| Revision as of 20:59, 23 September 2008 view sourceNick C (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Rollbackers9,205 editsm Reverted edits by 24.44.121.224 to last version by RFerreira (HG)← Previous edit | Revision as of 21:19, 23 September 2008 view source Atomicdor (talk | contribs)205 edits →HistoryNext edit → | ||
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
| During the early stages of the Scandinavian ], ] in ] and ] on ], in present-day Sweden, were flourishing trade centers. Remains of what is believed to have been a large market have been found in Ystad dating from 600–700 AD.<ref name="Sawyer" /> In Paviken, an important center of trade in the Baltic region during the ninth and tenth century, remains have been found of a large Viking Age harbour with shipbuilding yards and handicraft industries. Between 800 and 1000, trade brought an abundance of silver to Gotland and according to some scholars, the Gotlanders of this era hoarded more silver than the rest of the population of Scandinavia combined.<ref name="Sawyer">Sawyer, Birgit and Peter Sawyer (1993). ''Medieval Scandinavia: from Conversion to Reformation, Circa 800–1500''. University of Minnesota Press, 1993. ISBN 0816617392, pp. 150-153.</ref> | During the early stages of the Scandinavian ], ] in ] and ] on ], in present-day Sweden, were flourishing trade centers. Remains of what is believed to have been a large market have been found in Ystad dating from 600–700 AD.<ref name="Sawyer" /> In Paviken, an important center of trade in the Baltic region during the ninth and tenth century, remains have been found of a large Viking Age harbour with shipbuilding yards and handicraft industries. Between 800 and 1000, trade brought an abundance of silver to Gotland and according to some scholars, the Gotlanders of this era hoarded more silver than the rest of the population of Scandinavia combined.<ref name="Sawyer">Sawyer, Birgit and Peter Sawyer (1993). ''Medieval Scandinavia: from Conversion to Reformation, Circa 800–1500''. University of Minnesota Press, 1993. ISBN 0816617392, pp. 150-153.</ref> | ||
| ] introduced Christianity in 829, but the new religion did not begin to fully replace ] until the twelfth century. During the 11th century, Christianity became the most prevalent religion, and from the year 1050 Sweden is counted as a Christian nation. The period between 1100 and 1400 was characterized by internal power struggles and competition among the Nordic kingdoms. Swedish kings also began to expand the Swedish-controlled territory in ], creating conflicts with the ].<ref>Bagge, Sverre (2005). "The Scandinavian Kingdoms". In ''The New Cambridge Medieval History''. Eds. Rosamond McKitterick et al. Cambridge University Press, 2005. ISBN 052136289X, p. 724: "Swedish expansion in Finland led to conflicts with Rus', which were temporarily brought to an end by a peace treaty in 1323, dividing the Karelian peninsula and the northern areas between the two countries."</ref> | ] introduced Christianity in 829, but the new religion did not begin to fully replace ] until the twelfth century. During the ], Christianity became the most prevalent religion, and from the year 1050 Sweden is counted as a Christian nation. The period between 1100 and 1400 was characterized by internal power struggles and competition among the Nordic kingdoms. Swedish kings also began to expand the Swedish-controlled territory in ], creating conflicts with the ].<ref>Bagge, Sverre (2005). "The Scandinavian Kingdoms". In ''The New Cambridge Medieval History''. Eds. Rosamond McKitterick et al. Cambridge University Press, 2005. ISBN 052136289X, p. 724: "Swedish expansion in Finland led to conflicts with Rus', which were temporarily brought to an end by a peace treaty in 1323, dividing the Karelian peninsula and the northern areas between the two countries."</ref> | ||
| In the 14th century, Sweden was struck by the ] (]). During this period the Swedish cities also began to acquire greater rights and were strongly influenced by German merchants of the ], active especially at ]. In 1319, Sweden and Norway were united under King ] and in 1397 Queen ] effected the personal union of Sweden, Norway, and Denmark through the ]. However, Margaret’s successors, whose rule was also centred in Denmark, were unable to control the Swedish nobility. Real power was held for long periods by regents (notably those of the ] family) chosen by the Swedish parliament. King ], who asserted his claim to Sweden by force of arms, ordered a massacre in 1520 of Swedish nobles at Stockholm. This came to be known as the “]” and stirred the Swedish nobility to new resistance and, on 6 June (now Sweden's national holiday) in 1523, they made ] their king. This is sometimes considered as the ]. Shortly afterwards he rejected ] and led Sweden into the ]. Gustav Vasa is considered to be Sweden's "]". | In the ], Sweden was struck by the ] (]). During this period the Swedish cities also began to acquire greater rights and were strongly influenced by German merchants of the ], active especially at ]. In 1319, Sweden and Norway were united under King ] and in 1397 Queen ] effected the personal union of Sweden, Norway, and Denmark through the ]. However, Margaret’s successors, whose rule was also centred in Denmark, were unable to control the Swedish nobility. Real power was held for long periods by regents (notably those of the ] family) chosen by the Swedish parliament. King ], who asserted his claim to Sweden by force of arms, ordered a massacre in 1520 of Swedish nobles at Stockholm. This came to be known as the “]” and stirred the Swedish nobility to new resistance and, on 6 June (now Sweden's national holiday) in 1523, they made ] their king. This is sometimes considered as the ]. Shortly afterwards he rejected ] and led Sweden into the ]. Gustav Vasa is considered to be Sweden's "]". | ||
| ===Swedish Empire=== | ===Swedish Empire=== | ||
| Line 149: | Line 149: | ||
| ''Britannica Concise'', 2007, webpage: | ''Britannica Concise'', 2007, webpage: | ||
| . | . | ||
| </ref> The 17th century saw Sweden engaged in many |
</ref> The ] saw Sweden engaged in many ]s, for example with the ] with both sides competing for territories of today's ], with the disastrous ] being one of the highlights.<ref></ref> | ||
| This period also saw ]—the Swedish invasion of the ]. After more than half a century of almost constant warfare, the Swedish economy had deteriorated. It would become the lifetime task of Charles' son, ] (1655-1697), to rebuild the economy and refit the army. His legacy to his son, the coming ruler of Sweden ], was one of the finest arsenals in the world, a large standing army and a great fleet. Sweden's largest threat at this time, Russia, had a larger army but was far behind in both equipment and training. | This period also saw ]—the Swedish invasion of the ]. After more than half a century of almost constant warfare, the Swedish economy had deteriorated. It would become the lifetime task of Charles' son, ] (1655-1697), to rebuild the economy and refit the army. His legacy to his son, the coming ruler of Sweden ], was one of the finest arsenals in the world, a large standing army and a great fleet. Sweden's largest threat at this time, Russia, had a larger army but was far behind in both equipment and training. | ||
| Line 158: | Line 158: | ||
| Charles XII attempted to invade Norway 1716; however, he was shot dead at ] in 1718. The Swedes weren't militarily defeated at Fredriksten, but the whole structure and organisation of the Norwegian campaign fell apart with the King's death and the army withdrew. Forced to cede large areas of land in the ] in 1721, Sweden also lost its place as an empire and as the dominant state on the Baltic Sea. With Sweden's lost influence, Russia emerged as an ] and became one of Europe's dominant nations. | Charles XII attempted to invade Norway 1716; however, he was shot dead at ] in 1718. The Swedes weren't militarily defeated at Fredriksten, but the whole structure and organisation of the Norwegian campaign fell apart with the King's death and the army withdrew. Forced to cede large areas of land in the ] in 1721, Sweden also lost its place as an empire and as the dominant state on the Baltic Sea. With Sweden's lost influence, Russia emerged as an ] and became one of Europe's dominant nations. | ||
| In the 18th century, Sweden did not have enough resources to maintain its territories outside Scandinavia and most of them were lost, culminating with the 1809 loss of Finland to Russia which became the semi-autonomous ] in ]. | In the ], Sweden did not have enough resources to maintain its territories outside Scandinavia and most of them were lost, culminating with the 1809 loss of Finland to Russia which became the semi-autonomous ] in ]. | ||
| After Denmark-Norway was defeated in the ], Norway was ceded to the king of Sweden on 14 January 1814 in exchange for northern German provinces, at the ]. The Norwegian attempts to keep their status as a sovereign state were rejected by the Swedish king, ]. He launched a military campaign against Norway on July 27, 1814, ending in the ], which forced Norway into a ] with Sweden under the Swedish crown, which was not dissolved until 1905. The 1814 campaign was the last war in which Sweden participated as a combatant. | After Denmark-Norway was defeated in the ], Norway was ceded to the king of Sweden on 14 January 1814 in exchange for northern German provinces, at the ]. The Norwegian attempts to keep their status as a sovereign state were rejected by the Swedish king, ]. He launched a military campaign against Norway on July 27, 1814, ending in the ], which forced Norway into a ] with Sweden under the Swedish crown, which was not dissolved until 1905. The 1814 campaign was the last war in which Sweden participated as a combatant. | ||
Revision as of 21:19, 23 September 2008
- "Sverige" redirects here. For other uses, see Sweden (disambiguation) and Sverige (disambiguation).
| Kingdom of Sweden Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Motto: (Royal) Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) "For Sweden – In the Time" | |
| Anthem: Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) Thou ancient, thou freeRoyal anthem: Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) The Song of the King | |
 Location of Sweden (orange) Location of Sweden (orange)– in Europe (tan & white) | |
| Capitaland largest city | Stockholm (pop. city 802,611, Metro 2 million) |
| Official languages | None (Swedish de facto) |
| Demonym(s) | Swedish or Swedes |
| Government | Parliamentary democracy and Constitutional monarchy |
| • Monarch | King Carl XVI Gustaf |
| • Prime Minister | Fredrik Reinfeldt |
| • Speaker of the Riksdag | Per Westerberg |
| Consolidation Prehistoric | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 449,964 km (173,732 sq mi) (55th) |
| • Water (%) | 8.7 |
| Population | |
| • 2008 census | 9 223 766 ( Source: www.scb.se) |
| • Density | 20/km (51.8/sq mi) (194th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2007 estimate |
| • Total | $333.1 billion (33rd) |
| • Per capita | $36,900 (25th) |
| GDP (nominal) | 2007 estimate |
| • Total | $455 billion (20th) |
| • Per capita | $49,655 (8th) |
| Gini (2005) | 23 low inequality |
| HDI (2004) | Error: Invalid HDI value (6th) |
| Currency | Swedish krona (SEK) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Calling code | 46 |
| ISO 3166 code | SE |
| Internet TLD | .se |
| |
Sweden, officially the Kingdom of Sweden (Swedish: Konungariket Sverige ), is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden has land borders with Norway and Finland, and is connected to Denmark by the Oresund Bridge. It has been a member of the European Union since January 1, 1995. Its capital and largest city is Stockholm, with a population of 800,000 and metropolitan area of 2 million.
At 449,964 km (173,732 sq mi), Sweden is the largest country by area in Northern Europe and fourth largest in Europe. With a total population of over 9.1 million, Sweden has a low population density of 20 people per km² (52 per sq. mi). About 84% of the population live in urban areas. Sweden emerged out of the Kalmar Union formed in 1397, and by the unification of the country by King Gustav Vasa in the 16th century. In the 17th century the country expanded its territories to form the Swedish empire. Most of the conquered territories outside the Scandinavian Peninsula were lost during the 18th and 19th centuries. The eastern half of Sweden constituted by the eastern half of Norrland and Österland was lost to Russia in 1809. The last war in which Sweden was directly involved was in 1814, when Sweden by military means forced Norway into a personal union with Sweden, a union which lasted until 1905. Since 1814, Sweden has been at peace, adopting a non-aligned foreign policy in peacetime and neutrality in wartime.
Etymology
Main article: Etymology of Sweden
The modern name Sweden is derived through back-formation from Old English Sweoðeod, which meant "people of the Swedes" (Old Norse Svíþjóð, Latin Suetidi). This word is derived from Sweon/Sweonas (Old Norse Sviar, Latin Suiones). The Swedish name Sverige literally means "Realm of the Swedes", excluding the Geats in Götaland.
The etymology of Swedes, and thus Sweden, is generally not agreed upon but suggestively deriving from Proto-Germanic *Swihoniz meaning "one's own", referring to one's own Germanic tribe.
History
Main article: History of SwedenPrehistory
Main article: Prehistoric SwedenSweden's prehistory begins in the Allerød warm period c. 12,000 BC with Late Palaeolithic reindeer-hunting camps of the Bromme culture at the edge of the ice in what is now the country's southernmost province. This period was characterized by small bands of hunter-gatherer-fishers using flint technology.

