| Revision as of 20:54, 2 August 2009 edit189.217.98.215 (talk) →Spain← Previous edit | Revision as of 11:21, 7 August 2009 edit undoBeno1000 (talk | contribs)Pending changes reviewers3,659 editsm →British IndiaNext edit → | ||
| Line 258: | Line 258: | ||
| ===British India=== | ===British India=== | ||
| As British females began arriving to ] in large numbers around the early to mid-19th century, miscegenation became increasingly uncommon there and was later despised after the events of the ], known as "]" to the Indians and as the "Sepoy Mutiny" to the British, where Indian ]s rebelled against the British East India Company. While incidents of ] committed by Indian rebels against English women and girls were generally uncommon during the rebellion, this was exaggerated to great effect by the ] in order to justify vicious reprisals in the short run and continued ] in the ] in the long run.<ref>{{citation|title=Vanishing Women: Magic, Film, and Feminism|first=Karen Redrobe|last=Beckman|publisher=]|year=2003|isbn=0822330741|pages=31–3}}</ref> | As British females began arriving to ] in large numbers around the early to mid-19th century, miscegenation became increasingly uncommon there and was later despised after the events of the ], known as "]" to the Indians and as the "Sepoy Mutiny" to the British, where Indian ]s rebelled against the ]. While incidents of ] committed by Indian rebels against English women and girls were generally uncommon during the rebellion, this was exaggerated to great effect by the ] in order to justify vicious reprisals in the short run and continued ] in the ] in the long run.<ref>{{citation|title=Vanishing Women: Magic, Film, and Feminism|first=Karen Redrobe|last=Beckman|publisher=]|year=2003|isbn=0822330741|pages=31–3}}</ref> | ||
| Despite the questionable authenticity of many colonial accounts regarding the rebellion, the ] "dark-skinned rapist" occurred frequently in ] of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The idea of protecting English "female chastity" from the "lustful Indian male" had a significant influence on the the policies of the ]. However, while widespread prejudice, and the fear of professional and personal ruin prevented significant numbers from inter-marrying, there were no formal laws prohibiting marriage between Britons and Indians in British-ruled India. | Despite the questionable authenticity of many colonial accounts regarding the rebellion, the ] "dark-skinned rapist" occurred frequently in ] of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The idea of protecting English "female chastity" from the "lustful Indian male" had a significant influence on the the policies of the ]. However, while widespread prejudice, and the fear of professional and personal ruin prevented significant numbers from inter-marrying, there were no formal laws prohibiting marriage between Britons and Indians in British-ruled India. | ||
Revision as of 11:21, 7 August 2009
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Anti-miscegenation laws" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Race |
|---|
| History |
| Society |
| Race and... |
| By location |
| Related topics |
Anti-miscegenation laws, also known as miscegenation laws, were laws that banned interracial marriage and sometimes interracial sex between members of two different races. In the United States, interracial marriage, cohabitation and sex have since 1863 been termed "miscegenation." Contemporary usage of the term "miscegenation" is less frequent. In North America, laws against interracial marriage and interracial sex existed and were enforced in the Thirteen Colonies from the late seventeenth century onwards, and subsequently in several US states and US territories until 1967. Similar laws were also enforced in Nazi Germany, from 1935 until 1945, and in South Africa during the Apartheid era, from 1949 until 1985.
United States
The term miscegenation, a word invented by American journalists to discredit the Abolitionist movement by stirring up debate over the prospect of white-black intermarriage after the abolition of slavery, was first coined in 1863, during the American Civil War. Yet in the Thirteen Colonies laws banning the intermarriage of whites and blacks were enacted as far back as the late seventeenth century.
In the United States, anti-miscegenation laws (also known as miscegenation laws) were state laws passed by individual states to prohibit miscegenation, nowadays more commonly referred to as interracial marriage and interracial sex. Typically defining miscegenation as a felony, these laws prohibited the solemnization of weddings between persons of different races and prohibited the officiating of such ceremonies. Sometimes, the individuals attempting to marry would not be held guilty of miscegenation itself, but felony charges of adultery or fornication would be brought against them instead. All anti-miscegenation laws banned the marriage of whites and non-white groups, primarily blacks, but often also Native Americans and Asians. In many states, anti-miscegenation laws also criminalized cohabitation and sex between whites and non-whites. In addition, the state of Oklahoma in 1908 banned marriage "between a person of African descent" and "any person not of African descent", and Kentucky and Louisiana in 1932 banned marriage between Native Americans and African Americans. While anti-miscegenation laws are often regarded as a Southern phenomenon, many northern states had anti-miscegenation laws as well.
Although anti-miscegenation amendments were proposed in United States Congress in 1871, 1912-1913 and 1928, a nation-wide law against racially mixed marriages was never enacted. From the 19th century into the 1950s, most US states enforced anti-miscegenation laws. From 1913 to 1948, 30 out of the then 48 states did so. In 1967, the United States Supreme Court unanimously ruled in Loving v. Virginia that anti-miscegenation laws are unconstitutional. With this ruling, these laws were no longer in effect in the remaining 16 states that at the time still enforced them.
