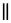| Revision as of 15:27, 5 March 2009 editFgrosshans (talk | contribs)357 editsm →Occurrence: link typo← Previous edit | Revision as of 08:07, 10 April 2009 edit undoBeno1000 (talk | contribs)Pending changes reviewers3,659 edits →OccurrenceNext edit → | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | colspan="2" align="center"| ] ||align="center"| ''isi'''Xh'''osa'' ||align="center"| {{IPA| }}||align="center"| 'Xhosa language'|| Tenuis, ], ], and ] lateral clicks. | | colspan="2" align="center"| ] ||align="center"| ''isi'''Xh'''osa'' ||align="center"| {{IPA| }}||align="center"| 'Xhosa language'|| Tenuis, ], ], and ] lateral clicks. | ||
| |- | |||
| | colspan="2" align="center"| ] ||align="center"| '''''x'''o'''x'''a'' || align="center"| {{IPA|}}||align="center"| 'to converse' || | |||
| |} | |} | ||
Revision as of 08:07, 10 April 2009
The lateral clicks are click consonants found only in Africa. The clicking sound used by equestrians to urge on their horses is a lateral click, although it isn't a speech sound in that context. Alveolar lateral clicks are found throughout southern Africa and Tanzania; some of the Juu languages also have other lateral clicks.
Alveolar lateral clicks
| IPA number | 180 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Audio sample | |||
| source · help | |||
| Encoding | |||
| X-SAMPA | |\|\ | ||
| |||
Most lateral clicks are alveolar. These are found in all Khoisan languages as well as in several Bantu languages. The only languages with non-alveolar lateral clicks are in the Juu family (see below).
The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the forward articulation of these sounds is ǁ, a double vertical bar. This must be combined with a symbol for the rear articulation to represent an actual speech sound. Attested alveolar lateral clicks include:
- or voiceless velar–alveolar lateral click (may also be aspirated, ejective, affricated, etc.)
- or voiced velar–alveolar lateral click (may also be breathy voiced, affricated, etc.)
- or nasal velar–alveolar lateral click (may also be voiceless, aspirated, etc.)
- or voiceless uvular–alveolar lateral click
- or voiced uvular–alveolar lateral click (commonly prenasalized)
- or nasal uvular–alveolar lateral click
- glottalized alveolar lateral click
The last is what is heard in the sound sample above, as non-native speakers tend to glottalize clicks to avoid nasalizing them.
Prior to 1989, was the IPA representation of the voiceless velar–alveolar lateral click.
Features
Features of alveolar lateral clicks:
- The manner of articulation is a noisy, affricate-like release in southern Africa, but abrupt in Hadza and Sandawe in East Africa.
- The rear closure may be voiced, nasal, ejective, or affricate, and have any of several phonations.
- The forward place of articulation is alveolar, which means it is articulated with the tip of the tongue against the alveolar ridge. The rear place of articulation may be either velar or uvular.
- Lateral clicks may be either oral or nasal, which means air is allowed to escape either through the mouth or the nose.
- They are lateral consonants, which means they are produced by allowing the airstream to flow over the sides of the tongue, rather than the middle of the tongue. Some speakers pronounce them on one side of the mouth, some on both.
- The airstream mechanism is velaric ingressive (AKA lingual ingressive), which means the pocket of air trapped between the two closures is rarefied by a "sucking" action of the tongue, rather than by the glottis or the lungs. The release of the forward closure produces the 'click' sound.
Occurrence
| Language | Word | IPA | Meaning | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ǃKung | 'Tylosema' | ||||
| Hadza | 'to listen' | ||||
| 'to crowd' | |||||
| 'to be a pair' | |||||
| 'a split, fork' | |||||
| Xhosa | isiXhosa | 'Xhosa language' | Tenuis, murmured, aspirated, and nasal lateral clicks. | ||
| Zulu | xoxa | 'to converse' | |||
Dental lateral clicks
In addition to alveolar articulations, dental lateral clicks are reported from speakers of an Angolan ǃXũũ dialect now residing in Mangetti Dune, Namibia. These include at least voiceless, voiced, and nasal phonations, and are reflexes of the retroflex clicks of Proto-Juu. They are provisionally written with three pipes, <ǀǀǀ>, rather than the two of the alveolar lateral <ǁ>. They are laminal alveolar or dent-alveolar, , while the clicks transcribed as <ǁ> are apical postalveolar, .
Contrasting lateral clicks in Mangetti Dune ǃXũũ:
| 'Tylosema' | |
| 'Eland' | |
| 'inside' |
Palatal lateral clicks
Another ǃXũũ dialect has a family of palatal lateral clicks. These are reflexes of the retroflex clicks of Proto-Juu. They are provisionally written ǂǂ, as they have no IPA symbol. These clicks are scheduled to be investigated more fully in 2009.
References
- Pullum, Geoffrey K. (1996). Phonetic Symbol Guide. University of Chicago Press. p. 178.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)