Farming and animal husbandry, along with monumental burial, polished flint axes and decorated pottery, arrived from the Continent with the Funnel-beaker Culture in c. 4,000 BC. Sweden's southern third was part of the stock-keeping and agricultural Nordic Bronze Age Culture's area, most of it being peripheral to the culture's Danish centre. The period began in c. 1,700 BC with the start of bronze imports from Europe. Copper mining was never tried locally during this period, and Scandinavia has no tin deposits, so all metal had to be imported. It was largely cast into local designs on arrival.
The Nordic Bronze Age was entirely pre-urban, with people living in hamlets and on farmsteads with single-story wooden long-houses.
In the absence of any Roman occupation, Sweden's Iron Age is reckoned up to the introduction of stone architecture and monastic orders about 1100. Much of the period is proto-historical, that is, there are written sources but most are of low credibility. The scraps of written matter are either much later than the period in question, written in distant areas, or, while local and coeval, extremely brief.

The climate took a turn for the worse, forcing farmers to keep cattle indoors over the winters, leading to an annual build-up of manure that could now for the first time be used systematically for soil improvement.
A Roman attempt to move the Imperial border forward from the Rhine to the Elbe was aborted in AD 9 when Germans under Roman-trained leadership defeated the legions of Varus by ambush in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. About this time, there was a major shift in the material culture of Scandinavia, reflecting increased contact with the Romans.
Starting in the 2nd century, much of southern Sweden's agricultural land was parcelled up with low stone walls. They divided the land into permanent infields and meadows for winter fodder on one side of the wall, and wooded outland where the cattle was grazed on the other side. This principle of landscape organization survived into the 19th century. The Roman Period also saw the first large-scale expansion of agricultural settlement up the Baltic coast of the country's northern two thirds.
Sweden enters proto-history with the Germania of Tacitus in AD 98. Whether any of the brief information he reports about this distant barbaric area was well-founded is uncertain, but he does mention tribal names that correspond to the Swedes (Suiones) and the Sami (Fenni) of later centuries. As for literacy in Sweden itself, the runic script was invented among the south Scandinavian elite in the 2nd century, but all that has come down to the present from the Roman Period is curt inscriptions on artefacts, mainly of male names, demonstrating that the people of south Scandinavia spoke Proto-Norse at the time, a language ancestral to Swedish and other North Germanic languages.
Viking and Middle ages

The Swedish Viking Age lasted roughly between the eighth and eleventh centuries. During this period, it is believed that the Swedes expanded from eastern Sweden and incorporated the Geats to the south. While Vikings from what is today Norway, Denmark and the west coast and south of Sweden travelled south and west, Swedish vikings and Gutar travelled east and south, going to Finland, the Baltic countries, Russia, the Mediterranean and further as far as Baghdad. Their routes passed the rivers of Russia down south to Constantinople (Byzantine Empire) (present-day Istanbul, Turkey) on which they did numerous raids. The Byzantine Emperor Theophilos noticed their great skills in war, and invited them to serve as his personal bodyguard, known as the varangian guard. The Swedish vikings (Rus) were the founding fathers of Russia. The adventures of these Swedish Vikings are commemorated on many runestones in Sweden, such as the Greece Runestones and the Varangian Runestones. There was also considerable participation in expeditions westwards, which are commorated on stones such as the England Runestones. The last major Swedish Viking expedition appears to have been the ill-fated expedition of Ingvar the Far-Travelled to Serkland, the region south-east of the Caspian Sea. Its members are commemorated on the Ingvar Runestones, none of which mentions any survivor. What happened to the crew is unknown, but it is believed that they died of sickness.
It is not known when and how the kingdom of Sweden was born, but the list of Swedish monarchs is drawn from the first kings who ruled Svealand (Sweden) and Götaland (Gothia) as one with Erik the Victorious. Sweden and Gothia were two separate nations long before that. It is not known how long they existed, Beowulf described semi-legendary Swedish-Geatish wars in the 6th century.

During the early stages of the Scandinavian Viking Age, Ystad in Scania and Paviken on Gotland, in present-day Sweden, were flourishing trade centers. Remains of what is believed to have been a large market have been found in Ystad dating from 600–700 AD. In Paviken, an important center of trade in the Baltic region during the ninth and tenth century, remains have been found of a large Viking Age harbour with shipbuilding yards and handicraft industries. Between 800 and 1000, trade brought an abundance of silver to Gotland and according to some scholars, the Gotlanders of this era hoarded more silver than the rest of the population of Scandinavia combined.
St. Ansgar introduced Christianity in 829, but the new religion did not begin to fully replace paganism until the twelfth century. During the 11th century, Christianity became the most prevalent religion, and from the year 1050 Sweden is counted as a Christian nation. The period between 1100 and 1400 was characterized by internal power struggles and competition among the Nordic kingdoms. Swedish kings also began to expand the Swedish-controlled territory in Finland, creating conflicts with the Rus.
In the 14th century, Sweden was struck by the Black Death (bubonic plague). During this period the Swedish cities also began to acquire greater rights and were strongly influenced by German merchants of the Hanseatic League, active especially at Visby. In 1319, Sweden and Norway were united under King Magnus Eriksson and in 1397 Queen Margaret I of Denmark effected the personal union of Sweden, Norway, and Denmark through the Kalmar Union. However, Margaret’s successors, whose rule was also centred in Denmark, were unable to control the Swedish nobility. Real power was held for long periods by regents (notably those of the Sture family) chosen by the Swedish parliament. King Christian II of Denmark, who asserted his claim to Sweden by force of arms, ordered a massacre in 1520 of Swedish nobles at Stockholm. This came to be known as the “Stockholm blood bath” and stirred the Swedish nobility to new resistance and, on 6 June (now Sweden's national holiday) in 1523, they made Gustav Vasa their king. This is sometimes considered as the foundation of modern Sweden. Shortly afterwards he rejected Catholicism and led Sweden into the Protestant Reformation. Gustav Vasa is considered to be Sweden's "Father of the Nation".
Swedish Empire

Sweden proper Kexholm County Swedish Ingria Swedish Estonia Livonia Swedish Pomerania, Abp Bremen and Bp Verden Scania, Blekinge, Halland, Gotland and Bohuslän Trøndelag and Møre og Romsdal Jämtland, Härjedalen, Idre & Särna

During the early 1600s, under Gustavus Adolphus greatly thanks to his involvement in the Thirty Years' War from which Sweden emerged as a great power. Sweden reached its largest territorial extent during this time under the rule of Charles X (1622–1660) after the treaty of Roskilde in 1658. The foundation of Sweden's success during this period is credited to Gustav I's major changes on the Swedish economy in the mid-1500s, and his introduction of Protestantism. The 17th century saw Sweden engaged in many wars, for example with the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth with both sides competing for territories of today's Baltic states, with the disastrous Battle of Kircholm being one of the highlights.
This period also saw the Deluge—the Swedish invasion of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After more than half a century of almost constant warfare, the Swedish economy had deteriorated. It would become the lifetime task of Charles' son, Charles XI (1655-1697), to rebuild the economy and refit the army. His legacy to his son, the coming ruler of Sweden Charles XII, was one of the finest arsenals in the world, a large standing army and a great fleet. Sweden's largest threat at this time, Russia, had a larger army but was far behind in both equipment and training.
After the Battle of Narva in 1700, one of the first battles of the Great Northern War, the Russian army was so severely decimated that Sweden had an open chance to invade Russia. However, Charles did not pursue the Russian army—instead turning against Poland-Lithuania and defeating the Polish king Augustus II and his Saxon allies at the Battle of Kliszow in 1702. This gave the Russian Tsar time to rebuild and modernize his army. After the success of invading Poland Charles decided to make an invasion attempt of Russia which ended in a decisive Russian victory at the Battle of Poltava in 1709. After a long march exposed to cossack raids, the Russian Tsar Peter the Great's scorched-earth techniques and the cold Russian climate, the Swedes stood weakened with a shattered morale, and enormously outnumbered against the Russian army at Poltava. The defeat meant the beginning of the end for the Swedish empire.