Origins in the Colonial Era
The first laws criminalizing marriage and sex between whites and blacks were enacted in the colonial era in the English colonies of Virginia and Maryland, which depended economically on unpaid labor such as indentured servitude and slavery.
At first, in the 1660s, the first laws in Virginia and Maryland regulating marriage between whites and blacks only pertained to the marriages of whites with black (and mulatto) slaves and indentured servants. In 1664, Maryland enacted a law which criminalized such marriages. Virginia (1691) was the first English colony in North America to pass a law forbidding free blacks and whites to intermarry, followed by Maryland in 1692. This was the first time in American history that a law was invented that restricted access to marriage partners solely on the basis of "race", not class or condition of servitude. Later these laws also spread to colonies in the Thirteen Colonies with fewer slaves and free blacks, such as Pennsylvania and Massachusetts. Moreover, after the independence of the United States had been established, similar laws were enacted in territories and states which outlawed slavery.
A sizable number of the early indentured servants in the British American colonies were brought over from the Indian subcontinent by the East India Company. Anti-miscegenation laws discouraging interracial marriage between white Americans and non-whites affected South Asian immigrants as early as the 17th century. For example, a Eurasian daughter born to an Indian father and Irish mother in Maryland in 1680 was classified as a "mulatto" and sold into slavery . Anti-miscegenation laws there continued into the early 20th century. For example, the Bengali revolutionary Tarak Nath Das's white American wife, Mary K. Das, was stripped of her American citizenship for her marriage to an "alien ineligible for citizenship." In 1918, there was considerable controversy in Arizona when an Indian farmer B. K. Singh married the sixteen year-old daughter of one of his white tenants.
In 1724, the French government issued a special Code Noir restricted to Louisiana, which banned the marriage of whites and blacks in that colony. However, interracial cohabitation and interracial sex were never prohibited in French Louisiana (see plaçage). Under Spanish rule, interracial marriage was possible with parental consent under the age of 25 and without it when the partners were older. In 1806, three years after the U.S. gained control over the state, interracial marriage was once again banned.
It has been argued that the first laws banning all marriage between whites and blacks, enacted in Virginia and Maryland, were a response by the planter elite to the problems they were facing due to the socio-economic dynamics of the plantation system in the Southern colonies. However, the bans in Virginia and Maryland were established at a time when slavery was not yet fully institutionalized. At the time, most forced laborers on the plantations were indentured servants, and they were mostly white. Some historians have suggested that the at-the-time unprecedented laws banning interracial marriage were originally invented by planters as a divide and rule tactic after the uprising of servants in Bacon's Rebellion. According to this theory, the ban on interracial marriage was issued to split up the racially mixed, increasingly mixed-race labor force into whites, who were given their freedom, and blacks, who were later treated as slaves rather than as indentured servants. By outlawing interracial marriage, it became possible to keep these two new groups separated and prevent a new rebellion.
After American Independence
In the 18th, 19th, and early 20th century, many American states passed anti-miscegenation laws, which were often defended by invoking racist interpretations of the Bible, particularly of the story of Phinehas and the "Curse of Ham". In 1776, seven out of the Thirteen Colonies that declared their independence enforced laws against interracial marriage. Although slavery was gradually abolished in the North after independence, this at first had little impact on the enforcement of anti-miscegenation laws. An exception was Pennsylvania, which repealed its anti-miscegenation law in 1780, together with some of the other restrictions placed on free blacks, when it enacted a bill for the gradual abolition of slavery in the state. Later, in 1843, Massachusetts repealed its anti-miscegenation law after abolitionists protested against it. However, as the US expanded, all the new slave states as well as many new free states such such as Illinois and California enacted such laws.
Arkansas, Florida, Louisiana, Texas, South Carolina and Alabama legalized interracial marriage for some years during the Reconstruction period. Anti-miscegenation laws rested unenforced, were overturned by courts or repealed by the state government (in Arkansas and Louisiana). However, after conservative white Democrats took power in the South during Redemption, anti-miscegenation laws were once more enforced, and in addition Jim Crow laws were enacted in the South which enforced racial segregation.
A number of northern and western states permanently repealed their anti-miscegenation laws during the nineteenth century. This, however, did little to halt anti-miscegenation sentiments in the rest of the country. Newly established western states continued to enact laws banning interracial marriage in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century. Between 1913 and 1948, 30 out of the then 48 states enforced anti-miscegenation laws. Only Connecticut, New Hampshire, New York, New Jersey, Vermont, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Alaska, Hawaii, and the federal District of Columbia never enacted them.
Anti-Miscegenation Laws and the US Constitution
The constitutionality of anti-miscegenation laws was upheld by the U.S. Supreme Court in the 1883 case Pace v. Alabama (106 U.S. 583). The Supreme Court ruled that the Alabama anti-miscegenation statute did not violate the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution. According to the court, both races were treated equally, because whites and blacks were punished in equal measure for breaking the law against interracial marriage and interracial sex. This judgment was overturned in 1967 in the Loving v. Virginia case, where the Supreme Court declared anti-miscegenation laws a violation of the Fourteenth Amendment and therefore unconstitutional.
