| Revision as of 18:59, 27 May 2024 editBernanke's Crossbow (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users7,894 edits →Miscellaneous devices: ???← Previous edit | Revision as of 19:00, 27 May 2024 edit undoBernanke's Crossbow (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users7,894 edits →Capacitors (historical): ???Next edit → | ||
| Line 317: | Line 317: | ||
| All of the following are obsolete capacitor symbols. | All of the following are obsolete capacitor symbols. | ||
| <gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| File:Polarized capacitor symbol 5.png | Obsolete capacitor |
File:Polarized capacitor symbol 5.png | Obsolete capacitor (very old style) | ||
| File:Capacitor old.svg | Obsolete capacitor | File:Capacitor old.svg | Obsolete capacitor | ||
| File:Capacitor old with polarity.svg | Obsolete capacitor | File:Capacitor old with polarity.svg | Obsolete capacitor | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 27 May 2024
Pictogram used to represent various electrical and electronic devices or functions
An electronic symbol is a pictogram used to represent various electrical and electronic devices or functions, such as wires, batteries, resistors, and transistors, in a schematic diagram of an electrical or electronic circuit. These symbols are largely standardized internationally today, but may vary from country to country, or engineering discipline, based on traditional conventions.
Standards for symbols
The graphic symbols used for electrical components in circuit diagrams are covered by national and international standards, in particular:
- IEC 60617 (also known as BS 3939).
- There is also IEC 61131-3 – for ladder-logic symbols.
- JIC JIC (Joint Industrial Council) symbols as approved and adopted by the NMTBA (National Machine Tool Builders Association). They have been extracted from the Appendix of the NMTBA Specification EGPl-1967.
- ANSI Y32.2-1975 (also known as IEEE Std 315-1975 or CSA Z99-1975).
- IEEE Std 91/91a: graphic symbols for logic functions (used in digital electronics). It is referenced in ANSI Y32.2/IEEE Std 315.
- Australian Standard AS 1102 (based on a slightly modified version of IEC 60617; withdrawn without replacement with a recommendation to use IEC 60617).
The number of standards leads to confusion and errors. Symbols usage is sometimes unique to engineering disciplines, and national or local variations to international standards exist. For example, lighting and power symbols used as part of architectural drawings may be different from symbols for devices used in electronics.
Common electronic symbols
Symbols shown are typical examples, not a complete list.
Traces

Grounds
The shorthand for ground is GND. Optionally, the triangle in the middle symbol may be filled in.
-
 General ground (IEC‑style)
General ground (IEC‑style)
-
 Signal/low-noise ground (the asterisk is not part of the symbol)
Signal/low-noise ground (the asterisk is not part of the symbol)
-
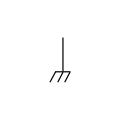 Chassis ground (IEC‑style)
Chassis ground (IEC‑style)
Sources
-
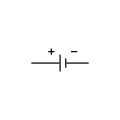 Battery, single-cell
Battery, single-cell
-
 Battery, multi-cell
Battery, multi-cell
-
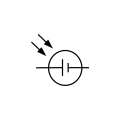 Solar (photovoltaic) cell
Solar (photovoltaic) cell
-
 DC voltage source
DC voltage source
-
 Controlled DC voltage source
Controlled DC voltage source
-
 Current source
Current source
-
 Controlled current source
Controlled current source
-
 AC voltage source
AC voltage source
Resistors
See also: ResistorIt is very common for potentiometer and rheostat symbols to be used for many types of variable resistors and trimmers.
-
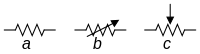 ANSI‑style: (a) Resistor, (b) Rheostat, (c) Potentiometer / Trimmer
ANSI‑style: (a) Resistor, (b) Rheostat, (c) Potentiometer / Trimmer
-
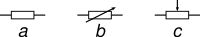 IEC‑style: (a) Resistor, (b) Rheostat, (c) Potentiometer / Trimmer
IEC‑style: (a) Resistor, (b) Rheostat, (c) Potentiometer / Trimmer
-
 Photoresistor (ANSI)
Photoresistor (ANSI)
-

- Thermistor (ANSI).
- Use -t for NTC symbol.
- Use +t for PTC symbol.
-
 Varistor (ANSI)
Varistor (ANSI)
Capacitors
See also: Capacitor-
 General capacitor (IEC‑style); sometimes drawn with one plate curved
General capacitor (IEC‑style); sometimes drawn with one plate curved
-
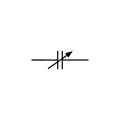 Variable capacitor
Variable capacitor
-
 Ganged (co‑moving) variable capacitors (IEC‑style)
Ganged (co‑moving) variable capacitors (IEC‑style)
-
 Trimmer variable capacitor
Trimmer variable capacitor
-
 Polarized capacitor (American‑style), such as electrolytic and tantalum capacitors
Polarized capacitor (American‑style), such as electrolytic and tantalum capacitors
Diodes
See also: DiodeOptionally, the triangle in these symbols may be filled in. Note: The words anode and cathode typically aren't part of the diode symbols.