Charles XII attempted to invade Norway 1716; however, he was shot dead at Fredriksten fortress in 1718. The Swedes weren't militarily defeated at Fredriksten, but the whole structure and organisation of the Norwegian campaign fell apart with the King's death and the army withdrew. Forced to cede large areas of land in the Treaty of Nystad in 1721, Sweden also lost its place as an empire and as the dominant state on the Baltic Sea. With Sweden's lost influence, Russia emerged as an empire and became one of Europe's dominant nations.
In the 18th century, Sweden did not have enough resources to maintain its territories outside Scandinavia and most of them were lost, culminating with the 1809 loss of Finland to Russia which became the semi-autonomous Duchy of Finland in Imperial Russia.
After Denmark-Norway was defeated in the Napoleonic Wars, Norway was ceded to the king of Sweden on 14 January 1814 in exchange for northern German provinces, at the Treaty of Kiel. The Norwegian attempts to keep their status as a sovereign state were rejected by the Swedish king, Charles XIII. He launched a military campaign against Norway on July 27, 1814, ending in the Convention of Moss, which forced Norway into a personal union with Sweden under the Swedish crown, which was not dissolved until 1905. The 1814 campaign was the last war in which Sweden participated as a combatant.
Modern history
The 18th and 19th centuries saw a significant population increase, which the writer Esaias Tegnér in 1833 famously attributed to "the peace, the (smallpox) vaccine, and the potatoes". Between 1750 and 1850, the population in Sweden doubled. According to some scholars, mass emigration to America became the only way to prevent famine and rebellion; over 1 percent of the population emigrated annually during the 1880s. Nevertheless, Sweden remained poor, retaining a nearly entirely agricultural economy even as Denmark and Western European countries began to industrialize. Many looked towards America for a better life during this time. It is believed that between 1850 and 1910 more than one million Swedes moved to the United States. In the early 20th century, more Swedes lived in Chicago than in Gothenburg (Sweden's second largest city). Most Swedish immigrants moved to the Midwestern United States, with a large population in Minnesota. Some Swedes moved to Delaware. Some also moved to Canada and others in smaller numbers to Argentina.
Despite the slow rate of industrialization into the 19th century, many important changes were taking place in the agrarian economy due to innovations and the large population growth. These innovations included government-sponsored programs of enclosure, aggressive exploitation of agricultural lands, and the introduction of new crops such as the potato. Due also to the fact that the Swedish peasantry had never been enserfed as elsewhere in Europe, the Swedish farming culture began to take on a critical role in the Swedish political process, which has continued through modern times with modern Agrarian party (now called the Centre Party). Between 1870 and 1914, Sweden began developing the industrialized economy that exists today.
Strong grassroots movements sprung up in Sweden during the latter half of the nineteenth century (trade unions, temperance groups, and independent religious groups), creating a strong foundation of democratic principles. In 1889 The Swedish Social Democratic Party was founded. These movements precipitated Sweden's migration into a modern parliamentary democracy, achieved by the time of World War I. As the Industrial Revolution progressed during the twentieth century, people gradually began moving into cities to work in factories, and became involved in socialist unions. A socialist revolution was avoided in 1917, following the re-introduction of parliamentarism, and the country was democratized.
World Wars
See also: Sweden during World War II.
Sweden remained officially neutral during World War I and World War II, although its neutrality during World War II has been vigorously debated. Sweden was under German influence for most of the war, as ties to the rest of the world were cut off through blockades. The Swedish government felt that it was in no position to openly contest Germany, and therefore collaborated with Hitler. Swedish volunteers in Nazi SS units were among the first to invade the Soviet Union in Operation Barbarossa. Sweden also supplied steel and machined parts to Germany throughout the war. Toward the end of the war however, when the defeat of Germany seemed imminent, Sweden began to play a role in humanitarian efforts and many refugees, among them many Jews from Nazi-occupied Europe, were saved partly because of the Swedish involvement in rescue missions at the internment camps and partly because Sweden served as a haven for refugees, primarily from the Nordic countries and the Baltic states. Nevertheless, internal and external critics have argued that Sweden could have done more to resist the Nazi war effort, even if risking occupation.
Cold War
See also: Cold War SwedenSweden publicly claimed to be a neutral country and the image was forcefully maintained, but unofficially Sweden's leadership had strong ties with the United States. In the early 1960s Sweden and the United States agreed to deploy nuclear submarines off the Swedish west coast. In the same year Sweden made a defense pact with the United States. Knowledge of this alliance was kept secret from the Swedish public until 1994.
Following the war, Sweden took advantage of an intact industrial base, social stability and its natural resources to expand its industry to supply the rebuilding of Europe. Sweden was part of the Marshall Plan and participated in the Organisation of Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). During most of the post-war era, the country was governed by the Swedish Social Democratic Party (in Swedish: Socialdemokraterna). Social democrats imposed corporatist policies: favoring big capitalist corporations and big unions, especially Swedish Trade Union Confederation, affiliated with Social Democrats. The amount of bureaucrats rose from normal levels in the 1960s to very high levels by 1980s. Sweden was open to trade and pursued internationally competitive manufacturing sector. Growth was good until 1970s.
Sweden, like countries around the globe, entered a period of economic decline and upheaval, following the oil embargoes of 1973-74 and 1978-79. In the 1980s pillars of Swedish industry were massively restructured. Shipbuilding was discontinued, wood pulp was integrated into modernized paper production, the steel industry was concentrated and specialized, and mechanical engineering was robotized.
Between 1970 and 1990 the overall tax burden rose by over ten percentage points and the growth was very low compared to most other countries in Western Europe. The marginal income tax for workers reached over 80%. Eventually government spent over half of the country's gross domestic product. Sweden steadily declined from its perennial top five GDP per capita ranking. Since the late 1970s, Sweden's economic policies were increasingly questioned by economists and Ministry of Finance officials.
Prime Minister Olof Palme was murdered in 1986.
Recent history
See also: Sweden after the Cold WarA bursting real estate bubble caused by inadequate controls on lending combined with an international recession and a policy switch from anti-unemployment policies to anti-inflationary policies resulted in a fiscal crisis in the early 1990s. Sweden's GDP declined by around 5%. In 1992 there was a run on the currency, the central bank briefly jacking up interest to 500% in an unsuccessful effort to defend the currency's fixed exchange rate. Total employment fell by almost 10% during the crisis.The response of the government was to cut spending and institute a multitude of reforms to improve Sweden's competitiveness, among them reducing the welfare state and privatizing public services and goods. Much of the political establishment promoted EU membership, and the Swedish referendum passed by 52-48% in favour of joining the EU on 13 November 1994. Sweden joined the European Union on 1 January 1995, after the collapse of the Soviet Union. During the Cold War, Europe's non-aligned Western countries, except the Republic of Ireland, had considered membership unwise, as the EU predecessor, the European Community, had been strongly associated with NATO countries. Following the end of the Cold War, however, Sweden, Austria and Finland joined, though in Sweden's case without adopting the Euro. Sweden remains non-aligned militarily, although it participates in some joint military exercises with NATO and some other countries, in addition to extensive cooperation with other European countries in the area of defence technology and defence industry. Among others, Swedish companies export weapons that are used by the American military in Iraq. Sweden also has a long history of participating in international military operations, including most recently, Afghanistan, where Swedish troops are under NATO command, and in EU sponsored peacekeeping operations in UN protectorate Kosovo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Cyprus. Foreign minister Anna Lindh was murdered in 2003.
Geography and climate
Main article: Geography of Sweden

Situated in Northern Europe, Sweden lies west of the Baltic Sea and Gulf of Bothnia, providing a long coastline, and forms the eastern part of the Scandinavian Peninsula. To the west is the Scandinavian mountain chain (Skanderna), a range that separates Sweden from Norway.
Sweden is surrounded by Norway (west), Finland (northeast), the Skagerrak, Kattegat and Öresund straits (southwest) and the Baltic Sea (east). It has maritime borders with Denmark, Germany, Poland, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia, and it is also linked to Denmark (southwest) by the Öresund Bridge. At 449,964 km (173,732 sq mi), Sweden is the 55th largest country in the world. It is the 5th largest in Europe, and the largest in Northern Europe. The land area is slightly larger than the U.S. state of California, or equal to Uzbekistan with a population in 2006 of 9.1 million people.
The lowest elevation in Sweden is in the bay of Lake Hammarsjön, near Kristianstad at −2.41 m (−7.91 ft) below sea level. The highest point is Kebnekaise at 2,111 m (6,926 ft) above sea level.
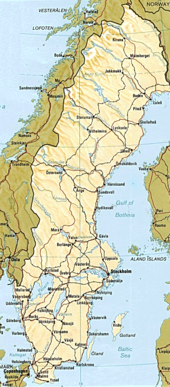
Sweden has 25 provinces or landskap (landscapes), based on culture, geography and history; Bohuslän, Blekinge, Dalarna, Dalsland, Gotland, Gästrikland, Halland, Hälsingland, Härjedalen, Jämtland, Lapland, Medelpad, Norrbotten, Närke, Skåne, Småland, Södermanland, Uppland, Värmland, Västmanland, Västerbotten, Västergötland, Ångermanland, Öland and Östergötland.

While these provinces serve no political or administrative purpose, they play an important role for people's self-identification. The provinces are usually grouped together in three large lands, parts, the northern Norrland, the central Svealand and southern Götaland. The scarcely populated Norrland encompasses almost 60% of the country.
About 15% of Sweden lies north of the Arctic Circle. Southern Sweden is predominantly agricultural, with increasing forest coverage northward. The highest population density is in the Öresund region in southern Sweden, and in the valley of lake Mälaren near to Stockholm. Gotland and Öland are Sweden's largest islands; Vänern and Vättern are Sweden's largest lakes. The lake Vänern is the largest lake in Northern Europe and the third largest in all Europe, after Lake Ladoga and Lake Onega in Russia.
Climate
Sweden has a temperate climate despite its northern latitude with four distinct seasons and mild temperatures both in winter and summer. Sweden is much warmer than other places in the same latitude, mainly because of the Gulf Stream. In the mountains of northern Sweden a sub-Arctic climate predominates. North of the Arctic Circle, the sun never sets for part of each summer, and in the winter, night is similarly unending. In the rest of the country, days are very long during the summer, but short daylight during winter. Stockholm's daylight extends 18 hours in late june, but only 6 hours in late december.
In southern and central Sweden, summers are warm and pleasant, while the north experiences cooler temperatures. Occasional heatwaves and temperatures of around 25 - 30°C (77 - 86°F) occurs on many days during the summer, possibly even a few times in the north. During winter, temperatures are around freezing point in south, slightly below freezing in the central regions, and very cold, snowy and below freezing for around 6 months in the extreme north.
Yearly average precipitation in most of the country is between 500 and 800 millimeter per year. In some parts though the average is between 1000 and 1700 millimeters. Thunderstorms account for most of the precipitation in the summer. Snowfall usually occurs between November and April, but in northern regions, snow could fall from September to May and stay on the ground for almost 6 months.
| Average high and low temperatures in various cities in Sweden (°C) | ||||||||||||
| City | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kiruna (north) | -10/-19 | -8/-18 | -4/-14 | 1/-8 | 7/-1 | 14/5 | 17/7 | 14/6 | 8/1 | 2/-5 | -5/-12 | -8/-17 |
| Östersund (central) | -6/-12 | -4/-11 | -2/-7 | 4/-3 | 12/3 | 17/7 | 18/9 | 16/8 | 11/5 | 6/1 | 2/-5 | -3/-9 |
| Stockholm (central) | -1/-5 | -1/-5 | 3/-3 | 8/1 | 16/6 | 21/11 | 22/13 | 20/12 | 15/9 | 9/5 | 4/1 | 1/-3 |
| Gothenburg (south) | 1/-3 | 2/-4 | 5/-1 | 9/2 | 16/7 | 19/11 | 20/13 | 20/12 | 16/9 | 11/6 | 6/2 | 3/-2 |
| Visby (south) | 1/-3 | 1/-3 | 3/-2 | 7/1 | 14/6 | 18/11 | 20/13 | 19/13 | 15/10 | 11/6 | 6/2 | 3/-1 |
| Malmö (south) | 3/-1 | 2/-2 | 5/0 | 9/2 | 16/7 | 19/11 | 21/13 | 21/12 | 16/10 | 12/7 | 7/3 | 4/2
|
Administration and politics
Main article: Politics of SwedenSweden is a constitutional monarchy, in which King Carl XVI Gustaf is head of state, but royal power has long been limited to official and ceremonial functions. The Economist Intelligence Unit, while acknowledging that democracy is difficult to measure, listed Sweden in first place in its index of democracy assessing 167 countries. The nation's legislative body is the Riksdag (Swedish Parliament), with 349 members, which chooses the Prime Minister. Parliamentary elections are held every four years, on the third Sunday of September.
Counties and municipalities
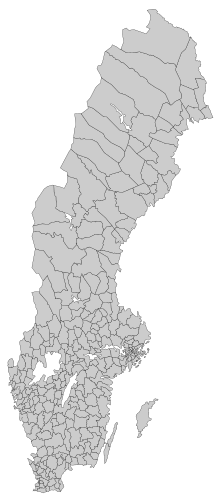
Sweden is a unitary state, currently divided into twenty-one counties ( Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)). Each county has a County Administrative Board or länsstyrelse, which is appointed by the government (the first Swedish County Administrative Board was made up by the Swedish Prime Minister Axel Oxenstierna in 1634). In each county there is also a separate County Council or landsting, which is elected directly by the people.
Each county further divides into a number of municipalities or kommuner, with a total of 290 municipalities in 2004. Municipal government in Sweden is similar to city commission government and cabinet-style council government. A legislative municipal assembly (kommunfullmäktige) of between 31 and 101 members (always an uneven number) is elected from party-list proportional representation at municipal elections, held every four years in conjunction with the national parliamentary elections.
The municipalities are also divided into a total of 2,512 parishes, or församlingar (2000). These have traditionally been a subdivision of the Church of Sweden, but still have importance as districts for census and elections.
There are also older historical divisions, primarily the twenty-five provinces and three lands, which still retain cultural significance. The Swedish government is investigating the possibilities of merging the current 21 counties into circa 9 larger regions along the lines of the current riksområden used for statistical purposes. If approved, these would come into effect around 2015.
Further information: Subdivisions of SwedenPolitical history

