
- David Houston
- Joe Houston
- Ivory Joe Hunter
- Tab Hunter
- Burl Ives
- Bull Moose Jackson
- Mahalia Jackson
- Elmore James
- Etta James
- Harry James
- Homesick James
- Joni James
- Sonny James
- Waylon Jennings
- Kris Jensen
- Dr. John
- Little Willie John
- Hank Jones
- Jimmy Jones
- Louis Jordan
- Don Julian
- Kitty Kallen
- Chris Kenner
- Anita Kerr
- Albert King
- B.B. King
- Ben E. King
- Earl King
- Freddie King
- Pee Wee King
- Saunders King
- Eartha Kitt
- Christine Kittrell
- Baker Knight
- Sonny Knight
- Buddy Knox
- Gene Krupa
- Frankie Laine
- Major Lance
- Mario Lanza
- Ellis Larkins
- Brenda Lee
- Dickie Lee
- Peggy Lee
- Lazy Lester
- Jerry Lee Lewis
- Smiley Lewis
- Little Willie Littlefield
- Julie London
- Joe Hill Louis
- Willie Love
- Robin Luke
- Frankie Lymon
- Loretta Lynn
- Carl Mann
- Dean Martin
- Grady Martin
- Janis Martin
- Johnny Mathis
- Jimmy McCracklin
- Skeets McDonald
- Big Jay McNeely
- Clyde McPhatter
- Max Merritt
- Big Maceo Merriweather
- Amos Milburn
- Chuck Miller
- Mitch Miller
- Ned Miller
- Roy Milton
- Garnet Mimms
- Charles Mingus
- Carmen Miranda
- Bobby Mitchell
- Guy Mitchell
- Thelonious Monk
- Bill Monroe
- Vaughn Monroe
- Wes Montgomery
- Benny Moré
- Moon Mullican
- Rose Murphy
- Jimmy Nelson
- Ricky Nelson
- Sandy Nelson
- Robert Nighthawk
- Willie Nix
- Jimmy Nolen
- Nervous Norvus
- Donald O'Conner
- St. Louis Jimmy Oden
- Odetta
- Gene O'Quin
- Roy Orbison
- Johnny Otis
- Patti Page
- Charlie Parker
- Junior Parker
- Dolly Parton
- Les Paul
- Art Pepper
- Carl Perkins
- Oscar Peterson
- Phil Phillips
- Sam Phillips
- Édith Piaf
- Webb Pierce
- Gene Pitney
- Pérez Prado
- Elvis Presley
- Jimmy Preston
- Johnny Preston
- Lloyd Price
- Ray Price
- Louis Prima
- Johnnie Ray
- Tampa Red
- Jerry Reed
- Jimmy Reed
- Della Reese
- Django Reinhardt
- Slim Rhodes
- Buddy Rich
- Charlie Rich
- Cliff Richard
- Little Richard
- Tommy Ridgley
- Billy Lee Riley
- Tex Ritter
- Johnny Rivers
- Max Roach
- Marty Robbins
- Jimmie Rodgers
- Arsenio Rodríguez
- Kenny Rogers
- Bobby Rydell
- Kyu Sakamoto
- Washboard Sam
- Tommy Sands
- Mabel Scott
- Neil Sedaka
- Pete Seeger
- Johnny Shines
- Dinah Shore
- Frank Sinatra
- Memphis Slim
- Sunnyland Slim
- Huey "Piano" Smith
- Ray Smith
- Warren Smith
- Hank Snow
- Kay Starr
- Joan Sutherland
- Art Tatum
- Jesse Thomas
- Rufus Thomas
- Hank Thompson
- Big Mama Thornton
- Johnny Tillotson
- Merle Travis
- Ernest Tubb
- Big Joe Turner
- Ike Turner
- Sammy Turner
- Conway Twitty
- Ritchie Valens
- Sarah Vaughan
- Bobby Vee
- Gene Vincent
- T-Bone Walker
- Little Walter
- Mercy Dee Walton
- Baby Boy Warren
- Dinah Washington
- Muddy Waters
- Johnny "Guitar" Watson
- Joe Weaver
- Ben Webster
- Lenny Welch
- Speedy West
- Josh White
- Slim Whitman
- Andy Williams
- Big Joe Williams
- Cootie Williams
- Hank Williams
- Larry Williams
- Otis Williams
- Tex Williams
- Ralph Willis
- Bob Wills
- Howlin' Wolf
- Malcolm Yelvington
- Faron Young
- Johnny "Man" Young
- Timi Yuro
Bands
-
The Platters 1955
-
 The Clovers 1955
