| Revision as of 23:46, 1 July 2024 editIra Leviton (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users331,006 editsm Fixed another date.← Previous edit | Revision as of 23:34, 31 August 2024 edit undoCitation bot (talk | contribs)Bots5,404,402 edits Add: pmid, authors 1-1. Removed parameters. Some additions/deletions were parameter name changes. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by KamillaŚ | #UCB_toolbarNext edit → | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| Unlike the dura mater, which receives a rich vascular supply from numerous arteries, the arachnoid mater is avascular (lacking blood vessels). | Unlike the dura mater, which receives a rich vascular supply from numerous arteries, the arachnoid mater is avascular (lacking blood vessels). | ||
| The arachnoid mater and dura mater are very close together throughout the cranium and spinal canal all the way to S2, where the two layers fuse into one and end in the ], which attaches to the coccygeal end of the spinal canal. Sandwiched between the dura and arachnoid maters lie some veins that connect the brain's venous system with the venous system in the dura mater.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Weller |first=R.O. |date=March 2005 |title=Microscopic morphology and histology of the human meninges |url=https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1286011505832357 |journal=Morphologie |language=en |volume=89 |issue=284 |pages=22–34 |doi=10.1016/S1286-0115(05)83235-7}}</ref>{{fcn|reason=journal missing as well as most other details that would make this verifiable|date=September 2023}} | The arachnoid mater and dura mater are very close together throughout the cranium and spinal canal all the way to S2, where the two layers fuse into one and end in the ], which attaches to the coccygeal end of the spinal canal. Sandwiched between the dura and arachnoid maters lie some veins that connect the brain's venous system with the venous system in the dura mater.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Weller |first=R.O. |date=March 2005 |title=Microscopic morphology and histology of the human meninges |url=https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1286011505832357 |journal=Morphologie |language=en |volume=89 |issue=284 |pages=22–34 |doi=10.1016/S1286-0115(05)83235-7|pmid=15943078 }}</ref>{{fcn|reason=journal missing as well as most other details that would make this verifiable|date=September 2023}} | ||
| The arachnoid mater covering the brain is referred to as the ''arachnoidea encephali'', and the portion covering the spinal cord as the ''arachnoidea spinalis''. The arachnoid and pia mater are sometimes considered as a single structure, the leptomeninx, or the plural version, ] (''lepto'', from the Greek root meaning "thin"). Similarly, the dura in this situation is called the pachymeninx. | The arachnoid mater covering the brain is referred to as the ''arachnoidea encephali'', and the portion covering the spinal cord as the ''arachnoidea spinalis''. The arachnoid and pia mater are sometimes considered as a single structure, the leptomeninx, or the plural version, ] (''lepto'', from the Greek root meaning "thin"). Similarly, the dura in this situation is called the pachymeninx. | ||
| There are two subdivisions of arachnoid mater surrounding the subarachnoid space, the dorsal layer and the ventral layer. | There are two subdivisions of arachnoid mater surrounding the subarachnoid space, the dorsal layer and the ventral layer. | ||
| The dorsal layer covers internal cerebral veins and fixes them to the surrounding ]. The ventral layer of arachnoid membrane, on the other hand, is a direct anterior extension of this arachnoid envelope that the dorsal layer forms over the pineal region.<ref>{{Cite journal | |
The dorsal layer covers internal cerebral veins and fixes them to the surrounding ]. The ventral layer of arachnoid membrane, on the other hand, is a direct anterior extension of this arachnoid envelope that the dorsal layer forms over the pineal region.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Zhang |first1=Xi-an |last2=Qi |first2=Songtao |last3=Fan |first3=Jun |last4=Huang |first4=Guanglong |last5=Peng |first5=Junxiang |last6=Xu |first6=Jiaming |date=September 2012 |title=The distribution of arachnoid membrane within the velum interpositum |url=http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00701-012-1436-8 |journal=Acta Neurochirurgica |language=en |volume=154 |issue=9 |pages=1711–1715 |doi=10.1007/s00701-012-1436-8 |pmid=22782652 |issn=0001-6268}}</ref>{{clarify|reason=Incoherent reference. Two different titles; missing quotation mark; access date is meaningless without a URL. Ignoring the first title, this presumably refers to DOI 10.1007/s00701-012-1436-8 |date=September 2023}} | ||
| ==Function== | ==Function== | ||
Revision as of 23:34, 31 August 2024
Web-like middle layer of the three meninges "Arachnoidea" redirects here. For the genus of bryozoans, see Arachnoidea (bryozoan).| Arachnoid mater | |
|---|---|
 Image showing arachnoid mater and the underlying subarachnoid space Image showing arachnoid mater and the underlying subarachnoid space | |
 Image showing parts of the arachnoid mater, including arachnoid granulations. Image showing parts of the arachnoid mater, including arachnoid granulations. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Meninges |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arachnoidea mater |
| MeSH | D001099 |
| NeuroNames | 1464 |
| TA98 | A14.1.01.201 |
| TA2 | 5386 |
| FMA | 9591 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy[edit on Wikidata] | |
The arachnoid mater (or simply arachnoid) is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neural crest mesoectoderm in the embryo.