The actual age of the kingdom of Sweden is unknown. It depends mostly on whether Sweden should be considered a nation when the Svear (Swedes) ruled Svealand or if the emergence of the nation started with the Svear and the Götar (Geats) of Götaland being united under one ruler. In the first case, Sweden was first mentioned to have one single ruler in the year 98 by Tacitus, but it is almost impossible to know for how long it had been this way. However, historians usually start the line of Swedish monarchs from when Svealand and Götaland were ruled under the same king, namely Erik the Victorious and his son Olof Skötkonung in the 10th century. These events are often described as the consolidation of Sweden, although substantial areas were conquered and incorporated later.
Earlier kings, for which no reliable historical sources exist, can be read about in mythical kings of Sweden and semi-legendary kings of Sweden. Many of these kings are only mentioned in various saga and blend with Norse mythology.
The title Sveriges och Götes Konung was last used for Gustaf I of Sweden, after which the title became "King of Sweden, of the Goths and of the Wends" (Sveriges, Götes och Vendes Konung) in official documentation. Up until the beginning of the 1920s, all laws in Sweden were introduced with the words, "We, the king of Sweden, of the Goths and Wends". This title was used up until 1973. The present King of Sweden, Carl XVI Gustaf, was the first monarch officially proclaimed "King of Sweden" (Sveriges Konung) with no additional peoples mentioned in his title.
The term Riksdag was used for the first time in the 1540s, although the first meeting where representatives of different social groups were called to discuss and determine affairs affecting the country as a whole took place as early as 1435, in the town of Arboga. During the assemblies of 1527 and 1544, under King Gustav Vasa, representatives of all four estates of the realm (clergy, nobility, townsmen and peasants) were called on to participate for the first time. The monarchy became hereditary in 1544.
Executive power was historically shared between the King and a noble Privy Council until 1680, followed by the King's autocratic rule initiated by the common estates of the Parliament. As a reaction to the failed Great Northern War, a parliamentary system was introduced in 1719, followed by three different flavours of constitutional monarchy in 1772, 1789 and 1809, the latter granting several civil liberties. The monarch remains as the formal, but merely symbolic, head of state with ceremonial duties.
The Riksdag of the Estates consisted of two chambers. In 1866 Sweden became a constitutional monarchy with a bicameral parliament, with the First Chamber indirectly elected by local governments, and the Second Chamber directly elected in national elections every four years. In 1971 the Riksdag became unicameral. Legislative power was (symbolically) shared between king and parliament until 1975. Swedish taxation is controlled by the Riksdag (parliament).
Modern political system

Constitutionally, the 349-member Riksdag (Parliament) holds supreme authority in modern Sweden. The Riksdag is responsible for choosing the prime minister, who then appoints the government (the ministers). The legislative power is then shared between the parliament and the Prime Minister led government. The executive power is exercised by the government, while the judiciary is independent. Sweden lacks compulsory judicial review, although the non-compulsory review carried out by lagrådet (Law Council) is mostly respected in technical matters but less so in controversial political matters. Acts of the parliament and government decrees can be made inapplicable at every level if they are manifestly against constitutional laws. However, due to the restrictions in this form of judicial review and a weak judiciary, this has had little practical consequence.
Legislation may be initiated by the cabinet or by members of Parliament. Members are elected on the basis of proportional representation for a four-year term. The Constitution of Sweden can be altered by the Riksdag, which requires a simple but absolute majority and two decisions with general elections in between. Sweden has three other constitutional laws: the Act of Royal Succession, the Freedom of Press Act and the Fundamental Law on Freedom of Expression.

The Swedish Social Democratic Party has played a leading political role since 1917, after Reformists had confirmed their strength and the revolutionaries left the party. After 1932, the cabinets have been dominated by the Social Democrats. Only four general elections (1976, 1979, 1991 and 2006) have given the centre-right bloc enough seats in Parliament to form a government. However, poor economic performance since the beginning of the 1970s, and especially the crisis at the beginning of the 1990s, have forced Sweden to reform its political system to become more like other European countries. In the 2006 general election the Moderate Party, allied with the Centre Party, Liberal People's Party, and the Christian Democrats, with a common political platform, won a majority of the votes. Together they have formed a majority government under the leadership of the Moderate party's leader Fredrik Reinfeldt. The next elections will be held in September 2010
Election turnout in Sweden has always been high by international comparison, although it has declined in recent decades, and is currently around 80% (80.11 in general election of 2002, 81.99 in general election of 2006). Swedish politicians enjoyed a high degree of confidence from the citizens in the 1960s but it has since declined steadily and has a markedly lower level of trust than its Scandinavian neighbours.
Some Swedish political figures that have become known worldwide include Raoul Wallenberg, Folke Bernadotte, former Secretary General of the United Nations Dag Hammarskjöld, former Prime Minister Olof Palme, former Prime Minister and Foreign minister Carl Bildt, former President of the General Assembly of the United Nations Jan Eliasson, and former International Atomic Energy Agency Iraq inspector Hans Blix.
Political movements
Sweden has a history of strong political involvement by ordinary people through its "popular movements" (Folkrörelser), the most notable being trade unions, the independent Christian movement, the temperance movement, the women's movement and—more recently—the sports movement.
Sweden is currently leading the EU in statistics measuring equality in the political system and equality in the education system. Gudrun Schyman founded the first Swedish feminist party, the Feminist Initiative party, commonly referred to simply as F!, in 2005. Ms. magazine quoted Schyman's view of Sweden's reputation for progressive initiatives: "In Sweden there’s a gap between words and reality.... Internationally a lot of people look upon Sweden as equality paradise, but that is not the truth – and now things are actually going backwards." In fact the pay gap between men and women in Sweden is 16%; a bit higher than the EU average of 15%. Sweden compares unfavourably with the EU average when it comes to providing full-time jobs for women, with a high fraction of employed women working part-time.
Law, law enforcement and judicial system

The Supreme Court of Sweden is the third and final instance in all civil and criminal cases in Sweden. Before a case can be decided by the Supreme Court, leave to appeal must be obtained, and with few exceptions, leave to appeal can be granted only when the case is of interest as a precedent. The Supreme Court consists of 16 Councillors of Justice or justitieråd which are appointed by the government, but the court as an institution is independent of the Riksdag, and the government is not able to interfere with the decisions of the court.
Law enforcement in Sweden is carried out by several government entities. The Swedish Police Service is a Government agency concerned with police matters. The National Task Force is a national SWAT unit within the National Criminal Investigation Department. Swedish Security Service's responsibilities are counter-espionage, anti-terrorist activities, protection of the constitution and protection of sensitive objects and people.
According to a victimization survey of 1,201 residents in 2005, Sweden has above average crime rates compared to other EU countries. Sweden has high or above average levels of assaults, sexual assaults, hate crimes, and consumer fraud. Sweden has low levels of burglary, car theft and drug problems. Bribe seeking is rare.
Foreign policy
Throughout the twentieth century, Swedish foreign policy was based on the principle of non-alignment in peacetime and neutrality in wartime. "Sweden's government was left to pursue an independent course based on a foreign policy defined as nonalignment in times of peace so that neutrality would be possible in the event of war."
Sweden's doctrine of neutrality is often traced back to the 19th century as the country has not participated in any war since the end of the Swedish campaign against Norway in 1814. During World War II Sweden joined neither the allied nor axis powers. This has been disputed by many since in effect Sweden allowed the Nazi regime to use its railroad system to transport troops and goods, especially iron ore from the rich mines in northern Sweden, which was vital to the German war machine.
During the early Cold War era, Sweden combined its policy of non-alignment with a low profile in international affairs, although it also pursued a security policy based on strong national defence to deter attack. At the same time, the country maintained relatively close informal connections with the Western bloc, especially in the realm of intelligence exchange. In 1952, a Swedish DC-3 was shot down over the Baltic Sea by a Soviet MiG-15 jet fighter. Later investigations revealed that the plane was actually gathering information for NATO. Another plane, a Catalina search and rescue plane, was sent out a few days later and shot down by the Soviets as well. Olof Palme, the former prime minister of Sweden, visited Cuba during the 1970s and showed his support for Cuba in his speech.
Beginning in the late 1960s, Sweden for a period attempted to play a more significant and independent role in international relations. This involved significant activity in international peace efforts, especially through the United Nations, and in support to the Third World. Since the murder of Olof Palme in 1986 and the end of the Cold War, this has been significantly toned down, although Sweden remains comparatively active in peace keeping missions and maintains a generous foreign aid budget.
In 1981 a Soviet Whiskey class submarine ran aground close to the Swedish naval base at Karlskrona in the southern part of the country. It has never been clearly established whether the submarine ended up on the shoals through a navigational mistake or if it was a matter of espionage against Swedish military potential. The incident triggered a diplomatic crisis between Sweden and the Soviet Union.
Since 1995 Sweden has been a member of the European Union, and as a consequence of a new world security situation the country's foreign policy doctrine has been partly modified, with Sweden playing a more active role in European security co-operation.
Military

The Försvarsmakt (Swedish Armed Forces) is a government agency reporting to the Swedish Ministry of Defence and responsible for the peacetime operation of the armed forces of Sweden. The primary task of the agency is to train and deploy peace support forces abroad, while maintaining the long-term ability to refocus on the defence of Sweden in the event of war. The armed forces are divided into Army, Air Force and Navy. The head of the armed forces is the Supreme Commander of the Swedish Armed Forces (Överbefälhavaren, ÖB), after the sovereign the most senior officer in the country.
Until the end of the Cold War, nearly all males reaching the age of military service were conscripted. In recent years, the number of conscripted males has shrunk dramatically, while the number of female volunteers has increased slightly. Recruitment has generally shifted towards finding the most motivated recruits, rather than solely those otherwise most fit for service. All soldiers serving abroad must by law be volunteers. In 1975 the total number of conscripts was 45,000. By 2003 it was down to 15,000. After the Defence Proposition of 2004, the number of troops in training will decrease even more to between 5,000 and 10,000 each year. The need to recruit only the soldiers later prepared to volunteer for international service will be emphasized. The total forces gathered would consist of about 60,000 men. This could be compared with the 80s before the fall of the Soviet Union, when Sweden could gather up to 1,000,000 men.
Swedish units have taken part in peacekeeping operations in the Democratic Republic of Congo, Cyprus, Bosnia, Kosovo, Liberia, Lebanon and Afghanistan.
Currently, one of the most important tasks for the Swedish Armed Forces is to form a Swedish-led EU Battle Group to which Norway, Finland, Ireland and Estonia will also contribute. The Nordic Battle Group (NBG) is to have a 10-day deployment readiness during the first half of 2008 and, although Swedish led, will have its Operational Headquarters (OHQ) in Northwood, outside London.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Sweden

