| Revision as of 18:54, 10 May 2008 editTankred (talk | contribs)7,836 edits →Legacy: format fixed← Previous edit | Revision as of 19:58, 10 May 2008 edit undoCoolKoon (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers2,163 edits This part of the sentence is incomprehensible: "whose Great Moravian origin has been advanced by modern scholars"Next edit → | ||
| Line 143: | Line 143: | ||
| Great Moravian centers (''e.g.'', Bratislava, Nitra, ], and Zemplín) also retained their functions afterwards, although the identification of Bratislava, Tekov and Zemplín as Great Moravian castles is not generally accepted.<ref name='Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon'>{{cite book | last = Kristó | first = Gyula (editor) | authorlink = | coauthors = | title = Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon (9-14. század) ''(Encyclopedia of the Early Hungarian History - 9-14th centuries)''| publisher = Akadémiai Kiadó | date = 1994 | location = Budapest | pages = 84, 553, 743| url = | doi = | id = | isbn = 963 05 6722 9}}</ref> Since the same castles became the seats of early Hungarian ] (counties), historians posit that the administrative division of Great Moravia was just adopted by new rulers.<ref name="stefanovicova">{{cite book| last =Štefanovičová| first =Tatiana| author-link =| title =Osudy starých Slovanov| publisher =Osveta| date =1989| location =Bratislava}}</ref><ref name="sedlak">{{cite book| last =Sedlák| first =Vincent| chapter=Onomastika a historiografia|title =Príspevky k slovenským dejinám| editor=Karin Fábrová| publisher =Prešovská univerzita v Prešove| date =2005| location =Prešov| url=http://www.pulib.sk/elpub/FF/Fabrova1/index.htm}}</ref> On the other hand, several sources suggest that the Hungarian rulers followed the contemporary German or Bulgar patents when they established the new administrative system in their kingdom, or they introduced a new system.<ref name='Kristó 3'>{{cite book | pages = 21-100}}</ref> Moreover, the territorial administration of the Kingdom of Hungary was developing gradually, ''i.e.'', counties with larger territory were divided into smaller ones, while the scarcely habitated parts of the kingdom (''e.g.'', the northern and north-eastern territories of present-day Slovakia or the ] in today Hungary) were originally the kings' private forests, then they were organized into "forest counties" (12-13th centuries) and the latter, following their colonization, developed into or were divided among counties around 1300.<ref name='Kristó 3'>{{cite book | pages = 331-427}}</ref> | Great Moravian centers (''e.g.'', Bratislava, Nitra, ], and Zemplín) also retained their functions afterwards, although the identification of Bratislava, Tekov and Zemplín as Great Moravian castles is not generally accepted.<ref name='Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon'>{{cite book | last = Kristó | first = Gyula (editor) | authorlink = | coauthors = | title = Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon (9-14. század) ''(Encyclopedia of the Early Hungarian History - 9-14th centuries)''| publisher = Akadémiai Kiadó | date = 1994 | location = Budapest | pages = 84, 553, 743| url = | doi = | id = | isbn = 963 05 6722 9}}</ref> Since the same castles became the seats of early Hungarian ] (counties), historians posit that the administrative division of Great Moravia was just adopted by new rulers.<ref name="stefanovicova">{{cite book| last =Štefanovičová| first =Tatiana| author-link =| title =Osudy starých Slovanov| publisher =Osveta| date =1989| location =Bratislava}}</ref><ref name="sedlak">{{cite book| last =Sedlák| first =Vincent| chapter=Onomastika a historiografia|title =Príspevky k slovenským dejinám| editor=Karin Fábrová| publisher =Prešovská univerzita v Prešove| date =2005| location =Prešov| url=http://www.pulib.sk/elpub/FF/Fabrova1/index.htm}}</ref> On the other hand, several sources suggest that the Hungarian rulers followed the contemporary German or Bulgar patents when they established the new administrative system in their kingdom, or they introduced a new system.<ref name='Kristó 3'>{{cite book | pages = 21-100}}</ref> Moreover, the territorial administration of the Kingdom of Hungary was developing gradually, ''i.e.'', counties with larger territory were divided into smaller ones, while the scarcely habitated parts of the kingdom (''e.g.'', the northern and north-eastern territories of present-day Slovakia or the ] in today Hungary) were originally the kings' private forests, then they were organized into "forest counties" (12-13th centuries) and the latter, following their colonization, developed into or were divided among counties around 1300.<ref name='Kristó 3'>{{cite book | pages = 331-427}}</ref> | ||
| Social differentiation in Great Moravia reached the state of early ], creating the social basis for development of later medieval states in the region.<ref name="kucera">{{cite book| last =Kučera| first =Matúš| author-link =| title =Slovensko po páde Veľkej Moravy| publisher =Veda| date =1974| location =Bratislava}}</ref> The question what happened to Great Moravian noble families after 907 is still under debate. On the one hand, recent research indicates that a significant part of the local aristocracy remained more or less undisturbed by the fall of Great Moravia and their descendants became nobles in the newly formed Kingdom of Hungary.<ref name="lukacka">{{cite book| last =Lukačka| first =Ján| author-link =| title =Formovanie vyššej šľachty na západnom Slovensku| publisher =Mistrál| date =2002| location =Bratislava}}</ref><ref name='centreandperiphery'/><ref name='dvorakova'/> The most prominent example are the powerful families of ] and ].<ref name="lukacka"/> On the other hand, both ] and ], two chroniclers of the early history of Hungary, recorded that the prominent noble families of the kingdom descended either from leaders of the Magyar tribes or from immigrants, and they did not connect any of them to Great Moravia. For example, the ancestors of the clan Hunt- |
Social differentiation in Great Moravia reached the state of early ], creating the social basis for development of later medieval states in the region.<ref name="kucera">{{cite book| last =Kučera| first =Matúš| author-link =| title =Slovensko po páde Veľkej Moravy| publisher =Veda| date =1974| location =Bratislava}}</ref> The question what happened to Great Moravian noble families after 907 is still under debate. On the one hand, recent research indicates that a significant part of the local aristocracy remained more or less undisturbed by the fall of Great Moravia and their descendants became nobles in the newly formed Kingdom of Hungary.<ref name="lukacka">{{cite book| last =Lukačka| first =Ján| author-link =| title =Formovanie vyššej šľachty na západnom Slovensku| publisher =Mistrál| date =2002| location =Bratislava}}</ref><ref name='centreandperiphery'/><ref name='dvorakova'/> The most prominent example are the powerful families of ] and ].<ref name="lukacka"/> On the other hand, both ] and ], two chroniclers of the early history of Hungary, recorded that the prominent noble families of the kingdom descended either from leaders of the Magyar tribes or from immigrants, and they did not connect any of them to Great Moravia. For example, the ancestors of the clan Hunt-Pázmán (''Hont-Pázmány''), were mentioned to have arrived from the ] to the kingdom in the late 10th century.<ref name='Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon'>{{cite book | page = 269}}</ref> <ref name='Fügedi'>{{cite book | last = Fügedi | first = Erik | authorlink = | coauthors = | title = Ispánok, bárók, kiskirályok ''(Counts, barons and petty kings)''| publisher = Magvető Könyvkiadó | date = 1986 | location = Budapest | pages = 12, 24| url = | doi = | id = | isbn = 963 14 0582 6}}</ref> <ref name='Sources'>{{cite book | last = Benda | first = Gyula | last2 = Bertényi | first2 = Iván | last3 = Pótó | first3 = János (editors) | title = Anonymus: A magyarok cselekedetei – Kézai Simon: A magyarok cselekedetei ''(Anonymous: The Deeds of the Hungarians – Simon of Kéza: The Deeds of Hungarians)'' | publisher = Osiris | date = 2004 | location = Budapest | page = 120-122 | isbn = 963 389 606 1}}</ref> | ||
