| Revision as of 22:13, 20 June 2009 view source99.229.230.20 (talk) →External links← Previous edit | Revision as of 18:05, 22 June 2009 view source J04n (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators162,685 editsm Repairing link to disambiguation page - You can help!Next edit → | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| {{History of Iran}} | {{History of Iran}} | ||
| The '''Ghaznavids''' ({{lang-fa|غزنویان}}) were an ] and ] dynasty of ] '']''<ref></ref> origin which existed from 975 to 1187 and ruled much of ], ], and the northern parts of the ].<ref name="EIr">C.E. Bosworth: The Ghaznavids. Edinburgh, 1963</ref><ref>], ''"Ghaznavids"'', in ], Online Edition 2006, ()</ref><ref name="EI">], ''"Ghaznavids"'', in ], Online Edition; Brill, Leiden; 2006/2007</ref> The Ghaznavid state was centered in ], a city in present ]. Due to the political and cultural influence of their predecessors - that of the ] ] - the originally Turkic Ghaznavids became thoroughly ].<ref name="EIr" /><ref name="EI"/><ref name="Shahrbanu">M.A. Amir-Moezzi, ''"Shahrbanu"'', ], Online Edition, (): ''"... here one might bear in mind that non-Persian dynasties such as the Ghaznavids, Saljuqs and Ilkhanids were rapidly to adopt the Persian language and have their origins traced back to the ancient kings of Persia rather than to Turkish heroes or Muslim saints ..."''</ref><ref name="E.Yar."></ref><ref>B. Spuler, "The Disintegration of the Caliphate in the East", in the Cambridge History of Islam, Vol. IA: ''The Central islamic Lands from Pre-Islamic Times to the First World War, ed. by P.M. Holt, Ann K.S. Lambton, and Bernard Lewis (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1970). pg 147: ''One of the effects of the renaissance of the Persian spirit evoked by this work was that the Ghaznavids were also Persianized and thereby became a Persian dynasty.</ref><ref>Anatoly M Khazanov, André Wink, "Nomads in the Sedentary World", Routledge, 2padhte padhte to pagla jayega aadmi, "A History of Russia, Central Asia and Mongolia", Blackwell Publishing, 1998. pg 370: "Though Turkic in origin and, apparently in speech, Alp Tegin, Sebuk Tegin and Mahmud were all thoroughly Persianized"</ref><ref>Robert L. Canfield, Turko-Persia in historical perspective, Cambridge University Press, 1991. pg 8: "The Ghaznavids (989-1149) were essentially Persianized Turks who in manner of the pre-Islamic Persians encouraged the development of high culture"</ref> | The '''Ghaznavids''' ({{lang-fa|غزنویان}}) were an ] and ] dynasty of ] '']''<ref></ref> origin which existed from 975 to 1187 and ruled much of ], ], and the northern parts of the ].<ref name="EIr">C.E. Bosworth: The Ghaznavids. Edinburgh, 1963</ref><ref>], ''"Ghaznavids"'', in ], Online Edition 2006, ()</ref><ref name="EI">], ''"Ghaznavids"'', in ], Online Edition; Brill, Leiden; 2006/2007</ref> The Ghaznavid state was centered in ], a city in present ]. Due to the political and cultural influence of their predecessors - that of the ] ] - the originally Turkic Ghaznavids became thoroughly ].<ref name="EIr" /><ref name="EI"/><ref name="Shahrbanu">M.A. Amir-Moezzi, ''"Shahrbanu"'', ], Online Edition, (): ''"... here one might bear in mind that non-Persian dynasties such as the Ghaznavids, Saljuqs and Ilkhanids were rapidly to adopt the Persian language and have their origins traced back to the ancient kings of Persia rather than to Turkish heroes or Muslim saints ..."''</ref><ref name="E.Yar."