Proposed Anti-Miscegenation Amendments
In 1871, Representative Andrew King (Democrat of Missouri) was the first politician in Congress to propose a constitutional amendment to make interracial marriage illegal nation-wide. King proposed this amendment because he feared that the Fourteenth Amendment, ratified in 1868 to give equal civil rights to the emancipated ex-slaves (the Freedmen) as part of the process of Reconstruction, would render laws against interracial marriage unconstitutional.
In December 1912 and January 1913, Representative Seaborn Roddenbery (Democrat of Georgia) again introduced a proposal in the United States House of Representatives to insert a prohibition of miscegenation into the US Constitution and thus create a nation-wide ban on interracial marriage. According to the wording of the proposed amendment, "Intermarriage between negros or persons of color and Caucasians... within the United States... is forever prohibited." Roddenbery's proposal was more severe because it defined the racial boundary between whites and "persons of color" by applying the one-drop rule. In his proposed amendment, anyone with "any trace of African or Negro blood" was banned from marrying a white spouse.
Roddenbery's proposed amendment was also a direct reaction to African American heavyweight champion Jack Johnson's marriages to white women, first to Etta Duryea and then to Lucille Cameron. In 1908, Johnson had become the first black boxing world champion, having beaten Tommy Burns. After his victory, the search was on for a white boxer, a "Great White Hope", to beat Johnson. Those hopes were dashed in 1912, when Johnson beat former world champion Jim Jeffries. This victory ignited race riots all over America as frustrated whites attacked celebrating African Americans . Johnson's marriages to and affairs with white women further infuriated white Americans. In his speech introducing his bill before the United States Congress, Roddenbery compared the marriage of Johnson and Cameron to the enslavement of white women, and warned of future civil war that would ensue if interracial marriage was not made illegal nationwide:
"No brutality, no infamy, no degradation in all the years of southern slavery, possessed such villainious character and such atrocious qualities as the provision of the laws of Illinois, Massachusetts, and other states which allow the marriage of the negro, Jack Johnson, to a woman of Caucasian strain. . Gentleman, I offer this resolution ... that the States of the Union may have an opportunity to ratifty it. ...
Intermarriage between whites and blacks is repulsive and averse to every sentiment of pure American spirit. It is abhorrent and repugnant to the very principles of Saxon government. It is subversive of social peace. It is destructive of moral supremacy, and ultimately this slavery of white women to black beasts will bring this nation a conflict as fatal as ever reddened the soil of Virginia or crimsoned the mountain paths of Pennsylvania.
... Let us uproot and exterminate now this debasing, ultra-demoralizing, un-American and inhuman leprosy"
Congressional Record, 62d. Congr., 3d. Sess., December 11, 1912, pp. 502–503.
Spurred on by Roddenbery's introduction of the anti-miscegenation amendment, politicians in many of the 19 states lacking anti-miscegenation laws proposed their enactment. However, Wyoming in 1913 was the only state lacking such a law that enacted one. Also in 1913, the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, which had abolished its anti-miscegenation law in 1843, enacted a measure that prevented couples who could not marry in their home state from marrying in Massachusetts. In 1928, Senator Coleman Blease (Democrat of South Carolina) proposed an amendment to the U.S. Constitution that went beyond the previous ones because it required that Congress set a punishment for interracial couples attempting to get married and for people officiating an interracial marriage. This amendment was also never enacted.
The repeal of Anti-miscegenation laws, 1948-1967
The constitutionality of anti-miscegenation laws only began to be widely called into question after the World War II. In 1948, the California Supreme Court in Perez v. Sharp ruled that the Californian anti-miscegenation statute violated the Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution and was therefore unconstitutional. This was the first time since Reconstruction that a state court had declared an anti-miscegenation law unconstitutional. California was the first state since Ohio in 1887 to repeal its anti-miscegenation law.
As a result, during the 1950s, anti-miscegenation laws were repealed or overturned in state after state, except in the South. Nonetheless, in the 1950s, the repeal of anti-miscegenation laws was still a controversial issue in the U.S., even among supporters of racial integration.
In 1958, the political theorist Hannah Arendt, an emigre from Nazi Germany, wrote in an essay in response to the Little Rock Crisis, the Civil Rights struggle for the racial integration of public schools which took place in Little Rock, Arkansas in 1957, that anti-miscegenation laws were an even deeper injustice than the racial segregation of public schools. The free choice of a spouse, she argued in Reflections on Little Rock, was "an elementary human right": "Even political rights, like the right to vote, and nearly all other rights enumerated in the Constitution, are secondary to the inalienable human rights to 'life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness' proclaimed in the Declaration of Independence; and to this category the right to home and marriage unquestionably belongs." Arendt was severely criticized by fellow liberals, who feared that her essay would arouse the racist fears common among whites and thus hinder the struggle of African-Americans for Civil Rights and racial integration. Commenting on the Supreme Court's ruling in Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka against de jure racial segregation in education, Arendt argued that anti-miscegenation laws were more basic to racial segregation than racial segregation in education.