The Clovers 1955
-
 Buddy Holly & The Crickets 1958
Buddy Holly & The Crickets 1958
- The Accents
- Jay & The Americans
- The Ames Brothers
- The Andrews Sisters
- Dave Appell & the Applejacks
- The Bell Notes
- The Belmonts
- Dion & The Belmonts
- Travis & Bob
- The Bobbettes
- The Bonnie Sisters
- The Bosstones
- The Buchanan Brothers
- The Cadets
- The Cadillacs
- The Capris
- The Cardinals
- The Castells
- The Champs
- The Chantels
- The Charioteers
- Otis Williams and the Charms
- The Chimes
- The Chips
- The Chordettes
- The Cleftones
- The Clovers
- The Coasters
- The Collegians
- Bill Haley and the Comets
- The Corsairs
- The Counts
- The Crew Cuts
- The Crescendos
- The Crests
- The Crows
- Danny & the Juniors
- Jan & Dean
- The Dells
- The Del-Satins
- The Delta Rhythm Boys
- The Del-Vikings
- Deep River Boys
- The Dovells
- The Dubs
- The Duprees
- The Diamonds
- The Drifters
- The Earls
- The Echoes
- The Edsels
- The El Dorados
- The Elegants
- The Emotions
- The Escorts
- The Everly Brothers
- The Fairfield Four
- The Falcons
- The Flamingos
- The Flairs
- The Fleetwoods
- The Fiestas
- The Five Satins
- The Five Discs
- The Five Keys
- The Five Sharps
- The Fontane Sisters
- The Four Aces
- The Four Buddies
- The Four Freshmen
- The Four Knights
- The Four Lads
- The Four Lovers
- The Four Preps
- The Four Seasons
- The Four Tunes
- The Gaylords
- The G-Clefs
- The Golden Gate Quartet
- The Harptones
- The Hearts
- The Heathertones
- The Hilltoppers
- The Hollywood Flames
- Johnny & The Hurricanes
- The Impalas
- Little Anthony and the Imperials
- The Ink Spots
- The Isley Brothers
- The Jewels
- The Jesters
- The Jive Bombers
- The Jive Five
- Marvin & Johnny
- Robert & Johnny
- Don & Juan
- The Jubalaires
- The Jordanaires
- The Kingston Trio
- The Knockouts
- The Larks
- The Lettermen
- Frankie Lymon & The Teenagers
- The McGuire Sisters
- The Medallions
- The Mello-Kings
- The Mello-Moods
- The Mills Brothers
- The Midnighters
- The Monotones
- The Moonglows
- The Mystics
- The Nutmegs
- The Oak Ridge Boys
- The Orioles
- The Paragons
- The Penguins
- The Pied Pipers
- The Platters
- The Pony-Tails
- The Quarrymen
- The Quotations
- Randy & The Rainbows
- The Ravens
- The Rays
- The Regents
- The Righteous Brothers
- Norman Fox & The Rob-Roys
- The Robins
- The Rock-A-Teens
- The Sensations
- The Shadows
- The Shepherd Sisters
- The Silhouettes
- The Solitaires
- Sons of The Pioneers
- The Spaniels
- The Sparkletones
- The Spiders
- The Spinners
- Joey Dee & The Starliters
- The Stereos
- The Swallows
- Mickey & Sylvia
- Tátrai Quartet
- The Teenagers
- The Teen Queens
- The Tokens
- The Tornados
- The Turbans
- The Tymes
- The Valentines
- The Ventures
- The Virtues
- The Volumes
- Billy Ward & The Dominoes
- The Wrens
- Maurice Williams and the Zodiacs
- Windsbacher Knabenchor
Sports figures
- Hank Aaron (baseball player)
- Ernie Banks (baseball player)
- Roger Bannister (English track and field athlete)
- Carmen Basilio (boxing|boxer)
- Yogi Berra (baseball player)
- József Bozsik
