| Revision as of 17:23, 25 December 2022 editCmglee (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users11,907 edits →Construction and relation to the rhombicuboctahedron: Explain differences← Previous edit | Revision as of 03:07, 20 March 2024 edit undoDedhert.Jr (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users8,330 edits →Construction and relation to the rhombicuboctahedron: rewrite the section, sources laterNext edit → | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| {{Johnson solid}} | {{Johnson solid}} | ||
| == Construction |
== Construction == | ||
| The elongated square gyrobicupola can be constructed similarly to the ], by attaching two regular ]s onto the bases of ], a process known as ]. The difference between these two polyhedrons is that one of two square cupolas of the elongated square gyrobicupola is twisted by 45 degrees, a process known as ''gyro'', making the triangular faces staggered vertically. The resulting polyhedron has 8 ] and 18 ]s. Because of the similarity of a rhombicuboctahedron, it has the alternative name '''pseudo-rhombicuboctahedron''' and occasionally been referred to as "the fourteenth Archimedean solid". A ] polyhedron in which all of the faces are ]s is the Johnson solid, and the elongated square gyrobicupola is among them, enumerated as the 37th Johnson solid <math> J_{37} </math> | |||
| As the name suggests, it can be constructed by elongating a ] (''J''<sub>29</sub>) and inserting an ]al ] between its two halves. | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| | image1 = Small rhombicuboctahedron.png | |||
| {| class="wikitable" | |||
| | image2 = Exploded rhombicuboctahedron.png | |||
| |]<br />Rhombicuboctahedron:<br />the triangles (in blue)<br />are aligned vertically | |||
| | image3 = Pseudorhombicuboctahedron.png | |||
| |]<br />Exploded sections of<br />rhombicuboctahedron | |||
| | footer = Process of the construction of the elongated square gyrobicupola | |||
| |]<br />Pseudo-<br />rhombicuboctahedron:<br />the triangles are<br />staggered vertically | |||
| | total_width = 400 | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| | align = center | |||
| ⚫ | }} | ||
| The solid can also be seen as the result of twisting one of the ]e (''J''<sub>4</sub>) on a ] (one of the ]s; a.k.a. the elongated square orthobicupola) by 45 degrees. It is therefore a '''gyrate rhombicuboctahedron'''. Its similarity to the rhombicuboctahedron gives it the alternative name '''pseudo-rhombicuboctahedron'''. It has occasionally been referred to as "the fourteenth Archimedean solid". | |||
| This property does not carry over to its pentagonal-faced counterpart, the ]. | |||
| == Symmetry and classification == | == Symmetry and classification == | ||
Revision as of 03:07, 20 March 2024
37th Johnson solid| Elongated square gyrobicupola | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Johnson J36 – J37 – J38 |
| Faces | 8 triangles 18 squares |
| Edges | 48 |
| Vertices | 24 |
| Vertex configuration | 8+16(3.4) |
| Symmetry group | D4d |
| Dual polyhedron | Pseudo-deltoidal icositetrahedron |
| Properties | convex, singular vertex figure, canonical |
| Net | |
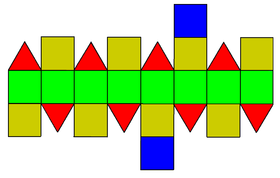 | |