></ref><ref>B. Spuler, "The Disintegration of the Caliphate in the East", in the Cambridge History of Islam, Vol. IA: ''The Central islamic Lands from Pre-Islamic Times to the First World War, ed. by P.M. Holt, Ann K.S. Lambton, and Bernard Lewis (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1970). pg 147: ''One of the effects of the renaissance of the Persian spirit evoked by this work was that the Ghaznavids were also Persianized and thereby became a Persian dynasty.</ref><ref>Anatoly M Khazanov, André Wink, "Nomads in the Sedentary World", Routledge, 2padhte padhte to pagla jayega aadmi, "A History of Russia, Central Asia and Mongolia", Blackwell Publishing, 1998. pg 370: "Though Turkic in origin and, apparently in speech, Alp Tegin, Sebuk Tegin and Mahmud were all thoroughly Persianized"</ref><ref>Robert L. Canfield, Turko-Persia in historical perspective, Cambridge University Press, 1991. pg 8: "The Ghaznavids (989-1149) were essentially Persianized Turks who in manner of the pre-Islamic Persians encouraged the development of high culture"</ref> | ||
| The dynasty was founded by ] upon his succession to rule of territories centered around the city of ] from his father-in-law, ], a break-away ex-general of the Samanid sultans.<ref name="EB">Encyclopedia Britannica, ''Ghaznavid Dynasty'', Online Edition 2007 ()</ref> Sebuktigin's son, ], expanded the empire in the region that stretched from the ] to the ] and the ]; and in the west it reached ] and ]. Under the reign of ] it experienced major territorial losses. It lost its western territories to the ] in the ] resulting in a restriction of its holdings to ], ] and the ]. In 1151, Sultan Bahram Shah lost Ghazni to Ala'uddin Hussain of ] and the capital was moved to ] until its subsequent capture by the ] in 1186. | The dynasty was founded by ] upon his succession to rule of territories centered around the city of ] from his father-in-law, ], a break-away ex-general of the Samanid sultans.<ref name="EB">Encyclopedia Britannica, ''Ghaznavid Dynasty'', Online Edition 2007 ()</ref> Sebuktigin's son, ], expanded the empire in the region that stretched from the ] to the ] and the ]; and in the west it reached ] and ]. Under the reign of ] it experienced major territorial losses. It lost its western territories to the ] in the ] resulting in a restriction of its holdings to ], ] and the ]. In 1151, Sultan Bahram Shah lost Ghazni to Ala'uddin Hussain of ] and the capital was moved to ] until its subsequent capture by the ] in 1186. | ||
Revision as of 18:05, 22 June 2009
غزنویان Ghaznavian Ghaznavid Empire | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 963–1187 | |||||||||||
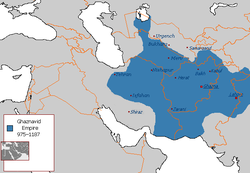 Ghaznavid Empire at its greatest extent Ghaznavid Empire at its greatest extent | |||||||||||
| Capital | Ghazni (until 1151) Lahore (from 1151) | ||||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||||||||
| Government | Empire | ||||||||||
| shah | |||||||||||
| • 963-977 | Alptigin | ||||||||||
| • 1160-1187 | Khusrau Malik | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Medieval | ||||||||||
| • Established | 963 | ||||||||||
| • Disestablished | 1187 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The Ghaznavids (Template:Lang-fa) were an Islamic and Persianate dynasty of Turkic mamluk origin which existed from 975 to 1187 and ruled much of Persia, Transoxania, and the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent. The Ghaznavid state was centered in Ghazni, a city in present Afghanistan. Due to the political and cultural influence of their predecessors - that of the Persian Samanid Empire - the originally Turkic Ghaznavids became thoroughly Persianized.