| Many Slavic words related to politics, law, and agriculture were ] into the ].<ref name="stefanovicova">{{cite book| last =Štefanovičová| first =Tatiana| author-link =| title =Osudy starých Slovanov| publisher =Osveta| date =1989| location =Bratislava}}</ref><ref name="sedlak">{{cite book| last =Sedlák| first =Vincent| chapter=Onomastika a historiografia|title =Príspevky k slovenským dejinám| editor=Karin Fábrová| publisher =Prešovská univerzita v Prešove| date =2005| location =Prešov| url=http://www.pulib.sk/elpub/FF/Fabrova1/index.htm}}</ref> Nevertheless, it is sometimes difficult to decide whether a certain word was borrowed from which Slavic language; ''e.g.'', the Hungarian word for county ''("megye")'' was borrowed from a ], but it may have taken either from the ] or from the ].<ref name='Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon'>{{cite book | last = Kristó | first = Gyula (editor) | authorlink = | coauthors = | title = Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon (9-14. század) ''(Encyclopedia of the Early Hungarian History - 9-14th centuries)''| publisher = Akadémiai Kiadó | date = 1994 | location = Budapest | pages = 646| url = | doi = | id = | isbn = 963 05 6722 9}}</ref> | Many Slavic words related to politics, law, and agriculture were ] into the ].<ref name="stefanovicova">{{cite book| last =Štefanovičová| first =Tatiana| author-link =| title =Osudy starých Slovanov| publisher =Osveta| date =1989| location =Bratislava}}</ref><ref name="sedlak">{{cite book| last =Sedlák| first =Vincent| chapter=Onomastika a historiografia|title =Príspevky k slovenským dejinám| editor=Karin Fábrová| publisher =Prešovská univerzita v Prešove| date =2005| location =Prešov| url=http://www.pulib.sk/elpub/FF/Fabrova1/index.htm}}</ref> Nevertheless, it is sometimes difficult to decide whether a certain word was borrowed from which Slavic language; ''e.g.'', the Hungarian word for county ''("megye")'' was borrowed from a ], but it may have taken either from the ] or from the ].<ref name='Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon'>{{cite book | last = Kristó | first = Gyula (editor) | authorlink = | coauthors = | title = Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon (9-14. század) ''(Encyclopedia of the Early Hungarian History - 9-14th centuries)''| publisher = Akadémiai Kiadó | date = 1994 | location = Budapest | pages = 646| url = | doi = | id = | isbn = 963 05 6722 9}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 19:58, 10 May 2008
Great Moravia (see Name section) was a Slavic state that existed in Central Europe from the 9th century to the early 10th century. There is some controversy as to the actual location of its core territory. According to mainstream historians, its core territory laid on both sides of the Morava river, in present-day Slovakia and the Czech Republic, but the empire also extended into what are today parts of Hungary, Romania, Poland, Austria, Germany, Serbia, Slovenia, Croatia. This theory also states that Great Moravia was inhabited by the ancestors of modern Moravians and Slovaks. According to alternate theories, the core territory of Great Moravia was situated South of the Danube river, in Slavonia or in the southern parts of the Carpathian Basin.
Great Moravia was founded when Mojmír I unified by force two neighboring states, referred to by the modern historiography as the "Principality of Nitra" and the "Principality of Moravia", in 833. The rulers of the emerging state periodically accepted the supremacy of the Kings of East Francia, but they continuously endeavored to strengthen the independent status of their country.
Unprecedented cultural development resulted from the mission of Saints Cyril and Methodius, who came during the reign of Prince Rastislav in 863. The empire reached its greatest territorial extent under Svatopluk I (871-894), although the borders of his dominions are still under debate. He also achieved to have his independent status acknowledged by Pope John VIII who styled Svatopluk "king" in a letter.
Weakened by internal struggle and frequent wars with the Carolingian Empire, Great Moravia was ultimately overrun by the Magyars, who invaded the Carpathian Basin around 896. Its remnants were later divided among Poland, Kingdom of Hungary, Bohemia and the Holy Roman Empire. Although some contemporary sources mention that Great Moravia vanished, archaeological researches and toponyms suggest the continuity of Slavic population in the valleys of the rivers of the Inner Western Carpathians. Most castles and towns survived the destruction of the empire, but the identification of some castles is still debated and some scholars even claim that Great Moravia, in fact, disappeared without trace.
Great Moravia left behind a lasting legacy in Central and Eastern Europe. The Glagolitic script and its successor Cyrillic were disseminated to other Slavic countries, charting a new path in their cultural development. The administrative system of Great Moravia may have influenced the development of the administration of the Kingdom of Hungary. Great Moravia also became a favorite issue in the Czech and Slovak romantic nationalism of the 19th century.

Name
The designation "Great Moravia" ("Μεγάλη Μοραβία") originally stems from the work De Administrando Imperio written by the Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitos around 950. Although the name Great Moravia is used by the modern historiography to refer to a medieval polity in the northern part of the Carpathian Basin, the Emperor himself referred to a different country, located south of or in the southern part of the Carpathian Basin or he mismatched the location.
The word "Great Moravia" used by modern authors not only refers to present-day Moravia, but to a country situated on both sides of the Morava river whose capital was also plausibly called Morava. Alternatively, "Moravia" could also refer to country whose capital was Morava. It is not always clear whether an early medieval written source names a country or a town called Morava. The adjective "Great" nowadays denotes Moravia plus the annexed territories. Some authors interpret the original meaning as "distant", because Byzantine texts used to distinguish between two countries of the same name using the attribute "little" for the territory closer to the Byzantine Empire (such as the Morava rivers in Serbia) and "great" for the more distant territory (such as the Morava river between Moravia and Slovakia).
The adjective "Μεγάλη" may also mean "old" in Byzantine texts and some scholars argue Old Moravia is the correct name.
The names of Great Moravia in other languages are Велья Морава in Old Church Slavonic, Veľká Morava in Slovak, Velká Morava in Czech, Magna Moravia in Latin, Velika Moravska (Велика Моравска) in Serbian and Croatian, and Nagymorva Birodalom in Hungarian. In English, the forms Greater Moravia and Moravia Magna are also sometimes used.
The use of the term (Great) Slovak Empire instead of Great Moravia is promoted by some Slovak authors who attempt to define it as an early Slovak state. The use of this term would contradict the theory that the distinct Slavic nations had not yet emerged by the 9th century and the culture and language of various Slavic tribes in central Europe were indistinguishable from each other.
History
Foundation
The formation of Great Moravia resulted from the political and social development that is documented by archaeological findings, but scarcely described by contemporary chroniclers. The first state of the Slavs living on the Middle Danube was Samo's Realm, a tribal confederation existing between 623 and 658. It encompassed the territories of Moravia, Slovakia, Lower Austria, Carantania, Sorbia at the Elbe, and probably also Bohemia, which lies between Sorbia and other parts of the realm. Although this tribal confederation plausibly did not survive its founder, it created favorable conditions for the formation of the local Slavic aristocracy.
Graves dated to the period after King Samo's death show that the Avars returned to some of their lost territories and they even could expand their area of settlement not only over the western parts of the present-day Slovakia but also over the Vienna Basin when a new population of the "griffin and tendril" archaeological culture (identified as Onogurs) appeared in the 670s. However, archaeological findings from the same period (such as an exquisite noble tomb in Blatnica) also indicate formation of a Slavic upper class on the territory that later became the nucleus of Great Moravia.
In the late 8th century, the Morava river basin and present-day western Slovakia, inhabited by the Slavs and situated at the Frankish border, flourished economically. Construction of numerous river valley settlements as well as hill forts indicates that political integration was driven by regional strongmen protected by their armed retinues. The Blatnica-Mikulčice horizon, a rich archaeological culture partially inspired by the contemporaneous Carolingian and Avar art, arose from this economic and political development. In the 790s, the Slavs who had settled on the middle Danube overthrew the Avar yoke in connection with Charlemagne's campaigns against the Avars. Further centralization of power and progress in creation of state structures of the Slavs living in this region followed. As a result, two major states emerged: the Moravian Principality originally situated in present-day southeastern Moravia and westernmost Slovakia (with the probable center in Mikulčice) and the Principality of Nitra, located in present-day western and central Slovakia (with the center in Nitra).