-
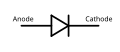 Diode (rectifier)
Diode (rectifier)
-
 Schottky diode
Schottky diode
-
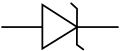 Zener diode
Zener diode
-
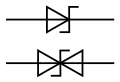 Transient-voltage-suppression diode (TVS)
Transient-voltage-suppression diode (TVS)
-
 Light-emitting diode (LED)
Light-emitting diode (LED)
-
 Photodiode
Photodiode
-
 Tunnel diode
Tunnel diode
-
 Varicap
Varicap
-
 Shockley diode
Shockley diode
-
 Silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR)
Silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR)
-
 Diac (may be a varistor in older schematics)
Diac (may be a varistor in older schematics)
-
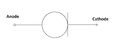 Constant-current diode
Constant-current diode
-
 Opto-isolator: LED (left), photo transistor (right)
Opto-isolator: LED (left), photo transistor (right)
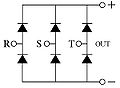
Bridge rectifiers
See also: Bridge rectifierThere are many ways to draw a single-phase bridge rectifier symbol. Some show the internal diode circuit, some don't.
Inductors
See also: InductorAn inductor can be drawn either as a series of loops, or series of half-circles.
-
 Inductor symbol (series of loops)
Inductor symbol (series of loops)
-
 Air-core inductor (IEC‑style)
Air-core inductor (IEC‑style)
-
 Magnetic-core inductor (IEEE‑style)
Magnetic-core inductor (IEEE‑style)
-
 Tapped inductor (IEC‑style)
Tapped inductor (IEC‑style)
-
 Ferrite bead (IEEE‑style)
Ferrite bead (IEEE‑style)
-
 Variable inductor
Variable inductor
-
 Trimmer variable inductor
Trimmer variable inductor
Transformers
See also: Transformer-
 Transformer
Transformer
-
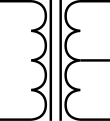 Transformer with center tap on secondary winding (right side)
Transformer with center tap on secondary winding (right side)
-
 Transformer with two secondary windings (right side)
Transformer with two secondary windings (right side)
-
 Current transformer
Current transformer
-
 Zero-sequence current transformer (ZSCT) (also known as a window-type current transformer)
Zero-sequence current transformer (ZSCT) (also known as a window-type current transformer)
-
 Bushing-type current transformer
Bushing-type current transformer
-
 Voltage transformer
Voltage transformer
Transistors
See also: TransistorOptionally, transistor symbols may include a circle. Note: The pin letters B/C/E and G/D/S aren't part of the transistor symbols.
Bipolar
See also: Bipolar junction transistor-
 NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
-
 PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
-
 NPN Darlington transistor
NPN Darlington transistor
-
 PNP Darlington transistor
PNP Darlington transistor
-
 NPN Phototransistor
NPN Phototransistor
Unipolar
See also: Field-effect transistor-
 N-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
N-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
-
 P-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
P-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
-
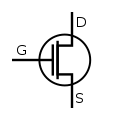 Metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET)
Metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET)
-
 Enhancement mode, N‑channel MOSFET
Enhancement mode, N‑channel MOSFET
-
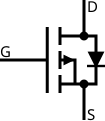 Enhancement mode, P‑channel MOSFET
Enhancement mode, P‑channel MOSFET
Vacuum tubes
See also: Vacuum tube-
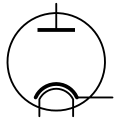 Vacuum tube diode
Vacuum tube diode
-
 Vacuum tube triode
Vacuum tube triode
-
 Vacuum tube tetrode
Vacuum tube tetrode
(pin letters not part of symbol) -
 Vacuum tube pentode
Vacuum tube pentode
Switches
See also: SwitchFor multiple pole switches, a dotted or dashed line can be included to indicate two or more switch at the same time (see DPST and DPDT examples below).