The dynasty was founded by Sebuktigin upon his succession to rule of territories centered around the city of Ghazni from his father-in-law, Alp Tigin, a break-away ex-general of the Samanid sultans. Sebuktigin's son, Shah Mahmoud, expanded the empire in the region that stretched from the Oxus river to the Indus Valley and the Indian Ocean; and in the west it reached Rayy and Hamadan. Under the reign of Mas'ud I it experienced major territorial losses. It lost its western territories to the Seljuqs in the Battle of Dandanaqan resulting in a restriction of its holdings to Afghanistan, Balochistan and the Punjab. In 1151, Sultan Bahram Shah lost Ghazni to Ala'uddin Hussain of Ghor and the capital was moved to Lahore until its subsequent capture by the Ghurids in 1186.
Rise to power
Two military families arose from the Turkic Slave-Guards of the Samanids — the Simjurids and Ghaznavids — who ultimately proved disastrous to the Samanids. The Simjurids received an appanage in the Kohistan region of eastern Khorasan. Alp Tigin founded the Ghaznavid fortunes when he established himself at Ghazna (modern Ghazni, Afghanistan) in 962. He and Abu al-Hasan Simjuri, as Samanid generals, competed with each other for the governorship of Khorasan and control of the Samanid empire by placing on the throne emirs they could dominate when Abdul Malik I of Samanid died in 961. But when the Samanid Emir Abdul Malik I died in 961 CE it created a succession crisis between Abdul Malik's brothers. A court party instigated by men of the scribal class—civilian ministers as contrasted with Turkic generals—rejected Alp Tigin's candidate for the Samanid throne. Mansur I was installed, and Alp Tigin prudently retired to his fief of Ghazna. The Simjurids enjoyed control of Khorasan south of the Oxus but were hard-pressed by a third great Iranian dynasty, the Buwayhids, and were unable to survive the collapse of the Samanids and the rise of the Ghaznavids.
The struggles of the Turkic slave generals for mastery of the throne with the help of shifting allegiance from the court's ministerial leaders both demonstrated and accelerated the Samanid decline. Samanid weakness attracted into Transoxania the Qarluq Turks, who had recently converted to Islam. They occupied Bukhara in 992 to establish in Transoxania the Qarakhanid, or Ilek Khanid, dynasty. Alp Tigin had been succeeded at Ghazna by Sebüktigin (died 997). Sebüktigin's son Mahmud made an agreement with the Qarakhanids whereby the Oxus was recognized as their mutual boundary.
Domination
Saboktekin made himself lord of nearly all the present territory of Afghanistan and of the Punjab by conquest of Samanid and Shahi lands. In 997, Mahmud, the son of Sebük Tigin, succeeded his father upon his death, and with him Ghazni and the Ghaznavid dynasty have become perpetually associated. He completed the conquest of Samanid, Shahi lands, the Ismaili Kingdom of Multan, Sindh as well as some Buwayhid territory. Under him all accounts was the golden age and the height of the Ghaznevid Empire. Mahmud carried out seventeen expeditions through northern India establishing his control and setting up tributary states. His raids also resulted in the looting of a great deal of plunder. From the borders of Kurdistan to Samarkand, from the Caspian Sea to the Yamuna, he established his authority.
The wealth brought back from the Indian expeditions to Ghazni was enormous, and contemporary historians (e.g. Abolfazl Beyhaghi, Ferdowsi) give glowing descriptions of the magnificence of the capital, as well as of the conquerors munificent support of literature. Mahmud died in (1030). Even though there was some revival of importance under Ibrahim (1059-1099), the empire never reached anything like the same splendor and power. It was soon overshadowed by the Seljuqs of Iran.