Moravian legates were sent to Frankish emperors in 811 and 815. In 822, the Royal Frankish Annals record that the Marvani paid homage to the Frankish Emperor at the Diet in Frankfurt. The first Moravian ruler known by name, Mojmír I, was baptized in 831 by Reginhar, bishop of Passau.
There is not much information in the contemporary primary sources (only two remarks in a Western documents) about the polity referred to as the "Principality of Nitra" by later historians. Nevertheless, during the first decades of the 9th century, the Slavic people living in the north-western parts of the Carpathian Basin were under the rule of a tribal leader (styled as prince by later historians) whose seat was in Nitra. In 828, Pribina, although probably still a pagan himself, built the first Christian church within the borders of modern Slovakia in his possession called Nitrava.
In 833, Mojmír I expelled Pribina from Nitra and the two principalities became united under the same ruler. Excavations revealed that at least three Nitrian castles (Pobedim, Čingov, and Ostrá skala) were destroyed around the time of the conquest (i.e., around the time when Pribina was expelled from his possession). But Pribina escaped to the Franks and their king Louis the German granted him parts of Pannonia around the Zala River, referred usually in modern works as the Balaton Principality.
After unification

What modern historians designate as "Great" Moravia arose around 830 when Moimír unified the Slavic tribes settled north of the Danube and extended the Moravian supremacy over them. When Mojmír I endeavoured to secede from the supremacy of the king of East Francia in 846, King Louis the German deposed him and assisted Moimír's nephew, Rastislav (846–870) in acquiring the throne. Although he was originally chosen by the Frankish king, the new monarch pursued an independent policy. After stopping a Frankish attack in 855, he also sought to weaken influence of Frankish priests preaching in his realm. Rastislav asked the Byzantine Emperor Michael III to send teachers who would interpret Christianity in the Slavic vernacular. By establishing relations with Constantinople, Rastislav wanted to weaken influence of Frankish preachers, who served the interests of the Frankish Emperor. He also desired to counter an anti-Moravian alliance recently concluded between the Franks and Bulgarians. Upon Rastislav's request, two brothers, Byzantine officials and missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius came in 863. Cyril developed the first Slavic alphabet and translated the Gospel into the Old Church Slavonic language. Texts translated or written by Cyril and Methodius are considered to be the oldest literature in the Slavic languages. Rastislav was also preoccupied with the security and administration of his state. Numerous fortified castles built throughout the country are dated to his reign and some of them (e.g., Dowina, sometimes identified with Devín Castle) are also mentioned in connection with Rastislav by Frankish chronicles. The nomadic Magyar tribes invaded the Carpathian Basin for the first time during his reign, in 861, and afterwards, the Magyars were occasionally hired by several rulers of the territory in order to intervene in their wars against the opposite party.

During Rastislav's reign, the Principality of Nitra was given to his nephew Svatopluk as an appanage. The rebellious prince allied himself with the Franks and overthrew his uncle in 870. The beginning of Svatopluk I’s reign was turbulent as his former Frankish allies refused to leave the western part of his empire. The young prince was even taken captive by the Franks and the country rallied around Slavomír who led an uprising against the invaders in 871. Svatopluk was finally released and took over the command of the insurgents, driving the Franks from Great Moravia. In the subsequent years, he successfully defended the independence of his realm from Eastern Francia and subjected many neighboring lands. Similarly to his predecessor, Svatopluk I (871–894) assumed the title of the king (rex). During his reign, the Great Moravian Empire reached its greatest territorial extent, when not only present-day Moravia and Slovakia but also present-day northern and central Hungary, Lower Austria, Bohemia, Silesia, Lusatia, southern Poland and northern Serbia belonged to the empire, but the exact borders of his domains are still disputed by modern authors. Svatopluk also withstood attacks of Magyar tribes and the Bulgarian Empire, although sometimes it was he who hired the Magyars when waging war against East Francia.
In 880, Pope John VIII issued the bull Industriae Tuae, by which he set up an independent ecclesiastical province in Great Moravia with Archbishop Methodius as its head. He also named the German cleric Wiching the Bishop of Nitra, and Old Church Slavonic was recognized as the fourth liturgical language, along with Latin, Greek and Hebrew.
Decline and fall

After the death of King Svatopluk in 894, his sons Mojmír II (894-906?) and Svatopluk II succeeded him as the King of Great Moravia and the Prince of Nitra respectively. However, they started to quarrel for domination of the whole empire. Weakened by an internal conflict as well as by constant warfare with Eastern Francia, Great Moravia lost most of its peripheral territories.
In the meantime, the Magyar tribes, having suffered a catastrophic defeat from the similarly nomadic Pechenegs, left their territories east of the Carpathian Mountains, invaded the Carpathian Basin and started to occupy the territory gradually around 896. Their armies' advance may have been promoted by continuous wars among the countries of the region whose rulers still hired them occasionally to intervene in their struggles. The Bavarians and the Moravians accused each other of having formed alliances, even by "taking oath upon dogs and wolves", with the pagan Magyars.
Both Mojmír II and Svatopluk II probably died in battles with the Magyars between 904 and 907 because their names are not mentioned in written sources after 906. In three battles (July 4-5 and August 9, 907) near Bratislava, the Magyars routed Bavarian armies. Historians traditionally put this year as the date of the breakup of the Great Moravian Empire.
Although some contemporary sources mention that Great Moravia disappeared without trace and its inhabitants left for the Bulgars, Croats and Magyars following the latters' victories, but archaeological researches and toponyms suggest the continuity of Slavic population in the valleys of the rivers of the Inner Western Carpathians. Toponyms may prove that the nomadic Magyars occupied the Western Pannonian Plain in present-day Slovakia, while the hills were inhabited by a mixed (Slav and Hungarian) population and people living in the valleys of the mountains spoke Slavic language.
Moreover, there are sporadic references to Great Moravia from later years: In 924/925, both Folkuin in his Gesta abb. Lobiensium and Ruotger in Archiepiscopi Coloniensis Vita Brunonis mention Great Moravia. From 925 until 931, there are several references to certain counts Mojmír and Svatopluk in official documents from Salzburg, though the origin of the two nobles is not clear. In 942, Magyar warriors captured in Al Andalus said that Moravia is the northern neighbor of their people. The fate of the northern and western parts of former Great Moravia in the 10th century is thus largely unclear.
The western part of the Great Moravian core territory (present-day Moravia) became the Frankish March of Moravia. Originally a buffer against Magyar attacks, the march became obsolete after the Battle of Lechfeld (955). After the battle, it was given to the Bohemian duke Boleslaus I. In 999 it was taken over by Poland under Boleslaus I of Poland and returned to Bohemia in 1019.
As for the eastern part of the Great Moravian core territory (present-day Slovakia), its southernmost parts fell under domination of the old Magyar Árpád dynasty after 955. The rest remained under the rule of the local Slavic aristocracy and was gradually integrated into the Kingdom of Hungary in a process finished in the 14th century. In 1000 or 1001, all of present-day Slovakia was taken over by Poland under Boleslaus I and much of this territory became part of the Kingdom of Hungary by 1031. Since the 10th century, the population of Slovakia has been evolving into the present-day Slovaks.
Territory
The territory of Great Moravia was extending gradually in the course of the 9th century and it reached its largest extension between 874 and 894, following the conquests of Svatopluk I. However, the territories ruled by Svatopluk has not been exactly determined, yet. For example, it is under debate whether the "Balaton Principality" (administered probably by counts appointed by the King of East Francia during this period) or parts of the Carpathian Basin east of the Danube or the Tisza (Tisa) ("the territories of the Avars") were controlled by King Svatopluk.