- Jim Brown (American football player)
- László Budai
- Jenő Buzánszky
- Roy Campanella (baseball player)
- Ezzard Charles (boxer)
- Maureen Connolly (tennis player)
- Bob Cousy (basketball player)
- Zoltán Czibor
- Joe DiMaggio (baseball player)
- Harrison Dillard (American track and field athlete)
- Larry Doby (baseball player)
- Juan Manuel Fangio (motor racing driver)
- Nino Farina (motor racing driver)
- Whitey Ford (baseball player)
- Gyula Grosics
- Nándor Hidegkuti
- Ben Hogan (golf)
- Gordie Howe (Canadian ice hockey player)
- Rafer Johnson (American track and field athlete)
- Ingemar Johansson (boxer)
- Al Kaline (baseball player)
- Sándor Kocsis
- John Landy (Australian track and field athlete)
- Mihály Lantos
- Gyula Lóránt
- Mickey Mantle (baseball player)
- Rocky Marciano (boxer)
- Billy Martin (baseball player)
- Eddie Mathews (baseball player)
- Stanley Matthews (association footballer)
- Willie Mays (baseball player)
- George Mikan (basketball player)
- Stirling Moss (motor racing driver)
- Archie Moore (boxer)
- Stan Musial (baseball player)
- Bobo Olson (boxer)
- Floyd Patterson (boxer)
- Pelé (association footballer)
- Bob Pettit
- Ferenc Puskás (association footballer)
- Maurice Richard (Canadian ice hockey player)
- Jackie Robinson (baseball player)
- Frank Robinson (baseball player)
- Sugar Ray Robinson (boxer)
- Wilma Rudolph
- Bill Russell (basketball player)
- Sam Snead (golf)
- Duke Snider (baseball player)
- Warren Spahn (baseball player)
- Casey Stengel (baseball manager, former player)
- Chuck Taylor
- Johnny Unitas (American football player)
- Mal Whitfield (American track and field athlete)
- Ted Williams (baseball player)
- Billy Wright (association footballer)
- Lev Yashin (association footballer)
- József Zakariás
- Emil Zátopek
See also
Timeline
The following articles contain brief timelines which list the most prominent events of the decade:
1950 • 1951 • 1952 • 1953 • 1954 • 1955 • 1956 • 1957 • 1958 • 1959
References
- "The Pentagon Papers, Volume 1, Chapter 5, Section 3, "Origins of the Insurgency in South Vietnam, 1964–1970"". Archived from the original on 2017-10-19. Retrieved 2010-01-15.
- "Greenland (Kalaallit Nunaat)". World Statesmen. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- Stratton, J. M. (1969). Agricultural Records. John Baker. ISBN 978-0-212-97022-3.
- "Inflation and CPI Consumer Price Index 1950–1959". Inflation Data. InflationData.com. Retrieved 23 April 2014.
- "1960 - Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) Transistor Demonstrated". The Silicon Engine. Computer History Museum.
- Bassett, Ross Knox (2007). To the Digital Age: Research Labs, Start-up Companies, and the Rise of MOS Technology. Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 22. ISBN 9780801886393.
- Chan, Yi-Jen (1992). Studies of InAIAs/InGaAs and GaInP/GaAs heterostructure FET's for high speed applications. University of Michigan. p. 1.
The Si MOSFET has revolutionized the electronics industry and as a result impacts our daily lives in almost every conceivable way.