Decline

Mahmud's son Mas'ud was unable to preserve the empire and following a disastrous defeat at the Battle of Dandanaqan in (1040) lost all the Ghaznavid lands in Iran and Central Asia to the Seljuks and plunged the realm into a "Time of troubles". Mas'ud's son Ibrahim who re-established a truncated empire on a firmer basis by arriving at a peace agreement with the Seljuks and a restoration of cultural and political linkages. Under Ibrahim and his successors saw a period of sustained tranquility for the empire. Shorn of its western land it was increasingly sustained by riches accrued from raids across Northern India where it faced stiff resistance from Rajput rulers such as the Paramara of Malwa and the Gahadvala of Kannauj. Signs of weakness in the state became apparent when Masud III died in 1115 with internal strife between his sons ending with the ascension of Sultan Bahram Shah as a Seljuk Vassal. Sultan Bahram Shah, was the last Ghaznavid King ruling Ghazni, the first and main Ghaznavid capital. Ala'uddin Hussain, a Ghorid King, conquered the city of Ghazni in 1151, for the revenge of his brother's death. He razed all the city, and burned it for 7 days, after which he got famous as "Jahānsoz" (World Burner). Ghazni was restored to the Ghaznavids by the intervention of the Seljuks who came to Behrams aid. Ghaznavid struggles with the Ghurids continued in the subsequent years as they nibbled away at Ghaznavid territory and Ghazni and Zabulistan was lost a group of Oghuz Turks before captured by the Gurids. Ghaznavid power in northern India continued until the conquest of Lahore from Khusrau Malik in 1186.
Legacy

The Ghaznavid empire grew to cover much of present-day Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and northwest India, and the Ghaznavids are generally credited with launching Islam into Hindu-dominated India. In addition to the wealth accumulated through raiding Indian cities, and exacting tribute from Indian Rajas the Ghaznavids also benefited from their position as an intermediary along the trade routes between China and the Mediterranean. They were however unable to hold power for long and by 1040 the Seljuks had taken over their Persian domains and a century later the Ghurids took over their remaining sub-continental lands.
Culture
Although the Ghaznavids were of Turkic origin and their military leaders were generally of the same stock, as a result of the original involvement of Sebuktigin and Mahmud in Samanid affairs and in the Samanid cultural environment, the dynasty became thoroughly Persianized, so that in practice one cannot consider their rule over Iran one of foreign domination. In terms of cultural championship and the support of Persian poets, they were far more Persian than the ethnically Iranian Buyids rivals, whose support of Arabic letters in preference to Persian is well known.
In fact with the adoption of Persian administrative and cultural ways the Ghaznavids threw off their original Turkish steppe background and became largely integrated with the Perso-Islamic tradition.
The Ghaznavid Dynasty
- Alptigin (963-977)
- Sebük Tigin, (Abu Mansur) (977-997)
- Ismail (997-998)
- Mahmud (Yamin ud-Dawlah ) (998-1030)
- Mohammed (Jalal ud-Dawlah) (1030-1031)
- Mas'ud I (Shihab ud-Dawlah) (1031–1041)
- Mohammed (Jalal ud-Dawlah (second time) (1041)
- Maw'dud (Shihab ud-Dawlah) (1041-1050)
- Mas'ud II (1050)
- Ali (Baha ud-Dawlah) (1050)
- Abd ul-Rashid (Izz ud-Dawlah) (1053)
- Toğrül (Tughril) (Qiwam ud-Dawlah) (1053)
- Farrukhzad (Jamal ud-Dawlah) (1053-1059)
- Ibrahim (Zahir ud-Dalah) (1059-1099)
- Mas'ud III (Ala ud-Dawlah) (1099-1115)
- Shirzad (Kemal ud-Dawlah) (1115)
- Arslan Shah (Sultan ud-Dawlah) (1115-1118)
- Bahram Shah (Yamin ud-Dawlah ) (1118-1152)
- Khusrau Shah (Mu'izz ud-Dawlah) (1152-1160)
- Khusrau Malik (Taj ud-Dawlah) (1160-1187)
See also
Footnotes
- "Encyclopedia Britannica - Ghaznavid Dynasty"
- ^ C.E. Bosworth: The Ghaznavids. Edinburgh, 1963
- C.E. Bosworth, "Ghaznavids", in Encyclopaedia Iranica, Online Edition 2006, (LINK)
- ^ C.E. Bosworth, "Ghaznavids", in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Online Edition; Brill, Leiden; 2006/2007
- M.A. Amir-Moezzi, "Shahrbanu", Encyclopaedia Iranica, Online Edition, (LINK): "... here one might bear in mind that non-Persian dynasties such as the Ghaznavids, Saljuqs and Ilkhanids were rapidly to adopt the Persian language and have their origins traced back to the ancient kings of Persia rather than to Turkish heroes or Muslim saints ..."