Structure
The arachnoid mater is interposed between the two other meninges, the more superficial (closer to the surface) and much thicker dura mater and the deeper pia mater, from which it is separated by the subarachnoid space. The delicate arachnoid layer is not attached to the inside of the dura but against it and surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It does not line the brain down into its sulci (folds), as does the pia mater, with the exception of the longitudinal fissure, which divides the left and right cerebral hemispheres. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flows under the arachnoid in the subarachnoid space, within a meshwork of trabeculae which span between the arachnoid and the pia. The arachnoid mater makes arachnoid villi, small protrusions through the dura mater into the venous sinuses of the brain, which allow CSF to exit the subarachnoid space and enter the blood stream.
Unlike the dura mater, which receives a rich vascular supply from numerous arteries, the arachnoid mater is avascular (lacking blood vessels).
The arachnoid mater and dura mater are very close together throughout the cranium and spinal canal all the way to S2, where the two layers fuse into one and end in the filum terminale, which attaches to the coccygeal end of the spinal canal. Sandwiched between the dura and arachnoid maters lie some veins that connect the brain's venous system with the venous system in the dura mater.
The arachnoid mater covering the brain is referred to as the arachnoidea encephali, and the portion covering the spinal cord as the arachnoidea spinalis. The arachnoid and pia mater are sometimes considered as a single structure, the leptomeninx, or the plural version, leptomeninges (lepto, from the Greek root meaning "thin"). Similarly, the dura in this situation is called the pachymeninx.
There are two subdivisions of arachnoid mater surrounding the subarachnoid space, the dorsal layer and the ventral layer. The dorsal layer covers internal cerebral veins and fixes them to the surrounding tela choroidea. The ventral layer of arachnoid membrane, on the other hand, is a direct anterior extension of this arachnoid envelope that the dorsal layer forms over the pineal region.
Function
See also: Cerebrospinal fluid and Subarachnoid spaceCSF circulates in the subarachnoid space (between arachnoid and pia mater). Cerebrospinal fluid is produced by the choroid plexus (inside the ventricles of the brain, which are in direct communication with the subarachnoid space so the CSF can flow freely through the nervous system). Cerebrospinal fluid is a transparent, colourless fluid and it is produced at about 500 ml/day. Its electrolyte levels, glucose levels, and pH are very similar to those in plasma, but the presence of blood in cerebrospinal fluid is always abnormal.
Etymology
The arachnoid mater is named after the Greek word arachne ("spider"), the suffix -oid ("in the image of"), and the Latin word mater ("mother"), because of the fine spider-web–like appearance of the delicate fibres of the arachnoid (arachnoid trabeculae) which extend down through the subarachnoid space and attach to the pia mater.
Additional images
-
 Meninges
Meninges
-
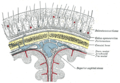 Diagrammatic section of scalp.
Diagrammatic section of scalp.
-
 The arachnoid mater lies under the dura mater, and arteries and veins run on top of it.
The arachnoid mater lies under the dura mater, and arteries and veins run on top of it.
-
 Brain with arachnoid mater, and an area where it is removed, showing cerebral gyri covered by the translucent pia mater.
Brain with arachnoid mater, and an area where it is removed, showing cerebral gyri covered by the translucent pia mater.
-
 Spinal dura mater opened, arachnoid mater visible.
Spinal dura mater opened, arachnoid mater visible.
-
 The medulla spinalis and its membranes.
The medulla spinalis and its membranes.
-
Spinal cord. Spinal membranes and nerve roots. Deep dissection. Posterior view.
-
Meninges and superficial cerebral veins. Deep dissection. Superior view.
-
Meninges and superficial cerebral veins. Deep dissection. Superior view.
The arachnoid cells continue inside the brain, covering the so-called Virchow-Robin spaces or perivascular spaces. For that reason some meningiomas can appear as completely inside the brain.
References
- Weller, R.O. (March 2005). "Microscopic morphology and histology of the human meninges". Morphologie. 89 (284): 22–34. doi:10.1016/S1286-0115(05)83235-7. PMID 15943078.
- Zhang, Xi-an; Qi, Songtao; Fan, Jun; Huang, Guanglong; Peng, Junxiang; Xu, Jiaming (September 2012). "The distribution of arachnoid membrane within the velum interpositum". Acta Neurochirurgica. 154 (9): 1711–1715. doi:10.1007/s00701-012-1436-8. ISSN 0001-6268. PMID 22782652.
- Adeeb, Nimer; Deep, Aman; Griessernauer, Christoph; Mortazavi, Martin; Watanabe, Koichi; Loukas, Marios; Tubbs, R.; Cohen, Aaron (January 2013). "The intracranial arachnoid mater". Child's Nervous System. 29 (1): 17–33. doi:10.1007/s00381-012-1910-x. PMID 22961357. S2CID 13822999.
- Orlando Regional Healthcare, Education and Development. 2004. "Overview of Adult Traumatic Brain Injuries". Retrieved on 2008-01-16.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 02:05-09 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Slide Archived 2007-03-11 at the Wayback Machine
| Meninges of the brain and spinal cord | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layers |
| ||||||||||||
| Spaces | |||||||||||||
| Spinal cord | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General features | |||||||||||||||||
| Grey columns |
| ||||||||||||||||
| White matter |
| ||||||||||||||||
| External features | |||||||||||||||||