The following map presents the territorial extension of Great Moravia as it appears in , , and .
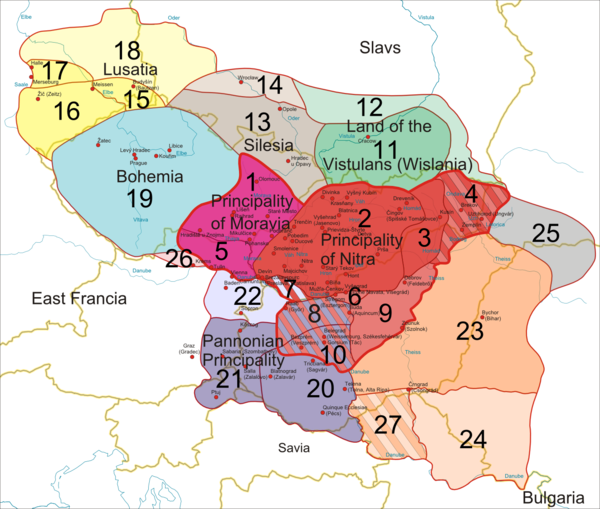
2. Core territory, Principality of Nitra before 833
3. Either part of the Principality of Nitra before 833, or conquered later by Mojmír I or by Rastislav.
4. Conquered by Mojmír I or by Rastislav, administered from Nitra.
5. Part of the Principality of Moravia or conquered no later than 853.
6. Conquered in 858, administered from Nitra and lost in 894.
7. Either part of Nitra or the Balaton Principality. Conquered either in 833 or 883, administered from Nitra. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
8. Conquered in 858 or 883, administered from Nitra and lost in 894. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
9. Conquered by Rastislav or Svatopluk I, administered from Nitra and lost in 896. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
10. Conquered in 858 or 883, administered from Nitra. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
11. Vistulans conquered in 874.
12. Probably conquered in 874 along with the Vistulan territory.
13. Silesia probably annexed in 880.
14. Probably conquered together with Silesia.
15. Lusatia controlled in 890-897.
16. Probably part of the Great Moravian Lusatia.
17. Probably part of the Great Moravian Lusatia.
18. Probably part of the Great Moravian Lusatia.
19. Bohemia controlled in 888-894.
20. The Balaton Principality controlled in 883-894. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
21. Probably part of the conquered Balaton Principality. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
22. Probably part of the conquered Balaton Principality. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
23. Transtheissia controlled in 881-896. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
24. Probably part of Transtheissia. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
25. Conquered by Svatopluk I and lost in 896. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
26. Conquered by Svatopluk I.
27. Probably part of Transtheissia. (The supremacy of Great Moravia over the territory is under debate.)
(yellow lines: current borders
blue lines: rivers
red dots: main castles and settlements)
As for the history of Bohemia—annexed by Great Moravia for eleven years (from 883 to 894), the crucial year is 895, when the Bohemians broke away from the empire and became vassals of Arnulf of Carinthia. Independent Bohemia, ruled by the dynasty of Přemyslids, began to gradually emerge.
Alternate theories
An alternative theory, proposed by Imre Boba independently of the similar theories of earlier authors (e.g., Daniele Farlatti, Gelasius Dobner working in the 18th century) in the 1970s, suggests that the core territory of the empire was situated south of the Danube river in Pannonia/Slavonia. The theory is based on Boba's reading of primary written sources (e.g., De administrando imperio, the Bavarian Geographer and Annales Fuldenses), which in his opinion were misread or ignored by other historians. Moreover, he also utilized the results of archaeological researches and his knowledge of Slavic studies. A short summary of his statements and their criticism follows:
- Boba claimed that some primary sources (e.g., De administrando imperio, the Bavarian Geographer) clearly locate the territory of Great Moravia south of the Danube and other primary sources do not contradict them. His opponents pointed out that the sources cited by Boba were written by foreigners "at a considerable distance from the events narrated" and their understanding of geography is not very precise. It is also true that some of the primary sources (such as Life of Methodius and Life of St. Clement of Ohrid, referred also by Boba) seem to contradict Boba's theory. For example, the escape of the Slavonic priests to Bulgaria, as described in the primary sources, indicates that Great Moravia was not located south of the Danube.
- Boba also emphasized that Saint Methodius was made Archbishop of Syrmium, a town south of the Danube. The opposite view states that the see in Syrmium was only symbolic, because Syrmium had formerly been the see of an archdiocese in the past, but Boba and his followers indicated that Method's consecration for a symbolic see would have violated canon law in the 9th century. Boba's opponents also pointed out that the church claimed by Boba to be the resting place of Methodius in Syrmium turned out to be founded two hundred years after Methodius' death and no medieval settlement existed in Syrmium before AD 1000.
- In addition, Boba argued that the continuity of the Slavonic liturgy and the uninterrupted use of Glagolitic alphabet in the Catholic Church can be proven south of the Danube, while such tradition did not exist uninterruptedly north of the Danube. In reality, the Slavonic liturgy survived in some places north of the Danube until 1097. Boba claimed that this tradition came to the Monastery of Sázava from Vyshhorod in the Kievan Rus'.
- Great Moravia was often mentioned as Sclavonia in the primary sources and this denomination may have survived the fall of the empire in the name of Slavonia (a territory south of the Danube) until the 20th century. But Boba's opponents pointed out that the same Latin name Sclavonia also referred to Slovakia and those northern parts of Hungary that were inhabited by Slavs. On the other hand, the Latin denomination Sclavonia for the territories of present-day Slovakia was documented only in 1512.
- Another Boba's claim was that archaeological findings attributed to the Moravians north of the Danube should be reclassified because they show clear nomadic characteristics (i.e., men and their horses buried together). But these characteristics are known only from some of the earliest graveyards, from the regions influenced by the nomad Avars. There is also a "sharp contrast in the archaeological record" between the politically and economically developed regions of Moravia and Slovakia (the location of Boba's opponents) on the one hand, and the sparsely populated Slavonia (Boba's location) on the other hand.
In 1983, the Japanese Senga Toru, based on the primary sources, argued that Great Moravia was located around the territory where the Drava joins the Danube, i.e., south of and in the southern parts of the Carpathian Basin on both sides of the Danube. He also stated that another polity named Moravia (without the adjective "Great") existed in the 9th century in the territory of present-day Moravia and in the western regions of present-day Slovakia, and the two polities were unified by Svatopluk I.
In the 1990s, the Hungarian historian, Gyula Kristó also mentioned that some sources allow to suppose that Great Moravia was located around the Great Morava River, south of the Danube. Later, he stated that some primary sources refer to the existence of two Moravian polities ("Great Moravia" and "Moravia") lying on the territories where Senga Toru located them.
People
The inhabitants of Great Moravia were designated Slovene, which is an old Slavic word meaning the "Slavs". The same name was used by the ancestors of Slovaks, Slovenes and Slavonians at that time and the present-day native names of these nations (for example Slovensko, the Slovak name of Slovakia) are still derived from the root Slovene. People of Great Moravia were sometimes referred to as "Moravian peoples" by Slavic texts, and "Sclavi" (i.e. the Slavs), "Winidi" (another name for the Slavs), "Moravian Slavs" or "Moravians" by Latin texts.
As in all medieval states, life in Great Moravia was difficult compared to the modern standards: 40 percent of men and 60 percent of women died before reaching the age of 40 years. However, Great Moravian cemeteries also document rich nutrition and advanced health care. Inhabitants of Great Moravia even had better teeth than people today: a third of the examined skeletons had no caries or lost teeth.