Sweden is an export-oriented market economy featuring a modern distribution system, excellent internal and external communications, and a skilled labour force. Timber, hydropower, and iron ore constitute the resource base of an economy heavily oriented toward foreign trade. Sweden's engineering sector accounts for 50% of output and exports. Telecommunications, the automotive industry and the pharmaceutical industries are also of great importance. Agriculture accounts for 2 percent of GDP and employment.
The 20 largest (by turnover in 2007) companies registered in Sweden are Volvo, Ericsson, Vattenfall, Skanska, Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications AB, Svenska Cellulosa Aktiebolaget, Electrolux, Volvo Personvagnar, TeliaSonera, Sandvik, Scania, ICA, Hennes & Mauritz, Nordea, Preem, Atlas Copco, Securitas, Nordstjernan, and SKF. Sweden's industry is overwhelmingly in private control; unlike some other industrialized Western countries, such as Austria and Italy, publicly owned enterprises were always of minor importance.
Some 4.5 million residents are working, out of which around a third with tertiary education. GDP per hour worked is the world's 9th highest at 31 USD in 2006, compared to 22 USD in Spain and 35 USD in United States. According to OECD, deregulation, globalization, and technology sector growth have been key productivity drivers. GDP per hour worked is growing 2½ per cent a year for the economy as a whole and trade-terms-balanced productivity growth 2%. Sweden is a world leader in privatized pensions and pension funding problems are relatively small compared to many other Western European countries. Swedish labor market has become more flexible, but it still has some widely acknowledged problems. The typical worker receives only 40% of his income after the tax wedge. The slowly declining overall taxation, 51.1% of GDP in 2007, is still nearly double of that in the United States or Ireland. State and municipal bureaucrats amount to a third of Swedish workforce, multiple times the proportion in many other countries. Overall, GDP growth has been fast since reforms in the early 1990s, especially in manufacturing.
World Economic Forum 2008 competitiveness index ranks Sweden 4th most competitive, behind Denmark. The Index of Economic Freedom 2008 ranks Sweden the 27th most free out of 162 countries, or 14th out of 41 European countries. Sweden ranked 9th in the IMD Competitiveness Yearbook 2008, scoring high in private sector efficiency. According to the book, The Flight of the Creative Class, by the U.S. economist, Professor Richard Florida of the University of Toronto, Sweden is ranked as having the best creativity in Europe for business and is predicted to become a talent magnet for the world’s most purposeful workers. The book compiled an index to measure the kind of creativity it claims is most useful to business — talent, technology and tolerance.
Swedes have rejected euro in a popular vote and Sweden maintains its own currency, the Swedish krona (SEK). The Swedish Riksbank—founded in 1668 and thus making it the oldest central bank in the world — is currently focusing on price stability with its inflation target of 2%. According to Economic Survey of Sweden 2007 by OECD, the average inflation in Sweden has been one of the lowest among European countries since the mid-1990s, largely because of deregulation and quick utilization of globalization.
The largest trade flows are with Germany, United States, Norway, United Kingdom, Denmark, and Finland.
Infrastructure
Main article: Transport in Sweden See also: Nordic energy market, Nuclear power phase-out in Sweden, and Oil phase-out in SwedenSweden's energy market is largely privatized. Nordic energy market is one of the first liberalized energy markets in Europe and it's traded in Nord Pool. In 2006, out of a total electricity production of 139 TWh, electricity from hydropower accounted for 61 TWh (44%), and nuclear power delivered 65 TWh (47%). At the same time, the use of biofuels, peat etc. produced 13 TWh (9%) of electricity, while wind power produced 1 TWh (1%). Sweden was a net importer of electricity by a margin of 6 TWh. Biomass is mainly used to produce heat for district heating and central heating and industry processes.
The 1973 oil crisis strengthened Sweden's commitment to decrease dependence on imported fossil fuels. Since then, electricity has been generated mostly from hydropower and nuclear power. The use of nuclear power has been limited, however. Among other things, the accident of Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station (USA) prompted the Swedish parliament to ban new nuclear plants. In March 2005, an opinion poll showed that 83% supported maintaining or increasing nuclear power. Politicians have made announcements about oil phase-out in Sweden, decrease of nuclear power, and multi-billion dollar investments in renewable energy and energy efficiency. The country has for many years pursued a strategy of indirect taxation as an instrument of environmental policy, including energy taxes in general and carbon dioxide taxes in particular.

Sweden has 162,707 km paved road and 1,428 km of expressways. Motorways run through Sweden, Denmark and over the Öresund Bridge to Stockholm, Gothenburg, Uppsala and Uddevalla. The system of motorways is still under construction and a new motorway from Uppsala to Gävle was finished on October 17, 2007. Sweden had left-hand traffic (Vänstertrafik in Swedish) from approximately 1736 and continued to do so well into the 20th century. Voters rejected right-hand traffic in 1955, but after the Riksdag passed legislation in 1963 changeover took place in 1967, known in Swedish as Dagen H.
The rail transport market is privatized, but while there many privately-owned enterprises, many operators are still owned by state or municipalities. Operators include SJ, Veolia Transportation, Connex, Green Cargo, Tågkompaniet, Inlandsbanan, and a number of regional companies. Most of the railways are owned and operated by Banverket.
The largest airports include Stockholm-Arlanda Airport (17.91 million passengers in 2007), Gothenburg-Landvetter Airport (4.3 million passengers in 2006), and Stockholm-Skavsta Airport (2.0 million passengers). Sweden hosts the two largest port companies in Scandinavia, Port of Göteborg AB (Gothenburg) and the transnational Copenhagen Malmö Port AB.
Public policy
See also: Nordic model and Swedish welfareSweden has always provided solid support for free trade (except agriculture), free immigration, and strong property rights. After World War II a succession of governments increased the welfare state and the tax burden, and Sweden's GDP per capita ranking fell from the 4th to 14th place in a few decades.
Sweden started to move away from this model in the 1980s, and according to OECD and McKinsey, Sweden has recently been relatively fast in liberalization compared to countries such as France. Deregulation-induced competition helped Sweden to halt the economic decline and restore strong growth rates in the 2000s. The current Swedish government is continuing the trend to pursue moderate reforms. Growth has been higher than in many other EU-15 countries.
Since the late 1960s, Sweden had the highest tax quota (as percentage of GDP) in the industrialized world, although today the gap has narrowed and Denmark has surpassed Sweden as the most heavily taxed country among developed countries. Sweden has a two step progressive tax scale with a municipal income tax of about 30% and an additional high-income state tax of 20–25% when a salary exceeds roughly 320,000 SEK per year. The employing company pays an additional 32% of an "employer's fee." In addition, a national VAT of 25% is added to many things bought by private citizens, with the exception of food (12% VAT), transportation, and books (6% VAT). Certain items are subject to additional taxes, e.g. electricity, petrol/diesel and alcoholic beverages. As of 2007, total tax revenue was 47.8% of GDP, the second highest tax burden among developed countries, down from 49.1% 2006. Inverted tax wedge - the amount going to the service worker's wallet - is approximately 15% compared to 10% in Belgium, 30% in Ireland and 50% in United States. Public sector spending amounts to 53% of the GDP. State and municipal employees total around a third of the workforce, much more than in most Western countries. Only Denmark has a larger bureaucracy (38% of Danish workforce). Spending on transfers is also high.
Eighty percent of the workforce is organized through the trade-unions which have the right to elect two representatives to the board in all Swedish companies with more than 25 employees. Sweden has by far the highest amount of sick leaves per worker: average worker loses 24 days due to sickness. Swedish unemployment figures are contested in politics. Unemployment is higher amongst younger people. Because of the contradiction—unemployment despite a growing commercial enterprise economy—politicians and analysts often speak of the "jobless growth". According to Eurostat the unemployment rate in February 2007 was at 6.7% down from 7.4% from February 2006. No new net jobs have been produced in the Swedish private sector since 1950. None of top 50 companies on the Stockholm stock exchange has been started since 1970.
Education
Main article: Education in SwedenAll young children from 1-5 years old are guaranteed a place in public day-care facility (förskola or dagis). Between ages 6-16, children attend compulsory comprehensive school. Swedish 15-years-old pupils have the 22nd highest average score in the PISA assessments, being neither significantly higher nor lower than the OECD average.

After completing the ninth grade, 90% continue with a three-year upper secondary school (gymnasium) leading sometimes to a vocational diploma and always to qualifications for further studies at a university or university college (högskola). However, to be eligible to apply to most of the more demanding degrees at the universities you need to have a final grade from the theoretical programmes of the gymnasium. Both upper secondary school and university studies are financed by taxes. Some Swedes go straight to work after secondary school.

There are universities and university colleges in Sweden. Only a few countries like Canada, United States, and Japan have higher levels of tertiary degree holders. Along with several other European countries, the government also subsidizes tuition of international students pursuing a degree at Swedish institutions, although there has been talk of this being changed.
Uniquely, Sweden is known for being a leader in free-market revolution. While most pre-tertiary students are still enrolled in municipality-managed schools, Sweden introduced education vouchers in 1992, one of the first in the world after Netherlands. Anyone can establish a for-profit school and the municipality must pay new schools the same amount as municipal schools get. For instance, the biggest school chain, Kunskapsskolan, offers 30 schools and a web-based environment, teaches nearly 10,000 pupils, and makes decent profit. Over 10% of pupils were enrolled in private schools in 2008 and numbers are growing fast.
Demographics

As of April 2007, the total population of Sweden was estimated to be 9,131,425. The population exceeded 9,000,000 for the first time as of approximately 12 August 2004 according to Statistics Sweden. Of the 2007 population approximately 16.7% (1.53 million) had at least one parent born abroad or were themselves born abroad. This reflects the inter-Nordic migrations, earlier periods of labour immigration, and later decades of refugee and family immigration. Sweden has been transformed from a nation of emigration ending after World War I to a nation of immigration from World War II onwards. In 2006, immigration to Sweden reached its highest level since records began.

The largest immigrant group living in Sweden as of 2005 consists of people born in Finland, followed by people born in Iraq, Former Yugoslavia, Germany, Denmark, Norway, Turkey, Poland, Russia and Iran.
Today, Sweden has one of the largest exile communities of Assyrian and Syriac Christians (also known as Chaldeans).
Immigration from the other Nordic countries reached a peak of more than 40,000 per year in 1969-70 when the new immigration rules introduced in 1967 had made it more difficult for immigrants from outside the Nordic region to settle in Sweden for labour market policy reasons. Immigration by refugees and immigrating relatives of refugees from outside the Nordic region increased drastically during the late 1980s, with many of the immigrants arriving from Asia and America, especially from Iran and Chile. During the 1990s and onwards another large immigrant group came from former Yugoslavia and the Middle East.
Language
The primary language of Sweden is Swedish, a North Germanic language, related and very similar to Danish and Norwegian, but differing in pronunciation and orthography. Norwegians have little difficulty understanding Swedish, and Danes can also understand it, with slightly more difficulty than the Norwegians. Although Swedish is the dominant language, it is not an official language. Sweden Finns are Sweden's largest linguistic minority, comprising about 3 percent of Sweden's population and Finnish is recognised as a minority language. Four other minority languages are also recognised (Meänkieli, Sami, Romani and Yiddish). The issue of whether Swedish should be declared the official language has been raised and the parliament voted on the matter in 2005 but the proposal narrowly failed.
In varying degrees, depending largely on frequency of interaction with English, a majority of Swedes, especially those born after World War II, understand and speak English thanks to trade links, the popularity of overseas travel, a strong Anglo-American influence and the tradition of subtitling rather than dubbing foreign television shows and films. English became a compulsory subject for secondary school students studying natural sciences as early as 1849, and has been a compulsory subject for all Swedish students since the late 1940s. Depending on the local school authorities, English is currently a compulsory subject between first grade and ninth grade, with all students continuing in secondary school studying English for at least another year. Most students also study one and sometimes two additional languages. These include (but are not limited to) German, French and Spanish. Some Danish and Norwegian is at times also taught as part of the Swedish course for native speakers.
Religion
Main article: Religion in Sweden
Before the eleventh century, Swedes adhered to Norse paganism, worshiping Æsir gods, with its centre at the Temple in Uppsala. With Christianization in the 11th century, the laws of the country were changed, forbidding worship of other deities into the late nineteenth century.
After the Protestant Reformation in the 1530s, a change significantly affected by Martin Luther's Swedish associate Olaus Petri, the Church and state were separated and the authority of Roman Catholic bishops abolished, allowing Lutheranism to prevail. This process was completed by the Uppsala Synod of 1593. During the era following the Reformation, usually known as the period of Lutheran Orthodoxy, small groups of non-Lutherans, especially Calvinist Dutchmen, the Moravian Church and Walloons or French Huguenots from Belgium, played a significant role in trade and industry, and were quietly tolerated as long as they kept a low religious profile. The Sami originally had their own shamanistic religion, but they were converted to Lutheranism by Swedish missionaries in the 17th and 18th centuries.