Arendt's analysis of the centrality of laws against interracial marriage to white supremacy echoed the conclusions of Gunnar Myrdal. In his essay, Social Trends in America and Strategic Approaches to the Negro Problem (1948), Myrdal ranked the social areas where restrictions were imposed by Southern whites on the freedom of African-Americans through racial segregation from the least to the most important: jobs, courts and police, politics, basic public facilities, "social equality" including dancing and handshaking, and most importantly, marriage. This ranking was indeed reflective of the way in which the barriers against desegregation fell under the pressure of the protests of the emerging Civil Rights movement. First, legal segregation in the army, in education and in basic public services fell, then restrictions on the voting rights of African-Americans were lifted. These victories were ensured by the Civil Rights Act of 1964. But the bans on interracial marriage were the last to go, in 1967.
Most white Americans in the 1950s were opposed to interracial marriage and did not see laws banning interracial marriage as an affront to the principles of American democracy. A 1958 Gallup poll showed that 96 percent of white Americans disapproved of interracial marriage. However, attitudes towards bans on interracial marriage quickly changed in the 1960s.
By the 1960s, civil rights organizations were helping interracial couples who were being penalized for their relationships to take their cases to the Supreme Court. Since Pace v. Alabama, the court had declined to make a judgment in such cases. But in 1964, the Warren Court decided to issue a ruling in the case of an interracial couple from Florida who had been convicted because they had cohabited. In McLaughlin v. Florida, the Supreme Court ruled that the Florida state law which prohibited cohabitation between whites and non-whites was unconstitutional and based solely on a policy of racial discrimination. However, the court did not rule on the Florida's ban on marriage between whites and non-whites, despite the appeal of the plaintiffs to do so and the argument made by the state of Florida that its ban on cohabitation between whites and blacks was ancillary to its ban on marriage between whites and blacks. However, in 1967, the court did decide to rule on the remaining anti-miscegenation laws when it was presented with the case of Loving v. Virginia.
Loving v. Virginia
Main article: Loving v. Virginia
This file may be deleted after Monday, 6 July 2009. , Mildred Jeter and Richard Loving
All bans on interracial marriage were lifted only after an interracial couple from Virginia, Richard and Mildred Loving, began a legal battle in 1963 for the repeal of the anti-miscegenation law which prevented them from living as a couple in their home state of Virginia. The Lovings were supported by the NAACP Legal Defense Fund, the Japanese American Citizens League and a coalition of Catholic bishops.
In 1958, Richard and Mildred Loving had married in Washington, D.C. to evade Virginia's anti-miscegenation law (the Racial Integrity Act). Having returned to Virginia, they were arrested in their bedroom for living together as an interracial couple. The judge suspended their sentence on the condition that the Lovings would leave Virginia and not return for 25 years. In 1963, the Lovings, who had moved to Washington, D.C, decided to appeal this judgment. In 1965, Virginia trial court Judge Leon Bazile, who heard their original case, refused to reconsider his decision. Instead, he defended racial segregation, writing:
"Almighty God created the races white, black, yellow, and red, and he placed them on separate continents. And but for the interference with his arrangement there would be no cause for such marriages. The fact that he separated the races shows that he did not intend for the races to mix."
The Lovings then took their case to the Supreme Court of Virginia, which invalidated the original sentence but upheld the state's Racial Integrity Act. Finally, the Lovings turned to the U.S Supreme Court. The court, which had previously avoided taking miscegenation cases, agreed to hear an appeal. In 1967, 84 years after Pace v. Alabama in 1883, the Supreme Court ruled unanimously in Loving v. Virginia that:
"Marriage is one of the 'basic civil rights of man,' fundamental to our very existence and survival.... To deny this fundamental freedom on so unsupportable a basis as the racial classifications embodied in these statutes, classifications so directly subversive of the principle of equality at the heart of the Fourteenth Amendment, is surely to deprive all the State's citizens of liberty without due process of law. The Fourteenth Amendment requires that the freedom of choice to marry not be restricted by invidious racial discriminations. Under our Constitution, the freedom to marry, or not to marry, a person of another race resides with the individual and cannot be infringed by the State."
The Supreme Court condemned Virginia's anti-miscegenation law as "designed to maintain White supremacy".
In 1967, 17 Southern states (all the former slave states plus Oklahoma) still enforced laws prohibiting marriage between whites and people of color. Maryland repealed its law in response to the start of the proceedings at the Supreme Court. After the ruling of the Supreme Court, the remaining laws were no longer in effect. Nonetheless, it took South Carolina until 1998 and Alabama until 2000 to officially amend their states' constitutions to remove language prohibiting miscegenation. In the respective referendums, 62% of voters in South Carolina and 59% of voters in Alabama voted to remove these laws.