Government and society
Great Moravia was ruled by a hereditary monarch from the House of Mojmír. He was aided by a council of noblemen. The heir of the dynasty resided in Nitra, ruling the Principality of Nitra as an appanage. He enjoyed a great deal of autonomy, as documented by the Papal correspondence that addressed Rastislav and his heir Svatopluk in the same way. Some parts of the Great Moravian territory were ruled by vassal princes, such as Borivoj I of Bohemia. The realm was further divided into counties, headed by župans. The number of counties is estimated to 11 at the beginning of the 9th century and to 30 in the second half of the 9th century. This system also influenced the later Hungarian administrative division, often with the same castles serving as the seats of a county both under the Great Moravian and under the later Hungarian rule. However, historians has not reached a consensus yet, for example, whether administrative units in the Kingdom of Hungary (e.g., the vármegye) followed foreign (Bulgarian, Moravian or German) patterns or the administrative system was an internal innovation. Most of the population was formed by freemen, who were obliged to pay an annual tax. Slavery and feudal dependency are also recorded.
Warfare
Very little is known about the Great Moravian way of warfare. Earlier Byzantine sources mention the javelin as the favorite weapon of Slavic warriors. Great Moravia also probably employed spear and axe armed infantry, including the powerful royal bodyguard called druzhina. The druzhina was a princely retinue composed of professional warriors, who were responsible for collecting tribute and punishing wrongdoers. In general, Slavs used cavalry rarely, which made them particularly vulnerable to the Magyar horse archers. Despite a relative scarcity of horses among the Slavs, a contemporary Arab traveler reported that Svatopluk I had plenty of riding horses. The Great Moravian heavy cavalry emulated the contemporary Frankish predecessors of knights, with the expensive equipment that only the highest social strata could afford. Facing larger and better equipped Frankish armies, Slavs often preferred ambushes, skirmishes, and raids to regular battles. An important element of Great Moravian defense was to hide behind strong fortifications, which were difficult to besiege with the then prevailing forms of military organization. For example, a Frankish chronicler wrote with awe about "Rastislav's indescribable fortress" that stopped a Frankish invasion. The army was led by the king or, in case of his absence, by a commander-in-chief called voivode.
Culture
Architecture


Great Moravia had an exceptionally developed system of fortresses and fortified towns. Geographus Bavarus, when listing the neighbouring territories, mentioned "Beheimare, where 15 civitates are situated. The Marharii have 11 civitates. The territories of the Vulgari are extensive and populated by many people and they have 5 civitates; they do not need civitates, because they number so many people. There are people, called Merehanos, having 30 civitates". The sentences of the mediæval author are sometimes interpreted that 30 out of the 41 Great Moravian castles (civitates) were situated on the territory of present-day Slovakia and the remaining 11 in Moravia. These numbers are also corroborated by archaeological evidence. The only castles which are mentioned by name in written texts are Nitrawa (828; identified with Nitra), Dowina (864; sometimes identified with Devín Castle) and Brezalauspurc (907; usually identified with Bratislava Castle). Some sources claim that Uzhhorod in Ukraine (903) was also a fortress of the empire. Many other castles were identified by excavations.
Although location of the Great Moravian capital has not been safely identified, the fortified town of Mikulčice with its palace and 12 churches is the most widely accepted candidate. However, it is fair to note that early medieval kings spent a significant part of their lives campaigning and traveling around their realms due to the lack of reliable administrative capacities. It is thus very likely that they also resided from time to time in other important royal estates. For instance, Devín Castle is sometimes identified with a "fortress of Prince Rastislav" mentioned in the Annales Fuldenses.
Mikulčice was fortified in the 7th century and it later developed into a large (2 sq km) agglomeration composed of various villages and forts, spread over several river islands. The area enclosed by the fortifications was only slightly smaller than the area of the contemporary Frankish Emperor's capital of Regensburg. The population, estimated at 2,000, lived off trade and crafts. Mikulčice was also a foremost religious center, with the first stone churches built around 800. The largest among them was a three-nave basilica with the inside dimensions 35 m by 9 m and a separate baptistery. The only church safely identified as Great Moravian and at the same time still remaining above ground is situated in nearby Kopčany.
Nitra, the second center of the Empire, was ruled autonomously by the heir of the dynasty as an appanage. Nitra consisted of five large fortified settlements and twenty specialized craftsmen's villages, making it a real metropolis of its times. Crafts included production of luxury goods, such as jewelry and glass. The agglomeration was surrounded by a number of smaller forts and religious buildings (e.g. in Dražovce and Zobor).
Bratislava Castle had a stone two-story palace and a spacious three-nave basilica, built in the mid-9th century. Excavations of the cemetery situated by the basilica brought findings of the Great Moravian jewelry, similar in style and quality to that from Mikulčice. The castle's name was first recorded in 907, during the fall of Great Moravia, as Brezalauspurc. This name literally means "Braslav's Castle" and Braslav of Pannonia was a count appointed by King Arnulf of East Francia.
The sturdy Devín Castle, in vicinity of Bratislava, guarded Great Moravia against frequent attacks from the West. Although some authors claim that it was built only later as a stronghold of the Kings of Hungary, excavations have unearthed an older Slavic fortified settlement founded in the 8th century. During the Great Moravian period, Devín Castle was a seat of a local lord, whose retainers were buried around a stone Christian church. These two castles were reinforced by smaller fortifications in Devínska Nová Ves, Svätý Jur, and elsewhere.
Most Great Moravian castles were rather large hill forts, fortified by wooden palisades, stone walls and in some cases, moats. The typical Great Moravian ramparts combined an outer drystone wall with an internal timber structure filled with earth. The fortifications usually formed several contiguous enclosures, with the elite buildings concentrated in the center and crafts in the outer enclosures. Most buildings were made of timber, but ecclesiastical and residential parts were made of stone. Sometimes, earlier, prehistoric (Devín Castle) or Roman (Bratislava Castle) fortifications were integrated. At least some churches (e.g. in Bratislava, Devín Castle, and Nitra) were decorated by frescoes, plausibly painted by Italian masters since the chemical composition of colors was the same as in northern Italy. In Nitra and Mikulčice, several castles and settlements formed a huge fortified urban agglomeration. Many castles served as regional administrative centers, ruled by a local nobleman. For example, Ducové was the center of the Váh river valley and Zemplín Castle controlled the Zemplín region. Their form was probably inspired by Carolingian estates called curtis. The largest castles were usually protected by a chain of smaller forts. Smaller forts (e.g. Beckov Castle) were also built to protect trade routes and to provide shelter for peasants in case of a military attack.
Only few examples of Great Moravian architecture are fully preserved or reconstructed. The only still standing building is the church in Kopčany, though several other early medieval churches (for example in Kostoľany pod Tribečom, Michalovce, and Nitra) may be Great Moravian too. Two open air museums, in Modrá near Uherské Hradiště and in Ducové, are devoted to the Great Moravian architecture.
Religion
Due to the lack of written documents, very little is known about the original Slavic religion and mythology. Several cult places used prior the Christianization are known from Moravia (Mikulčice and Pohansko). However, we do not know what these objects, such as a ring ditch with a fire, a horse sacrifice, or human limbs ritually buried in a cemetery, meant for Great Moravians. A cult object in Mikulčice was used until the evangelization of the Moravian elite in the mid-9th century and idols in Pohansko were raised on the site of a demolished church during the pagan backlash in the 10th century. The period of the Great Moravian ascent in European history is associated more with the spread of Christianity.

The territory of Great Moravia was originally evangelized by missionaries coming from the Frankish Empire or Byzantine enclaves in Italy and Dalmatia since the early 8th century and sporadically earlier. The first Christian church of the Western and Eastern Slavs known to the written sources was built in 828 by Pribina in Nitra. The church, consecrated by Bishop Adalram of Salzburg, was built in a style similar to contemporaneous Bavarian churches, while architecture of two Moravian churches from the early 9th century (in Mikulčice and Modrá) indicates influence of Irish missionaries. Despite the formal endorsement by the elites, the Great Moravian Christianity was described as containing many pagan elements as late as in 852. Grave goods, such as food, could be found even in church graveyards. The Church organization in Great Moravia was supervised by the Bavarian clergy until the arrival of the Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius in 863.