-
 Pushbutton, normally open, push-to-make (horizontal line on top)
Pushbutton, normally open, push-to-make (horizontal line on top)
-
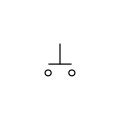 Pushbutton, normally open, push-to-make (IEEE-style)
Pushbutton, normally open, push-to-make (IEEE-style)
-
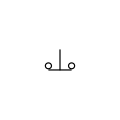 Pushbutton, normally closed, push-to-break (IEEE-style)
Pushbutton, normally closed, push-to-break (IEEE-style)
-
 Pushbutton, normally closed, two circuits (IEEE-style)
Pushbutton, normally closed, two circuits (IEEE-style)
-
 Switch, 1P1T, SPST (single-pole single-throw)
Switch, 1P1T, SPST (single-pole single-throw)
-
 Switch, 1P2T, SPDT (single-pole double-throw)
Switch, 1P2T, SPDT (single-pole double-throw)
-
 Switch, 2P1T, DPST (double-pole single-throw)
Switch, 2P1T, DPST (double-pole single-throw)
-
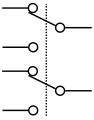 Switch, 2P2T, DPDT (double-pole double-throw)
Switch, 2P2T, DPDT (double-pole double-throw)
-
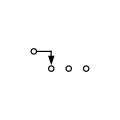 Slide switch, 1P3T,
Slide switch, 1P3T,
break-before-make, nonshorting style -
 Slide switch, 1P4T,
Slide switch, 1P4T,
break-before-make, nonshorting style -
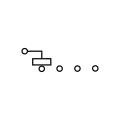 Slide switch, 1P4T,
Slide switch, 1P4T,
make-before-break, shorting style
-
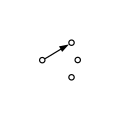 Rotary switch, 1P3T,
Rotary switch, 1P3T,
break-before-make, nonshorting style -
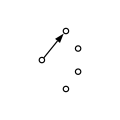 Rotary switch, 1P4T,
Rotary switch, 1P4T,
break-before-make, nonshorting style -
 Rotary switch, 1P4T,
Rotary switch, 1P4T,
make-before-break, shorting style
-
 Reed switch, normally open
Reed switch, normally open
Relays
See also: RelayRelays symbols are a combination of an inductor symbol and switch symbol.
Note: The pin letters in these symbols aren't part of the standard relay symbol.
Lamps
LED is located in diode section.
-
 Neon lamp
Neon lamp
-
 Indicating lamp (IEEE‑style)
Indicating lamp (IEEE‑style)
-
 Incandescent lamp
Incandescent lamp
-
 Indicatory incandescent light bulb
Indicatory incandescent light bulb
-
 Light bulb
Light bulb
Current limiters
-
 IEC fuse (b), equivalent symbols (a, c) (IEEE Std 315-1975)
IEC fuse (b), equivalent symbols (a, c) (IEEE Std 315-1975)
-
 Molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB)
Molded-case circuit breaker (MCCB)
-
 Fuse: IEC (top) and American (lower two)
Fuse: IEC (top) and American (lower two)
Electro-acoustic devices
Speaker symbols sometimes include an internal inductor symbol.
-
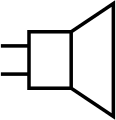 Loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
(IEEE-style) -
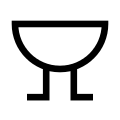 Buzzer
Buzzer
(IEC-style) -
 Microphone
Microphone
(IEEE-style) -
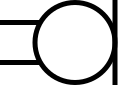 Microphone
Microphone
(IEC-style)
Antennas
See also: Antenna (radio)-
 General antenna
General antenna
(IEC-style) -
 Dipole antenna
Dipole antenna
(IEC-style) -
 Loop antenna
Loop antenna
(IEC-style) -
 Loop antenna
Loop antenna
(IEEE-style)
Cables
See also: Electrical cable-
 Cable, Shielded 1 conductor
Cable, Shielded 1 conductor
-
 Cable, 2 conductor
Cable, 2 conductor
-
 Cable, Shielded 2 conductor with shield connected to ground
Cable, Shielded 2 conductor with shield connected to ground
-
 Cable, 5 conductor
Cable, 5 conductor
-
 Cable, Shielded 5 conductor
Cable, Shielded 5 conductor
Connectors
See also: Electrical connectorThere are numerous connector symbol variations.
-
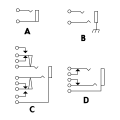 TRS phone jacks
TRS phone jacks
-
 UEXT connector based on a 5x2 shrouded header with notch key
UEXT connector based on a 5x2 shrouded header with notch key
ICs
See also: Integrated circuitLogic gates
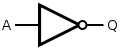
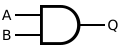
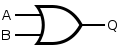
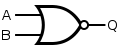
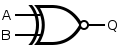
See also: Logic gatesFor the symbols below: A and B are inputs, Q is output. Note: These letters are not part of the symbols.
There are variations of these logic gate symbols. Depending on the IC, the two-input gates below may have: 1) two or more inputs; 2) infrequently some have a second inverted Q output too.
The above logic symbols may have additional I/O variations too: 1) schmitt trigger inputs, 2) tri-state outputs, 3) open-collector or open-drain outputs (not shown).
-
 Buffer gate with schmitt trigger input
Buffer gate with schmitt trigger input
-
 Buffer gate with tri-state output control.