Anti-miscegenation Laws enacted in the Thirteen Colonies and the United States
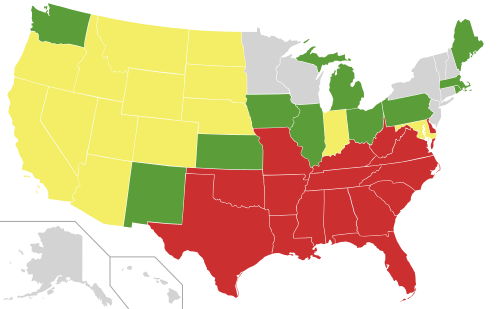
Anti-miscegenation laws repealed until 1887
| State | First law passed | Law repealed | Races banned from marrying whites | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Illinois | 1829 | 1874 | Blacks | |
| Iowa | 1839 | 1851 | Blacks | |
| Kansas | 1855 | 1859 | Blacks | Law repealed before reaching statehood |
| New Mexico | 1857 | 1866 | Blacks | Law repealed before reaching statehood |
| Maine | 1821 | 1883 | Blacks, Native Americans | |
| Massachusetts | 1705 | 1843 | Blacks, Native Americans | Passed the 1913 law preventing out-of-state couples from circumventing their home-state anti-miscegenation laws |
| Michigan | 1838 | 1883 | Blacks | |
| Ohio | 1861 | 1887 | Blacks | Last state to repeal its anti-miscegenation law before California did so in 1948 |
| Pennsylvania | 1725 | 1780 | Blacks | |
| Rhode Island | 1798 | 1881 | Blacks, Native Americans | |
| Washington | 1855 | 1868 | Blacks, Native Americans | Law repealed before reaching statehood |
Anti-miscegenation laws repealed 1948-1967
| State | First law passed | Law repealed | Races banned from marrying whites | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | 1865 | 1962 | Blacks, Asians, Filipinos, Indians | Filipinos ("Malays") and Indians ("Hindus") added to list of "races" in 1931 |
| California | 1850 | 1948 | Blacks, Asians, Filipinos | Anti-miscegenation law overturned by state judiciary in Supreme Court of California case Perez v. Sharp |
| Colorado | 1864 | 1957 | Blacks | |
| Idaho | 1864 | 1959 | Blacks, Native Americans, Asians | |
| Indiana | 1818 | 1965 | Blacks | |
| Maryland | 1692 | 1967 | Blacks, Filipinos | Repealed its law in response to the start of the Loving v. Virginia case |
| Montana | 1909 | 1953 | Blacks, Asians | |
| Nebraska | 1855 | 1963 | Blacks, Asians | |
| Nevada | 1861 | 1959 | Blacks, Native Americans, Asians, Filipinos | |
| North Dakota | 1909 | 1955 | Blacks | |
| Oregon | 1862 | 1951 | Blacks, Native Americans, Asians, Native Hawaiians | |
| South Dakota | 1909 | 1957 | Blacks, Asians, Filipinos | |
| Utah | 1852 | 1963 | Blacks, Asians, Filipinos | |
| Wyoming | 1913 | 1965 | Blacks, Asians, Filipinos |
Anti-miscegenation laws overturned on 12 June 1967 by Loving v. Virginia
| State | First law passed | Races banned from marrying whites | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | 1822 | Blacks | Repealed during Reconstruction, law later reinstated |
| Arkansas | 1838 | Blacks | Repealed during Reconstruction, law later reinstated |
| Delaware | 1721 | Blacks | |
| Florida | 1832 | Blacks | Repealed during Reconstruction, law later reinstated |
| Georgia | 1750 | All non-whites | |
| Kentucky | 1792 | Blacks | |
| Louisiana | 1724 | Blacks | Repealed during Reconstruction, law later reinstated |
| Mississippi | 1822 | Blacks, Asians | Repealed during Reconstruction, law later reinstated |
| Missouri | 1835 | Blacks, Asians | |
| North Carolina | 1715 | Blacks, Native Americans | |
| Oklahoma | 1897 | Blacks | |
| South Carolina | 1717 | All non-whites | Repealed during Reconstruction, law later reinstated |
| Tennessee | 1741 | Blacks, Native Americans | |
| Texas | 1837 | Blacks, Filipinos | |
| Virginia | 1691 | All non-whites | Previous anti-miscegenation law made more severe by Racial Integrity Act of 1924 |
| West Virginia | 1863 | Blacks |
Arab World
With the rise of Arab nationalism in the 20th century, inter-ethnic marriage has become an issue in several modern Arab nations, where laws and customs exist which revoke the civil rights of women who marry men not native to the woman's country of birth, or to men who are non-Muslim in particular. Women who follow through on this choice run a risk of being subjected to honor killings by male family members.