- Wong, Kit Po (2009). Electrical Engineering - Volume II. EOLSS Publications. p. 7. ISBN 9781905839780.
- "13 Sextillion & Counting: The Long & Winding Road to the Most Frequently Manufactured Human Artifact in History". Computer History Museum. April 2, 2018. Retrieved 28 July 2019.
- Baker, R. Jacob (2011). CMOS: Circuit Design, Layout, and Simulation. John Wiley & Sons. p. 7. ISBN 978-1118038239.
- R. S. Denisoff, W. L. Schurk, Tarnished gold: the record industry revisited (Transaction Publishers, 3rd edn., 1986), p. 13.
- M. Campbell, ed., Popular Music in America: And the Beat Goes on (Cengage Learning, 3rd edn., 2008), pp. 168–9.
- Kallen, Stuart (1999). A Cultural History of the United States. San Diego: Lucent.
- American History. ABC-CLIO, 2012. Web. 11 Dec. 2012.
- ^ Thomas, Pauline. "1950s Fashion History 50s Glamour, Dior New Look". www.fashion-era.com. Retrieved 2016-10-31.
- ^ Stevenson, N. J. (2012). Fashion: A Visual History from Regency & Romance to Retro & Revolution: A Complete Illustrated Chronology of Fashion from the 1800s to the Present Day. New York City: St. Martin's Griffin.
- "Cristobal Balenciaga : Fashion, History". theredlist.com. Archived from the original on 2016-11-01. Retrieved 2016-10-31.
- "Cristóbal Balenciaga". LoveToKnow. Retrieved 2016-10-31.
- "Coco Chanel Biography". Biography.com. August 12, 2016.
- ^ Krick, Jessa. "Gabrielle "Coco" Chanel (1883–1971) and the House of Chanel | Essay | Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History | The Metropolitan Museum of Art". The Met’s Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. Retrieved 2016-10-31.
Further reading
- Bessel, Richard and Dirk Schumann, eds. Life after Death: Approaches to a Cultural and Social History of Europe During the 1940s and 1950s (2003), essays by scholars on recovery from the war
- Judt, Tony. Postwar: A History of Europe Since 1945 (2005)
- London Institute of World Affairs, The Year Book of World Affairs 1957 (London 1957), comprehensive reference book covering 1956 in diplomacy, international affairs and politics for major nations and regions
Great Britain
- Montgomery, John. The Fifties (1960), On Britain.
- Sandbrook, Dominic. Never had it so good: a history of Britain from Suez to the Beatles Hachette UK, (2015).
- Bering, Henrik. "Taking the great out of Britain." Policy Review, no. 133, (2005), p. 88+. online review
- Wybrow, Robert J. "Britain Speaks Out, 1937-87" (1989), Summaries of public opinion polls in Britain
United States
- Dunar, Andrew J. America in the fifties (2006)
- Halberstam, David. The Fifties (1993) excerpt and text search
- Levine, Alan J. The Myth of the 1950s (2008) excerpt and text search
- Marling, Karal Ann. As Seen on TV: The Visual Culture of Everyday Life in the 1950s (Harvard University Press, 1996) 328 pp.
- Miller, Douglas T. and Marion Nowak. The fifties: the way we really were (1977)
- Stoner, John C., and Alice L. George. Social History of the United States: The 1950s (2008)
- Wills, Charles. America in the 1950s (Decades of American History) (2005)
External links
- Heroes of the 1950s – slideshow by Life magazine
- "The Golden Age of Couture: Paris and London 1947–57, exhibition about 1950s fashion". Victoria and Albert Museum.
- Footage from the 1950s
- 1950s Video Timeline
| Events by month | |
|---|---|
| 1959 | |
| 1958 | |
| 1957 | |
| 1956 | |
| 1955 | |
| 1954 | |
| 1953 | |
| 1952 | |
| 1951 | |
| 1950 | |
| History of the 20th century | |
|---|---|
| Topics | |
| Lists |
|