Buffer gate with tri-state output control.
(B is the tri-state control)
Flip-flops
See also: Flip-flopsFor the symbols below: Q is output, Q is inverted output, E is enable input, internal triangle shape is clock input, S is Set, R is Reset (some datasheets use clear (CLR) instead of reset along the bottom).
There are variations of these flip-flop symbols. Depending on the IC, a flip-flop may have: 1) one or both outputs (Q only, Q only, both Q & Q); 2) one or both forced inputs along top & bottom (R only, S only, both R & S); 3) some inputs may be inverted.
-
 Simple SR flip-flop (inverted S & R inputs)
Simple SR flip-flop (inverted S & R inputs)
-
 Gated SR flip-flop
Gated SR flip-flop
-
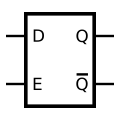 Gated D flip-flop (Transparent Latch)
Gated D flip-flop (Transparent Latch)
-
 Clocked D flip-flop
Clocked D flip-flop
(Set & Reset inputs) -
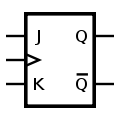 Clocked JK flip-flop
Clocked JK flip-flop
-
 Clocked T flip-flop
Clocked T flip-flop
OpAmps
Note: The outside text isn't part of these symbols.
-
 Operational amplifier (opamp)
Operational amplifier (opamp)
-
 Comparator
Comparator
Oscillators
See also: Electronic oscillator-
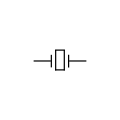 Crystal oscillator (IEEE‑style)
Crystal oscillator (IEEE‑style)
-
 Ceramic resonator (3 pins)
Ceramic resonator (3 pins)
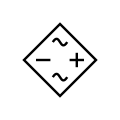
Miscellaneous devices
-
 Hall-effect sensor
Hall-effect sensor
-
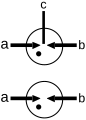 Gas-discharge tubes (GDT) for ESD discharge
Gas-discharge tubes (GDT) for ESD discharge
-
 Spark gap for ESD discharge
Spark gap for ESD discharge
Historical electronic symbols
The shape of some electronic symbols have changed over time. The following historical electronic symbols can be found in old electronic books / magazines / schematics, and now considered obsolete.
Capacitors (historical)
All of the following are obsolete capacitor symbols.
-
 Obsolete capacitor (very old style)
Obsolete capacitor (very old style)
-
 Obsolete capacitor
Obsolete capacitor
-
 Obsolete capacitor
Obsolete capacitor
-
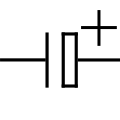 Obsolete capacitor
Obsolete capacitor
-
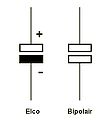 Obsolete capacitor
Obsolete capacitor
See also
References
- "IEEE Standard American National Standard Canadian Standard Graphic Symbols for Electrical and Electronics Diagrams (Including Reference Designation Letters)," in IEEE Std 315-1975 (Reaffirmed 1993), vol., no., pp.i-244, 1993, doi:10.1109/IEEESTD.1993.93397.
- Guidelines for Drawing Schematics.
- Circuit Symbols for all Electronic Components. Talking Electronics, 2013. Retrieved 01 Apr 2015.
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic Symbols. RapidTables, 2012. Retrieved 17 April 2016.
- "Standards for Resistor Symbols". EePower. EETech Media. Retrieved September 13, 2021.
- "A4.11 Envelope or Enclosure". ANSI Y32.2-1975 (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2022-10-09. Retrieved 2020-12-29.
The envelope or enclosure symbol may be omitted from a symbol referencing this paragraph, where confusion would not result
Further reading
- Standards
- IEC 60617 : Graphical Symbols for Diagrams; 2012.
- IEEE 315 : Graphic Symbols for Electrical and Electronics Diagrams (including Reference Designation Letters); 1975.
- U.S. DoD MIL-STD-806B : Graphical Symbols for Logic Diagrams; 1962. (RevB in 1962)
- Books
- Beginner's Guide to Reading Schematics; 4th Ed; Stan Gibilisco; McGraw-Hill, 224 pages; 2018; ISBN 978-1260031119.
- How to Read Schematic Diagrams; 5th Ed; Donald Herrington; Literary Licensing; 130 pages; 2011; ISBN 978-0672224577. (4ed in 1986)(2ed in 1967)
- How to Read Electronic Circuit Diagrams; 2nd Ed; Robert Brown, Paul Lawrence, James Whitson; Tab Books; 214 pages; 1988; ISBN 978-0830628803. (2ed in 1988)
- Engineer's Mini-Notebook : Schematic Symbols, Device Packages, Design and Testing; 1st Ed; Forrest M. Mims III; Radio Shack; 48 pages; 1988. (1ed in 1988)