Asia
China
There have been various periods in the history of China where large numbers of Arabs, Persians and Turks from the "Western Regions" (Central Asia and West Asia) migrated to China, beginning with the arrival of Islam during the Tang Dynasty in the 7th century. Due to the majority of these immigrants being male, they often intermarried with local Han Chinese females. There were laws and policies which discouraged miscegenation during the Tang Dynasty, 836 AD, a decree forbidding Chinese to have relations with peoples of color, such as Iranians, Arabs, Indians, Malays, Sumatrans, and so on. Race riots and massacres resulting in the deaths of several thousand Muslim merchants like Arabs and Persians in Hangzhou occurred. These laws were later relaxed during the Song Dynasty, which allowed third-generation immigrants with official titles to intermarry with Chinese imperial princesses. Immigration to China increased under the Mongol Empire, when large numbers of West and Central Asians were brought over to help govern Yuan China in the 13th century. Intermarriage was later encouraged during the Ming Dynasty.
During the Qing dynasty, Manchus and Mongols were prohibited from marrying the Han Chinese but those within the Eight Banners were exempt, usually a Manchu bannerman to a Han bannerwoman. In 1822, all Manchu men were given the right to marry Han women. The edict prohibiting miscegenation was thoroughly repealed on February 1, 1902.
British India
As British females began arriving to British India in large numbers around the early to mid-19th century, miscegenation became increasingly uncommon there and was later despised after the events of the Indian Rebellion of 1857, known as "India's First War of Independence" to the Indians and as the "Sepoy Mutiny" to the British, where Indian sepoys rebelled against the British East India Company. While incidents of war rape committed by Indian rebels against English women and girls were generally uncommon during the rebellion, this was exaggerated to great effect by the British media in order to justify vicious reprisals in the short run and continued British colonialism in the Indian subcontinent in the long run.
Despite the questionable authenticity of many colonial accounts regarding the rebellion, the stereotype of the Indian "dark-skinned rapist" occurred frequently in English literature of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The idea of protecting English "female chastity" from the "lustful Indian male" had a significant influence on the the policies of the British Raj. However, while widespread prejudice, and the fear of professional and personal ruin prevented significant numbers from inter-marrying, there were no formal laws prohibiting marriage between Britons and Indians in British-ruled India.
Malaysia
In Malaysia, the majority of inter-ethnic marriages are between Chinese and Indians. The offspring of such marriages are informally known as "Chindian", though the Malaysian government only classifies them by their father's ethnicity. As the majority of these intermarriages usually involve an Indian groom and Chinese bride, the majority of Chindians in Malaysia are usually classified as "Indian" by the Malaysian government. Certain anti-miscegenation laws apply to the Malays, however, who are predominantly Muslim. Legal restrictions in Malaysia make it very difficult for Malays to intermarry with either the Chinese or Indian populations.
Pakistan
In 2008, several Pakistani senators defended the practice of burying young women alive who were judged guilty by tribal elders of having engaged in a relationship with men not of their tribe.
Europe
Spain
After the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in the 8th century, the Islamic state of Al-Andalus was established in the Iberian Peninsula, where it was common for Arab and Berber males from North Africa to intermarry with the local Visigothic, Suebi, Roman and Iberian females of Hispania. The offspring of such marriages were known as Muladi or Muwallad, an Arabic term still used in the modern Arab world to refer to people with an Arab parent and a non-Arab parent. This term was also the origin for the Spanish word Mulatto.
By the 11th or 12th century, the Muslim population of Al-Andalus had merged into a homogeneous group of people known as the "Moors". After the Reconquista, which was completed in 1492, most of the Moors were forced to either flee to Morocco or convert to Christianity. The ones who converted to Christianity were known as Moriscoes, and they were often targeted by the Spanish Inquisition as suspects of heresy on the basis of the Limpieza de sangre ("Cleanliness of blood") or "blue blood" doctrine, under which anti-miscegenation laws were implemented in Spain, which prevented miscegenation between those with pure European blood and those with Moorish or Jewish blood. Anyone whose ancestors had miscegenated with the Moors or Jews were also especially monitored by the Inquisition to prevent their return to the Islamic or Jewish faiths.
France
During World War I, there were 135,000 soldiers from British India, a large number of soldiers from French North Africa, and 20,000 labourers from South Africa, who served in France. Much of the French male population had gone to war, leaving behind a surplus of French females, many of whom formed interracial relationships with non-white soldiers, mainly Indian and North African. British and French authorities allowed foreign Muslim soldiers to intermarry with local French females on the basis of Islamic law, which allows marriage between Muslim males and Christian and Jewish females. On the other hand, Hindu soldiers in France were restricted from intermarriage on the basis of the Indian caste system.
While the French were not as concerned about interracial relationships, the British made attempts to prevent their Indian troops from engaging in such relationships with white females, by implementing curfews and preventing female nurses from servicing wounded Indian troops in British-run hospitals. On the other hand, French-run hospitals had no problem with having female nurses servicing wounded Indian and North African soldiers, though contacts with black African labourers and soldiers were more severely restricted by both British and French authorities.
United Kingdom
Following World War I, there was a large surplus of females in the United Kingdom, and there were increasing numbers of seamen arriving from the Indian subcontinent, Arab World, Far East and Caribbean. This led to increased intermarriage and cohabitation with local white females, which raised concerns over miscegenation and led to several race riots at the time. In the 1920s to 1940s, several legal scholars raised concerns about an increasing 'mixed-breed' population, born mainly from foreign Muslim (mostly Indian as well as Arab, Malayan and Somali) fathers and local white mothers, occasionally out of wedlock. They denounced white girls who mixed with foreign Muslim men as 'shameless' and called for a legistlative ban on the breeding of 'half-caste' children. These calls for anti-miscegenation laws were unsuccessful, however.