In geometry, the elongated square gyrobicupola or pseudo-rhombicuboctahedron is one of the Johnson solids (J37). It is not usually considered to be an Archimedean solid, even though its faces consist of regular polygons that meet in the same pattern at each of its vertices, because unlike the 13 Archimedean solids, it lacks a set of global symmetries that map every vertex to every other vertex (though Grünbaum has suggested it should be added to the traditional list of Archimedean solids as a 14th example). It strongly resembles, but should not be mistaken for, the rhombicuboctahedron, which is an Archimedean solid. It is also a canonical polyhedron.
This shape may have been discovered by Johannes Kepler in his enumeration of the Archimedean solids, but its first clear appearance in print appears to be the work of Duncan Sommerville in 1905. It was independently rediscovered by J. C. P. Miller by 1930 (by mistake while attempting to construct a model of the rhombicuboctahedron) and again by V. G. Ashkinuse in 1957.
A Johnson solid is one of 92 strictly convex polyhedra that is composed of regular polygon faces but are not uniform polyhedra (that is, they are not Platonic solids, Archimedean solids, prisms, or antiprisms). They were named by Norman Johnson, who first listed these polyhedra in 1966.
Construction
The elongated square gyrobicupola can be constructed similarly to the rhombicuboctahedron, by attaching two regular square cupolas onto the bases of octagonal prism, a process known as elongation. The difference between these two polyhedrons is that one of two square cupolas of the elongated square gyrobicupola is twisted by 45 degrees, a process known as gyro, making the triangular faces staggered vertically. The resulting polyhedron has 8 equilateral triangles and 18 squares. Because of the similarity of a rhombicuboctahedron, it has the alternative name pseudo-rhombicuboctahedron and occasionally been referred to as "the fourteenth Archimedean solid". A convex polyhedron in which all of the faces are regular polygons is the Johnson solid, and the elongated square gyrobicupola is among them, enumerated as the 37th Johnson solid

 Process of the construction of the elongated square gyrobicupola
Process of the construction of the elongated square gyrobicupola
Symmetry and classification

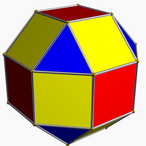
The pseudo-rhombicuboctahedron possesses D4d symmetry. It is locally vertex-regular – the arrangement of the four faces incident on any vertex is the same for all vertices; this is unique among the Johnson solids. However, the manner in which it is "twisted" gives it a distinct "equator" and two distinct "poles", which in turn divide its vertices into 8 "polar" vertices (4 per pole) and 16 "equatorial" vertices. It is therefore not vertex-transitive, and consequently not usually considered to be one of the Archimedean solids.
With faces colored by its D4d symmetry, it can look like this:
| The pseudo-deltoidal icositetrahedron (right) is the dual polyhedron. | |
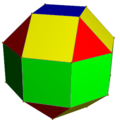 
|
 
|
There are 8 (green) squares around its equator, 4 (red) triangles and 4 (yellow) squares above and below, and one (blue) square on each pole.
Related polyhedra and honeycombs
The elongated square gyrobicupola can form a space-filling honeycomb with the regular tetrahedron, cube, and cuboctahedron. It can also form another honeycomb with the tetrahedron, square pyramid and various combinations of cubes, elongated square pyramids, and elongated square bipyramids.

The pseudo great rhombicuboctahedron is a nonconvex analog of the pseudo-rhombicuboctahedron, constructed in a similar way from the nonconvex great rhombicuboctahedron.
In chemistry
The polyvanadate ion has a pseudo-rhombicuboctahedral structure, where each square face acts as the base of a VO5 pyramid.
References
- Sommerville, D. M. Y. (1905), "Semi-regular networks of the plane in absolute geometry", Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 41: 725–747, doi:10.1017/s0080456800035560. As cited by Grünbaum (2009).
- Rouse Ball (1939), Coxeter, H. S. M. (ed.), Mathematical recreations and essays (11 ed.), p. 137
- Grünbaum, Branko (2009), "An enduring error" (PDF), Elemente der Mathematik, 64 (3): 89–101, doi:10.4171/EM/120, MR 2520469 Reprinted in Pitici, Mircea, ed. (2011). The Best Writing on Mathematics 2010. Princeton University Press. pp. 18–31..
- Johnson, Norman W. (1966), "Convex polyhedra with regular faces", Canadian Journal of Mathematics, 18: 169–200, doi:10.4153/cjm-1966-021-8, MR 0185507, Zbl 0132.14603.
- "J37 honeycombs", Gallery of Wooden Polyhedra, retrieved 2016-03-21
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 986. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
Further reading
- Anthony Pugh (1976), Polyhedra: A visual approach, California: University of California Press Berkeley, ISBN 0-520-03056-7 Chapter 2: Archimedean polyhedra, prisma and antiprisms, p. 25 Pseudo-rhombicuboctahedron
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Elongated square gyrobicupola" ("Johnson solid") at MathWorld.
- George Hart: pseudo-rhombicuboctahedra