Not until liberalization in the late 18th century, however, were believers of other faiths, including Judaism and Roman Catholicism, allowed to openly live and work in Sweden, and it remained illegal until 1860 for Lutheran Swedes to convert to another religion. The 19th century saw the arrival of various evangelical free churches, and, towards the end of the century secularism, leading many to distance themselves from Church rituals. Leaving the Church of Sweden became legal with the so-called dissenter law of 1860, but only under the provision of entering another denomination. The right to stand outside any religious denomination was established in the Law on Freedom of Religion in 1951.
Today about 75% of Swedes belong to the Church of Sweden (Lutheran), but the number is decreasing by about 1% every year, and Church of Sweden services are sparsely attended (hovering in the single digit percentages of the population). The reason for the large number of inactive members is partly that until 1996, children became members automatically at birth if at least one of the parents was a member. Since 1996, all children that are christened become members. Some 275,000 Swedes are today members of various free churches (where congregation attendance is much higher), and, in addition, immigration has meant that there are now some 92,000 Roman Catholics and 100,000 Eastern Orthodox Christians living in Sweden. Because of immigration, Sweden also has a significant Muslim population. Almost half a million are Muslims by tradition, but approximately 5% (25,000) of these are practising Islam (in the sense of attending Friday prayer and praying five times a day). (See Islam in Sweden.)
Health
See also: Healthcare in Sweden and Swedish National Board of Health and WelfareHealthcare in Sweden is similar in quality to other developed nations. Sweden ranks in the top five countries with respect to low infant mortality. It also ranks high in life expectancy and in safe drinking water. A person seeking care first contacts a clinic for a doctor's appointment, and may then be referred to a specialist by the clinic physician, who may in turn recommend either in-patient or out-patient treatment, or an elective care option. The health care is governed by the 21 landsting of Sweden and is mainly funded by taxes, with nominal fees for patients. One major criticism leveled at Swedish health care are long waiting times before treatment.
Culture

Sweden has many authors of worldwide recognition including August Strindberg, Astrid Lindgren, and Nobel Prize winners Selma Lagerlöf and Harry Martinson. In total seven Nobel Prizes in Literature have been awarded to Swedes. The nation's most well-known artists are painters such as Carl Larsson and Anders Zorn, and the sculptors Tobias Sergel and Carl Milles.
Swedish twentieth-century culture is noted by pioneering works in the early days of cinema, with Mauritz Stiller and Victor Sjöström. In the 1920s–1980s, the filmmaker Ingmar Bergman and actors Greta Garbo and Ingrid Bergman became internationally noted people within cinema. More recently, the films of Lukas Moodysson and Lasse Hallström have received international recognition.
Throughout the 1960s and 1970s Sweden was seen as an international leader in what is now referred to as the "sexual revolution", with gender equality having particularly been promoted. At the present time, the number of single people is one of the highest in the world. The early Swedish film I Am Curious (Yellow) (1967) reflected a liberal view of sexuality, including scenes of love making that caught international attention, and introduced the concept of the "Swedish sin". Sweden has also become, in recent decades, fairly liberal regarding homosexuality, as is reflected in the popular acceptance of films such as Show Me Love, which is about two young lesbians in the small Swedish town of Åmål. In the absence of legislation on same-sex marriages, Sweden offers both registered partnerships and domestic partnerships for same-sex couples. Cohabitation (sammanboende) by couples of all ages, including teenagers as well as elderly couples, is widespread although in recent years it has become administratively problematical with regard to proof in claims of "spousal" social security. Recently, Sweden is experiencing a baby boom.
Music

Sweden has a rich musical tradition, ranging from medieval folk ballads to hip hop music. The music of the pre-Christian Norse has been lost to history, although historical re-creations have been attempted based on instruments found in Viking sites. Instruments used were the lur (a sort of trumpet), simple string instruments, wooden flutes and drums. It is possible that the Viking musical legacy lives on in some of the old Swedish folk music.
Sweden has a significant folk-music scene, both in the traditional style as well as more modern interpretations which often mix in elements of rock and jazz. Väsen is more of a traditionalist group, using a unique traditional Swedish instrument called the nyckelharpa while Garmarna, Nordman, and Hedningarna have more modern elements. There is also Saami music, called the joik, which is actually a type of chant which is part of the traditional Saami animistic spirituality but has gained recognition in the international world of folk music as well. Sweden has a major market for new age and ecologically or environmentally aware music, as well a large portion of pop and rock music have liberal and left-wing political messages.
Sweden also has a prominent choral music tradition, deriving in part from the cultural importance of Swedish folk songs. In fact, out of a population of 9.1 million, it is estimated that five to six hundred thousand people sing in choirs.

Sweden is the third largest music exporter in the world, with over 800 million dollars in revenue last year, surpassed only by the US and the UK. ABBA was one of the first internationally well-known popular music bands from Sweden, and still ranks among the most prominent bands in the world, with about 370 million records sold. With ABBA, Sweden entered into a new era, in which Swedish pop music gained international prominence. There have been many other internationally successful bands since, such as Roxette, Ace of Base, and the Cardigans to name some of the biggest, and recently there has been a surge of Swedish Indie pop bands such as Peter, Bjorn & John, Mando Diao and Sahara Hotnights. Sweden has also exported a multitude of rock bands throughout the last ten years, for example The Hives, Sahara Hotnights, The Hellacopters, Mando Diao, Millencolin, and Carolina Rain (partially American; majority of members from Sweden).
Sweden has also become known for a large number of heavy metal (mostly death metal and melodic death metal ) as well as progressive- and power metal bands. Some examples are At the Gates, Scar Symmetry, In Flames, Dark Tranquillity, Opeth, Dissection, Arch Enemy, Soilwork, HammerFall, Amon Amarth and Meshuggah. The neoclassical power metal guitarist Yngwie Malmsteen also is from Sweden. Sweden has a rather lively jazz scene. During the last sixty years or so it has attained a remarkably high artistic standard, stimulated by domestic as well as external influences and experiences. The Centre for Swedish Folk Music and Jazz Research has published an overview of jazz in Sweden by Lars Westin.
Media

Swedes are among the greatest consumers of newspapers in the world, and nearly every town is served by a local paper. The country's main quality morning papers are Dagens Nyheter (liberal), Göteborgs-Posten (liberal), Svenska Dagbladet (liberal conservative) and Sydsvenska Dagbladet (liberal).. The two largest evening tabloids are Aftonbladet (social democratic) and Expressen (liberal). The ad-financed, free international morning paper, Metro International, was originally founded in Stockholm, Sweden. The country's news is reported in English by, among others, The Local (liberal).
The public broadcasting companies held a monopoly on radio and television for a long time in Sweden. Licence funded radio broadcasts started in 1925. A second radio network was started in 1954 and a third opened 1962 in response to pirate radio stations. Non-profit community radio was allowed in 1979 and in 1993 commercial local radio started.
The licence funded television service was officially launched in 1956. A second channel, TV2, was launched in 1969. These two channels (operated by Sveriges Television since the late '70s) held a monopoly until the 1980s when cable and satellite television became available. The first Swedish language satellite service was TV3 which started broadcasting from London in 1987. It was followed by Kanal 5 in 1989 (then known as Nordic Channel) and TV4 in 1990.
In 1991 the government announced it would begin taking applications from private television companies wishing to broadcast on the terrestrial network. TV4, which had previously been broadcasting via satellite, was granted a permit and began its terrestrial broadcasts in 1992, becoming the first private channel to broadcast television content from within the country.
Around half the population are connected to cable television. Digital terrestrial television in Sweden started in 1999 and the last analogue terrestrial broadcasts were terminated in 2007.
Literature
Main article: Swedish literatureThe first literary text from Sweden is the Rök Runestone, carved during the Viking Age circa 800 AD. With the conversion of the land to Christianity around 1100 AD, Sweden entered the Middle Ages, during which monastic writers preferred to use Latin. Therefore there are only a few texts in the Old Swedish from that period. Swedish literature only flourished when the Swedish language was standardized in the 16th century, a standardization largely due to the full translation of the Bible into Swedish in 1541. This translation is the so-called Gustav Vasa Bible.

With improved education and the freedom brought by secularisation, the 17th century saw several notable authors develop the Swedish language further. Some key figures include Georg Stiernhielm (17th century), who was the first to write classical poetry in Swedish; Johan Henric Kellgren (18th century), the first to write fluent Swedish prose; Carl Michael Bellman (late 18th century), the first writer of burlesque ballads; and August Strindberg (late 19th century), a socio-realistic writer and playwright who won worldwide fame. The early 20th century continued to produce notable authors, such as Selma Lagerlöf, (Nobel laureate 1909), Verner von Heidenstam (Nobel laureate 1916) and Pär Lagerkvist (Nobel laureate 1951).
In recent decades, a handful of Swedish writers have established themselves internationally, including the detective novelist Henning Mankell and the writer of spy fiction Jan Guillou. But the only Swedish writer to have made a significant mark on world literature is the children's book writer Astrid Lindgren, and her books about Pippi Longstocking, Emil of Maple Hills, and others.
Inventions
Main article: Swedish inventions
In the 18th century Sweden's scientific revolution took off. Previously, technical progress had mainly come from professionals who had immigrated from mainland Europe. In 1739, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences was founded, with people such as Carolus Linnaeus and Anders Celsius as early members. From the 1870s, engineering companies were created at an unmatched rate and engineers became heroes of the age. Many of the companies founded by early pioneers are still internationally familiar. Gustaf Dalén founded AGA, and received the Nobel Prize for his sun valve. Alfred Nobel invented dynamite and instituted the Nobel Prizes. Lars Magnus Ericsson started the company bearing his name, Ericsson, still one of the largest telecom companies in the world. Jonas Wenström was an early pioneer in alternating current and is along with Serbian inventor Tesla credited as one of the inventors of the three-phase electrical system.
The traditional engineering industry is still a major source of Swedish inventions, but pharmaceuticals, electronics and other high-tech industries are gaining ground. Tetra Pak is an invention for storing liquid foods, invented by Erik Wallenberg. Håkan Lans invented the Automatic Identification System, a worldwide standard for shipping and civil aviation navigation. Losec, an ulcer medicine, was the world's best-selling drug in the 1990s and was developed by AstraZeneca. A large portion of the Swedish economy is to this day based on the export of technical inventions, and many large multinational corporations from Sweden have their origins in the ingenuity of Swedish inventors.
Sweden has a total of 33523 patents as of 2007 according to the United States Patent and Trademark Office, and only ten other countries have more patents than Sweden.
Holidays
Main article: Public holidays in Sweden
Apart from traditional Protestant Christian holidays, Sweden also celebrates some unique holidays, some of a pre-Christian tradition. They include Midsummer celebrating the summer solstice; Walpurgis Night (Valborgsmässoafton) on 30 April lighting bonfires; and Labour Day or Mayday on 1 May is dedicated to socialist demonstrations. The day of giver-of-light Saint Lucia, 13 December, is widely acknowledged in elaborate celebrations which betoken its Italian origin and commence the month-long Christmas season. 6 June is the National Day of Sweden and, as of 2005, a public holiday. Furthermore, there are official flag day observances and a Namesdays in Sweden calendar. In August many Swedes have kräftskivor (crayfish dinner parties). Martin of Tours Eve is celebrated in Scania in November with Mårten Gås parties, where roast goose and svartsoppa ('black soup', made of goose stock, fruit, spices, spirits and goose blood) are served. The Sami, one of Sweden's indigenous minorities, have their holiday on February 6 and Scania celebrate their Scanian Flag day on the third Sunday in July.
Cuisine