Nazi Germany
In Germany, an anti-miscegenation law was enacted by the National Socialist government in September 1935 as part of the Nuremberg Laws. The Gesetz zum Schutze des deutschen Blutes und der deutschen Ehre (Protection of German Blood and German Honor Act), enacted on 15 September 1935, forbade marriage and extramarital sexual relations between persons of Jewish origin and persons of “German or related blood”. On November 14, the law was extended to Gypsies and Blacks. Such intercourse was marked as Rassenschande (lit. race-disgrace) and could be punished by imprisonment (usually followed by the deportation to a concentration camp) and even by death. The Nuremberg Laws were discarded after the capitulation of the Nazi regime to the Allies in May 1945.
South Africa under Apartheid
South Africa’s Prohibition of Mixed Marriages Act, passed in 1949 under Apartheid, forbade marriages between whites and non-whites. The Population Registration Act (No. 30) of 1950 provided the basis for separating the population of South Africa into different races. Under the terms of this act, all residents of South Africa were to be classified as white, coloured, or native (later called Bantu) people. Indians were included under the category "Asian" in 1959. Also in 1950, the Immorality Act was passed, which criminalized all sexual relations between whites and non-whites. The Immorality Act of 1950 extended an earlier ban on sexual relations between whites and blacks (the Immorality Act of 1927) to a ban on sexual relations between whites and any non-whites. Both Acts were repealed in 1985.
Footnotes
"Jack Johnson and White Women: The National Impact", Al-Tony Gilmore, Journal of Negro History (Vol. 58, No. 1, 18-38, Jan., 1973).
See also
- Amalgamation (history)
- Apartheid
- Interracial marriage
- Judicial aspects of race in the United States
- Miscegenation
- Jim Crow laws
- Nuremberg laws
- 1913 law
- Racial Integrity Act of 1924
- Pace v. Alabama
- Perez v. Sharp
- McLaughlin v. Florida
- Loving v. Virginia
- Loving Day
- Race (historical definitions)
- Social interpretations of race
- Scientific racism
- Hypodescent
- One drop rule
References
- David Hollinger (2003) Amalgamation and Hypodescent: The Question of Ethnoracial Mixture in the History of the United States, American Historical Review, Vol. 108, Iss. 5
- Fredrickson, George M. (1987), The Black Image in the White Mind, Wesleyan University Press, p. 172, ISBN 0819561886
- Chin, Gabriel J. & Hrishi Karthikeyan, Preserving Racial Identity: Population Patterns and the Application of Anti-Miscegenation Statutes to Asian Americans, 1910-1950, 9 Asian Law Journal 1 (2002)
- The History of Jim Crow
- Courtroom History, Loving Day, retrieved 2008-01-02
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - Edward Stein (2004), PAST AND PRESENT PROPOSED AMENDMENTS TO THE UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION REGARDING MARRIAGE∗ (pdf), vol. 82, Washing State University Law Quarterly, retrieved 2008-01-04
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help), archived from the original on 2006-08-12. - Frank W Sweet (January 1, 2005), The Invention of the Color Line: 1691—Essays on the Color Line and the One-Drop Rule, Backentyme Essays, retrieved 2008-01-04
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - Francis C. Assisi (2005). "Indian-American Scholar Susan Koshy Probes Interracial Sex". INDOlink. Retrieved 2009-01-02.
- "Echoes of Freedom: South Asian Pioneers in California, 1899-1965 - Chapter 9: Home Life". The Library, University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved 2009-01-08.
- Interracial Marriage and Cohabitation Laws, Redbone Heritage Foundation, retrieved 2008-01-04
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - Kimberly S. Hanger, Bounded Lives, Bounded Places: Free Black Society in Colonial New Orleans,1769-1803. Durham N.C., and London: Duke University Press, 1997.
- Stephen R. Haynes (2002), Noah's Curse: The Biblical Justification of American Slavery, Oxford University Press US, retrieved 2008-01-07
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - Steiner, Mark. “The Lawyer as Peacemaker: Law and Community in Abraham Lincoln’s Slander Cases”. The History Cooperative
- enacted similar anti-miscegenation laws.“Chinese Laborers in the West”Smithsonian Asian Pacific American Program
- Robinson II, Charles F., University of Arkansas, Fayetteville. The Encyclopedia of Arkansas History & Culture. (accessed January 4, 2007).
- Miscegenation and competing definitions of race in twentieth-century Louisiana.
- Wallenstein, Peter, Tell the Court I love my wife
- Where were interracial couples illegal?, Loving Day, retrieved 2008-01-04
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - Tucker, Neely (June 13, 2006). “Loving Day Recalls a Time When the Union of a Man And a Woman Was Banned”. Washington Post.