Foundation of the first Slavic bishopric (870), archbishopric (880), and monastery was the politically relevant outcome of the Byzantine mission initially devised by Prince Rastislav to strengthen his early feudal state. It is not known where the Great Moravian archbishop resided (a papal document mentions him as the archbishop of Morava, Morava being the name of a town), but there are several references to bishops of Nitra. Big three-nave basilicas unearthed in Mikulčice, Staré Město, Bratislava, and Nitra were the most important ecclesiastical centers of the country, but their very construction may have predated the Byzantine mission. Nitra and Uherské Hradiště are also sites where monastic buildings have been excavated. A church built at Devín Castle is clearly inspired by Byzantine churches in Macedonia (from where Cyril and Methodius came) and rotundas, particularly popular among Great Moravian nobles, also have their direct predecessors in the Balkans.
Literature

But yields of the mission of Cyril and Methodius extended beyond the religious and political sphere. The Old Church Slavonic became the fourth liturgical language of the Christian world, though its use in Great Moravia proper had gradually declined until it virtually vanished in the late Middle Ages. Its late form still remains the liturgical language of the Russian, Bulgarian, and Serbian Orthodox Church. Cyril also invented the Glagolitic alphabet, suitable for Slavic languages. He translated the Gospel and the first translation of the Bible into a Slavic language was later completed by his brother Methodius.
Methodius wrote the first Slavic legal code, combining the local customary law with the advanced Byzantine law. Similarly, the Great Moravian criminal law code was not merely a translation from Latin, but it also punished a number of offenses originally tolerated by the pre-Christian Slavic moral standards yet prohibited by Christianity (mostly related to sexual life). The canon law was simply adopted from the Byzantine sources.
There are not many literary works that can be unambiguously identified as originally written in Great Moravia. One of them is Proglas, a cultivated poem in which Cyril defends the Slavic liturgy. Vita Cyrilli (attributed to Clement of Ohrid) and Vita Methodii (written probably by Methodius' successor Gorazd) are biographies with precious information about Great Moravia under Rastislav and Svatopluk I.
The brothers also founded an academy, initially led by Methodius, which produced hundreds of Slavic clerics. A well-educated class was essential for administration of all early-feudal states and Great Moravia was no exception. Vita Methodii mentions bishop of Nitra as Svatopluk I’s chancellor and even Prince Koceľ of the Balaton Principality was said to master the Glagolitic script. Location of the Great Moravian academy has not been identified, but the possible sites include Mikulčice (where some styli have been found in an ecclesiastical building), Devín Castle (with a building identified as a probable school), and Nitra (with its Episcopal basilica and monastery). When Methodius’ disciples were expelled from Great Moravia in 885, they disseminated their knowledge (including the Glagolitic script) to other Slavic countries, such as Bulgaria, Croatia, and Bohemia. They created the Cyrillic alphabet, which became the standard alphabet in the Slavic Orthodox countries, including Russia. The Great Moravian cultural heritage survived in Bulgarian seminaries, paving the way for evangelization of Eastern Europe.
Arts and crafts
In the first half of the 9th century, Great Moravian craftsmen were inspired by contemporary Carolingian art. In the second half of the 9th century, Great Moravian jewelry was influenced by Byzantine, Eastern Mediterranean, and Adriatic styles. But, in the words of Czech archaeologist Josef Poulík, "these new forms and techniques were not copied passively, but were transformed in the local idiom, establishing in this way the roots of the distinctive Great Moravian jewelery style." The typical Great Moravian jewelry included silver and golden earrings decorated by fine granular filigree, as well as silver and gilded bronze buttons covered by foliate ornaments.
The most important industry was iron metallurgy. An example of highly developed tool production are asymmetrical plowshares.
Legacy
Destruction of the Great Moravian Empire was rather gradual. Since excavations of Great Moravian castles show continuity of their settlement and architectural style after the alleged disintegration of the Empire, local political structures must have remained untouched by the disaster. Another reason is that the originally nomad old Magyars lacked siege engines to conquer Great Moravian fortifications, although this did not hinder them from conquering strong fortresses, documented by primary written sources (e.g., Blatnograd, Bratislava Castle). Nevertheless, the core of Great Moravia was finally integrated into the newly established states of Bohemia and the Kingdom of Hungary.
Great Moravian centers (e.g., Bratislava, Nitra, Tekov, and Zemplín) also retained their functions afterwards, although the identification of Bratislava, Tekov and Zemplín as Great Moravian castles is not generally accepted. Since the same castles became the seats of early Hungarian administrative units (counties), historians posit that the administrative division of Great Moravia was just adopted by new rulers. On the other hand, several sources suggest that the Hungarian rulers followed the contemporary German or Bulgar patents when they established the new administrative system in their kingdom, or they introduced a new system. Moreover, the territorial administration of the Kingdom of Hungary was developing gradually, i.e., counties with larger territory were divided into smaller ones, while the scarcely habitated parts of the kingdom (e.g., the northern and north-eastern territories of present-day Slovakia or the Bakony Hills in today Hungary) were originally the kings' private forests, then they were organized into "forest counties" (12-13th centuries) and the latter, following their colonization, developed into or were divided among counties around 1300.
Social differentiation in Great Moravia reached the state of early feudalism, creating the social basis for development of later medieval states in the region. The question what happened to Great Moravian noble families after 907 is still under debate. On the one hand, recent research indicates that a significant part of the local aristocracy remained more or less undisturbed by the fall of Great Moravia and their descendants became nobles in the newly formed Kingdom of Hungary. The most prominent example are the powerful families of Hunt and Pázmán. On the other hand, both Anonymous and Simon of Kéza, two chroniclers of the early history of Hungary, recorded that the prominent noble families of the kingdom descended either from leaders of the Magyar tribes or from immigrants, and they did not connect any of them to Great Moravia. For example, the ancestors of the clan Hunt-Pázmán (Hont-Pázmány), were mentioned to have arrived from the Duchy of Swabia to the kingdom in the late 10th century.
Many Slavic words related to politics, law, and agriculture were taken into the Hungarian language. Nevertheless, it is sometimes difficult to decide whether a certain word was borrowed from which Slavic language; e.g., the Hungarian word for county ("megye") was borrowed from a South Slavic language, but it may have taken either from the Slovene or from the Serbo-Croatian.
The territories mentioned as "Tercia pars regni" (literally "one-third part of the Kingdom of Hungary") in the medieval sources are referred to as the "Duchy" in Hungarian scholarly works and as the "Principality of Nitra" in Slovak academic sources. These territories were ruled autonomously by members of the Árpád dynasty residing in Bihar (today Biharea in Romania) or in Nitra - a practice reminiscent of the Great Moravian appanage system, but also similar to that of some other dynasties in the Early Middle Ages (e.g., the Ruriks in the Kievan Rus'). The existence of an autonomous political unit centered around Nitra is often considered by Slovak scholars an example of political continuity from the Great Moravian period.
There are also documents indicating that the Church organization survived the invasion of the pagan Magyars at least to some degree. For example, continuity of the formal Church organization is confirmed by an uninterrupted list of Moravian bishops from the 14th century.
Neither the demographic change was dramatic. As far as the graves can tell, there had been no influx of the Magyars into the core of former Great Moravia before 955. Afterwards, Magyar settlers appear in some regions of Southern Slovakia, but graves indicate a kind of cultural symbiosis (resulting in the common Belobrdo culture), not domination. Due to cultural changes, archaeologists are not able to identify the ethnicity of graves after the half of the 11th century. This is also why integration of central, eastern, and northern territories of present-day Slovakia into the Hungarian Kingdom is difficult to be documented by archeology, and written sources have to be used.