Swedish cuisine, like that of the other Scandinavian countries (Denmark and Norway), was traditionally simple. Fish (particularly herring), meat and potatoes played prominent roles. Spices were sparse. Famous dishes include Swedish meatballs, traditionally served with gravy, boiled potatoes and lingonberry jam; pancakes, lutfisk, and Smörgåsbord, or lavish buffet. Akvavit is a popular alcoholic distilled beverage, and the drinking of snaps is of cultural importance. The traditional flat and dry crisp bread has developed into several contemporary variants. Regionally important foods are the surströmming (a fermented fish) in Northern Sweden and eel in Scania in Southern Sweden. However, Swedes have traditionally also been very open to foreign influences, ranging from the French cuisine during the eighteenth century, to the sushi and cafe latte of today.
Film
Main article: Cinema of SwedenSwedes have been fairly prominent in the film area through the years, several successful Swedish Hollywood actors can be mentioned: Ingrid Bergman, Greta Garbo, Max von Sydow, Dolph Lundgren, Lena Olin, Stellan Skarsgård, Peter Stormare, Izabella Scorupco, Pernilla August, Ann Margaret, Anita Ekberg, Alexander Skarsgård, Harriet Andersson, Bibi Andersson, Ingrid Thulin, Malin Akerman and Gunnar Björnstrand. Amongst several directors who have made internationally successful films can be mentioned: Ingmar Bergman, Lukas Moodysson, Dolph Lundgren and Lasse Hallström.
Fashion
Sweden has in late years taken an interest in the fashion industry, through headquartering famous brands like Hennes & Mauritz (operating as H&M), J. Lindeberg (operating as JL), Gina Tricot, Tiger of Sweden, Odd Molly, Dagmar, Cheap Monday, Gant, Lexington, Svea, Resteröds, WESC and Filippa K within its borders. These companies, however, are comprised largely of buyers who import fashionable goods from throughout Europe and the Americas, continuing the trend of Swedish business toward multinational economic dependency like many of its neighbours.
Sports