- Alabama removes ban on interracial marriage, USA Today, November 7, 2000, retrieved 2008-01-04
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - "Violence Against Women and "Honor" Crimes". Human Rights Watch. Retrieved 2001-04-06.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - Jody K. Biehl (2005-03-02). "The death of a Muslim woman - "The Whore Lived Like a German"". Retrieved 2008-09-20.
- Hillary Mayell (2002-02-12). "Thousands of Women Killed for Family "Honor"". Retrieved 2008-09-20.
- Gernet, Jacques (1996), A History of Chinese Civilization (2 ed.), Cambridge University Press, p. 294, ISBN 0521497817, ISBN 9780521497817.
- "Chinese of Arab and Persian descent". ColorQ World. Retrieved 2008-12-23.
- Ebrey, Patricia (1993). Chinese Civilization: A Sourcebook. Simon and Schuster,
- Beckman, Karen Redrobe (2003), Vanishing Women: Magic, Film, and Feminism, Duke University Press, pp. 31–3, ISBN 0822330741
- Daniels, Timothy P. (2005), Building Cultural Nationalism in Malaysia, Routledge, p. 189, ISBN 0415949718
- Ahmed Hassan, Dawn Newspaper (Pakistan) (2008-04-09). "Pakistan: Activists respond to women buried alive; no cultural justifications for murder!". Retrieved 2008-09-20.
- Thomas F. Glick, Islamic and Christian Spain in the Early Middle Ages
- Ivan van Sertima (1992), Golden Age of the Moor, Transaction Publishers, ISBN 1560005815
- Kees Versteegh, et al. Encyclopedia of Arabic Language and Linguistics, BRILL, 2006.
- Izquierdo Labrado, Julio. "La esclavitud en Huelva y Palos (1570-1587)" (in Spanish). Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- Salloum, Habeeb. "The impact of the Arabic language and culture on English and other European languages". The Honorary Consulate of Syria. Retrieved 2008-07-14.
- Robert Lacey (1983), Aristocrats, p. 67, Little, Brown and Company
- ^ Enloe, Cynthia H. (2000), Maneuvers: The International Politics of Militarizing Women's Lives, University of California Press, p. 61, ISBN 0520220714
- Greenhut, Jeffrey (April 1981), "Race, Sex, and War: The Impact of Race and Sex on Morale and Health Services for the Indian Corps on the Western Front, 1914", Military Affairs, 45 (2), Society for Military History: 71–74, doi:10.2307/1986964
- Levine, Philippa (1998), "Battle Colors: Race, Sex, and Colonial Soldiery in World War I", Journal of Women's History, 9
- Greenhut, Jeffrey (April 1981), "Race, Sex, and War: The Impact of Race and Sex on Morale and Health Services for the Indian Corps on the Western Front, 1914", Military Affairs, 45 (2), Society for Military History: 71–74 , doi:10.2307/1986964
- Dowling, Timothy C. (2006), Personal Perspectives: World War I, ABC-CLIO, pp. 35–6, ISBN 1851095659
- ^ Omissi, David (2007), "Europe Through Indian Eyes: Indian Soldiers Encounter England and France, 1914–1918", English Historical Review, CXXII (496), Oxford University Press: 371–96, doi:10.1093/ehr/cem004
- Greenhut, Jeffrey (April 1981), "Race, Sex, and War: The Impact of Race and Sex on Morale and Health Services for the Indian Corps on the Western Front, 1914", Military Affairs, 45 (2), Society for Military History: 71–74, doi:10.2307/1986964
- Bland, Lucy (April 2005), "White Women and Men of Colour: Miscegenation Fears in Britain after the Great War", Gender & History, 17 (1): 29–61 , doi:10.1111/j.0953-5233.2005.00371.x
- Ansari, Humayun (2004), The Infidel Within: The History of Muslims in Britain, 1800 to the Present, C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, p. 94, ISBN 1850656851
- Bland, Lucy (April 2005), "White Women and Men of Colour: Miscegenation Fears in Britain after the Great War", Gender & History, 17 (1): 29–61, doi:10.1111/j.0953-5233.2005.00371.x
- Ansari, Humayun (2004), The Infidel Within: The History of Muslims in Britain, 1800 to the Present, C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, pp. 93–4, ISBN 1850656851
- US Holocaust Memorial Museum. "Nuremberg Laws: Nazi Racial Policy 1935".
- Rita M. Byrnes, ed. (1996), "Legislative Implementation of Apartheid", South Africa: A Country Study, Washington: GPO for the Library of Congress, retrieved 2008-01-04
{{citation}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help)
External links
- Loving v. Virginia (No. 395) Cornell Law School Legal Information Institute
- Loving at Thirty by Harvard Law School Professor Randall Kennedy at SpeakOut.com
- Loving Day: Celebrate the Legalization of Interracial Couples
| Segregation in countries by type (in some countries, categories overlap) | |
|---|---|
| Religious | |
| Ethnic and racial | |
| Gender | |
| Dynamics | |
| Related topics |
|