The Byzantine double-cross thought to have been brought by Cyril and Methodius is part of the symbol of Slovakia until today and the Constitution of Slovakia refers to Great Moravia in its preamble. Interest about that period rose as a result of the national revival in the 19th century. Great Moravian history has been regarded as a cultural root of several Slavic nations in Central Europe (especially the Slovaks, as it was the only significant Slavic state Slovakia had ever been a part of) and it was employed in vain attempts to create a single Czechoslovak identity in the 20th century.
Notes
- ^ Štefanovičová, Tatiana (1989). Osudy starých Slovanov. Bratislava: Osveta.
- ^ Sommer, Petr (2007), "Bohemia and Moravia", in Berend, Nora (ed.), Christianization and the rise of Christian monarchy : Scandinavia, Central Europe and Rus' c. 900-1200, Cambridge, UK ; New York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 214–262
{{citation}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coeditors=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Bruce-Mitford, Rupert Leo Scott (1975). Recent archaeological excavations in Europe. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul. ISBN 071007963X.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Marsina, Richard (1997). "Ethnogenesis of Slovaks". Human Affairs. 7 (1): 15–23.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Charles R. Bowlus (1987). "Imre Boba's Reconsiderations of Moravia's Early History and Arnulf of Carinthia's Ostpolitik (887-892)". Medieval Academy of America. Retrieved 2008-05-05.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Boba, Imre (1996). Morávia története új megvilágításban (in Hungarian).
{{cite book}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ^ Čaplovič, Dušan (2000). Dejiny Slovenska. Bratislava: AEP.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Kirschbaum, Stanislav J. (1995). A History of Slovakia: The Struggle for Survival. New York: Palgrave Macmillan; St. Martin's Press. ISBN 978-0-312-10403-0.
- ^ Kristó, Gyula (1996). Magyar honfoglalás - honfoglaló magyarok. Kossuth Könyvkiadó. pp. 131–132, 141. ISBN 963 09 3836 7.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) Cite error: The named reference "Kristó 2" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ Kniezsa, István (2000). Magyarország népei a XI. században. Lucidus Kiadó. p. 26. ISBN 963 85954 3 4.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) Cite error: The named reference "Kniezsa" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ Sedlák, Vincent (2005). "Onomastika a historiografia". In Karin Fábrová (ed.). Príspevky k slovenským dejinám. Prešov: Prešovská univerzita v Prešove.
- "Nacionalizmus és régészet Közép- és Kelet-Európában" (in Hungarian). Hungarian Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 2008-04-28.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Constantine Porphyrogenitus (1967). De Administrando Imperio; Greek text edited by Gy. Moravcsik ; English translation by R.J.H. Jenkins (new, rev. ed. ed.). Washington, D.C.: Dumbarton Oaks Center for Byzantine Studies.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - De Administrando Imperio: "The following nations border the Turks: in the regions west of them, lies Franconia, there are the Petchenegs north of them; and in the regions south of them, lies Great Moravia, i.e., Sphendoplokos' country that was devastated and occupied by them."
- ^ Havlík, Lubomír E. (1992). Kronika o Velké Moravě. Brno: Iota.
- Kunstmann, Heinrich (1996). Die Slaven: Ihr Name, ihre Wanderung nach Europa und die Anfänge (in German). Franz Steiner Verlag. ISBN 3515068163. Retrieved 2008-05-08.
{{cite book}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Kristó, Gyula (1993). A Kárpát-medence és a magyarság régmultja (1301-ig). Szeged: Szegedi Középkorász Műhely. ISBN 963 04 2914 4.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) Cite error: The named reference "Kristó" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - Veteška, Tomáš J. (1987). Veľkoslovenská ríša. Hamilton: MSA ZMS.
- Bartl, Július (1997). "Ďurica, M. S.: Dejiny Slovenska a Slovákov". Historický časopis. 45 (1): 114–122.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Poulik, Josef (1978). "The Origins of Christianity in Slavonic Countries North of the Middle Danube Basin". World Archaeology. 10 (2): 158–171.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Váňa, Zdeněk (1983). The world of the ancient Slavs. London: Orbis Pub.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Barford, P. M. (2001). The early Slavs : culture and society in early medieval Eastern Europe. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Annales regni Francorum, inde ab a. 741. usque ad a. 829., qui dicuntur Annales laurissenses maiores et Einhardi. Post editionem G.H. Pertzii recognovit Fridericus Kurze. Hannover: Imprensis Bibliopolii Hahniani. 1950.
- Royal Frankish Annals: "Id quo conventu omnium orientalium Sclavorum, id est Abodritorum, Soraborum, Wilzorum, Beheimorum, Marvanorum, Prædecentorum, et in Pannonia residentium Abarorum legationes cum muneribus ad se directas audivit." ("At this assembly, he /the king/ gave audience also to the delegates sent with presents to him by all the Eastern Slavonic people, namely, by the Obotrites, Sorbs, Veleti, Czech, Moravians and Prædecents and the Avars settled in Pannonia.")
- Angi, János; Bárány, Attila; Orosz, István; Papp, Imre; Pósán, László (1997). Európa a korai középkorban (3-11. század) (Europe in the Early Middle Ages - 3-11th centuries). Debrecen: dup, Multiplex Media - Debrecen U. P. p. 360. ISBN 963 04 9196 6.
- ^ Bartoňková Dagmar; et al., eds. (1969). "Libellus de conversione Bagoariorum et Carantanorum (i.e. Conversio)". Magnae Moraviae fontes historici III. Praha: Statni pedagogicke nakl.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|editor=(help) - Conversio Bagoariorum et Carantanorum: "Adalramus archepiscopus ultra Danubium in sua proprietate loco vocato Nitrava consecravit ecclesiam." ("Archbishop Adalram consecrated a church for him over the Danube on his possession called Nitra.")
- Conversio Bagoariorum et Carantanorum: "...quidam Priwina exulatus a Moimaro duce Maravorum supra Danubium venit ad Ratbodum" ("... a certain Priwina, who had been expelled by Moimar, Duke of the Moravians living over the Danube, came to Ratbod").
- Conversio Bagoariorum et Carantanorum: "Aliqua vero interim occasione percepta, rogantibus prædicti regis fidelibus præstavit rex Priwinæ aliquam inferioris Pannoniæ in beneficium partem circa fluvium qui dicitur Sala" ("In the meantime, when an opportunity offered, the king, on the request of his above-mentioned faithful men, granted the parts of Lower Pannonia around the river called Zala to Pribina as a benefice").
- Angi, János; Bárány, Attila; Orosz, István; Papp, Imre; Pósán, László (1997). Európa a korai középkorban (3-11. század) (Europe in the Early Middle Ages - 3-11th centuries). Debrecen: dup, Multiplex Media - Debrecen U. P. p. 360. ISBN 963 04 9196 6.
- ^ Kristó, Gyula (editor) (1994). Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon (9-14. század) (Encyclopedia of the Early Hungarian History - 9-14th centuries). Budapest: Akadémiai Kiadó. p. 467. ISBN 963 05 6722 9.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) Cite error: The named reference "Korai Magyar Történeti Lexikon" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - Annales Fuldenses: "(...) circa medium mensem Augustum cum exercitu ad Sclavos Margenses defectionem molientes profectus est. Ubi ordinatis et iuxta libitum suum conpositis rebus ducem eis constituit Rastizen nepotem Moirmari; (...)" ("(...) around the middle of August, he went with his armies to the Sclavi Margenses who were about to secede. There, he arranged the issues at his discretion and appointed a prince, Rastisen, the nephew/grandson of Moimir, for them; (...)").