- Encyclopaedia Iranica, Iran: Islamic Period - Ghaznavids, E. Yarshater
- B. Spuler, "The Disintegration of the Caliphate in the East", in the Cambridge History of Islam, Vol. IA: The Central islamic Lands from Pre-Islamic Times to the First World War, ed. by P.M. Holt, Ann K.S. Lambton, and Bernard Lewis (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1970). pg 147: One of the effects of the renaissance of the Persian spirit evoked by this work was that the Ghaznavids were also Persianized and thereby became a Persian dynasty.
- Anatoly M Khazanov, André Wink, "Nomads in the Sedentary World", Routledge, 2padhte padhte to pagla jayega aadmi, "A History of Russia, Central Asia and Mongolia", Blackwell Publishing, 1998. pg 370: "Though Turkic in origin and, apparently in speech, Alp Tegin, Sebuk Tegin and Mahmud were all thoroughly Persianized"
- Robert L. Canfield, Turko-Persia in historical perspective, Cambridge University Press, 1991. pg 8: "The Ghaznavids (989-1149) were essentially Persianized Turks who in manner of the pre-Islamic Persians encouraged the development of high culture"
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica, Ghaznavid Dynasty, Online Edition 2007 (LINK)
- ^ Encyclopedia Iranica, Ghaznavids, Edmund Bosworth, Online Edition 2007, (LINK)
- Encyclopedia Iranica, Iran, EHSAN YARSHATER, Online Edition 2008, ()
- Clifford Edmund Bosworth, The new Islamic dynasties: a chronological and genealogical manual, Edition: 2, Published by Edinburgh University Press, 2004, ISBN 0748621377, p. 297
Further reading
- Bosworth, Clifford Edmund (1963) The Ghaznavids: Their Empire in Afghanistan and Eastern Iran 994–1040 Edinburgh University Press, Edinburgh, OCLC 3601436
- Bosworth, Clifford Edmund (1977) The Later Ghaznavids: Splendour and Decay, The Dynasty in Afghanistan and Northern India 1040–1186 Columbia University Press, New York, ISBN 0-231-04428-3
- M. Ismail Marcinkowski (2003) Persian Historiography and Geography: Bertold Spuler on Major Works Produced in Iran, the Caucasus, Central Asia, India and Early Ottoman Turkey Pustaka Nasional, Singapore, ISBN 9971-77-488-7
External links
- Columbia Encyclopedia (Sixth Edition) - Mahmud of Ghazna
- Encylopaedia Britannica (Online Edition) - Mahmud
- Encyclopaedia Britannica (Online Edition) - Ghaznavid Dynasty
- Encyclopaedia Britannica (Online Edition) - Ghaznavids and Ghurids
- Mahmud Ghaznavi's 17 invasions of India
- Elliot, Sir H. M., Edited by Dowson, John. The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. The Muhammadan Period; published by London Trubner Company 1867–1877. (Online Copy: The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. The Muhammadan Period; by Sir H. M. Elliot; Edited by John Dowson; London Trubner Company 1867–1877 - Online version posted by: The Packard Humanities Institute; Persian Texts in Translation)
- Afghan secrets revealed on Google Earth
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. {{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)
| Empires | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ancient (colonies) | |||
| Post-classical |
| ||
| Modern |
| ||
| Lists | |||
| Miscellaneous |
| ||