Sport activities are a national movement with half of the population actively participating, much thanks to the heavy government subsidies of sport associations (föreningsstöd). The two main spectator sports are association football and ice hockey (several famous Swede ice hockey players include Mats Sundin, Peter Forsberg, Markus Näslund, Daniel and Henrik Sedin, and Nicklas Lidström). Second to football, horse sports have the highest number of practitioners, mostly women. Thereafter follow golf, athletics, and the team sports of handball, floorball, basketball and bandy.
Sweden has been a very successful sport nation throughout the years, and has a row of sportsmen that are considered to be the best in history in their type of sport. Björn Borg is considered not only to be the most successful player in his genre of sport, tennis, but also to be one of the most successful players in the history of sports. Jan-Ove Waldner the table tennis player known as 'the Mozart of table tennis' is a legend in both his native Sweden as well as in China. Gunnar Nordahl (football player) is still the best goalscorer of all time with 225 goals in 291 matches, and remains record holder for the most goals in a season in Italy, with 35 goals 1949-1950. Skier Ingemar Stenmark is considered to be one of the greatest alpine skiers of all time with 86 World Cup Victories. The greatest female Golf player of all time, Annika Sörenstam, have 90 international tournament wins as a professional make her the female golf player with the most wins to her name. She also tops the LPGA's career money list.
The Swedish ice hockey team Tre Kronor is regarded as one of the very best in the world and has won the World Championships eight times, which makes them third in the medal count. They won Olympic gold medals in 1994 and 2006. In 2006, as the first nation in history, they won both the Olympic and world championships in the same year. The Swedish national football team has seen some success at the World Cup in the past, finishing second when they hosted the tournament in 1958, and third twice, in 1950 and 1994.
Athletics has enjoyed a surge in popularity due to several successful athletes in recent years, such as: Carolina Klüft, Stefan Holm, Christian Olsson, Patrik Sjöberg, Johan Wissman, Kajsa Bergqvist.
In schools, on meadows and in parks, the game brännboll, a sport similar to baseball, is commonly played for fun. Other leisure sports are the historical game of kubb, and boules among the older generation.
Sweden hosted the 1912 Summer Olympics and the FIFA World Cup in 1958. Other big sports events held here include 1992 UEFA European Football Championship, FIFA Women's World Cup 1995, and several championships of ice hockey, curling, athletics, skiing, bandy, figure skating and swimming.
International rankings
| Name | Year | Place | Out of # | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIA World Factbook – GDP per capita (PPP) | 2008 | 26th | 229 | |
| CIA World Factbook – life expectancy | 2008 | 9th | 223 | |
| World Economic Forum – Enabling Trade Index ranking | 2008 | 3rd | 118 | |
| Yale University / Columbia University - Environmental Performance Index | 2008 | 3rd | 149 | |
| The Economist Intelligence Unit - e-readiness | 2008 | 3rd | 70 | |
| The Economist Intelligence Unit - Global Peace Index | 2008 | 13th | 140 | |
| United States Patent and Trademark Office's list of patents by country | 2007 | 11th | 172 | |
| Save the Children - Mother's Index Rank | 2007 | 1st | 141 | |
| Save the Children - Women's Index Rank | 2007 | 1st | 141 | |
| Save the Children - Children's Index Rank | 2007 | 4th | 141 | |
| Wall Street Journal / The Heritage Foundation - Index of Economic Freedom | 2007 | 27th | 157 | |
| United Nations - Human Development Index | 2007 | 6th | 177 | |
| World Economic Forum - Global Competitiveness Report 2007-2008 | 2007 | 4th | 131 | |
| World Economic Forum - The Global Gender Gap Report 2007 | 2007 | 1st | 128 | |
| World Bank - Ease of Doing Business Index | 2007 | 14th | 178 | |
| Reporters Without Borders - Worldwide Press Freedom Index | 2007 | 5th | 169 | |
| Transparency International - Corruption Perceptions Index | 2008 | 1th | 180 | |
| The Economist Intelligence Unit - Index of Democracy | 2007 | 1st | 167 | |
| Privacy International - Privacy index (EU and 11 other selected countries) | 2006 | 28th | 36 | |
| New Economics Foundation - Happy Planet Index | 2006 | 119th | 178 | |
| The Economist Intelligence Unit - Quality-of-life index | 2005 | 5th | 111 | |
| Save the Children - % seats in the national government held by women | 2004 | 1st (47%) | 141 | |
| World Health Organization - suicide rates by country | 31st | 100 | ||
| NationMaster's index of civil and political liberties | 13th | 140 | ||
| NationMaster's index of asylum seekers (per capita) | 4th | 28 | ||
| NationMaster's index of economic aid (donor, per capita) | 5th | 24 | ||
| NationMaster's index of total tax wedge (single worker) | 4th | 29 | ||
| NationMaster's index of technological achievement | 3rd | 68 |
See also
- List of Sweden-related topics
- Government agencies in Sweden
- Non-governmental organizations in Sweden
- Communications in Sweden
- Tourism in Sweden
- Civil unions in Sweden
- Swedish people
Notes
- "Är svenskan också officiellt språk i Sverige?" (in Swedish). Språkrådet (Language Council of Sweden). 2008-02-01. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- "Huvudspråk". Sveriges Radio. Retrieved 2008-06-22.
- Statistics Sweden. Yearbook of Housing and Building Statistics 2007. Statistics Sweden, Energy, Rents and Real Estate Statistics Unit, 2007. ISBN 9789161813612. Available online in PDF format.
- U.S. State Department Background Notes: Sweden
- Hellquist, Elof (1922). Svensk etymologisk ordbok. Stockholm: Gleerups förlag. p. 915.
- The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. 2001-05
- ^ Sawyer, Birgit and Peter Sawyer (1993). Medieval Scandinavia: from Conversion to Reformation, Circa 800–1500. University of Minnesota Press, 1993. ISBN 0816617392, pp. 150-153.
- Bagge, Sverre (2005). "The Scandinavian Kingdoms". In The New Cambridge Medieval History. Eds. Rosamond McKitterick et al. Cambridge University Press, 2005. ISBN 052136289X, p. 724: "Swedish expansion in Finland led to conflicts with Rus', which were temporarily brought to an end by a peace treaty in 1323, dividing the Karelian peninsula and the northern areas between the two countries."
- "A Political and Social History of Modern Europe V.1./Hayes..." Hayes, Carlton J. H. (1882-1964), Title: A Political and Social History of Modern Europe V.1., 2002-12-08, Project Gutenberg, webpage: Infomot-7hsr110.
- However, Sweden's largest territorial extent lasted from 1319 to 1343 with Magnus Eriksson ruling all of the traditional lands of Sweden and Norway.
- "Gustav I Vasa - Britannica Concise" (biography), Britannica Concise, 2007, webpage: EBConcise-Gustav-I-Vasa.
- Battle of Kircholm 1605
- Encyclopedia of Canada's Peoples. University of Minnesota Press. 1998. p. 1220. ISBN 0-8020-2938-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Einhorn, Eric and John Logue (1989). Modern Welfare States: Politics and Policies in Social Democratic Scandinavia. Praeger Publishers, p.9: "Though Denmark, where industrialization had begun in the 1850s, was reasonably prosperous by the end of the nineteenth century, both Sweden and Norway were terribly poor. Only the safety valve of mass emigration to America prevented famine and rebellion. At the peak of emigration in the 1880s, over 1% of the total population of both countries emigrated annually."
- Koblik, Steven (1975). Sweden's Development from Poverty to Affluence 1750-1970, University of Minnesota Press, p.8-9, "In economic and social terms the eighteenth century was more a transitional than a revolutionary period. Sweden was, in light of contemporary Western European standards, a relatively poor but stable country. It has been estimated that 75-80% of the population was involved in agricultural pursuits during the late eighteenth century. One hundred years later, the corresponding figure was still 72%."
- Einhorn, Eric and John Logue (1989), p.8.
- Ulf Beijbom, "European emigration", The House of Emigrants, Växjö, Sweden.
- ^ Koblik, Steven (1975). Sweden's Development from Poverty to Affluence 1750-1970 University of Minnesota Press, pp. 9-10.
- Sweden: Social and economic conditions (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 19 February 2007.
- Koblik, Steven (1975). Sweden's Development from Poverty to Affluence 1750-1970 University of Minnesota Press, p. 11: "The agrarian revolution in Sweden is of fundamental importance for Sweden's modern development. Throughout Swedish history the countryside has taken an unusually important role in comparison with other European states."
- Koblik, Steven (1975). Sweden's Development from Poverty to Affluence 1750-1970 University of Minnesota Press, p. 90. "It is usually suggested that between 1870 and 1914 Sweden emerged from its primarily agrarian economic system into a modern industrial economy."
- ^ Koblik, pp. 303-313.
- Nordstrom, p. 315: "Sweden's government attempted to maintain at least a semblance of neutrality while it bent to the demands of the prevailing side in the struggle. Although effective in preserving the country's sovereignty, this approach generated criticism at home from many who believed the threat to Sweden was less serious than the government claimed, problems with the warring powers, ill feelings among its neighbours, and frequent criticism in the postwar period."
- ^ Nordstrom, pp. 313-319.
- Zubicky, Sioma (1997). Med förintelsen i bagaget (in Swedish). Stockholm: Bonnier Carlsen. p. 122. ISBN 91-638-3436-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ Nordstrom, pp. 335-339.
- ^ Globalization and Taxation: Challenges to the Swedish Welfare State. By Sven Steinmo.
- Nordstrom, p. 344: "During the last twenty-five years of the century a host of problems plagued the economies of Norden and the West. Although many were present before, the 1973 and 1980 global oil crises acted as catalysts in bringing them to the fore."
- Krantz, Olle and Lennart Schön. 2007. Swedish Historical National Accounts, 1800-2000. Lund: Almqvist and Wiksell International.
- Englund, P. 1990. "Financial deregulation in Sweden." European Economic Review 34 (2-3): 385-393. Korpi TBD. Meidner, R. 1997. "The Swedish model in an era of mass unemployment." Economic and Industrial Democracy 18 (1): 87-97. Olsen, Gregg M. 1999. "Half empty or half full? The Swedish welfare state in transition." Canadian Review of Sociology & Anthropology, 36 (2): 241-268.
- The Local. "New Swedish weapon in Iraq". Retrieved 2007-06-23.
- "SMHI - Sveriges klimat". Sveriges meteorologiska och hydrologiska institut. Retrieved 2007-10-28.
- Weather.com
- "Sweden in Brief/A Political Society". Sweden.se. Retrieved 2007-02-14.
- "Economist Intelligence Unit democracy index 2006" (PDF). Economist Intelligence Unit. 2007. Retrieved 2007-10-09.
- Förord
- Hadenius, Stig; Nilsson, Torbjörn; Åselius, Gunnar (1996) Sveriges historia: vad varje svensk bör veta. Bonnier Alba, Borås. ISBN 91-34-51857-6 (in Swedish) (1996:13):
Hur och när det svenska riket uppstod vet vi inte. Först under 1100-talet börjar skriftliga dokument produceras i Sverige i någon större omfattning How and when the Swedish kingdom appeared is not known. It is not until the 12th century that written document begin to be produced in Sweden in any larger extent - Kungl. Maj:ts kungörelse med anledning av konung Gustaf VI Adolfs frånfälle. SFS 1973:702. Justitiedepartementet L6, 19 September 1973.
- ^ The Swedish Parliament. The history of the Riksdag. Retrieved 13 February 2007.
- The Official Website of the Swedish Election Authority. "Val till riksdagen".
- Sören Holmberg (1999). Pippa Norris (ed.). Critical Citizens: Global Support for Democratic Government. Oxford University Press. pp. 103–123. ISBN 0198295685.
- ^ European Commission Directorate General for Employment, Social Affairs And Equal Opportunities, Report On The Equality Between Men And Women,http://ec.europa.eu/employment_social/publications/2006/keaj06001_en.pdf February 2006
- Mosey, Chris. "Vote F! for Feminism." Ms. magazine. Fall 2006.
- van Dijk, Jan (2005). "EUICS report, The Burden of Crime in the EU, A Comparative Analysis of the" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Nordstrom p. 302: "In fact, the plans were mostly a ruse to establish control of the crucial Norwegian port of Narvik and the iron mines of northern Sweden, which were vitally important to the German war efforts."
- Nordstrom, p 336: "As a corollary, a security policy based on strong national defenses designed to discourage, but not prevent, attack was pursued. For the next several decades, the Swedish poured an annual average of about 5% of GDP into making their defenses credible."
- National Geographical News, web article, Cold War Spy Plane Found in Baltic Sea 10 November 2003.
- Swedish Ministry of Defence (2008-01-08). "The EU Battlegroup Concept and the Nordic Battlegroup". Government Offices of Sweden. Retrieved 2008-01-19.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - 20 largest companies in Sweden
- ^ Economic survey of Sweden 2007
- Pension Reform in Sweden: Lessons for American Policymakers by Goran Normann, Ph.D. and Daniel J. Mitchell, Ph.D. June 29, 2000.
- ^ OECD Economic Surveys: Sweden - Volume 2005 Issue 9 by OECD Publishing
- World Economic Forum - Global Competitiveness Report
- IMD Competitiveness Yearbook 2008
- ""Sweden most creative country in Europe & top talent hotspot", Invest in Sweden Agency, 25 June 2005.
- Kraftläget i Sverige, Vattensituationen
- "Nuclear Power in Sweden" - Uranium Information Centre, Australia
- ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Sweden. Agenda 21 - Natural Resource Aspects - Sweden. 5th Session of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development, April 1997.
- Vidal, John. Sweden plans to be world's first oil-free economy. The Guardian, 2/8/06. Retrieved 2/13/07.
- ^ EU versus USA, Fredrik Bergström & Robert Gidehag
- Sweden's balancing lessons for Europe, McKinsey IMG institute 2006
- Moderate revolution, The Economist Sep 13th 2007
- Westerlund, Kenneth (2008-03-11). "Danmark har högsta skattetrycket". DN. Retrieved 2008-03-11.
- The Swedish Parliament
- Eurostat February 2007 – Euro area unemployment down to 7.3%, March 30, 2007
- "Fees and costs - SWEDEN.SE". Retrieved 2007-06-18.
- ^ The Swedish model, The Economist
- Statistics Sweden.Preliminary Population Statistics, by month, 2004 - 2006. Population statistics, 1 January 2007. Retrieved 14 February 2007.
- SCB. Sveriges befolkning, kommunala jämförelsetal, 31/12/2006 31 December 2006. (In Swedish). Retrieved 3 April 2007.
- Record immigration to Sweden in 2006
- ^ The Swedish Integration Board (2006). Pocket Facts: Statistics on Integration. Integrationsverket, 2006. ISBN 9189609301. Available online in pdf format. Retrieved 14 February 2007.
- Nordstrom, p. 353. (Lists Former Yugoslavia and Iran as top two countries in terms of immigration beside "Other Nordic Countries," based on Nordic Council of Ministers Yearbook of Nordic Statistics, 1996, 46-47)
- ^ "Karlstad University" (on languages taught/spoken), Karlstad University, 2006, webpage: Kau-SE-Languages.
- Svenskan blir inte officiellt språk, Sveriges Television, 2005-12-07. Retrieved on July 23 2006. (in Swedish)
- "English spoken - fast ibland hellre än bra" (in Swedish). Lund University newsletter 7/1999.
- Church of Sweden, Members 1972-2006, Excel document in Swedish
- Statistics about free churches and immigration churches from Swedish Misplaced Pages - in Swedish
- Sydsvenskan (a Swedish newspaper) - in Swedish
- "The Swedish Myths: True, False, or Somewhere In Between?". Sweden.se.
{{cite news}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameters:|1=and|3=(help); Text "http://www.sweden.se/templates/cs/Article____12355.aspx" ignored (help) - Durant, Colin (2003). Choral Conducting: philosophy and practice, Routledge, pp. 46-47. ISBN 0415943566: "Sweden has a strong and enviable choral singing tradition. All those interviewed placed great emphasis on the social identification through singing and also referred to the importance of Swedish folk song in the maintenance of the choral singing tradition and national identity."
- http://www.swedenabroad.com/Page____59218.aspx
- Lars Westin: Jazz in Sweden - an overview
- ^ "Swedish inventions and discoveries" (PDF). Fact Sheet FS 91 e. Swedish Institute. 2007. Retrieved 2007-10-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Patents By Country, State, and Year - All Patent Types (December 2007)
References
- Bagge, Sverre (2005). "The Scandinavian Kingdoms". In The New Cambridge Medieval History. Eds. Rosamond McKitterick et al. Cambridge University Press, 2005. ISBN 052136289X.
- CIA World Factbook – Sweden
- Council for Official Statistics. "Preliminär befolkningsstatistik 2006"Statistics Sweden.
- Durant, Colin (2003). Choral Conducting: philosophy and practice, Routledge, pp. 46-47. ISBN 0415943566.
- Einhorn, Eric and John Logue (1989). Modern Welfare States: Politics and Policies in Social Democratic Scandinavia. Praeger Publishers, 1989. ISBN 0275931889.
- Invest in Sweden Agency (ISA) (2005). Sweden most creative country in Europe and top talent hotspot. Press release, 25 June 2005.
- Koblik, Steven (1975). Sweden's Development from Poverty to Affluence 1750-1970. University of Minnesota Press. ISBN 0816607575.
- Magocsi, Paul Robert (1998). Encyclopedia of Canada's Peoples. University of Minnesota Press, 1998. ISBN 0802029388.
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Sweden. Agenda 21 – Natural Resource Aspects - Sweden. 5th Session of the United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development, April 1997.
- Nordstrom, Byron J. (2000). Scandinavia since 1500. University of Minnesota Press, 2000. ISBN 0816620989.
- Sawyer, Birgit and Peter Sawyer (1993). Medieval Scandinavia: from Conversion to Reformation, Circa 800–1500. University of Minnesota Press, 1993. ISBN 0816617392.
- Ståhl, Solveig. (1999). "English spoken – fast ibland hellre än bra". LUM, Lunds universitet meddelar, 7:1999, 3 September 1999. In Swedish.
- Statistics Sweden. 2006 census.
- Statistics Sweden. Preliminary Population Statistics, by month, 2004–2006. Population statistics, 1 January 2007.
- Statistics Sweden. Yearbook of Housing and Building Statistics 2007. Statistics Sweden, Energy, Rents and Real Estate Statistics Unit, 2007. ISBN 9789161813612. Available online in pdf format.
- "Sweden". In The Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition, 2001-05.
- Sweden. In Encyclopædia Britannica, 1911.
- Sweden: Social and economic conditions (2007). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- Swedish National Debt Office
- The Swedish Parliament: Laws
- United States Department of State – Sweden
- World History Database – Sweden
- Uddhammar, Emil (1993). Partierna och den stora staten: en analys av statsteorier och svensk politik under 1900-talet. Stockholm, City University Press.
- "RADICAL PRINCIPLES AND THE LEGAL INSTITUTION OF MARRIAGE: DOMESTIC RELATIONS LAW AND SOCIAL DEMOCRACY IN SWEDEN -- BRADLEY 4 (2): 154 -- International Journal of Law, Policy and the Family". Retrieved 2007-06-13.
External links
- Template:Wikitravel
- Swedish Royal Court – Official website of the Swedish Royal House
- VisitSweden.com – Official travel and tourism website for Sweden
- SWEDEN.SE – The Official Gateway to Sweden
- Radio Sweden Template:En icon – Public service
- The Swedish Government – Official site
- The Swedish Parliament – Official site
- Study in Sweden – Official guide to studying in Sweden
- Statistiska Centralbyrån – Statistics Sweden (governmental)
- Invest in Sweden Agency – Government agency
- Swedish Trade Council
- Sweden – Economic Growth and Structural Change, 1800-2000 — EH.Net Encyclopedia
- The Local - Sweden's news in English – Independent English language news site
| International membership and relationships | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