- ^ Obolensky, Dimitri (1994). Byzantium and the Slavs. Crestwood, N.Y.: St. Vladimir’s Seminary Press.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Annales Fuldenses, sive, Annales regni Francorum orientalis ab Einhardo, Ruodolfo, Meginhardo Fuldensibus, Seligenstadi, Fuldae, Mogontiaci conscripti cum continuationibus Ratisbonensi et Altahensibus / post editionem G.H. Pertzii recognovit Friderious Kurze ; Accedunt Annales Fuldenses antiquissimi. Hannover: Imprensis Bibliopolii Hahniani. 1978.." Cite error: The named reference "fulda" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Benda, Kálmán (editor) (1981). Magyarország történeti kronológiája ("The Historical Chronology of Hungary"). Budapest: Akadémiai Kiadó. pp. 50–52. ISBN 963 05 2661 1.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) Cite error: The named reference "Történeti Kronológia" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - ^ Tóth, Sándor László (1998). Levediától a Kárpát-medencéig ("From Levedia to the Carpathian Basin"). Szeged: Szegedi Középkorász Műhely. p. 199. ISBN 963 482 175 8.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) Cite error: The named reference "Tóth" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - Róna-Tas, András (1999). Hungarians and Europe in the early Middle Ages : an introduction to early Hungarian history. Budapest ; New York: Central European University Press. ISBN 9639116483.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Tibenský, Ján; et al. (1971). Slovensko: Dejiny. Bratislava: Obzor.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ Lukačka, Ján (2002). Formovanie vyššej šľachty na západnom Slovensku. Bratislava: Mistrál.
- Pástor, Zoltán (2000). Dejiny Slovenska: Vybrané kapitoly. Banská Bystrica: Univerzita Mateja Bela.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Boba, Imre (1971). Moravia’s history reconsidered; a reinterpretation of medieval sources. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Curta, Florin (2006). Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500-1250. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Boba, Imre (1990). "Reviewed work: Slovensko v Dobe Vel'Komoravskej. by Peter Ratkos". The American Association for the Advancement of Slavic Studies. Retrieved 2008-05-05.
- ^ Dvořáková, Daniela (2007). Kôň a človek v stredoveku: K spolužitiu človeka a koňa v Uhorskom kráľovstve. Budmerice: Rak.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Senga, Toru (1983/2). Morávia bukása és a honfoglaló magyarok ("The fall of Moravia and the Hungarians occupying their country"). Budapest: Századok. pp. 307–345.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help): - ^ Havlík, Lubomír E. (1989), "Great Moravia between the Franconians, Byzantium and Rome", in Champion, T. (ed.), Centre and Periphery: Comparative Studies in Archaeology, London, Boston: Routledge, pp. 227–237
{{citation}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameters:|coeditors=and|coauthors=(help) - ^ Kristó, Gyula (1988). A vármegyék kialakulása Magyarországon ("The formation of counties in Hungary"). Budapest: Magvető Könyvkiadó. pp. 21–100. ISBN 963 14 1189 3.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) Cite error: The named reference "Kristó 3" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page). - Dvornik, Francis (1956). The Slavs: their early history and civilization. Boston: American Academy of Arts and Sciences.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Curta, Florin (2001). History and Archaeology of the Lower Danube Region, c. 500–700. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Goldberg, Eric Joseph (2006). Struggle for empire : kingship and conflict under Louis the German, 817-876. Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Bartoňková Dagmar; et al., eds. (1969). "Descriptio civitatum et regionum ad septentrionalem plagam Danubii". Magnae Moraviae fontes historici III. Praha: Statni pedagogicke nakl.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|editor=(help) - Špiesz, Anton (2001). Bratislava v stredoveku. Bratislava: Perfekt.
- ^ Poulík, Josef (1975). Mikulčice: Sídlo a pevnost knížat velkomoravských. Praha: Academia.
- "Kostol sv. Margity Antiochijskej v kopčanoch". Retrieved 2007-06-21.
- Engel, Pál (1996). Magyarország világi archontológiája (1301-1457) I. Budapest: História - MTA Történettudományi Intézete. p. 300. ISBN 963 8312 44 0 I.k..
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ Stanislav, Ján (1934). Životy slovanských apoštolov Cyrila a Metoda. Panonsko-moravské legendy. Bratislava, Praha: Vydané spoločne nakladateľstvom Slovenskej ligy a L. Mazáča.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Cibulka, Josef (1958). Velkomoravský kostel v Modré u Velehradu a začátky křesťanství na Moravě. Praha: ČSAV.
- Kučera, Matúš (1974). Slovensko po páde Veľkej Moravy. Bratislava: Veda.
- Fügedi, Erik (1986). Ispánok, bárók, kiskirályok (Counts, barons and petty kings). Budapest: Magvető Könyvkiadó. pp. 12, 24. ISBN 963 14 0582 6.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Benda, Gyula; Bertényi, Iván; Pótó, János (editors) (2004). Anonymus: A magyarok cselekedetei – Kézai Simon: A magyarok cselekedetei (Anonymous: The Deeds of the Hungarians – Simon of Kéza: The Deeds of Hungarians). Budapest: Osiris. p. 120-122. ISBN 963 389 606 1.
{{cite book}}:|first3=has generic name (help) - Heller, Mihail (2000). Orosz történelem - Az Orosz Birodalom története (Russian History - A History of the Russian Empire). Budapest: Osiris Kiadó. p. 37. ISBN 963 379 243 6 I. köt.
{{cite book}}: Check|isbn=value: invalid character (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Ján, Steinhübel (2004). Nitrianske kniežatstvo: Počiatky stredovekého Slovenska. Budmerice: Rak. ISBN 80-224-0812-3.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)
Sources
Primary sources
- Annales regni Francorum, annals covering the years 741-829.
- Annales Bertiniani, a continuation of Annales regni Francorum covering the period 830-82.
- Annales Fuldenses, a continuation of Annales regni Francorum until 901.
- Geographus Bavarus, written sometime between the 830s and 870s.
- Libellus de conversione Bagoariorum et Carantanorum (i.e. Conversio), written in 870.
- Vita Methodii, a biography of Saint Methodius written in Great Moravia shortly after 885.
- Annales Iuvavenses, annals written in the 9th and 10th centuries in Salzburg.
- De Administrando Imperio, written by Constantine VII Porphyrogenitos between 948 and 952.
Primary documents can be found in the following volumes:
- Havlík, Lubomír E. (1966-1977). Magnae Moraviae Fontes Historici I.-V., Brno: Masarykova univerzita.
- Marsina, Richard (1971). Codex diplomaticus et epistolaris Slovaciae I., Bratislava: Veda.
- Ratkoš, Peter (1964). Pramene k dejinám Veľkej Moravy, Bratislava: Vydavateľstvo Slovenskej akadémie vied.
Secondary sources
- Dekan, Jan (1981). Moravia Magna: The Great Moravian Empire, Its Art and Time, Minneapolis: Control Data Arts. ISBN 0-89893-084-7
- Havlík, Lubomír E. (1992). Kronika o Velké Moravě, Brno: Iota.
- Kučera, Matúš (1974). Slovensko po páde Veľkej Moravy, Bratislava: Veda.
- Lukačka, Ján (2002). Formovanie vyššej šľachty na západnom Slovensku, Bratislava: Mistrál.
- Poulík, Josef (1975). Mikulčice: Sídlo a pevnost knížat velkomoravských, Praha.
- Štefanovičová, Tatiana (1989). Osudy starých Slovanov, Bratislava: Osveta.
- Wieczorek, Alfried and Hans-Martin Hinz (Hrsg.) (2000). Europas Mitte um 1000, Stuttgart. ISBN 3-8062-1545-6 or ISBN 3-8062-1544-8
External links
|
|
- Articles about Great Moravia and text of many primary sources Template:Cs icon
- Brief overview
- Detailed timeline
- Reconstruction of a Great Moravian settlement Template:Cs icon

